Personalized Tensor Decomposition Based High-order Complementary Cloud API Recommendation
-
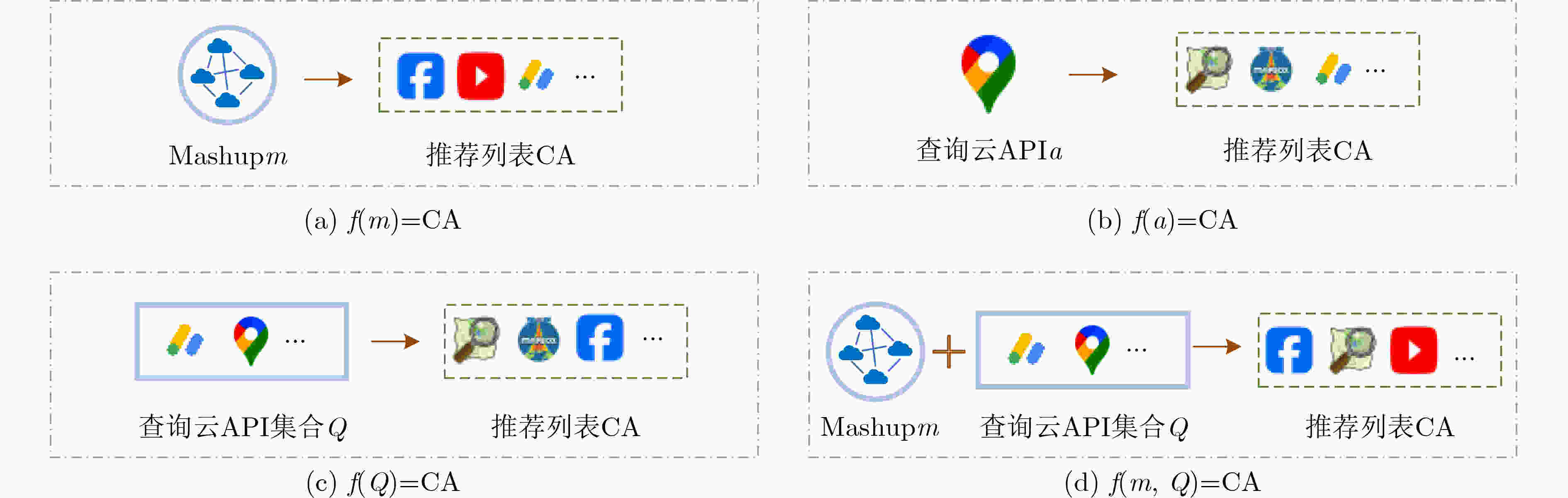
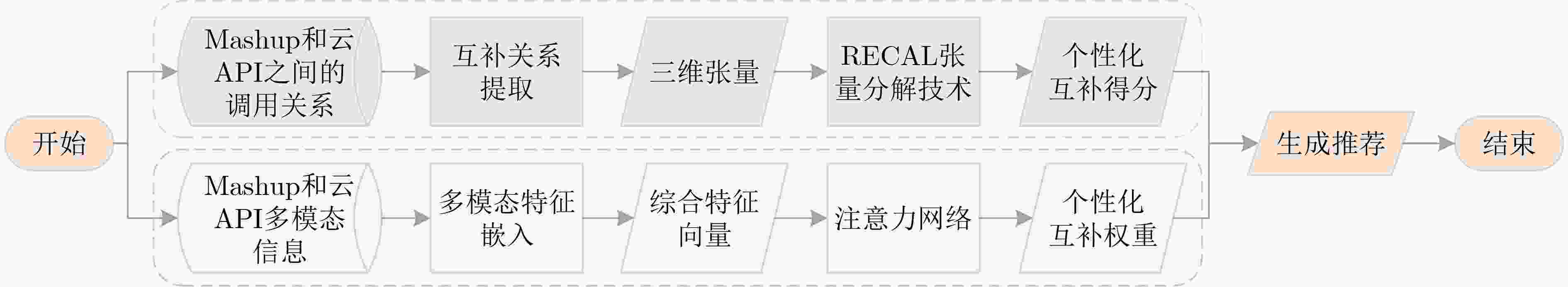
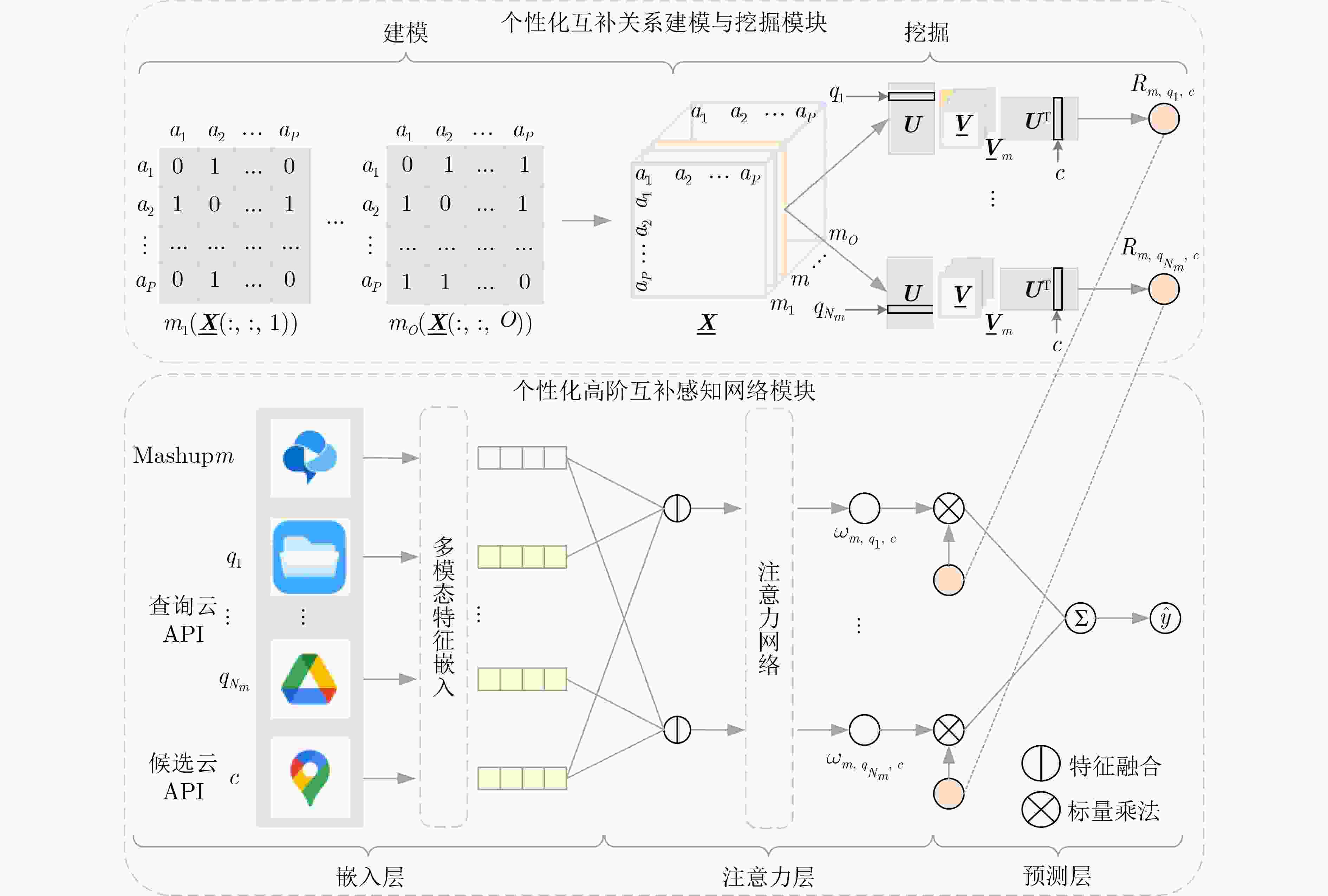
摘要: 在万物互联的云时代,云应用程序编程接口(API)是数字经济建设和服务化软件开发的关键数字基础设施。然而,云API数量的持续增长给用户决策和推广带来挑战,设计有效的推荐方法成为亟待解决的重要问题。现有研究多利用调用偏好、搜索关键词或二者结合进行建模,主要解决为给定Mashup推荐合适云API的问题,未考虑开发者对个性化高阶互补云API的实际需求。该文提出一种基于个性化张量分解的高阶互补云API推荐方法(Personalized Tensor Decomposition based High-order Complementary cloud API Recommendation, PTDHCR)。首先,将Mashup与云API之间的调用关系,以及云API与云API之间的互补关系建模为三维张量,并利用RECAL张量分解技术对这两种关系进行共同学习,以挖掘云API之间的个性化非对称互补关系。然后,考虑到不同互补关系对推荐结果的影响程度不同,构建个性化高阶互补感知网络,充分利用Mashup、查询云API以及候选云API的多模态特征,动态计算Mashup对不同查询和候选云API之间互补关系的关注程度。在此基础上,将个性化互补关系拓展到高阶,得到候选云API与查询云API集合的整体个性化互补性。最后,利用两个真实云API数据集进行实验,结果表明,相较于传统方法,PTDHCR在挖掘个性化互补关系和推荐方面具有较大的优势。Abstract:
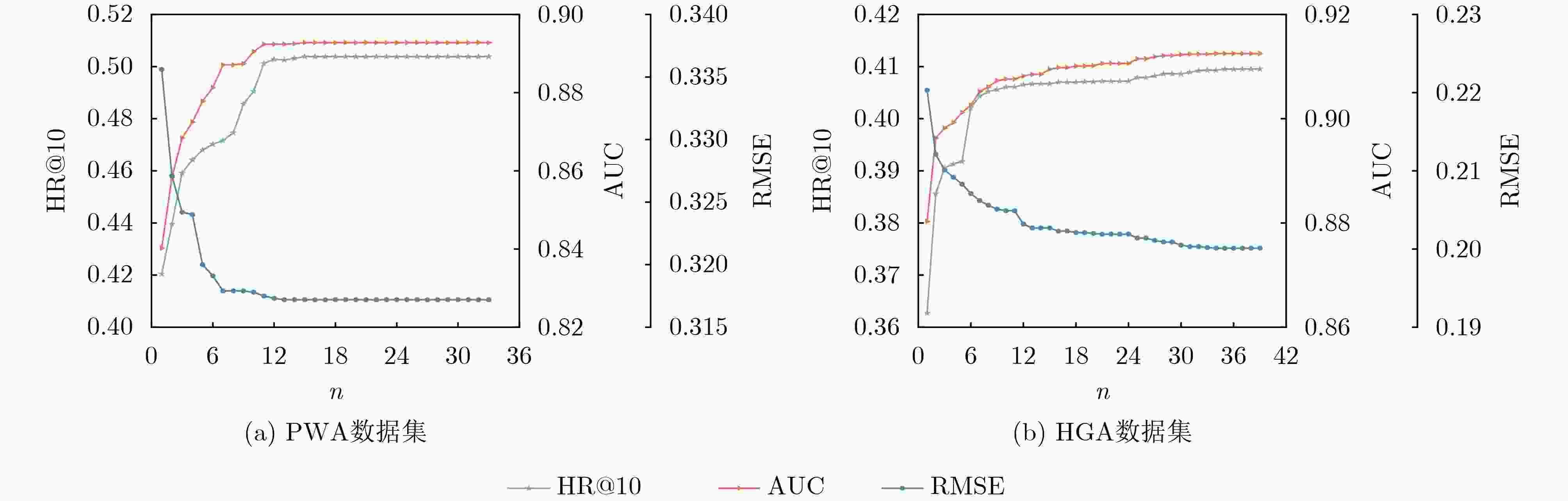
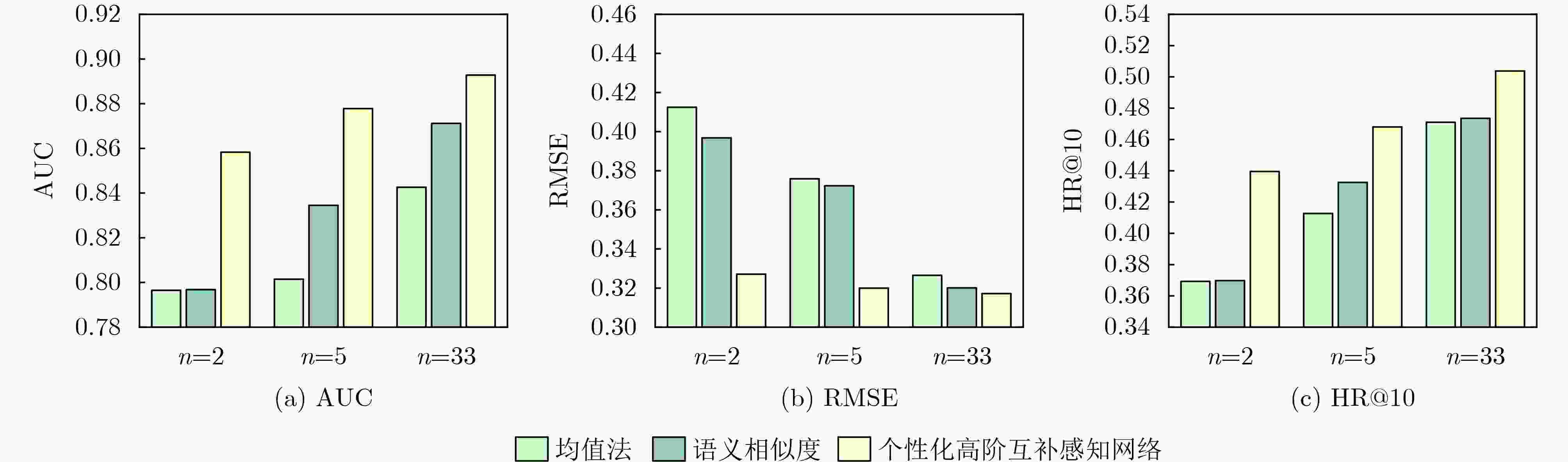
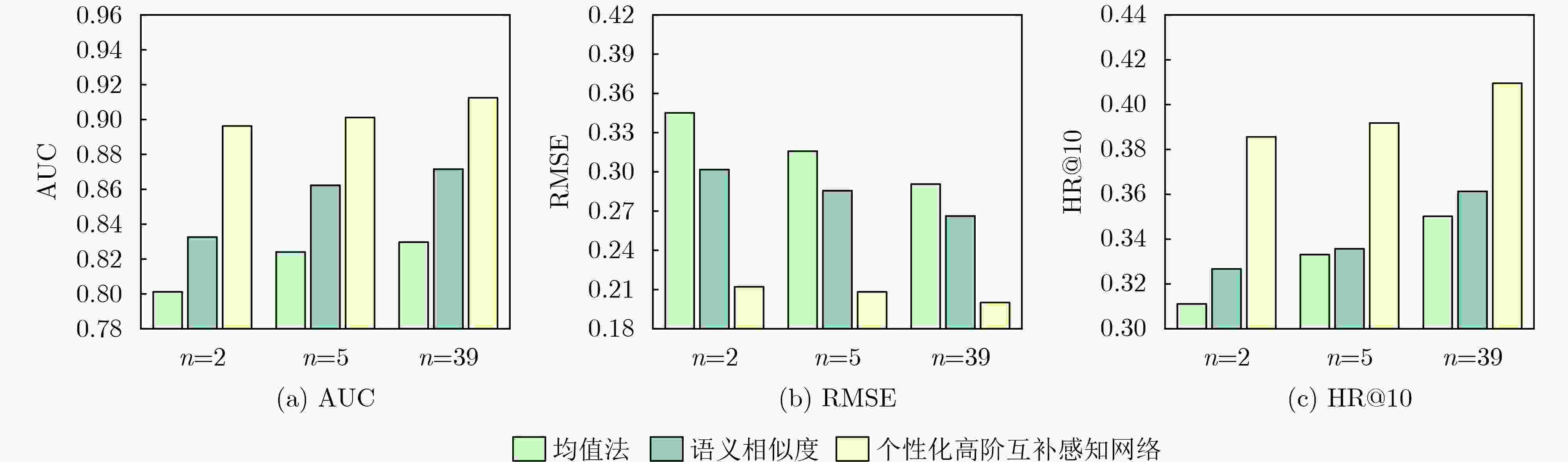
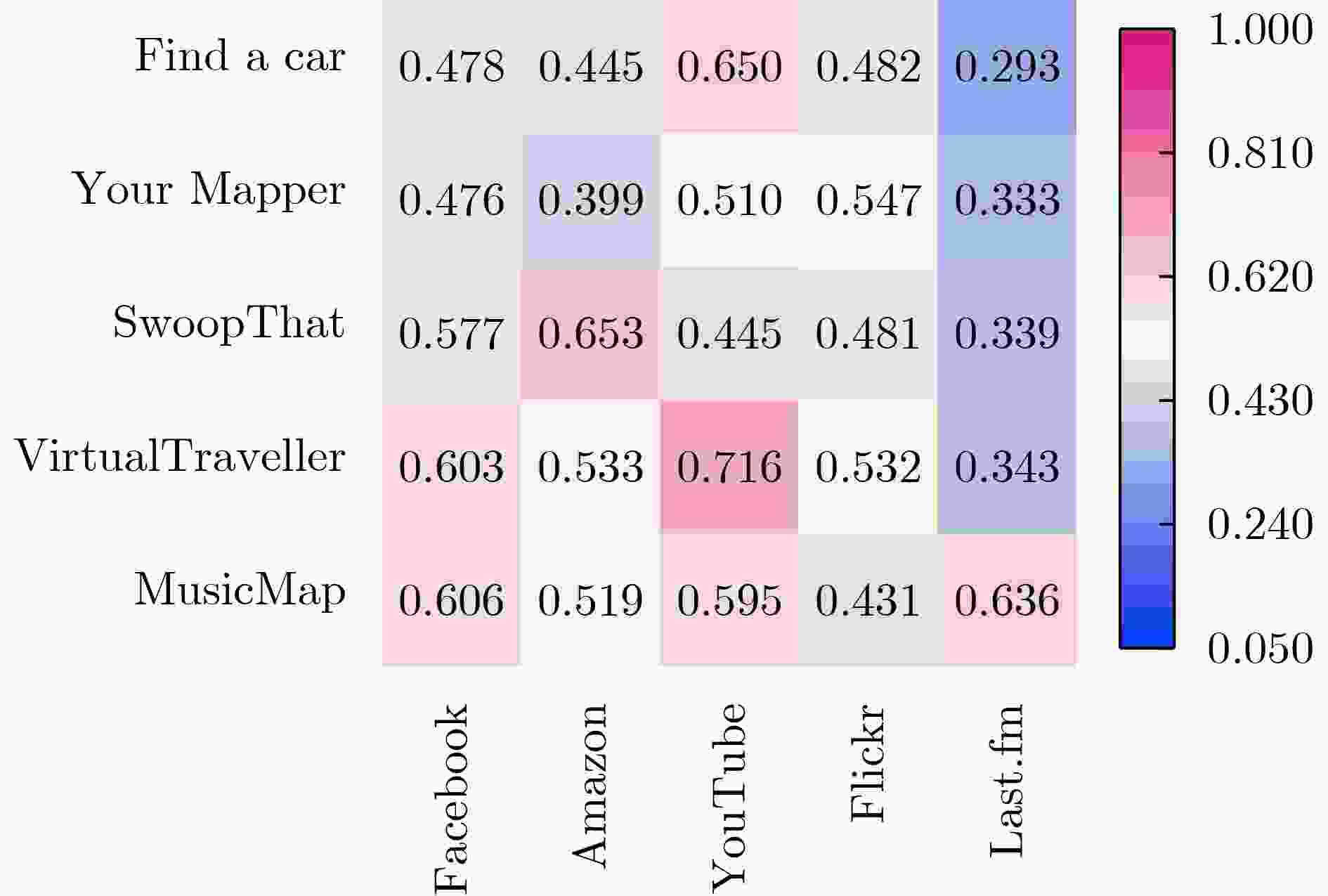
Objective With the emergence of the cloud era in the Internet of Things, cloud Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) have become essential for managing data element dynamics, facilitating AI algorithm implementation, and coordinating access to computing resources. Cloud APIs have developed into critical digital infrastructure that supports the digital economy and the operation of service-oriented software. However, the rapid expansion of cloud APIs has impacted users’ decision-making processes and complicated the promotion of cloud APIs. This situation underscores the urgent need for effective cloud API recommendation methods to foster the development of the API economy and encourage the widespread adoption of cloud APIs. While existing research has focused on modeling invocation preferences, search keywords, or a combination of both to recommend suitable cloud APIs for a given Mashup, it does not address the need for personalized high-order complementary cloud APIs in practical software development. Personalized high-order complementary cloud API recommendation aims to provide developers with APIs that align with their personalized invocation preferences and complement the other APIs in their query set, thereby addressing the developers’ joint interests. Methods To address this issue, a Personalized Tensor Decomposition-based High-order Complementary cloud API Recommendation (PTDHCR) method is proposed. First, the invocation relationships between Mashups and cloud APIs, as well as the complementary relationships between cloud APIs, are represented as a three-dimensional tensor. RECAL tensor decomposition is applied to jointly learn and uncover personalized asymmetric complementary relationships between cloud APIs. Second, a personalized high-order complementary perception network is designed to account for the varying influence of different complementary relationships on recommendations. This network dynamically calculates the attention of a Mashup to the complementary relationships between different query and candidate cloud APIs using the multi-modal features of the Mashup, query cloud APIs, and candidate cloud APIs. Finally, the personalized complementary relationships are extended to higher orders, yielding a comprehensive personalized complementarity between candidate cloud APIs and the query set. Results and Discussions Extensive experiments are conducted on two real cloud API datasets. First, PTDHCR is compared with 11 baseline methods suitable for personalized high-order complementary cloud API recommendation. The experimental results ( Tables 2 and3 ) show that, on the PWA dataset, PTDHCR outperforms the best baseline by 0.12%, 0.14%, 1.46%, and 2.93% in terms of AUC. HR@10 improves by 0.91%, 1.01%, 3.45%, and 10.84%, while RMSE decreases by 0.33%, 0.7%, 1.36%, and 2.67%. PTDHCR also performs well on the HGA dataset, significantly outperforming the baseline methods in AUC, HR@10, and RMSE metrics. Second, experiments are conducted with varying complementary thresholds to evaluate PTDHCR’s performance at different complementary orders. The experimental results (Figure 4 ) indicate that PTDHCR’s recommendation performance improves progressively as the complementary order increases. This improvement is attributed to the method’s ability to incorporate more complementary information, thereby enhancing its recommendation capability. Next, a comparison experiment is performed to assess whether the personalized high-order complementary perception network can better capture high-order complementary relationships than the mean-value and semantic similarity-based methods. The experimental results (Figures 5 and6 ) demonstrate that the personalized high-order complementary perception network outperforms other methods. This is due to the network’s ability to consider the contribution of different complementary relationships and dynamically compute the Mashup’s attention to each complementary relationship. Finally, an example is provided, evaluating the predicted probability of a Mashup invoking other candidate cloud APIs, given that it has already invoked the “Google Maps API” and the “Google AdSense API.” This example illustrates the personalized nature of the high-order complementary cloud API recommendation achieved by the PTDHCR method.Conclusions Existing methods fail to address the actual needs of developers for personalized high-order complementary cloud APIs in the development of service-oriented software. This paper defines the recommendation problem of personalized high-order complementary cloud APIs and proposes a solution. A personalized high-order complementary cloud API recommendation method based on tensor decomposition is introduced. Initially, the invocation relationships between Mashups and cloud APIs, as well as the complementary relationships between cloud APIs, are modeled as a three-dimensional tensor. RECAL tensor decomposition technology is then applied to jointly learn and explore the personalized asymmetric complementary relationships. Additionally, a high-order complementary perception network is constructed to dynamically compute Mashups’ attention towards various complementary relationships, which extends these relationships to higher orders. Experimental results show that PTDHCR outperforms state-of-the-art cloud API recommendation methods on real cloud API datasets. PTDHCR offers an effective approach to address the cloud API selection problem and contributes to the healthy development and popularization of the cloud API economy. -
表 1 超参数设置
数据集\参数 U的维度d 正则化参数λ 特征嵌入维度L 正负样本比r 学习率lr 训练批次bsize 训练步数steps PWA 64 0.001 128 3 0.0001 512 10000 HGA 32 0.002 64 3 0.0001 512 20000 表 2 基于PWA数据集的方法比较结果
方法 n=1 n=2 n=5 n=33 (最高阶) AUC RMSE HR@10 AUC RMSE HR@10 AUC RMSE HR@10 AUC RMSE HR@10 Random - - 0.0179 - - 0.0235 - - 0.1052 - - 0.1986 Popular-N - - 0.3423 - - 0.3496 - - 0.3517 - - 0.3702 FM 0.7772 0.3656 0.3905 0.8442 0.3372 0.4221 0.8423 0.3312 0.4342 0.8422 0.3307 0.4202 WDL 0.8096 0.3585 0.3958 0.8481 0.3353 0.4251 0.8551 0.3322 0.4473 0.8564 0.3332 0.4303 AFM 0.8206 0.3407 0.4158 0.8481 0.3372 0.4232 0.8562 0.3353 0.4377 0.8571 0.3361 0.4307 DCN 0.8190 0.3512 0.4086 0.8512 0.3350 0.4320 0.8565 0.3297 0.4392 0.8531 0.3397 0.4351 xDeepFM 0.8162 0.3513 0.4024 0.8515 0.3316 0.4291 0.8640 0.3298 0.4493 0.8615 0.3298 0.4474 AutoInt 0.8138 0.3526 0.3968 0.8514 0.3332 0.4265 0.8535 0.3317 0.4425 0.8620 0.3383 0.4504 DCNv2 0.8295 0.3573 0.4162 0.8530 0.3342 0.4317 0.8652 0.3244 0.4524 0.8614 0.3259 0.4518 EDCN 0.8066 0.3602 0.3954 0.8544 0.3294 0.4351 0.8644 0.3300 0.4520 0.8645 0.3274 0.4510 FinalMLP 0.8392 0.3367 0.4166 0.8571 0.3321 0.4292 0.8637 0.3291 0.4480 0.8674 0.3261 0.4544 PTDHCR 0.8402 0.3356 0.4204 0.8583 0.3271 0.4395 0.8778 0.3200 0.4680 0.8928 0.3172 0.5038 提升 0.12% –0.33% 0.91% 0.14% –0.70% 1.01% 1.46% –1.36% 3.45% 2.93% –2.67% 10.87% 表 3 基于HGA数据集的方法比较结果
方法 n=1 n=2 n=5 n=39 (最高阶) AUC RMSE HR@10 AUC RMSE HR@10 AUC RMSE HR@10 AUC RMSE HR@10 Random - - 0.0125 - - 0.0176 - - 0.0182 - - 0.1025 Popular-N - - 0.2014 - - 0.2078 - - 0.2142 - - 0.2259 FM 0.8706 0.2376 0.3286 0.8711 0.2337 0.3415 0.8752 0.2306 0.3535 0.8702 0.2215 0.3532 WDL 0.8748 0.2267 0.3482 0.8769 0.2209 0.3619 0.8771 0.2200 0.3685 0.8701 0.2159 0.3671 AFM 0.8750 0.2269 0.3489 0.8762 0.2269 0.3603 0.8784 0.2262 0.3692 0.8715 0.2203 0.3686 DCN 0.8729 0.2351 0.3369 0.8759 0.2235 0.3701 0.8811 0.2207 0.3712 0.8769 0.2164 0.3701 xDeepFM 0.8759 0.2275 0.3554 0.8712 0.2248 0.3692 0.8802 0.2212 0.3702 0.8812 0.2201 0.3692 AutoInt 0.8734 0.2307 0.3461 0.8693 0.2268 0.3732 0.8792 0.2207 0.3738 0.8732 0.2196 0.3731 DCNv2 0.8745 0.2280 0.3472 0.8765 0.2265 0.3715 0.8796 0.2206 0.3721 0.8724 0.2156 0.3719 EDCN 0.8749 0.2269 0.3479 0.8891 0.2207 0.3753 0.8812 0.2198 0.3738 0.8759 0.2185 0.3729 FinalMLP 0.8752 0.2262 0.3569 0.8803 0.2209 0.3749 0.8816 0.2196 0.3742 0.8802 0.2162 0.3737 PTDHCR 0.8803 0.2203 0.3627 0.8963 0.2121 0.3856 0.9012 0.2083 0.3918 0.9125 0.2001 0.4095 提升 0.50% –2.61% 1.63% 0.81% –3.90% 2.74% 2.22% –5.15% 4.70% 3.67% –7.19% 9.58% -
[1] WU Di, ZHANG Peng, HE Yi, et al. A double-space and double-norm ensembled latent factor model for highly accurate web service QoS prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2023, 16(2): 802–814. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2022.3178543. [2] KALLA D, SMITH N, KURAKU S, et al. Study and analysis of chat GPT and its impact on different fields of study[J]. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology, 2023, 8(3): 827–833. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.10250455. [3] CHEN Zhen, BAO Taiyu, QI Wenchao, et al. Poisoning QoS-aware cloud API recommender system with generative adversarial network attack[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238: 121630. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121630. [4] ZHANG Yiwen, WANG Kaibin, HE Qiang, et al. Covering-based web service quality prediction via neighborhood-aware matrix factorization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2021, 14(5): 1333–1344. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2019.2891517. [5] NGUYEN M, YU Jian, NGUYEN T, et al. Attentional matrix factorization with context and co-invocation for service recommendation[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 186: 115698. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115698. [6] ALMARIMI N, OUNI A, BOUKTIF S, et al. Web service API recommendation for automated mashup creation using multi-objective evolutionary search[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 85: 105830. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105830. [7] LI Hongchao, LIU Jianxun, CAO Buqing, et al. Integrating tag, topic, co-occurrence, and popularity to recommend web APIs for mashup creation[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 84–91. doi: 10.1109/SCC.2017.19. [8] WU Hao, DUAN Yunhao, YUE Kun, et al. Mashup-oriented web API recommendation via multi-model fusion and multi-task learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2022, 15(6): 3330–3343. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2021.3098756. [9] SANG Chunyan, DENG Xinyan, and LIAO Shigen. Mashup-oriented web API recommendation via full-text semantic mining of developer requirements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2023, 16(4): 2755–2768. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2023.3245652. [10] HE Pengfei, QI Wenchao, LIU Xiaowei, et al. Seizing the long tail: Neural complementary recommendation for cloud API delivery[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Smartworld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Scalable Computing & Communications, Digital Twin, Privacy Computing, Metaverse, Autonomous & Trusted Vehicles, Haikou, China, 2022: 1954–1961. doi: 10.1109/SmartWorld-UIC-ATC-ScalCom-DigitalTwin-PriComp-Metaverse56740.2022.00283. [11] 陈真, 谢登辉, 王小龙, 等. 基于概率逻辑推理的高阶互补云API推荐方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2024, 47(8): 1922–1948. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.01922.CHEN Zhen, XIE Denghui, WANG Xiaolong, et al. Probabilistic logic reasoning for high-order complementary cloud API recommendation[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2024, 47(8): 1922–1948. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.01922. [12] ENTEZARI N, PAPALEXAKIS E E, WANG Haixun, et al. Tensor-based complementary product recommendation[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Orlando, USA, 2021: 409–415. doi: 10.1109/BigData52589.2021.9671938. [13] BIBAS K, SHALOM O S, and JANNACH D. Semi-supervised adversarial learning for complementary item recommendation[C]. Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, Austin, USA, 2023: 1804–1812. doi: 10.1145/3543507.3583462. [14] ZHANG Yin, LU Haokai, NIU Wei, et al. Quality-aware neural complementary item recommendation[C]. Proceedings of the 12th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 77–85. doi: 10.1145/3240323.3240368. [15] HAO Junheng, ZHAO Tong, LI Jin, et al. P-companion: A principled framework for diversified complementary product recommendation[C]. Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, 2020: 2517–2524. doi: 10.1145/3340531.3412732. [16] YAN An, DONG Chaosheng, GAO Yan, et al. Personalized complementary product recommendation[C]. Proceedings of the Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 2022: 146–151. doi: 10.1145/3487553.3524222. [17] WANG Ke, ZHU Yanmin, ZANG Tianzi, et al. Review-enhanced hierarchical contrastive learning for recommendation[C]. Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 9107–9115. doi: 10.1609/AAAI.V38I8.28761. [18] LIU Xiaowei, SUN Mengmeng, CHEN Wenhui, et al. Complementarity analysis of cloud API ecosystems: An empirical study on ProgrammableWeb and Huawei AppGallery datasets[C]. Proceedings of 2024 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, Shenzhen, China, 2024: 364–370. doi: 10.1109/ICWS62655.2024.00058. [19] RENDLE S. Factorization machines[C]. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Sydney, Australia, 2010: 995–1000. doi: 10.1109/ICDM.2010.127. [20] CHENG H T, KOC L, HARMSEN J, et al. Wide & deep learning for recommender systems[C]. Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Deep Learning for Recommender Systems, Boston, USA, 2016: 7–10. doi: 10.1145/2988450.2988454. [21] XIAO Jun, YE Hao, HE Xiangnan, et al. Attentional factorization machines: Learning the weight of feature interactions via attention networks[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 3119–3124. doi: 10.24963/IJCAI.2017/435. [22] WANG Ruoxi, FU Bin, FU Gang, et al. Deep & cross network for ad click predictions[C]. Proceedings of the ADKDD’17, Halifax, Canada, 2017: 12. doi: 10.1145/3124749.3124754. [23] LIAN Jianxun, ZHOU Xiaohuan, ZHANG Fuzheng, et al. xDeepFM: Combining explicit and implicit feature interactions for recommender systems[C]. Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 2018: 1754–1763. doi: 10.1145/3219819.3220023. [24] SONG Weiping, SHI Chence, XIAO Zhiping, et al. Autoint: Automatic feature interaction learning via self-attentive neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Beijing, China, 2019: 1161–1170. doi: 10.1145/3357384.3357925. [25] WANG Ruoxi, SHIVANNA R, CHENG D, et al. DCN V2: Improved deep & cross network and practical lessons for web-scale learning to rank systems[C]. Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2021: 1785–1797. doi: 10.1145/3442381.3450078. [26] CHEN Bo, WANG Yichao, LIU Zhirong, et al. Enhancing explicit and implicit feature interactions via information sharing for parallel deep CTR models[C]. Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Queensland, Australia, 2021: 3757–3766. doi: 10.1145/3459637.3481915. [27] MAO Kelong, ZHU Jieming, SU Liangcai, et al. FinalMLP: An enhanced two-stream MLP model for CTR prediction[C]. Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 4552–4560. doi: 10.1609/AAAI.V37I4.25577. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
