Multi-Objective Optimization of UAV-Assisted Wireless Power Transfer Mobile Edge Computing System
-
摘要: 针对物联网设备计算能力有限、电池供电受限等问题导致的数据处理延迟与能量不足,该文提出一种改进的多目标深度确定性策略梯度算法,用于优化边缘计算系统中无人机资源的调度与分配。该方法将资源优化建模为一个多目标决策问题,综合考虑总数据速率、总收集能量、系统能耗和边缘计算传输时延4个关键指标进行联合优化。无人机采用“飞行-悬停-通信”协议,并在悬停阶段以全双工模式与物联网设备通信,同时考虑推进功耗与非线性能量收集模型。智能体通过环境交互学习最优调度策略,动态响应设备优先级与数据卸载需求,有效降低传输延迟与数据溢出风险。实验结果显示,所提算法在不同场景下均能实现4项性能指标的协同优化,尤其在总能量收集方面始终优于对比方案,验证了该方法在复杂环境下的适应性和有效性。Abstract:
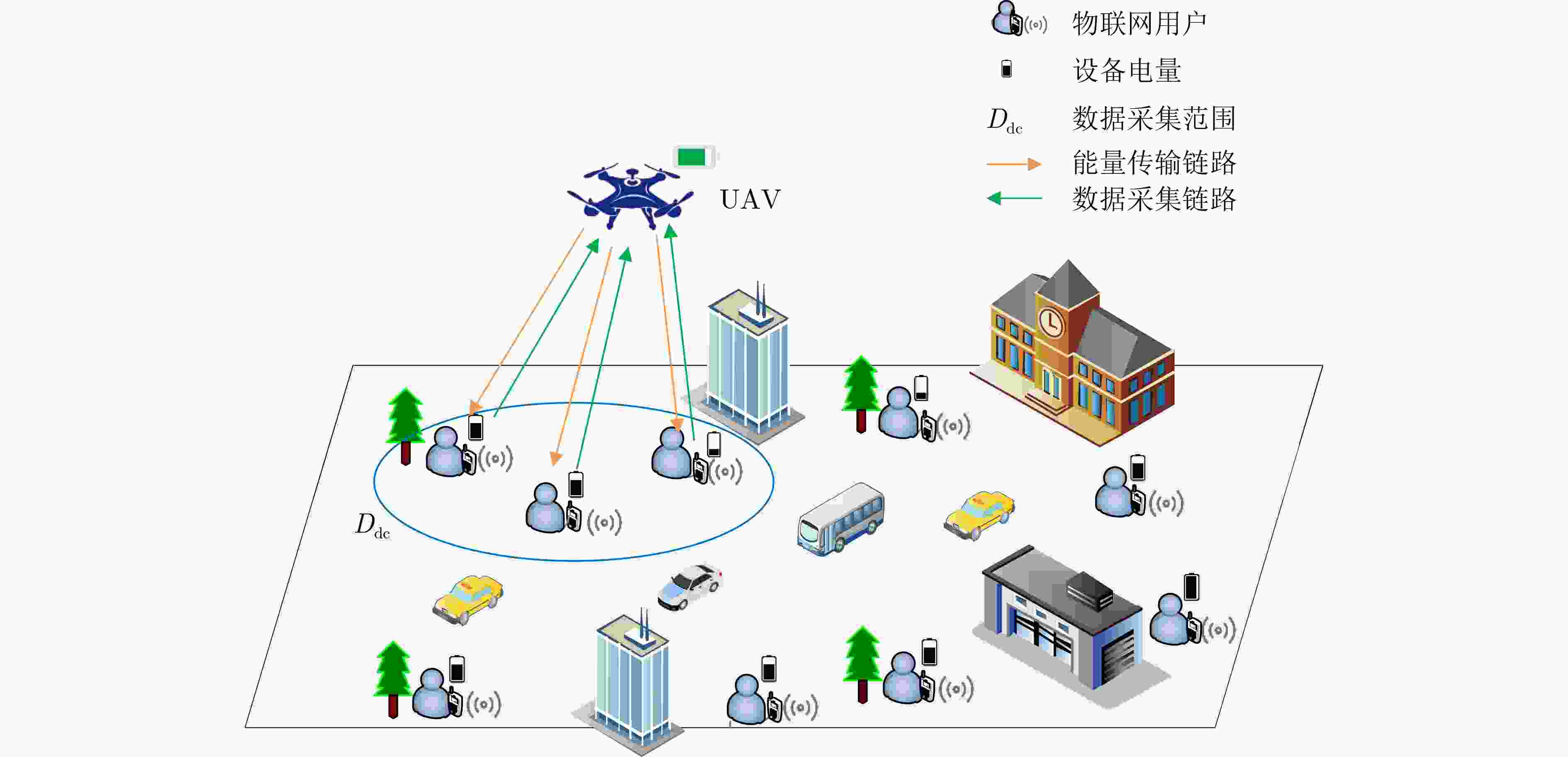
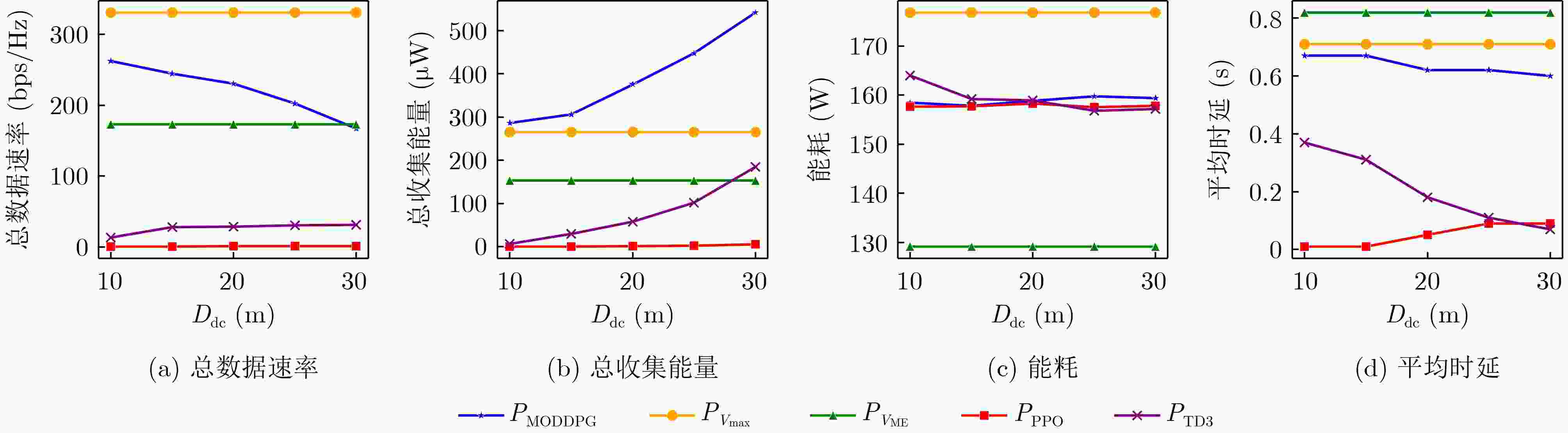
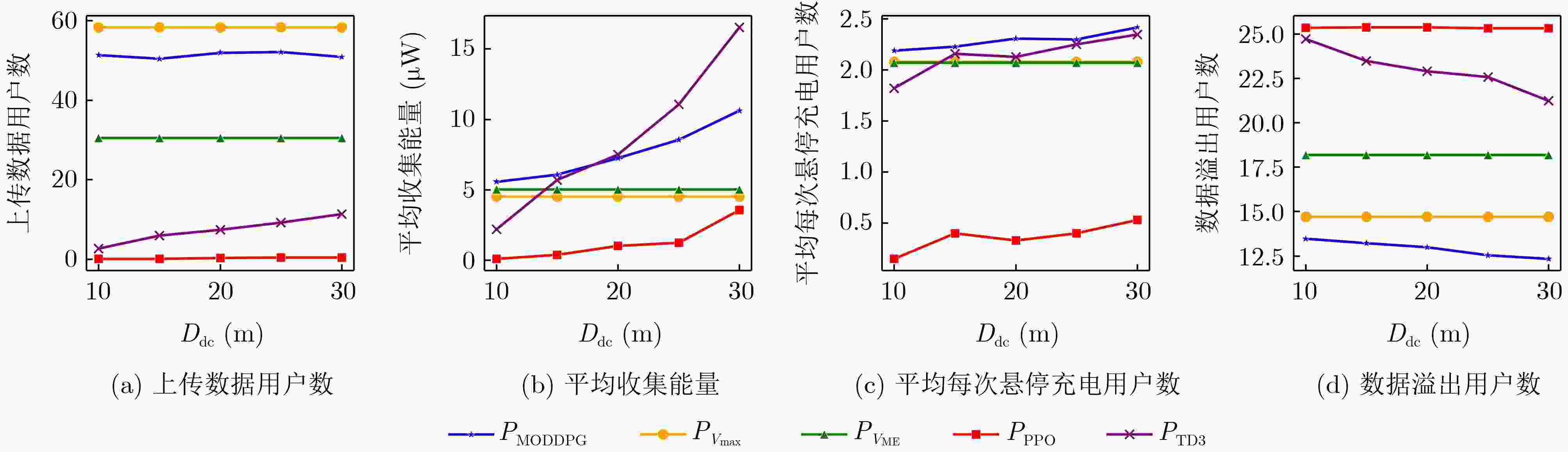
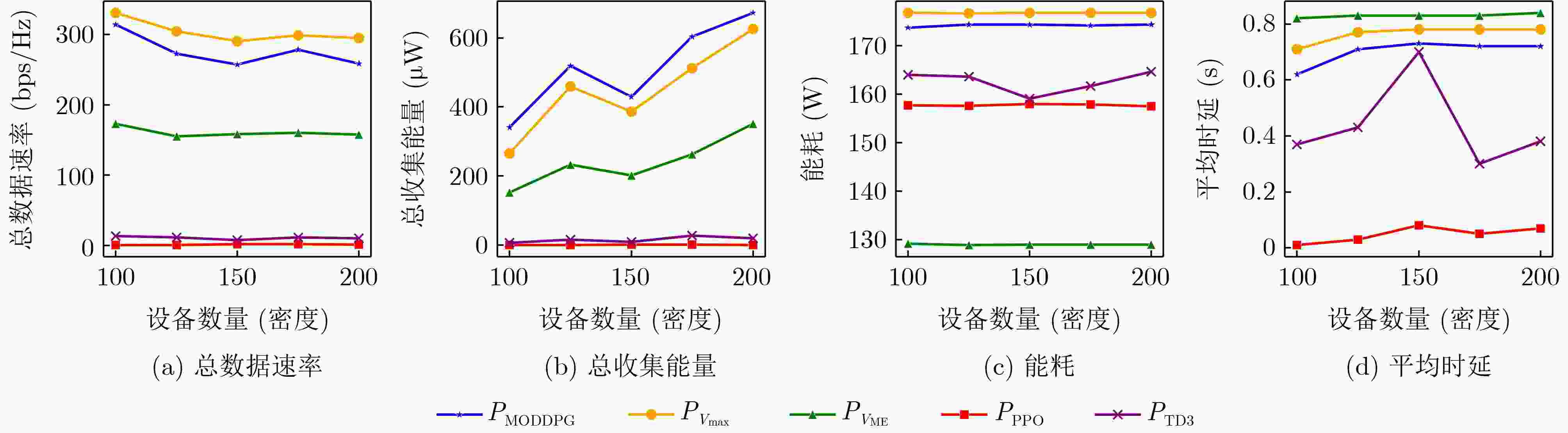
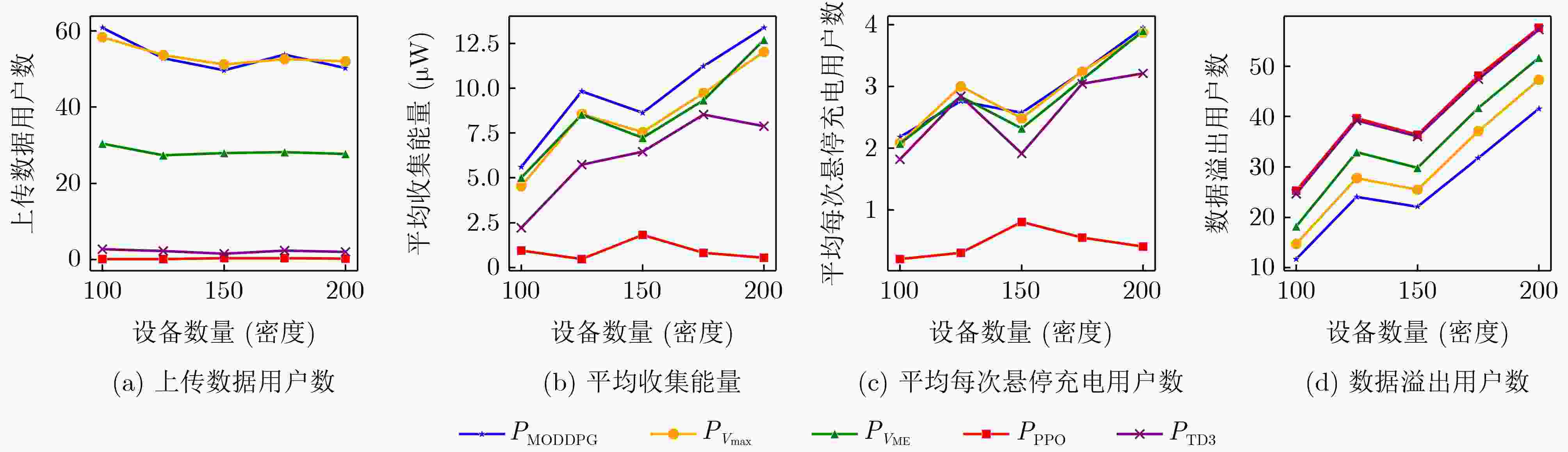
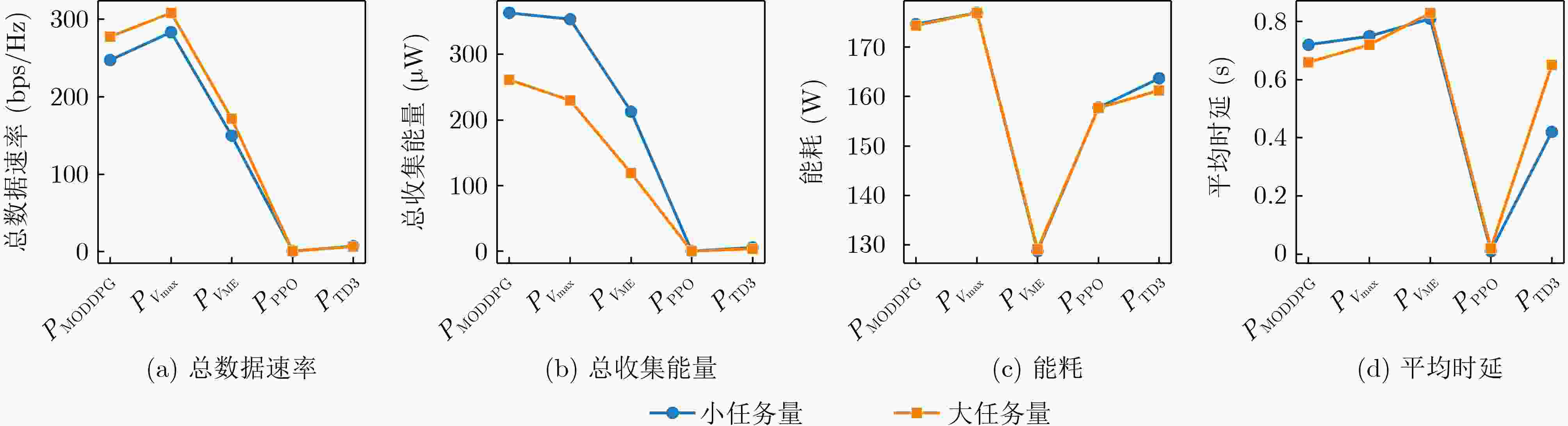
Objective With the rapid growth of data volume at the edge of the Internet of Things (IoT), traditional centralized computing architectures are inadequate to meet real-time processing requirements. Due to the limited computing and storage capabilities of IoT devices, data overflow frequently occurs when handling large volumes of information. Meanwhile, the reliance on battery power exacerbates energy shortages, further hindering continuous operation and data processing. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), with their flexible deployment capabilities, are increasingly being integrated into distributed computing environments to improve IoT data processing efficiency. However, the stochastic and dynamic nature of IoT user demands presents significant challenges for existing resource scheduling schemes, which struggle to effectively coordinate UAV deployments. Moreover, most studies focus on single-objective optimization, making it difficult to simultaneously balance energy harvesting, energy consumption, system latency, and data transmission rates under complex environmental conditions. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an optimization framework for a UAV-assisted, wireless-powered Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) system based on an improved Multi-Objective Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MODDPG) algorithm. The proposed method jointly optimizes task offloading, energy harvesting, flying energy consumption, and system latency, enhancing the overall performance and feasibility of IoT systems. Methods This paper designs a UAV-assisted, wireless-powered MEC system model, where the UAV follows a “fly-hover-communicate” protocol and operates in full-duplex mode during hovering to simultaneously perform data collection and energy transmission. The system model integrates a propulsion energy consumption model and a nonlinear energy harvesting model, formulating a multi-objective optimization problem based on task generation, energy state, and wireless channel conditions of IoT devices. To address this optimization problem, an improved MODDPG algorithm is proposed. A multi-dimensional reward function is constructed to maximize the data transmission rate and total harvested energy while minimizing system energy consumption and task offloading latency within a unified reinforcement learning framework. The agent continuously interacts with the dynamic environment to optimize the UAV’s flight trajectory, task offloading ratio, and energy transmission strategy. The proposed method is implemented and validated through extensive simulations conducted on the Python platform under various experimental settings. Results and Discussions To evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm, comparative experiments are conducted against four other control strategies. The impact of different data collection coverage radii on the proposed strategy is analyzed ( Fig. 3 ,Fig. 4 ). In terms of total data transmission rate, the ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ strategy consistently ranks second to the maximum throughput strategy across all coverage settings, while significantly outperforming the other three strategies (Fig. 3(a) ). Regarding total harvested energy, ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ achieves the highest energy collection in all scenarios, with performance improving as the coverage radius increases (Fig. 3(b) ), demonstrating its capability to enhance energy transmission coverage and system efficiency. In terms of system energy consumption, the ${P_{{V_{\max }}}}$ strategy exhibits the highest energy usage, whereas ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ effectively controls flight energy consumption, maintaining significantly lower energy usage compared to high-speed flying strategies (Fig. 3(c) ). For average latency, ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ achieves lower latency than the $P_{V_{\max}} $ strategy and the $P_{V_{\mathrm{ME}}} $ strategy method in most cases (Fig. 3(d) ). In terms of service performance, ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ demonstrates superior results across multiple metrics, including the number of uploading users, average harvested energy, average number of charged users per hovering instance, and the number of users experiencing data overflow, with particularly significant advantages in energy collection and reducing data overflow rates. (Fig. 4 (a),Fig. 4 (b),Fig. 4 (c),Fig. 4 (d)). In experiments with varying IoT device densities (Fig. 5 ,Fig. 6 ), ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ exhibits strong environmental adaptability. As device density increases and resource competition intensifies, ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ intelligently optimizes flight paths and resource scheduling, maintaining high data transmission rates and energy harvesting levels while effectively suppressing system latency and data overflow. Furthermore, simulation results under different task load scenarios (small and large tasks) (Fig. 7 ) indicate that ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ can flexibly adjust its strategy based on task load variations, maximizing resource utilization. Even under heavy load conditions, the proposed algorithm maintains superior data rates, energy harvesting efficiency, and system stability, effectively coping with dynamic traffic variations. Notably, ${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ not only delivers outstanding optimization performance but also demonstrates significantly faster convergence during training compared to traditional methods such as Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and TD3. Overall,${P_{\rm{MODDPG}}}$ outperforms existing strategies in multi-objective optimization, system energy efficiency enhancement, task scheduling flexibility, and environmental adaptability.Conclusions This paper addresses the critical challenges of energy limitations, data overflow, and high latency in IoT environments by proposing an optimization framework for a UAV-assisted wireless-powered MEC system, which integrates UAV, MEC, and Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) technologies. In the proposed system, IoT devices’ data upload demands are updated in real time, with the UAV sequentially accessing each device based on the priority of its demands using a "fly-hover-communicate" protocol. An improved MODDPG algorithm, based on deep reinforcement learning, is introduced to jointly optimize data transmission rate, energy harvesting, energy consumption, and system latency. Training results demonstrate that, under all optimization scenarios, the proposed scheme consistently achieves the highest total harvested energy while simultaneously balancing the other three optimization objectives. Compared to other baseline strategies, the proposed method exhibits better adaptability by dynamically adjusting to environmental changes and varying device priorities, ultimately achieving coordinated multi-objective optimization and superior performance across different conditions. Future research will focus on extending this work to address multi-UAV cooperative task allocation, resource management, energy harvesting coordination, and multi-UAV trajectory planning. -
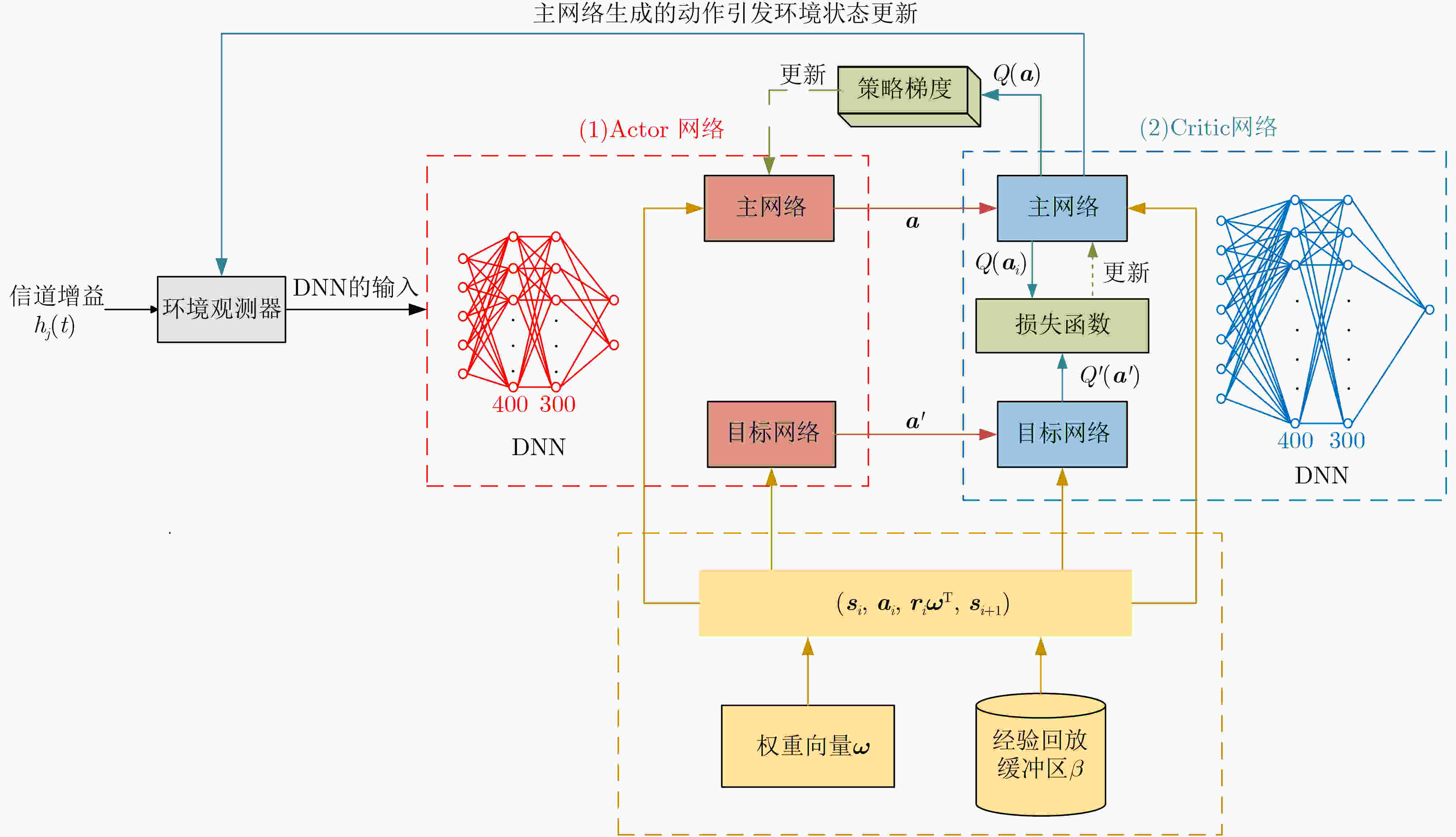
1 MODDPG算法
输入:权重向量${\boldsymbol{\omega}} = [{\omega _{\rm{dc}}},{\omega _{\rm{eh}}},{\omega _{\rm{ec}}},{\omega _\Delta },{\omega _{{\mathrm{aux}}}}]$ 1: 初始化网络、经验回放缓冲区$ \mathcal{B} $,设置${\sigma ^2} = 2.0$,
$ \varepsilon = 0.999\;9 $用于动作探索2: for episode :=1, 2, ···, M do 3: for step t :=1, 2, ···, T do 4: 更新状态空间并观察当前状态${s_t}$ 5: 根据$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}}_{t}{\text{~}}\mathcal{N}(\mu ({{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{t}\mid {\theta }^{\mu }),\epsilon{\sigma }^{2}) $选择动作 6: 执行动作${a_t}$,观察奖励${{\boldsymbol{r}}_t}$,转移到下一个状态$ {{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1}} $ 7: 将经验元组$({{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{r}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1}})$存储到经验回放缓冲区$ \mathcal{B} $中 8: if需要更新then 9: 随机从经验回放缓冲区$ \mathcal{B} $中采样一个小批量数据 10: 计算${y_i}=$
$ \left\{\begin{aligned}& {{\boldsymbol{r}}}_{i}{{\boldsymbol{\omega}} }^{\rm T},\qquad\qquad\quad 对于终止状态{{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{i+1}\\ & {{\boldsymbol{r}}}_{i}{{\boldsymbol{\omega}} }^{{\mathrm{T}}}+\gamma {Q}^{\prime }({{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{i+1},{\mu }^{\prime }({{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{i+1},{\theta }^{{\mu }^{\prime }})|{\theta }^{{Q}^{\prime }}),其他\end{aligned} \right.$11: 通过最小化Critic网络损失更新Critic网络(39) 12: 通过最大化Actor网络损失更新Actor网络(40) 13: 更新目标网络:
${\theta ^{Q'}} \leftarrow \tau {\theta ^Q} + (1 - \tau ){\theta ^{Q'}}$ (41)
${\theta ^{\mu '}} \leftarrow \tau {\theta ^\mu } + (1 - \tau ){\theta ^{\mu '}}$ (42)14: 衰减动作随机性:${\sigma ^2} \leftarrow {\sigma ^2}\varepsilon $ 15: end if 16: end for 17: end for 表 1 仿真参数
参数 数值 参数 数值 带宽$(B)$ 1 MHz 参考信道功率增益$({\gamma _0})$ –30 dB 噪声功率$(\eta _n^2)$ –90 dBm 非视距链路的衰减系数$(\mu )$ 0.2 路径损耗指数$(\tilde a)$ 2.3 视距概率的参数$(a,b)$ 10, 0.6 叶片轮廓功率$({P_0})$ 79.86 诱导功率$({P_i})$ 88.63 旋翼叶片的尖端速度$({U_{{\text{tip}}}})$ 120 m/s 悬停时旋翼诱导的平均速度$({v_0})$ 4.03 机身阻力系数$({d_0})$ 0.6 空气密度$(\rho )$ 1.225 km/m3 旋翼实度$(s)$ 0.05 旋翼圆盘面积$(A)$ 0.503 m2 最大直流输出功率$ ({P_{{\mathrm{limit}}}}) $ 9.079 μW 能量收集模型的参数$(c,d)$ 47083 , 2.9 μWUAV的计算能力$({f_{{\text{UAV}}}})$ 1.2 GHz 处理每bit所需的CPU周期数$(s)$ 1000 cycle/bit用户计算能力$({f_j})$ 0.6 GHz 表 2 网络参数
参数 数值 参数 数值 Actor网络结构 [400, 300] 经验回放缓冲区大小 8000 Critic网络结构 [400, 300] 批处理大小 64 训练轮次 1600 初始探索方差 2.0 Actor学习率 10–3 最终探索方差 0.1 Critic学习率 10–3 软更新参数 0.001 奖励折扣因子 0.9 -
[1] 董裕民, 张静, 谢昌佐, 等. 云边端架构下边缘智能计算关键问题综述: 计算优化与计算卸载[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 765–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230390.DONG Yumin, ZHANG Jing, XIE Changzuo, et al. A survey of key issues in edge intelligent computing under cloud-edge-terminal architecture: Computing optimization and computing offloading[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 765–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230390. [2] RAEISI-VARZANEH M, DAKKAK O, HABBAL A, et al. Resource scheduling in edge computing: Architecture, taxonomy, open issues and future research directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 25329–25350. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3256522. [3] LOUTFI S I, SHAYEA I, TURELI U, et al. An overview of mobility awareness with mobile edge computing over 6G network: Challenges and future research directions[J]. Results in Engineering, 2024, 23: 102601. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102601. [4] KONG Linghe, TAN Jinlin, HUANG Junqin, et al. Edge-computing-driven internet of things: A survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(8): 174. doi: 10.1145/3555308. [5] PRAUZEK M, KUCOVA T, KONECNY J, et al. IoT sensor challenges for geothermal energy installations monitoring: A survey[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(12): 5577. doi: 10.3390/s23125577. [6] DIAO Xianbang, CAI Yueming, YU Baoquan, et al. Location and complex status update strategy optimization in UAV-assisted IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(13): 11588–11604. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3244541. [7] BHAROT N, GHANGARE N, and VERMA P. Optimizing transfer efficiency in multi-cloud storage systems with edge and fog computing[C/OL]. 2023 IEEE 2nd Industrial Electronics Society Annual On-Line Conference (ONCON), 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ONCON60463.2023.10431110. [8] MOLOUDIAN G, HOSSEINIFARD M, KUMAR S, et al. RF energy harvesting techniques for battery-less wireless sensing, industry 4.0, and internet of things: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(5): 5732–5745. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3352402. [9] BAIDYA T, NABI A, and MOH S. Trajectory-aware offloading decision in UAV-aided edge computing: A comprehensive survey[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(6): 1837. doi: 10.3390/s24061837. [10] LI Min, LI Hao, MA Pengfei, et al. Energy maximization for ground nodes in UAV-enabled wireless power transfer systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(19): 17096–17109. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3274549. [11] ROSABAL O M, LÓPEZ O L A, ALVES H, et al. Sustainable RF wireless energy transfer for massive IoT: Enablers and challenges[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 133979–133992. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3337214. [12] GU Xiaohui and ZHANG Guo’an. A survey on UAV-assisted wireless communications: Recent advances and future trends[J]. Computer Communications, 2023, 208: 44–78. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2023.05.013. [13] DAI Minghui, HUANG Ning, WU Yuan, et al. Unmanned-aerial-vehicle-assisted wireless networks: Advancements, challenges, and solutions[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(5): 4117–4147. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3230786. [14] WANG Zemin, PING Jianmiao, FU Junwei, et al. Research on the design of power supply gateway and wireless power transmission based on edge computing[J]. International Journal of Distributed Systems and Technologies, 2024, 15(1): 1–18. doi: 10.4018/IJDST.340941. [15] LU Weidang, XU Xiaohan, YE Qibin, et al. Power optimisation in UAV‐assisted wireless powered cooperative mobile edge computing systems[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(15): 2516–2523. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2019.1063. [16] LI Qian, SHI Liqin, ZHANG Zhongjun, et al. Resource allocation in UAV-enabled wireless-powered MEC networks with hybrid passive and active communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(3): 2574–2588. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3214539. [17] WANG Xinran, WU Peng, HU Yulin, et al. Joint trajectories and resource allocation design for multi-UAV-assisted wireless power transfer with nonlinear energy harvesting[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(6): 354. doi: 10.3390/drones7060354. [18] GOU Xiaogang, SUN Zhaojie, and HUANG Kaiyuan. UAV-aided dual-user wireless power transfer: 3D trajectory design and energy optimization[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(6): 2994. doi: 10.3390/s23062994. [19] LI Bin, LIU Wenshuai, XIE Wancheng, et al. Energy-efficient task offloading and trajectory planning in UAV-enabled mobile edge computing networks[J]. Computer Networks, 2023, 234: 109940. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109940. [20] NGUYEN G H, NGUYEN A N, LE H H, et al. Energy harvesting and computation offloading for UAV-assisted MEC with NOMA in IoT network[M]. SHARMA H, SHRIVASTAVA V, TRIPATHI A K, et al. Communication and Intelligent Systems. Singapore, Singapore: Springer, 2024: 381–392. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-2082-8_27. [21] KIM J, HONG E, JUNG J, et al. Energy minimization in reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted unmanned aerial vehicle-enabled wireless powered mobile edge computing systems with rate-splitting multiple access[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(12): 688. doi: 10.3390/drones7120688. [22] LAKEW D S, TRAN A T, MASOOD A, et al. A review on AI-driven aerial access networks: Challenges and open research issues[C]. 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Bali, Indonesia, 2023: 718–723. doi: 10.1109/ICAIIC57133.2023.10067056. [23] ADIL M, SONG Houbing, MASTORAKIS S, et al. UAV-assisted IoT applications, cybersecurity threats, AI-enabled solutions, open challenges with future research directions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(4): 4583–4605. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3309548. [24] BAI Yu, ZHAO Hui, ZHANG Xin, et al. Toward autonomous multi-UAV wireless network: A survey of reinforcement learning-based approaches[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(4): 3038–3067. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3323344. [25] FRATTOLILLO F, BRUNORI D, and IOCCHI L. Scalable and cooperative deep reinforcement learning approaches for multi-UAV systems: A systematic review[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(4): 236. doi: 10.3390/drones7040236. [26] AMODU O A, JARRAY C, MAHMOOD R A R, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for AoI minimization in UAV-aided data collection for WSN and IoT applications: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 108000–108040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3425497. [27] AHMAD S, ZHANG Jinling, NAUMAN A, et al. Deep-EERA: DRL-based energy-efficient resource allocation in UAV-empowered beyond 5G networks[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2025, 30(1): 418–432. doi: 10.26599/TST.2024.9010071. [28] LIN Na, FAN Yanbo, ZHAO Liang, et al. GREEN: A global energy efficiency maximization strategy for multi-UAV enabled communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(12): 7104–7120. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3207791. [29] HOANG L T, NGUYEN C T, and PHAM A T. Deep reinforcement learning-based online resource management for UAV-assisted edge computing with dual connectivity[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(6): 2761–2776. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2023.3263538. [30] ZENG Yong, XU Jie, and ZHANG Rui. Energy minimization for wireless communication with rotary-wing UAV[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(4): 2329–2345. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2902559. [31] KHALID R, SHAH Z, NAEEM M, et al. Computational efficiency maximization for UAV-assisted MEC networks with energy harvesting in disaster scenarios[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(5): 9004–9018. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3322001. [32] BEN HALIMA N. Non orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) using a nonlinear energy harvesting model[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2024, 135(4): 2165–2175. doi: 10.1007/s11277-024-11129-9. [33] WANG Yunpeng, FANG Weiwei, DING Yi, et al. Computation offloading optimization for UAV-assisted mobile edge computing: A deep deterministic policy gradient approach[J]. Wireless Networks, 2021, 27(4): 2991–3006. doi: 10.1007/s11276-021-02632-z. [34] XU Bin, KUANG Zhufang, GAO Jie, et al. Joint offloading decision and trajectory design for UAV-enabled edge computing with task dependency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(8): 5043–5055. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3231408. [35] HICKLING T, ZENATI A, AOUF N, et al. Explainability in deep reinforcement learning: A review into current methods and applications[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(5): 125. doi: 10.1145/3623377. [36] HUANG Hao, CHAI Zhengyi, SUN Baoshan, et al. Multiobjective deep reinforcement learning for computation offloading and trajectory control in UAV-base-station-assisted MEC[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(19): 31805–31821. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3420884. [37] SUMIEA E H, ABDULKADIR S J, ALHUSSIAN H S, et al. Deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm: A systematic review[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(9): e30697. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30697. [38] MIAO Jiansong, BAI Shanling, MUMTAZ S, et al. Utility-oriented optimization for video streaming in UAV-aided MEC network: A DRL approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2024, 8(2): 878–889. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2024.3352173. [39] PARK J, LEE H, EOM S, et al. UAV-aided wireless powered communication networks: Trajectory optimization and resource allocation for minimum throughput maximization[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 134978–134991. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941278. [40] YU Yu, TANG Jie, HUANG Jiayi, et al. Multi-objective optimization for UAV-assisted wireless powered IoT networks based on extended DDPG algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(9): 6361–6374. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3089476. [41] AUNG P S, KANG S M, and HONG C S. Proximal policy optimization for energy-efficient MEC systems with STAR-RIS assistance[C]. 2024 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2024: 239–244. doi: 10.1109/ICOIN59985.2024.10572179. [42] ZHAO Liang, YAO Yujun, GUO Jianmeng, et al. Collaborative computation offloading and wireless charging scheduling in multi-UAV-assisted MEC networks: A TD3-based approach[J]. Computer Networks, 2024, 251: 110615. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110615. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
