Acoustic DOA Estimation in Underwater Environments by Integrating Spatial Domain Wiener Filtering and Convolutional Neural Networks
-
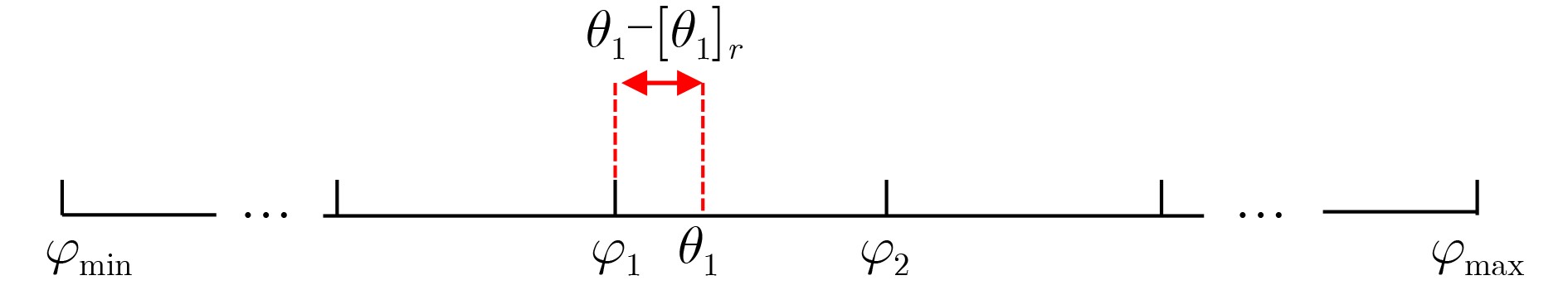
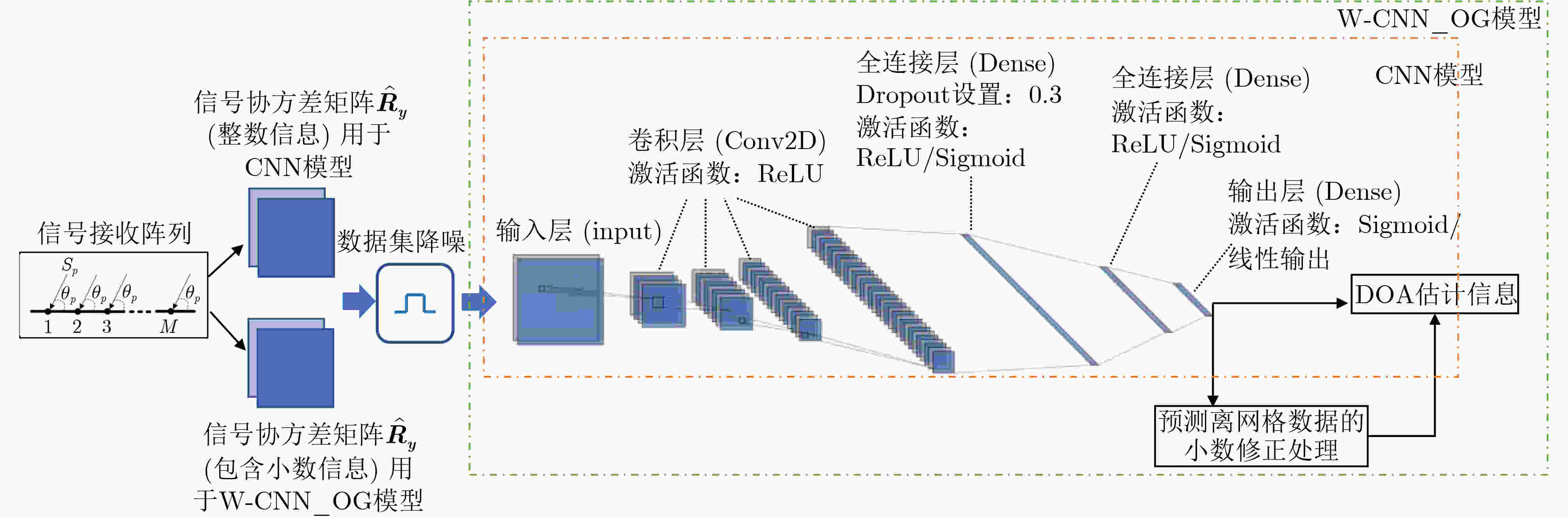
摘要: 针对实际海域中来自水流、船舶、海洋生物等噪声源的干扰使得接收信号的信噪比较低,进而导致传统波达方向(DOA)估计算法性能下降的问题。该文提出一种结合维纳滤波降噪的深度学习算法。首先,维纳滤波算法在频域需要依靠噪声和信号功率谱,然而这些参数往往难以获取,因此将其转化为对信号空间域进行降噪,并使用降噪后的数据集进行神经网络训练,从而减小低信噪比条件下对方位角估计的影响。其次,为了实现网络的分类和回归估计功能,使用改进的二进制交叉熵函数作为网络的损失函数。最后,在模型训练完成后,通过小数标签策略预测网络输出结果中的离格误差,并对这些误差进行修正以提高算法估计精度。仿真结果与海试数据验证结果表明,在低信噪比情况下,以均方根误差为性能指标,网络整体性能提升了25.20%,在–20 dB信噪比条件下,所提方法的均方根误差相较MUSIC和ESPRIT算法分别降低了93.42%和92.14%。研究结果表明,本文算法能够充分提取空间特征,满足实际应用对算法鲁棒性的需求,为浅海复杂环境的目标检测和定位任务提供了新的方案。Abstract:
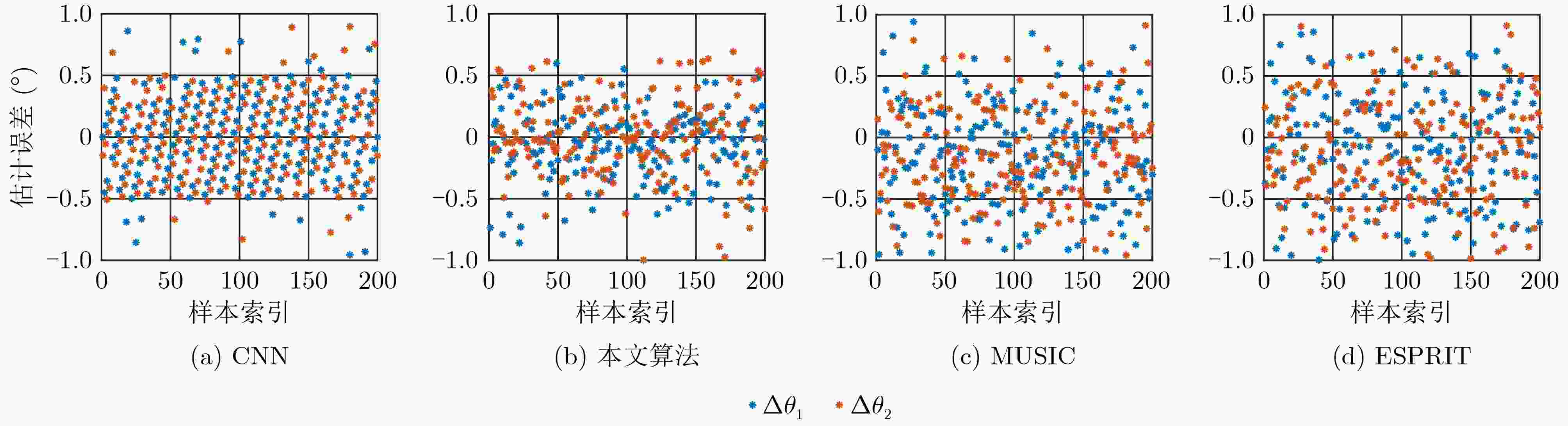
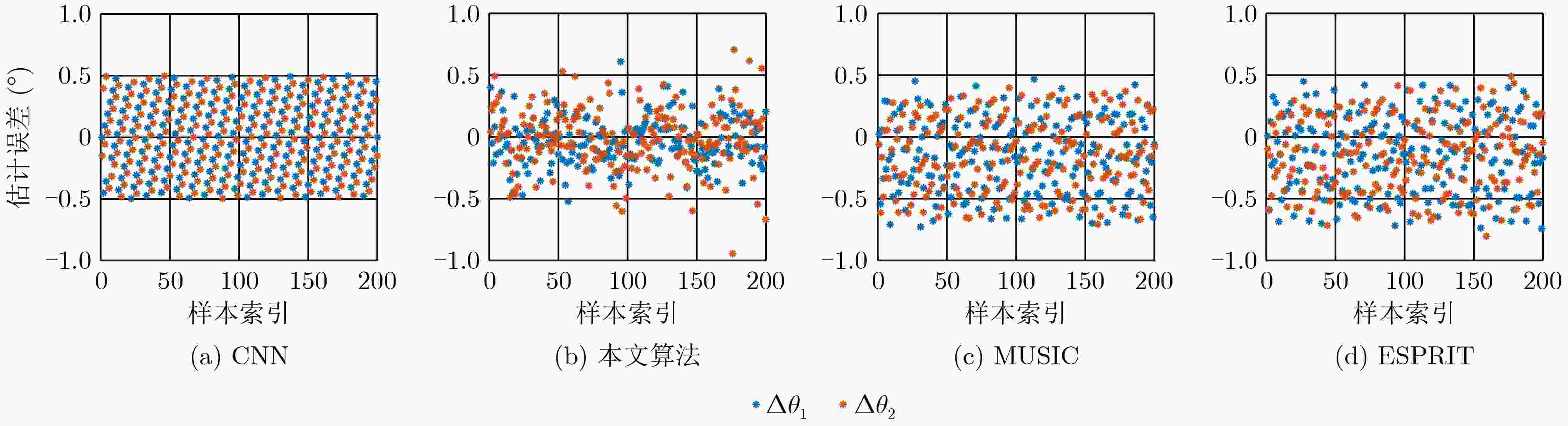
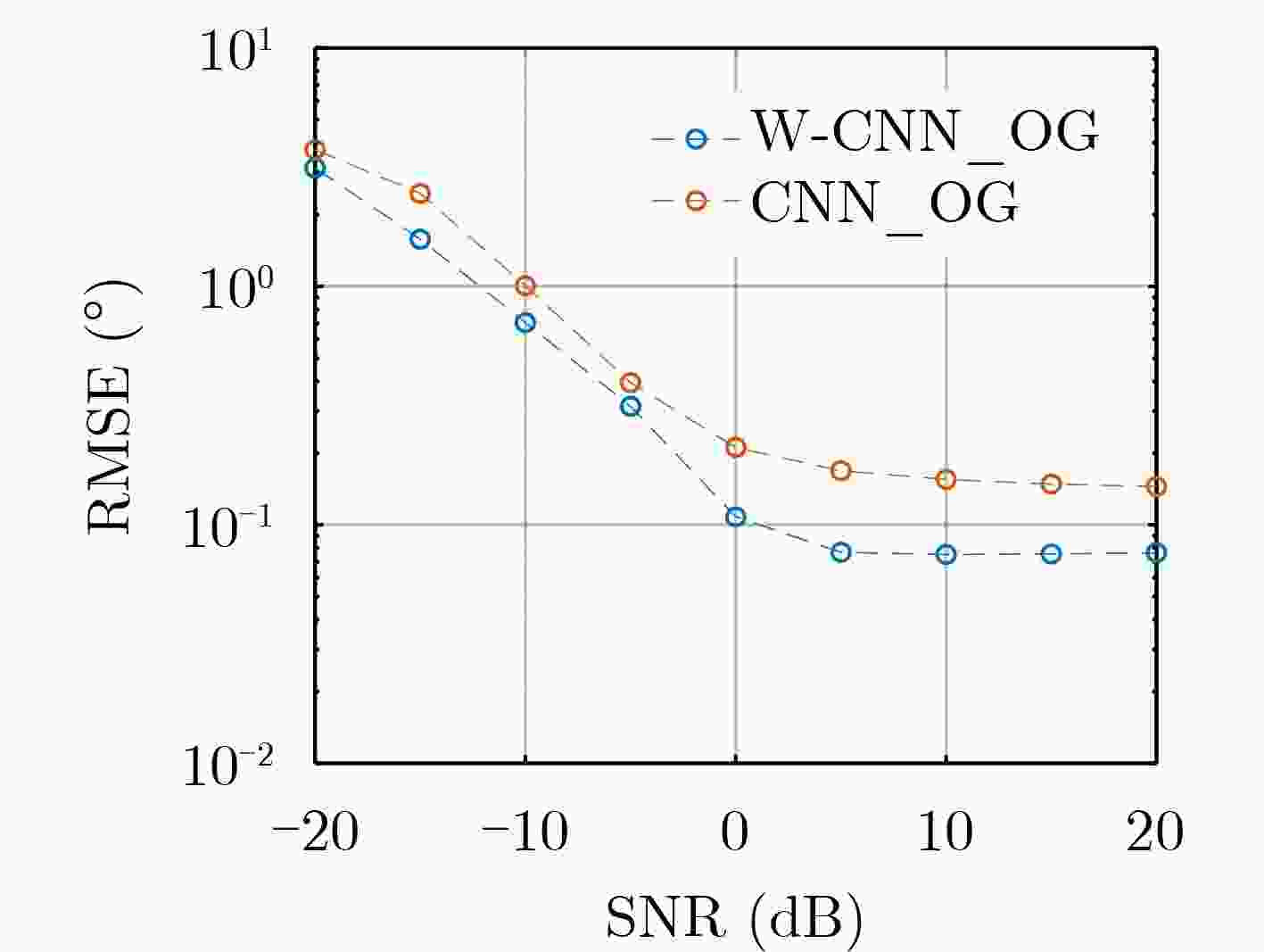
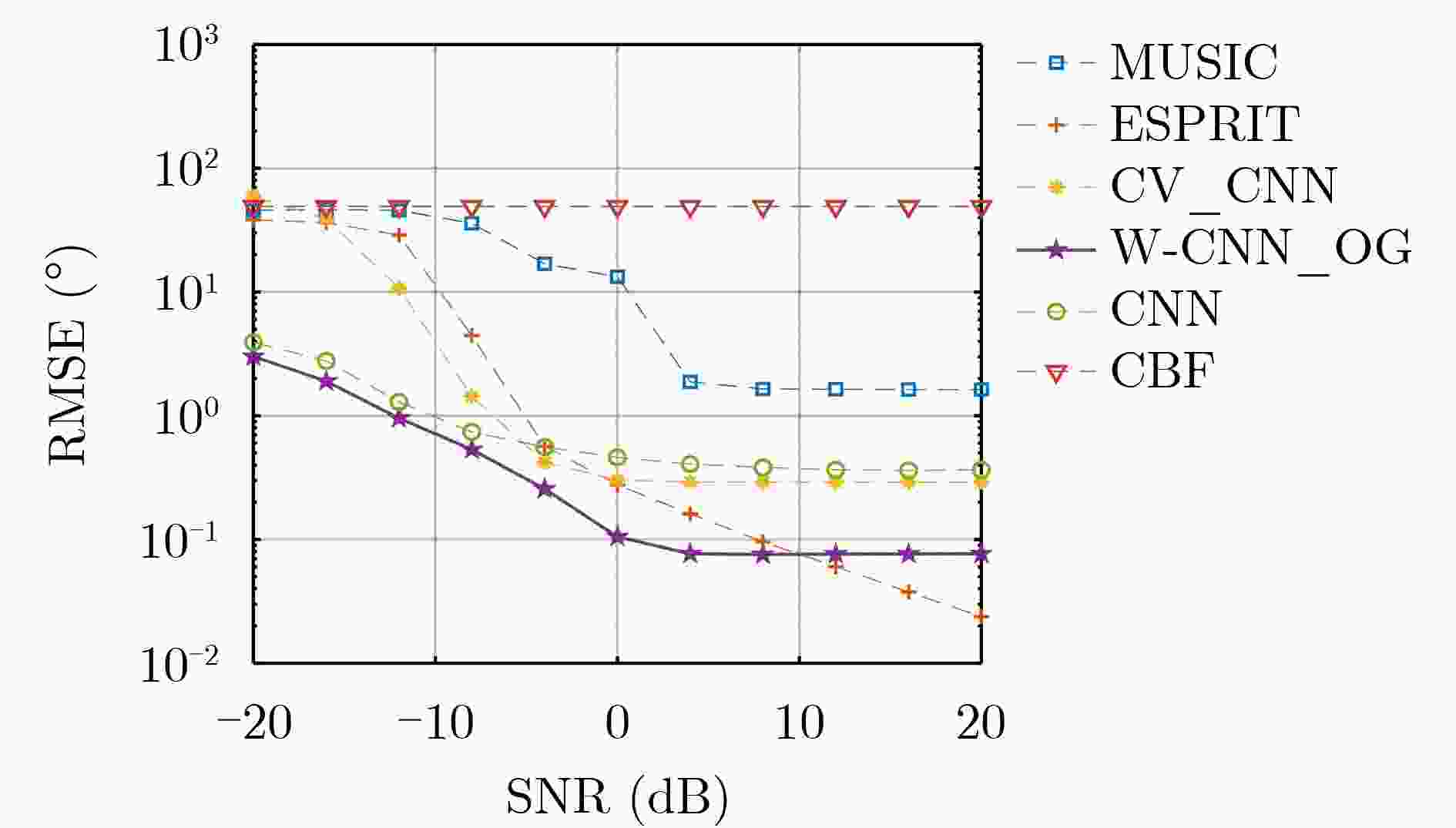
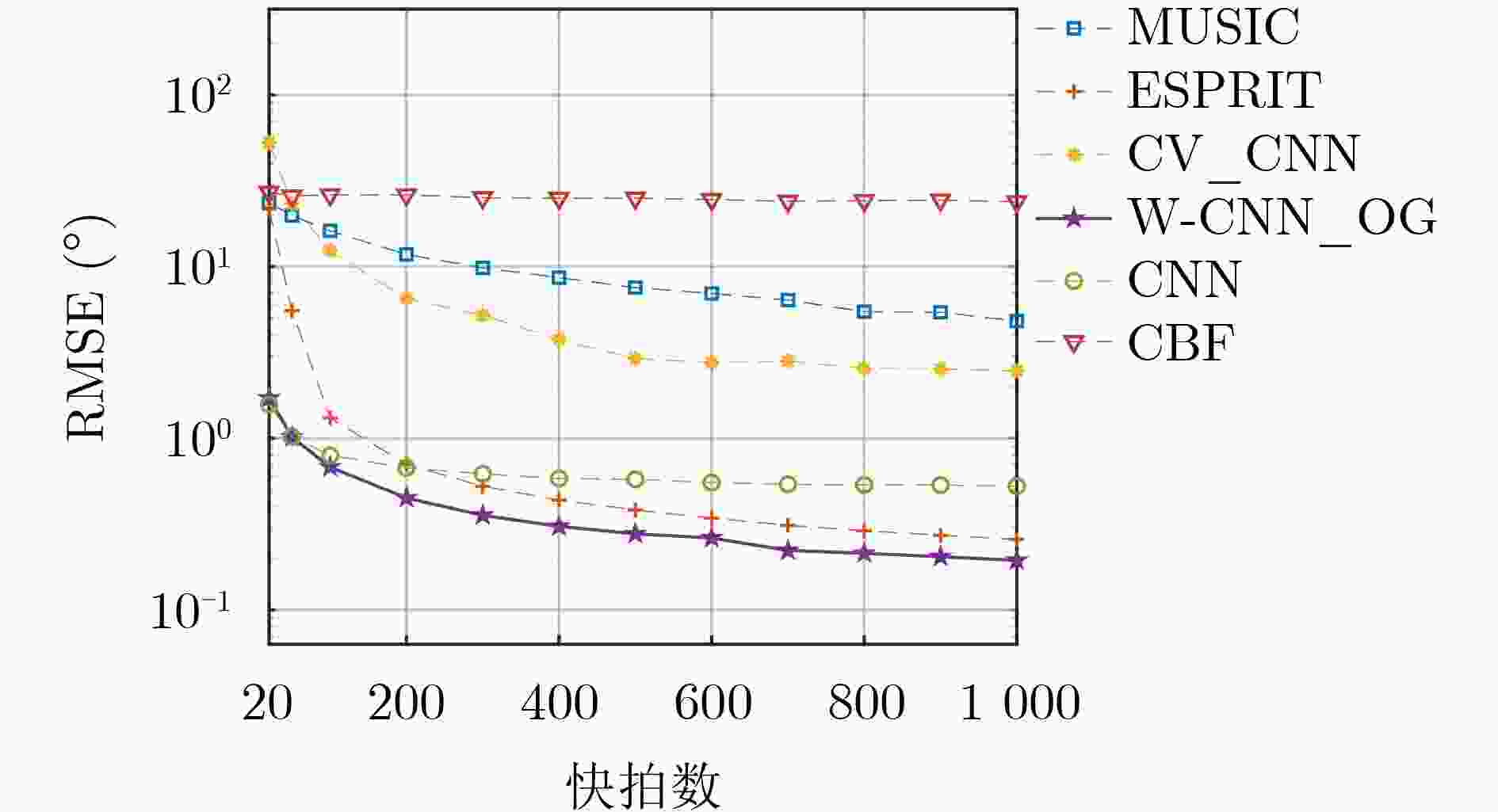
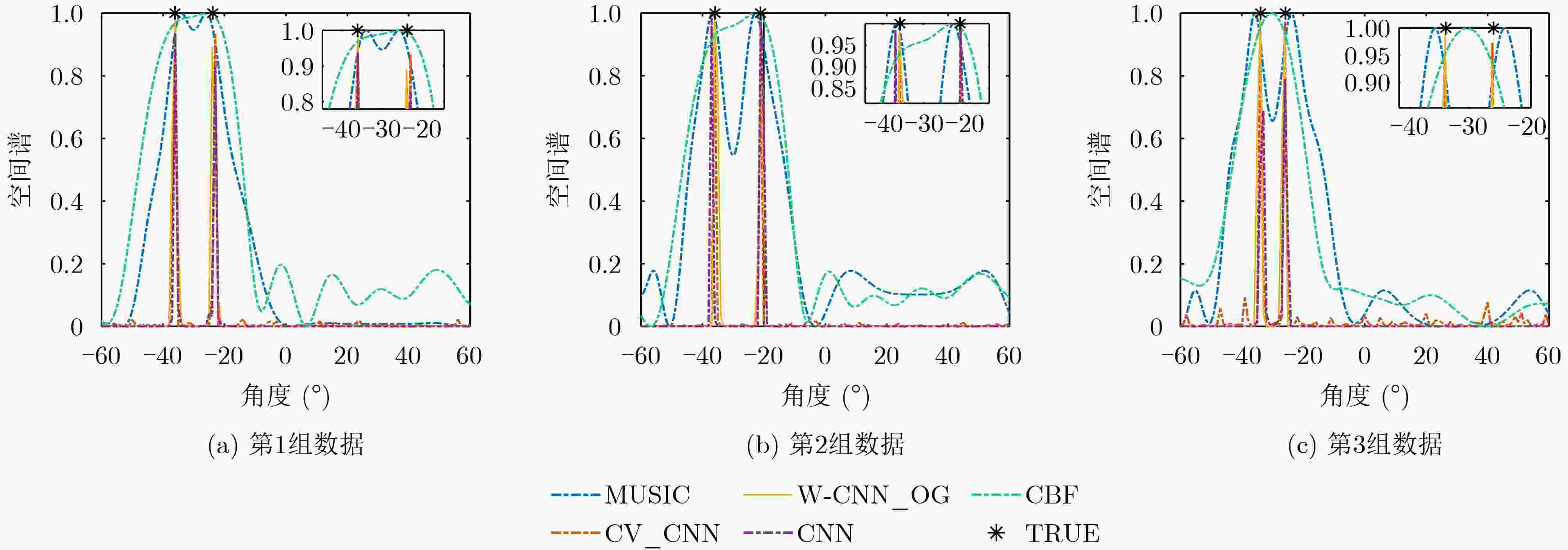
Objective Human activities in shallow-sea regions have increased with the progressive development and utilization of marine environments. However, interference from noise sources such as water currents, vessels, and marine organisms substantially reduces the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of received signals, leading to performance degradation in conventional Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation algorithms. These limitations affect accurate target localization and detection, which are essential for underwater acoustic applications. This paper proposes a method that combines Wiener filtering with deep learning, specifically an improved Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), to enhance the robustness and accuracy of DOA estimation in shallow-sea environments by addressing challenges such as noise interference and grid mismatch. Methods The proposed algorithm integrates Wiener filtering and deep learning to optimize DOA estimation. First, Wiener filtering is applied to the covariance matrix of the received signals to reduce noise. Considering the complexity of underwater acoustic environments, this preprocessing step is essential for preserving spatial signal features and enhancing the effectiveness of network training. Second, an improved CNN architecture is designed to perform both classification and regression tasks, enabling accurate DOA angle estimation while correcting off-grid errors. A fractional label correction strategy is introduced to mitigate grid mismatch, allowing prediction errors to be compensated and the estimated angles to align more closely with true values. The network is trained using a large-scale dataset of simulated underwater acoustic signals, and its feasibility is verified through real-world sea trial data. Results and Discussions The proposed method is validated using both simulation data and sea trial data, demonstrating superior performance under low SNR conditions. Simulation results show that incorporating Wiener filtering improves overall network performance by 25.20% ( Fig. 5 ). The proposed algorithm achieves lower estimation errors in low SNR environments (Fig. 6 ). Compared with the MUSIC and ESPRIT algorithms, the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is reduced by 93.42% and 92.14%, respectively, at an SNR of –20 dB. Moreover, as the SNR increases, the algorithm exhibits a gradual reduction in estimation error (Fig. 6 ). In sea trial experiments, the algorithm accurately identifies target azimuths and achieves lower estimation errors compared to conventional methods (Fig. 9 ,Table 1 ). These results indicate that the proposed method meets the requirements for robustness and accuracy in practical underwater acoustic applications.Conclusions This paper proposes a method for direction estimation in shallow-water environments that integrates Wiener filtering with a deep learning-based CNN to address the performance degradation caused by low SNR conditions in conventional algorithms. The combination of noise reduction preprocessing with CNN model training enhances both network efficiency and estimation accuracy. Simulation and sea trial experiments yield the following results: (1) Overall network performance is improved by 25.20% through Wiener filtering optimization; (2) The improved binary cross-entropy loss function enables the network to perform both classification and regression tasks for DOA estimation; (3) The algorithm demonstrates higher robustness to noise interference and grid mismatch, particularly under low SNR and limited snapshot conditions, making it suitable for practical deployment. However, the network is trained using datasets with known source numbers. Future research will focus on network designs that accommodate more diverse source conditions, including blind source scenarios and adaptive noise reduction models. -
Key words:
- DOA estimation /
- Deep learning /
- Wiener filtering /
- Grid mismatch
-
表 1 3组实测数据中各算法估计的RMSE(°)
算法名称 (–36.1°, –23.8°) (–35.9°, –21.1°) (–33.9°, –25.8°) (–35.5°, –23.8°) (–40.5°, –20.1°) MUSIC 2.10 1.32 1.85 1.69 0.92 CNN 0.65 0.47 0.54 0.76 0.24 CV_CNN 0.36 0.30 0.36 0.38 0.28 W-CNN_OG 0.28 0.25 0.29 0.26 0.21 -
[1] XU Zhezhen, LI Hui, and YANG Kunde. A modified differential beamforming and its application for DOA estimation of low frequency underwater signal[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(16): 8890–8902. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2988025. [2] 张旭, 朱晓春, 徐付佳, 等. 模型误差条件下声矢量圆阵多重信号分类测向改进算法[J]. 声学学报, 2024, 49(3): 533–549. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023058.ZHANG Xu, ZHU Xiaochun, XU Fujia, et al. An improved multiple signal classification method for a circular acoustic vector sensor array in the presence of model errors[J]. Acta Acustica, 2024, 49(3): 533–549. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023058. [3] 王旭东, 仲倩, 闫贺, 等. 一种二维信号波达方向估计的改进多重信号分类算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2137–2142. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181090.WANG Xudong, ZHONG Qian, YAN He, et al. An improved MUSIC algorithm for two dimensional direction of arrival estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2137–2142. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181090. [4] NING Yuming, MA Shuang, MENG Fanyi, et al. DOA estimation based on ESPRIT algorithm method for frequency scanning LWA[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(7): 1441–1445. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2988020. [5] BARAT M, KARIMI M, and MASNADI-SHIRAZI M A. High-order maximum likelihood methods for direction of arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 2: 359–369. doi: 10.1109/OJSP.2021.3093866. [6] 刘素娟, 崔程凯, 郑丽丽, 等. 基于压缩感知的贪婪类重构算法原子识别策略综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(1): 361–370. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211297.LIU Sujuan, CUI Chengkai, ZHENG Lili, et al. A review of atom recognition strategies for greedy class reconstruction algorithms based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(1): 361–370. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211297. [7] AGHABABAIYAN K, SHAH-MANSOURI V, and MAHAM B. High-precision OMP-based direction of arrival estimation scheme for hybrid non-uniform array[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(2): 354–357. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2952595. [8] 赵洋, 石屹然, 石要武. 基于噪声子空间矢量的OMP离格DOA估计[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2020, 28(10): 2384–2391. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202810.2384.ZHAO Yang, SHI Yiran, and SHI Yaowu. DOA estimation based on OMP modified by noise subspace vectors[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(10): 2384–2391. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202810.2384. [9] DAI Jisheng and SO H C. Real-valued sparse Bayesian learning for DOA estimation with arbitrary linear arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 4977–4990. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3106741. [10] JIN Yi, HE Di, WEI Shuang, et al. Off-grid DOA estimation method based on sparse Bayesian learning with clustered structural-aware prior information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(4): 5469–5483. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3335959. [11] 明超, 牛海强, 李整林, 等. 结合稀疏贝叶斯学习的快速运动目标方位估计方法[J/OL]. 声学学报, 2025: 1–21. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2065.o4.20250127.1320.001, 2025.MING Chao, NIU Haiqiang, LI Zhenglin, et al. Azimuth estimation of fast-moving targets based on sparse Bayesian learning[J/OL]. Acta Acustica, 2025: 1–21. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2065.o4.20250127.1320.001, 2025. [12] PAPAGEORGIOU G, SELLATHURAI M, and ELDAR Y. Deep networks for direction-of-arrival estimation in low SNR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 3714–3729. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3089927. [13] 王珍珠, 王文博, 李赫, 等. 波束域特征融合的浅海水平阵目标方位估计[J]. 声学学报, 2024, 49(5): 939–955. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023029.WANG Zhenzhu, WANG Wenbo, LI He, et al. Direction of arrival estimation using a horizontal array with beamforming domain feature fusion in shallow water[J]. Acta Acustica, 2024, 49(5): 939–955. doi: 10.12395/0371-0025.2023029. [14] QIN Yanhua. Deep networks for direction of arrival estimation with sparse prior in low SNR[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 44637–44648. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3273126. [15] ZHENG Shilian, ZHUANG Yang, SHEN Weiguo, et al. Deep learning-based DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(3): 819–835. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2024.3360527. [16] 俞帆, 陈格格, 沈明威. 基于双通道复数卷积神经网络的DOA估计算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(12): 81–86. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.012.YU Fan, CHEN Gege, and SHEN Mingwei. DOA estimation algorithm based on dual-channel complex-valued convolutional neural network[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(12): 81–86. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.012. [17] CHUNG H, SEO H, JOO J, et al. Off-grid DOA estimation via two-stage cascaded neural network[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(1): 228. doi: 10.3390/en14010228. [18] LIU Mingda, NIU Haiqiang, LI Zhengli, et al. A convolutional neural network combining classification and regression for source localization in shallow water[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2023, 2486(1): 012068. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2486/1/012068. [19] 袁野. 基于深度学习的高性能信号波达方向估计方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2022: 112–113. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2022.000011.YUAN Ye. Research on deep learning based direction-of-arrival estimation with high performance[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2022: 112–113. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2022.000011. [20] 高明哲, 祝明波. 噪声对维纳滤波反卷积算法性能影响的分析[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2012, 32(12): 35–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2012.12.011.GAO Mingzhe and ZHU Mingbo. Analysis on noise's impact on the performance of wiener filter deconvolution algorithm[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2012, 32(12): 35–36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2012.12.011. [21] 李晨, 田应伟, 赵久瑞, 等. 基于维纳滤波的船载地波雷达海流反演方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2025, 47(6): 1–7. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.20231217001.LI Chen, TIAN Yingwei, ZHAO Jiurui, et al. A current inversion method based on wiener filtering for shipborne surface wave radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2025, 47(6): 1–7. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.20231217001. [22] 董赛蒙, 邢传玺, 魏光春, 等. 多目标水声信号的稀疏重构反卷积测向算法[J]. 声学技术, 2024, 43(5): 636–646. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2024.05.005.DONG Saimeng, XING Chuanxi, WEI Guangchun, et al. Deconvolution direction finding algorithm for sparse reconstruction of multi-target underwater acoustic signals[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2024, 43(5): 636–646. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2024.05.005. [23] SRIVASTAVA N, HINTON G, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929–1958. [24] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2014: 1–15. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
