Integrating Intelligent Sensing, Transmission, and Control for Industrial IoT Networks: Key Technologies and Future Directions
-
摘要: 大规模工业物联网设备的高效互联互通与智能管控是我国制造业数字化、网络化、智能化转型升级和高质量发展的关键。由于通信、计算和网络资源受限,传输环境复杂,感知、传输和控制系统分离设计,传统工业网络面临感知传输效率低、异构系统互操作性差和难以高效协同的严峻挑战。首先,该文调研并总结了工业物联网发展的核心需求与瓶颈问题,其次,重点聚焦智能感传控融合的工业网络架构、工业物联网智能感知方法、认知智能驱动的工业语义通信以及边缘智能感知-高效传输-最优控制联合设计等关键技术问题,讨论了工业物联网智能感知-传输-控制融合的研究进展,最后总结了工业大模型与工业智能体、工业5.0、工业跨模态协同交互和工业数字孪生等具有重要意义和发展潜力的未来研究方向。Abstract:
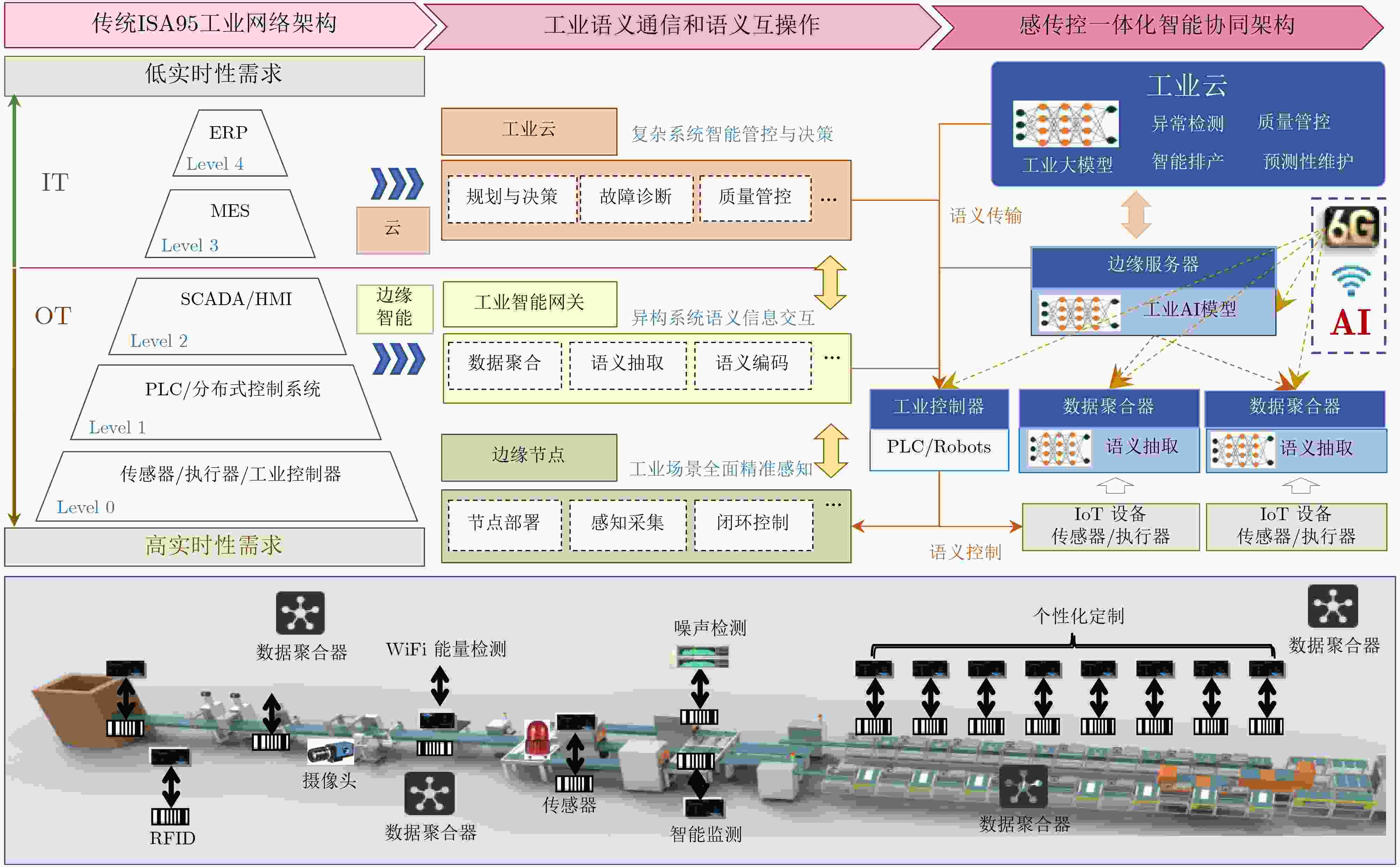
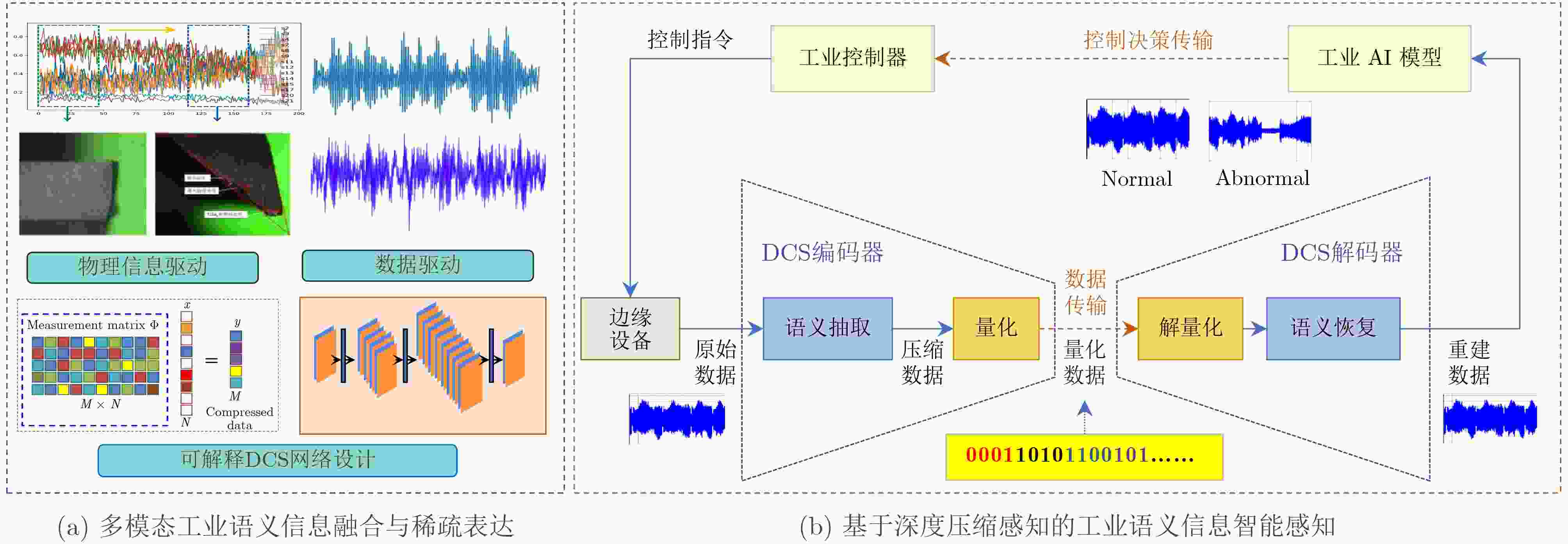
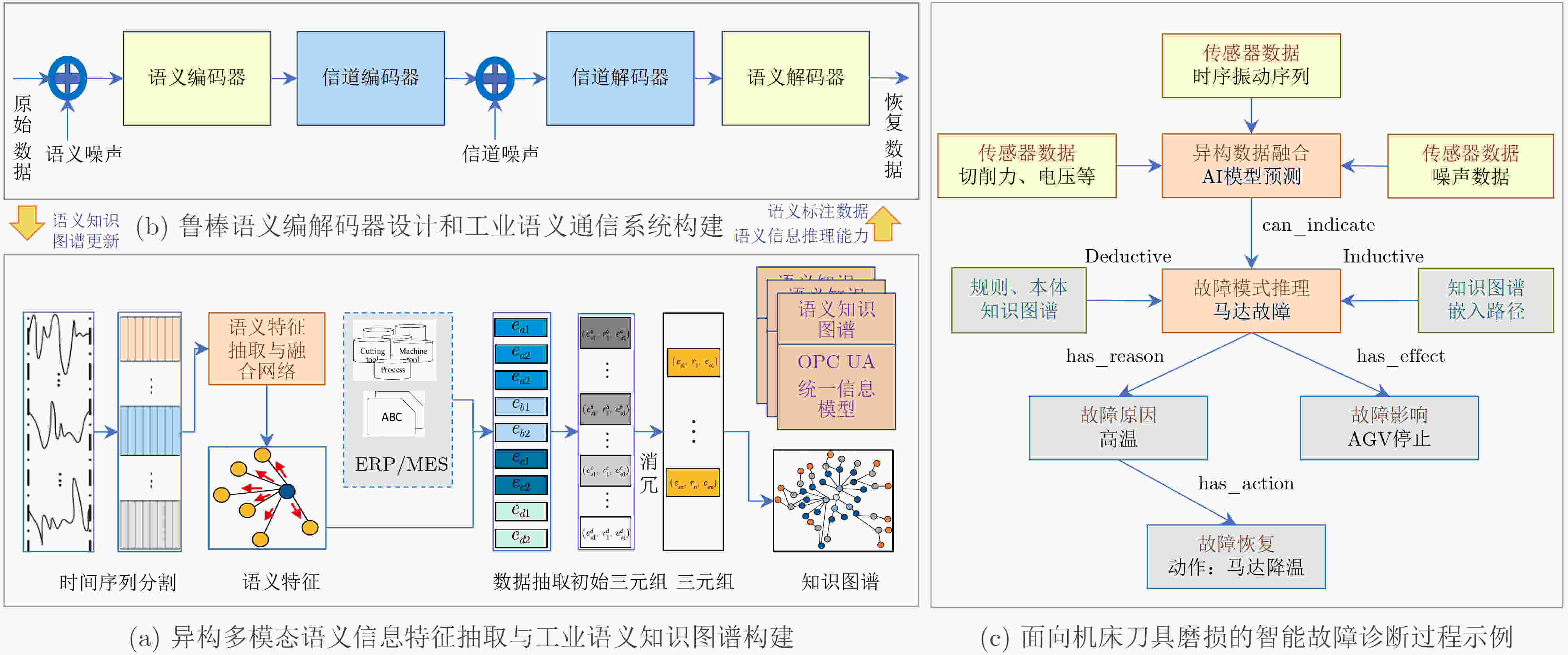
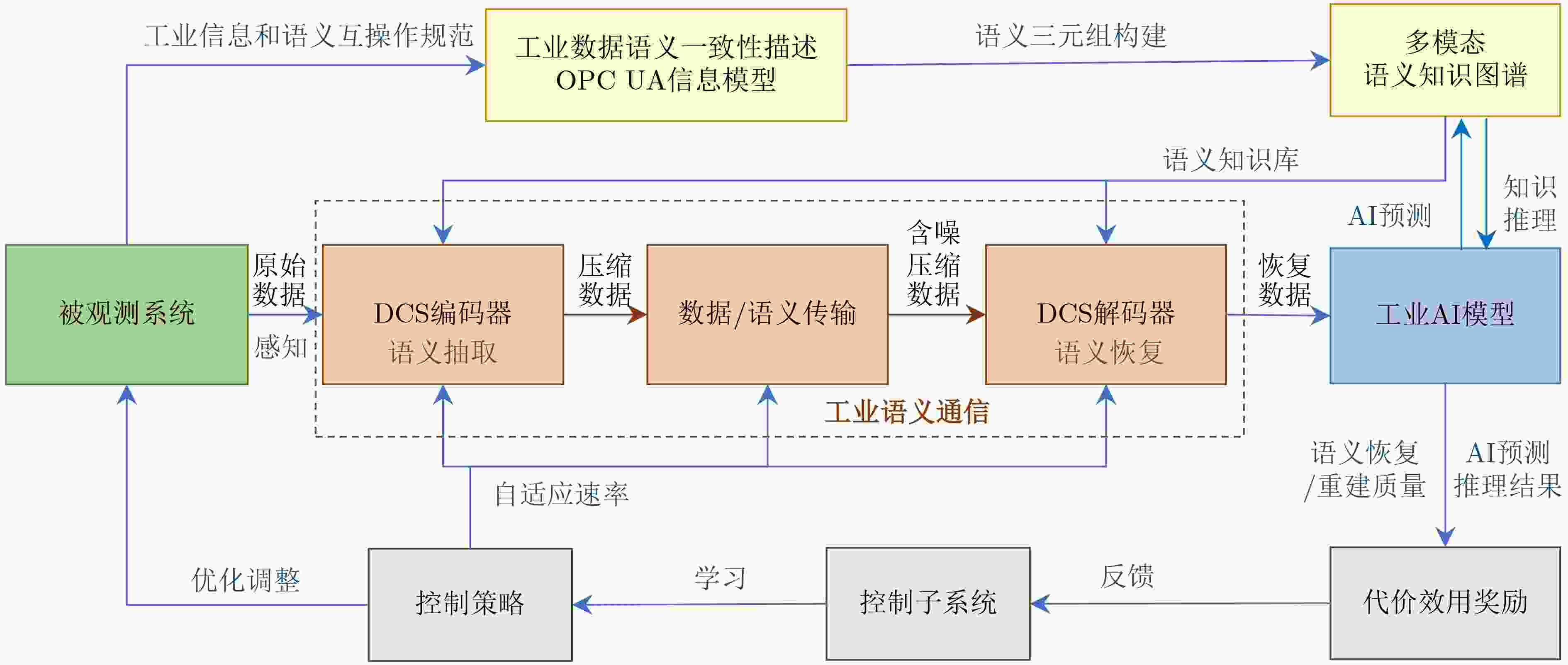
Significance The edge intelligence-enhanced sixth-generation (6G) mobile networks aim to build an integrated architecture that combines sensing, communication, and computation, continuing the trend of 5G’s rapid expansion into vertical industries. Looking ahead, Industry 5.0—defined by human-centric design and large-scale personalized customization—requires 6G-enabled industrial networks to simultaneously meet the demands of sensing, transmission, and control. The efficient interconnection, communication, and intelligent management of large-scale Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices remains fundamental to the digital, networked, and intelligent transformation of the manufacturing sector and its high-quality development. However, limited device resources, complex industrial environments, and the fragmented design of sensing, transmission, and control systems present major challenges. These include limited capability for comprehensive and accurate information sensing, inefficient interaction among heterogeneous devices and systems, and difficulties in achieving intelligent closed-loop collaboration across sensing, transmission, and control. Integrating Intelligent Sensing, Transmission, and Control (ISTC) is essential to enabling intelligent communications in industrial scenarios, facilitating the intelligent interconnection of humans, machines, objects, and environments, and enhancing intelligent management and control across production lines. Progress Achieving semantic interoperability across heterogeneous industrial systems is the core barrier to the integrated design of sensing, transmission, and control, and is also critical to enabling agile interaction between diverse systems, reducing subsystem development and deployment costs, and building autonomous, self-managing industrial networks. Modern IIoT systems typically integrate parallel subsystems across Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) domains, each with independent data models and semantic specifications, resulting in natural interoperability barriers. These barriers restrict efficient interaction and expected collaborative operation across vendors and platforms, significantly limiting large-scale interconnection and data sharing. Therefore, comprehensive and accurate information sensing, reliable and efficient transmission, and responsive feedback control have become key requirements for future IIoT networks. Specifically: (1) Intelligent Sensing: Overcoming the limitations of the Nyquist sampling theorem through interpretable intelligent sensing is a prerequisite for ISTC. (2) Semantic Transmission: The effective extraction and unified representation of industrial semantics, combined with intelligent semantic-level interaction, are critical to ensuring interoperability in heterogeneous systems while maintaining operational efficiency and sustainable performance. (3) Integrated ISTC: Joint design of edge-intelligent sensing, efficient transmission, and optimal control enables streamlined workflows in industrial scenarios, reducing system response time, improving control accuracy, and optimizing energy efficiency. Conclusions This paper proposes an intelligent collaborative architecture for IIoT networks comprising edge nodes or terminals, intelligent gateways, and industrial cloud platforms. The focus is placed on three key technologies within Integrating ISTC: (1) Intelligent sensing methods for IIoT networks: These methods enhance sensing efficiency and accuracy by applying interpretable, physics-informed deep compressed sensing approaches to IIoT devices and systems. (2) Robust Industrial Semantic Communications (ISC) driven by cognitive intelligence: This technology combines industrial knowledge graphs with semantic communication mechanisms to improve semantic interoperability and transmission efficiency across heterogeneous industrial systems. (3) Joint design of edge-intelligent sensing, efficient semantic transmission, and optimal control: By clarifying the intrinsic coupling among sensing, transmission, and control processes, this approach optimizes the collaborative service capability of heterogeneous industrial networks and systems. Prospects Despite progress, ISTC still faces considerable challenges. Future research may focus on the following directions: (1) Industrial large models and intelligent agents: The development of specialized AI models remains essential, particularly in core industrial domains where implicit knowledge is concentrated. (2) Industry 5.0: Achieving efficient, semantic-level human-machine collaborative interaction will be a key breakthrough for future industrial scenarios. (3) Industrial cross-modal collaborative interaction: Integrating data across modalities and mining knowledge from diverse sources present significant challenges but are essential for enabling advanced collaborative interaction in IIoT networks. (4) Industrial digital twins: For complex industrial environments and physical systems, continued advances in digital twin technology—particularly in high-precision semantic perception, real-time efficient interaction, and adaptive fault-tolerant control, will play a critical role in accelerating ISTC development. -
表 1 深度压缩感知算法特点与主要任务
方法 文献 年份 提出的算法 算法特点 主要任务 深度压缩感知 [24] 2010 LISTA 稀疏编码的最佳近似 稀疏编码与重建 [25] 2015 SDA 堆叠降噪自编码器,可学习测量矩阵 数据重建与恢复 [26] 2017 CSGM 基于生成对抗网络,不考虑稀疏性 数据重建 [27] 2019 DCS 基于元学习和生成对抗网络,隐变量优化 数据重建 [28] 2021 LISTA-based 网络深度的动态调整 稀疏信号恢复 [30] 2022 CASNet 自适应采样率分配、细粒度可扩展 数据重建与恢复 [31] 2023 TransCL 基于块CS,不同退化的鲁棒适应性 分类、分割、重建 [32] 2023 DPC-DUN 性能-复杂度权衡来实现动态调整 数据重建 [33] 2025 IDM 两级可逆重构机制 数据重建与恢复 表 2 物理信息神经网络算法特点与主要任务
方法 文献 年份 提出的算法 算法特点 主要任务 物理信息神经网络 [42] 2019 PINN 逆问题求解,时空函数逼近 偏微分方程发现 [43] 2021 PIML 引入物理定律约束的机器学习方法 逆问题求解,综述 [44] 2021 PINN-SR 稀疏回归,多维非线性时空PDE、交替方向优化 数据稀缺偏微分方程 [45] 2023 PICS Navier-Stokes问题求解更新先验,CS稀疏采样恢复 数据重建与恢复 [46] 2021 CNN-based 数据、物理驱动损失函数设计 故障检测 [47] 2024 PINN-based 以经验退化和状态空间方程建模 电池状态监测 [48] 2025 MLP-based 物理知识引入损失函数设计 剩余寿命预测 表 3 信源信道联合编码算法特点与主要任务
方法 文献 年份 提出的算法 算法特点 主要任务和使用的数据集 信源信道联合编码 [61] 2019 DeepJSCC 自编码器压缩、降噪,抗“悬崖效应” 图像通信,Cifar10, ImageNet, Kodak [62] 2020 DeepJSCC-f 利用信道反馈提升重建质量 图像通信,Cifar10, ImageNet, Kodak [63] 2023 Generative JSCC 基于生成对抗网络实现率-失真-感知折中 图像通信,CelebA-HQ, ImageNet [64] 2023 DeepJSCC-V 动态压缩比,预测自适应码率控制 图像通信,Cifar10, ImageNet, Cifar100, Kodak [65] 2025 SwinJSCC Transformer-单模型适应多信道和速率 图像通信,DIV2K, Kodak, CLIC2021, Cifar10 [66] 2025 D2-JSCC 两步速率控制、自适应先验建模 图像通信,Kodak, CLIC2021 -
[1] SISINNI E, SAIFULLAH A, HAN Song, et al. Industrial Internet of Things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(11): 4724–4734. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2852491. [2] 中国通信院. 主要国家和地区推动制造业数字化转型的政策研究报告[R]. 2022.China Academy of Information and Communications Technology. Research report on policies promoting digital transformation of manufacturing in major countries and regions[R]. 2022. [3] CERQUITELLI T, PAGLIARI D J, CALIMERA A, et al. Manufacturing as a data-driven practice: Methodologies, technologies, and tools[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(4): 399–422. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2021.3056006. [4] LETAIEF K B, SHI Yuanming, LU Jianmin, et al. Edge artificial intelligence for 6G: Vision, enabling technologies, and applications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(1): 5–36. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3126076. [5] MADDIKUNTA P K R, PHAM Q V, PRABADEVI B, et al. Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2022, 26: 100257. doi: 10.1016/J.JII.2021.100257. [6] TALLAT R, HAWBANI A, WANG Xingfu, et al. Navigating industry 5.0: A survey of key enabling technologies, trends, challenges, and opportunities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024, 26(2): 1080–1126. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3329472. [7] 洪学海, 蔡迪. 面向“互联网+”的OT与IT融合发展研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2020, 22(4): 18–23. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2020.04.015.HONG Xuehai and CAI Di. Convergence of OT and IT for internet plus[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2020, 22(4): 18–23. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2020.04.015. [8] 关新平, 陈彩莲, 杨博, 等. 工业网络系统的感知-传输-控制一体化: 挑战和进展[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 25–36. doi: 10.16383/J.AAS.C180484.GUAN Xinping, CHEN Cailian, YANG Bo, et al. Towards the integration of sensing, transmission and control for industrial network systems: Challenges and recent developments[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 25–36. doi: 10.16383/J.AAS.C180484. [9] 中国信通院. 中国智能制造发展研究报告-智能工厂[R]. 2022.China Academy of Information and Communications Technology. Research Report on the Development of Intelligent Manufacturing in China - Smart Factory[R]. 2022. [10] GANZHA M, PAPRZYCKI M, PAWŁOWSKI W, et al. Semantic interoperability in the Internet of Things: An overview from the INTER-IoT perspective[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2017, 81: 111–124. doi: 10.1016/J.JNCA.2016.08.007. [11] HAZRA A, ADHIKARI M, AMGOTH T, et al. A comprehensive survey on interoperability for IIoT: Taxonomy, standards, and future directions[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2021, 55(1): 9. doi: 10.1145/3485130. [12] YAO Shengshi, LU Yanpeng, NIU Kai, et al. Semantic information processing for interoperability in the Industrial Internet of Things[J]. Fundamental Research, 2024, 4(1): 8–12. doi: 10.1016/J.FMRE.2023.06.003. [13] AHMED I, JEON G, and PICCIALLI F. From artificial intelligence to explainable artificial intelligence in industry 4.0: A survey on what, how, and where[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(8): 5031–5042. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3146552. [14] LENG Jiewu, ZHU Xiaofeng, HUANG Zhiqiang, et al. Unlocking the power of industrial artificial intelligence towards Industry 5.0: Insights, pathways, and challenges[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 73: 349–363. doi: 10.1016/J.JMSY.2024.02.010. [15] DeepSeek-AI. Deepseek-v3 technical report[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2412.19437, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.19437. [16] LIANG Jiachen, ZHANG Shusheng, ZHANG Yajun, et al. A knowledge graph-based approach to modeling & representation for machining process design intent[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2024, 62: 102645. doi: 10.1016/J.AEI.2024.102645. [17] DAI Wenbin, NISHI H, VYATKIN V, et al. Industrial edge computing: Enabling embedded intelligence[J]. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine, 2019, 13(4): 48–56. doi: 10.1109/MIE.2019.2943283. [18] ZHANG Mingqiang, ZHANG Haixia, YUAN Dongfeng, et al. Learning-based sparse data reconstruction for compressed data aggregation in IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(14): 11732–11742. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3059735. [19] ZHANG Mingqiang, ZHANG Haixia, ZHANG Chuanting, et al. Communication-efficient quantized deep compressed sensing for edge-cloud collaborative industrial IoT networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(5): 6613–6623. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3202203. [20] 徐文伟, 张弓, 白铂, 等. 后香农时代ICT领域的十大挑战问题[J]. 中国科学: 数学, 2021, 51(7): 1095–1138. doi: 10.1360/SSM-2021-0013.XU Wenwei, ZHANG Gong, BAI Bo, et al. Ten key ICT challenges in the post-Shannon era[J]. Scientia Sinica Mathematica, 2021, 51(7): 1095–1138. doi: 10.1360/SSM-2021-0013. [21] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582. [22] HAUPT J, BAJWA W U, RABBAT M, et al. Compressed sensing for networked data[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 92–101. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.914732. [23] XIANG Liu, LUO Jun, and ROSENBERG C. Compressed data aggregation: Energy-efficient and high-fidelity data collection[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2013, 21(6): 1722–1735. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2012.2229716. [24] GREGOR K and LECUN Y. Learning fast approximations of sparse coding[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 2010: 399–406. [25] MOUSAVI A, PATEL A B, and BARANIUK R G. A deep learning approach to structured signal recovery[C]. 2015 53rd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, USA, 2015: 1336–1343. doi: 10.1109/ALLERTON.2015.7447163. [26] BORA A, JALAL A, PRICE E, et al. Compressed sensing using generative models[C]. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 537–546. [27] WU Yan, ROSCA M, and LILLICRAP T. Deep compressed sensing[C]. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6850–6860. [28] CHEN Wei, ZHANG Bowen, JIN Shi, et al. Solving sparse linear inverse problems in communication systems: A deep learning approach with adaptive depth[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(1): 4–17. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3036959. [29] ZHANG Jian and GHANEM B. ISTA-Net: Interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1828–1837. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00196. [30] CHEN Bin and ZHANG Jian. Content-aware scalable deep compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 5412–5426. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3195319. [31] MOU Chong and ZHANG Jian. TransCL: Transformer makes strong and flexible compressive learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(4): 5236–5251. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3194001. [32] SONG Jiechong CHEN Bin, and ZHANG Jian. Dynamic path-controllable deep unfolding network for compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 2202–2214. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3263100. [33] CHEN Bin, ZHANG Zhenyu, LI Weiqi, et al. Invertible diffusion models for compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2025, 47(5): 3992–4006. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2025.3538896. [34] ANTUN V, RENNA F, POON C, et al. On instabilities of deep learning in image reconstruction and the potential costs of AI[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(48): 30088–30095. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.1907377117. [35] PAPYAN V, HAN X Y, and DONOHO D L. Prevalence of neural collapse during the terminal phase of deep learning training[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(40): 24652–24663. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.2015509117. [36] TISHBY N and ZASLAVSKY N. Deep learning and the information bottleneck principle[C]. 2015 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Jerusalem, Israel, 2015: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ITW.2015.7133169. [37] SHWARTZ-ZIV R and TISHBY N. Opening the black box of deep neural networks via information[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.00810, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1703.00810. [38] LEE B, KO K, HONG J, et al. Information bottleneck measurement for compressed sensing image reconstruction[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 1943–1947. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2022.3205275. [39] CHAN K H R, YU Yaodong, YOU Chong, et al. ReduNet: A white-box deep network from the principle of maximizing rate reduction[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2022, 23(1): 4907–5009. [40] WRIGHT J and MA Yi. High-Dimensional Data Analysis with Low-Dimensional Models: Principles, Computation, and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022. [41] YU Yaodong, BUCHANAN S, PAI D, et al. White-box transformers via sparse rate reduction: Compression is all there is?[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2024, 25(1): 14426–14553. [42] RAISSI M, PERDIKARIS P, and KARNIADAKIS G E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686–707. doi: 10.1016/J.JCP.2018.10.045. [43] KARNIADAKIS G E, KEVREKIDIS I G, LU Lu, et al. Physics-informed machine learning[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3(6): 422–440. doi: 10.1038/s42254-021-00314-5. [44] CHEN Zhao, LIU Yang, and SUN Hao. Physics-informed learning of governing equations from scarce data[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 6136. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26434-1. [45] KONTOGIANNIS A and JUNIPER M P. Physics-informed compressed sensing for PC-MRI: An inverse Navier-Stokes problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 281–294. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3228172. [46] SHEN Sheng, LU Hao, SADOUGHI M, et al. A physics-informed deep learning approach for bearing fault detection[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 103: 104295. doi: 10.1016/J.ENGAPPAI.2021.104295. [47] WANG Fujin, ZHAI Zhi, ZHAO Zhibin, et al. Physics-informed neural network for lithium-ion battery degradation stable modeling and prognosis[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 4332. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48779-z. [48] LIAO Wangang, LONG Xiangyun, and JIANG Chao. A physics-informed neural network method for identifying parameters and predicting remaining life of fatigue crack growth[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2025, 191: 108678. doi: 10.1016/J.IJFATIGUE.2024.108678. [49] BRUCKNER D, STĂNICĂ M P, BLAIR R, et al. An introduction to OPC UA TSN for industrial communication systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(6): 1121–1131. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2888703. [50] LI Xiaobin, ZHANG Shucheng, JIANG Pei, et al. Knowledge graph based OPC UA information model automatic construction method for heterogeneous devices integration[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2024, 88: 102736. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2024.102736. [51] BAO Jie, BASU P, DEAN M, et al. Towards a theory of semantic communication[C]. 2011 IEEE Network Science Workshop, West Point, USA, 2011: 110–117. doi: 10.1109/NSW.2011.6004632. [52] XIE Huiqiang, QIN Zhijin, LI G Y, et al. Deep learning enabled semantic communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 2663–2675. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3071210. [53] LUO Xuewen, CHEN H H, and GUO Qing. Semantic communications: Overview, open issues, and future research directions[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(1): 210–219. doi: 10.1109/MWC.101.2100269. [54] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 语义通信技术研究报告&语义通信及语义认知网络架构研究[R]. 2023.IMT-2030 (6G) Promotion Group. Research Report on Semantic Communication Technology & Research on Semantic Communication and Semantic Cognitive Network Architecture[R]. 2023. [55] CHACCOUR C, SAAD W, DEBBAH M, et al. Less data, more knowledge: Building next generation semantic communication networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2025, 27(1): 37–76. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2024.3412852. [56] GETU T M, KADDOUM G, and BENNIS M. Semantic communication: A survey on research landscape, challenges, and future directions[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2024, 112(11): 1649–1685. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2024.3520707. [57] 鹏城实验室, 北京邮电大学, 香港中文大学(深圳). 面向现代语义通信的语义知识库技术白皮书[R]. 2023.Pengcheng Laboratory, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, The Chinese University of Hong Kong (Shenzhen). White Paper on Semantic Knowledge Base Technology for Modern Semantic Communication[R]. 2023. [58] 牛凯, 鲁延鹏, 董超. 面向工业互联网的语义编码传输方法及应用[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版中英文, 2025, 64(1): 51–60. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.ZR20240204.NIU Kai, LU Yanpeng, and DONG Chao. Semantic coding transmission method and application for industrial internet[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2025, 64(1): 51–60. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.ZR20240204. [59] LU Yuqian and ASGHAR M R. Semantic communications between distributed cyber-physical systems towards collaborative automation for smart manufacturing[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2020, 55: 348–359. doi: 10.1016/J.JMSY.2020.05.001. [60] ZHANG Mingqiang, YANG Yajuan, SONG Baokun, et al. Industrial semantic communications for tool wear monitoring in industrial IoT networks[C]. 2024 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), Hangzhou, China, 2024: 248–253. doi: 10.1109/ICCCWorkshops62562.2024.10693780. [61] BOURTSOULATZE E, KURKA D B, and GÜNDÜZ D. Deep joint source-channel coding for wireless image transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(3): 567–579. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2919300. [62] KURKA D B and GÜNDÜZ D. DeepJSCC-f: Deep joint source-channel coding of images with feedback[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory, 2020, 1(1): 178–193. doi: 10.1109/JSAIT.2020.2987203. [63] ERDEMIR E, TUNG T Y, DRAGOTTI P L, et al. Generative joint source-channel coding for semantic image transmission[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(8): 2645–2657. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3288243. [64] ZHANG Wenyu, ZHANG Haijun, MA Hui, et al. Predictive and adaptive deep coding for wireless image transmission in semantic communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(8): 5486–5501. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3234408. [65] YANG Ke, WANG Sixian, DAI Jincheng, et al. SwinJSCC: Taming swin transformer for deep joint source-channel coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2025, 11(1): 90–104. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2024.3424842. [66] HUANG Jianhao, YUAN Kai, HUANG Chuan, et al. D2-JSCC: Digital deep joint source-channel coding for semantic communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2025, 43(4): 1246–1261. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2025.3531546. [67] 孙亚萍, 崔曙光, 张平. 面向语义通信的语义知识库综述[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2023, 29(2): 19–23. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202302005.SUN Yaping, CUI Shuguang, and ZHANG Ping. Survey on semantic knowledge base for semantic communications[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2023, 29(2): 19–23. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202302005. [68] CHI Yuanfang, DONG Yanjie, WANG Z J, et al. Knowledge-based fault diagnosis in Industrial Internet of Things: A survey[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(15): 12886–12900. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3163606. [69] ZHU Xiangru, LI Zhixu, WANG Xiaodan, et al. Multi-modal knowledge graph construction and application: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024, 36(2): 715–735. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2022.3224228. [70] ZHOU Bin, SHEN Xingwang, LU Yuqian, et al. Semantic-aware event link reasoning over industrial knowledge graph embedding time series data[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2023, 61(12): 4117–4134. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2021.2022803. [71] LI Baoxue and ZHAO Chunhui. Federated zero-shot industrial fault diagnosis with cloud-shared semantic knowledge base[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(13): 11619–11630. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3243401. [72] SUN Yaping, CHEN Hao, XU Xiaodong, et al. Semantic knowledge base-enabled zero-shot multi-level feature transmission optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(5): 4904–4917. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3323380. [73] REN Jinke, ZHANG Zezhong, XU Jie, et al. Knowledge base enabled semantic communication: A generative perspective[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2024, 31(4): 14–22. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2300553. [74] HU Qiyu, ZHANG Guangyi, QIN Zhijin, et al. Robust semantic communications with masked VQ-VAE enabled codebook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 8707–8722. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3265201. [75] XIE Huiqiang, QIN Zhijin, and LI G Y. Semantic communication with memory[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(8): 2658–2669. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3288236. [76] PENG Xiang, QIN Zhijjin, TAO Xiaoming, et al. A robust semantic text communication system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(9): 11372–11385. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3381950. [77] PENG Xiang, QIN Zhijjin, TAO Xiaoming, et al. A robust image semantic communication system with multi-scale vision transformer[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2025, 43(4): 1278–1291. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2025.3531413. [78] ZHOU Kequan, ZHANG Guangyi, CAI Yunlong, et al. ROME: Robust model ensembling for semantic communication against semantic jamming attacks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2501.01172, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2501.01172. [79] WENG Zhenzi, QIN Zhijin, and LI G Y. Robust semantic communications for speech transmission[C]. ICASSP 2025–2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 2025: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49660.2025.10889160. [80] PARK T, HONG E, JEON Y S, et al. Robust deep joint source channel coding for task-oriented semantic communications[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2503.12907, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.12907. [81] PEI Jianhua, FENG Cheng, WANG Ping, et al. Latent diffusion model-enabled low-latency semantic communication in the presence of semantic ambiguities and wireless channel noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(5): 4055–4072. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3535714. [82] JI Zhiduo, CHEN Cailian, HE Jianping, et al. Edge sensing and control co-design for industrial cyber-physical systems: Observability guaranteed method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(12): 13350–13362. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3079149. [83] HUANG Jiwei, GAO Han, WAN Shaohua, et al. AoI-aware energy control and computation offloading for industrial IoT[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2023, 139: 29–37. doi: 10.1016/J.FUTURE.2022.09.007. [84] QIAO Yyue, FU Yusun, and YUAN Muyun. Communication–control co-design in wireless networks: A cloud control AGV example[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(3): 2346–2359. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3211766. [85] CHANG Bo, TANG Wei, YAN Xiaoyu, et al. Integrated scheduling of sensing, communication, and control for mmWave/THz communications in cellular connected UAV networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2103–2113. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3157366. [86] WANG Zijie, LIU Rongke, LIU Qirui, et al. QoS-oriented sensing–communication–control co-design for UAV-enabled positioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2023, 7(1): 497–511. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2023.3234139. [87] GUAN Xinping. Network system capacity: Towards integrating sensing, communication and control[J]. National Science Open, 2024, 3(1): 20230036. doi: 10.1360/nso/20230036. [88] DIAO Yufeng, ZHANG Yichi, DE MARTINI D, et al. Task-oriented co-design of communication, computing, and control for edge-enabled industrial Cyber-Physical Systems[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2503.08661, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.08661. [89] LU Binbin, HUANG Xumin, WU Yuan, et al. Joint optimization of compression, transmission and computation for cooperative perception aided intelligent vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(5): 8201–8214. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3528026. [90] LU Jingwei, WANG Xingxia, CHENG Xiang, et al. Parallel factories for smart industrial operations: From big AI models to field foundational models and scenarios engineering[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(12): 2079–2086. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.106094. [91] REN Lei, WANG Haiteng, DONG Jiabao, et al. Industrial foundation model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2025, 55(5): 2286–2301. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2025.3527632. [92] GUO Shaolong, WANG Yuntao, ZHANG Ning, et al. A survey on semantic communication networks: Architecture, security, and privacy[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024: 1–1. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2024.3516819. [93] YANG Kun, XU Zhi, YANG Dingkang, et al. Robust multi-agent collaborative perception via spatio-temporal awareness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025, 35(6): 5644–5658. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3528980. [94] LENG Jiewu, SHA Weinan, WANG Baicun, et al. Industry 5.0: Prospect and retrospect[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 65: 279–295. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.09.017. [95] KATSAMPIRIS-SALGADO K, DIMITROPOULOS N, GKRIZIS C, et al. Advancing human-robot collaboration: Predicting operator trajectories through AI and infrared imaging[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 74: 980–994. doi: 10.1016/J.JMSY.2024.05.015. [96] YU Weigang, LV Jianhao, ZHUANG Weibin, et al. Rescheduling human-robot collaboration tasks under dynamic disassembly scenarios: An MLLM-KG collaboratively enabled approach[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 80: 20–37. doi: 10.1016/J.JMSY.2025.02.015. [97] WANG Shenglin, ZHANG Jingqiong, WANG Peng, et al. A deep learning-enhanced Digital Twin framework for improving safety and reliability in human–robot collaborative manufacturing[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2024, 85: 102608. doi: 10.1016/J.RCIM.2023.102608. [98] ZHENG Chen, DU Yuyang, XIAO Jinhua, et al. Semantic map construction approach for human-robot collaborative manufacturing[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2025, 91: 102845. doi: 10.1016/J.RCIM.2024.102845. [99] PENG Liwen, JIAN Songlei, LI Minne, et al. A unified multimodal classification framework based on deep metric learning[J]. Neural Networks, 2025, 181: 106747. doi: 10.1016/J.NEUNET.2024.106747. [100] WANG Ye, CHEN Lixing, BAI Yang, et al. Through diverse lenses: Multi-modal collaborative perception for indoor scenes in smart home systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(11): 15697–15709. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3533046. [101] LI Baojiang, LI Liang, WANG Haiyan, et al. TVT-Transformer: A Tactile-visual-textual fusion network for object recognition[J]. Information Fusion, 2025, 118: 102943. doi: 10.1016/J.INFFUS.2025.102943. [102] TAO Fei, ZHANG He, and ZHENG Chenyuan. Advancements and challenges of digital twins in industry[J]. Nature Computational Science, 2024, 4(3): 169–177. doi: 10.1038/s43588-024-00603-w. [103] BARATA J and KAYSER I. How will the digital twin shape the future of industry 5.0?[J]. Technovation, 2024, 134: 103025. doi: 10.1016/J.TECHNOVATION.2024.103025. [104] XU Hansong, WU Jun, PAN Qianqian, et al. A survey on digital twin for Industrial Internet of Things: Applications, technologies and tools[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(4): 2569–2598. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3297395. [105] 陶飞, 张辰源, 戚庆林, 等. 数字孪生成熟度模型[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2022, 28(5): 1267–1281. doi: 10.13196/J.CIMS.2022.05.001.TAO Fei, ZHANG Chenyuan, QI Qinglin, et al. Digital twin maturity model[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 28(5): 1267–1281. doi: 10.13196/J.CIMS.2022.05.001. [106] WANG Baicun, ZHOU Huiying, LI Xingyu, et al. Human digital twin in the context of Industry 5.0[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2024, 85: 102626. doi: 10.1016/J.RCIM.2023.102626. [107] SUN Jiacheng, WANG Dong, LIU Zhenyu, et al. Tool digital twin based on knowledge embedding for precision CNC machine tools: Wear prediction for collaborative multi-tool[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 80: 157–175. doi: 10.1016/J.JMSY.2025.02.021. [108] LI Tong, LONG Qingyue, CHAI Haoye, et al. Generative AI empowered network digital twins: Architecture, technologies, and applications[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2025, 57(6): 157. doi: 10.1145/3711682. [109] LI Bin, CAI Haichen, LIU Lei, et al. Delay-Aware digital twin synchronization in mobile edge networks with semantic communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(7): 10974–10983. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3548844. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
