LLM Channel Prediction Method for TDD OTFS Low-Earth-Orbit Satellite Communication Systems
-
摘要: 正交时频空间(OTFS)调制技术在低轨卫星与地面通信场景下具有良好的应用前景。然而,LEO高多普勒频移变化率和高延迟会导致信道老化问题,实时的信道估计不仅增大了星载接收机计算复杂度,而且大量的信令开销降低了传输效率。本文针对Ka频段MISO-OTFS星地通信系统,设计了一种基于上行信道估计的下行信道预测方案,提出了一种基于数据辅助匹配滤波的高精度信道估计方法提取上行信道状态信息,构建了一种基于大语言模型的信道预测网络(ASLLM)预测下行信道状态信息。仿真结果将所提出的方法与其他现有方法对比,证明其在可接受计算复杂度内具有更优的NMSE和BER预测性能以及多场景泛化能力。Abstract:
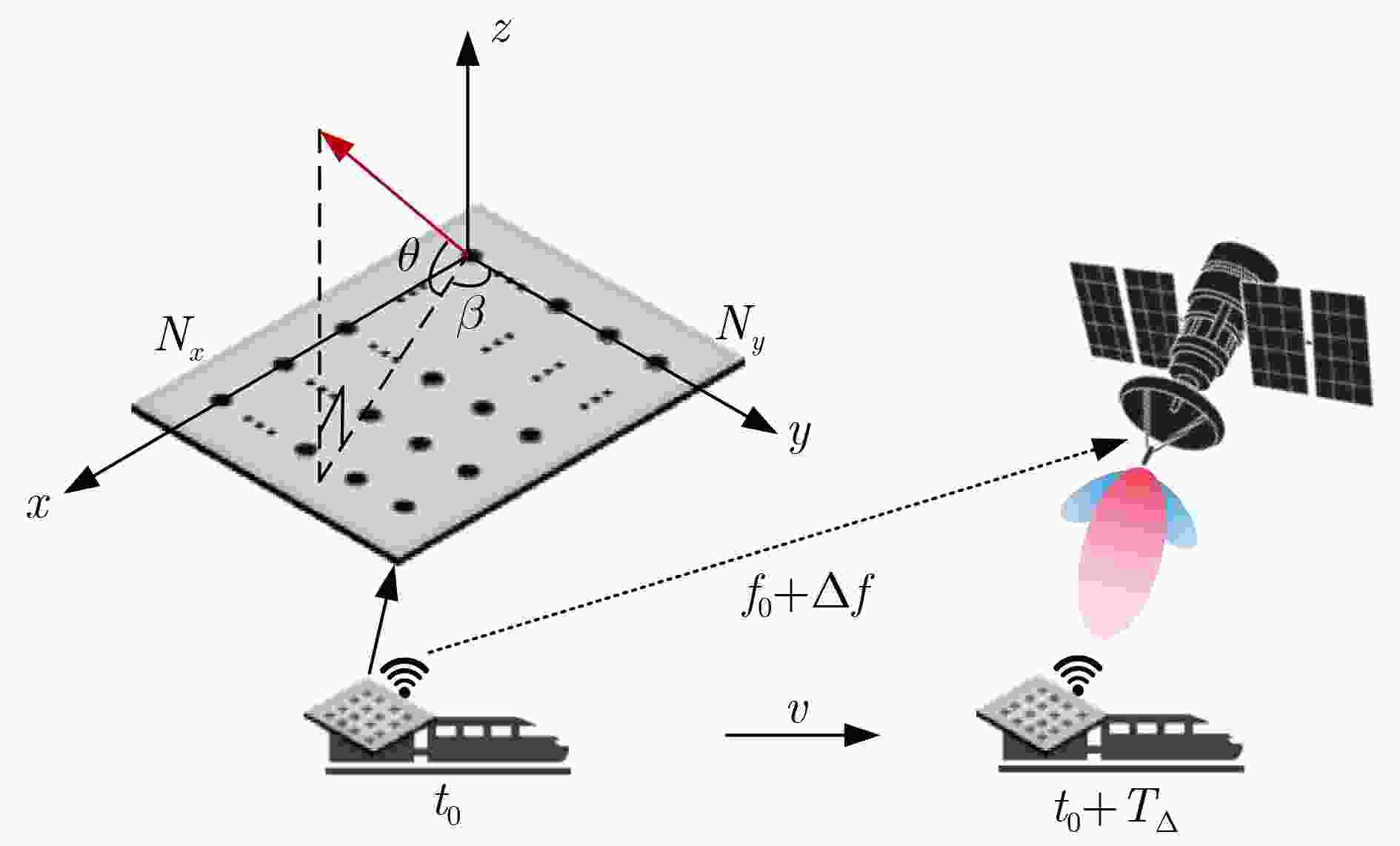
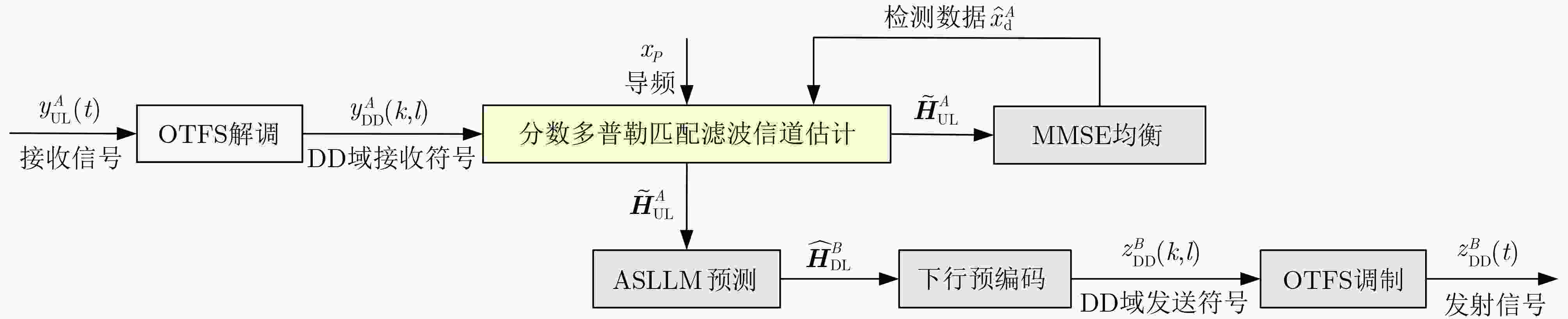
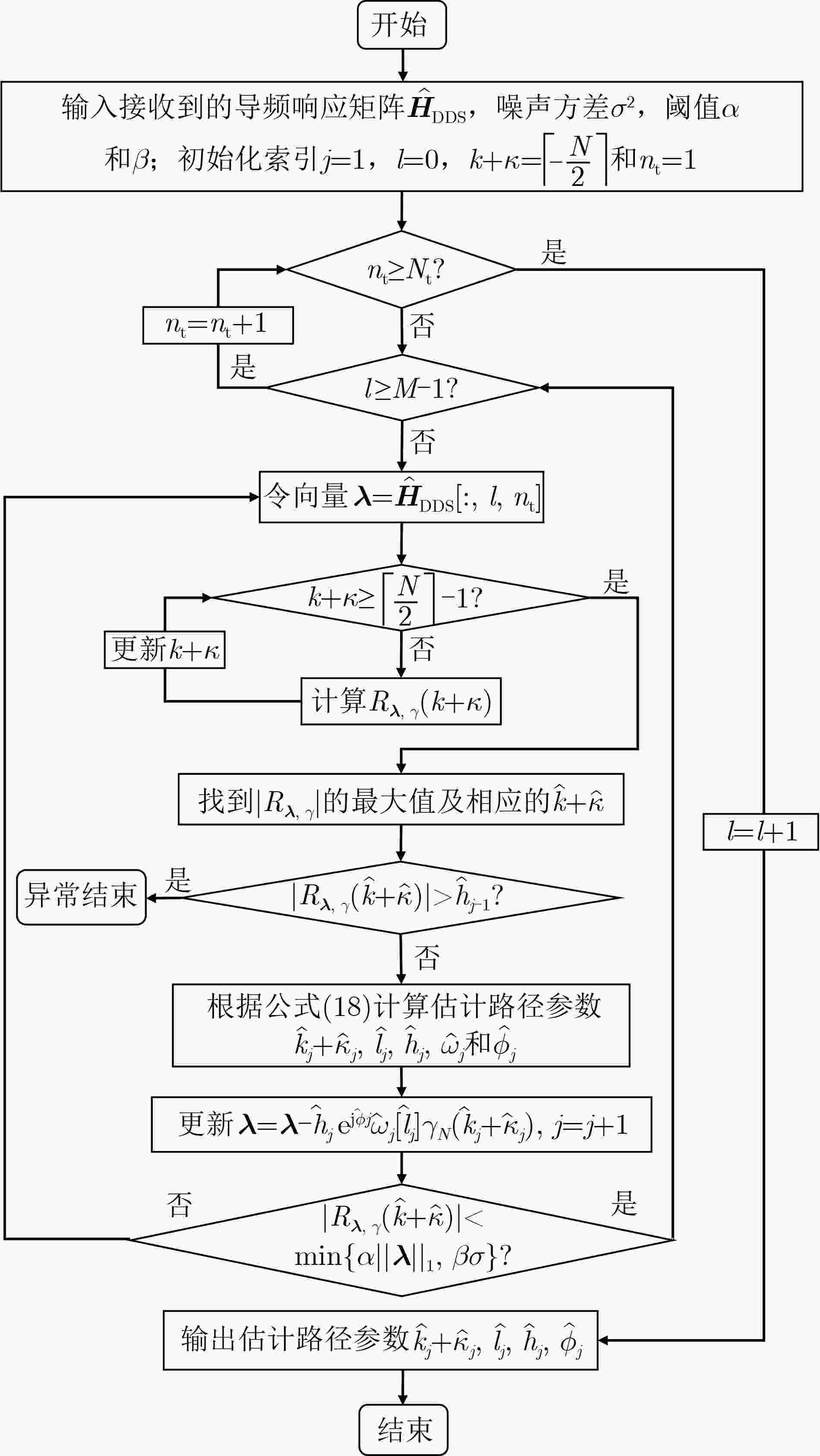
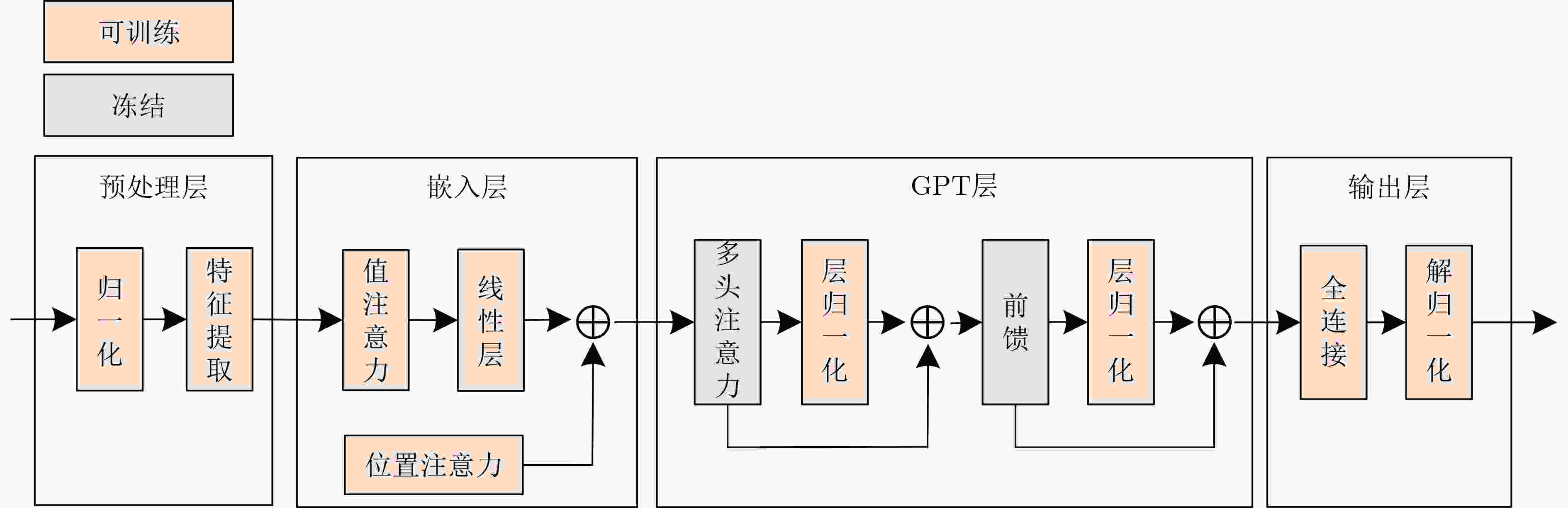
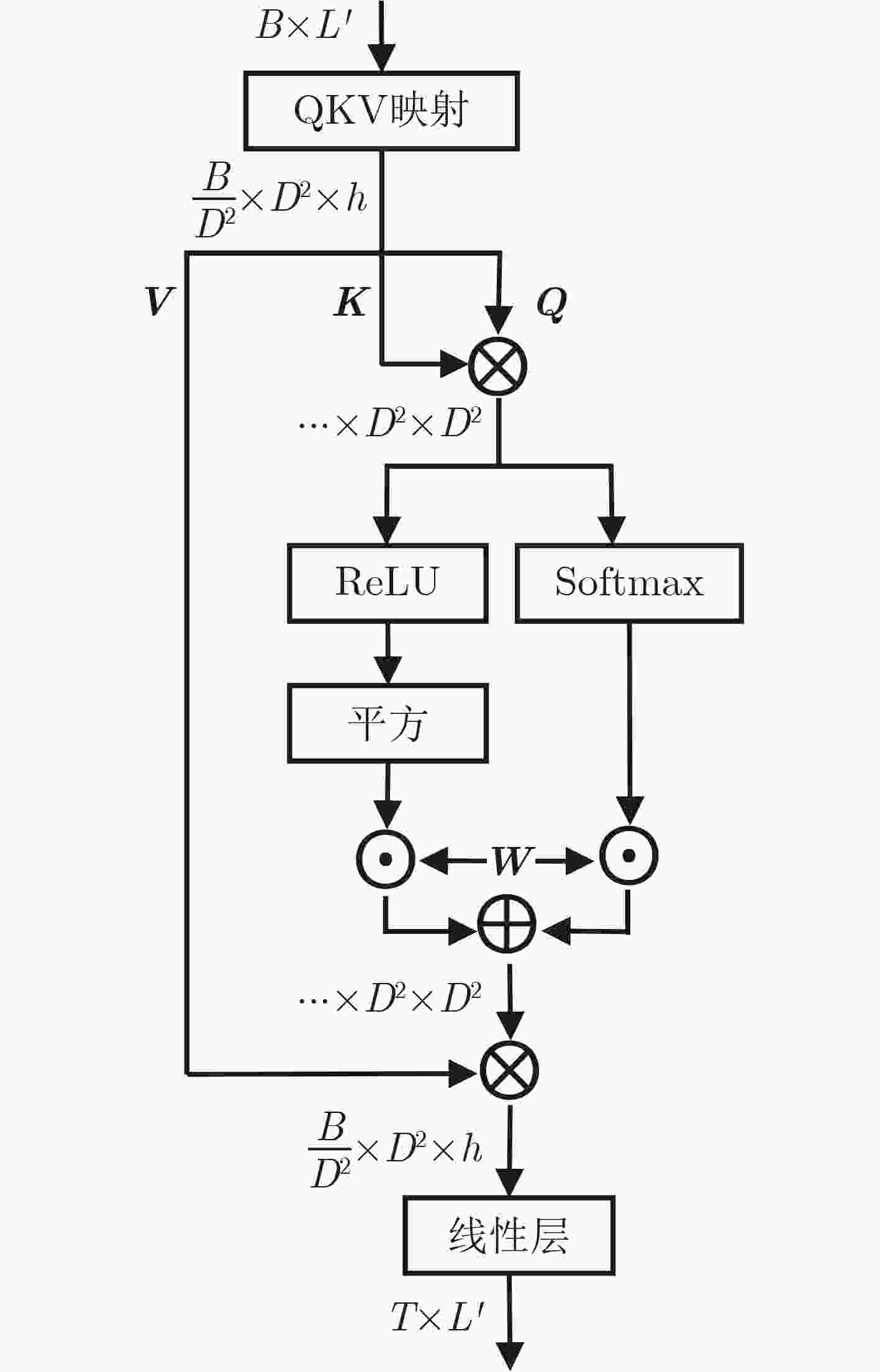
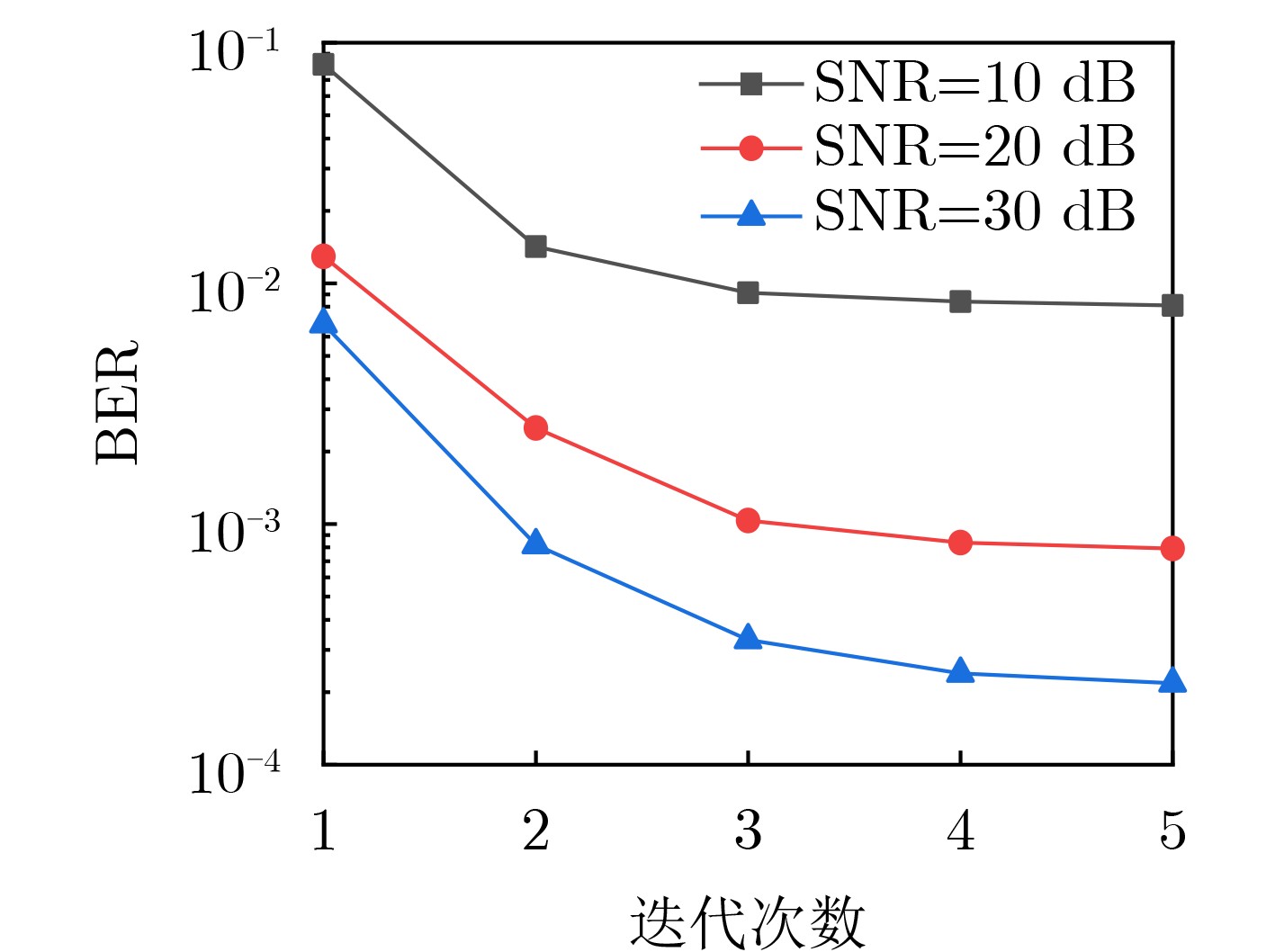
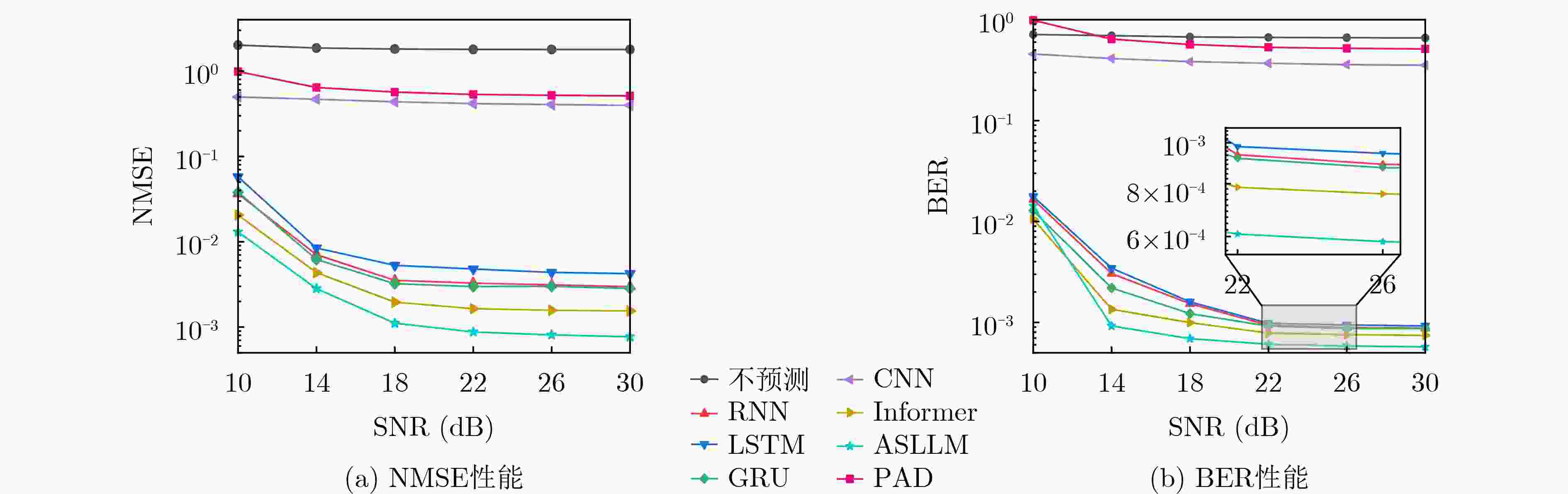
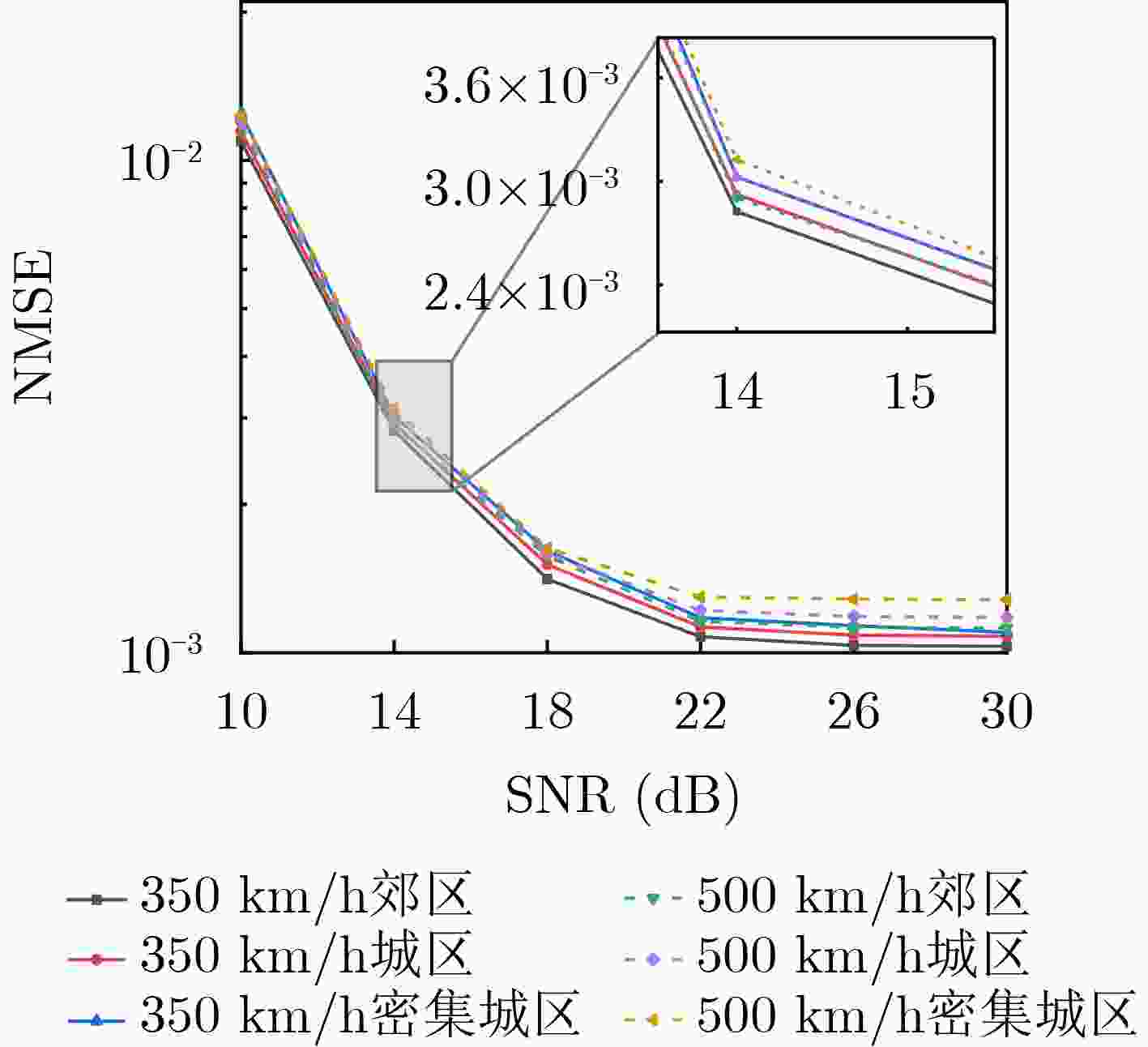
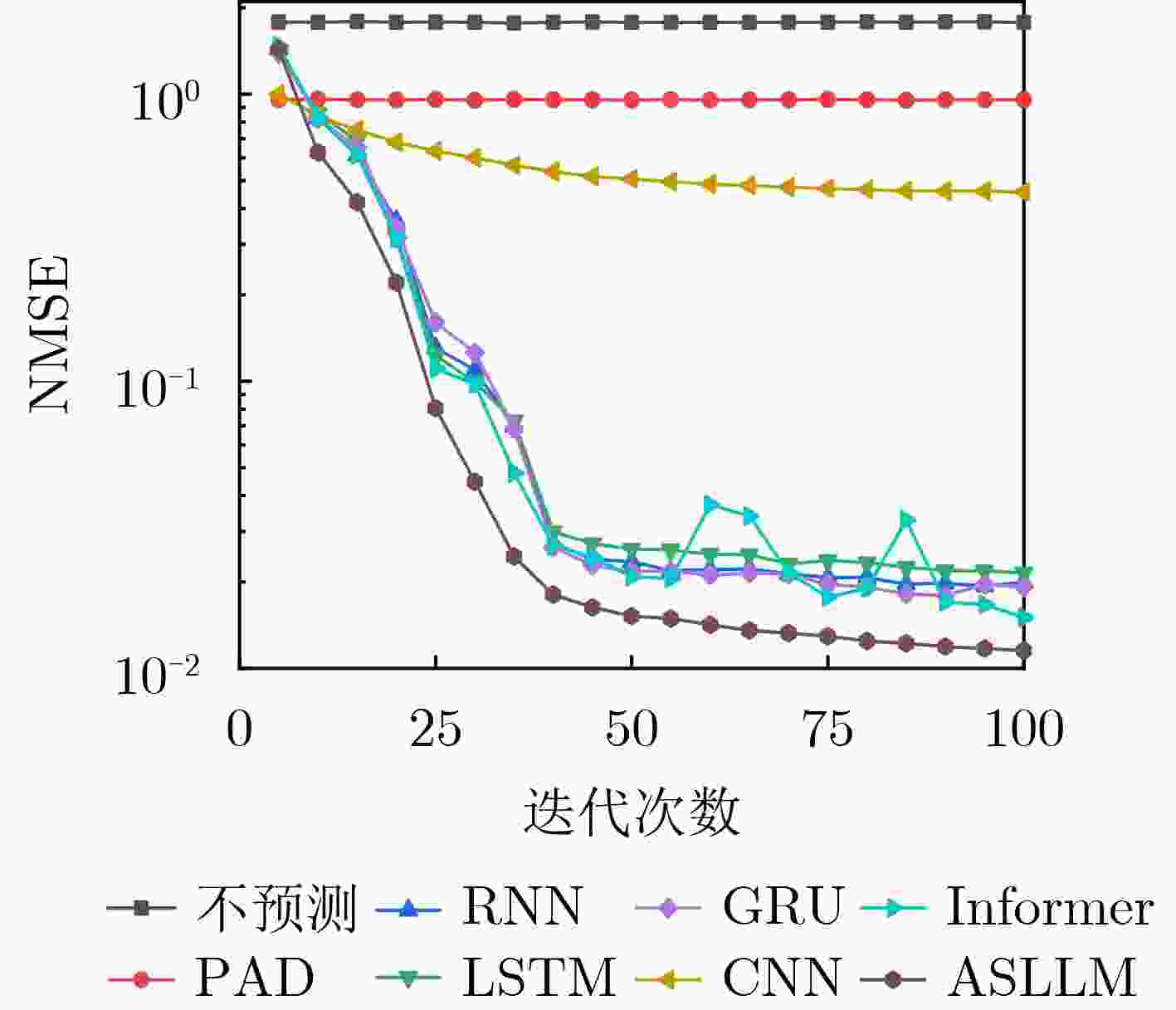
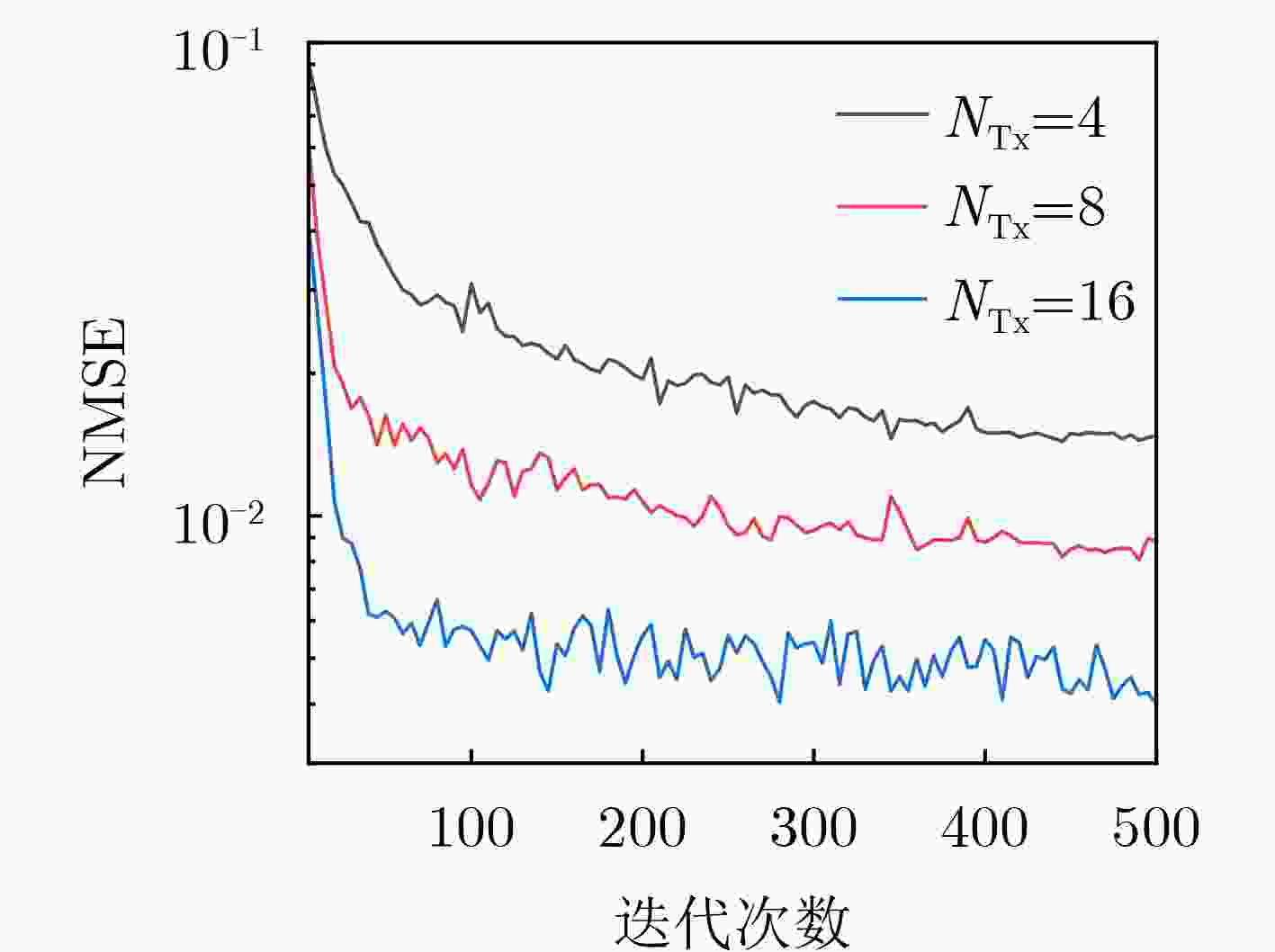
Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) modulation shows promise in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite-to-ground communications. However, rapid Doppler shift variation and high latency in LEO systems lead to channel aging. Real-time channel estimation increases the computational complexity of onboard receivers and reduces transmission efficiency due to substantial pilot overhead. This study addresses a Ka-band Multiple-Input Single-Output (MISO) OTFS satellite-to-ground communication system by designing a Downlink (DL) channel prediction scheme based on Uplink (IL) channel estimation. A high-precision channel estimation method is proposed, combining matched filtering with data detection to extract UL Channel State Information (CSI). An Adaptive Sparse Large Language Model (ASLLM)-based channel prediction network is then constructed to predict DL CSI. Compared with existing methods, simulations show that the proposed approach achieves lower Normalized Mean Square Error (NMSE) and Bit Error Rate (BER), with improved generalization across multiple scenarios and within an acceptable computational complexity range. Objective LEO satellite communication systems offer advantages over Medium-Earth-Orbit (MEO) and Geostationary-Earth-Orbit (GEO) systems, particularly in terms of reduced transmission latency and lower path loss. Therefore, LEO satellites are considered a key element of the Sixth-Generation (6G) Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) satellite internet architecture. However, high-mobility channels between LEO satellites and ground stations introduce significant challenges for conventional Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), resulting in marked performance degradation. OTFS modulation, which operates in the Delay-Doppler (DD) domain, has been shown to outperform OFDM in high-mobility scenarios, Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems, and millimeter-wave frequency bands. This performance advantage is attributed to its robustness to Doppler shifts and inter-symbol interference. In modern Time Division Duplexing (TDD) satellite communication systems, OTFS receivers require high-complexity real-time channel estimation, and transmitters rely on extensive pilot overhead to encode CSI for reliable data recovery. To mitigate these limitations, channel prediction schemes using UL CSI to predict DL CSI have been proposed. However, broadband MISO-OTFS systems with large antenna arrays and high-resolution transmission demand precise and efficient CSI prediction under rapidly varying DD-domain conditions. The dynamic and rapidly aging characteristics of DD domain CSI present significant challenges for accurate prediction in broadband, high-mobility, and large-scale antenna communication systems. To address this, an ASLLM-based channel prediction method is developed. The proposed method enables accurate prediction of DD-domain CSI under these conditions. Methods By modeling the input–output relationship of a MISO OTFS satellite-to-ground communication system, this study proposes a data-assisted fractional Doppler matched filtering algorithm for channel estimation. This method leverages the shift property of correlation functions and integrates iterative optimization through Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) signal detection to achieve accurate estimation of DD domain CSI. The resulting high-precision CSI serves as a reliable input for the subsequent prediction network. The task of predicting DL slot CSI from UL slot CSI is formulated as a minimization of the NMSE between the network’s predicted CSI and the true DL CSI. The proposed ASLLM prediction network consists of a preprocessing layer, an embedding layer, a Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) layer, and an output layer. The raw DD-domain CSI is first processed through the preprocessing layer to extract convolutional features. In the embedding layer, a value attention module and a position attention module are applied to convert the CSI features into a structured, text-like input suitable for GPT processing. The value attention module adaptively extracts sparse feature values of the CSI, while the position attention module encodes positional characteristics in a non-trainable manner. The core of the prediction network is a pre-trained, open-source GPT-2 backbone, which is used to model and forecast the CSI sequence. The network output is then passed through a linear transformation layer to recover the predicted DD-domain CSI. Results and Discussions The satellite-to-ground channel is modeled using the NTN-TDL-D dual mobility channel and simulated with QuaDRiGa. First, the performance of the data-assisted matched filtering channel estimation method is validated ( Fig. 7 ). At a Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of 20 dB, the BER reaches the order of 0.001 after three iterations. Next, training loss curves for several neural network models are compared (Fig. 8 ). The ASLLM model exhibits the fastest convergence and highest stability. It also achieves superior NMSE and BER performance in MMSE data detection compared with other approaches (Fig. 9 ). ASLLM demonstrates strong generalization across different channel models and varying terminal velocities (Fig. 10 ). However, in cross-frequency generalization scenarios, a small number of additional training samples are still required to maintain accuracy (Fig. 11 ). Finally, ablation experiments confirm the contribution of each core module within the ASLLM architecture (Table 2 ). Comparisons of network parameters, training time, and inference time indicate that the computational complexity of ASLLM remains within an acceptable range (Table 3 ).Conclusions This study proposes a channel prediction method for TDD MISO OTFS systems, termed ASLLM, tailored to high-mobility scenarios such as communication between LEO satellites and high-speed trains. The approach leverages high-precision historical UL CSI, obtained through a data-assisted matched filtering algorithm, to predict future DL CSI. By extracting sparse features from DD domain CSI, the method fine-tunes a pre-trained GPT-2 model—originally trained on general knowledge—to improve predictive accuracy. Simulation results show that: (1) considering both computational complexity and estimation accuracy, optimal stopping criteria for the channel estimation algorithm are defined as an iteration number of 3 and a threshold of 0.001; (2) ASLLM outperforms existing prediction methods in terms of convergence speed, NMSE, BER, and generalization capability; and (3) each module of the network contributes effectively to performance, while overall computational complexity remains within a feasible range. -
表 1 系统仿真参数
参数 取值 OTFS网格尺寸(M,N) (256,32) 系统带宽 7.68 MHz 载波频率 30 GHz 调制方式 QPSK 子载波间隔 30 kHz 多普勒分辨率 937.5 Hz 时延分辨率 0.13 μs 导频占比 25:128 训练批量大小 256 预测网络迭代次数 500 初始学习率 0.001 优化器 Adam(betas=(0.9,0.999)) (α,β) (0.05,0.1) 表 2 消融实验结果
指标 ASLLM 无特征提取 无稀疏注意力 无密集注意力 无LLM骨干网 NMSE(${10^{ - 3}}$) 3.238 4.391 5.758 4.534 7.259 BER(${10^{ - 3}}$) 2.934 3.154 4.022 3.830 5.103 表 3 网络参数量(可训练参数量/总参数量)和每批的训练、响应时间
指标 PAD RNN LSTM GRU CNN Informer ASLLM 网络参数(${10^6}$) 0/0 0.53/0.53 1.51/1.51 1.16/1.16 0.28/0.28 2.70/2.70 2.58/ 85.67 训练时间(ms) 0 5.46 8.66 7.95 1.83 25.88 8.21 推理时间(ms) 53.53 4.38 4.55 5.02 0.97 22.29 7.65 -
[1] SHI Jia, LI Zan, HU Junfan, et al. OTFS enabled LEO satellite communications: A promising solution to severe Doppler effects[J]. IEEE Network, 2024, 38(1): 203–209. doi: 10.1109/MNET.129.2200458. [2] 张勇, 黄永华, 张更新. 低轨卫星通信系统中OFDM多普勒频移补偿研究综述[C]. 第十七届卫星通信学术年会论文集, 北京, 中国, 2021: 165–170. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2021.032805.ZHANG Yong, HUANG Yonghua, and ZHANG Gengxin. A review of OFDM doppler frequency shift compensation in low-orbit satellite communication systems[C]. The 17th Satellite Communication Academic Annual Conference, Beijing, China, 2021: 165–170. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2021.032805. [3] HADANI R, RAKIB S, MOLISCH A F, et al. Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) modulation for millimeter-wave communications systems[C]. 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Honololu, USA, 2017: 681–683. doi: 10.1109/MWSYM.2017.8058662. [4] SUN H G, WILDEMEERSCH M, SHENG M, et al. D2D enhanced heterogeneous cellular networks with dynamic TDD[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(8): 4204–4218. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2418192. [5] PFADLER A, JUNG P, SHALA V, et al. Short-term prediction of doubly-dispersive channels for pulse-shaped OTFS using 2D-ConvLSTM[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Seoul, Korea, 2022: 939–944. doi: 10.1109/ICCWorkshops53468.2022.9814574. [6] 方昕, 颜永庆, 尤肖虎. 最优信道质量预测算法的研究和实现[J]. 通信学报, 2004, 25(5): 93–100. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2004.05.012.FANG Xin, YAN Yongqing, and YOU Xiaohu. Study and realization of optimum channel prediction algorithm[J]. Journal of China Institute of Communications, 2004, 25(5): 93–100. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-436X.2004.05.012. [7] ZHANG Yanfeng, ZHU Xu, LIU Yujie, et al. Basis expansion extrapolation based DL channel prediction with UL channel estimates for TDD MIMO-OTFS systems[C]. ICC 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 2023: 2270–2275. doi: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10279677. [8] YING Daidong and YE Feng. Deep learning supported path prediction and channel estimation for MIMO-OTFS system with high delay resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(3): 3584–3597. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3493921. [9] YIN Haifan, WANG Haiquan, LIU Yingzhuang, et al. Addressing the curse of mobility in massive MIMO with prony-based angular-delay Domain channel predictions[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(12): 2903–2917. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3005473. [10] ALLEN E, SAID K, CALDERBANK R, et al. MIMO precoding at the speed of wireless: Precoder prediction for MIMO-OTFS systems[C]. 2024 IEEE 100th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2024-Fall), Washington, USA, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTC2024-Fall63153.2024.10757975. [11] SU Jing, JIANG Chufeng, JIN Xin, et al. Large language models for forecasting and anomaly detection: A systematic literature review[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.10350, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2402.10350. [12] ZHOU Hao, HU Chengming, YUAN Ye, et al. Large Language Model (LLM) for telecommunications: A comprehensive survey on principles, key techniques, and opportunities[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, doi: 10.1109/COMST.2024.3465447. [13] 张帅, 张晓林. 星地链路高速数传系统快时变信道估计方法[J]. 遥测遥控, 2013, 34(6): 33–39. doi: 10.13435/j.cnki.ttc.002584.ZHANG Shuai and ZHANG Xiaolin. Channel estimation method for time-selective channel in satellite-earth link high rate data transmission systems[J]. Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2013, 34(6): 33–39. doi: 10.13435/j.cnki.ttc.002584. [14] KODHELI O, GUIDOTTI A, and VANELLI-CORALLI A. Integration of satellites in 5G through LEO constellations[C]. GLOBECOM 2017 - 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, Singapore, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2017.8255103. [15] 吕宏春. 基于北斗Ka星间链路体制的星地时间同步方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学(中国科学院国家授时中心), 2017.LV Hongchun. Research on method of satellite-ground time synchronization base on Ka band ISL system of BDS[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (National Time Service Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017. [16] 3GPP. Study on New Radio (NR) to Support Non-terrestrial Networks: TR 38.811 (V15.3. 0) Release 15[S]. 2020. [17] SHI Ding, WANG Wenjie, YOU Li, et al. Deterministic pilot design and channel estimation for downlink massive MIMO-OTFS systems in presence of the fractional Doppler[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(11): 7151–7165. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3081164. [18] HASHIMOTO N, OSAWA N, YAMAZAKI K, et al. Channel estimation and equalization for CP-OFDM-based OTFS in fractional Doppler channels[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ICCWorkshops50388.2021.9473532. [19] 王彪, 方梓德, 朱雨男, 等. 低复杂度水声多输入多输出正交时频空调制通信方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(1): 83–91. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230183.WANG Biao, FANG Zide, ZHU Yunan, et al. Research on low complexity underwater acoustic multiple input multiple output orthogonal time frequency space modulation communication method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(1): 83–91. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230183. [20] SHEN Boxiao, WU Yongpeng, AN Jianping, et al. Random access with massive MIMO-OTFS in LEO satellite communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(10): 2865–2881. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3196128. [21] RAVITEJA P, PHAN K T, and HONG Y. Embedded pilot-aided channel estimation for OTFS in delay–doppler channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4906–4917. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2906357. [22] 蒋占军, 刘庆达, 张鈜, 等. 高速移动通信系统中OTFS分数多普勒信道估计加窗研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(2): 646–653. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210561.JIANG Zhanjun, LIU Qingda, ZHANG Hong, et al. Study on OTFS fractional Doppler channel estimation and windowing in high-speed mobile communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(2): 646–653. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210561. [23] OUCHIKH R, AÏSSA-EL-BEY A, CHONAVEL T, et al. Iterative channel estimation and data detection algorithm for OTFS modulation[C]. ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 5263–5267. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747191. [24] ZHOU Shihao, CHEN Duosheng, PAN Jinshan, et al. Adapt or perish: Adaptive sparse transformer with attentive feature refinement for image restoration[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2024: 2952–2963. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00285. [25] LIU Boxun, LIU Xuanyu, GAO Shijian, et al. LLM4CP: Adapting large language models for channel prediction[J]. Journal of Communications and Information Networks, 2024, 9(2): 113–125. doi: 10.23919/JCIN.2024.10582829. [26] TOUVRON H, MARTIN L, STONE K, et al. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2307.09288, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2307.09288. [27] YENDURI G, RAMALINGAM M, SELVI G C, et al. GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer)— a comprehensive review on enabling technologies, potential applications, emerging challenges, and future directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 54608–54649. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3389497. [28] JAECKEL S, RASCHKOWSKI L, BÖRNER K, et al. QuaDRiGa: A 3-D multi-cell channel model with time evolution for enabling virtual field trials[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(6): 3242–3256. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2310220. [29] 3GPP. Study on channel model for frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz: TR 38. 901 (V15.1. 0) Release 15[S]. 2019. [30] 肖卓然. 基于物理启发式学习的MIMO信道预测方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 浙江大学, 2023. doi: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2023.000537.XIAO Zhuoran. Research on MIMO channel prediction based on physics-inspired learning[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2023. doi: 10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2023.000537. [31] JIANG Wei and SCHOTTEN H D. Deep learning for fading channel prediction[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2020, 1: 320–332. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.2982513. [32] SINGHAL A, PRIYALAKSHMI B, SAGAR P, et al. Prediction of low estimation error for 5G CNN MIMO channel[C]. 2024 International Conference on Recent Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Ubiquitous Communication, and Computational Intelligence (RAEEUCCI), Chennai, India, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RAEEUCCI61380.2024.10547767. [33] ZHOU Haoyi, ZHANG Shanghang, PENG Jieqi, et al. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting[C]. Proceedings of the Thirty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 11106–11115. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i12.17325. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
