Multi-modal Joint Automatic Modulation Recognition Method Towards Low SNR Sequences
-
摘要: 针对单模态自动调制方式识别方法在低信噪比条件下难以实现可靠识别的问题,该文融合对比学习和Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理,提出一种面向低信噪比序列的多模态联合两阶段自动调制方式识别方法。第1阶段,构建对比学习模块,利用多模态数据在时间、强度等显著联系,实现时域Token和变换域Token序列的初步显式对齐;第2阶段,设计特征融合模块,利用长短时记忆网络LSTM、卷积神经网络CNN从初步对齐特征中提取时序特性,并利用表征学习增大类间距离,从多角度捕获时域和变换域两种模态特征之间的隐式对齐关系,实现多模态特征融合;最后,通过Kolmogorov-Arnold网络学习边缘权重,得到调制方式识别结果。在经典通信信号调制方式识别数据集RadioML2016.10a, RadioML2016.10b和HisarMod2019.1上的实验结果表明,在–20~0 dB信噪比条件下,该文方法的调制方式识别精度相比于经典的FEA-T, AMC-NET和MCLDNN等方法以相近的参数量提高了2.62%~11.63%。
-
关键词:
- 自动调制方式识别 /
- 跨模态特征融合 /
- 时间序列分析 /
- 对比学习 /
- Kolmogorov-Arnold网络
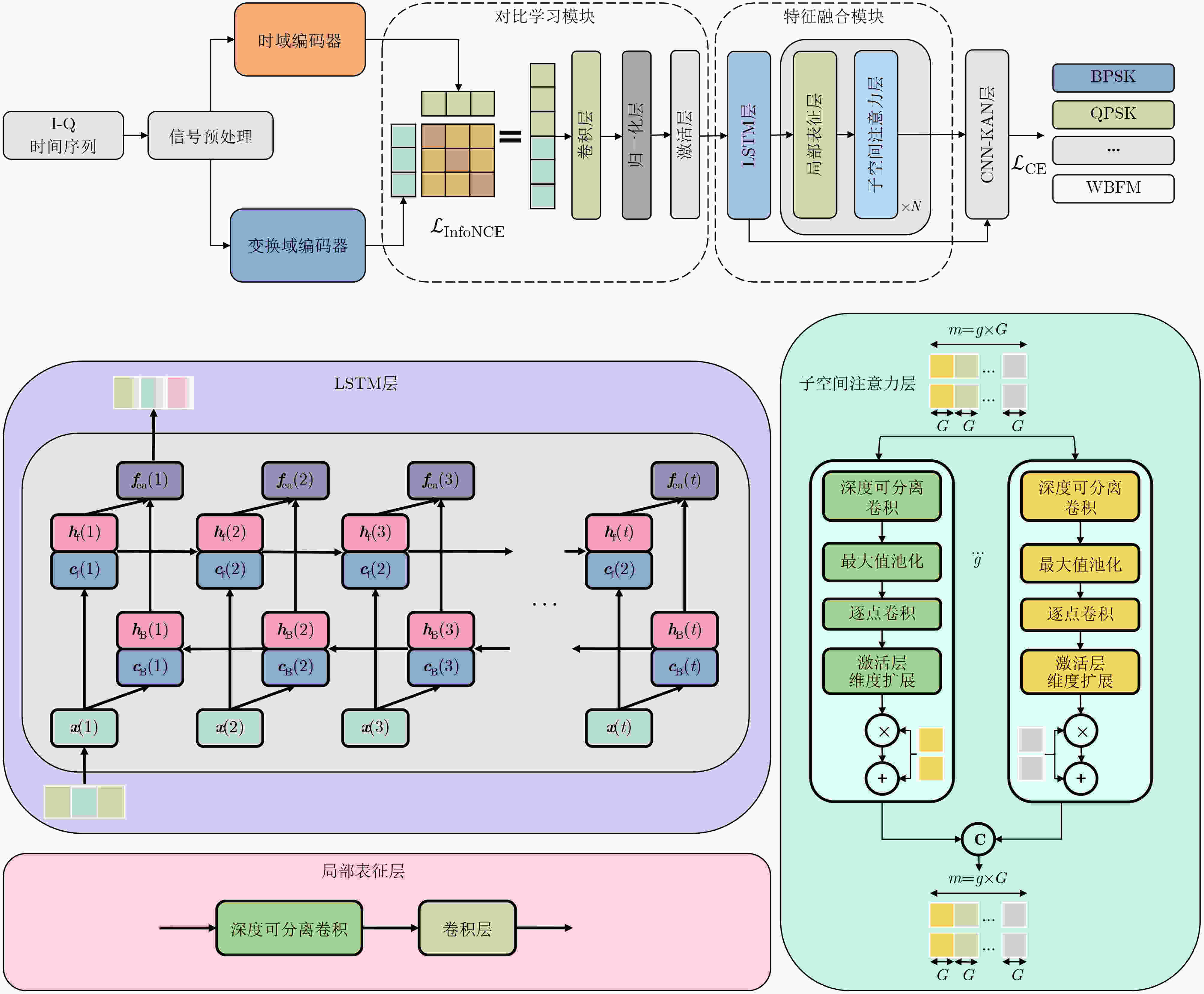
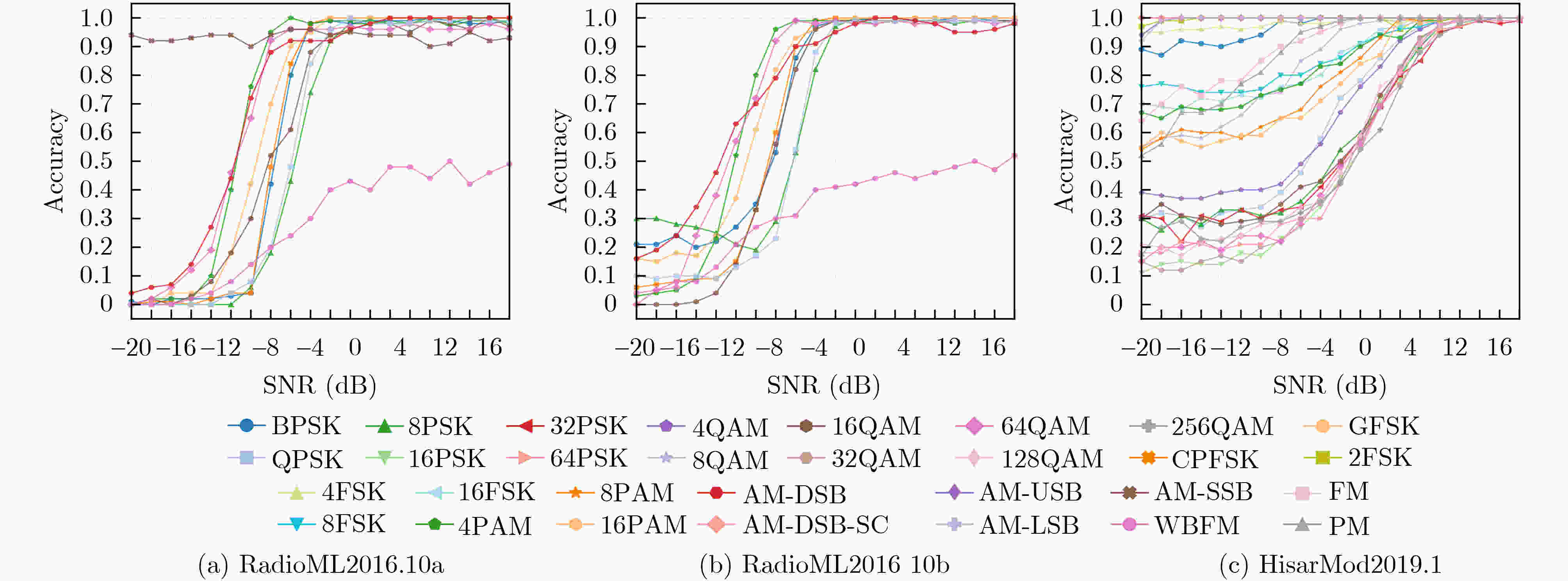
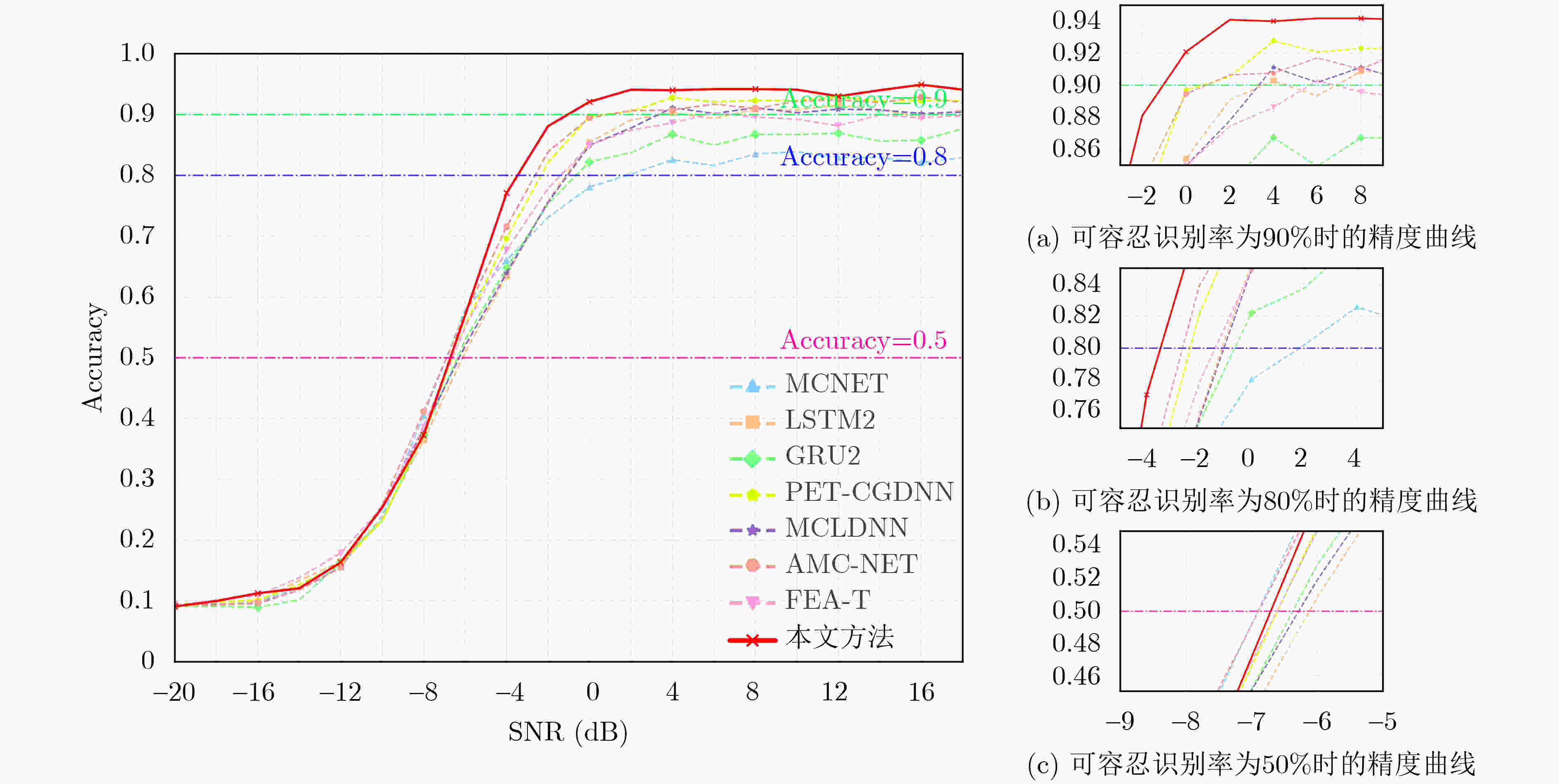
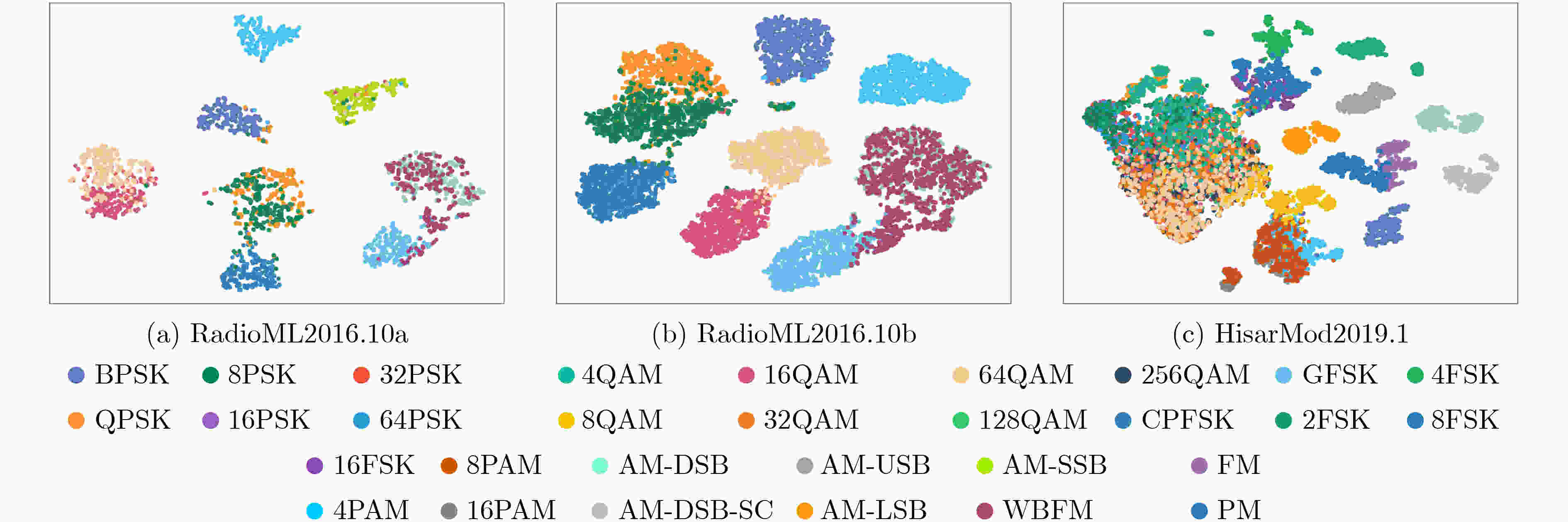
Abstract:Objective The rapid evolution of data-driven intelligent algorithms and the rise of multi-modal data indicate that the future of Automatic Modulation Recognition (AMR) lies in joint approaches that integrate multiple domains, use multiple frameworks, and connect multiple scales. However, the embedding spaces of different modalities are heterogeneous, and existing models lack cross-modal adaptive representation, limiting their ability to achieve collaborative interpretation. To address this challenge, this study proposes a performance-interpretable two-stage deep learning-based AMR (DL-AMR) method that jointly models the signal in the time and transform domains. The approach explicitly and implicitly represents signals from multiple perspectives, including temporal, spatial, frequency, and intensity dimensions. This design provides theoretical support for multi-modal AMR and offers an intelligent solution for modeling low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) time sequences in open environments. Methods The proposed AMR network begins with a preprocessing stage, where the input signal is represented as an in-phase and quadrature (I-Q) sequence. After wavelet thresholding denoising, the signal is converted into a dual-channel representation, with one channel undergoing Short-Time Fourier transform (STFT). This preprocessing yields a dual-stream representation comprising both time-domain and transform-domain signals. The signal is then tokenized through time-domain and transform-domain encoders. In the first stage, explicit modal alignment is performed. The token sequences from the time and transform domains are input in parallel into a contrastive learning module, which explicitly captures and strengthens correlations between the two modalities in dimensions such as temporal structure and amplitude. The learned features are then passed into the feature fusion module. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) and local representation layers are employed to capture temporally sparse features, enabling subsequent feature decomposition and reconstruction. To refine feature extraction, a subspace attention mechanism is applied to the high-dimensional sparse feature space, allowing efficient capture of discriminative information contained in both high-frequency and low-frequency components. Finally, Convolutional Neural Network—Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (CNN-KAN) layers replace traditional multilayer perceptrons as classifiers, thereby enhancing classification performance under low SNR conditions. Results and Discussions The proposed method is experimentally validated on three datasets: RadioML2016.10a, RadioML2016.10b, and HisarMod2019.1. Under high SNR conditions (SNR > 0 dB), classification accuracies of 93.36%, 93.13%, and 93.37% are achieved on the three datasets, respectively. Under low SNR conditions, where signals are severely corrupted or blurred by noise, recognition performance decreases but remains robust. When the SNR ranges from –6 dB to 0 dB, overall accuracies of 78.36%, 80.72%, and 85.43% are maintained, respectively. Even at SNR levels below –6 dB, accuracies of 17.10%, 21.30%, and 29.85% are obtained. At particularly challenging low-SNR levels, the model still achieves 43.45%, 44.54%, and 60.02%. Compared with traditional approaches, and while maintaining a low parameter count (0.33~0.41 M), the proposed method improves average recognition accuracy by 2.12%~7.89%, 0.45%~4.64%, and 6.18%~9.53% on the three datasets. The improvements under low SNR conditions are especially significant, reaching 4.89%~12.70% (RadioML2016.10a), 2.62%~8.72% (RadioML2016.10b), and 4.96%~11.63% (HisarMod2019.1). The results indicate that explicit modeling of time–transform domain correlations through contrastive learning, combined with the hybrid architecture consisting of LSTM for temporal sequence modeling, CNN for local feature extraction, and KAN for nonlinear approximation, substantially enhances the noise robustness of the model. Conclusions This study proposes a two-stage AMR method based on time-transform domain multimodal fusion. Explicit multimodal alignment is achieved through contrastive learning, while temporal and local features are extracted using a combination of LSTM and CNN. The KAN is used to enhance nonlinear modeling, enabling implicit feature-level multimodal fusion. Experiments conducted on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that, compared with classical methods, the proposed approach improves recognition accuracy by 2.62%~11.63% within the SNR range of –20 to 0 dB, while maintaining a similar number of parameters. The performance gains are particularly significant under low-SNR conditions, confirming the effectiveness of multimodal joint modeling for robust AMR. -
表 1 CNN–KAN结构和MLP, KAN结构的比较
模型 多层感知机(MLP) Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN) CNN–KAN 定理 通用逼近定理 Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理 通用逼近定理
Kolmogorov-Arnold表示定理思想 任意闭区间上的连续目标函数和非零误差,至少存在一个具有隐藏层的神经网络,用来逼近目标函数,其误差小于给定的非零误差 有界域上的任意多元连续函数可以写成有限个连续函数的复合单变量的二元运算 借助KAN非线性关系建模方面的优势,减少模型参数量并降低计算复杂性,补偿CNN的全局信息提取能力缺陷 公式 $ {\text{MLP}}({\boldsymbol{x}}) = ({{\mathbf{W}}_{{2}}} \circ \sigma \circ {{\mathbf{W}}_{{1}}} \circ \sigma \circ {{\mathbf{W}}_{{0}}})({\boldsymbol{x}}) $ $ {\text{KAN}}({\boldsymbol{x}}) = ({\phi _2} \circ {\phi _1} \circ {\phi _0})({\boldsymbol{x}}) $ $ {\text{C - K}}({\boldsymbol{x}}) = ({\phi _1} \circ {\phi _0} \circ {{\mathbf{W}}_1} \circ \sigma \circ {{\mathbf{W}}_{{0}}})({\boldsymbol{x}}) $ 架构 


表 2 数据集介绍
数据集 调制类型 序列
格式数据
规模信噪比
范围解释 RadioML
2016.10a11类
(8PSK, BPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, 4PAM, 16QAM, AM-DSB, AM-SSB, 64QAM, QPSK, WBFM)2×128 220,000条 –20:2:18 利用GNU radio生成 RadioML
2016.10b10类
(8PSK, BPSK, CPFSK, GFSK, 4PAM, 16QAM, AM-DSB, 64QAM, QPSK, WBFM)2×128 1,200,000条 –20:2:18 在RML2016.10a的基础上,移除了AM-SSB信号,并将每个SNR上的样本数量由
1 000条增加为6 000条HisarMod 2019.1 26类
(AM-DSB, AM-SC, AM-USB, AM-LSB, FM, PM, 2FSK, 4FSK, 8FSK, 16FSK, 4PAM, 8PAM, 16PAM, BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16PSK, 32PSK, 64PSK, 4QAM, 8QAM, 16QAM, 32QAM, 64QAM, 128QAM, 256QAM)2× 1024 780,000条 –20:2:18 在5个不同的通道条件下进行采集,总计包括26种调制类型,共780 000条样本 表 3 3个数据集上方法评估指标对比(A: RML2016.10a, B: RML2016.10b, C:HisarMod2019.01A)
模型 数据集 参数量 SNR(dB) 最高识别精度(%) 平均识别精度(%) –20~0 0~18 MCNET[27] A 0.12M 33.21 82.33 83.91 56.63 B 35.89 85.69 87.08 60.95 C 0.13M 48.39 89.12 89.33 69.85 LSTM2[28] A 0.2M 34.75 84.21 91.41 60.56 B 36.58 88.65 94.01 63.28 C 51.08 91.74 89.53 66.98 GRU2[28] A 0.15M 30.75 87.21 87.86 58.93 B 35.82 91.98 93.63 63.72 C 52.58 91.54 91.05 67.42 PET-CGDNN[29] A 0.07M 36.21 89.45 91.36 60.38 B 40.12 92.64 93.43 63.91 C 0.08M 55.53 79.98 89.39 67.24 MCLDNN[30] A 0.41M 37.27 91.68 92.86 61.93 B 40.91 93.02 93.86 64.46 C 52.08 86.62 98.01 68.62 AMC-NET[31] A 0.47M 38.56 91.32 92.82 62.40 B 41.92 93.34 93.86 65.14 C 4.61M 55.06 92.29 99.43 72.74 FEA-T[32] A 0.17M 37.31 88.54 90.09 60.55 B 40.81 93.12 93.89 64.44 C 0.34M 50.38 92.21 99.92 70.33 Semi-AMR[11] A - - 91.28 92.96 - AG-AMR[10] A 3.5M 32.10 90.50 91.50 60.16 本文模型 A 0.33M 43.45 93.36 93.36 64.52 B 44.54 93.13 94.30 65.59 C 0.41M 60.02 93.37 99.92 76.51 表 4 在数据集A上进行的消融实验
对比学习 表征学习 子空间注意力 SNR(dB) 最高识别精度(%) 平均识别精度(%) –20~0 0~18 $ \times $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 41.49 92.72 91.98 63.65 $ \surd $ $ \times $ $ \surd $ 42.99 93.69 94.34 64.41 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \times $ 29.31 79.55 82.31 55.07 $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 43.45 93.36 93.36 64.52 表 5 不同模型的复杂度分析
模型 输入序列长度 参数量(M) 推理速度
(数据/s)MCNET 128 0.12 1 253 1 024 834 LSTM2 128 0.20 1 442 1 024 858 GRU2 128 0.15 1 357 1 024 798 PET-CGDNN 128 0.08 2 481 1 024 2 375 MCLDNN 128 0.41 1 286 1 024 1 157 AMC-NET 128 0.47 1 458 1 024 4.60 1 420 FEA-T 128 0.17 3 682 1 024 3 465 本文模型 128 0.33 1 728 1 024 0.41 1 553 -
[1] MA Jitong, HU Mutian, CHEN Xiao, et al. Few-shot automatic modulation classification via semi-supervised metric learning and lightweight conv-transformer model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2025.3574312. [2] XU J L, SU Wei, and ZHOU Mengchu. Likelihood-ratio approaches to automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2011, 41(4): 455–469. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2010.2076347. [3] IGLESIAS V, GRAJAL J, ROYER P, et al. Real-time low-complexity automatic modulation classifier for pulsed radar signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(1): 108–126. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130183. [4] 郑庆河, 刘方霖, 余礼苏, 等. 基于改进Kolmogorov-Arnold混合卷积神经网络的调制识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(8): 2584–2597. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250161.ZHENG Qinghe, LIU Fanglin, YU Lisu, et al. An improved modulation recognition method based on hybrid kolmogorov-arnold convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(8): 2584–2597. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250161. [5] LI Mingkun, WANG Pengyu, DONG Yuhan, et al. Diffusion model empowered data augmentation for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2025, 14(4): 1224–1228. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2025.3539821. [6] 李钦, 刘伟, 牛朝阳, 等. 低信噪比下基于分裂EfficientNet网络的雷达信号调制方式识别[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(3): 675–686. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210656.LI Qin, LIU Wei, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Radar signal modulation recognition based on split EfficientNet under low signal-to-noise ratio[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(3): 675–686. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210656. [7] CHEN Zhuangzhi, CUI Hui, XIANG Jingyang, et al. SigNet: A novel deep learning framework for radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(2): 529–541. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2021.3120997. [8] KE Ziqi and VIKALO H. Real-time radio technology and modulation classification via an LSTM auto-encoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(1): 370–382. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3095855. [9] SHAO Mingyuan, LI Dingzhao, HONG Shaohua, et al. IQFormer: A novel transformer-based model with multi-modality fusion for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2025, 11(3): 1623–1634. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2024.3485118. [10] ZHAN Quanhai, ZHANG Xiongwei, SUN Meng, et al. Adversarial robust modulation recognition guided by attention mechanisms[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing, 2025, 6: 17–29. doi: 10.1109/OJSP.2025.3526577. [11] GUO Yuanpu, DAN Zhong, SUN Haixin, et al. SemiAMR: Semi-supervised automatic modulation recognition with corrected pseudo-label and consistency regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(1): 107–121. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3319530. [12] MA Jitong, HU Mutian, WANG Tianyu, et al. Automatic modulation classification in impulsive noise: Hyperbolic-tangent cyclic spectrum and multibranch attention shuffle network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 5501613. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3244798. [13] WANG Danshi, ZHANG Min, LI Ze, et al. Modulation format recognition and OSNR estimation using CNN-based deep learning[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2017, 29(19): 1667–1670. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2742553. [14] PENG Shengliang, JIANG Hanyu, WANG Huaxia, et al. Modulation classification based on signal constellation diagrams and deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(3): 718–727. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850703. [15] SHI Yunhao, XU Hua, ZHANG Yue, et al. GAF-MAE: A self-supervised automatic modulation classification method based on gramian angular field and masked autoencoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(1): 94–106. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3318414. [16] ZHANG Zufan, WANG Chun, GAN Chenquan, et al. Automatic modulation classification using convolutional neural network with features fusion of SPWVD and BJD[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2019, 5(3): 469–478. doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2019.2900201. [17] ZHENG Shilian, ZHOU Xiaoyu, ZHANG Luxin, et al. Toward next-generation signal intelligence: A hybrid knowledge and data-driven deep learning framework for radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2023, 9(3): 564–579. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3243899. [18] SHI Yunhao, XU Hua, QI Zisen, et al. STTMC: A few-shot spatial temporal transductive modulation classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Machine Learning in Communications and Networking, 2024, 2: 546–559. doi: 10.1109/TMLCN.2024.3387430. [19] WANG Feng, YANG Chenlu, HUANG Shanshan, et al. Automatic modulation classification based on joint feature map and convolutional neural network[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(6): 998–1003. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5549. [20] ZHUANG Long, LUO Kai, and YANG Zhibo. A multimodal gated recurrent unit neural network model for damage assessment in CFRP composites based on lamb waves and minimal sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 3506911. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3348884. [21] QU Yunpeng, LU Zhilin, ZENG Rui, et al. Enhancing automatic modulation recognition through robust global feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(3): 4192–4207. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3486079. [22] ZHANG Shu, ZHENG Dequan, HU Xinchen, et al. Bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification[C]. The 29th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation, Shanghai, China, 2015: 73–78. [23] ZHU Jinhua, XIA Yingce, WU Lijun, et al. Masked contrastive representation learning for reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3421–3433. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3176413. [24] HUANG Wenhao, GONG Haifan, ZHANG Huan, et al. BCNet: Bronchus classification via structure guided representation learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2025, 44(1): 489–498. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3448468. [25] SAINI R, JHA N K, DAS B, et al. ULSAM: Ultra-lightweight subspace attention module for compact convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass, CO, USA, 2020: 1616–1625. doi: 10.1109/WACV45572.2020.9093341. [26] LIU Ziming, WANG Yixuan, VAIDYA S, et al. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks[C]. 13th International Conference on Learning Representations, Singapore, Singapore, 2025. [27] HUYNH-THE T, HUA C H, PHAM Q V, et al. MCNet: An efficient CNN architecture for robust automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(4): 811–815. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2968030. [28] RAJENDRAN S, MEERT W, GIUSTINIANO D, et al. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low-cost spectrum sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(3): 433–445. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2835460. [29] ZHANG Fuxin, LUO Chunbo, XU Jialang, et al. An efficient deep learning model for automatic modulation recognition based on parameter estimation and transformation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3287–3290. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3102656. [30] XU Jialang, LUO Chunbo, PARR G, et al. A spatiotemporal multi-channel learning framework for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629–1632. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2999453. [31] ZHANG Jiawei, WANG Tiantian, FENG Zhixi, et al. AMC-Net: An effective network for automatic modulation classification[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10097070. [32] CHEN Yantao, DONG Binhong, LIU Cuiting, et al. Abandon locality: Frame-wise embedding aided transformer for automatic modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(1): 327–331. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3213523. [33] O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, and CHARLES CLANCY T. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks[C]. 17th International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Aberdeen, UK, 2016: 213–226. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-44188-7_16. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
