A Novel Automatic Registration Method for Fluorescein Fundus Angiography Sequences Based on Mutual Information
-
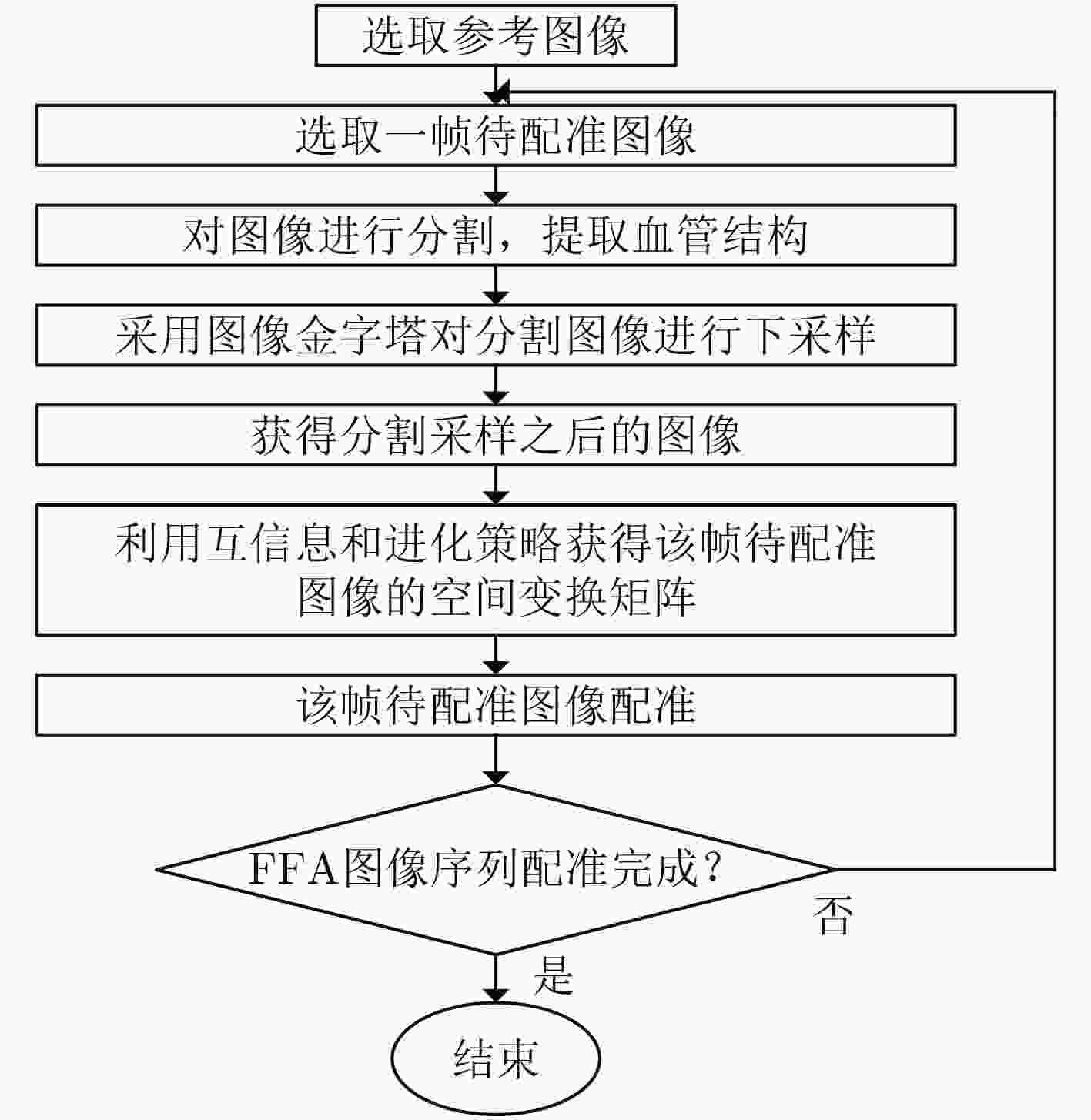
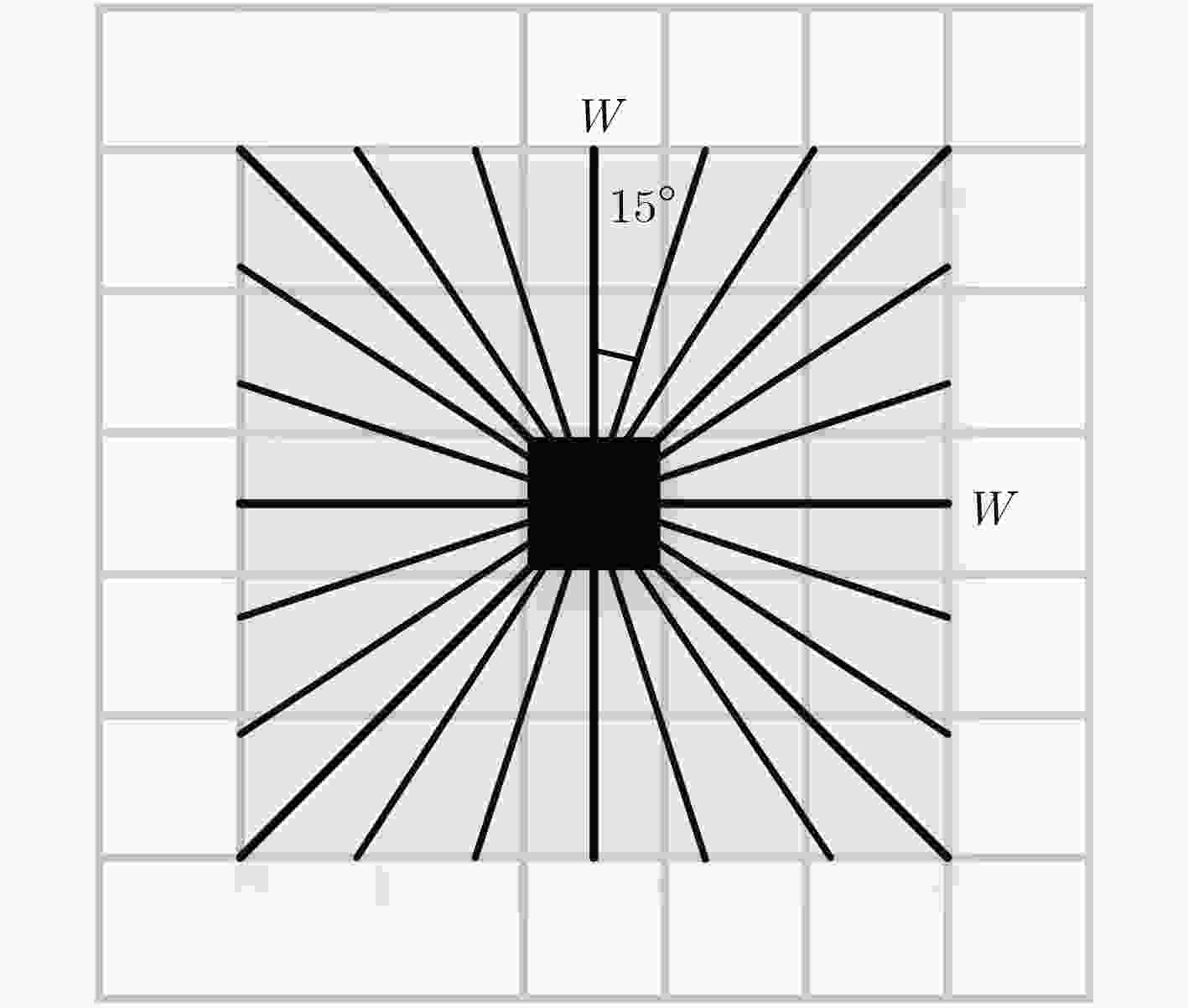
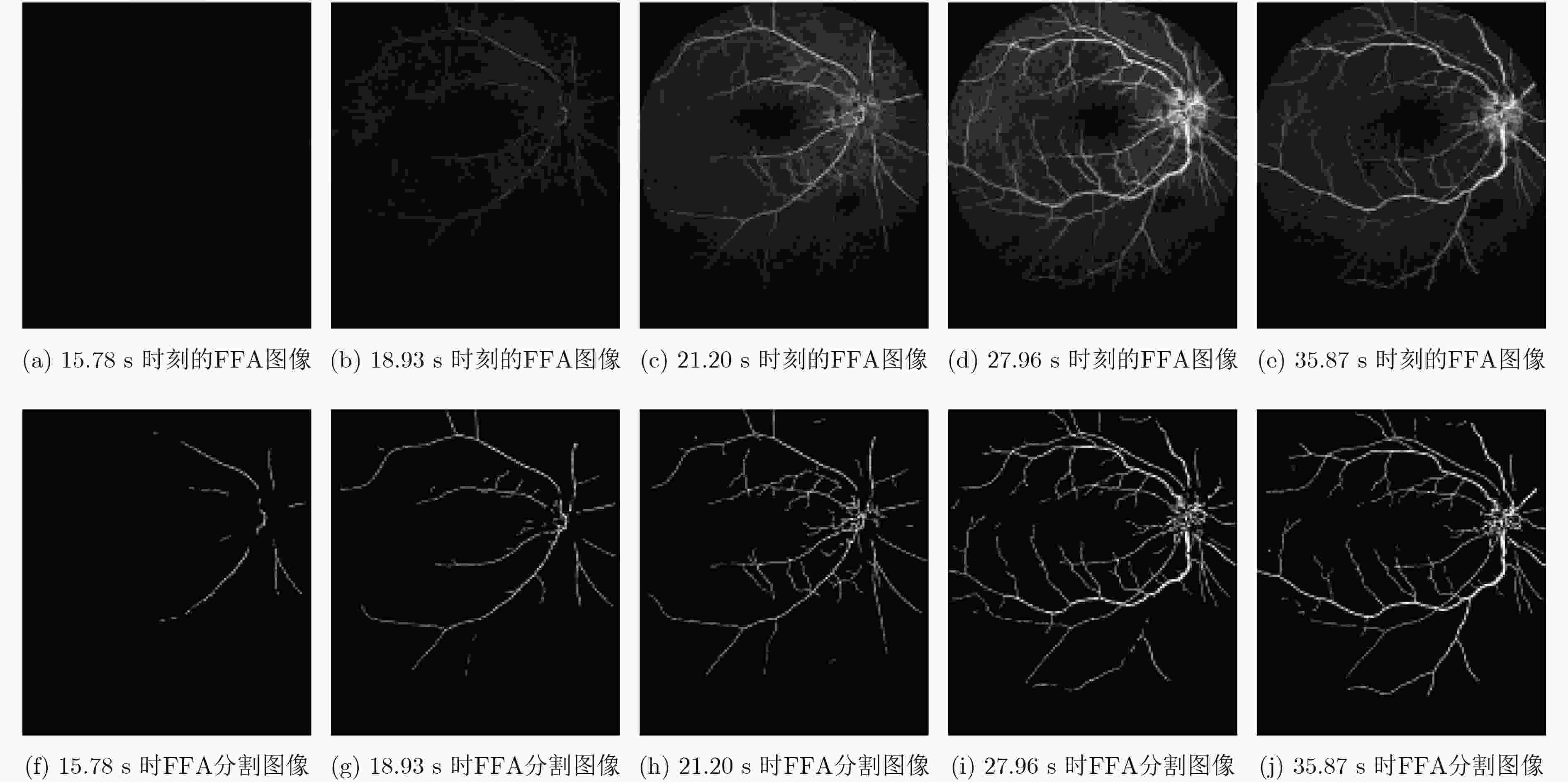
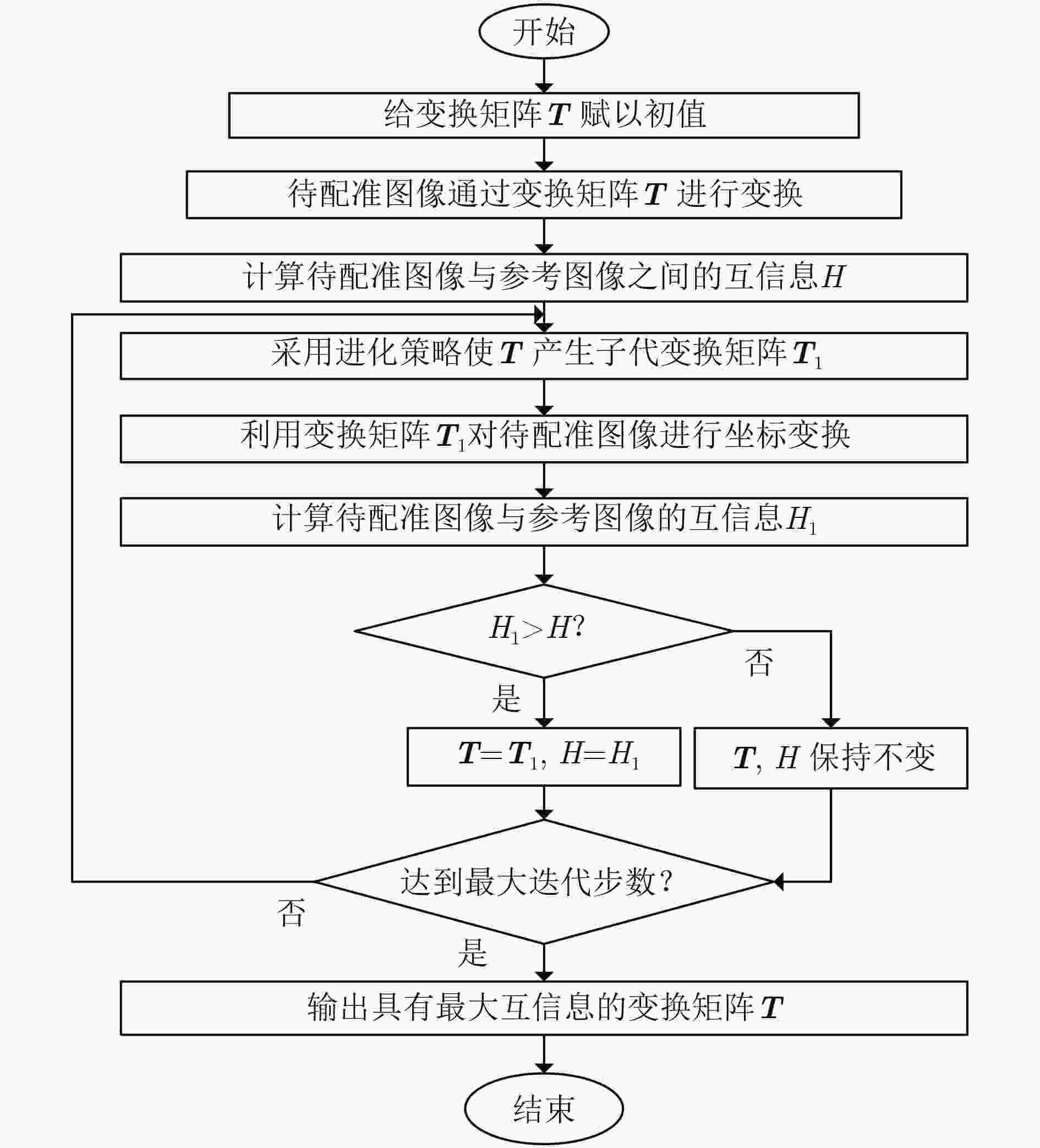
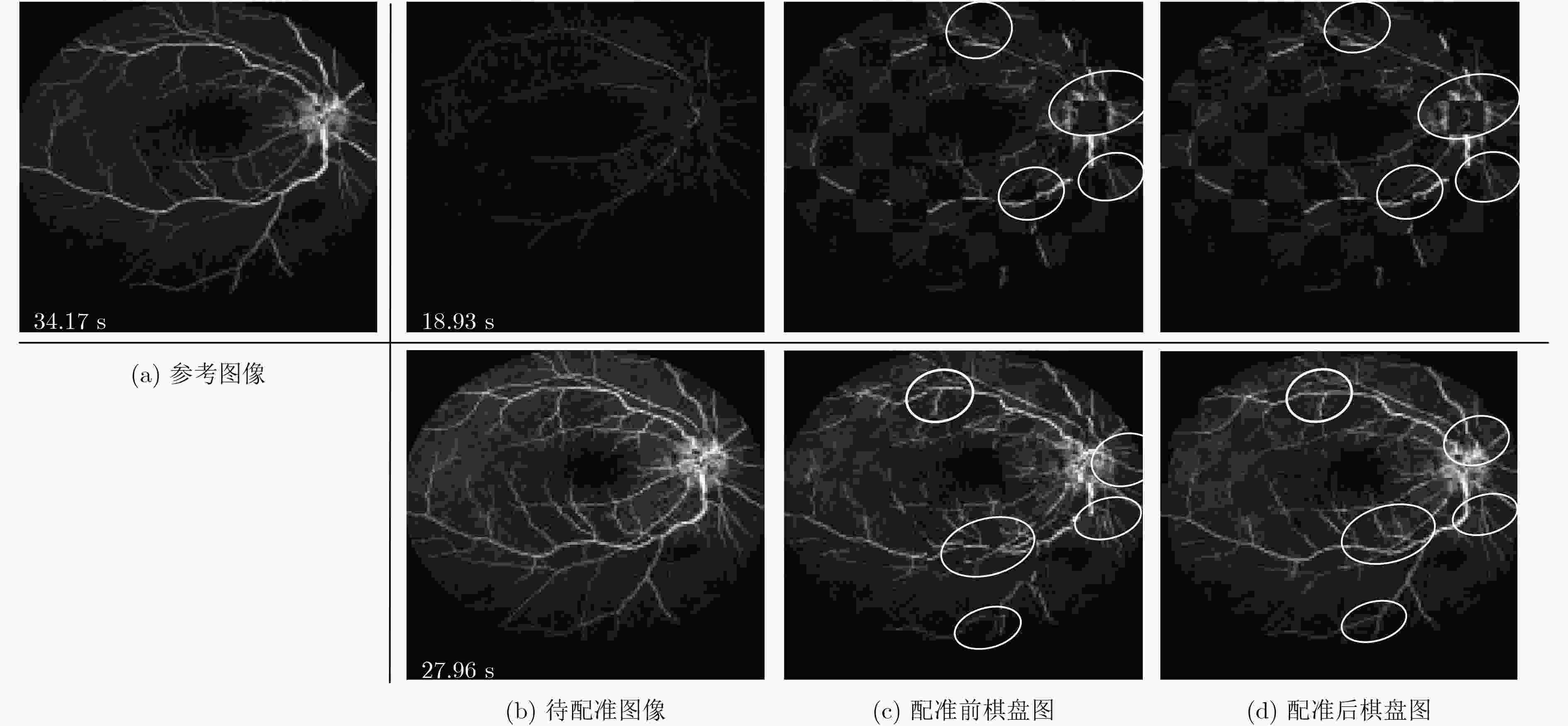
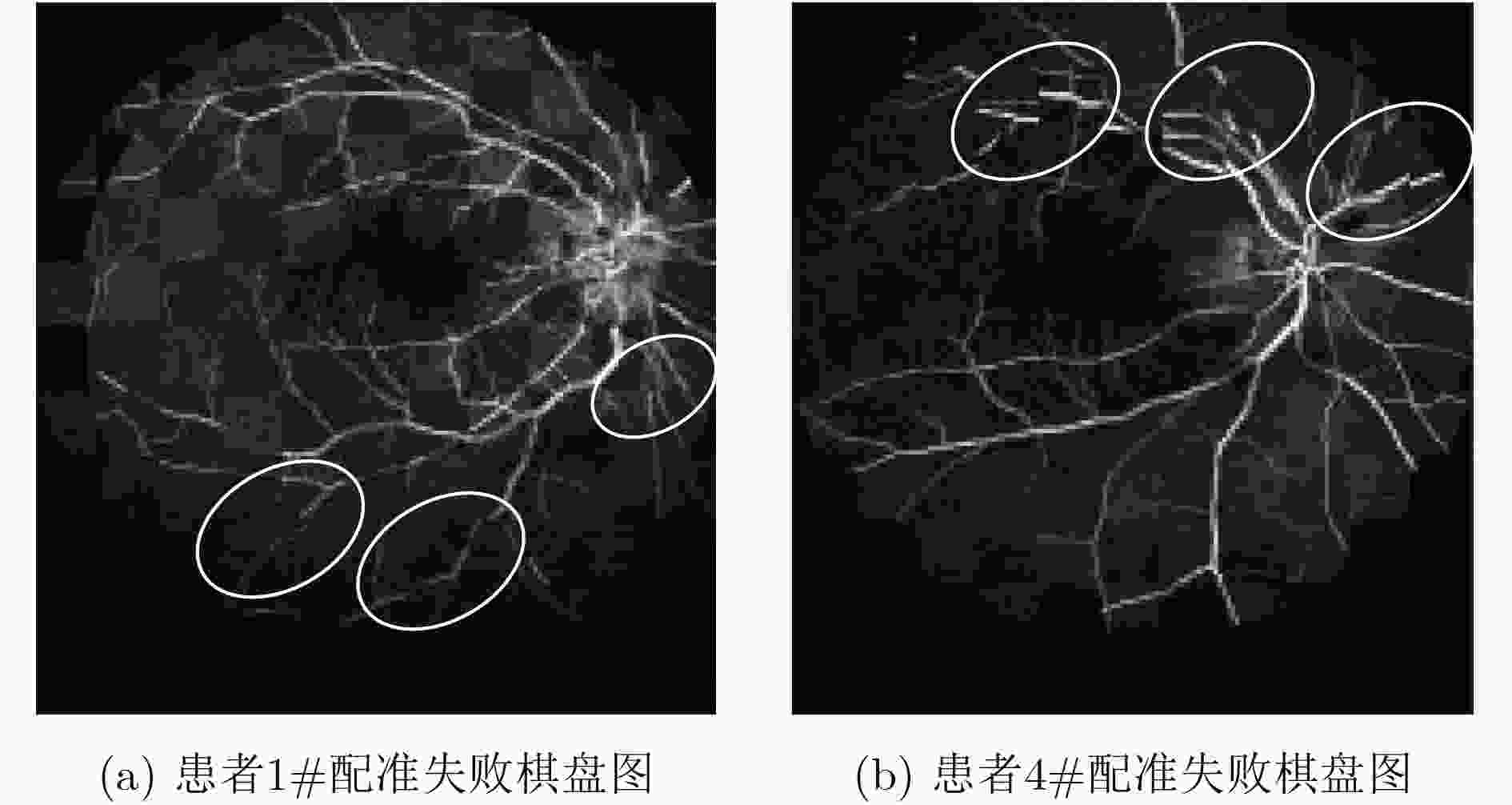
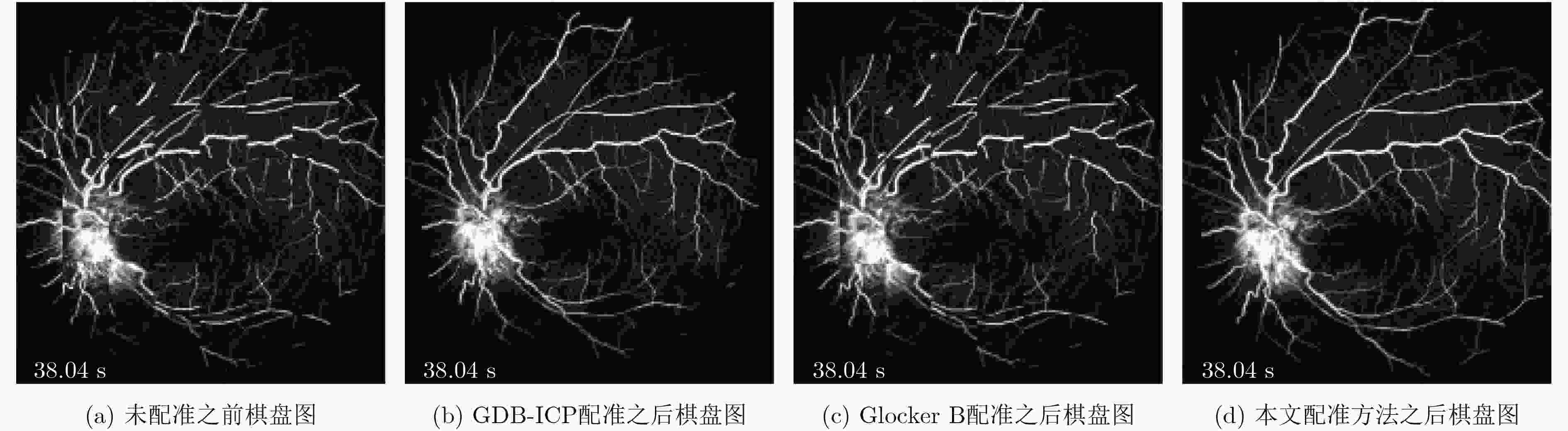
摘要: 荧光素眼底血管造影技术(FFA)是眼底疾病诊断的金标准,但是造影过程中病人不可避免地转动眼球,造成FFA图像序列中感兴趣区域(例如视网膜血管分支、新生血管)的位置发生变化,给后续的图像定量分析与病情准确评估诊断带来困难。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于互信息的FFA图像序列配准方法。首先采用多尺度线性滤波方法分割出图像中的血管,并利用图像金字塔对分割后的图像进行下采样,然后利用互信息计算待配准图像与参考图像的相似性,通过进化策略对配准参数进行优化,获得互信息最大时图像的空间变换矩阵,实现FFA图像的配准。采用上述方法,对4位患者共计1039帧FFA图像进行测试,总体配准率达到93%,失败率仅为1%;与常用的配准方法相比,所提方法的配准率、配准速度和鲁棒性等综合性能良好,为FFA影像的定量分析在未来的临床应用奠定了基础。Abstract: Fluorescein Fundus Angiography (FFA) is regarded as the golden diagnostic criteria for fundus diseases. However, dislocation or rotation of the interested images on anatomic landmark (like retinal vascular branches, neovascularization), caused by inevitable eyeball movement, brings about difficulties in subsequent quantitative analysis and progress assessment of the diseases. In order to solve the above problems, a novel method based on mutual information is proposed for automatic registration of FFA image sequence. Firstly, the vessels of image sequence are segmented by multi-scale linear filter and down sampled hereafter by image pyramid. Then, the similarity of sampled images is calculated by mutual information and the evolution strategy is adopted to optimize the registration parameters. Finally, the transformation matrix with maximum mutual information is obtained to register the FFA image. Tests with FFA image sequences of 4 patients (total 1039 frames) show that the overall registration rate of the algorithm reaches 93% and the failure rate is only 1%. Compared with the classical registration methods, the proposed method shows better comprehensive performance in terms of registration rate, computing speed as well as robustness. It lays basic foundations for quantitative analysis on FFA images and potential clinical application.
-
表 1 本文算法的配准精度测试结果
编号 FFA图像序列的总帧数n 配准效果 失败率(%) 配准率P(%) Y1类帧数 Y2类帧数 F1类帧数 F2类帧数 患者1# 218 195 10 12 1 0.4 94 患者2# 219 205 5 9 0 0 96 患者3# 261 232 13 8 8 3.0 94 患者4# 341 299 10 30 2 0.6 91 总计 1039 931 38 59 11 1.0 93 表 2 GDB-ICP算法对4位患者的FFA图像序列配准精度
编号 FFA图像序列的总帧数 配准效果 失败率(%) 配准率P(%) Y1类帧数 Y2类帧数 F1类帧数 F2类帧数 患者1# 218 170 2 14 32 15 79 患者2# 219 172 3 6 38 17 80 患者3# 261 244 1 6 10 4 94 患者4# 341 295 13 17 16 6 90 总计 1039 881 19 43 96 9 87 表 3 Glocker B算法对4位患者的FFA图像序列配准精度
编号 FFA图像序列的总帧数 配准效果 失败率(%) 配准率P(%) Y1类帧数 Y2类帧数 F1类帧数 F2类帧数 患者1# 218 106 1 1 110 50 49 患者2# 219 82 1 29 107 49 38 患者3# 261 75 3 60 123 47 30 患者4# 341 227 2 18 94 28 67 总计 1039 490 7 108 434 42 48 表 4 本文算法、GDB-ICP以及Glocker B算法的运行时间对比(min)
编号 FFA图像序列帧数 本文算法 GDB-ICP Glocker B 患者1# 218 32.45 68.17 13.08 患者2# 219 31.75 62.42 13.33 患者3# 261 37.93 101.13 15.32 患者4# 341 50.35 125.77 20.00 -
DREO J, NUNES J C, and SIARRY P. Robust rigid registration of retinal angiograms through optimization[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging & Graphics, 2006, 30(8): 453-463. DOI: 10.1016/j.compmedi mag.2006.07.004. LAAKSONEN L, CLARIDGE E, FÄLT P, et al. Comparison of image registration methods for composing spectral retinal images[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing & Control, 2017, 36: 234-245. DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2017.03.003. COPELAND A, MANGOUBI R, DESAI M, et al. Enhancing the surgeons reality: Smart visualization of bolus time of arrival and blood flow anomalies from time lapse series for safety and speed of cerebrovascular surgery[C]. IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 2009: 1–4. GHASSABI Z, SHANBEHZADEH J, and MOHAMMADZADEH A. A structure-based region detector for high-resolution retinal fundus image registration[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing & Control, 2016, 23: 52-61.DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2015.08.005 PEREZROVIRA A, CABIDO R, TRUCCO E, et al. RERBEE: Robust efficient registration via bifurcations and elongated elements applied to retinal fluorescein angiogram sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2012, 31(1): 140-150. DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2011.2167517. TSAI C L, LI Chunyi, YANG Gehua, et al. The edge-driven dual-bootstrap iterative closest point algorithm for registration of multimodal fluorescein angiogram sequence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2010, 29(3): 636-649. DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2030324. 汪立, 蒋念平. 基于改进Harris角点检测的视网膜图像配准[J]. 电子科技, 2017, 30(2): 119–122. DOI: 10.16180/j.cnki.issn1007-7820.2017.02.031.WANG Li and JIANG Nianping. Retinal image registration based on improved Harris corner detection[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2017, 30(2): 119–122. DOI: 10.16180/j.cnki.iss n1007-7820.2017.02.031. YAVUZ Z and KÖSE C. Retinal fundus image registration using bifurcation and crossover points[C]. Signal Processing and Communication Application Conference, Zonguldak, Turkey, 2016: 1485–1488. PALRAJ P and VENNILA I. Retinal fundus image registration via blood vessel extraction using binary particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging & Health Informatics, 2016, 6(2): 328-337. DOI: 10.1166/jmihi.2016.1701 SAHA S K, DI X, FROST S, et al. A two-step approach for longitudinal registration of retinal images[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2016, 40: 277. DOI: 10.1007/s10916-016-0640-0. CAN A, STEWART C V, TANENBAUM H L, et al. A Feature-based, robust, hierarchical algorithm for registering pairs of images of the curved human retina[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(3): 347-364. DOI: 10.1109/34.990136. 李英杰, 张俊举, 常本康, 等. 电子与信息学报, 2016. 38(1): 8-14. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT150479.LI Yingjie, ZHANG Junju, CHANG Benkang, et al. A multi - band infrared image joint registration and fusion method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016. 38(1): 8-14. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT150479. HENEGHAN C, MAGUIRE P, RYAN N, et al. Retinal image registration using control points[C]. Proceedings IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Washington, DC, USA, 2002: 349–352. doi: 10.1109/ISBI. 2002.1029265. 刘妍, 余淮, 杨文, 等. 利用SAR-FAST角点检测的合成孔径雷达图像配准方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(2): 430–436. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT160386.LIU Yan, YU Huai, YANG Wen, et al. Synthetic aperture radar image registration method using SAR - FAST corner detection [J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2017, 39(2): 430–436. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT160386. LALIBERTÉ F, GAGNON L, and SHENG Y. Registration and fusion of retinal images--an evaluation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Med Imaging, 2003, 22(5): 661-673. DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2003.812263. 任克强, 胡梦云. 基于改进SURF算子的彩色图像配准算法[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2016, 30(5): 748-756. DOI: 10.13382/j.jemi.2016.05.011.REN Keqiang and HU Mengyun. Color image registration algorithm based on improved SURF operator[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2016, 30(5): 748-756. DOI: 10.13382/j.jemi.2016.05.011. CHEN Jian, TIAN Jie, LEE N, et al. A partial intensity invariant feature descriptor for multimodal retinal image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2010, 57(7): 1707-1718. DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2042169. WANG Guang, WANG Zhicheng, CHEN Yufei, et al. Robust point matching method for multimodal retinal image registration[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing & Control, 2015, 19: 68-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2015.03.004. YANG G, STEWART C V, SOFKA M, et al. Registration of challenging image pairs: initialization, estimation, and decision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(11): 1973-1989. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1116. NUNES J C and BOUAOUNE Y. A multiscale elastic registration scheme for retinal angiograms[J]. Computer Vision & Image Understanding, 2004, 95(2): 129-149. DOI: 10.1016/j.cviu.2004.03.007. NGUYEN U T V, BHUIYAN A, PARK L A F, et al. An effective retinal blood vessel segmentation method using multi-scale line detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(3): 703-715. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.08.009. STYNER M, BRECHBÜHLER C, SZCKELY G, et al. Parametric estimate of intensity inhomogeneities applied to MRI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2000, 19(3): 153-165. DOI: 10.1109/42.845174. GLOCKER B, KOMODAKIS N, PARAGIOS N, et al. Inter and intra-modal deformable registration: Continuous deformations meet efficient optimal linear programming[C]. IPMI'07 Processings of the 20th International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, Kerkrade, The Netherlands, 2007: 408–420. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
