A Fake News Detection Approach Enhanced by Multi-Source Feature Fusion
-
摘要: 针对现有虚假新闻检测方法在提取和利用新闻多层次特征及捕获新闻传播高阶结构特征方面的局限性,该文提出一种多源特征融合增强(MSFFE)的虚假新闻检测方法。该方法利用多层次注意力机制,从结构、时序和内容3个维度提取新闻特征:首先,通过增强型超图神经网络提取新闻传播的结构特征;其次,利用多尺度时序模块捕获新闻传播的时序特征;最后,采用多头自注意力机制提取新闻内容特征。特别地,该方法设计了一种特征融合门控单元,用于动态调整不同特征维度的权重,从而实现多源异构特征的高效融合。在公开数据集Politifact和Gossipcop上的实验结果显示,该方法的检测性能较UPFD, HGNN, RTRUST(State-of-the-Art)等近年的基线方法有所提升。其中,与最先进的方法相比较,在Politifact数据集上,准确率提升了3.64%,F1分数提升了3.41%;在Gossipcop数据集上,准确率提升了0.55%,F1分数提升了0.56%。这些实验结果表明,该方法能够有效检测虚假新闻,为虚假新闻检测领域提供了新思路和技术支撑。Abstract:
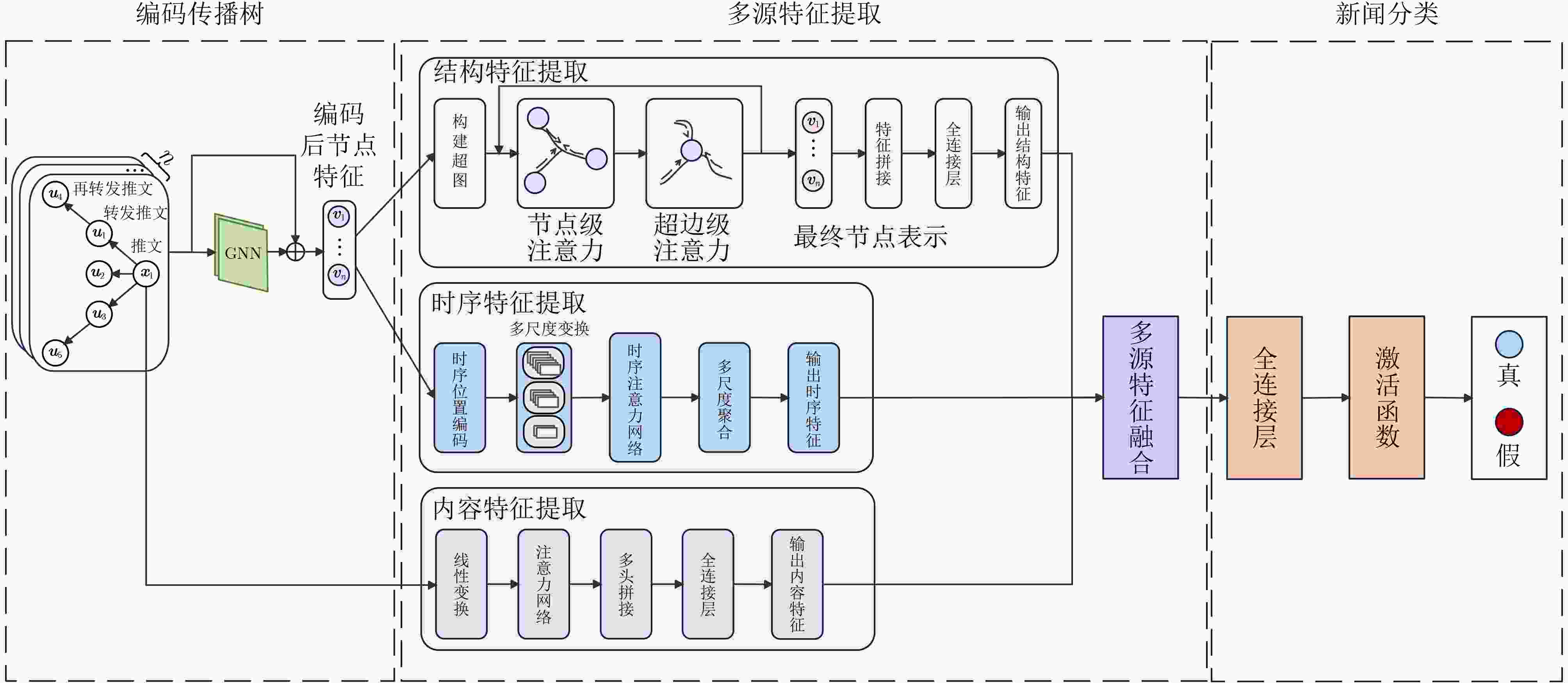
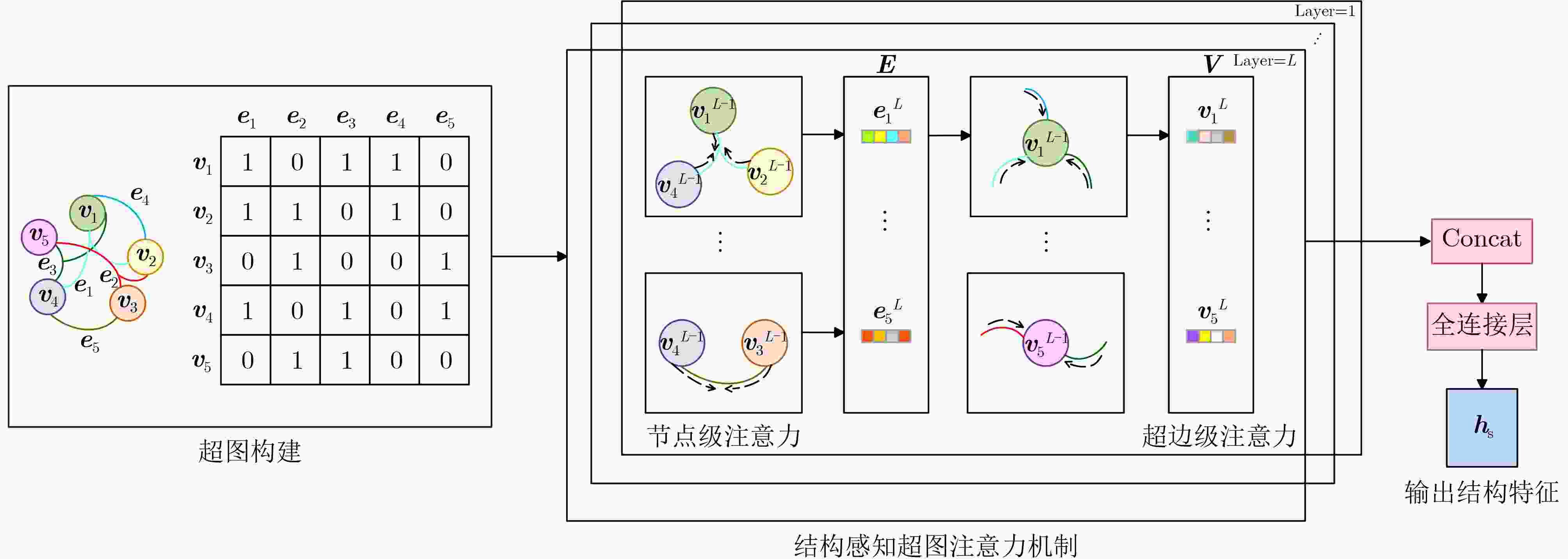
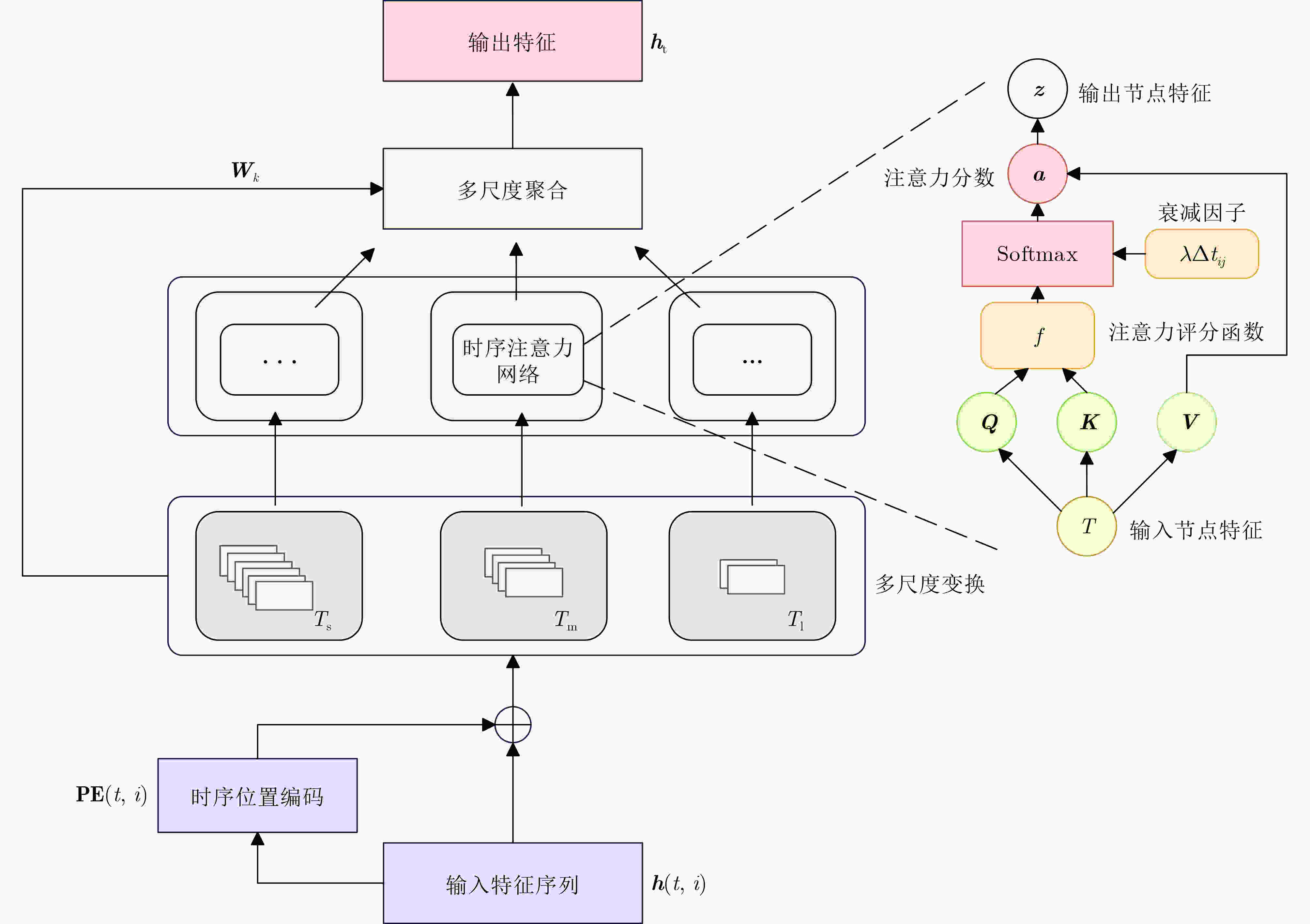
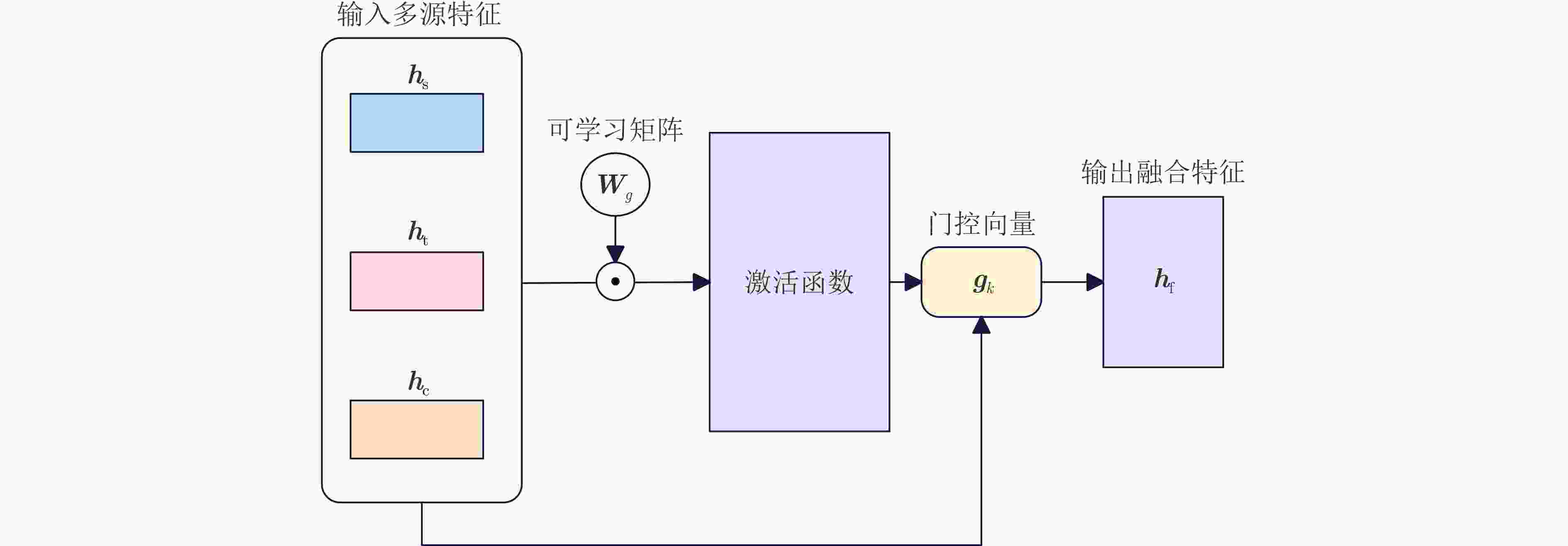
Objective News exhibits multidimensional complexity, comprising structural, temporal, and content features. Structural features are reflected in the propagation path, depth, and breadth. Fake news often exhibits distinctive structural patterns, such as rapid diffusion through a limited number of “opinion leader” nodes or the formation of densely connected propagation clusters. Temporally, fake news tends to spread quickly within short timeframes, characterized by unusually high dissemination speeds and elevated interaction rates. Content features include the information conveyed in headlines and body text; fake news often contains sensationalized headlines, emotive language, inaccurate data, or fabricated claims. Detection models that rely solely on a single feature type often demonstrate limited discriminative performance. Therefore, capturing the hierarchical and heterogeneous attributes of news is critical to improving detection accuracy and remains a major focus of ongoing research. Current approaches predominantly emphasize content features, with limited incorporation of structural characteristics. Although Graph Neural Networks (GNN) have been employed to model propagation structures, their integration of content and temporal information remains inadequate. To address these limitations, this study proposes a fake news detection approach based on multi-source feature fusion, which enables more comprehensive feature representation and substantially enhances detection performance. Methods To enhance fake news detection performance, this study proposes a Multi-Source Feature Fusion Enhancement (MSFFE) approach that extracts features from three sources: structural, temporal, and content, and integrates them using an adaptive fusion mechanism. This mechanism dynamically adjusts the weight of each feature type to generate a unified representation with comprehensive expressiveness. The model comprises three core components: propagation tree encoding, multi-source feature extraction, and news classification ( Fig. 2 ). In the propagation tree encoding component, a GNN is employed to represent the news propagation structure. Specifically, the GraphSAGE (Graph SAmple and aggreGatE) algorithm is used to aggregate node information from the propagation tree to the root node, enabling efficient capture of local structural patterns and temporal dynamics. Compared with conventional GNN methods, GraphSAGE improves scalability for large-scale graphs and reduces computational complexity by avoiding full-graph updates. In the multi-source feature extraction component, the model extracts structural, temporal, and content features. For structural features, the encoded propagation tree nodes are organized into a hypergraph. A hypergraph attention mechanism is then applied: first, hyperedge representations are updated via node-level attention; next, node representations are updated via hyperedge-level attention; and finally, structural-level features are obtained. For temporal features, node activity across multiple time windows is modeled using time-scale expansion and compression. A time decay attention mechanism is introduced to extract multi-scale temporal features, which are then fused into a unified temporal representation. For content features, the root node’s associated text is processed using a multi-head self-attention mechanism to capture semantic information, yielding content-level features. After extracting the three feature types, an adaptive multi-source fusion mechanism integrates them into a final news representation. This representation is passed through a fully connected layer and activation function for classification. The fully connected layer applies a linear transformation using a learnable weight matrix and bias term to produce predicted scores for each news instance. During training, model parameters are optimized to maximize classification accuracy. The final output is mapped to a probability in [0,1] using a Sigmoid activation function, indicating the likelihood of the news being classified as “true” or “fake.” A threshold of 0.5 is used for binary classification: probabilities above 0.5 are labeled “fake,” and those below are labeled “true.”Results and Discussions As shown in Table 3 , the ablation experiments demonstrate that incorporating features from different sources into the base model significantly improves fake news detection accuracy. This finding confirms the effectiveness of the core components in the proposed approach. The integration of multi-source features enhances the overall detection performance, highlighting the advantage of the fusion mechanism in identifying fake news. Comparative experiments further support these results. As shown in (Table 2 ), the proposed approach outperforms existing approaches on both the Politifact and Gossipcop datasets. On the Politifact dataset, it improves accuracy by 3.64% and the F1 score by 3.41% compared with the State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) method Robust Trust Evaluation Architecture (RTRUST). On the Gossipcop dataset, the accuracy and F1 score increase by 0.55% and 0.56%, respectively. These improvements are attributed to the approach’s ability to effectively model high-order structural features and integrate temporal and content features, resulting in more comprehensive and discriminative feature representations.Conclusions Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach effectively extracts and fuses multi-source features, substantially improving the performance of fake news detection. By enhancing the model’s ability to represent structural, temporal, and content characteristics, the approach contributes to more accurate classification. This has the potential to mitigate the societal consequences of fake news, including public misinformation, reputational damage to organizations, and policy misjudgments. -
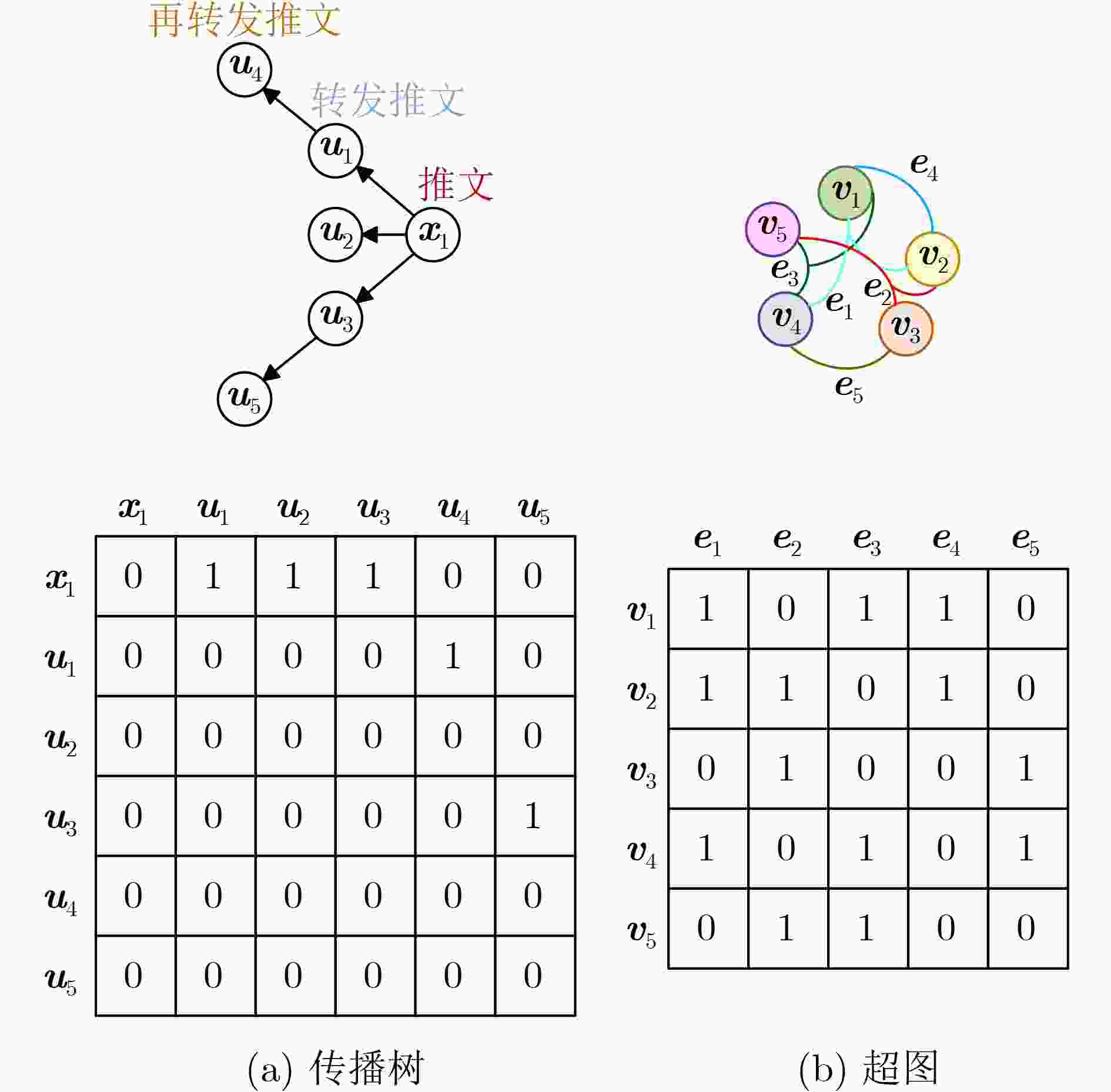
图 1 传播树和超图编码结构图[32]
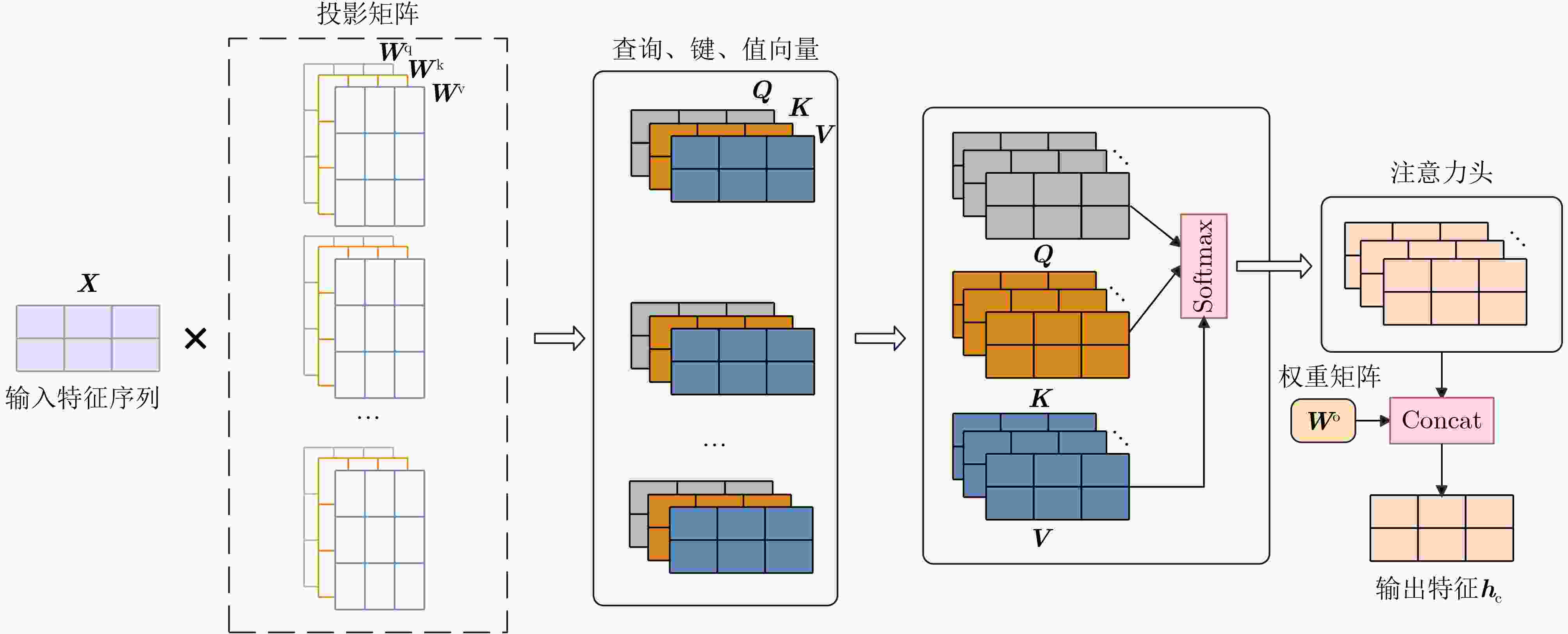
图 3 结构特征提取结构图[32]
图 4 时序特征提取结构图[39]
表 1 数据集的信息[22]
数据集 #图 #假新闻 #真新闻 #节点 #边 Politifact 314 157 157 41,054 50,740 Gossipcop 5,464 2,732 2,732 314,262 308,798 注:“#”代表数量。 方法 Politifact Gossipcop 准确率 F1分数 准确率 F1分数 GNN-CL 65.79±8.96 65.02±9.46 94.98±0.80 94.94±0.80 Bi-GCN 74.16±3.57 74.16±3.57 88.04±0.48 87.95±0.49 UPFD-GCN 80.27±4.35 80.16±4.41 95.55±0.63 95.51±0.64 UPFD-GAT 79.09±3.73 78.95±3.79 96.03±0.62 96.00±0.62 UPFD-SAGE 80.40±4.22 80.13±4.65 96.38±0.48 96.36±0.48 TGNF 74.28±1.74 74.09±1.81 85.07±0.08 85.07±0.08 GTN 81.67±4.16 81.53±4.35 92.41±0.98 92.38±0.98 HGAT 81.53±1.16 80.47±1.75 – – GCNFN 80.63±4.23 80.31±4.57 95.37±0.21 95.33±0.21 HGNN 79.96±4.89 79.28±5.16 93.38±0.49 93.38±0.49 RTRUST (SOTA, 2024) 90.11 89.86 97.46 97.41 MSFFE 93.75±1.56 93.27±1.68 98.01±0.08 97.97±0.08 表 3 消融实验结果(%)
特征类型 Politifact Gossipcop S T C F 准确率 F1分数 准确率 F1分数 × × × × 84.62 84.56 97.23 97.22 √ × × × 92.19 91.60 97.53 97.53 × √ × × 89.94 89.93 97.72 97.71 × × √ × 89.42 89.42 97.62 97.61 √ √ √ × 92.90 92.86 97.89 97.89 √ √ √ √ 93.75 93.27 98.01 97.97 表 4 虚假新闻检测案例分析
推文数量
(传播数量)推文发布
时间特征虚假新闻(英文原文) 虚假新闻(中文译文) MSFFE
敏感案例1 6304 短时间内
迅速扩散“SPECIAL REPORT: GEORGIA BECOMES
FIRST STATE TO BAN MUSLIM CULTURE
IN HISTORIC MOVE TO RESTORE
WESTERN VALUES!”“特别报道:佐治亚州成为首个
禁止穆斯林文化的州,历史性举措旨在
恢复西方价值观!”案例2 5122 短时间内
迅速扩散“Snapchat is shutting down!” “Snapchat即将关闭!” MSFFE
不敏感案例3 0 无推文转发 “Billy Bush” “比利·布什” 案例4 0 无推文转发 “Alabama Secretary of State” “阿拉巴马州国务卿” -
[1] TOUAHRI I and MAZROUI A. Survey of machine learning techniques for Arabic fake news detection[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2024, 57(6): 157. doi: 10.1007/s10462-024-10778-3. [2] OLAN F, JAYAWICKRAMA U, ARAKPOGUN E O, et al. Fake news on social media: The impact on society[J]. Information Systems Frontiers, 2024, 26(2): 443–458. doi: 10.1007/s10796-022-10242-z. [3] 李雯萱. 基于多模态深度融合的跨领域虚假新闻检测研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国人民公安大学, 2024. doi: 10.27634/d.cnki.gzrgu.2024.000330.LI Wenxuan. Cross-domain fake news detection based on multi-modal deep fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], People’s Public Security University of China, 2024. doi: 10.27634/d.cnki.gzrgu.2024.000330. [4] ZHANG Litian, ZHANG Xiaoming, ZHOU Ziyi, et al. Reinforced adaptive knowledge learning for multimodal fake news detection[C]. Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 16777–16785. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v38i15.29618. [5] 白轩瑜, 王陆一, 赵若思. 神经网络在船舶轨迹异常行为识别中的应用研究[J]. 信息与电脑(理论版), 2024, 36(18): 21–23.BAI Xuanyu, WANG Luyi, and ZHAO Ruosi. Research on the application of neural network in the recognition of abnormal behavior of ship trajectory[J]. Information & Computer, 2024, 36(18): 21–23. [6] 胡潇戈. 多模态特征融合的社交媒体虚假新闻检测研究[D]. [硕士论文], 武汉大学, 2020. doi: 10.27379/d.cnki.gwhdu.2020.001194.HU Xiaoge. Fake news detection on social media with multimodal feature fusion[D]. [Master dissertation], Wuhan University, 2020. doi: 10.27379/d.cnki.gwhdu.2020.001194. [7] CAPUANO N, FENZA G, LOIA V, et al. Content-based fake news detection with machine and deep learning: A systematic review[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 530: 91–103. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.02.005. [8] ALGHAMDI J, LIN Yuqing, and LUO Suhuai. Towards COVID-19 fake news detection using transformer-based models[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 274: 110642. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110642. [9] SU Xing, YANG Jian, WU Jia, et al. Mining user-aware multi-relations for fake news detection in large scale online social networks[C]. The Sixteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Singapore, Singapore, 2023: 51–59. doi: 10.1145/3539597.3570478. [10] RAZA S and DING Chen. Fake news detection based on news content and social contexts: A transformer-based approach[J]. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2022, 13(4): 335–362. doi: 10.1007/s41060-021-00302-z. [11] RUCHANSKY N, SEO S, and LIU Yan. CSI: A hybrid deep model for fake news detection[C]. 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Singapore, 2017: 797–806. doi: 10.1145/3132847.3132877. [12] SHU Kai, CUI Limeng, WANG Suhang, et al. dEFEND: Explainable fake news detection[C]. The 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, USA, 2019: 395–405. doi: 10.1145/3292500.3330935. [13] HU Guimin, LU Guangming, and ZHAO Yi. Bidirectional hierarchical attention networks based on document-level context for emotion cause extraction[C]. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 2021: 558–568. doi: 10.18653/v1/2021.findings-emnlp.51. [14] VATTER J, MAYER R, and JACOBSEN H A. The evolution of distributed systems for graph neural networks and their origin in graph processing and deep learning: A survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 56(1): 6. doi: 10.1145/3597428. [15] WU Zonghan, PAN Shirui, CHEN Fengwen, et al. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(1): 4–24. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2978386. [16] BHATTI U A, TANG Hao, WU Guilu, et al. Deep learning with graph convolutional networks: An overview and latest applications in computational intelligence[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2023, 2023(1): 8342104. doi: 10.1155/2023/8342104. [17] LI Zhifei, ZHAO Yue, ZHANG Yan, et al. Multi-relational graph attention networks for knowledge graph completion[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 251: 109262. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109262. [18] WU Haiyan, ZHANG Zhiqiang, SHI Shaoyun, et al. Phrase dependency relational graph attention network for aspect-based sentiment analysis[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 236: 107736. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107736. [19] HAN Yi, KARUNASEKERA S, and LECKIE C. Graph neural networks with continual learning for fake news detection from social media[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2007.03316, 2020. [20] BIAN Tian, XIAO Xi, XU Tingyang, et al. Rumor detection on social media with bi-directional graph convolutional networks[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 549–556. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i01.5393. [21] MONTI F, FRASCA F, EYNARD D, et al. Fake news detection on social media using geometric deep learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1902.06673, 2019. [22] DOU Yingtong, SHU Kai, XIA Congying, et al. User preference-aware fake news detection[C]. The 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, Canada, 2021: 2051–2055. doi: 10.1145/3404835.3462990. [23] REN Yuyang and ZHANG Jiawei. Fake news detection on news-oriented heterogeneous information networks through hierarchical graph attention[C]. 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN52387.2021.9534362. [24] 郎广智. 基于内容的虚假新闻检测方法研究及实现[D]. [硕士论文], 北京交通大学, 2022. doi: 10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2022.003502.LANG Guangzhi. Research and implementation of content-based fake news detection method[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing Jiaotong University, 2022. doi: 10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2022.003502. [25] BAI Song, ZHANG Feihu, and TORR P H S. Hypergraph convolution and hypergraph attention[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 110: 107637. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107637. [26] SAKONG D, VU V H, HUYNH T T, et al. Higher-order knowledge-enhanced recommendation with heterogeneous hypergraph multi-attention[J]. Information Sciences, 2024, 680: 121165. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2024.121165. [27] WANG Mengke, LIU Weifeng, YUAN Xinan, et al. Parallel hypergraph convolutional neural networks for image annotation[C]. 2022 41st Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hefei, China, 2022: 6582–6587. doi: 10.23919/CCC55666.2022.9901938. [28] JIN Yilun, YIN Wei, WANG Haoseng, et al. Capturing word positions does help: A multi-element hypergraph gated attention network for document classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 251: 124002. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124002. [29] SALAMANOS N, LEONIDOU P, LAOUTARIS N, et al. HyperGraphDis: Leveraging hypergraphs for contextual and social-based disinformation detection[C]. The 18th International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Buffalo, USA, 2024: 1381–1394. doi: 10.1609/icwsm.v18i1.31396. [30] ZHANG Ruochi, ZOU Yuesong, and MA Jian. Hyper-SAGNN: A self-attention based graph neural network for hypergraphs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1911.02613, 2019. [31] DING Kaize, WANG Jianling, LI Jundong, et al. Be more with less: Hypergraph attention networks for inductive text classification[C]. The 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2020: 4927–4936. doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.399. [32] JEONG U, DING Kaize, CHENG Lu, et al. Nothing stands alone: Relational fake news detection with hypergraph neural networks[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Osaka, Japan, 2022: 596–605. doi: 10.1109/BigData55660.2022.10020234. [33] GIORDANO G, CATONE M C, and PRIMERANO I. The fake news phenomenon in the scientific debate: Evidence from a bibliometric analysis[J]. Social Indicators Research, 2025, 177(1): 31–52. doi: 10.1007/s11205-024-03485-7. [34] ZHANG Chaowei, GUPTA A, QIN Xiao, et al. A computational approach for real-time detection of fake news[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 221: 119656. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119656. [35] HAMILTON W L, YING R, and LESKOVEC J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1025–1035. [36] KONDAMUDI M R, SAHOO S R, CHOUHAN L, et al. A comprehensive survey of fake news in social networks: Attributes, features, and detection approaches[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2023, 35(6): 101571. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.101571. [37] LIU Qi, JIN Yuanyuan, CAO Xuefei, et al. An entity ontology-based knowledge graph embedding approach to news credibility assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2024, 11(4): 5308–5318. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2023.3342873. [38] OUYANG Jihong, XUAN Chang, WANG Bing, et al. Aspect-based sentiment classification with aspect-specific hypergraph attention networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 248: 123412. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123412. [39] ZHANG Yitian, MA Liheng, PAL S, et al. Multi-resolution time-series transformer for long-term forecasting[C]. The 27th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, València, Spain, 2024: 4222–4230. [40] FAN Jin, ZHANG Ke, HUANG Yipan, et al. Parallel spatio-temporal attention-based TCN for multivariate time series prediction[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(18): 13109–13118. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-05958-z. [41] HASSANIN M, ANWAR S, RADWAN I, et al. Visual attention methods in deep learning: An in-depth survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 108: 102417. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102417. [42] CHITTY-VENKATA K T, MITTAL S, EMANI M, et al. A survey of techniques for optimizing transformer inference[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2023, 144: 102990. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2023.102990. [43] SUN Haoran, TANG Jinchuan, DANG Shuping, et al. Privacy and distribution preserving generative adversarial networks with sample balancing[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 258: 125181. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125181. [44] YANG Hongyu, ZHANG Jinjiao, ZHANG Liang, et al. MRAN: Multimodal relationship-aware attention network for fake news detection[J]. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 2024, 89: 103822. doi: 10.1016/j.csi.2023.103822. [45] 李旭. 基于应用分类的安卓恶意应用检测模型[D]. [硕士论文], 广州大学, 2019.LI Xu. Android malware detection model based on application classification[D]. [Master dissertation], Guangzhou University, 2019. [46] 卢楠滟. 风电功率爬坡事件识别技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华北电力大学, 2022. doi: 10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2022.000754.LU Nanyan. Research on wind power ramp recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], North China Electric Power University, 2022. doi: 10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2022.000754. [47] JIANG Nan, TU Ziang, PEI Kanglu, et al. RTrust: Toward robust trust evaluation framework for fake news detection in online social networks[J]. World Wide Web, 2024, 27(6): 76. doi: 10.1007/s11280-024-01317-9. [48] SONG Chenguang, SHU Kai, and WU Bin. Temporally evolving graph neural network for fake news detection[J]. Information Processing & Management, 2021, 58(6): 102712. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2021.102712. [49] MATSUMOTO H, YOSHIDA S, and MUNEYASU M. Propagation-based fake news detection using graph neural networks with transformer[C]. 2021 IEEE 10th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Kyoto, Japan, 2021: 19–20. doi: 10.1109/GCCE53005.2021.9621803. [50] YING Xue. An overview of overfitting and its solutions[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1168: 022022. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1168/2/022022. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
