Adaptive Scaling of Virtualized Network Function Resource Capacity
-
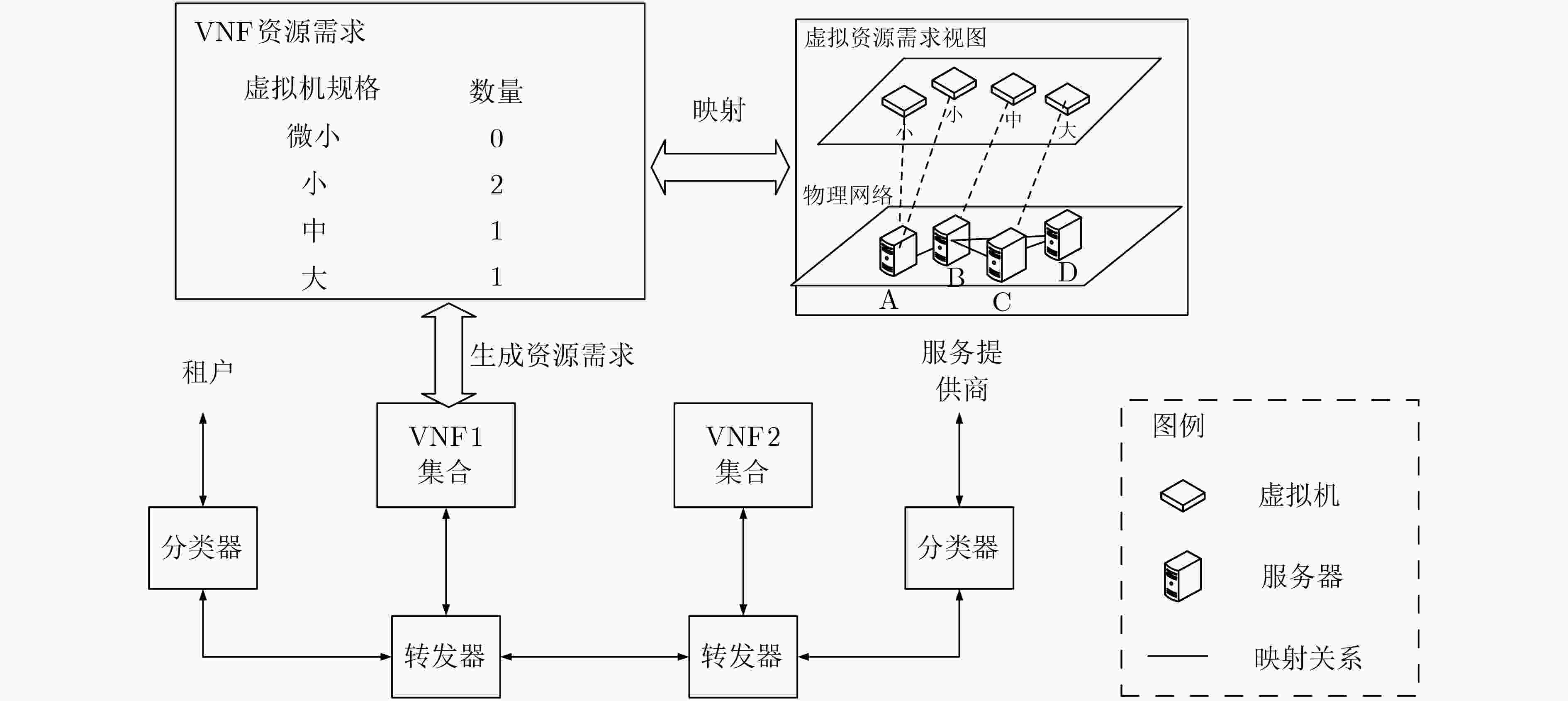
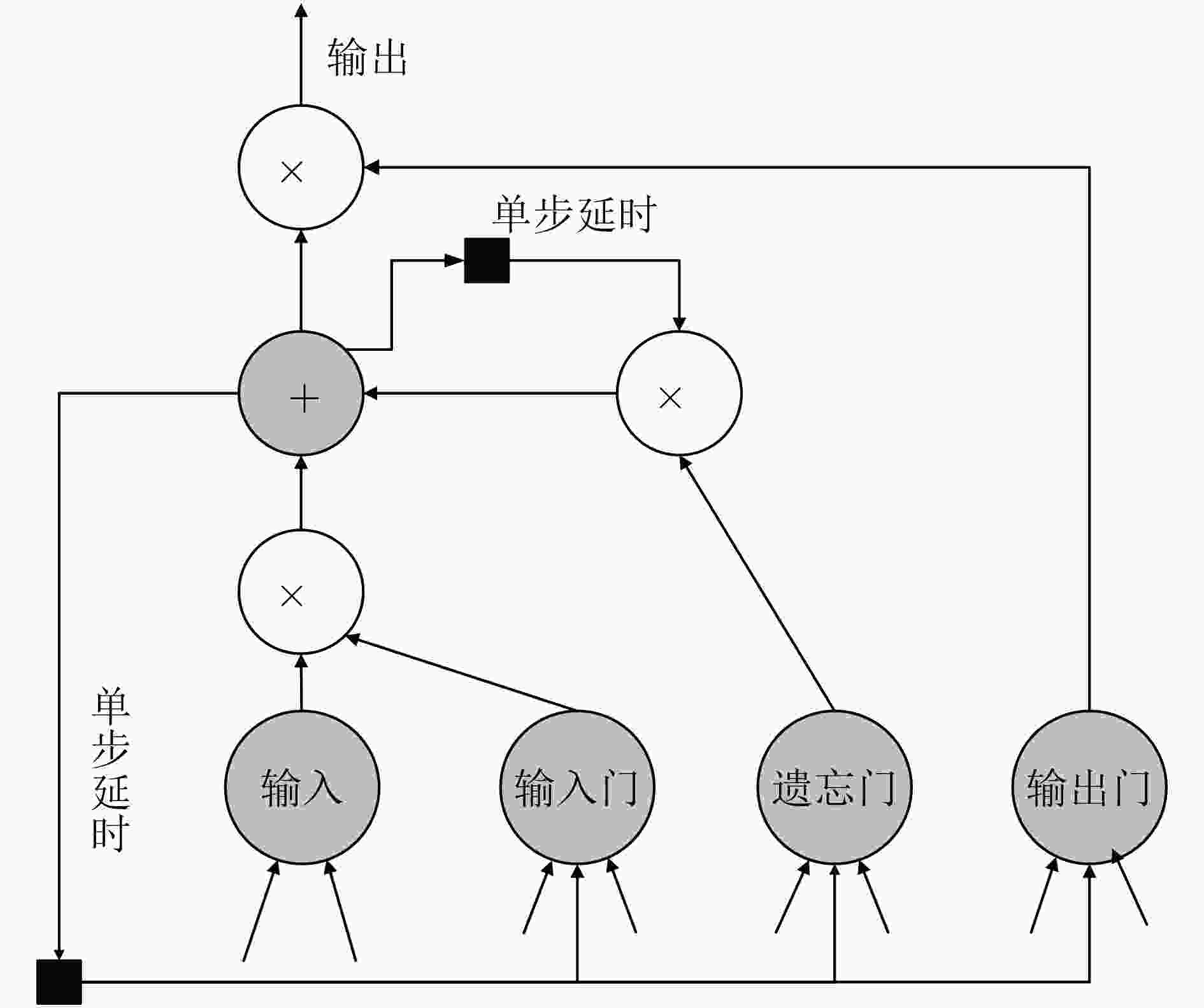
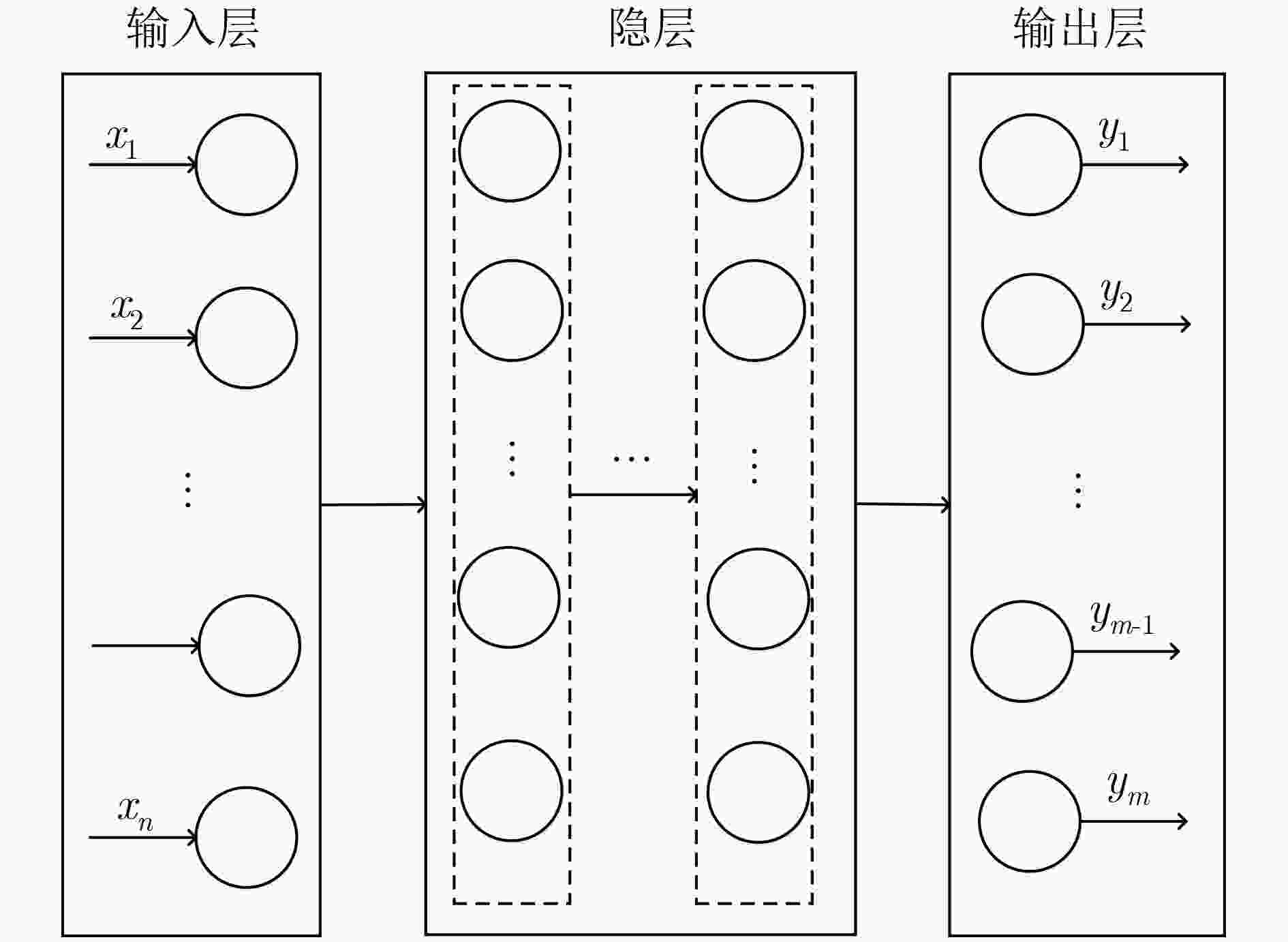
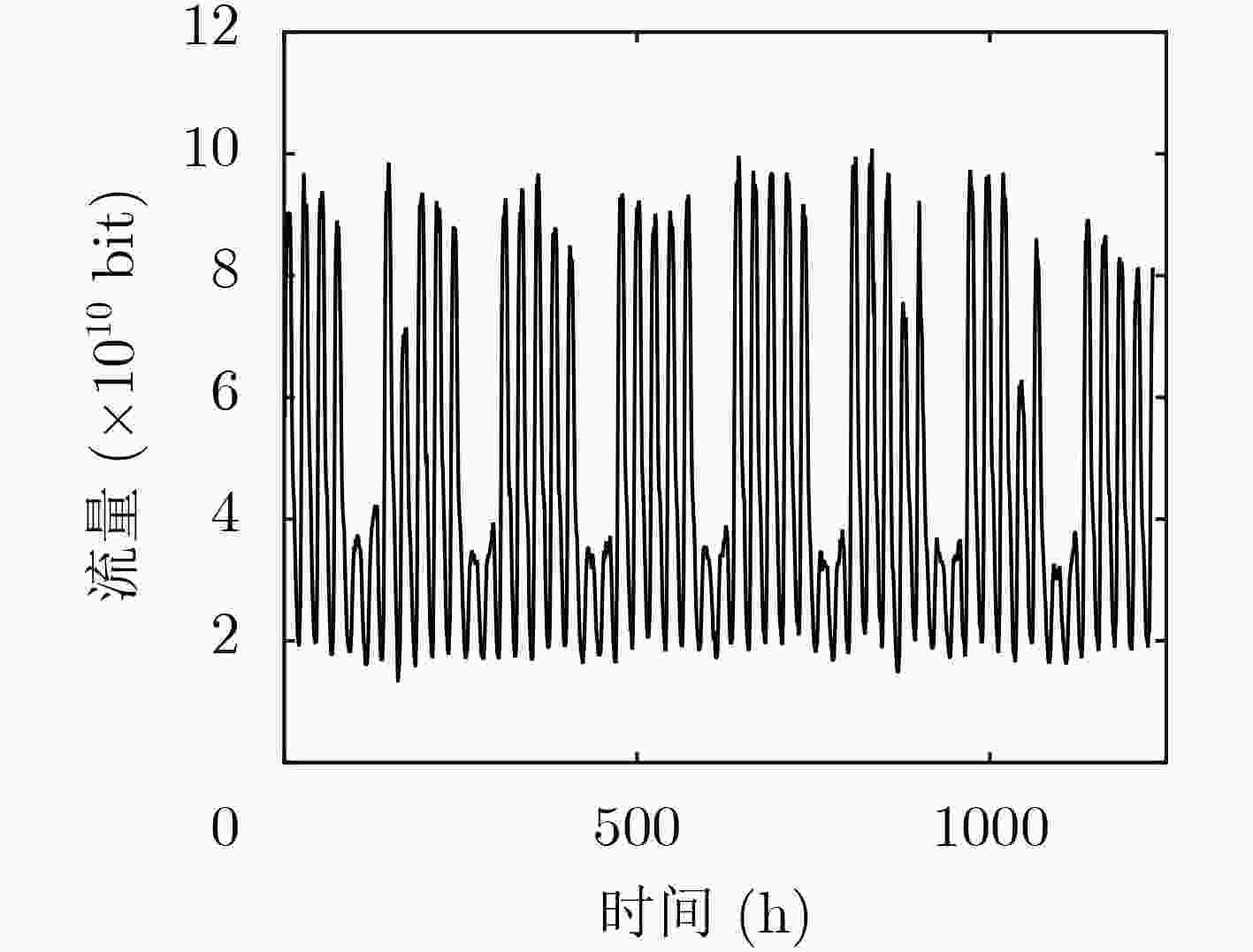
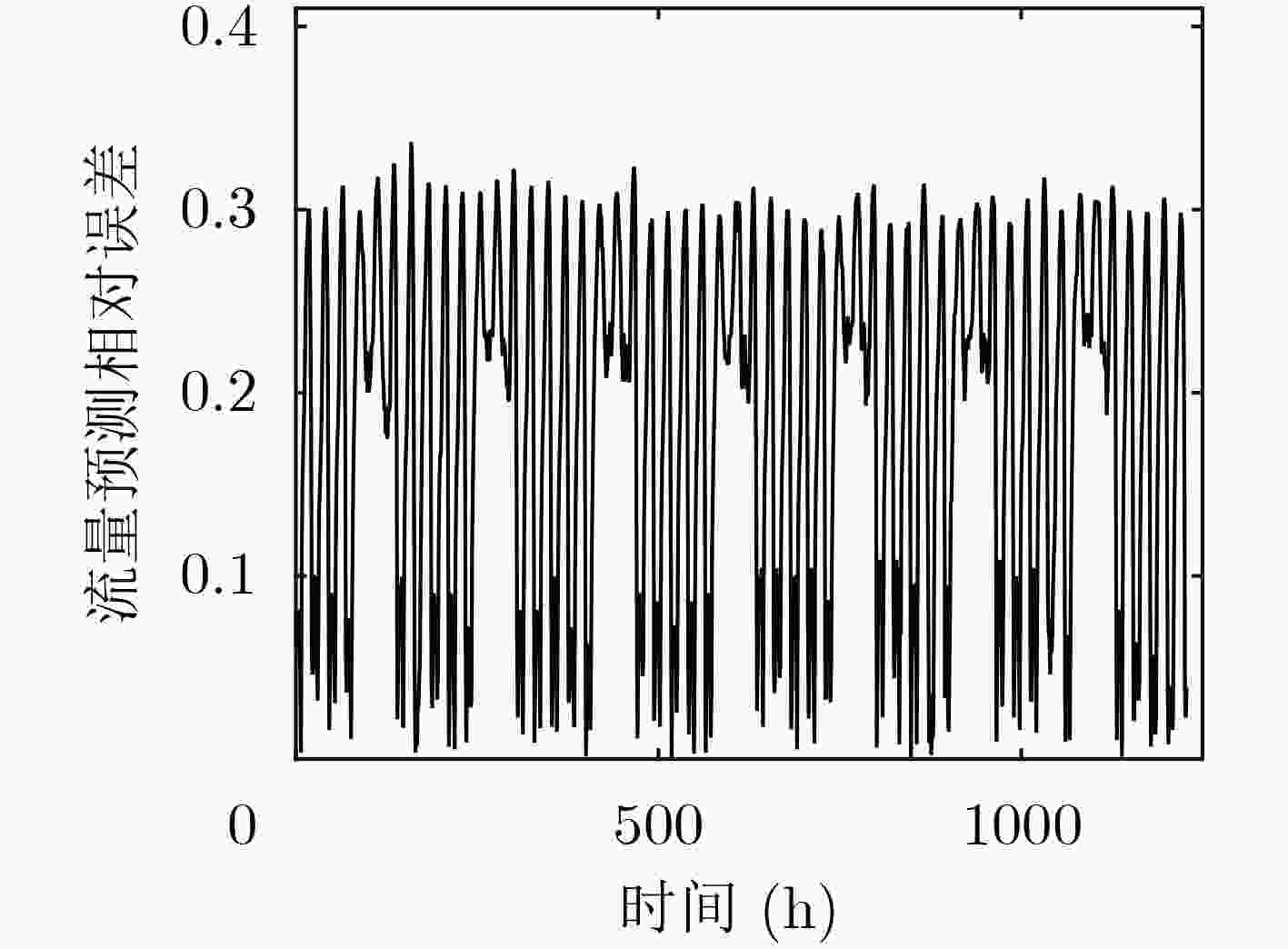
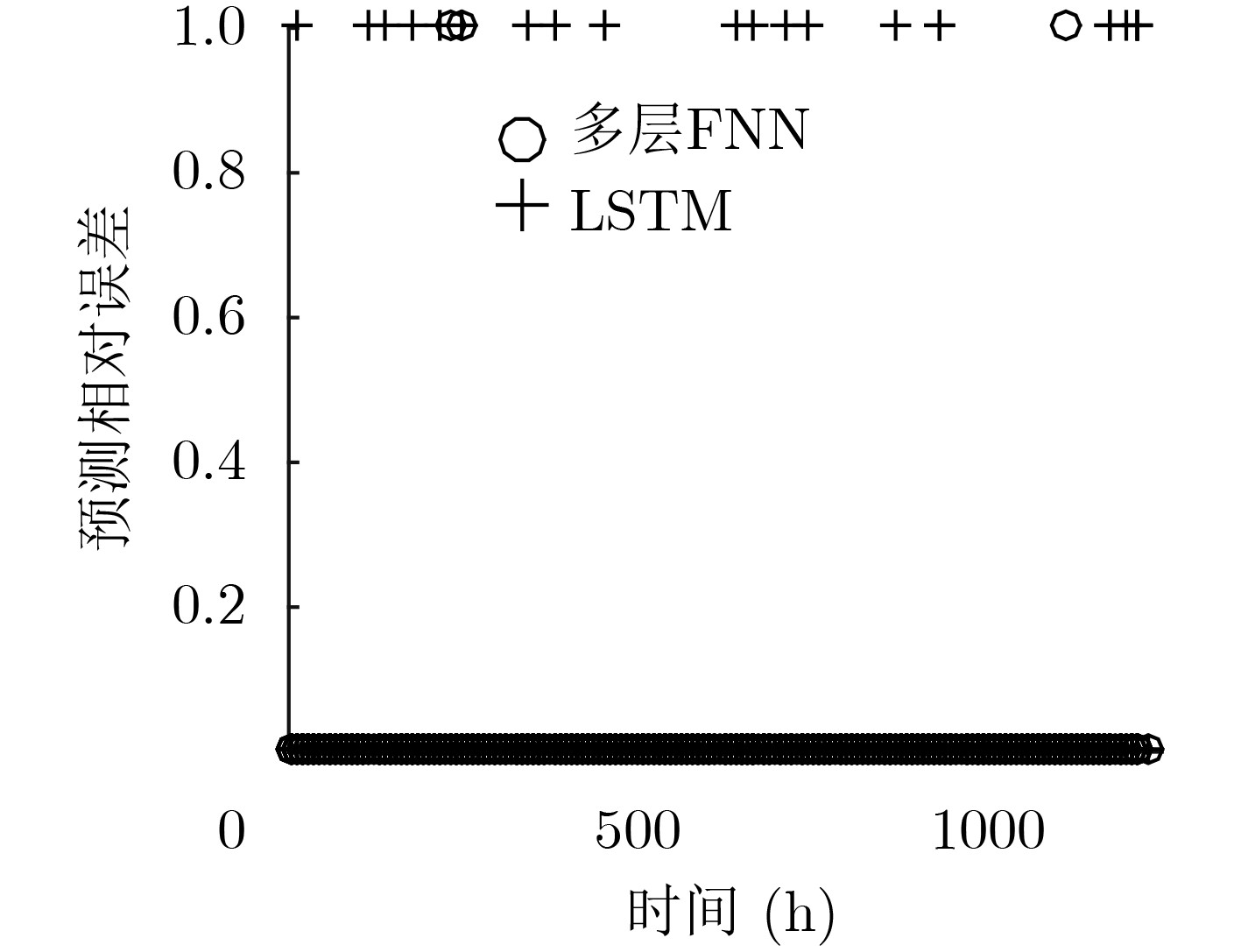
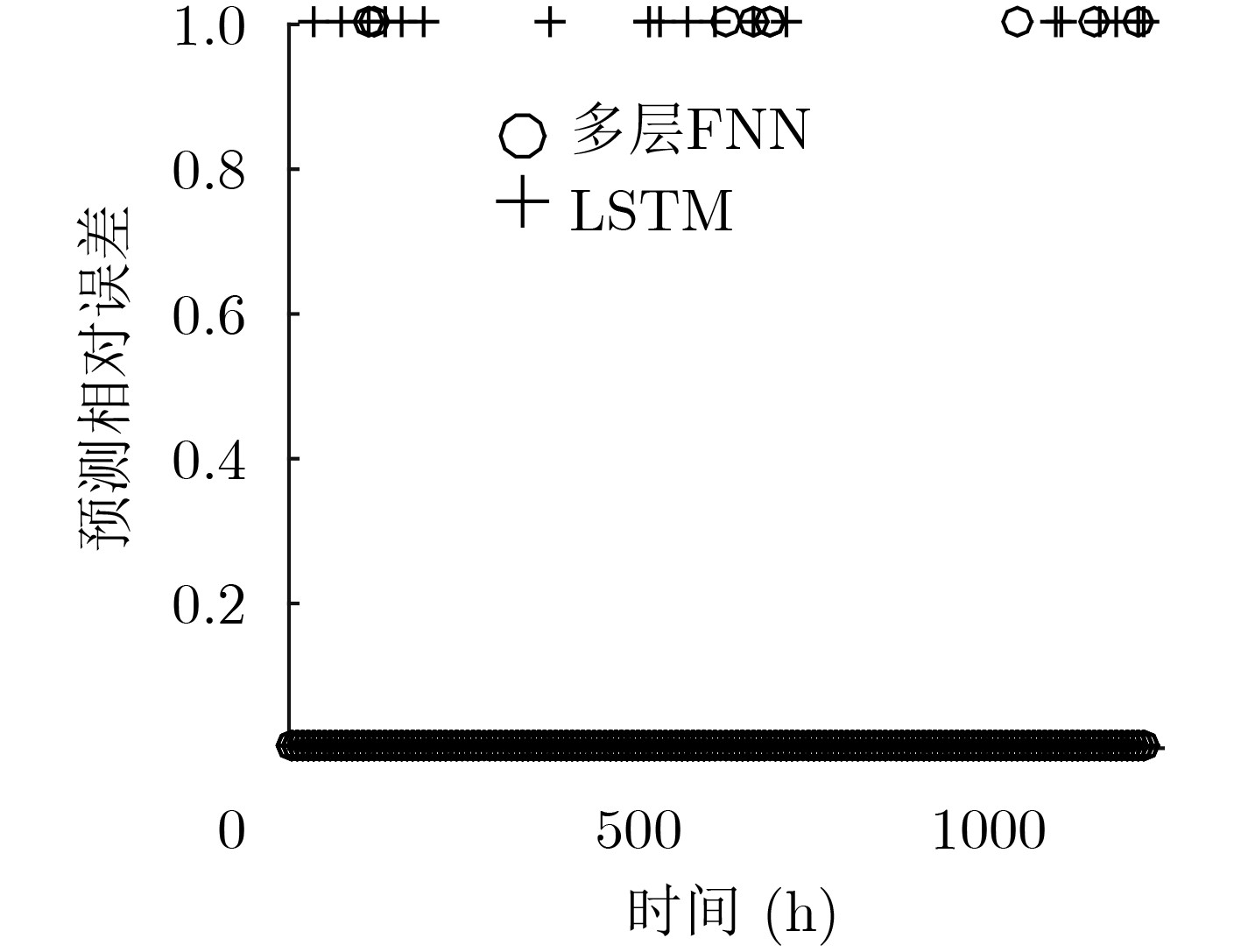
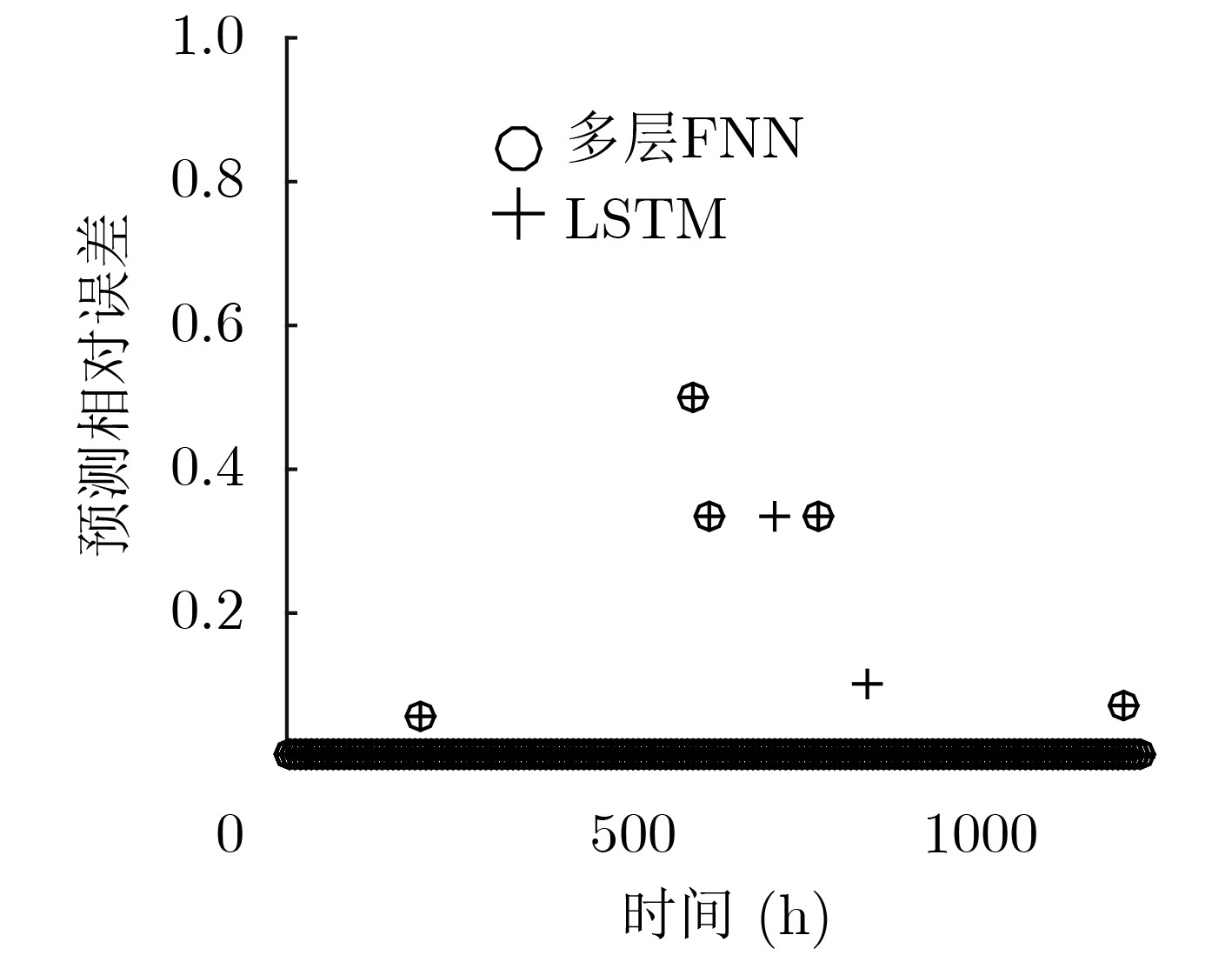
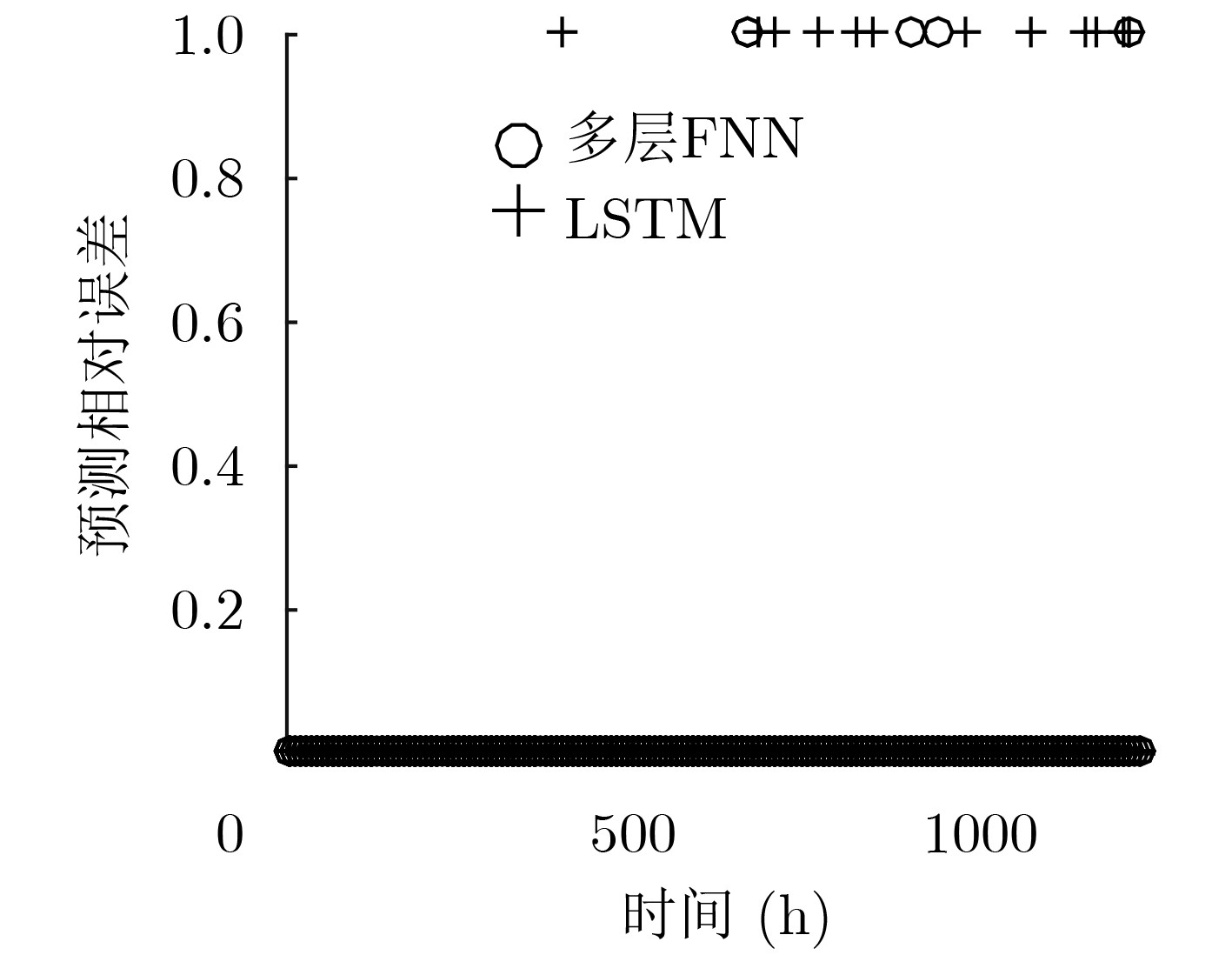
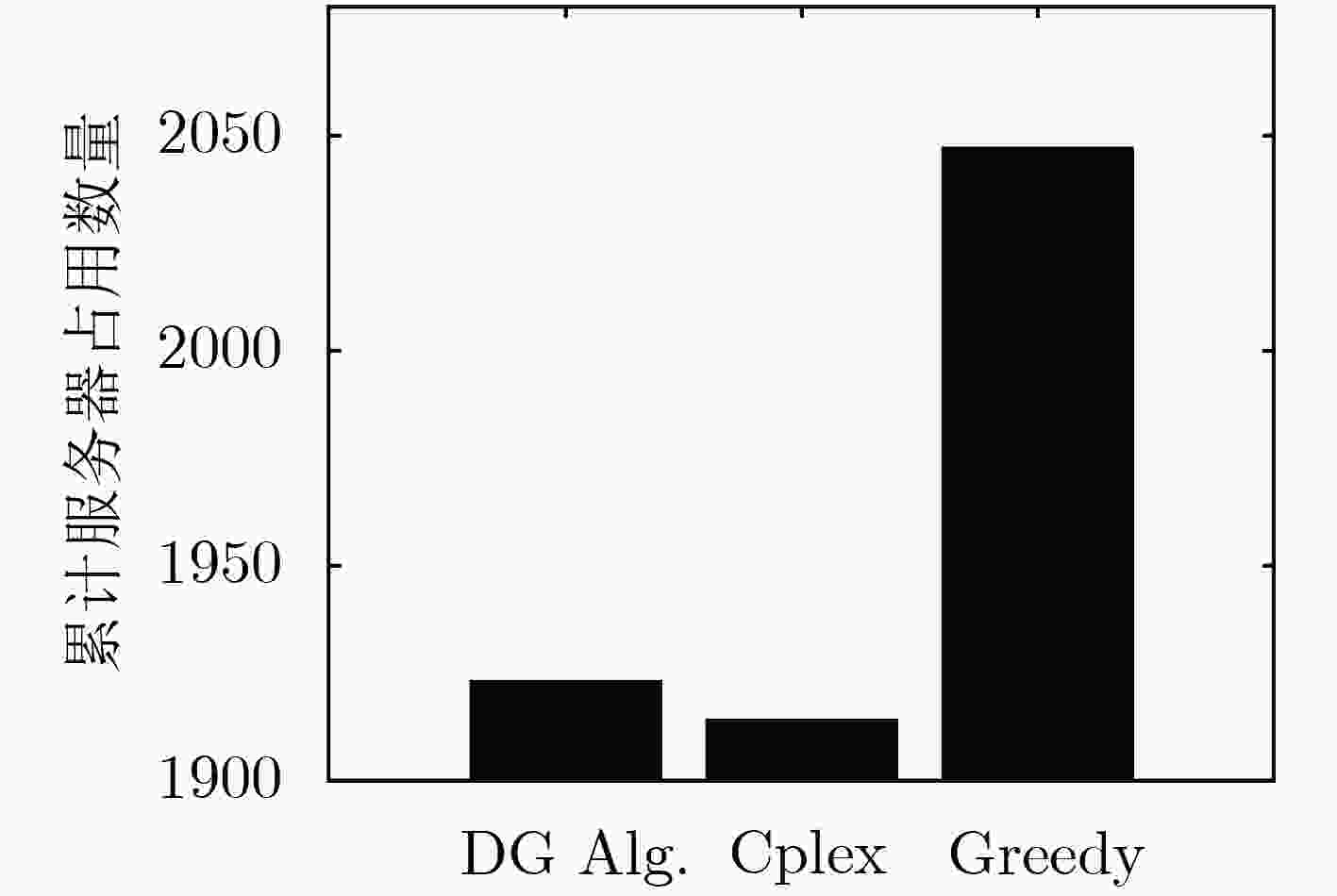
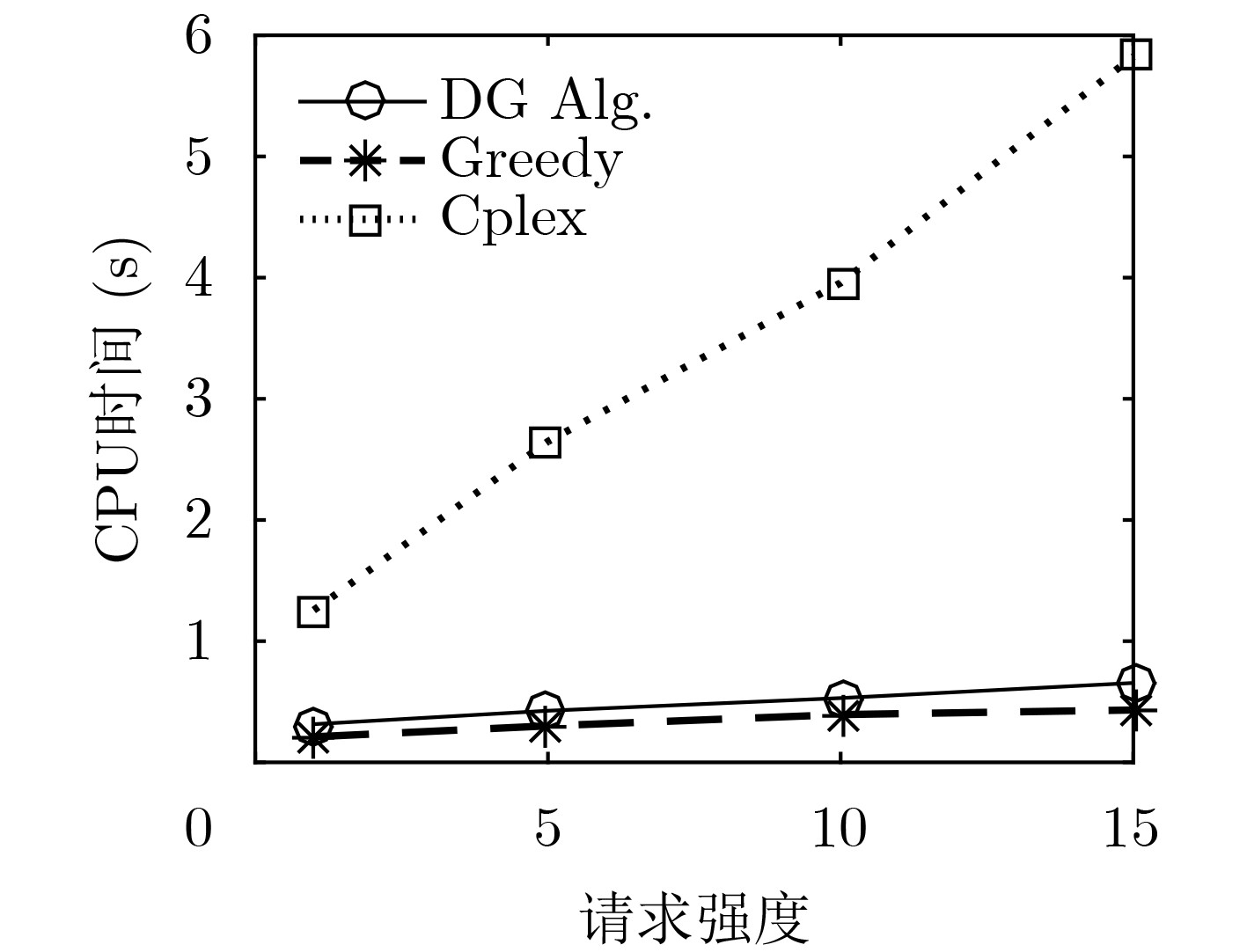
摘要: 为了实现网络功能虚拟化平台中物理资源的动态按需分配,该文提出一种虚拟网络功能资源容量自适应调整方法。该方法首先利用长短期记忆网络预测平台流量的变化趋势,然后结合流量预测结果设计了一种基于多层前馈神经网络的虚拟网络功能资源需求预测方法,最后根据资源需求预测结果,设计了一种基于动态编码遗传算法的虚拟网络功能动态部署方法,实现虚拟网络功能资源容量的自适应调整。实验结果表明,与现有的资源容量调整方法相比,该文提出的资源容量自适应调整方法能够降低流量预测误差对资源需求预测结果的影响,降低资源需求预测的相对误差,减少虚拟网络功能实例占用的服务器数量。
-
关键词:
- 网络功能虚拟化 /
- 虚拟网络功能资源分配 /
- 前馈神经网络 /
- 整数线性规划 /
- 遗传算法
Abstract: In order to realize on-demand physical resource allocation in network function virtualization platform, an adaptive virtualized network function scaling method is proposed. The proposed method first use long short term memory network to realize traffic forecasting. Then combining with the forecasting result, a forward neural network-based approach is designed to predict resource demand of requested virtualized network function. Finally, according to the result of resource demand prediction, a dynamic encoding genetic algorithm is proposed to realize dynamic deployment of virtualized network function instances. The experiment results show that compared with existing scaling methods, the proposed scaling method can reduce the negative impact of inaccurate traffic forecasting, decrease the relative error of resource demand prediction as well as the total number of servers occupied by requested virtualized network function instances. -
表 1
$t$ 时刻资源需求预测特征提取特征参数 意义 ${{L}}(t)$ 历史流量向量,包含$t - i$时刻到$t$时刻的实测流量数据${{L}}(t) = \{ l(t - i), ··· ,l(t)\} $ $p(t + 1)$ $t + 1$时刻的流量预测数据 ${\rm{ServerID}}$ 当前流量流经的接入网关服务器序号,用于区分 ${{R}}(t)$ 历史资源需求向量,包含$t$时刻的资源需求数据${{R}}(t) = \{ {r_1}(t), ··· ,{r_j}(t), ··· ,{r_m}(t)\} $,其中任意元素${r_j}(t)$表示$t$时刻平台实例化第$j$种规格VNF的数量 表 2 VNF动态部署算法(DG Alg.)
输入:$t$时刻资源容量需求向量${ {{{R}}} }(t)$;服务器资源容量矩阵${ {{{C}}} }(t)$;
服务器邻接矩阵${ {{{E}}} }(t)$输出:最优VNF部署决策矩阵${ { {{{X}}} }^*}(t)$ (1) 初始化遗传算法参数:种群规模${\rm{NIND}}$,最大遗传代数
${\rm{MAXGEN}}$,交叉和变异概率${P_x}$, ${P_m}$
(2) 计算$t$时刻染色体上的基因数目${N_g}(t) = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^m { {r_i}(t)}$(3) 随机初始化种群中的每个染色体,每个基因位的进制设为服
务器数量$n$(4) for $i = 1:{\rm{NIND}}$ (5) 根据${ {{{R}}} }(t)$分段统计各基因位的服务器序号,计算染色体$n$对
应的VNF部署决策变量${{{X}}_i}(t)$(6) if ${{{X}}_i}(t)$满足约束条件式(2)-式(5)do (7) 根据式(1)计算当前染色体的适应度 (8) else (9) 当前染色体对应的部署策略无法完成部署,适应度为惩罚值
${N_p}$(10) end if (11) end for (12) for ${\rm{gen = }}1:{\rm{MAXGEN}}$ (13) 根据适应度计算染色体参与遗传的优先级,以概率${P_x}$对候
选染色体上基因进行交叉遗传(14) 按照概率${P_m}$选择染色体上任意基因进行变异操作 (15) 获取子代种群,重复步骤(4)—步骤(11),计算子代种群各
个染色体的适应度(16) 用子代中适应度高的染色体替换父代中适应度低的染色
体,形成新的种群(17) end for (18) 保留最终代中最优染色体,返回其对应的VNF部署决策变
量${ { {{{X}}} }^*}(t)$表 3 服务器参数
型号 CPU 内存(GB) 硬盘(TB) 高配 28 CPUs x Intel(R) Xeon(R)
CPU E5-2660 v4 @ 2.00GHz128 14 低配 20 CPUs x Intel(R) Xeon(R)
CPU E5-2630 v4 @ 2.20GHz64 14 表 4 虚拟机规格参数
规格 VCPU(个) 内存(GB) 硬盘(GB) 微小 1 1 20 小 2 2 50 中 4 4 200 大 4 8 500 -
[1] ORDONEZ-LUCENA J, AMEIGEIRAS P, LOPEZ D, et al. Network slicing for 5G with SDN/NFV: Concepts, architectures, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(5): 80–87. doi: 10.1109/mcom.2017.1600935 [2] HERRERA J G and BOTERO J F. Resource allocation in NFV: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2016, 13(3): 518–532. doi: 10.1109/tnsm.2016.2598420 [3] ADAMUZ-HINOJOSA O, ORDONEZ-LUCENA J, AMEIGEIRAS P, et al. Automated network service scaling in NFV: Concepts, mechanisms and scaling workflow[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(7): 162–169. doi: 10.1109/mcom.2018.1701336 [4] RAHMAN S, AHMED T, HUYNH M, et al. Auto-scaling VNFs using machine learning to improve QoS and reduce cost[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–6. [5] TANG Hong, ZHOU D, and CHEN Duan. Dynamic network function instance scaling based on traffic forecasting and VNF placement in operator data centers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2018, 30(3): 530–543. doi: 10.1109/tpds.2018.2867587 [6] ALAWE I, HADJADJ-AOUL Y, KSENTINI A, et al. Smart scaling of the 5G core network: An RNN-based approach[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Abu Dhabi, The United Arab Emirates, 2018: 1–6. [7] ALAWE I, HADJADJ-AOUL Y, KSENTINIT A, et al. An efficient and lightweight load forecasting for proactive scaling in 5G mobile networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Conference on Standards for Communications and Networking, Paris, France, 2018: 1–6. [8] FEI Xincai, LIU Fangming, XU Hong, et al. Adaptive VNF scaling and flow routing with proactive demand prediction[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu USA, 2018: 486–494. [9] 唐伦, 周钰, 杨友超, 等. 5G网络切片场景中基于预测的虚拟网络功能动态部署算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2071–2078. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180894TANG Lun, ZHOU Yu, YANG Youchao, et al. Virtual network function dynamic deployment algorithm based on prediction for 5G network slicing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2071–2078. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180894 [10] REN Yi, PHUNG-DUC T, LIU Yikuan, et al. ASA: Adaptive VNF scaling algorithm for 5G mobile networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE 7th International Conference on Cloud Networking, Tokyo, Japan, 2018: 1–4. [11] WANG Xiaoke, WU Chuan, LE F, et al. Online VNF scaling in datacenters[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 140–147. [12] WANG Xiaoke, WU Chuan, LE F, et al. Online learning-assisted VNF service chain scaling with network uncertainties[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 205–213. [13] 史久根, 张径, 徐皓, 等. 一种面向运营成本优化的虚拟网络功能部署和路由分配策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 973–979. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180522SHI Jiugen, ZHANG Jing, XU Hao, et al. Joint optimization of virtualized network function placement and routing allocation for operational expenditure[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 973–979. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180522 [14] 张红旗, 黄睿, 常德显. 一种基于匹配博弈的服务链协同映射方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 385–393. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180385ZHANG Hongqi, HUANG Rui, and CHANG Dexian. A collaborative mapping method for service chain based on matching game[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 385–393. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180385 [15] ZHOU Songnian. A trace-driven simulation study of dynamic load balancing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 1988, 14(9): 1327–1341. doi: 10.1109/32.6176 [16] MEDHAT A M, TALEB T, ELMANGOUSH A, et al. Service function chaining in next generation networks: State of the art and research challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(2): 216–223. doi: 10.1109/mcom.2016.1600219rp [17] PARVEZ I, RAHMATI A, GUVENC I, et al. A survey on low latency towards 5G: RAN, core network and caching solutions[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(4): 3098–3130. doi: 10.1109/comst.2018.2841349 [18] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, and COURVILLE A. Deep Learning[M]. Cambridge, USA: MIT Press, 2016: 397–399. [19] HORNIK K. Approximation capabilities of multilayer feedforward networks[J]. Neural Networks, 1991, 4(2): 251–257. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(91)90009-t [20] LOIOLA E M, DE ABREU N M M, BOAVENTURA-NETTO P O, et al. A survey for the quadratic assignment problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 176(2): 657–690. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2005.09.032 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
