Low Complexity Sequential Decoding Algorithm of PAC Code for Short Packet Communication
-
摘要: 随着智能物联网的出现,海量物联网设备间的短包通信在低时延、高可靠和极短数据包长方面的严苛要求给信道编译码方案的设计带来了新的挑战。极化调整卷积(PAC)码在短码长下的某些码型下具有接近散度近似(DA)的纠错性能,但其极高的译码运算复杂度限制了在短包通信中的应用。针对这一问题,该文提出了低复杂度Fano序贯(LC-FS)译码算法和低复杂度堆栈(LC-S)译码算法。首先,LC-FS译码算法将译码码树中的特殊节点分为低码率和高码率两类,并提出了相应的特殊节点译码器和回溯策略,从而在译码码树更高层完成译码以避免冗余运算。其次,LC-FS译码算法中的特殊节点分类方法被扩展到堆栈类译码算法,进一步提出了LC-S译码算法。该算法在保留堆栈类译码算法低回溯次数特点的同时具有更低的运算复杂度。最后,仿真结果表明在对码长为256和信息长度为128的PAC码进行译码时,相较于快速Fano序贯(FFS)译码算法和传统堆栈译码算法,所提LC-FS译码算法和LC-S译码算法在保证纠错性能基本无损的同时运算复杂度平均降低了13.77%和56.48%。Abstract:
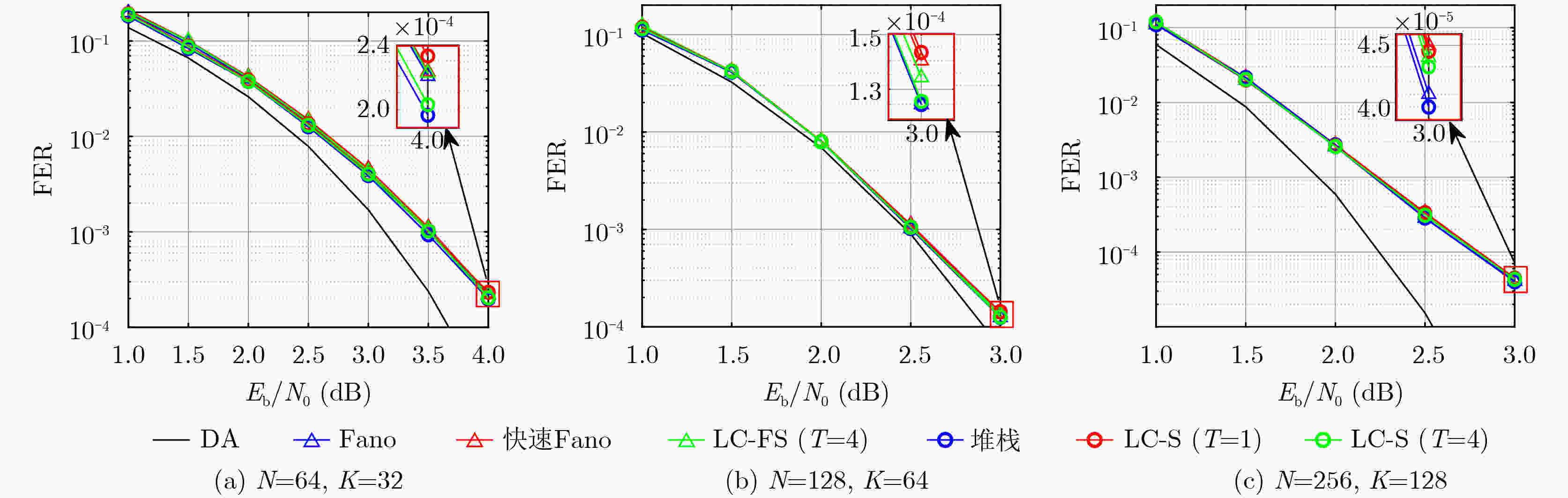
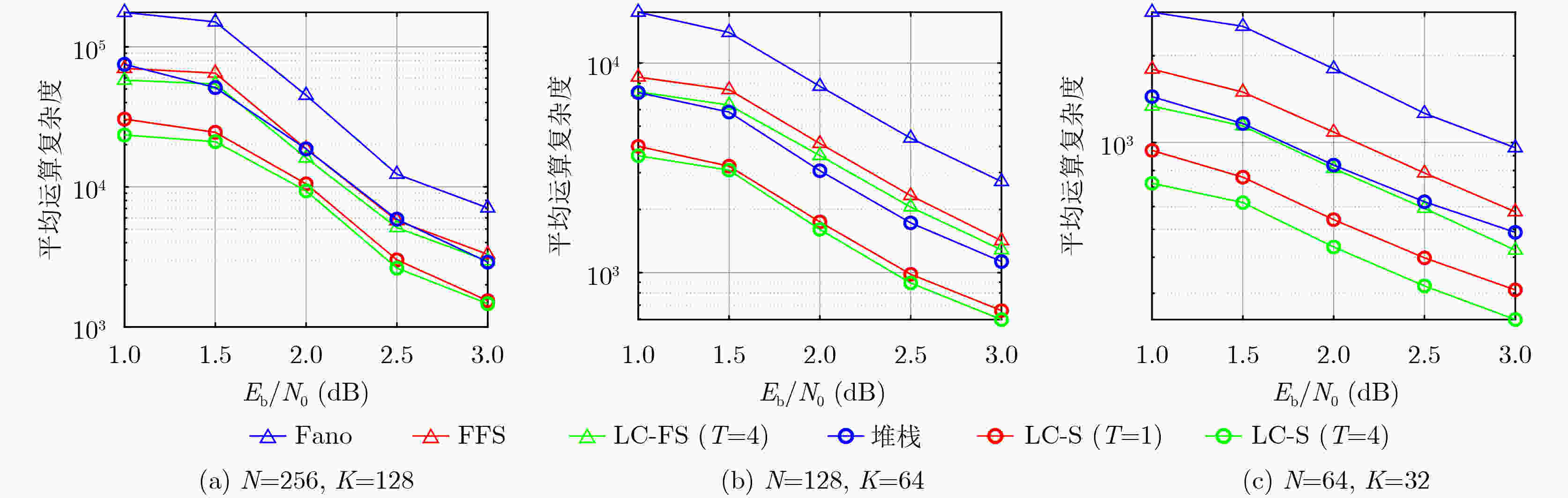
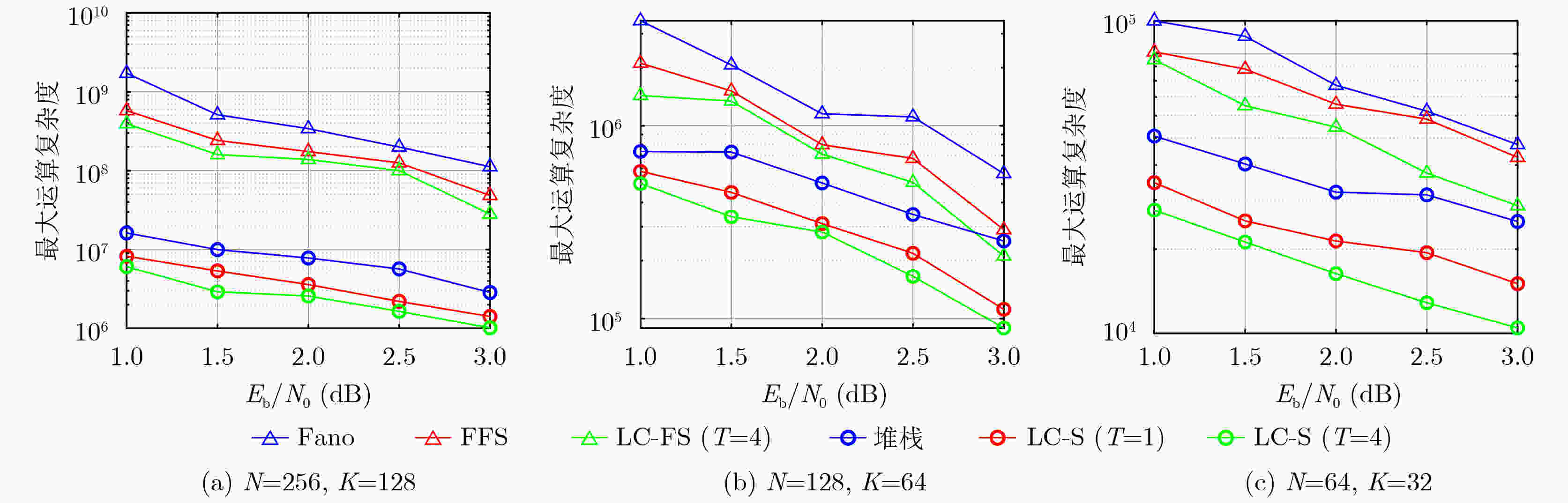
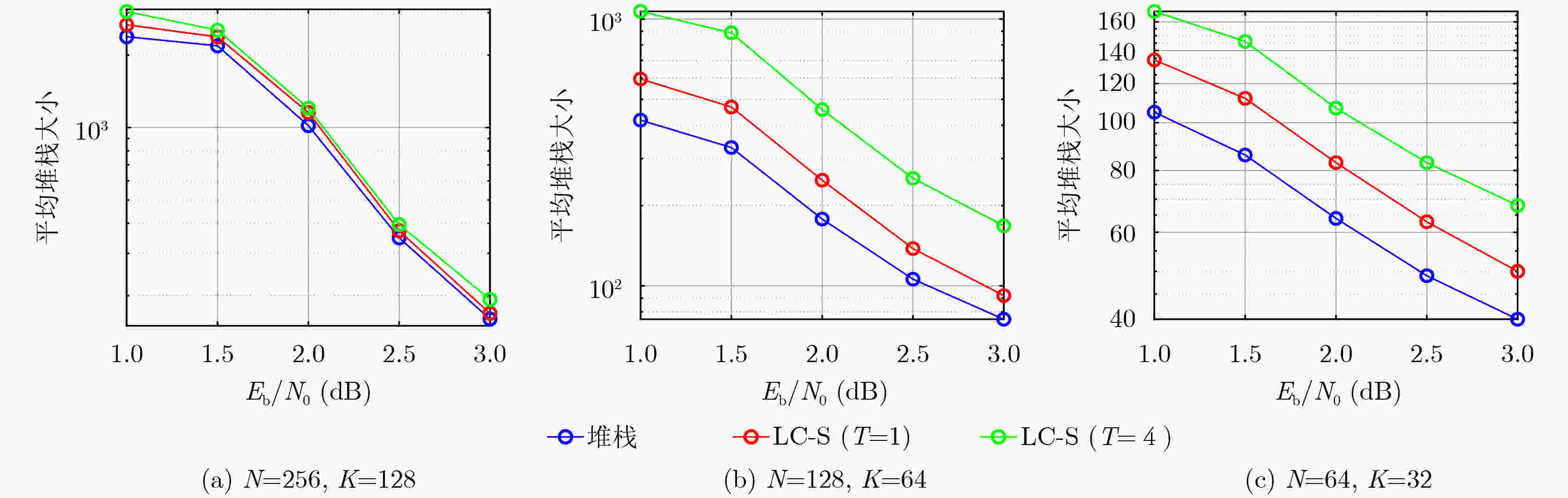
Objective With the rise of the intelligent Internet of Things (IoT), short packet communication among IoT devices must meet stringent requirements for low latency, high reliability, and very short packet length, posing challenges to the design of channel coding schemes. As an advanced variant of polar codes, Polarization-Adjusted Convolutional (PAC) codes enhance the error-correction performance of polar codes at medium and short code lengths, approaching the dispersion bound in some cases. This makes them promising for short packet communication. However, the high decoding complexity required to achieve near-bound error-correction performance limits their practicality. To address this, we propose two low complexity sequential decoding algorithms: Low Complexity Fano Sequential (LC-FS) and Low Complexity Stack (LC-S). Both algorithms effectively reduce decoding complexity with negligible loss in error-correction performance. Methods To reduce the decoding complexity of Fano-based sequential decoding algorithms, we propose the LC-FS algorithm. This method exploits special nodes to terminate decoding at intermediate levels of the decoding tree, thereby reducing the complexity of tree traversal. Special nodes are classified into two types according to decoder structure: low-rate nodes (Type-$ \mathrm{T} $ node) and high-rate nodes [Rate-1 and Single Parity-Check (SPC) nodes]. This classification minimizes unnecessary hardware overhead by avoiding excessive subdivision of special nodes. For each type, a corresponding LC-FS decoder and node-movement strategy are developed. To reduce the complexity of stack-based decoding algorithms, we propose the LC-S algorithm. While preserving the low backtracking feature of stack-based decoding, this method introduces tailored decoding structures and node-movement strategies for low-rate and high-rate special nodes. Therefore, the LC-S algorithm achieves significant complexity reduction without compromising error-correction performance. Results and Discussions The performance of the proposed LC-FS and LC-S decoding algorithms is evaluated through extensive simulations in terms of Frame Error Rate (FER), Average Computational Complexity (ACC), Maximum Computational Complexity (MCC), and memory requirements. Traditional Fano sequential, traditional stack, and Fast Fano Sequential (FFS) decoding algorithms are set as benchmarks. The simulation results show that the LC-FS and LC-S algorithms exhibit negligible error-correction performance loss compared with traditional Fano sequential and stack decoders ( Fig. 5 ). Across different PAC codes, both algorithms effectively reduce decoding complexity. Specifically, as increases, the reductions in ACC and MCC become more pronounced. For ACC, LC-FS decoding algorithm ($T = 4$) achieves reductions of 13.77% ($N = 256$, $K = 128$), 11.42% ($N = 128$, $K = 64$), and 25.52% ($N = 64$, $K = 32$) on average compared with FFS (Fig. 6 ). LC-S decoding algorithm ($T = 4$) reduces ACC by 56.48% ($N = 256$, $K = 128$), 47.63% ($N = 128$, $K = 64$), and 49.61% ($N = 64$, $K = 32$) on average compared with the traditional stack algorithm (Fig. 6 ). For MCC, LC-FS decoding algorithm ($T = 4$) achieves reductions of 29.71% ($N = 256$, $K = 128$), 21.18% ($N = 128$, $K = 64$), and 23.62% ($N = 64$, $K = 32$) on average compared with FFS (Fig. 7 ). LC-S decoding algorithm ($T = 4$) reduces MCC by 67.17% ($N = 256$, $K = 128$), 49.33% ($N = 128$, $K = 64$), and 51.84% ($N = 64$, $K = 32$) on average compared with the traditional stack algorithm (Fig. 7 ). By exploiting low-rate and high-rate special nodes to terminate decoding at intermediate levels of the decoding tree, the LC-FS and LC-S algorithms also reduce memory requirements (Table 2 ). However, as $T$ increases, the memory usage of LC-S rises because all extended paths of low-rate special nodes are pushed into the stack. The increase in $T$ enlarges the number of extended paths, indicating its critical role in balancing decoding complexity and memory occupation (Fig. 8 ).Conclusions To address the high decoding complexity of sequential decoding algorithms for PAC codes, this paper proposes two low complexity approaches: the LC-FS and LC-S algorithms. Both methods classify special nodes into low-rate and high-rate categories and design corresponding decoders and movement strategies. By introducing Type-$ \mathrm{T} $ nodes, the algorithms further eliminate redundant computations during decoding, thereby reducing complexity. Simulation results demonstrate that the LC-FS and LC-S algorithms substantially decrease decoding complexity while maintaining the error-correction performance of PAC codes at medium and short code lengths. -
Key words:
- Short-packet communication /
- PAC code /
- Low complexity /
- Sequential decoding /
- Special node
-
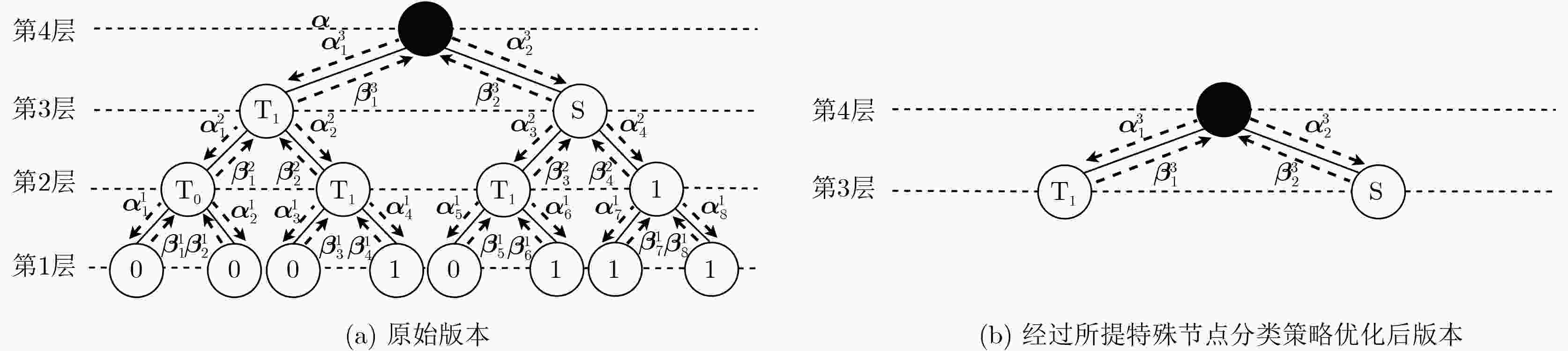
1 低码率特殊节点的LC-FS译码算法
输入:译码位置参数$ {\text{count}} $,节点位置参数$ {\text{CNT}} $,路径选择系数$ {\boldsymbol{\lambda}} $,特殊节点长度${N_{\mathrm{r}}}$,特殊节点信息比特个数${K_{\mathrm{r}}}$,Fano路径度量值
$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}} $,节点LLR向量${\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h$,估计的消息向量$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,卷积脉冲响应$ {\boldsymbol{c}} $输出:节点部分和向量${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h$,$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}} $, $ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,$ {\mathrm{count}} $,$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $ 初始化:$\chi = {2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}}$; $ {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^\sigma } = \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $;${\mathrm{ PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},\sigma } = {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}} $;$ \sigma \in [1:{2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}}] $; (1) if ${\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} - 1 \in A$ do {$ \chi = \chi /2 $;} (2) end if (3) for $i = 1:{2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}}$ do (4) if ${\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} - 1 \in A$ and $i \ge \chi $ do {$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^i}[{\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} - 1] = 0 $;$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^{i + \chi }}[{\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} - 1] = 1 $;$ {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,i + \chi } = 1 - {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,i} $;} (5) else {$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^i}[{\mathrm{count}}:{\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} - 1] = {\text{dec2bin}}(i - 1,{A_T},{N_{\mathrm{r}}}) $; $ {\hat {\boldsymbol{u}}^i} = {\mathrm{Conv}}({\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^i}[{\mathrm{count}}:{\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} - 1],c,{\mathrm{count}}) $; $ {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,i} = {\hat {\boldsymbol{u}}^i} $;} (6) end if (7) for $j = 1:{N_r}$ do {$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},i} = {{{\mathrm{PM}}\_{\mathrm{Com}}(}}{\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},i},{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,i}[j],{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h[j]{\text{)}} $;} (8) end for (9) end for (10) $ \partial = {\text{SortInd}}({\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},\sigma },'{\text{descend}}',{\boldsymbol{\lambda}} [{\mathrm{CNT}}]) $;$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}} + 1}^{\mathrm{F}} = {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},\partial } $; ${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h = {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,\partial }$;$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} = {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^\partial } $; $ {\mathrm{count}} = {\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} $;
$ {\mathrm{CNT}} = {\mathrm{CNT}} + 1 $。2 高码率特殊节点的LC-FS译码算法
输入:译码位置参数$ {\mathrm{count}} $,节点位置参数$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $,路径选择系数$ {\boldsymbol{\lambda}} $,特殊节点长度${N_{\mathrm{r}}}$,特殊节点起始比特位置$ {\text{node\_index}} $,Fano路径度
量值$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}} $,节点LLR向量${\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h$,估计的消息向量$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,卷积脉冲响应$ {\boldsymbol{c}} $输出:节点部分和向量${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h$,$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}} $,$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,$ {\mathrm{count}} $,$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $ 初始化:$ {\mathrm{count}} = {\mathrm{count}} + 1 $;$ i = {\mathrm{count}} - {\text{node\_index}} + 1 $;${\boldsymbol{\beta }}_w^{h,1}[i] = 0$;${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,2}[i] = 1$;$ \sigma \in [1:2] $; (1) $ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},1} = {{{\mathrm{PM}}\_{\mathrm{Com}}}}({\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}},{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,1}[i],{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h[i]) $;$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{F,2} = {\text{PM\_Com}}({\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}},{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,2}[i],{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h[i]) $; (2) if $i = = {N_{\mathrm{r}}}$ do (3) ${\hat {\boldsymbol{u}}^1} = {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,1}{F_{{N_{\mathrm{r}}}}}$; $ {\hat {\boldsymbol{u}}^2} = 1 - {\hat {\boldsymbol{u}}^1} $; (4) for $f = 1:2$ do (5) if 特殊节点为SPC节点 do {$ {\text{test\_bit}} = {\text{Conv1bit}}([\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}[1:{\text{start\_bit}} - 1],0],{\text{node\_index}},{\boldsymbol{c}}) $;$ {\text{SPC\_Flag}} = {\text{test\_bit}} \oplus {\text{sum}}({\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,f}) $;} (6) end if (7) if 特殊节点为SPC节点 and $ {\text{SPC\_Flag}} = = 1 $ do {$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},f} = - \infty $;} (8) else (9) for $j = 1:{N_r}$ do {$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^f}[1:{\text{node\_index}} + j - 1] = {\mathrm{ReConv1bit}}([{\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^f}[1:{\text{start\_bit}} + j - 2],0],{\hat {\boldsymbol{u}}^f}[j],{\text{node\_index}} + j - 1,c) $;} (10) end for (11) end if (12) end for (13)end if (14)$ \partial = {\text{SortInd}}({\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},\sigma },'{\text{descend}}',{\boldsymbol{\lambda}} [{\mathrm{CNT}}]) $;$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}} + 1}^{\mathrm{F}} = {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{{\mathrm{F}},\partial } $;${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h = {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,\partial }$;$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} = {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^\partial } $;$ {\mathrm{CNT}} = {\mathrm{CNT}} + 1 $。 3 LC-FS译码算法
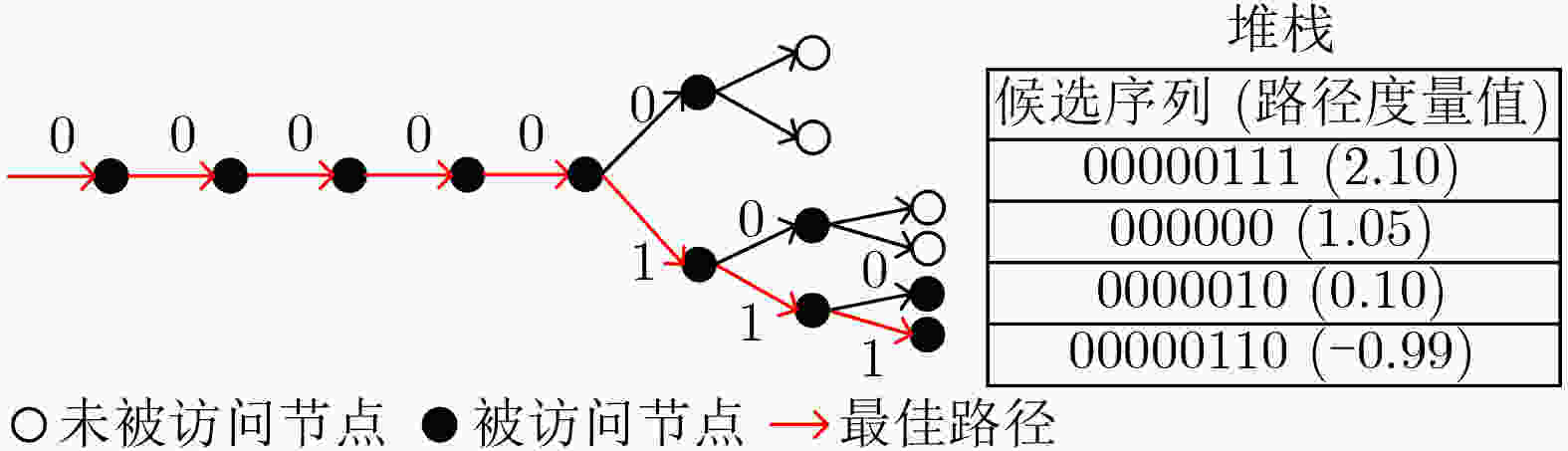
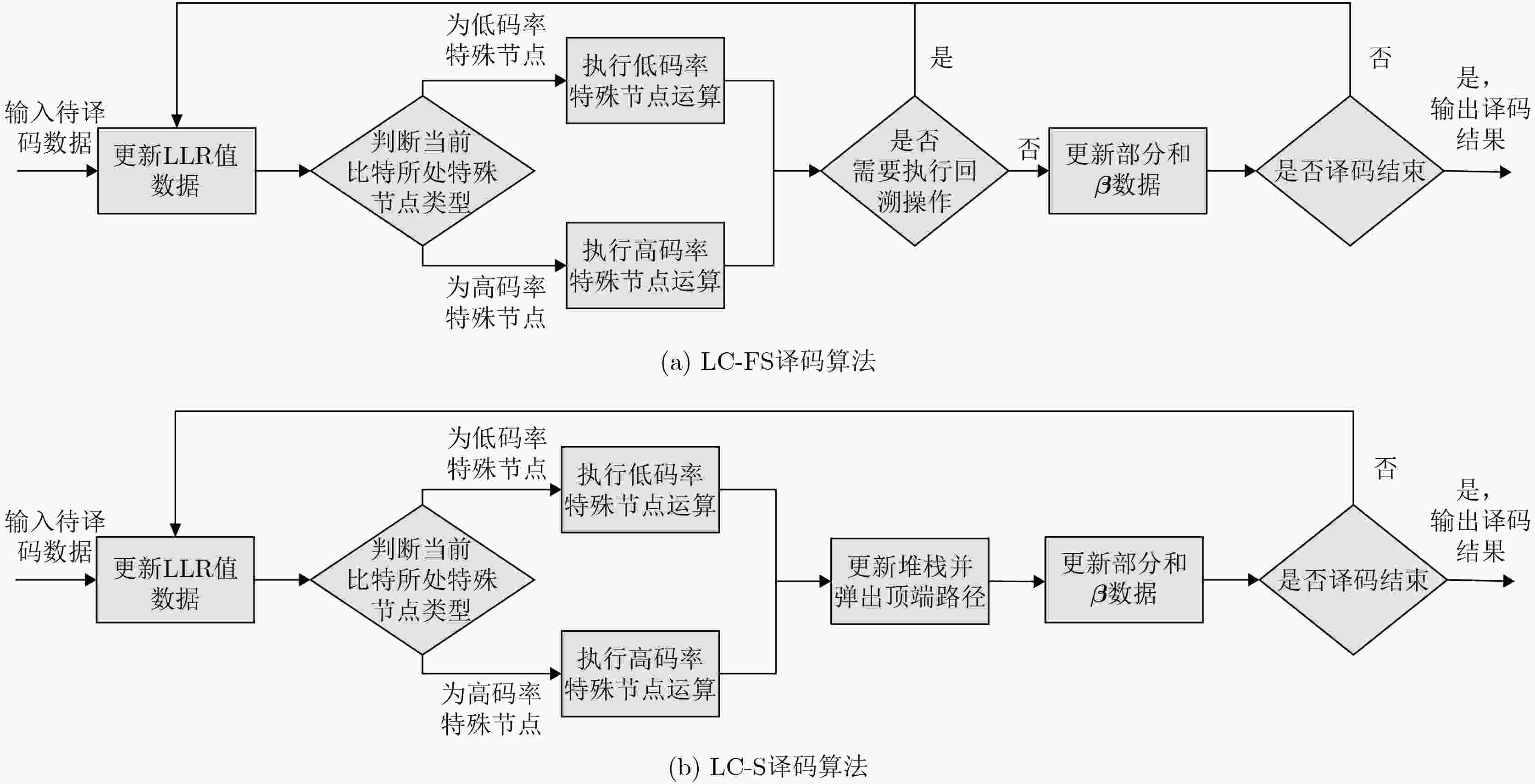
输入:初始LLR值向量$ {\boldsymbol{y}} $,Fano路径阈值$ M $,Fano路径移动值$ \varDelta $,路径选择系数${\boldsymbol{ \lambda}} $,路径选择系数阈值向量$ {{\boldsymbol{\lambda}} ^{\max }} $,卷积脉冲响应$ {\boldsymbol{c}} $ 输出:估计的消息向量$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $ 初始化:${\mathrm{count}} = 1$;${\mathrm{CNT}} = 1$;${\text{Move\_Flag}} = 0$; (1) while ${\mathrm{count}} \lt = N$ do (2) ${\boldsymbol{ \lambda}} [{\mathrm{CNT}}] = 1 $ (3) while $1$ do (4) 根据公式(5)~公式(6)得出向量${\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h$; (5) if ${\mathrm{CNT}}$位于低码率特殊节点 do {调用算法1;} (6) elseif ${\mathrm{CNT}}$位于高码率特殊节点 do {调用算法2;} (7) end if (8) if $ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^F \gt M $ do (9) if $ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}} - 1}^{\mathrm{F}} \lt M + \varDelta $ and ${\mathrm{ CNT}} \gt 1 $ do (10) while $ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{\mathrm{F}} \gt M + \varDelta $ do {$M = M + \varDelta $;} (11) end while (12) end if (13) ${\text{Move\_Flag}} = 1$;${\mathrm{CNT}} = {\mathrm{CNT}} + 1$;break; (14) else (15) ${\text{break\_flag}} = 0$ (16) while $ 1 $ do (17) if $ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}} - 2}^{\mathrm{F}} \lt M $ and $ {\mathrm{CNT}} \gt 2 $ do {$M = M - \varDelta $;${\text{break\_flag}} = 1$;${\text{Move\_Flag}} = 1$;break;} (18) else (19) ${\mathrm{CNT}} = {\mathrm{CNT}} - 1$;${\text{Move\_Flag}} = 0$; (20) if $ {\boldsymbol{\lambda}} [{\mathrm{CNT}}] \lt {{\boldsymbol{\lambda}} ^{\max }}[{\mathrm{CNT}}] $ do {$ {\boldsymbol{\lambda}} [{\mathrm{CNT}}] = {\boldsymbol{\lambda}} [{\mathrm{CNT}}] + 1 $;break;} (21) else {continue;} (22) end if (23) end if (24) end while (25) if ${\text{break\_flag}}$ do {break;} (26) end if (27) end if (28) if ${\text{Move\_Flag}}$ do {根据公式(7)更新向量$ {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h $;} (29) end if (30) end while (31) end while 4 低码率特殊节点的LC-S译码算法
输入:译码位置参数$ {\mathrm{count}} $,节点位置参数$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $,特殊节点长度${N_{\mathrm{r}}}$,特殊节点信息比特个数${K_{\mathrm{r}}}$,堆栈路径度量值$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S $,节点LLR向
量${\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h$,估计的消息向量$ \boldsymbol{\hat{v}} $,堆栈中路径的数目${S_{{\text{num}}}}$,堆栈大小$S$,堆栈$\Upsilon $,卷积脉冲响应$ {\boldsymbol{c}} $输出:节点部分和向量${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h$, $ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,$ {\mathrm{count}} $,$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $,${S_{{\text{num}}}}$,$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S $ 初始化:$\chi = {2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}}$;$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{v}}^\sigma } = \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $;$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,\sigma } = {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S $;$ \sigma \in [1:{2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}}] $; (1)执行算法1中步骤(1)~(2); (2)for $i = 1:{2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}}$ do (3) 执行算法1中步骤(4)~(6); (4) for $j = 1:{N_{\mathrm{r}}}$ do {$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,i} = {\text{PM\_Com(}}{\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,i},{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,i}[j],{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h[j]{\text{)}} $;} (5) end for (6) end for (7) $ \Upsilon = {\text{S\_Push(}}\Upsilon ,{\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,\sigma },{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,\sigma },{\boldsymbol{\alpha }}_w^h{\text{)}} $;$ {\text{S\_Sort(}}\Upsilon {\text{)}} $;$ {\mathrm{count}} = {\mathrm{count}} + {N_{\mathrm{r}}} $;$ {\mathrm{CNT}} = {\mathrm{CNT}} + 1 $;$ {S_{{\text{num}}}} = {S_{{\text{num}}}} + {2^{{K_{\mathrm{r}}}}} $; (8) if ${S_{{\text{num}}}} \gt S$ do {$ \Upsilon = {\text{S\_Delete(}}\Upsilon ,{S_{{\text{num}}}} - S{\text{)}} $;${S_{{\text{num}}}} = S$;} (9) end if 5 高码率特殊节点的LC-S译码算法
输入:译码位置参数$ {\mathrm{count}} $,节点位置参数$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $,特殊节点长度${N_{\mathrm{r}}}$,特殊节点信息比特个数${K_{\mathrm{r}}}$,堆栈路径度量值$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S $,节点LLR向
量${\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h$,估计的消息向量$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,堆栈中路径的数目${S_{{\text{num}}}}$,堆栈大小$S$,堆栈$\Upsilon $,卷积脉冲响应$ c $输出:堆栈路径度量值$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S $,节点部分和向量${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,i}$, $ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $,$ {\mathrm{count}} $,$ {\mathrm{CNT}} $,${S_{{\text{num}}}}$ 初始化:$ {\mathrm{count}} = {\mathrm{count}} + 1 $;$ i = {\mathrm{count}} - {\text{node\_index}} + 1 $;${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,1}[i] = 0$;${\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,2}[i] = 1$; (1) $ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,1} = {\text{PM\_Com(}}{\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S,{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,1}[i],{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h[i]{\text{)}} $;$ {\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,2} = {\text{PM\_Com(}}{\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^S,{\boldsymbol{\beta }}_w^{h,2}[i],{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h[i]{\text{)}} $; (2) 执行算法2中步骤(2)~步骤(13); (3) $ \Upsilon = {\text{S\_Push(}}\Upsilon ,{\mathrm{PM}}_{{\mathrm{CNT}}}^{S,\sigma },{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^{h,\sigma },{\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h{\text{)}} $;$ {\text{S\_Sort(}}\Upsilon {\text{)}} $;$ {\mathrm{CNT}} = {\mathrm{CNT}} + 1 $;${S_{{\text{num}}}} = {S_{{\text{num}}}} + 1$; (4) if ${S_{{\text{num}}}} \gt S$ do {$ \Upsilon = {\text{S\_Delete(}}\Upsilon ,{S_{{\text{num}}}} - S{\text{)}} $;${S_{{\text{num}}}} = S$;} (5) end if 6 LC-S译码算法
输入:初始LLR值向量$ {\boldsymbol{y}} $,堆栈大小$S$,堆栈$\Upsilon $,卷积脉冲响应$ {\boldsymbol{c}} $ 输出:估计的消息向量$ \hat {\boldsymbol{v}} $ 初始化:${\mathrm{count}} = 1$;${\mathrm{CNT}} = 1$; (1) while ${\mathrm{count}} \lt = N$ do (2) 根据公式(5)~公式(6)得出向量${\boldsymbol{\alpha}} _w^h$; (3) if ${\mathrm{CNT}}$位于低码率特殊节点 do {调用算法4;} (4) elseif ${\mathrm{CNT}}$位于高码率特殊节点 do {调用算法5;} (5) end if (6) $ {\text{S\_Pop(}}\Upsilon {\text{)}} $;根据公式(7)更新向量$ {\boldsymbol{\beta}} _w^h $; (7) end while 表 1 仿真测试条件
参数 配置 参数 配置 调制方式 二进制相移键控 堆栈大小$S$ $ \infty $ 传输信道 加性高斯白噪声信道 卷积长度$m$ 7 阈值间距参数$\varDelta $ 2 卷积脉冲响应${c}$ $(1,0,1,1,0,1,1)$ 表 2 不同译码算法的内存占用对比
译码算法 LLR向量 部分和向量 消息向量 路径度量值 路径选择系数 神经网络参数 Fano $N{\log _2}(N){Q_\alpha }$ $N - 1$ $N$ $N{Q_{{\text{PM}}}}$ $N$ 0 NN-LC[16] $L\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{{I_{{\text{pro}}}}} {N_{{\text{pro}}}^i{{\log }_2}(N_{{\text{pro}}}^i)} {Q_\alpha }$ $L(N - N_{{\text{pro}}}^{'})$ $L\times N$ $\max (L,{Y_{{\text{pro}}}}){Q_{{\text{PM}}}}$ $N$ ${N_{{\text{NN}}}}{Q_{{\text{MM}}}}$ FFS[18] $ \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{{I_{{\text{fast}}}}} {N_{{\text{fast}}}^i{{\log }_2}} (N_{{\text{fast}}}^i){Q_\alpha } $ $N - N_{{\text{fast}}}^{'}$ $N$ ${Y_{{\text{fast}}}}{Q_{{\text{PM}}}}$ $N$ 0 LC-FS $ \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{{I_{{\text{pro}}}}} {N_{{\text{pro}}}^i{{\log }_2}} (N_{{\text{pro}}}^i){Q_\alpha } $ $N - N_{{\text{pro}}}^{'}$ $N$ ${Y_{{\text{pro}}}}{Q_{{\text{PM}}}}$ $N$ 0 堆栈 ${S_{{\text{final}}}}N{\log _2}(N){Q_\alpha }$ ${S_{{\text{final}}}}(N - 1)$ $\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{{S_{{\text{final}}}}} {N_{{\text{stack}}}^i} $ ${S_{{\text{final}}}}{Q_{{\text{PM}}}}$ 0 0 LC-S $ {S_{{\text{final}}}}\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{{I_{{\text{pro}}}}} {N_{{\text{pro}}}^i{{\log }_2}(N_{{\text{pro}}}^i)} {Q_\alpha } $ $ {S_{{\text{final}}}}(N - N_{{\text{pro}}}^{'}) $ $ \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{{S_{{\text{final}}}}} {N_{{\text{stack}}}^i} $ ${S_{{\text{final}}}}{Q_{{\text{PM}}}}$ 0 0 -
[1] International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector. ITU-R M. 216-0 Framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2030 and beyond[S]. Geneva: Electronic Publication, 2023. [2] European Telecommunications Standards Institute. 3GPP TR 138.913 Study on scenarios and requirements for next generation access technologies[S]. Sophia Antipolis: 3GPP, 2017. [3] JIANG Wei, ZHOU Qiuheng, HE Jiguang, et al. Terahertz communications and sensing for 6G and beyond: A comprehensive review[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024, 26(4): 2326–2381. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2024.3385908. [4] ROWSHAN M, QIU Min, XIE Yixuan, et al. Channel coding toward 6G: Technical overview and outlook[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2024, 5: 2585–2685. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2024.3390000. [5] MIAO Sisi, KESTEL C, JOHANNSEN L, et al. Trends in channel coding for 6G[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2024, 112(7): 653–675. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2024.3416050. [6] ARIKAN E. Channel polarization: A method for constructing capacity-achieving codes for symmetric binary-input memoryless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(7): 3051–3073. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2021379. [7] European Telecommunications Standards Institute. 3GPP TS 38.212 Multiplexing and channel coding[S]. Sophia Antipolis: 3GPP, 2018. [8] ARIKAN E. From sequential decoding to channel polarization and back again[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.09594, 2019. [9] POLYANSKIY Y, POOR H V, and VERDU S. Channel coding rate in the finite blocklength regime[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(5): 2307–2359. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2043769. [10] FANO R. A heuristic discussion of probabilistic decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1963, 9(2): 64–74. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1963.1057827. [11] JELINEK F. Fast sequential decoding algorithm using a stack[J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 1969, 13(6): 675–685. doi: 10.1147/rd.136.0675. [12] ROWSHAN M, BURG A, and VITERBO E. Complexity-efficient Fano decoding of polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes[C]. 2020 International Symposium on Information Theory and Its Applications (ISITA), Kapolei, USA, 2020: 200–204. [13] MORADI M. On sequential decoding metric function of polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(12): 7913–7922. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3111018. [14] WU Yunzhi, LI Li, and FAN Pingzhi. A fast parallel SC-Fano decoding algorithm for PAC codes[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(5): 152301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3498-8. [15] ZHANG Li, LIU Haina, and HE Yejun. Improved stack decoding for PAC codes[C]. 2023 32nd Wireless and Optical Communications Conference (WOCC), Newark, USA, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/WOCC58016.2023.10139571. [16] DAI Jingxin, YIN Hang, LV Yansong, et al. Neural network aided low-complexity decoding for PAC codes[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2025, 14(6): 1638–1642. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2025.3551288. [17] 易方博, 蔡作鑫, 梁积卫, 等. CRC-MPAC码及其高效译码[J]. 移动通信, 2025, 49(2): 36–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20250101-0001.YI Fangbo, CAI Zuoxin, LIANG Jiwei, et al. CRC-MPAC codes and its efficient decoding[J]. Mobile Communications, 2025, 49(2): 36–42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20250101-0001. [18] JI Houren, SHEN Yifei, ZHANG Zaichen, et al. Low-complexity fast Fano decoding for PAC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(12): 15172–15184. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3298847. [19] MOHSEN M. Performance and computational analysis of polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Bilkent University, 2022. [20] DAI Jingxin, YIN Hang, LV Yansong, et al. Fast list decoding of PAC codes with new nodes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2024, 28(3): 449–453. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2024.3354490. [21] ZHU Hongfei, CAO Zhiwei, ZHAO Yuping, et al. Fast list decoders for polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes[J]. IET Communications, 2023, 17(7): 842–851. doi: 10.1049/cmu2.12587. [22] MORADI M and MOZAMMEL A. A Monte-Carlo based construction of polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes[J]. Physical Communication, 2025, 68: 102578. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2024.102578. [23] ROWSHAN M, BURG A, and VITERBO E. Polarization-adjusted convolutional (PAC) codes: Sequential decoding vs list decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(2): 1434–1447. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3052550. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
