Sparse Flight 3-D Imaging of Spaceborne SAR Based on Frequency Domain Sparse Compressed Sensing
-
摘要:
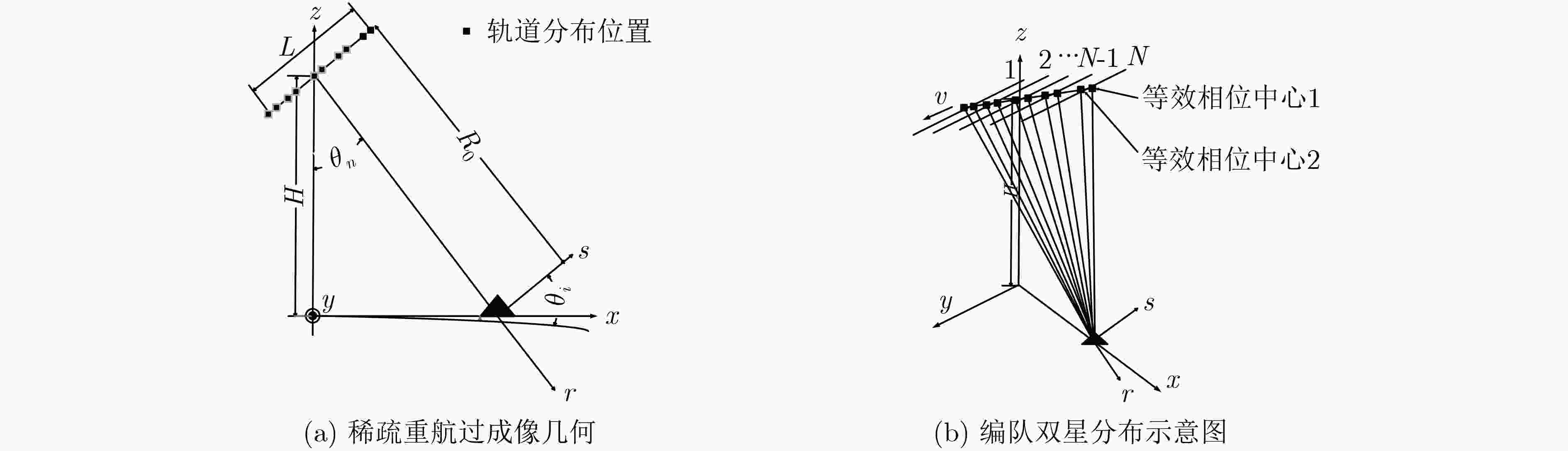
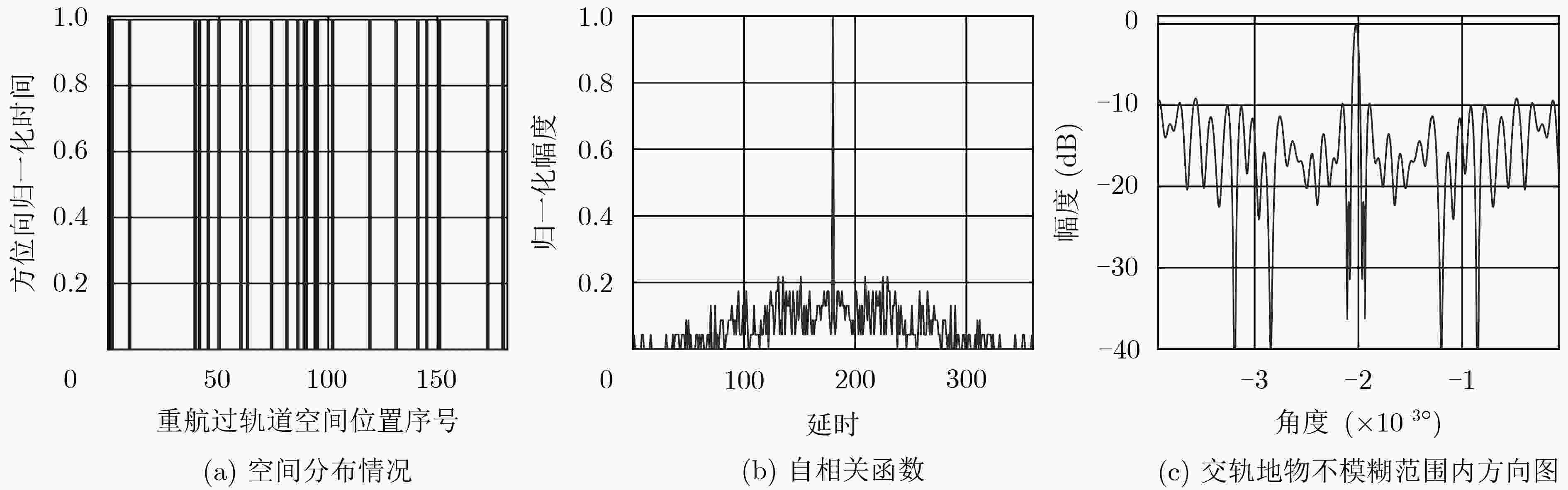
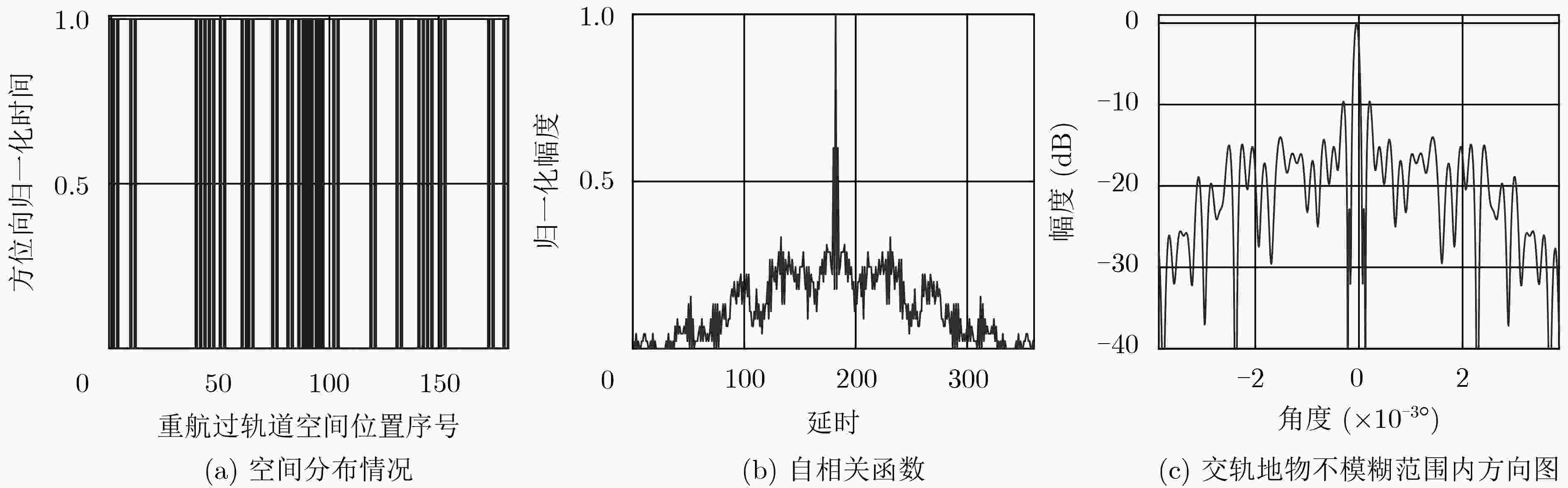
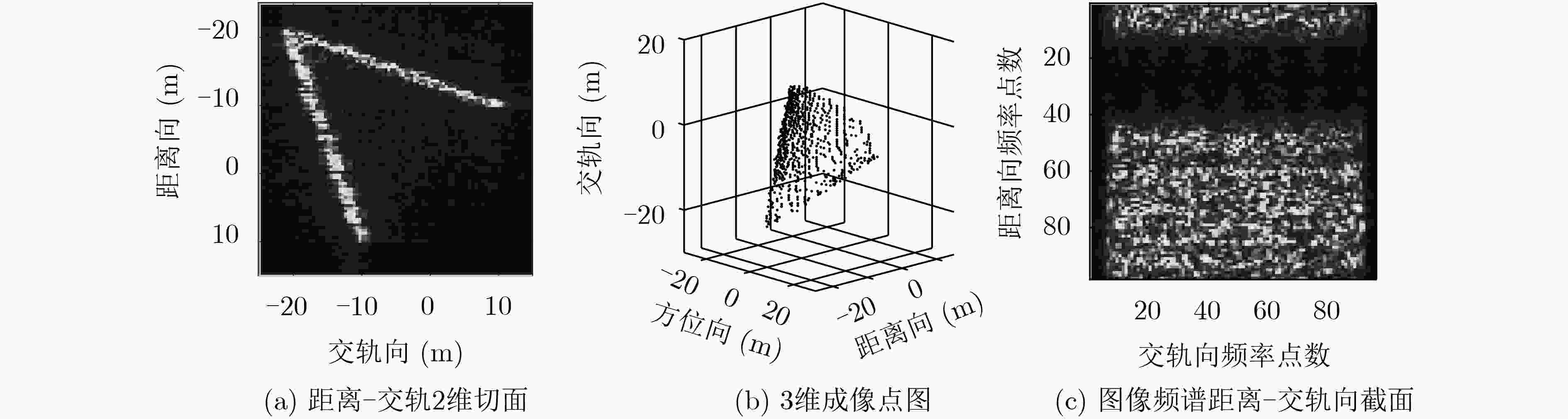
星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)稀疏重航过3维成像技术通过交轨向的多次飞行观测,获得观测场景的第3维分辨。该文给出了单颗卫星SAR稀疏重航过轨道分布,为有效缩短重访时间,同时给出了编队双星SAR轨道分布,对应的交轨向等效孔径长度为20 km。提出了一种基于干涉处理和频域压缩感知(CS)的稀疏3维成像方法,利用稀疏重航过中的部分回波形成参考3维复图像,对待重建SAR 3维图像信号进行干涉处理,使信号在频域具备稀疏性。在大轨道分布范围下,建立频域距离向-交轨向线性测量矩阵,利用CS理论联合求解稀疏表征下的图像频谱,避免交轨向和距离向的回波信号耦合。将求解所得频谱逆变换至空间域,可得到观测场景的3维图像重建结果。仿真结果表明,该文方法在稀疏采样率74.4%条件下,仍可获得与满采样成像性能相当的结果,验证了干涉处理频域稀疏方法在星载SAR 3维成像中的有效性。
Abstract:The space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sparse flight three-dimensional (3-D) imaging technology through the multiple observations in cross-track direction obtains the 3-D spatial distribution of the observed scene. In this paper, the orbit distribution of single satellite SAR sparse flight is given. In order to shorten effectively the satellite revisit time, the formation of double star SAR orbit distribution is given. The corresponding cross-track equivalent aperture length is 20 km. A sparse 3-D imaging method based on interferometry and compressed sensing is proposed. The referential complex image is formed by using part of the echoes of the sparse flight, and the SAR 3-D image signals which are to be reconstruct are processed by interferometry. This method makes the signal sparse in the frequency domain. Under the large orbit distribution range, the frequency domain range direction and cross-track linear measurement matrix is established, which is beneficial to the Compressed Sensing(CS) theory to solve jointly the image frequency spectrum under sparse representation, and avoid the echoes coupling between the range and cross-track direction. Inversely transforming the resulting spectrum into the spatial domain, the reconstruction result can be obtained. Simulation results show that under the condition of sparse sampling rate of 74.4%, the imaging performance of the proposed method is still comparable to that of full sampling.
-
Key words:
- Space-borne SAR /
- Sparse flight /
- Satellite formation flying /
- Compressed Sensing (CS) /
- Interferometry
-
表 1 卫星轨道漂移情况
时间(d) 0.285479 6.285773 12.28588 18.2858 24.28553 30.28536 36.28558 42.28562 经度漂移(km) 0 0.123000 0.180000 0.168000 0.087000 0.043000 0.141000 0.173000 距离漂移(km) 0 13.692300 20.037520 18.701680 9.684800 4.786740 15.696060 19.258280 时间(d) 48.285470 54.285150 60.285210 66.285380 72.285390 78.285250 84.284980 90.284810 经度漂移(km) 0.138000 0.039000 0.079000 0.159000 0.183000 0.152000 0.071000 0.029000 距离漂移(km) 15.362100 4.341462 8.794244 17.699810 20.371480 16.920570 7.903688 3.228267 时间(d) 96.285010 102.285100 108.285000 114.284900 120.284600 126.284500 132.284700 经度漂移(km) 0.119000 0.164000 0.167000 0.128000 0.049000 0.017000 0.117000 距离漂移(km) 13.247030 18.256410 18.590360 14.248900 5.454658 1.892432 13.02439 表 2 星载重航过SAR侧视3维成像仿真参数
参数 数值 参数 数值 工作波长$\lambda $ 0.03 m 单星轨道最小间隔 111.3 m 发射信号带宽${B_s}$ 300 MHz 编队双星间隔 222.6 m 参考平台高度$H$ 550 km 交轨采样最小间隔 111.3 m 入射角 45° 交轨等效孔径长度 20 km 方位分辨率 1 m 重复轨道次数 23 机载平台速度 7 km/s 表 3 图像重建结果误差分析
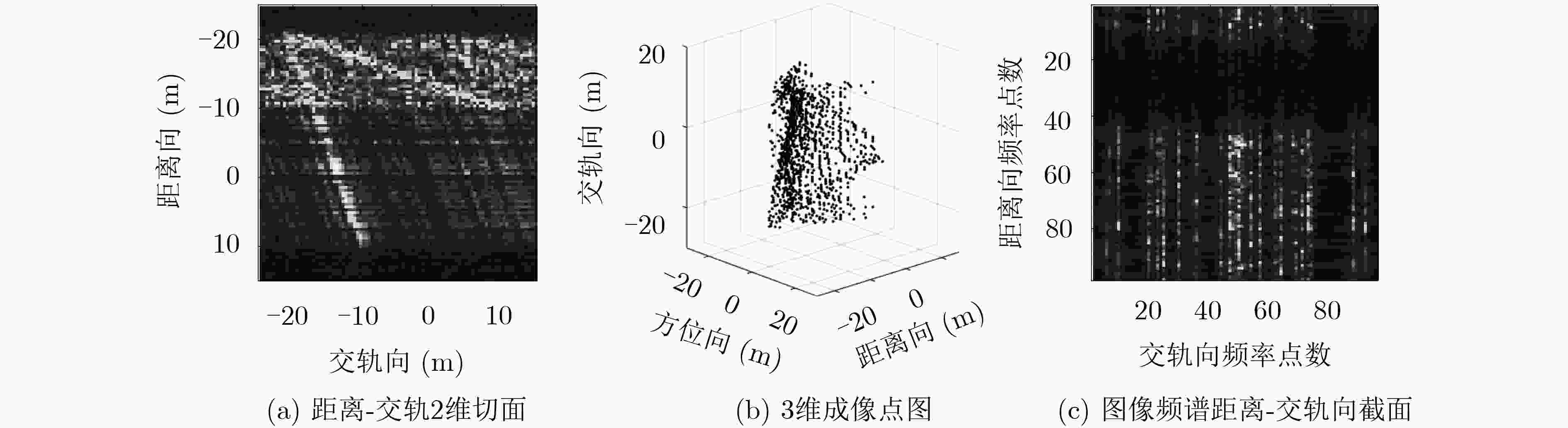
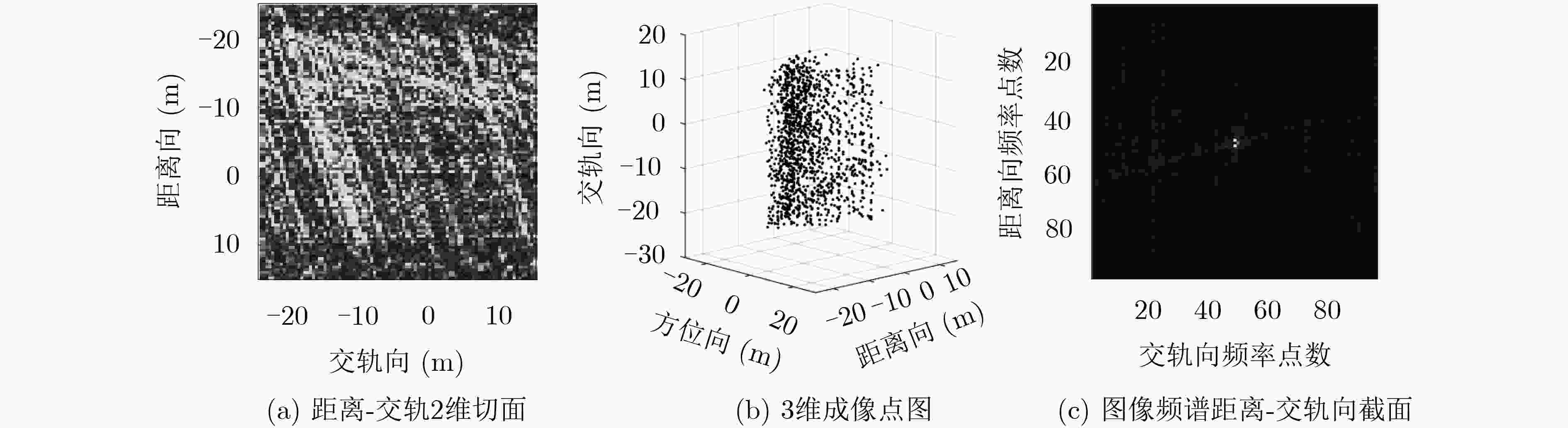
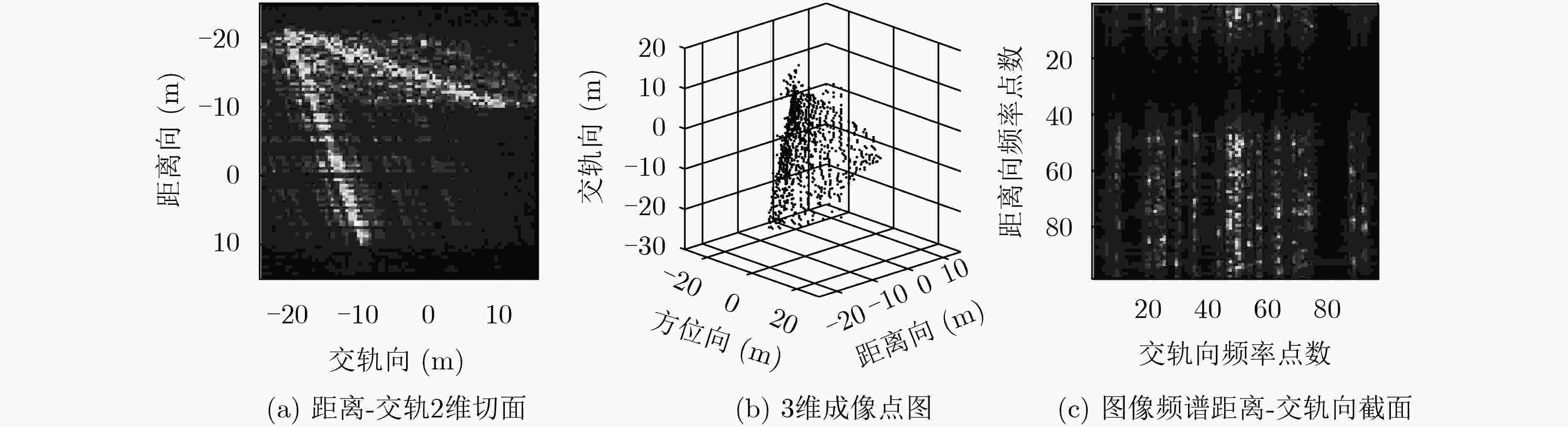
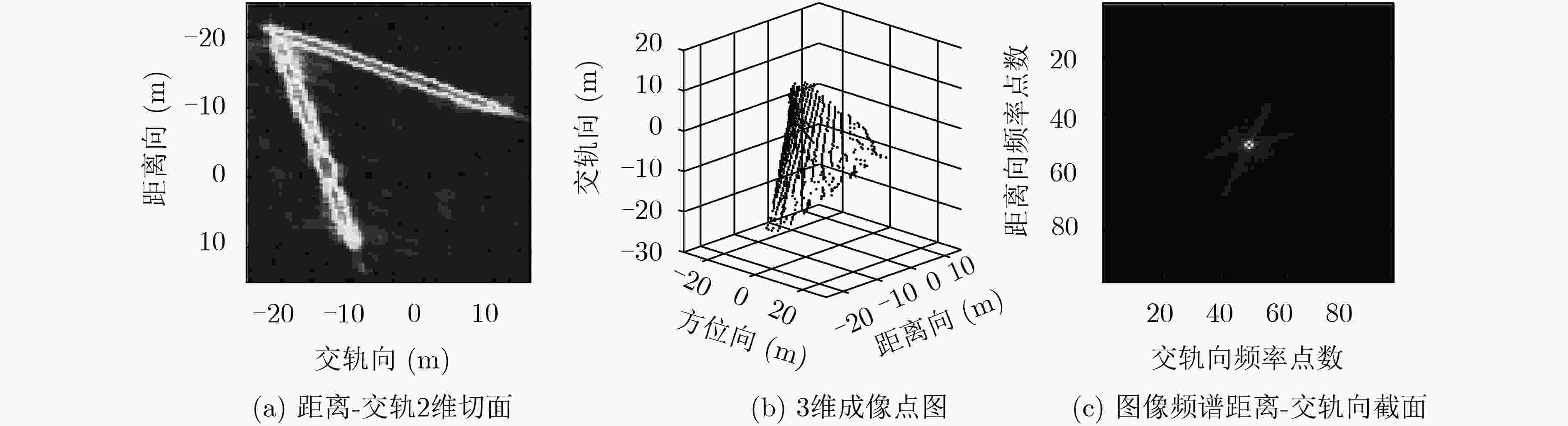
观测方式 算法 评价指标 图像熵 相关系数 均方根误差(m) 180次满采样重航过 3维BP成像 0.4532 单颗卫星23次稀疏重航过 3维BP成像 0.7214 0.6566 0.0604 编队双星23次稀疏重航过 3维BP成像 0.6980 0.7903 0.0453 单颗卫星23次稀疏重航过 空间域CS成像 0.0095 0.5902 0.0432 编队双星23次稀疏重航过 空间域CS成像 0.0093 0.6094 0.0414 单颗卫星23次稀疏重航过 频域CS成像 0.0503 0.7843 0.0405 编队卫星23次稀疏重航过 频域CS成像 0.0453 0.8280 0.0296 -
GIRET R, JEULAND H, and ENERT P. A study of a 3D-SAR concept for a millimeter wave imaging radar onboard an UAV[C]. The 1st European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2004: 201–204. REIGBER A, MOREIRA A, and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[C]. IEEE 1999 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Hamburg, Germany, 1999: 44–46. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1999.773395. CANDES E J, WAKIN M B. An introduction to compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 21–30. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914731 CANDÈS E J. Compressive sampling[C]. The International Congress of Mathematicians, Madrid, Spain, 2006: 1–20. DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 徐华平, 周荫清, 李春升. 分布式星载干涉SAR中空间基线的分析和设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2003, 25(9): 1194–1199.XU Huaping, ZHOU Yinqing, and LI Chunsheng. Baseline analysis and design for distributed spaceborne inteferometric SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2003, 25(9): 1194–1199. ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487 ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Sparse tomographic SAR reconstruction from mixed TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X data stacks[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 7468–7471. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351905. ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Let’s do the time warp: Multicomponent nonlinear motion estimation in differential SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 735–739. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2103298 GE Nan and ZHU Xiaoxiang. Bistatic-like differential SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5883–5893. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2902814 张清娟, 李道京, 李烈辰. 连续场景的稀疏阵列SAR侧视三维成像研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136ZHANG Qingjuan, LI Daojing, and LI Liechen. Research on continuous scene side-looking 3D imaging based on sparse array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136 李烈辰, 李道京. 基于压缩感知的连续场景稀疏阵列SAR三维成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645LI Liechen and LI Daojing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645 TIAN He and LI Daojing. Sparse flight array SAR downward-looking 3-D imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1395–1399. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2560238 田鹤, 李道京. 稀疏重航过阵列SAR运动误差补偿和三维成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 717–729. doi: 10.12000/JR18101TIAN He and LI Daojing. Motion compensation and 3-D imaging algorithm in sparse flight based airborne array SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 717–729. doi: 10.12000/JR18101 尹建凤, 张庆君, 刘杰, 等. 国外编队飞行干涉SAR卫星系统发展综述[J]. 航天器工程, 2018, 27(1): 116–122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2018.01.016YIN Jianfeng, ZHANG Qingjun, LIU Jie, et al. A review on development of formation flying interferometric SAR satellite system[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2018, 27(1): 116–122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2018.01.016 PETERSON E H, FOTOPOULOS G, and ZEE R E. A feasibility assessment for low-Cost InSAR formation-flying microsatellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(8): 2847–2858. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2017521 ZINK M, BARTUSCH M, and MILLER D. TanDEM-X mission status[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 2290–2293. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6049666. TRIDON D B, BACHMANN M, BÖER J, et al. TanDEM-X going for the DEM: Acquisition, performance, and further activities[C]. The 5th IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 2015: 163–168. doi: 10.1109/APSAR.2015.7306180. WANG Puzhong and SHI Changsheng. Antenna Principle[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1993. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
