Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making: Concepts, Framework, and Applications
-
摘要: 人机融合智能是人工智能发展到一定阶段的产物,构成了由弱人工智能向强人工智能过渡的关键中间智能形态。该领域的研究不仅涵盖人工智能基础理论与技术的探索,还涉及人类、机器与环境之间复杂关系的系统性分析。在军事、医疗和驾驶等应用场景中,探索人机融合智能在复杂决策中的应用具有重要的研究意义和实用价值。该文阐述了人机融合智能的概念,分析实现人机融合智能决策的意义;归纳了人机融合智能决策系统的一般框架,并依据决策任务的特性及其中体现的人机关系,总结了人机融合智能决策的3种具体方式,即人类主导型决策、机器主导型决策和人机协同型决策;介绍了人机融合智能决策的典型应用;讨论了人机融合智能决策存在的问题和未来的研究方向。Abstract:
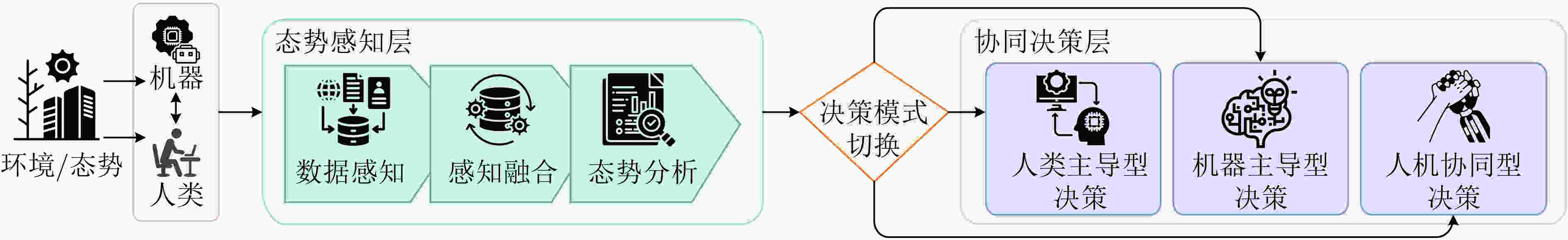
Significance The exponential growth of data volume, advances in computational power, and progress in algorithmic theory have accelerated the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Although AI offers unprecedented opportunities across industries, it continues to face limitations such as dependence on large datasets, poor interpretability of learning and decision-making mechanisms, limited robustness, and susceptibility to hallucinations. To overcome these challenges, integrating human cognitive decision-making capabilities and human-like cognitive models into AI systems is essential. This integration gives rise to a new form of intelligence—Human-Machine Fusion Intelligence—which combines physiological and physical characteristics. The core concept is to harness the complementary strengths of humans and machines in information processing and decision-making: humans provide intuitive judgment and contextual understanding, whereas machines are capable of high-speed computation and large-scale data analysis. By establishing a synergistic, collaborative “partnership,” Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making seeks to optimize decision quality through coordinated organic and probabilistic integration. This paradigm holds significant potential to improve decision reliability in mission-critical contexts, such as military operations, medical procedures, and autonomous driving, thus offering both theoretical research value and practical application relevance. Progress Unlike prior reviews that focus primarily on specific application domains, this article presents a comprehensive overview of Human-Machine Fusion Intelligence across four key dimensions: conceptual foundations, system framework, practical applications, and current challenges and future prospects. The core contributions of this review are summarized in the following four areas: First, it elucidates the advantages of Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making systems: (1) Improved decision-making accuracy—By combining machines’ strengths in data processing and logical reasoning with human capabilities in handling unstructured problems and ethically complex decisions, the system enables dynamic adjustment through a human-in-the-loop mechanism. (2) Enhanced interpretability of decision outcomes—The decision-making process bridges the cognitive gap between humans and machines, providing a transparent, traceable decision path and clarifying accountability boundaries. (3) Greater system robustness—By integrating machines’ risk monitoring and adaptive capabilities with human experiential judgment in complex or uncertain environments, the system establishes a closed-loop collaboration that balances technological rationality with human cognition. Second, the article highlights that Human-Machine Fusion systems cannot operate independently in safety-critical contexts due to imperfect trust mechanisms and ethical constraints. In response, it proposes a hierarchical architecture comprising two key layers: (1) Situational awareness layer, including three core processes: multimodal data perception, cross-modal information fusion, and situational analysis. (2) Collaborative decision-making layer, which distinguishes three decision-making paradigms based on task characteristics and human-machine interaction mode: (a) Human-led decision-making, suited for tasks with high uncertainty and open-ended conditions, where an enhanced intelligence model with a human-in-the-loop is adopted. (b) Machine-led decision-making, appropriate for tasks with lower uncertainty, emphasizing hybrid intelligence through cognitive model integration in automated workflows. (c) Human-machine collaborative decision-making, applicable when human and machine strengths are complementary, allowing for equal, synergistic cooperation to optimize decision efficiency. Third, the article synthesizes recent technological progress, summarizing representative applications of Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making in mission-critical domains such as the military, healthcare, and autonomous driving. Finally, it identifies six key directions for future development: optimization of multimodal perception, fusion of semantic and feature spaces, construction of deep collaborative feedback loops, dynamic task allocation mechanisms, enhancement of system reliability, and development of ethical guidelines. These directions aim to advance efficient collaboration and sustainable evolution of human-machine intelligence. Conclusions This review adopts a systematic research approach to examine Human-Machine Fusion Intelligence in decision-making across four core dimensions. First, it presents a theoretical analysis of the fundamental concepts underpinning Human-Machine Fusion Intelligence and highlights its unique advantages in complex decision-making contexts. Second, it proposes a general framework for Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making systems, emphasizing two key components: situational awareness and collaborative decision-making. Based on this framework, decision-making approaches are categorized into three types according to task characteristics and the nature of human-machine interaction: human-led, machine-led, and human-machine collaborative decision-making. Third, the review synthesizes recent practical advancements in representative application domains. Finally, it examines emerging trends in the development of Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making. Prospects Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making offers substantial research value and strong application potential for advancing emerging industries and enabling new intelligent paradigms. Although several exploratory efforts have been made, the field remains in its infancy, lacking a unified and mature theoretical or technological foundation. Key scientific and engineering challenges persist, including the optimization of multimodal perception and data fusion, bridging the semantic gap between human cognition and machine-represented feature spaces, and achieving deep integration of human and machine intelligence. Continued interdisciplinary collaboration will be essential to drive theoretical progress and technological innovation, further unlocking the potential of Human-Machine Fusion Intelligent Decision-Making. -
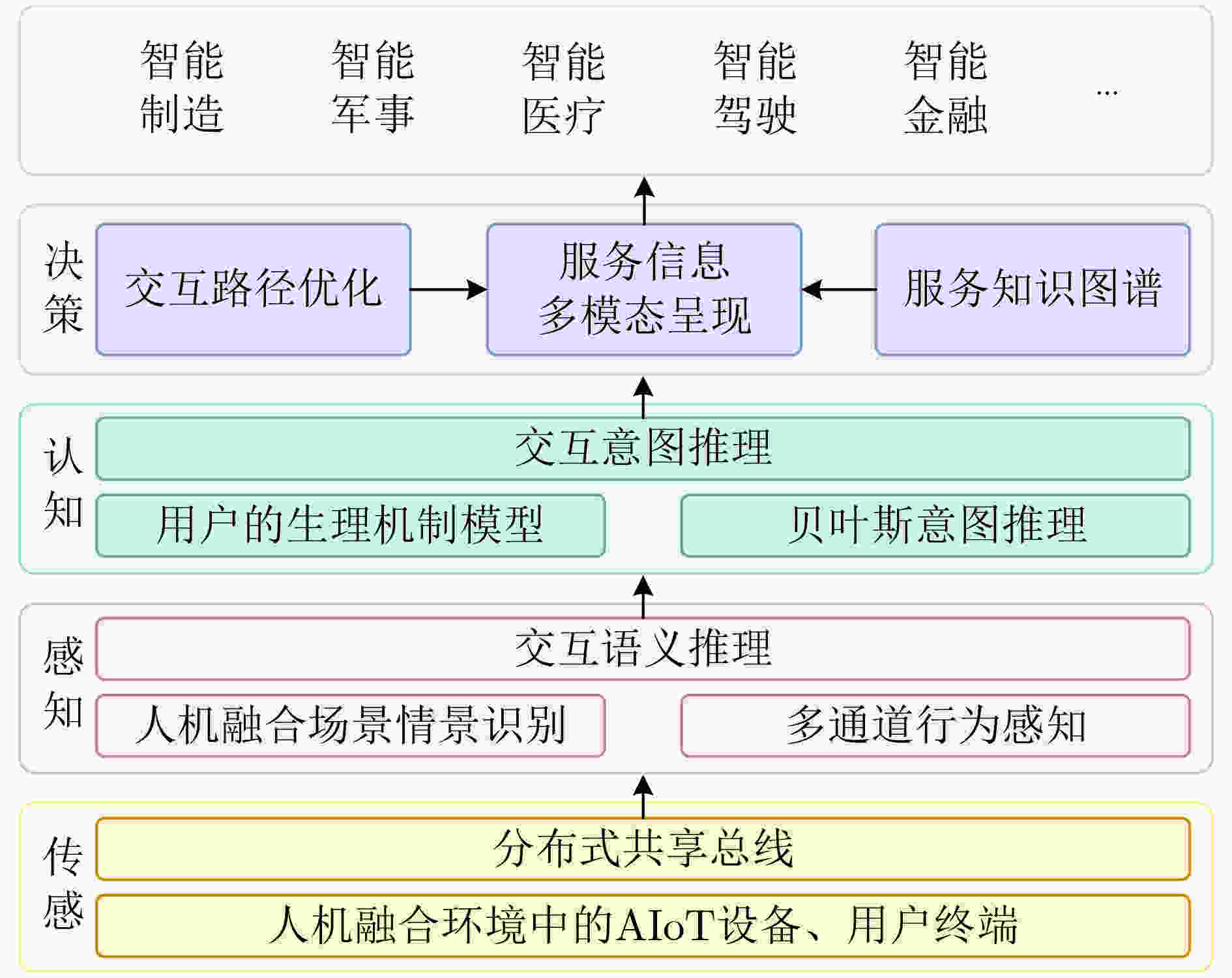
图 3 面向新型终端和人机融合场景的NUIX决策系统框架[45]
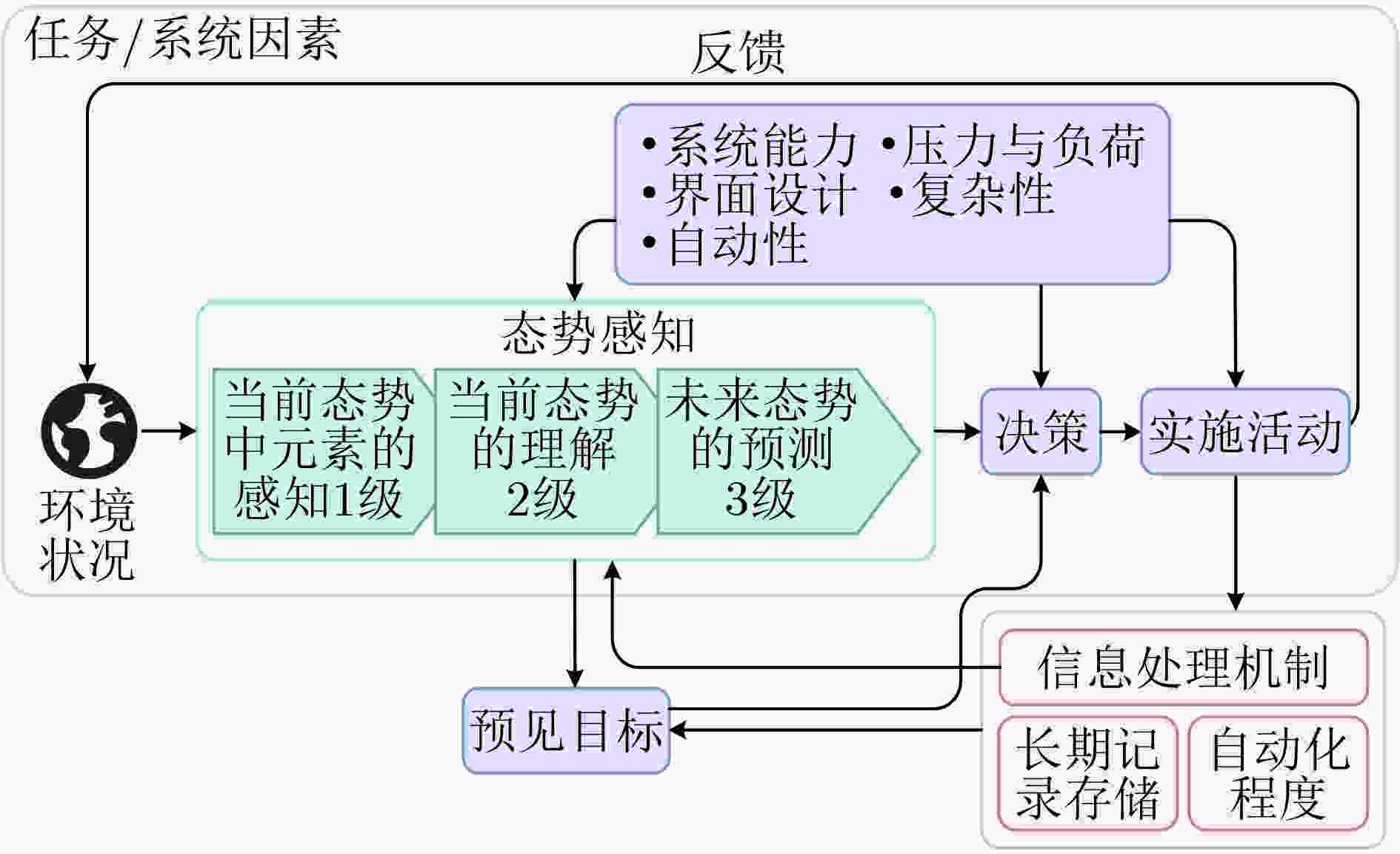
图 5 态势感知的模型架构[12]
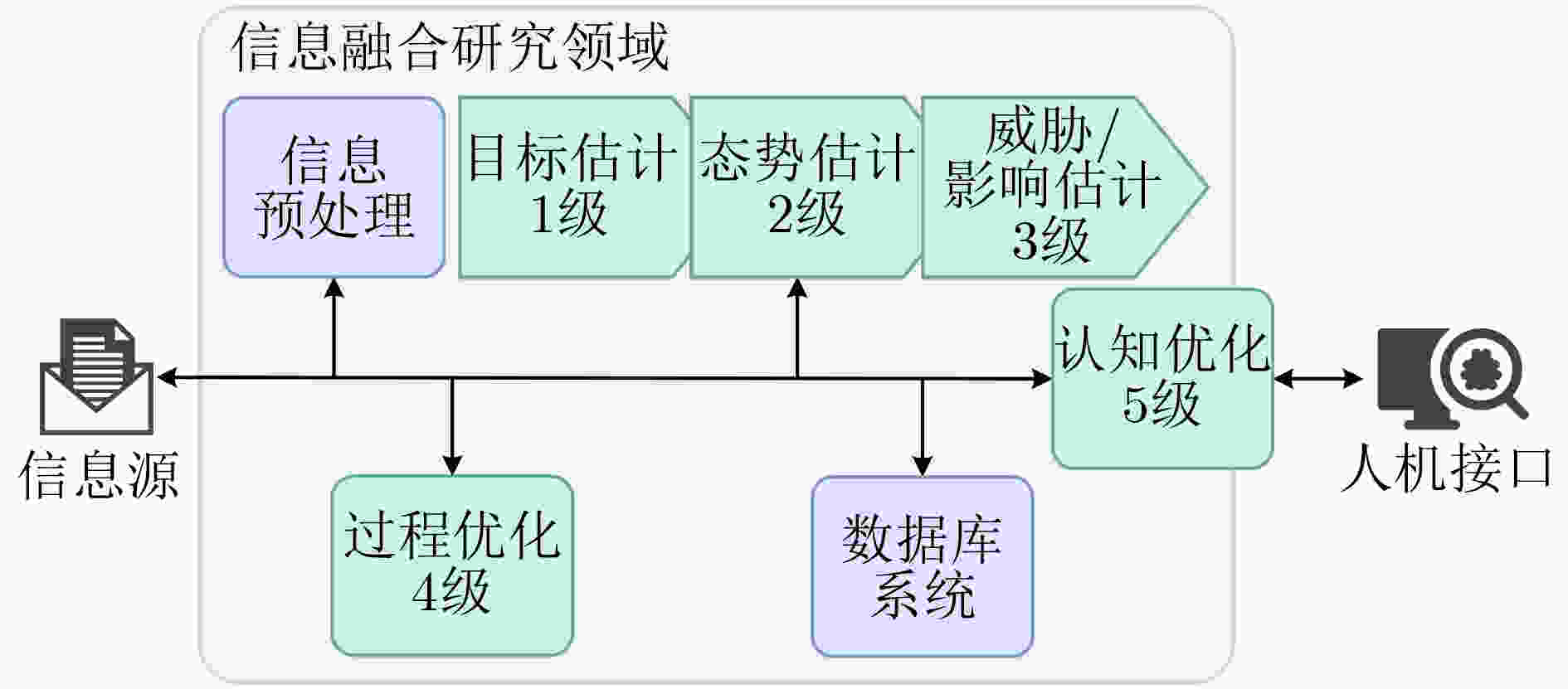
图 6 JDL数据融合模型架构[48]
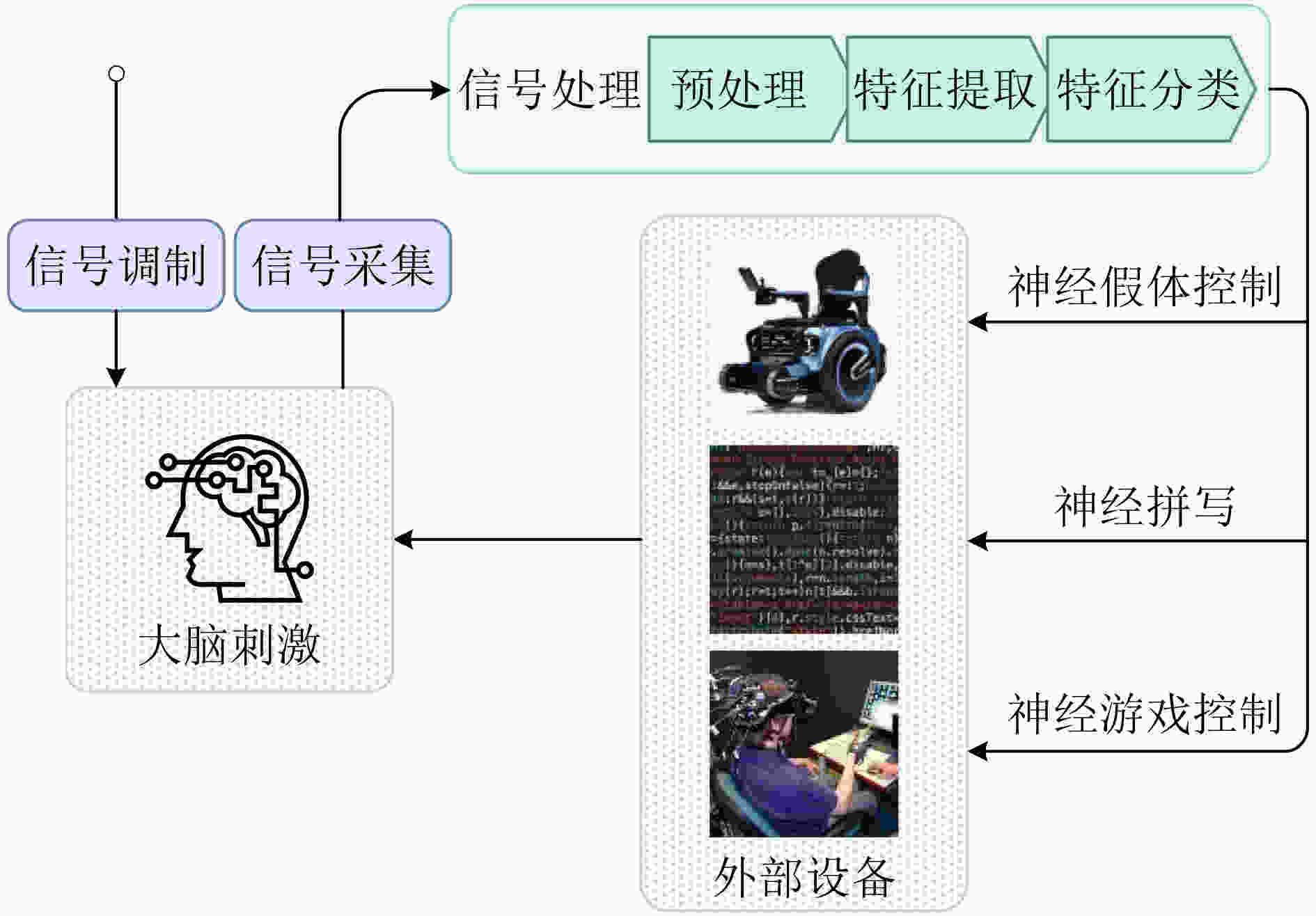
图 7 BCI系统结构示意图[56]
图 8 “超级Nyquist”示意图[57]
图 9 主控系统与T-HR3
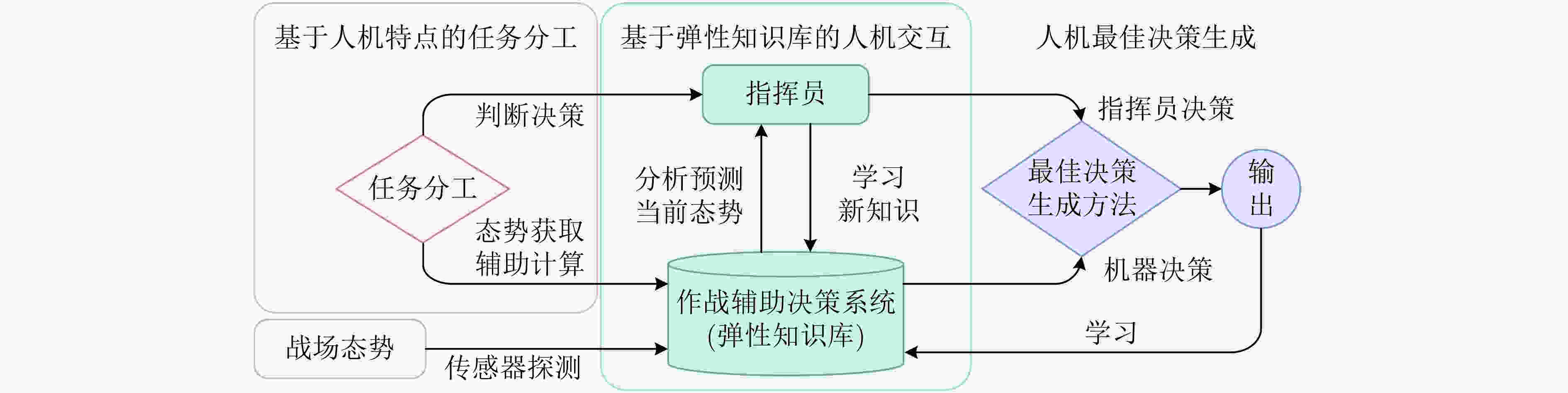
1 图 12 基于人机融合智能的态势认知机制[77]
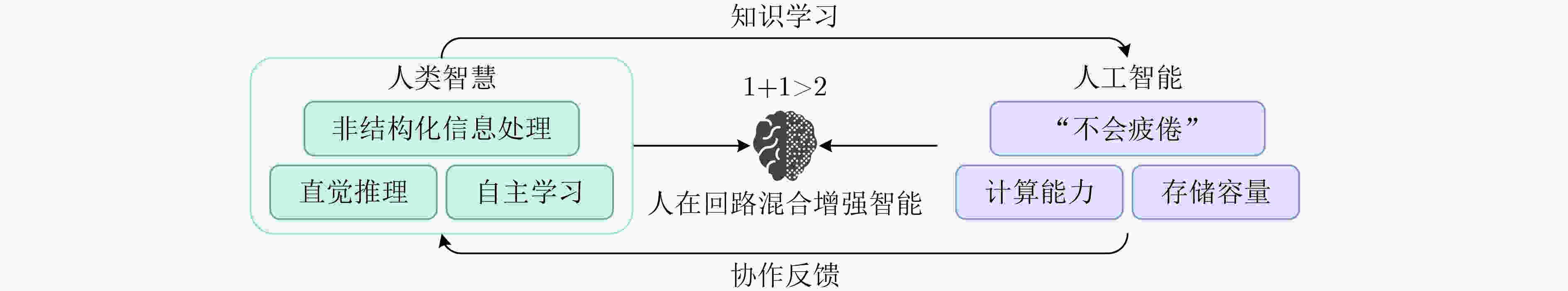
图 15 人在回路的混合增强智能[85]
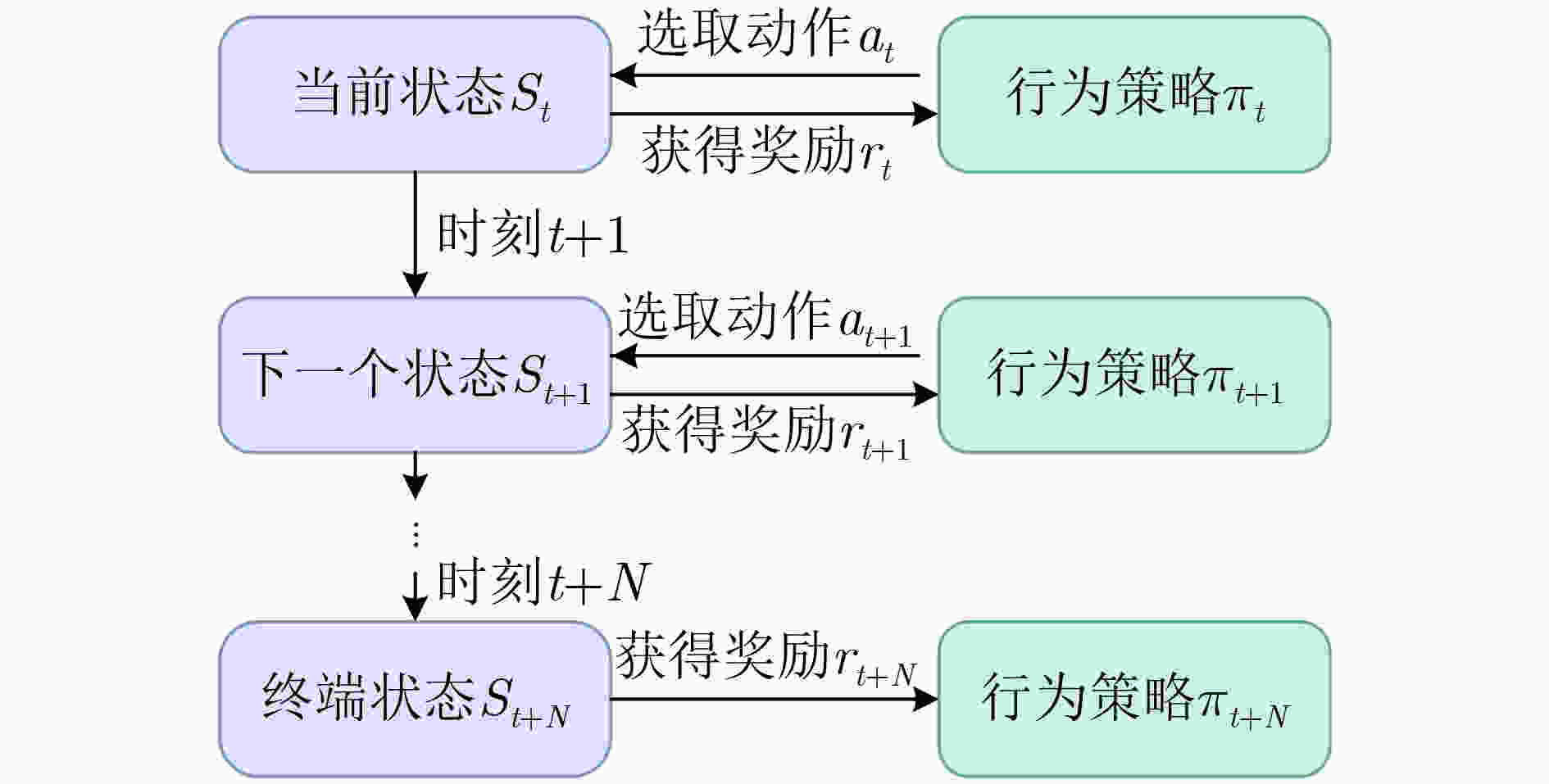
图 16 序贯决策的状态转移示意图[96]
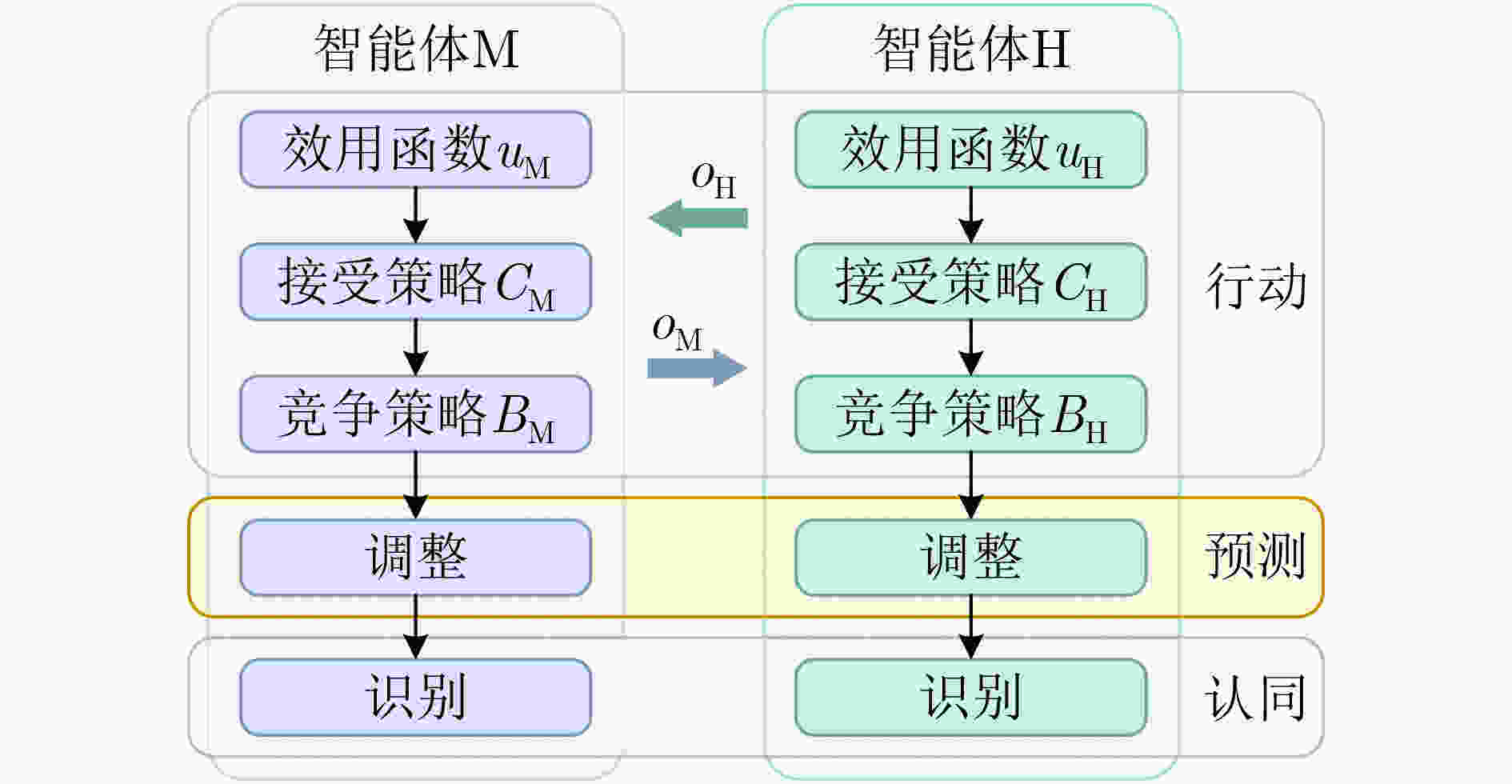
图 17 人机协同型人机融合智能决策系统基本框架[112]
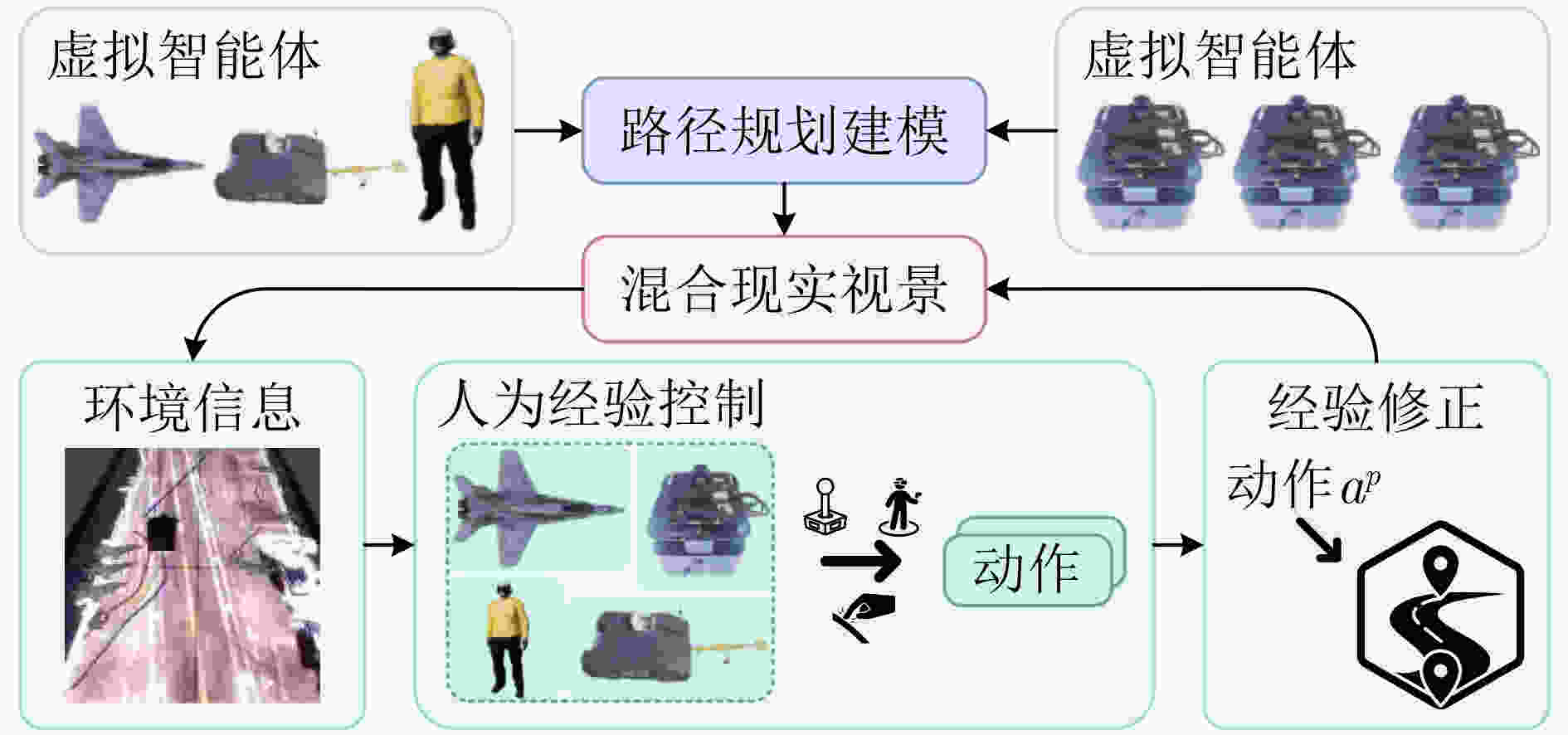
图 20 基于人机融合智能的异质多智能体路径规划[123]
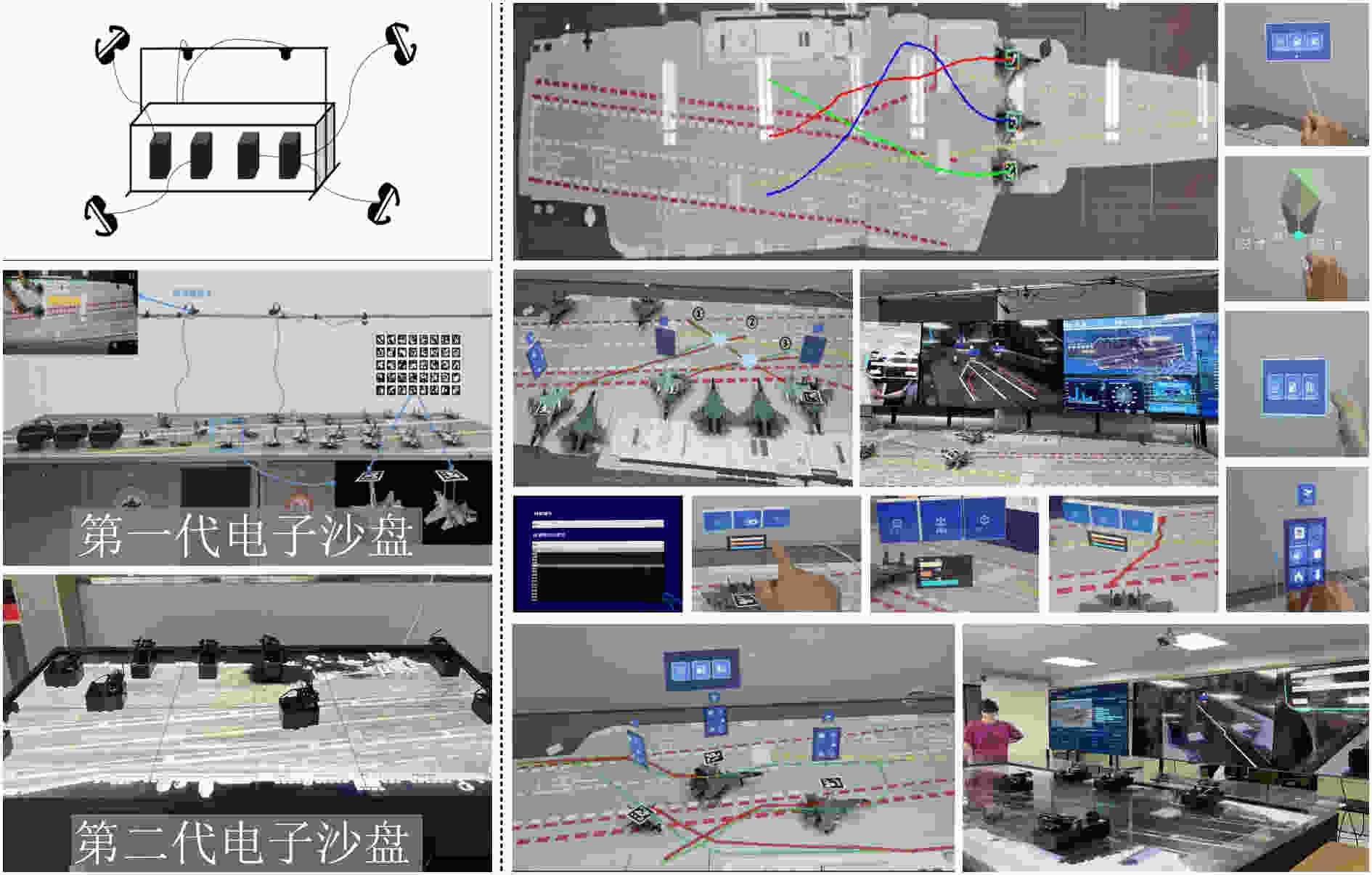
图 21 舰载机着舰引导感知与决策原型系统[124]
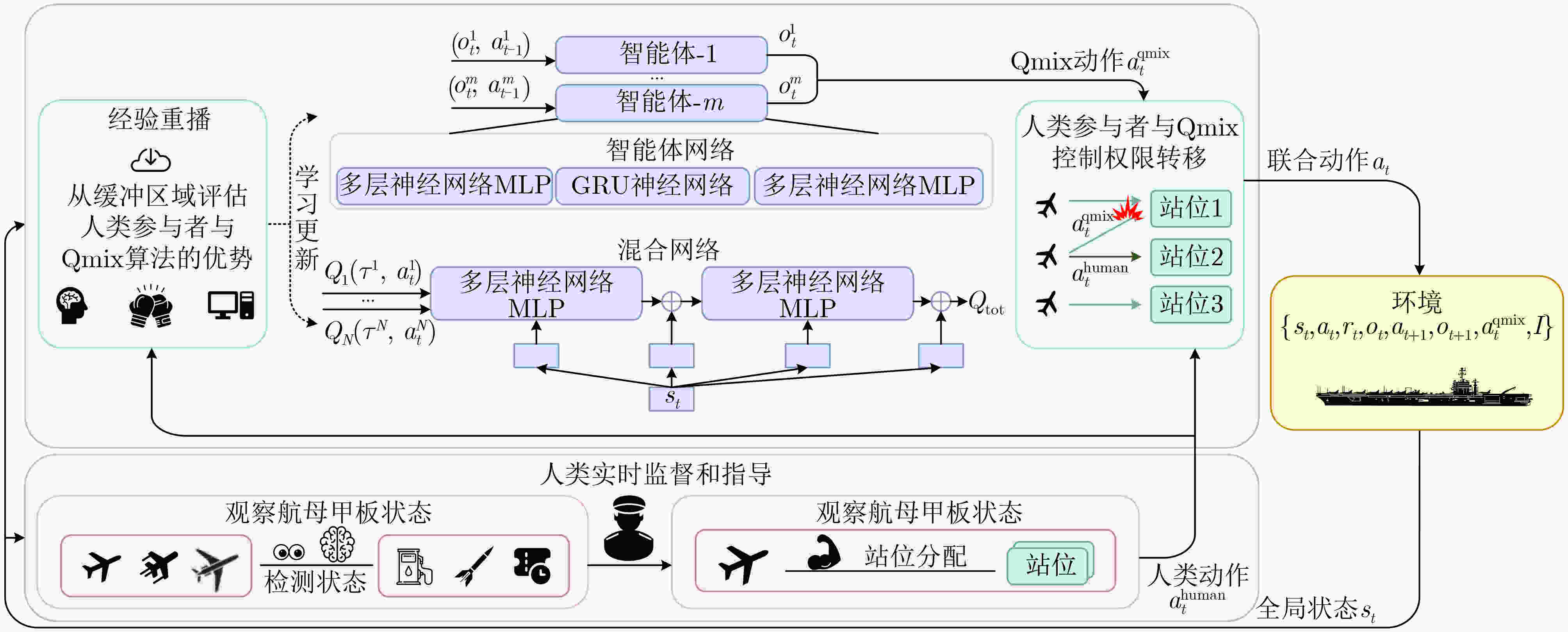
图 22 人机融合多智能体作业规划决策框架[126]
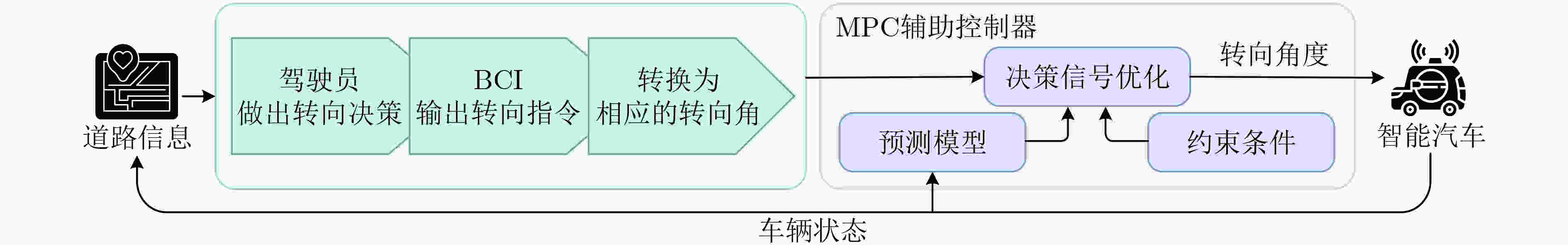
图 23 基于MPC控制器的脑控车辆系统框[141]
表 1 人机融合智能决策方法分类
标准 类型 描述 典型应用场景 人机关系 机主人辅 常用于业务决策问题的求解。关注经济与技术的合理性,外部影响因素较少,确定性因素较多,问题求解流程相对固定,决策过程以机器为主,仅在复杂情境下由人类介入辅助。 资源配置、
生产调度等人主机辅 常用于战略型决策问题的求解。人类在机器辅助下提出决策问题,明确目标与问题范围,规划求解技术路线,分阶段推进问题解决,并在系统支持下形成决策方案。 服务引擎等 人机共商 常用于管理类决策问题的求解。此类决策受未来环境中不确定因素影响较大,人类通常具备较深入的研究基础和理论方法,但在关键环节仍需依赖人机协同,以提高决策的科学性与执行效率。 交通规划、
移动Agent等人类角色 人在环外 该类决策由机器独立主导,依托预设规则、算法与模型实现全流程自主运行。人类仅作为旁观者,无需干预系统运作,也无法介入其决策过程。 对话系统、
无人车等人在环上 人类和机器拥有平等的决策权,人类通过感知外部环境并借助可视化界面实时查看与监督系统反馈,在识别机器难以胜任任务时可及时介入干预,确保决策过程的可靠性与灵活性。 外骨骼机器人、
智能假肢等人在环内 人类在与机器协同执行任务中处于主导地位,深度参与并主动控制决策过程,依据机器提供的信息进行分析判断,最终决策权与责任由人类承担,机器则作为辅助工具提供支持。 工业机器人、
医疗机器人等表 2 态势感知层文献总结
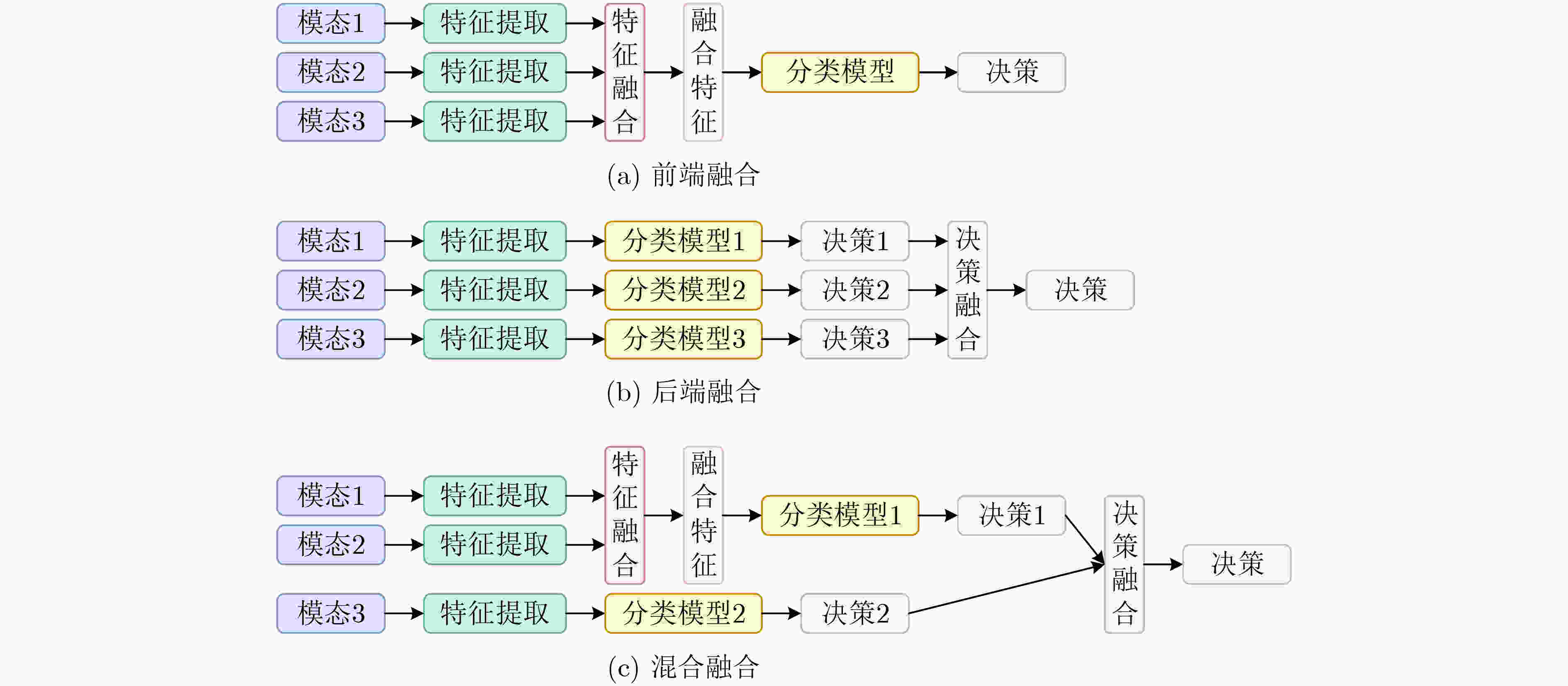
模态 文献 算法优势 算法局限 算法输入 算法输出 典型应用场景 多模态数据
感知Gao等人[51] 引入空间-通道注意力机制的SSD模型,精度高、延迟低,适用于实时检测场景。 依赖高分辨率RGB-D相机,遮挡场景下性能下降,需预训练手势数据集支持。 RGB-D图像 手部边界框坐标及关节位姿估计 空间站机器人遥控操作 Abdolrahmani等人[53] 融合语音指令与低功耗蓝牙和
超宽带定位,实现高精度室内定位,多模态反馈提升视障用户路径跟随
效果。依赖预部署的室内信标网络,复杂声学环境中语音识别率下降,多用户并行请求时系统响应延迟明显增加。 用户语音指令及定位信号 分层导航指令及触觉振动提示 视障人士室内无障碍导航 Liu等人[55] 思维链推理提升诊断准确率,优化诊疗方案降低决策成本,支持实时生成个性化治疗建议。 依赖高质量训练数据,低资源场景下泛化能力较弱,需临床医生复核以防生成错误建议,伦理决策能力有限。 患者病史、实时监测数据及临床指南 个性化治疗建议及置信度评估 肿瘤多学科
会诊跨模态感知
融合An等人[67] 统一语义映射提升准确率,动态模态加权机制增强低质场景鲁棒性,跨模态推理能力增强。 计算开销较大,跨模态幻觉问题突出,强依赖预训练LLM泛化能力。 多模态数据及领域知识图谱 跨模态语义向量及自然语言决策 智能客服 Trende等人[74] 融合EEG与肌电信号提升转向意图识别准确率,增量上下文整合机制缩短决策延时,动态博弈模型增强路口适应性。 依赖高密度脑电帽,强光照或颠簸路况下信号噪声显著增加,个体脑电特征差异需预校准。 EEG脑电信号、车辆状态及环境拓扑 转向意图分类及置信度 智能汽车人机共驾控制 Ghosh等人[76] 非语音音频识别精度提升,复杂场景推理能力增强,指令跟随响应延迟降低。 多模态同步依赖强,小样本泛化能力弱,计算负载较高。 原始音频波形、文本指令及环境上下文 自然语言语义描述、推理结论及决策建议 智能家居环境感知 态势
分析王玉虎等人[77] 融合人类智慧与机器智能提升态势理解准确率,动态任务分配机制缩短响应延迟,多源异构数据融合效率提升。 依赖高质量人类标注数据,突发态势下认知体协作效率较低,个体决策偏好建模需预
校准。多源战场情报、专家经验规则及环境
拓扑态势认知3元组及动态决策建议 军事指挥决策支持、应急响应系统 Huang等人[78] 自动化降级检测延迟,故障响应速度提升,模糊规则与强化学习融合的动态分配模型降低人机冲突率。 依赖高精度传感器实时监测,疲劳驾驶员控制权移交失败率升高,多源异构数据融合计算负载
较大。车辆状态、环境感知数据及自动化系统健康指标 动态控制权分配系数及降级补偿指令 自动驾驶系统降级应急 Huang等人[79] 人因工程优化降低职业灾害风险,虚拟仿真平台提升生产线布局效率,动态任务分配模型增强人机协作适应性。 依赖高精度传感器网络,部署成本较高,跨部门数据孤岛阻碍系统集成。 多源生产数据及环境参数 人机任务分配
矩阵及动态
调度策略汽车混线生产调度 表 3 协同决策层文献总结
模态 文献 算法优势 算法局限 算法输入 算法输出 典型应用场景 人类
主导型
决策Zhou等人[83] HCPS框架实现跨层级动态优化决策,人机混合增强智能提升复杂工艺参数优化效率。 跨行业通用性验证不足,中小企业数据基础设施薄弱制约实施,认知模块依赖高质量标注数据。 多源异构制造数据及人类专家知识规则 全生命周期
优化决策汽车柔性
生产线
动态调度Nikitin等人[84] 图神经网络融合设备拓扑关系提升维护优先级排序准确率,人在回路主动学习机制降低标注成本。 依赖高质量设备关联图谱与人类专家反馈,决策时效性降低,跨行业异构系统迁移需重新训练图模型。 多源设备传感器时序数据、维护历史及专家规则标注 维护优先级评分、
动态策略建议电网设备集群预测性维护 Shi等人[87] HuMAL算法通过人类反馈自适应学习个人价值观,道德显著样本选择机制减少标注需求。 依赖文本游戏简化环境,价值观冲突场景泛化能力有限,人类反馈延迟时决策质量下降。 文本游戏状态描述及人类道德评分反馈 道德对齐的
动作决策、
个人价值观策略人工智能伦理教育系统 机器
主导型
决策Liu等人[91] DDM量化驾驶员决策中的认知参数,蒙特卡洛仿真用于精准预测危险行为发生频率。 依赖高精度车辆轨迹数据,未整合个体差异,实时应用存在计算延迟。 车辆瞬时速度及信号相位时序 决策行为分类、
危险行为概率交叉口信号
时序优化Huang等人[94] 条件运动预测提升交互场景预测精度,IRL学习成本函数提升轨迹人类相似度,多模态候选轨迹生成支持动态博弈决策。 候选轨迹数量有限,预测模块依赖高精度地图标注,实时计算存在延迟。 多帧RGB图像、激光雷达点云及历史序列特征 鸟瞰图空间3D
检测框L4级自动
驾驶全栈
感知Robertazzi
等人[97]神经调节驱动的元学习框架动态调整超参数,双记忆系统模拟人脑巩固机制。 依赖预定义的神经递质动态规则,复杂多任务泛化能力未验证,需模拟“睡眠”巩固阶段,实时性有限。 冲突决策任务
信号动作抑制指令 驾驶紧急制动 Li等人[99] 博弈交互模块提升行人轨迹预测精度,安全约束机制降低危险行为,多模态生成能力支持个性化行人策略生成。 依赖高精度运动捕捉数据,复杂天气下传感器噪声未建模,实时计算延迟较高。 行人姿态序列、车辆运动状态及环境拓扑 行人未来轨迹分布
及交互行为分类自动驾驶行人避撞测试 人机
协同型
决策Zhao等人[109] MAToM-DM实现心理揣测,MAToM-SNN模拟前额叶皮层机制,冲突决策缩短延迟。 依赖预定义神经递质规则,复杂多任务泛化能力未验证,脉冲编码生物合理性牺牲实时性。 多智能体观测状态及任务目标
信号协同策略指令 多机器人
协同搜救Feng等人[110] RL策略模型动态优化人机协作时机,降低人类干预成本。 依赖高质量人机协作预训练数据集,实时环境动态适应性较弱,人类决策偏好建模需个性化校准。 任务状态描述、历史决策序列及环境反馈信号 协作策略及
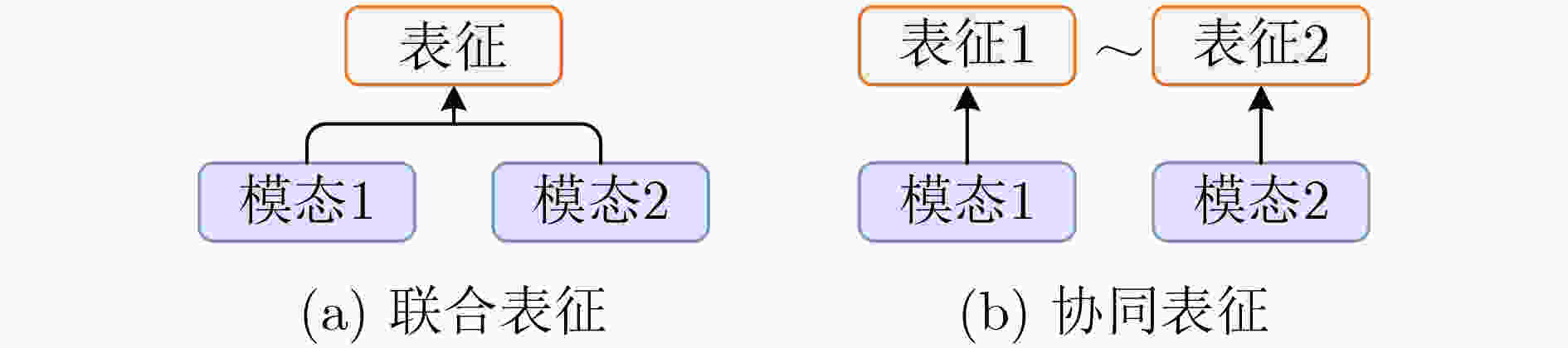
任务执行动作医疗诊断
决策支持Liu等人[111] 柔性时间窗调度降低乘客期望偏差,人机协同优化缩减车队规模,帕累托解集可视化提升决策效率。 依赖高质量乘客需求数据,突发路况扰动适应性较弱,多目标优化求解复杂度较高。 乘客起讫点数据、时间窗约束、车辆容量及路网拓扑 最优发车时刻表
及车辆-乘客
匹配方案城市需求
响应公交表 4 军事领域的人机融合智能决策系统
平台 用途 特点 研发机构 DARPA’s Insight 3 数据和情报分析
平台通过整合多源数据,结合高级算法与机器学习技术,实现实时情报分析与人机融合决策支持,提升系统的智能响应能力与协同决策水平。 英国宇航系统
公司Palantir Gotham 3 数据整合、分析
和可视化平台具备强大的数据处理能力,能够借助直观的可视化界面揭示数据中的潜在模式与关联关系,从而有效辅助用户做出更精准和高效的决策。 帕兰提尔
科技公司Joint Automated Deep Operations Coordination System 3 联合作战指挥 通过集成多源数据,实现实时战场态势感知与人机融合决策支持,助力指挥官开展深度作战协调,提升快速响应与动态战术调整能力。 美国国防部 Advanced Field Artillery Tactical Data System 3 野战炮兵作战
指挥系统具备快速计算与协调多种火力支援任务的能力,能够将实时数据反馈至指挥官,显著提升作战效率与打击精准度。 莱多斯控股公司 Aegis Combat System 3 舰载
综合作战系统通过集成先进传感器与武器控制技术,实现对敌方飞机、导弹及舰船目标的自动探测、跟踪与摧毁,具备全面防御与攻击能力,并为指挥官提供高效决策支持。 洛克希德·马丁
航天系统公司Command and Control, Battle Management, and Communications 3 导弹防御系统 具备实时态势感知、战术规划与人机融合智能决策支持能力,保障导弹防御系统高效运行与精准响应。 洛克希德·马丁
航天系统公司Net-Centric Enterprise Services 3 防务信息共享与
服务平台通过整合多源信息系统与数据,构建统一操作界面与人机融合决策支持工具,显著提升决策效率与操作便捷性。 美国国防部 Command Post of the Future 3 指挥和控制
决策支持系统提供实时战术信息与可视化工具,支持指挥官与决策者在虚拟环境中协同规划作业,提升指挥效率与人机融合决策质量。 通用动力任务
系统公司 -
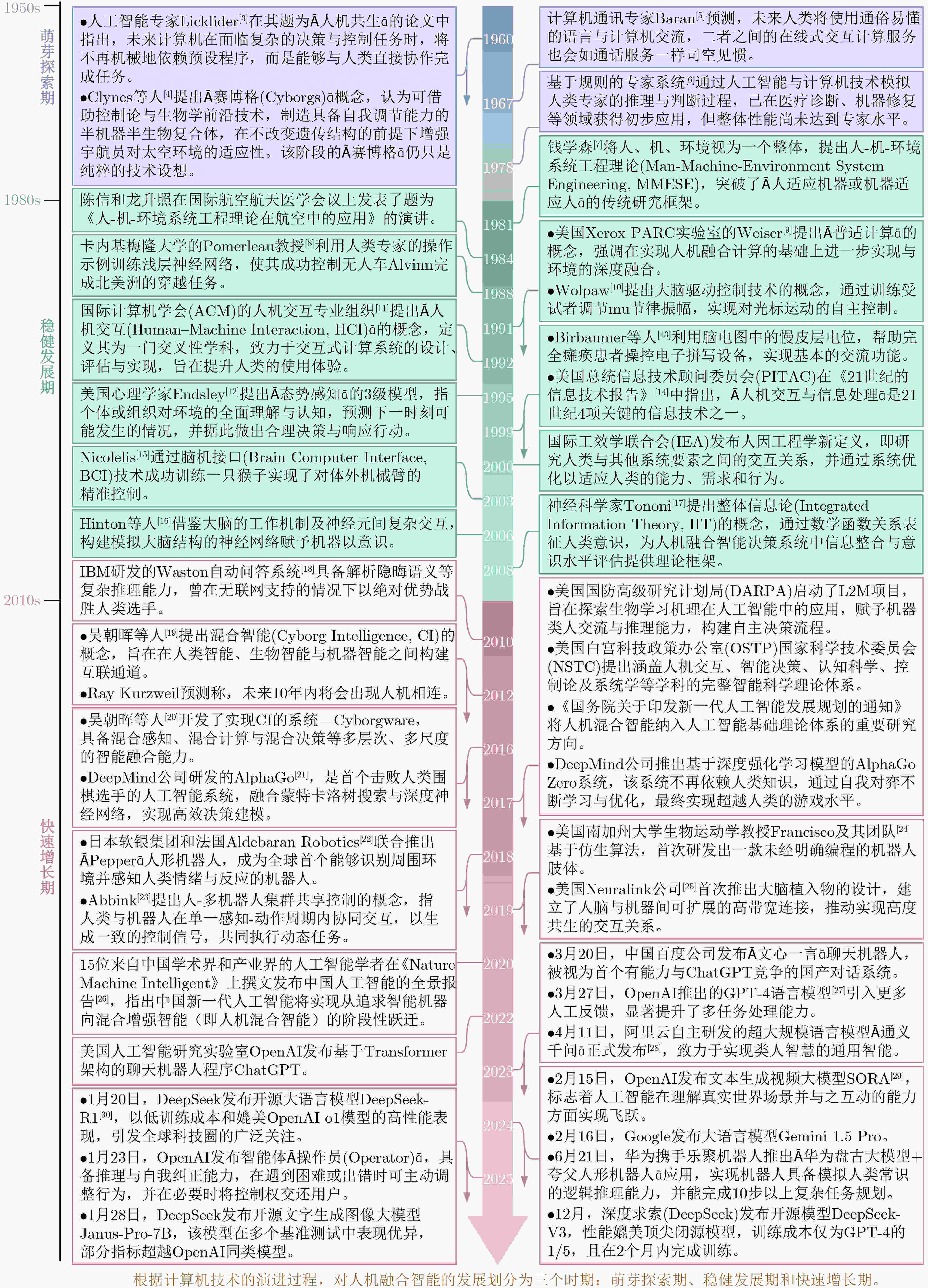
[1] 杨强, 范力欣, 朱军, 等. 可解释人工智能导论[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2022.YANG Qiang, FAN Lixin, ZHU Jun, et al. Introduction to Explainable Artificial Intelligence[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2022. [2] 刘伟, 谭文辉, 刘欣. 人机环境系统智能: 超越人机融合[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024.LIU Wei, TAN Wenhui, and LIU Xin. Human-Machine Environment System Intelligence: Beyond Human-Machine Fusion[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2024. [3] LICKLIDER J C R. Man-computer symbiosis[J]. RE Transactions on Human Factors in Electronics, 1960, HFE-1(1): 4–11. doi: 10.1109/THFE2.1960.4503259. [4] CLYNES M E and KLINE N S. Cyborgs and space[J]. Astronautics, 1960, 14(9): 26–27. [5] BARAN P. The future computer utility[J]. The Public Interest, 1967, 8: 81–92. [6] DREYFUS H. What Computers Can’t Do[M]. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1978. [7] 中国系统工程学会. 钱学森同志关于人-机-环境系统工程的讲话[C]. 第一届全国人-机-环境系统工程学术会议论文集, 北京, 1993: 1–2.Chinese Society of Systems Engineering. Speech by comrade Qian Xuesen on man-machine-environment system engineering (MMESE)[C]. The First National Conference on MMESE, Beijing, China, 1993: 1–2. [8] POMERLEAU D A. ALVINN: An autonomous land vehicle in a neural network[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, Colorado, USA, 1988: 305–313. [9] WEISER M. The computer for the 21st century[J]. Scientific American, 1991, 265(3): 94–104. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0991-94. [10] WOLPAW J R, MCFARLAND D J, NEAT G W, et al. An EEG-based brain-computer interface for cursor control[J]. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1991, 78(3): 252–259. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90040-B. [11] HEWETT T T, BAECKER R, CARD S, et al. ACM SIGCHI Curricula for Human-Computer Interaction[M]. New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery, 1992. doi: 10.1145/2594128. [12] ENDSLEY M R. Toward a theory of situation awareness in dynamic systems[J]. Human Factors, 1995, 37(1): 32–64. doi: 10.1518/001872095779049543. [13] BIRBAUMER N, GHANAYIM N, HINTERBERGER T, et al. A spelling device for the paralysed[J]. Nature, 1999, 398(6725): 297–298. doi: 10.1038/18581. [14] President’s Information Technology Advisory Committee. Information Technology Research: Investing in Our Future[R]. National Coordination Office for Computing, Information, and Communications, 1999. [15] NICOLELIS M A L. Brain-machine interfaces to restore motor function and probe neural circuits[J]. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2003, 4(5): 417–422. doi: 10.1038/nrn1105. [16] HINTON G E and SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504–507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647. [17] TONONI G. Consciousness as integrated information: A provisional manifesto[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 2008, 215(3): 216–242. doi: 10.2307/25470707. [18] FERRUCCI D, BROWN E, CHU-CARROLL J, et al. Building Watson: An overview of the DeepQA project[J]. AI Magazine, 2010, 31(3): 59–79. doi: 10.1609/aimag.v31i3.2303. [19] 吴朝晖, 郑能干. 混合智能: 人工智能的新方向[J]. 中国计算机学会通讯, 2012, 8(1): 59–64.WU Zhaohui and ZHENG Nenggan. Cyborg intelligence: The new direction of artificial intelligence[J]. Communications of the CCF, 2012, 8(1): 59–64. [20] WU Zhaohui, ZHOU Yongdi, SHI Zhongzhi, et al. Cyborg intelligence: Recent progress and future directions[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2016, 31(6): 44–50. doi: 10.1109/MIS.2016.105. [21] SILVER D, SCHRITTWIESER J, SIMONYAN K, et al. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354–359. doi: 10.1038/nature24270. [22] PANDEY A K and GELIN R. A mass-produced sociable humanoid robot: Pepper: The first machine of its kind[J]. IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, 2018, 25(3): 40–48. doi: 10.1109/MRA.2018.2833157. [23] ABBINK D A, CARLSON T, MULDER M, et al. A topology of shared control systems——finding common ground in diversity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2018, 48(5): 509–525. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2018.2791570. [24] MARJANINEJAD A, URBINA-MELÉNDEZ D, COHN B A, et al. Autonomous functional movements in a tendon-driven limb via limited experience[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(3): 144–154. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0029-0. [25] LOPATTO E. Elon Musk unveils Neuralink’s plans for brain-reading ‘threads’ and a robot to insert them[EB/OL]. https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/16/20697123/elon-musk-neuralink-brain-readingthread-robot, 2024. [26] WU Fei, LU Cewu, ZHU Mingjie, et al. Towards a new generation of artificial intelligence in China[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2020, 2(6): 312–316. doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-0183-4. [27] OpenAI. GPT-4 technical report[J]. arXiv: 2303.08774, 2023. [28] BAI Jinze, BAI Shuai, CHU Yunfei, et al. Qwen technical report[J]. arXiv: 2309.16609, 2023. [29] OpenAI. Video generation models as world simulators[EB/OL]. https://openai.com/index/video-generation-models-as-world-simulators/, 2024. [30] DeepSeek-AI. DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing reasoning capability in LLMs via reinforcement learning[J]. arXiv: 2501.12948, 2025. [31] STONE P, BROOK R, BRYNJOLFSSON E, et al. Artificial intelligence and life in 2030: The one hundred year study on artificial intelligence[J]. arXiv: 2211.06318, 2022. [32] 杨晓楠, 房浩楠, 李建国, 等. 智能制造中的人-信息-物理系统协同的人因工程[J]. 中国机械工程, 2023, 34(14): 1710–1722,1740. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2023.14.008.YANG Xiaonan, FANG Haonan, LI Jianguo, et al. Human factor engineering for human-cyber-physical system collaboration in intelligent manufacturing[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(14): 1710–1722,1740. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2023.14.008. [33] O’CALLAGHAN M. Decision Intelligence: Human-Machine Integration for Decision-Making[M]. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2023: 167–194. doi: 10.1201/b23322. [34] CHAUHAN H, JANG Y, and JEONG I. Predicting human trust in human-robot collaborations using machine learning and psychophysiological responses[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2024, 62: 102720. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2024.102720. [35] DUAN Ya, CAI Yandong, PENG Ran, et al. Research on interaction and trust theory model for cockpit human-machine fusion intelligence[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2024, 18: 1352736. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1352736. [36] MOYLE S, MARTIN A, and ALLOTT N. XAI human-machine collaboration applied to network security[J]. Frontiers in Computer Science, 2024, 6: 1321238. doi: 10.3389/fcomp.2024.1321238. [37] SAARILUOMA P, MYLLYLÄ M, KARVONEN A, et al. A human digital twin for the m-machine[J]. Discover Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 4(1): 61. doi: 10.1007/s44163-024-00164-x. [38] 陈能成, 张岩. 人机融合智能与数字孪生城市[J]. 中国人工智能学会通讯, 2022, 12(8): 36–41.CHEN Nengcheng and ZHANG Yan. Human-machine integration intelligence and digital twin city[J]. Communications of the CCF, 2022, 12(8): 36–41. [39] 梅宏, 曹东刚, 谢涛. 泛在操作系统: 面向人机物融合泛在计算的新蓝海[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2022, 37(1): 30–37. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20211117009.MEI Hong, CAO Donggang, and XIE Tao. Ubiquitous operating system: Toward the blue ocean of human-cyber-physical ternary ubiquitous computing[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022, 37(1): 30–37. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20211117009. [40] XIANG Chengguan and YU Zhen. Human-machine hybrid augmented intelligence: Human-machine relationship, collaboration and mutual enhancement[C]. 2023 China Automation Congress (CAC), Chongqing, China, 2023: 7471–7478. doi: 10.1109/CAC59555.2023.10451218. [41] 张立华, 杨鼎康, 翟鹏, 等. 人机融合智能研究现状与展望[J]. 中国人工智能学会通讯, 2022, 12(8): 19–22.ZHANG Lihua, YANG Dingkang, ZHAI Peng, et al. Current status and prospects of human-machine fusion intelligence research[J]. Communications of the CCF, 2022, 12(8): 19–22. [42] SHI Feifei, ZHOU Fang, LIU Hong, et al. Survey and tutorial on hybrid human-artificial intelligence[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2023, 28(3): 486–499. doi: 10.26599/TST.2022.9010022. [43] 於志文, 郭斌. 人机共融智能[J]. 中国计算机学会通讯, 2017, 13(12): 64–68.YU Zhiwen and GUO Bin. Human machine integration intelligence[J]. Communications of the CCF, 2017, 13(12): 64–68. [44] HARRIS M. NTSB investigation into deadly Uber self-driving car crash reveals lax attitude toward safety[R]. IEEE Spectrum, 2019. [45] 史元春, 喻纯, 石伟男. 从普适计算到人机境融合计算[J]. 中国计算机学会通讯, 2023, 19(5): 10–17.SHI Yuanchun, YU Chun, and SHI Weinan. From ubiquitous computing to human-machine environment fusion computing[J]. Communications of the CCF, 2023, 19(5): 10–17. [46] TOCCHETTI A, CORTI L, BALAYN A, et al. A. I. Robustness: A human-centered perspective on technological challenges and opportunities[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2025, 57(6): 141. doi: 10.1145/3665926. [47] LEE J, ABE G, SATO K, et al. Developing human-machine trust: Impacts of prior instruction and automation failure on driver trust in partially automated vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2021, 81: 384–395. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2021.06.013. [48] STEINBERG A N and BOWMAN C L. Revisions to the JDL Data Fusion Model[M]. LIGGINS II M, HALL D, LLINAS J. Handbook of Multisensor Data Fusion. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017: 65–88. [49] ZHAO Fei, ZHANG Chengcui, and GENG Baocheng. Deep multimodal data fusion[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(9): 216. doi: 10.1145/3649447. [50] GUO Yuan, ZHOU Jian, LI Xicheng, et al. A review of crowdsourcing update methods for high-definition maps[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2024, 13(3): 104. doi: 10.3390/ijgi13030104. [51] GAO Qing, ZHANG Xin, and PANG Wenrao. Fast and accurate hand visual detection by using a spatial-channel attention SSD for hand-based space robot teleoperation[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2022, 2022(1): 3396811. doi: 10.1155/2022/3396811. [52] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [53] ABDOLRAHMANI A, HOWES GUPTA M, VADER M L, et al. Towards more transactional voice assistants: Investigating the potential for a multimodal voice-activated indoor navigation assistant for blind and sighted travelers[C]. 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 2021: 495. doi: 10.1145/3411764.3445638. [54] ZHANG Hongzhi and SHAFIQ M O. Survey of transformers and towards ensemble learning using transformers for natural language processing[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2024, 11(1): 25. doi: 10.1186/s40537-023-00842-0. [55] LIU Siru, WRIGHT A P, PATTERSON B L, et al. Using AI-generated suggestions from ChatGPT to optimize clinical decision support[J]. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 2023, 30(7): 1237–1245. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocad072. [56] 许未晴, 陈磊, 隋秀峰, 等. 脑机接口——脑信息读取与脑活动调控技术[J]. 科学通报, 2023, 68(8): 927–943. doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0338.XU Weiqing, CHEN Lei, SUI Xiufeng, et al. Brain-computer interface—brain information reading and activity control[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2023, 68(8): 927–943. doi: 10.1360/TB-2022-0338. [57] ROBINSON A K, VENKATESH P, BORING M J, et al. Very high density EEG elucidates spatiotemporal aspects of early visual processing[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 16248. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16377-3. [58] 陈豫生, 张琴, 熊蔡华. 截瘫助行外骨骼研究综述: 从拟人设计依据到外骨骼研究现状[J]. 机器人, 2021, 43(5): 585–605. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.200549.CHEN Yusheng, ZHANG Qin, and XIONG Caihua. From anthropomorphic design basis to exoskeleton research status: A review on walking assist exoskeletons for paraplegics[J]. Robot, 2021, 43(5): 585–605. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.200549. [59] JIANG Xiangyang, WANG Dakai, BI Kunpeng, et al. MSHP3D: Multi-stage cross-modal fusion based on hybrid perception for indoor 3D object detection[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 112: 102591. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102591. [60] BALTRUSAITIS T, AHUJA C, and MORENCY L P. Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(2): 423–443. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2798607. [61] CIAMARRA A, BECATTINI F, SEIDENARI L, et al. FLODCAST: Flow and depth forecasting via multimodal recurrent architectures[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 150: 110337. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110337. [62] TSAI Y H H, BAI Shaojie, LIANG P P, et al. Multimodal transformer for unaligned multimodal language sequences[C]. The 57th Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 6558–6569. doi: 10.18653/v1/P19-1656. [63] AREVALO J, SOLORIO T, MONTES-Y-GÓMEZ M, et al. Gated multimodal units for information fusion[C]. The 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [64] QIANG Haopeng, WAN Yuan, XIANG Lun, et al. Deep semantic similarity adversarial hashing for cross-modal retrieval[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 400: 24–33. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.032. [65] LU Xu, LIU Li, NING Lixin, et al. Multi-facet weighted asymmetric multi-modal hashing based on latent semantic distribution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 7307–7320. doi: 10.1109/tmm.2024.3363664. [66] 陈建明, 李定鲣, 曾祥津, 等. 一种跨模态光学信息交互和模板动态更新的RGBT目标跟踪方法[J]. 光学学报, 2024, 44(7): 0715001. doi: 10.3788/AOS231907.CHEN Jianming, LI Dingjian, ZENG Xiangjin, et al. Cross-modal optical information interaction and template dynamic update for RGBT target tracking method[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(7): 0715001. doi: 10.3788/AOS231907. [67] AN Jisu, LEE J, LEE J, et al. Towards LLM-centric multimodal fusion: A survey on integration strategies and techniques[J]. arXiv: 2506.04788, 2025. [68] HWANG J J, XU Runsheng, LIN H, et al. EMMA: End-to-end multimodal model for autonomous driving[J]. Transactions on Machine Learning Research, 2025, 2025. [69] Gemini Team Google. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context[J]. arXiv: 2403.05530, 2024. [70] ZHU Linan, ZHU Zhechao, ZHANG Chenwei, et al. Multimodal sentiment analysis based on fusion methods: A survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 95: 306–325. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.02.028. [71] JAHN L L F, PARK S, LIM Y, et al. Enhancing lane detection with a lightweight collaborative late fusion model[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2024, 175: 104680. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2024.104680. [72] GUARRASI V, AKSU F, CARUSO C M, et al. A systematic review of intermediate fusion in multimodal deep learning for biomedical applications[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2025, 158: 105509. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2025.105509. [73] YE Jiancheng, HAI Jiarui, SONG Jiacheng, et al. Multimodal data hybrid fusion and natural language processing for clinical prediction models[J]. AMIA Summits on Translational Science Proceedings, 2024, 2024: 191–200. [74] TRENDE A, UNNI A, JABLONSKI M, et al. Driver’s turning intent recognition model based on brain activation and contextual information[J]. Frontiers in Neuroergonomics, 2022, 3: 956863. doi: 10.3389/fnrgo.2022.956863. [75] RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 8748–8763. [76] GHOSH S, KUMAR S, SETH A, et al. GAMA: A large audio-language model with advanced audio understanding and complex reasoning abilities[C]. 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Miami, USA, 2024: 6288–6313. [77] 王玉虎, 刘伟. 一种基于人机融合的态势认知模型[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2023, 9(1): 76–84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.01.0076.WANG Yuhu and LIU Wei. A situation cognition model based on human-machine hybrid fusion[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2023, 9(1): 76–84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.01.0076. [78] HUANG Chao, LV Chen, HANG Peng, et al. Human-machine adaptive shared control for safe driving under automation degradation[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2022, 14(2): 53–66. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2021.3065382. [79] HUANG Chao, HUANG Hailong, ZHANG Junzhi, et al. Human-machine cooperative trajectory planning and tracking for safe automated driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 12050–12063. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3109596. [80] WOLF A, FACKLER K, REULBACH M, et al. Computer aided ergonomics: Evaluation study of a interaction model for digital human models[J]. Proceedings of the Design Society, 2022, 2: 663–672. doi: 10.1017/pds.2022.68. [81] 于景元. 钱学森关于开放的复杂巨系统的研究[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 1992, 12(5): 8–12. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(1992)5-106514.YU Jingyuan. Qian Xuesen’s research on open complex giant systems[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 1992, 12(5): 8–12. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(1992)5-106514. [82] WU Huaining, ZHANG Xiumei, and LI Ruiguo. Synthesis with guaranteed cost and less human intervention for human-in-the-loop control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(8): 7541–7551. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3041033. [83] ZHOU Ji, ZHOU Yanhong, WANG Baicun, et al. Human-cyber-physical systems (HCPSs) in the context of new-generation intelligent manufacturing[J]. Engineering, 2019, 5(4): 624–636. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.07.015. [84] NIKITIN A. Probabilistic methods for predictive maintenance and beyond: Graph and human-in-the-loop machine learning[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Aalto University, 2024. [85] ZHENG Nanning, LIU Ziyi, REN Pengju, et al. Hybrid-augmented intelligence: Collaboration and cognition[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2017, 18(2): 153–179. doi: 10.1631/fitee.1700053. [86] 郑南宁. 人工智能新时代[J]. 智能科学与技术学报, 2019, 1(1): 1–3. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-6652.201914.ZHENG Nanning. The new era of artificial intelligence[J]. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2019, 1(1): 1–3. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-6652.201914. [87] SHI Zijing, FANG Meng, CHEN Ling, et al. Human-guided moral decision making in text-based games[C]. The 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 21574–21582. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v38i19.30155. [88] 龙升照, 姜淇远, 何开源, 等. 人-机系统中人的模糊控制模型[J]. 宇航学报, 1982(2): 12–17.LONG Shengzhao, JIANG Qiyuan, HE Kaiyuan, et al. Human fuzzy control model in man-machine systems[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 1982(2): 12–17. [89] KVAM P D. The Tweedledum and Tweedledee of dynamic decisions: Discriminating between diffusion decision and accumulator models[J]. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 2024, 32: 588–613. doi: 10.31234/osf.io/7bsc4. [90] HELLMANN S, ZEHETLEITNER M, and RAUSCH M. Simultaneous modeling of choice, confidence, and response time in visual perception[J]. Psychological Review, 2023, 130(6): 1521–1543. doi: 10.1037/rev0000411. [91] LIU Pengfei, ZHAO Jing, ZHANG Fanlei, et al. Modeling decision-making process of drivers during yellow signal phase at intersections based on drift–diffusion model[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2024, 105: 368–384. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2024.07.020. [92] ZARE M, KEBRIA P M, KHOSRAVI A, et al. A survey of imitation learning: Algorithms, recent developments, and challenges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(12): 7173–7186. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2024.3395626. [93] ARORA S and DOSHI P. A survey of inverse reinforcement learning: Challenges, methods and progress[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 297: 103500. doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2021.103500. [94] HUANG Zhiyu, LIU Haochen, WU Jingda, et al. Conditional predictive behavior planning with inverse reinforcement learning for human-like autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(7): 7244–7258. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3254579. [95] LUO Dongwen. Optimizing load scheduling in power grids using reinforcement learning and Markov decision processes[J]. arXiv: 2410.17696, 2024. [96] EDDY S R. What is dynamic programming?[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2004, 22(7): 909–910. doi: 10.1038/nbt0704-909. [97] ROBERTAZZI F, VISSANI M, SCHILLACI G, et al. Brain-inspired meta-reinforcement learning cognitive control in conflictual inhibition decision-making task for artificial agents[J]. Neural Networks, 2022, 154: 283–302. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2022.06.020. [98] MISHRA S. A reinforcement learning approach for training complex decision making models[J]. Journal of AI-Assisted Scientific Discovery, 2022, 2(2): 329–352. [99] LI Wenli, WANG Mengxin, LI Lingxi, et al. Game-generative adversarial imitation learning for pedestrian simulation during pedestrian-vehicle interaction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 1–12. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2024.3420943. [100] AMIRKHANI A and BARSHOOI A H. Consensus in multi-agent systems: A review[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(5): 3897–3935. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10097-x. [101] HU Yaru, ZHENG Jinhua, ZOU Juan, et al. Dynamic multi-objective optimization algorithm based decomposition and preference[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 571: 175–190. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.055. [102] ZHENG Jiaxiao and DE VECIANA G. Modeling and optimization of human-machine interaction processes via the maximum entropy principle[C]. The 57th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, USA, 2019: 824–831. doi: 10.1109/ALLERTON.2019.8919959. [103] HAQUE M U, DHARMADASA I, SWORNA Z T, et al. “I think this is the most disruptive technology”: Exploring sentiments of ChatGPT early adopters using Twitter data[J]. arXiv: 2212.05856, 2022. [104] STIENNON N, OUYANG Long, WU J, et al. Learning to summarize from human feedback[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 253. [105] OUYANG Long, WU J, JIANG Xu, et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 2011. [106] SHAO Zhihong, WANG Peiyi, ZHU Qihao, et al. DeepSeekMath: Pushing the limits of mathematical reasoning in open language models[J]. arXiv: 2402.03300, 2024. [107] REN Minglun, CHEN Nengying, and QIU Hui. Human-machine collaborative decision-making: An evolutionary roadmap based on cognitive intelligence[J]. International Journal of Social Robotics, 2023, 15(7): 1101–1114. doi: 10.1007/s12369-023-01020-1. [108] ZIEBA S, POLET P, VANDERHAEGEN F, et al. Principles of adjustable autonomy: A framework for resilient human-machine cooperation[J]. Cognition, Technology & Work, 2010, 12(3): 193–203. doi: 10.1007/s10111-009-0134-7. [109] ZHAO Zhuoya, ZHAO Feifei, ZHAO Yuxuan, et al. A brain-inspired theory of mind spiking neural network improves multi-agent cooperation and competition[J]. Patterns, 2023, 4(8): 100775. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100775. [110] FENG Xueyang, CHEN Zhiyuan, QIN Yujia, et al. Large language model-based human-agent collaboration for complex task solving[C]. The Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, Miami, USA, 2024: 1336–1357. [111] LIU Tao, YOU Hailin, GKIOTSALITIS K, et al. Human-machine collaborative decision-making approach to scheduling customized buses with flexible departure times[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2024, 187: 104184. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2024.104184. [112] ROTHFUß S. Human-Machine Cooperative Decision Making[M]. Karlsruhe: KIT Scientific Publishing, 2022. [113] MATTHIES D J C, SCHMIDT S O, HE Yuqi, et al. LoomoRescue: An affordable rescue robot for evacuation situations[C]. The 4th International Conference on Design, Operation and Evaluation of Mobile Communications, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2023: 53–73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-35921-7_5. [114] BONSIGNORIO F, CERVELLERA C, MACCIÒ D, et al. An imitation learning approach for the control of a low-cost low-accuracy robotic arm for unstructured environments[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Robotics and Applications, 2023, 7(1): 13–30. doi: 10.1007/s41315-022-00262-y. [115] 董志明, 朱广超, 徐享忠, 等. “人在回路”合成训练仿真总体设计及关键技术研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33(6): 1248–1257. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.21-0392.DONG Zhiming, ZHU Guangchao, XU Xiangzhong, et al. Research on the overall design and key technology of "Human in the Loop" synthetic training Simulation[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33(6): 1248–1257. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.21-0392. [116] RUAN Wanying, DUAN Haibin, and DENG Yimin. Autonomous maneuver decisions via transfer learning pigeon-inspired optimization for UCAVs in dogfight engagements[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(9): 1639–1657. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.105803. [117] 徐友春, 郭宏达, 娄静涛, 等. 无人车集群协同围捕发展现状分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(2): 456–471. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230122.XU Youchun, GUO Hongda, LOU Jingtao, et al. Analysis on current development situation of unmanned ground vehicle clusters collaborative pursuit[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(2): 456–471. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230122. [118] BOURAS C, GKAMAS A, and SALGADO S A K. Long range based IoT search and rescue system, a human-computer interaction preliminary study and implementation[J]. Computer Networks and Communications, 2022, 1(1): 2–16. doi: 10.37256/cnc.1120231753. [119] 周胜利, 沈寿林, 张国宁, 等. 人机智能融合的陆军智能化作战指挥模型体系[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(3): 34–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2020.03.006.ZHOU Shengli, SHEN Shoulin, ZHANG Guoning, et al. Research on army intelligent operational command model system based on man-machine intelligence fusion[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2020, 45(3): 34–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2020.03.006. [120] HUANG Yamin, CHEN Linying, NEGENBORN R R, et al. A ship collision avoidance system for human-machine cooperation during collision avoidance[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 217: 107913. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107913. [121] 王荣浩, 文晓, 向峥嵘. 人机融合系统协同与优化方法研究进展[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2024, 46(5): 103–113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2024.05.014.WANG Ronghao, WEN Xiao, and XIANG Zhengrong. Research status of collaboration and optimization method for human-machine fusion system[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2024, 46(5): 103–113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2024.05.014. [122] 李超超, 程兰惠, 杨赛赛, 等. 暗态势计算: 概念、方法与应用[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2025, 37(4): 568–582. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2023-00341.LI Chaochao, CHENG Lanhui, YANG Saisai, et al. Dark situation evaluating: Concepts, methods, and applications[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2025, 37(4): 568–582. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2023-00341. [123] 李超超, 邵文龙, 吕培, 等. 人机协同决策的异质多智能体路径规划[J/OL]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2925.tp.20250526.1717.002, 2025.LI Chaochao, SHAO Wenlong, LV Pei, et al. Heterogeneous multi-agent path planning with human-machine collaborative decision-making[J/OL]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2925.tp.20250526.1717.002, 2025. [124] 王可, 刘奕阳, 杨杰, 等. 基于自适应特征增强和融合的舰载机着舰拉制状态识别[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2025, 59(2): 274–282. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.263.WANG Ke, LIU Yiyang, YANG Jie, et al. Landing state recognition of carrier-based aircraft based on adaptive feature enhancement and fusion[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2025, 59(2): 274–282. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2023.263. [125] 王可, 徐明亮, 李亚飞, 等. 一种面向航空母舰甲板运动状态预估的鲁棒学习模型[J]. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(9): 1785–1793. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210664.WANG Ke, XU Mingliang, LI Yafei, et al. A robust learning model for deck motion prediction of aircraft carrier[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(9): 1785–1793. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210664. [126] 李亚飞, 高磊, 蒿宏杰, 等. 舰载机保障作业人机协同决策方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(12): 2493–2510. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0403.LI Yafei, GAO Lei, HAO Hongjie, et al. Human machine collaborative decision-making for carrier aircraft support operations[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2023, 53(12): 2493–2510. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0403. [127] AMARILLO A, SANCHEZ E, CACERES J, et al. Collaborative human-robot interaction interface: Development for a spinal surgery robotic assistant[J]. International Journal of Social Robotics, 2021, 13(6): 1473–1484. doi: 10.1007/s12369-020-00733-x. [128] CHEN Xiaoshi, GONG Li, ZHENG Lirong, et al. Soft exoskeleton glove for hand assistance based on human-machine interaction and machine learning[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Human-Machine Systems (ICHMS), Rome, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICHMS49158.2020.9209381. [129] LI H Y, NURADHA T, XAVIER S A, et al. Human-micromanipulator cooperation using a variable admittance controller[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(5): 50204. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9663-1. [130] GARCIA-MORENO F M, BERMUDEZ-EDO M, RODRÍGUEZ-FÓRTIZ M J, et al. A CNN-LSTM deep learning classifier for motor imagery EEG detection using a low-invasive and low-cost BCI headband[C]. 2020 16th International Conference on Intelligent Environments (IE), Madrid, Spain, 2020: 84–91. doi: 10.1109/IE49459.2020.9155016. [131] PAVÓN-PULIDO N, LÓPEZ-RIQUELME J A, and FELIÚ-BATLLE J J. IoT architecture for smart control of an exoskeleton robot in rehabilitation by using a natural user interface based on gestures[J]. Journal of Medical Systems, 2020, 44(9): 144. doi: 10.1007/s10916-020-01602-w. [132] CAI Hengrui, SHI Chengchun, SONG Rui, et al. Jump interval-learning for individualized decision making with continuous treatments[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2023, 24(1): 140. [133] 袁敏, 陈卓, 徐冰青. 面向数据特征的人机物融合服务分派方法[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(11): 3404–3422. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006090.YUAN Min, CHEN Zhuo, and XU Bingqing. Human-cyber-physical services dispatch approach for data characteristics[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(11): 3404–3422. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006090. [134] FANG Zhenwu, WANG Jinxiang, WANG Zejiang, et al. Human-machine shared control for path following considering driver fatigue characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(7): 7250–7264. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3347439. [135] WU Jian, ZHANG Junda, TIAN Yang, et al. A novel adaptive steering torque control approach for human-machine cooperation autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2021, 7(4): 2516–2529. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2021.3083679. [136] HAN Jiayi, ZHAO Jian, ZHU Bing, et al. Adaptive steering torque coupling framework considering conflict resolution for human-machine shared driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 10983–10995. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3098466. [137] WANG Lingguang, FERNANDEZ C, and STILLER C. High-level decision making for automated highway driving via behavior cloning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(1): 923–935. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3169207. [138] WU Jingda, ZHANG Zhiyu, TIAN Zhongxu, et al. Toward human-in-the-loop AI: Enhancing deep reinforcement learning via real-time human guidance for autonomous driving[J]. Engineering, 2023, 21: 75–91. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2022.05.017. [139] WANG Jiarong, BI Luzheng, and FEI Weijie. Multitask-oriented brain-controlled intelligent vehicle based on human-machine intelligence integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(4): 2510–2521. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3212744. [140] MOHAMMED K, ABDELHAFID M, KAMAL K, et al. Intelligent driver monitoring system: An Internet of things-based system for tracking and identifying the driving behavior[J]. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 2023, 84: 103704. doi: 10.1016/j.csi.2022.103704. [141] DONG Na, LI Xianzheng, and WU Zhiqiang. On integrated lateral and longitudinal control of brain-controlled vehicles[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 597: 127957. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127957. [142] MA Biao, LIU Yulong, NA Xiaoxiang, et al. A shared steering controller design based on steer-by-wire system considering human-machine goal consistency[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(8): 4397–4419. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.12.028. [143] HU Weiming, LI Xu, HU Jinchao, et al. A safe driving decision-making methodology based on cascade imitation learning network for automated commercial vehicles[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(11): 11285–11295. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3256704. [144] LIU Yiyang, WANG Ke, and CHENG Xinle. Human-machine collaborative classification model for industrial product defect[C]. The 2021 17th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (CIS), Chengdu, China, 2021: 141–145. doi: 10.1109/CIS54983.2021.00038. [145] 蔡恒进, 蔡天琪, 耿嘉伟. 人机智能融合的区块链系统[M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2019.CAI Hengjin, CAI Tianqi, and GENG Jiawei. A Blockchain System Integrating Human-Machine Intelligence[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2019. [146] MUSIĆ S and HIRCHE S. Control sharing in human-robot team interaction[J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2017, 44: 342–354. doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2017.09.017. [147] HASHEMI-PETROODI S E, THEVENIN S, KOVALEV S, et al. Operations management issues in design and control of hybrid human-robot collaborative manufacturing systems: A survey[J]. Annual Reviews in Control, 2020, 49: 264–276. doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.04.009. [148] GEBRU B, ZELEKE L, BLANKSON D, et al. A review on human-machine trust evaluation: Human-centric and machine-centric perspectives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2022, 52(5): 952–962. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2022.3144956. [149] HUANG Qingyang, GUO Mingyang, WEI Yuning, et al. Influence of automation level of human-machine system on operators’ mental load[J]. Journal of Safety and Sustainability, 2024, 1(1): 42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jsasus.2023.12.001. -





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
