A Review on Phase Rotation and Beamforming Scheme for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Assisted Wireless Communication Systems
-
摘要: 自2020年5G设备开始大规模商用部署后,全球业界已经开始了6G技术的研究。在5G/6G时代,通信系统需要适应更加复杂的信道环境,如超高密度的城市环境、远海、沙漠、森林等地域。因此,如果能够有一种低能耗的方式,对无线通信信道进行自适应的调整和重构,将不仅有助于无线通信设备向传输时延更低、传输速率更快、接收能力更强等方面进一步迈进,而且可以帮助无线通信设备更好地部署于复杂信道环境的地域。智能反射面(IRS)被认为是实现信道环境重构的一种有效的设备。这些IRS设备大多是无源设备,因此,不会带来过多的能耗。当IRS与单输入单输出(SISO)、多输入单输出(MISO)、多输入多输出(MIMO)等技术相结合时,将进一步提高无线通信传输的传输速率、降低无线通信的能耗、增强无线通信设备对复杂信道环境的适应性。该文对IRS辅助的SISO,MISO和MIMO系统的信号传输模型进行系统总结,分析了IRS辅助的SISO,MISO和MIMO的信号传输建模方式,并对IRS辅助的SISO,MISO和MIMO系统的波束赋形和相移技术进行了综述。Abstract:
Objective Since the large-scale commercial deployment of 5G networks in 2020 and the continued development of 6G technology, modern communication systems need to function under increasingly complex channel conditions. These include ultra-high-density urban environments and remote areas such as oceanic regions, deserts, and forests. To meet these challenges, low-energy solutions capable of dynamically adjusting and reconfiguring wireless channels are required. Such solutions would improve transmission performance by lowering latency, increasing data rates, and strengthening signal reception, and would support more efficient deployment in demanding environments. The Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS) has gained attention as a promising approach for reshaping channel conditions. Unlike traditional active relays, an IRS operates passively and adds minimal energy consumption. When integrated with communication architectures such as Single Input Single Output (SISO), Multiple Input Single Output (MISO), and Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO), an IRS can improve transmission efficiency, reduce power consumption, and enhance adaptability in complex scenarios. This paper reviews IRS-assisted communication systems, with emphasis on signal transmission models, beamforming methods, and phase-shift optimization strategies. Methods This review examines IRS technology in modern communication systems by analyzing signal transmission models across three fundamental configurations. The discussion begins with IRS-assisted SISO systems, in which IRS control of incident signals through reflection and phase shifting improves single-antenna communication by mitigating traditional propagation constraints. The analysis then extends to MISO and MIMO architectures, where the relationship between IRS phase adjustments and MIMO precoding is assessed to determine strategies that support high spectral efficiency. Based on these transmission models, this review surveys joint optimization and precoding methods tailored for IRS-enhanced MIMO systems. These algorithms can be grouped into four categories that meet different operational requirements. The first aims to minimize power consumption by reducing total energy use while maintaining acceptable communication quality, which is important for energy-sensitive applications such as IoT systems and green communication scenarios. The second seeks to maximize energy efficiency by optimizing the ratio of achievable data rate to power consumption rather than lowering energy use alone, thereby improving performance per unit of energy. The third focuses on maximizing the sum rate by increasing aggregated throughput across users to strengthen overall system capacity in high-density 5G and 6G environments. The fourth prioritizes fairness-aware rate maximization by applying resource allocation methods that ensure equitable bandwidth distribution among users while sustaining high Quality of Service (QoS). Together, these optimization approaches provide a framework for advancing IRS-assisted MIMO systems and allow engineers and researchers to balance performance, energy efficiency, and user fairness according to specific application needs in next-generation wireless networks. Results and Discussions This review shows that IRS assisted communication systems provide important capabilities for next-generation wireless networks through four major advantages. First, IRS strengthens system performance by reconfiguring propagation environments and improving signal strength and coverage in non-line-of-sight conditions, including urban canyons, indoor environments, and remote regions, while also maintaining reliable connectivity in high-mobility cases such as vehicular communication. Second, the technology supports high energy efficiency because of its passive operation, which adds minimal power overhead yet improves spectral efficiency. This characteristic is valuable for sustainable large-scale IoT deployments and green 6G systems that may incorporate energy-harvesting designs. Third, IRS shows strong adaptability when integrated with different communication architectures, including SISO for basic signal enhancement, MISO for improved beamforming, and MIMO for spatial multiplexing, enabling use across environments ranging from ultra-dense urban networks to remote or airborne communication platforms. Finally, recent progress in beamforming and phase-shift optimization strengthens system performance through coherent signal combining, interference suppression in multi-user settings, and low-latency operation for time-critical applications. Machine learning methods such as deep reinforcement learning are also being investigated for real-time optimization. Together, these capabilities position IRS as a key technology for future 6G networks with the potential to support smart radio environments and broad-area connectivity, although further study is required to address challenges in channel estimation, scalability, and standardization. Conclusions This review highlights the potential of IRS technology in next-generation wireless communication systems. By enabling dynamic channel reconfiguration with minimal energy overhead, IRS strengthens the performance of SISO, MISO, and MIMO systems and supports reliable operation in complex propagation environments. The surveyed signal transmission models and optimization methods form a technical basis for continued development of IRS-assisted communication frameworks. As research and industry move toward 6G, IRS is expected to support ultra-reliable, low-latency, and energy-efficient global connectivity. Future studies should address practical deployment challenges such as hardware design, real-time signal processing, and progress toward standardization. -
表 1 最小化功耗波束赋形典型优化算法总结
文献 核心目标 方法/算法 适用场景 优缺点 [6] 最小化发射功率,满足用户SINR约束 交替优化、半正定松弛 多用户MISO下行 优点:理论完整;缺点:假设连续相移,
不切实际[7] 离散相移下的功耗优化 分支定界、隐枚举法 硬件受限系统 优点:更实用;缺点:性能损失,复杂度高 [11] NOMA分簇下的功率最小化 ADMM算法 密集用户场景 优点:提升频谱效率;缺点:簇间干扰难控制 [12,13] SWIPT系统中功率最小化 最小均方误差+交替优化 能量收集通信 优点:能同时满足速率与能量约束;
缺点:非凸问题难收敛[16] 存在硬件损伤下的安全功耗优化 联合波束与相位设计 全双工NOMA安全系统 优点:考虑实际损伤;缺点:模型复杂,
难以实现表 2 最大化能效波束赋形典型优化算法总结
文献 核心目标 方法/算法 适用场景 优缺点 [21] 反射元器件分组服务的能效优化 基于位置的相位优化 多用户SISO系统 优点:复杂度低,易于实现;
缺点:性能受用户分布影响大[22] 用户中心网络的能效最大化 分式规划+最大值最小化算法 上行用户中心网络 优点:兼顾用户体验与能效;
缺点:需要精确的信道信息[23] 通感一体系统的能效优化 多约束联合优化 通信感知一体化 优点:实现通感功能平衡;
缺点:优化变量多,收敛性差[24] STAR-IRS赋能的能效优化 联合优化反射系数与功率分配 速率分割多址系统 优点:全空间覆盖,频谱效率高;
缺点:能量守恒约束增加复杂度[26] MIMO-SWIPT系统的能效优化 基于均方误差的交替优化 无线携能通信 优点:同时服务信息与能量接收端;
缺点:非凸问题求解困难表 3 最大化和速率束赋形典型优化算法总结
-
[1] KIRIK M, ALKANA'NEH A, AFEEF L, et al. Efficient interference management design for NTN/TN co-existence in HAP-based 6G networks[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2025, 6: 5434–5449. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2025.3580452. [2] LIU Guangyi, ZHU Yanhong, KANG Mancong, et al. Native design for 6G digital twin network: Use cases, architecture, functions, and key technologies[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(15): 29135–29151. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3553500. [3] LI Xinyao, FEI Teng, CHEN Ruogu, et al. Intelligent reflective surface assisted beamforming optimization[C]. 10th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing, Xi’an, China, 2025: 182–185. doi: 10.1109/ICSP65755.2025.11087112. [4] WU Qingqing, ZHENG Beixiong, YOU Changsheng, et al. Intelligent surfaces empowered wireless network: Recent advances and the road to 6G[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2024, 112(7): 724–763. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2024.3397910. [5] BASAR E, DI RENZO M, DE ROSNY J, et al. Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 116753–116773. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935192. [6] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025. [7] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for wireless network aided by intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1838–1851. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2958916. [8] BJÖRNSON E, ÖZDOGAN Ö, and LARSSON E G. Intelligent reflecting surface versus decode-and-forward: How large surfaces are needed to beat relaying?[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(2): 244–248. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2950624. [9] YU Xianghao, XU Dongfang, and SCHOBER R. Miso wireless communication systems via intelligent reflecting surfaces: (Invited paper)[C]. 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Changchun, China, 2019: 735–740. doi: 10.1109/ICCChina.2019.8855810. [10] HAN Huimei, ZHAO Jun, NIYATO D, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface aided network: Power control for physical-layer broadcasting[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9148827. [11] LI Yiqing, JIANG Miao, ZHANG Qi, et al. Joint beamforming design in multi-cluster MISO NOMA reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided downlink communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 664–674. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3032695. [12] VISHWAKARMA P, SUR S N, DHAR S, et al. IRS-assisted SWIPT: Power optimization strategies for green communications[C]. 17th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks, Bengaluru, India, 2025: 356–364. doi: 10.1109/COMSNETS63942.2025.10885691. [13] YASWANTH J, SINGH S K, SINGH K, et al. Energy-efficient beamforming design for RIS-aided MIMO downlink communication with SWIPT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2023, 7(3): 1164–1180. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2023.3273031. [14] JIANG Jinghan, WANG Yajun, LIAN Zhuxian, et al. Joint beamforming and phase shift design in intelligent reflecting surface-assisted wireless communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(19): 41170–41180. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3592309. [15] HAO Qin, JIA Zhu, ZOU Yulong, et al. Energy efficiency optimization for active reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multi-antenna jamming systems[J]. China Communications, 2025, 22(6): 44–56. doi: 10.23919/JCC.ja.2023-0672. [16] MEAD J A, SINGH K, ALLU R, et al. Transmit power minimization for secure RIS-aided full-duplex NOMA communications with HWI[C]. 2024 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Cape Town, South Africa, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshp64532.2024.11100374. [17] FU Min, ZHOU Yong, and SHI Yuanming. Intelligent reflecting surface for downlink non-orthogonal multiple access networks[C]. 2019 IEEE GLOBECOM Workshops, Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshps45667.2019.9024675. [18] ZHENG Beixiong, WU Qingqing, and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted multiple access with user pairing: NOMA or OMA?[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(4): 753–757. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2969870. [19] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 2019: 7830–7833. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683145. [20] ATA Y, ZEDINI E, VEGNI A M, et al. Reflect-and-amplify: A novel SWIPT technique through hybrid active/passive RIS[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(12): 22073–22089. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3549976. [21] KUMAR M P, SUMMAQ A, and CHINNADURAI S. Phase shift optimization for energy-efficient uplink communication in IRS-aided system[C]. 17th International Conference on Communication Systems and Networks (COMSNETS), Bengaluru, India, 2025: 1172–1177. doi: 10.1109/COMSNETS63942.2025.10885611. [22] ZHANG Chenwu, LU Hancheng, and CHEN Changwen. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces-enhanced uplink user-centric networks on energy efficiency optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 9013–9028. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3267819. [23] LIU Wenhui, JIAO Wanguo, ZHANG Xian, et al. Joint beamforming and reflection design for maximizing energy efficiency of RIS-assisted ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3596087. [24] GAO Chang, HUI Xiaonan, HUANG Chongwen, et al. Energy efficiency optimization of STAR-RIS empowered RSMA system with SWIPT[C]. IEEE 24th International Conference on Communication Technology, Chengdu, China, 2024: 1691–1696. doi: 10.1109/ICCT62411.2024.10946368. [25] NASIR A A. Max-min secure energy efficiency optimization for STAR-RIS-assisted near-field wideband THz communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2025. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2025.3541095. [26] TANG Jie, PENG Ziyao, SO D K C, et al. Energy efficiency optimization for a multiuser IRS-aided MISO system with SWIPT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(10)): 5950–5962. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3296631. [27] SUTHAKAR B, AKASH S, KUMARAVELU V B, et al. Data rate maximization in IRS-aided downlink with effective positioning[C]. 2024 International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication Systems, Kottayam, India, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ISENSE63713.2024.10872271. [28] YU Xianghao, XU Dongfang, and SCHOBER R. Optimal beamforming for MISO communications via intelligent reflecting surfaces[C]. 2020 IEEE 21st International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Atlanta, USA, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SPAWC48557.2020.9154337. [29] NING Boyu, CHEN Zhi, CHEN Wenjie, et al. Beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface assisted MIMO: A sum-path-gain maximization approach[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(7): 1105–1109. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2982140. [30] ZHU Wenhui, LI Beilun, WANG Xiaoqing, et al. Design of robust beamforming algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted MISO backscatter communication system[C]. 14th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory, Hefei, China, 2024: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISAPE62431.2024.10840581. [31] LIU Tianji, ZHOU Hu, LONG Ruizhe, et al. Improving physical layer security with RIS-assisted symbiotic radio[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communications, Denver, USA, 2024: 593–598. doi: 10.1109/ICC51166.2024.10622723. [32] YANG Yifei, ZHENG Beixiong, ZHANG Shuowen, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface meets OFDM: Protocol design and rate maximization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(7): 4522–4535. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2981458. [33] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, DEBBAH M, et al. Achievable rate maximization by passive intelligent mirrors[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 3714–3718. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461496. [34] YUAN Jie, LIANG Yingchang, JOUNG Jingon, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted cognitive radio system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 675–687. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3033006. [35] WANG Peilan, FANG Jun, YUAN Xiaojun, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted millimeter wave communications: Joint active and passive precoding design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 14960–14973. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3031657. [36] ABEYWICKRAMA S, ZHANG Rui, and YUEN C. Intelligent reflecting surface: Practical phase shift model and beamforming optimization[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9148961. [37] HAN Yu, TANG Wankai, JIN Shi, et al. Large intelligent surface-assisted wireless communication exploiting statistical CSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 8238–8242. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2923997. [38] ZHOU Xiaobo, ZHOU Xiuying, YAN Shihao, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided covert wireless communications with finite-alphabet inputs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(4): 6709–6714. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3508819. [39] MEI Yaowen, LI Na, and TAO Xiaofeng. A robust rate enhancement scheme for dual-RIS-aided air-ground integrated communication systems[C]. 2025 IEEE International Workshop on Radio Frequency and Antenna Technologies, Shenzhen, China, 2025: 212–217. doi: 10.1109/iWRFAT65352.2025.11103275. [40] XIE Daoyang, QIAO Jingping, MA Mingyu, et al. Secure terahertz communication with intelligent reflecting surface and energy harvesting[C]. 2025 IEEE International Workshop on Radio Frequency and Antenna Technologies, Shenzhen, China, 2025: 123–128. doi: 10.1109/iWRFAT65352.2025.11103407. [41] AWAD Y, AL-DHARRAB S, and MESBAH W. Performance analysis of RIS-assisted RF-based detection of unauthorized UAVs[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2025, 6: 1963–1976. doi: 10.1109/OJVT.2025.3586263. [42] YUAN Jide, HUANG Huan, and JIN Shi. On the performance of frequency-mixing reconfigurable intelligent surfaces-aided system: Achievable rates and reflective patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(4): 3117–3131. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3528002. [43] XI Zhipeng and JI Jianbo. Sum rate maximization for active RIS MISO systems based on DRL[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 4315–4325. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3525562. [44] YANG Shuo, XU Xiaorong, and BAO Jianrong. Secrecy rate based beamforming optimization strategy in IRS-assisted multiuser CR-SWIPT MIMO system[C]. 2024 China Automation Congress, Qingdao, China, 2024: 6030–6034. doi: 10.1109/CAC63892.2024.10865493. [45] ZHANG Shuowen and ZHANG Rui. Capacity characterization for intelligent reflecting surface aided MIMO communication[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(8): 1823–1838. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000814. [46] CORNELIS S, NOELS N, and MOENECLAEY M. Rate-maximizing zero-forcing hybrid Precoder for MU-MISO-OFDM[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 3275–3290. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3234866. [47] YING Keke, GAO Zhen, LYU Shanxiang, et al. GMD-based hybrid beamforming for large reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted millimeter-wave massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 19530–19539. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968456. [48] GUO Chang, LU Zhufei, GUO Zhe, et al. Maximum ergodic capacity of intelligent reflecting surface assisted MIMO wireless communication system[C]. 14th EAI International Conference of Communications and Networking, Shanghai, China, 2020: 331–343. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-41114-5_25. [49] XU Hao, NING Boyu, OUYANG Chongjun, et al. Spectral efficiency maximization for DMA-enabled multiuser MISO with statistical CSI[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(18): 39130–39144. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3588060. [50] ZHANG Yu, ZHONG Caijun, ZHANG Zhaoyang, et al. Sum rate optimization for two way communications with intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(5): 1090–1094. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2978394. [51] YOU Changsheng, ZHENG Beixiong, and ZHANG Rui. Channel estimation and passive beamforming for intelligent reflecting surface: Discrete phase shift and progressive refinement[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2604–2620. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007056. [52] RANJAN R, BHATTACHARYA A, MUKHOPADHYAY S, et al. A gradient ascent based low complexity rate maximization algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-aided OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(8): 2083–2087. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3289865. [53] GUO Huayan, LIANG Yingchang, CHEN Jie, et al. Weighted sum-rate maximization for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3064–3076. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2970061. [54] LIU Yihong, ZHANG Lei, YANG Bowen, et al. Programmable wireless channel for multi-user MIMO transmission using meta-surface[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9013433. [55] ZHOU Gui, PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface aided multigroup multicast MISO communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68(2): 3236–3251. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2990098. [56] PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, WANG Kezhi, et al. Multicell MIMO communications relying on intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(8): 5218–5233. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2990766. [57] WU Zhaoyu and ZHANG Wei. Joint transmit and reflect beamforming design for active-RIS-assisted secure ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2025, 29(8): 1769–1773. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2025.3572794. [58] HUANG Shihan, WANG Weijiang, REN Shiwei, et al. Min-max fairness-based beamforming design for coupled phase shift STAR-RIS-assisted MIMO system[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(3): 3145–3162. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3477422. [59] YANG Gang, XU Xinyue, and LIANG Yingchang. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted non-orthogonal multiple access[C]. 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Seoul, Korea (South), 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC45663.2020.9120476. [60] HU Sha, CHITTI K, RUSEK F, et al. User assignment with distributed large intelligent surface (LIS) systems[C]. IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Bologna, Italy, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2018.8580675. [61] YANG Yifei, ZHANG Shuowen, and ZHANG Rui. IRS-enhanced OFDMA: Joint resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(6): 760–764. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2968303. [62] ZHU Guangyu, MU Xidong, GUO Li, et al. STAR-RIS assisted SWIPT systems: Active or passive?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3611793. [63] RODRIGUES D V Q and SINGH T. Efficient power allocation strategies in hybrid active-passive reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2024, 28(1): 113–117. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3332514. [64] MU Xidong, LIU Yuanwei, GUO Li, et al. Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting (STAR) RIS aided wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(5): 3083–3098. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3118225. [65] PANG Lihua, WANG Yue, ZHANG Yang, et al. Coverage optimization of hybrid active-passive STAR-RIS-assisted indoor–outdoor communication under hardware impairments and imperfect CSI[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(18): 37705–37719. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3584077. [66] CAI Yujin, YU Wenwu, NIE Xiaokai, et al. Double STAR-RIS enhanced secure wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(8): 6596–6612. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3554769. [67] YANG Shaochuan, JIAO Yanzhen, WANG Yi, et al. Robust secure energy efficiency optimization for active STAR-RIS assisted ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2025, 6: 7459–7469. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2025.3605726. [68] SHAHWAR M, AHMED M, HUSSAIN T, et al. Secure THz communication in 6G: A two-stage DRL approach for IRS-assisted NOMA[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 85294–85306. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3569708. [69] BJÖRNSON E, WYMEERSCH H, MATTHIESEN B, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: A signal processing perspective with wireless applications[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2022, 39(2): 135–158. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2021.3130549. [70] DING Tongyu, FANG Linying, LIU Lu, et al. Design of an ultrawide-angle programmable metasurface based on hexagonal grid for 5G millimeter-wave applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2025, 24(10): 3764–3768. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2025.3603886. [71] ZHAO Huijin, FAN Fei, JI Yunyun, et al. Active terahertz beam manipulation with photonic spin conversion based on a liquid crystal Pancharatnam–Berry metadevice[J]. Photonics Research, 2022, 10(11): 2658–2666. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.471282. [72] ZHANG Zijian, DAI Linglong, CHEN Xibi, et al. Active RIS vs. passive RIS: Which will prevail in 6G?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(3): 1707–1725. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3231893. [73] LIU Yuanwei, XU Jiaqi, WANG Zhaolin, et al. Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting (STAR)RISs for 6G: Fundamentals, recent advances, and future directions[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2023, 24(12): 1689–1707. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2300490. [74] BASHARAT S, HASSAN S A, MAHMOOD A, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted backscatter communication: A new frontier for enabling 6G IoT networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(6): 96–103. doi: 10.1109/MWC.009.2100423. [75] SONG Lizhao, SQUIRES A, VAN DER LAAN T, et al. THz graphene-integrated metasurface for electrically reconfigurable polarization conversion[J]. Nanophotonics, 2024, 13(13): 2349–2359. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0916. -






 下载:
下载:
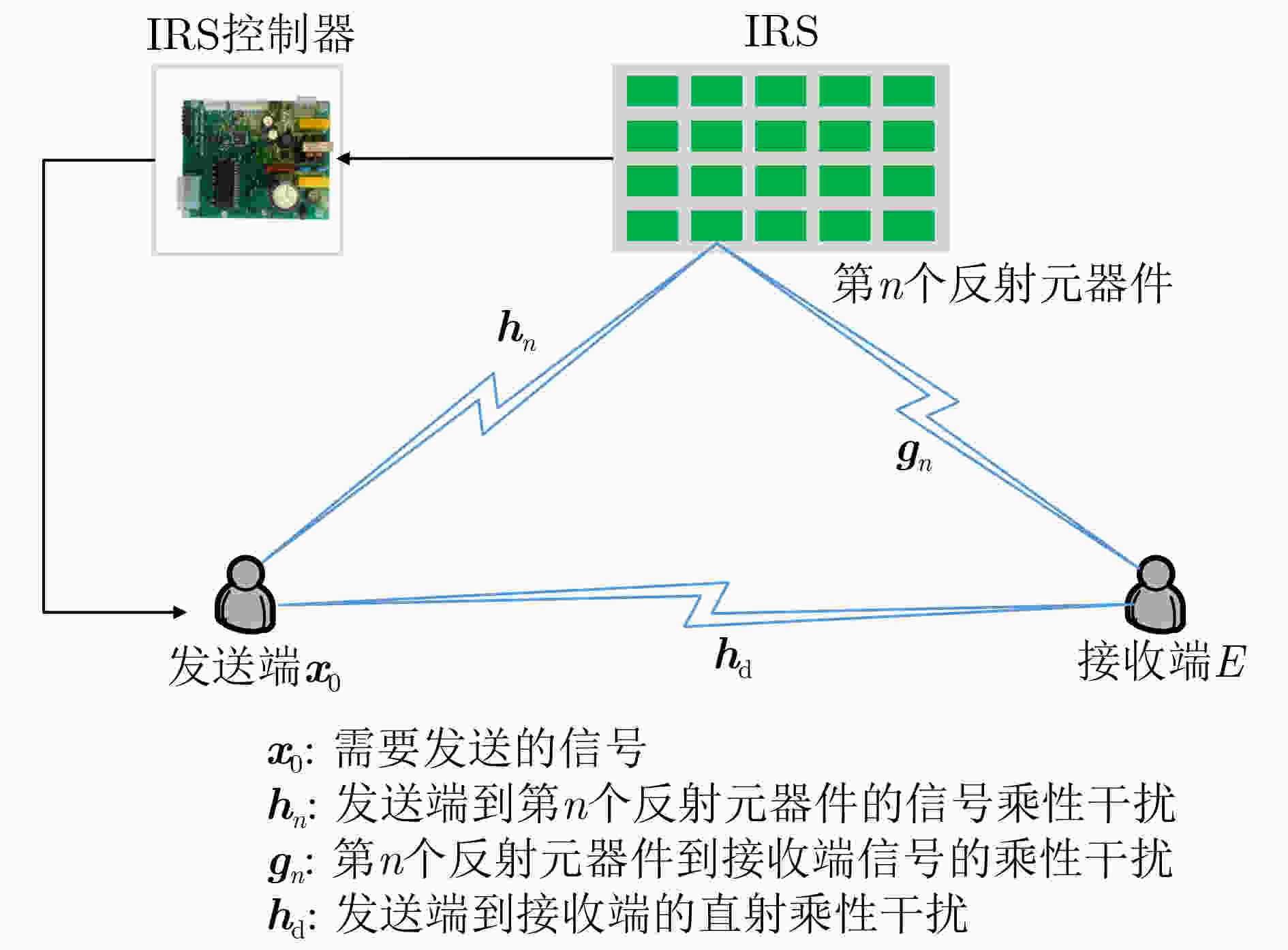
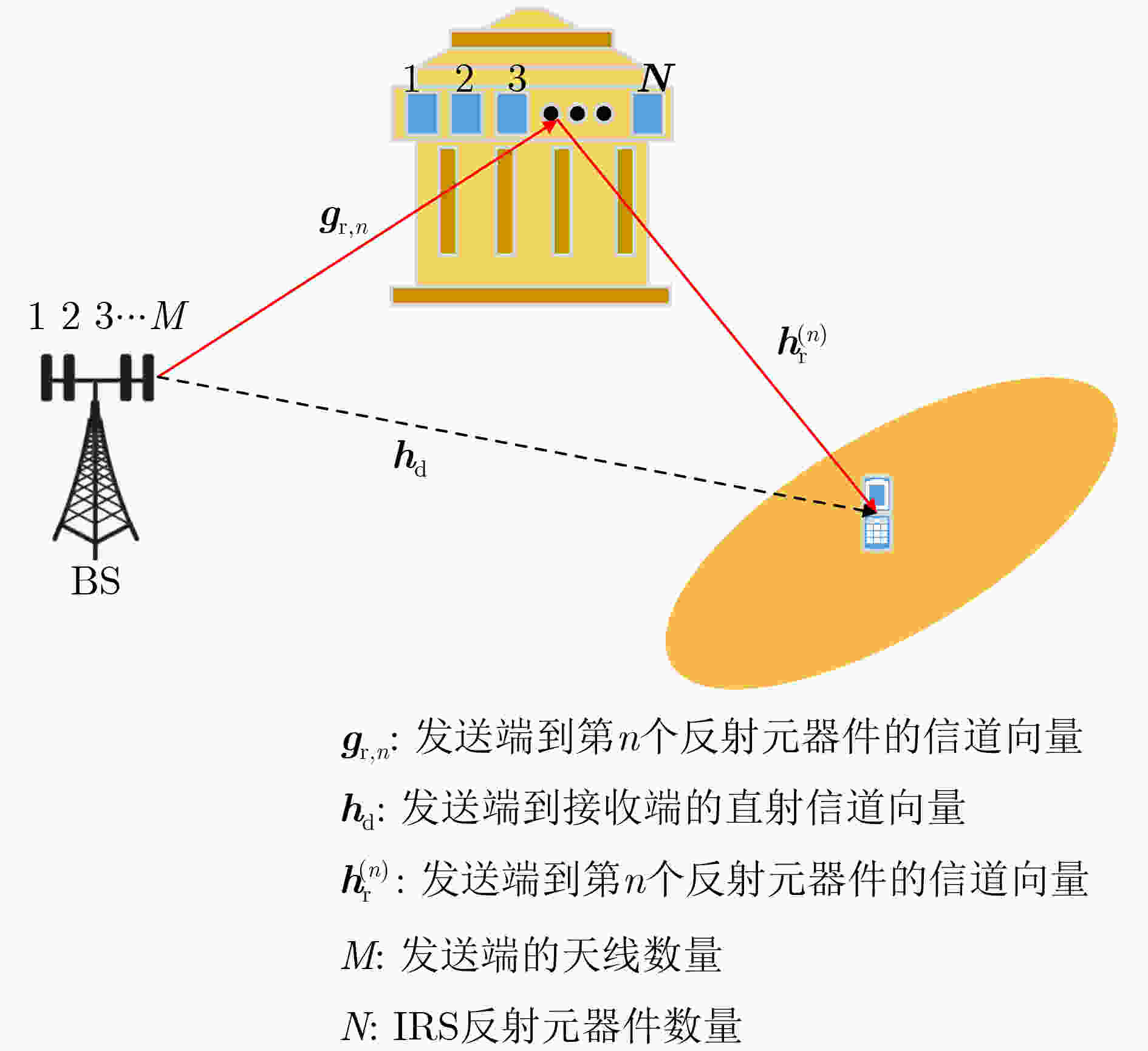
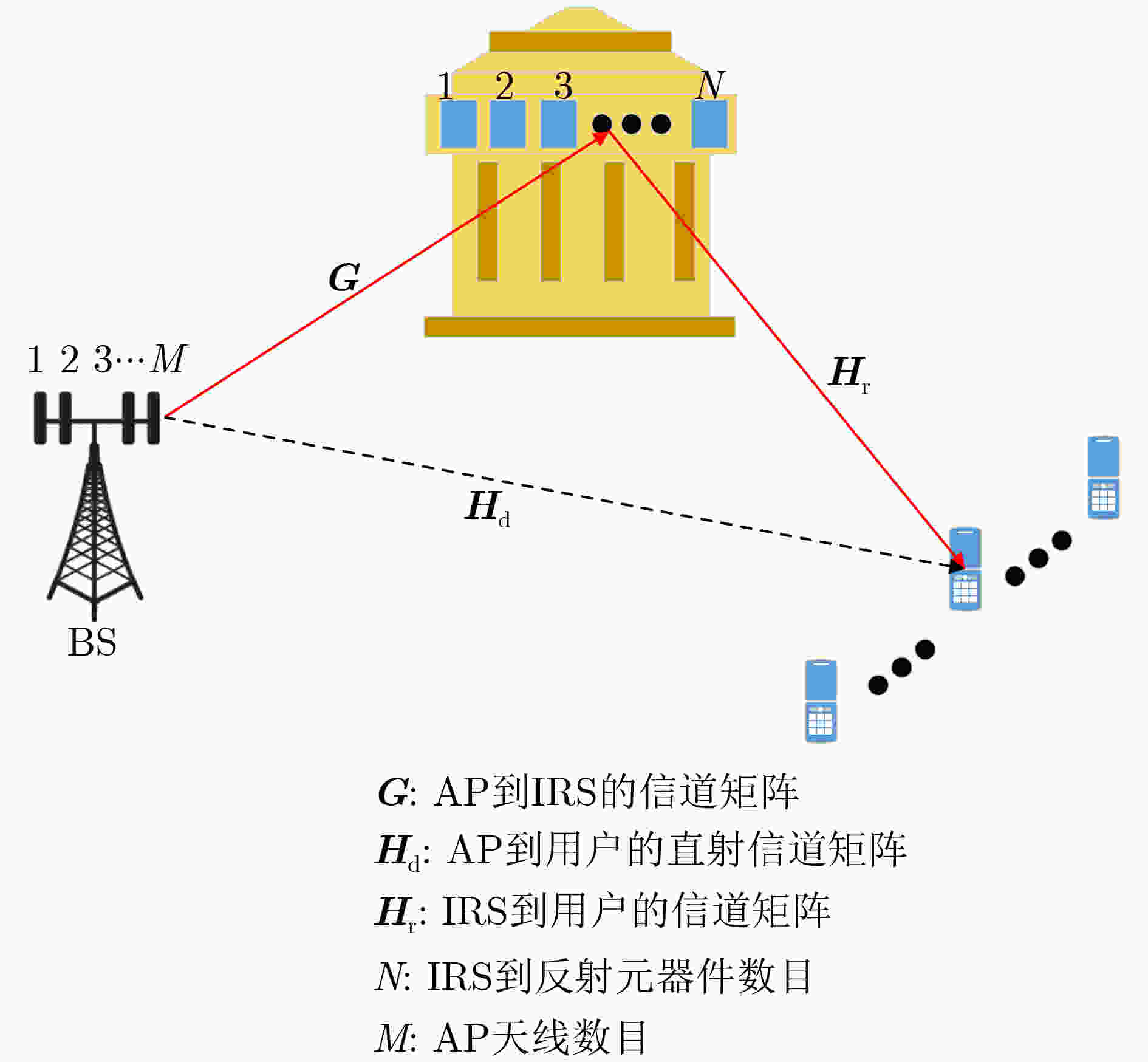


 下载:
下载:
