An Uncertainty-driven Pixel-level Adversarial Noise Detection Method for Remote Sensing Images
-
摘要: 现有对抗防御策略大多针对特定攻击方式进行对抗样本判别,计算复杂度高、迁移性差,且无法实现噪声的像素级检测。对于大尺寸遥感图像,对抗噪声往往集中于局部关键地物区域。为此,该文结合对抗噪声高不确定性特征,面向遥感图像提出一种不确定性驱动的像素级对抗噪声检测方法。首先设计带蒙特卡罗批归一化的特征提取网络,通过多次前向传播生成蒙特卡罗样本,并将样本的均值和标准差分别作为输出图像和不确定性图。依据输出图像的均方误差判断其是否属于对抗样本,若属于则进一步结合不确定性图实现多种类型对抗噪声的像素级检测。在遥感数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法能够准确检测出对抗噪声,并在不同攻击方式下展现出强鲁棒性与良好的泛化性能。Abstract:
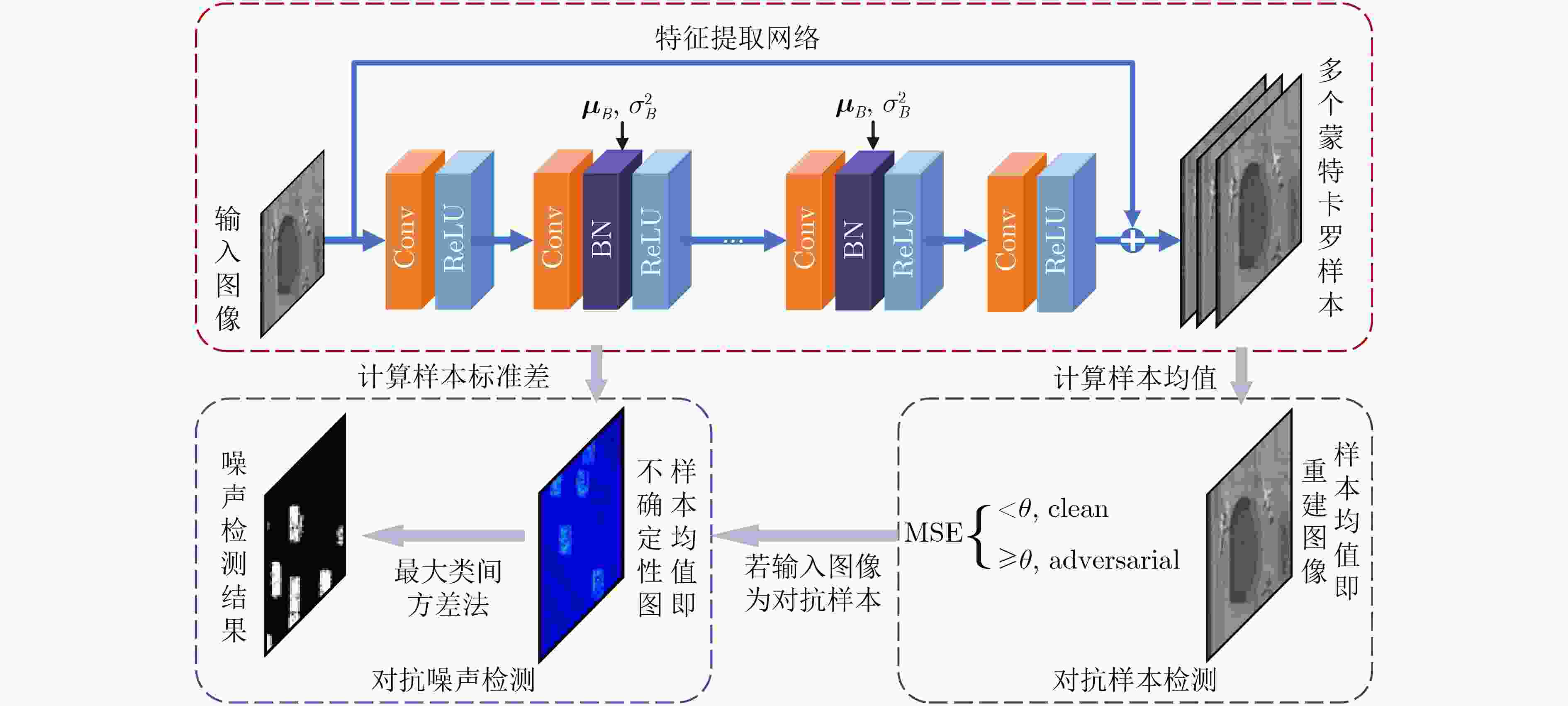
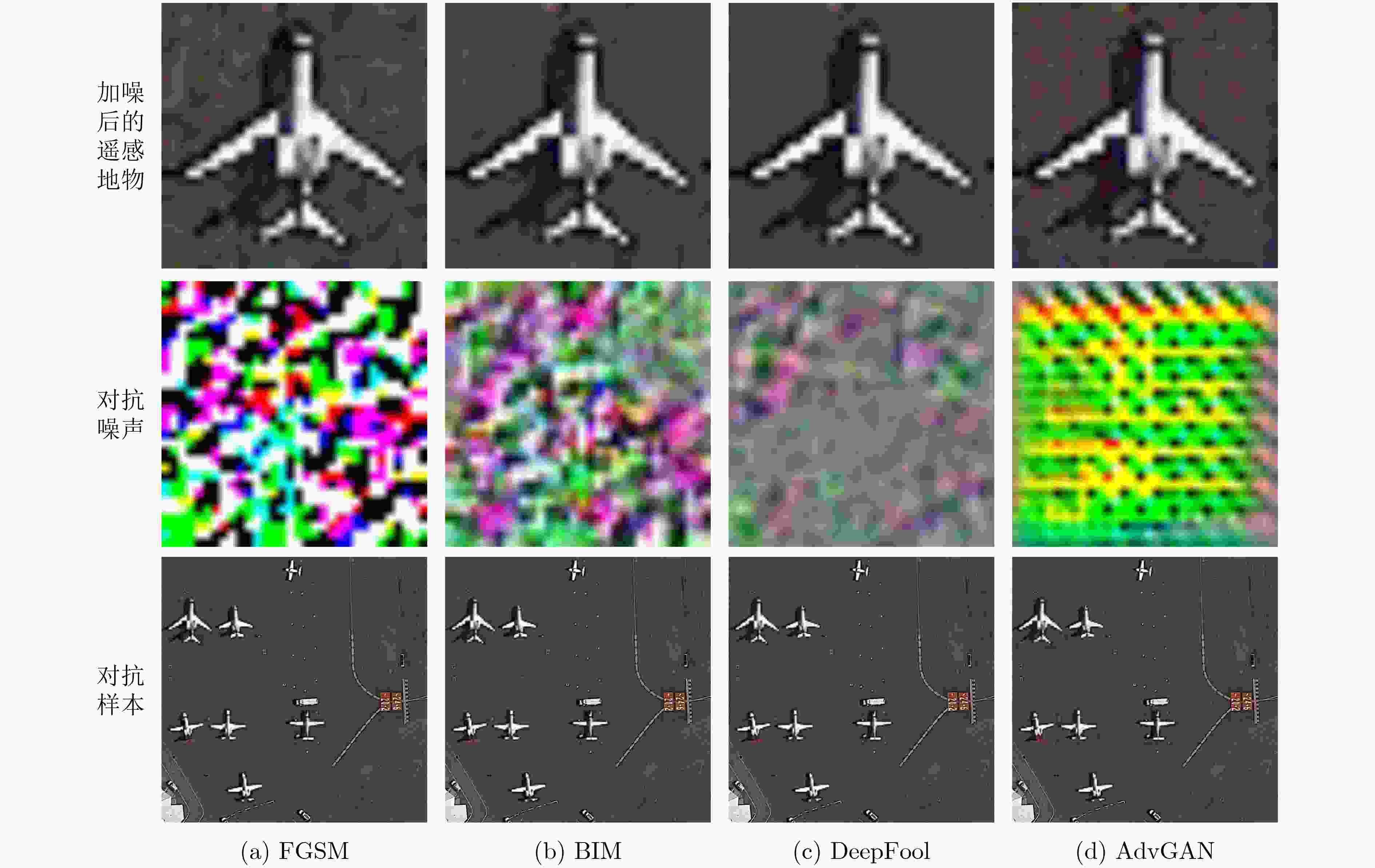
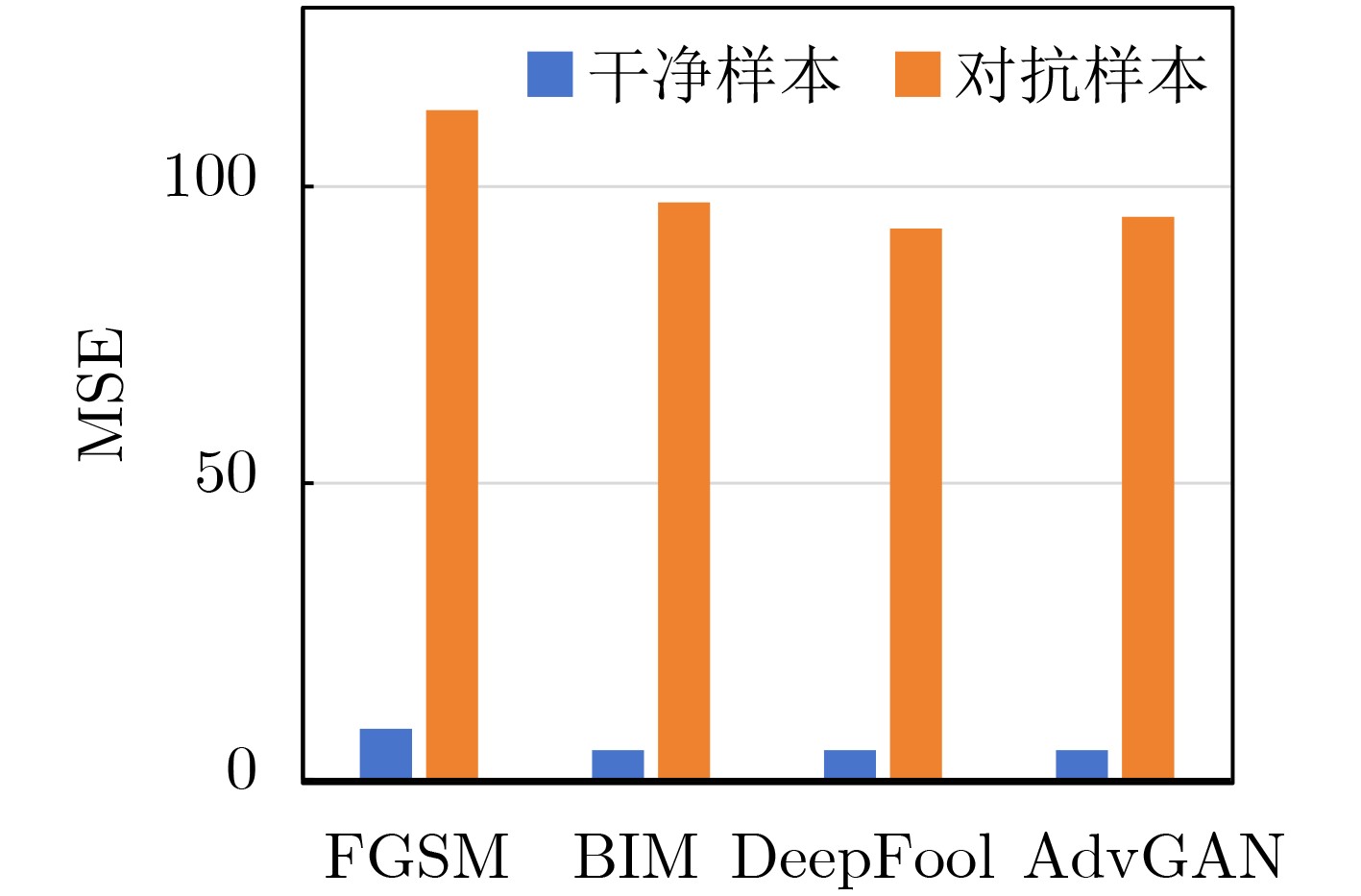
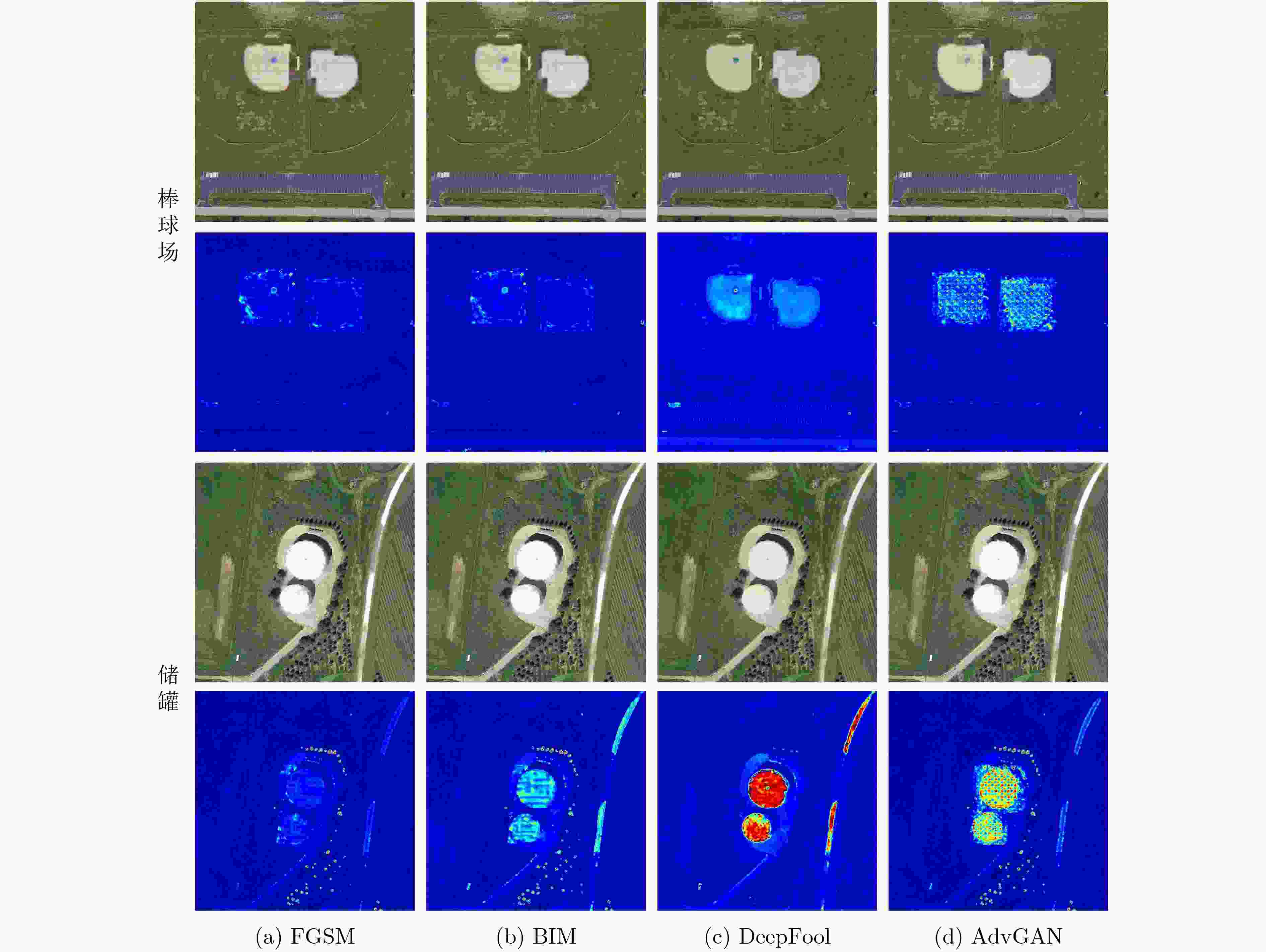
Objective The development of remote sensing technology has expanded its range of applications. However, during image acquisition and transmission, various factors can introduce noise that reduces image quality and clarity, affecting the extraction of ground object information. In particular, adversarial noise poses serious security risks, as it compromises the robustness of intelligent algorithms and may lead to decision failures. Evaluating the accuracy and reliability of remote sensing image data is therefore essential, highlighting the need for dedicated adversarial noise detection methods. Existing adversarial defense strategies primarily detect adversarial samples generated by specific attack methods, but these approaches often exhibit high computational cost, limited transferability, and lack pixel-level detection capabilities. In large-scale remote sensing images, adversarial noise is typically concentrated in key local regions containing ground objects. To address these limitations, this study proposes an uncertainty-driven, pixel-level adversarial noise detection method for remote sensing images. The method integrates adversarial noise characteristic analysis with uncertainty modeling, enabling precise localization of adversarial noise and improving the reliability of remote sensing applications. Methods To address the limitations of existing adversarial sample detection algorithms, an uncertainty-driven pixel-level adversarial noise detection method is proposed. The approach uses Monte Carlo Batch Normalization (MCBN) for uncertainty modeling and exploits the typically high uncertainty of adversarial noise to enable pixel-level detection. In deep neural networks, inference based on the stochasticity of the batch mean and variance in Batch Normalization (BN) layers is theoretically equivalent to variational inference in Bayesian models. This enables pixel-wise uncertainty estimation without modifying the network architecture or training process. In general, high-frequency regions such as edges exhibit greater uncertainty. In adversarial samples, however, artificially altered texture details introduce abnormal uncertainty. The uncertainty in these regions increases with the intensity of the adversarial noise. The proposed method comprises three main components: a feature extraction network, adversarial sample identification, and pixel-level adversarial noise detection. The input image is processed by a feature extraction network with BN layers to generate multiple Monte Carlo samples. The mean of these samples is treated as the reconstructed image, and the standard deviation is used to generate the uncertainty map. To identify adversarial samples, the algorithm calculates the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between the reconstructed image and the input image. If the image is classified as adversarial, the corresponding uncertainty map is further used to localize adversarial noise at the pixel level. Results and Discussions The experimental evaluation first quantifies the performance of the proposed method in adversarial sample detection and performs a comparative analysis with existing approaches. It also examines the effectiveness of pixel-level adversarial noise detection from both quantitative and qualitative perspectives. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves high detection performance and strong adaptability to various adversarial attacks, with robust generalization capability. Specifically, the method maintains detection accuracy above 0.87 against adversarial samples generated by four attack algorithms—FGSM, BIM, DeepFool, and AdvGAN—indicating consistent generalization across different adversarial methods. Although adversarial samples generated by DeepFool exhibit higher visual imperceptibility, the proposed method sustains stable performance across all evaluation metrics. This robustness highlights its adaptability even to potential unknown adversarial attacks. To further evaluate its effectiveness, the method is compared with existing adversarial sample detection algorithms, including MAD, PACA, E2E-Binary, and DSADF. The results indicate that the proposed method achieves competitive results in accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, reflecting strong overall performance in adversarial sample detection. For adversarial samples, the method also performs pixel-level adversarial noise detection. Results confirm its effectiveness in identifying various types of adversarial noise, with high accuracy in localizing noise within specific regions, such as baseball fields and storage tanks. It successfully detects most noise-affected areas in remote sensing images. However, complex textures and high-frequency details in some background regions cause increased uncertainty, which may lead to false positives, with non-adversarial regions misclassified as adversarial noise. Despite this limitation, the method maintains high overall detection accuracy and a low false negative rate, supporting its practical value in high-security applications. Conclusions To address the limitations of existing adversarial noise detection algorithms, this study proposes an uncertainty-driven pixel-level detection method for remote sensing images. The approach integrates MCBN into the feature extraction network to generate multiple Monte Carlo samples. The sample mean is used as the reconstructed image, while the sample standard deviation provides uncertainty modeling. The method determines whether an image is adversarial based on the difference in MSE between clean and adversarial samples, and the uncertainty map is utilized to localize adversarial noise at the pixel level across various attack scenarios. Experiments are conducted using the publicly available DIOR dataset, with adversarial samples generated by four representative attack algorithms: FGSM, BIM, DeepFool, and AdvGAN. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations confirm the method’s effectiveness in detecting adversarial noise at the pixel level and demonstrate strong generalization across attack types. The ability to localize noise improves the transparency and interpretability of adversarial sample identification, supporting more informed and targeted mitigation strategies. Despite its strong performance, the method currently relies solely on uncertainty estimation and thresholding for segmentation, which may result in misclassification in regions with complex textures or high-frequency details. Future research will explore the integration of uncertainty modeling with additional features to improve detection accuracy in such regions. -
表 1 所提方法在不同噪声类型对抗样本上的检测结果
对抗样本
生成方法准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 FGSM 0.874 0.927 0.812 0.866 BIM 0.884 0.951 0.806 0.872 DeepFool 0.881 0.958 0.790 0.866 AdvGAN 0.877 0.953 0.799 0.870 表 2 不同对抗样本检测方法的在DeepFool上的检测结果
对抗样本检测方法 准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 MAD 0.842 0.875 0.798 0.835 PACA 0.845 0.878 0.801 0.838 E2E-Binary 0.864 0.947 0.772 0.851 DSADF 0.885 0.980 0.786 0.872 本文方法 0.881 0.958 0.790 0.866 表 3 不同类型对抗噪声像素级检测定量评价
对抗样本
生成方法准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 FGSM 0.931 0.849 0.610 0.710 BIM 0.921 0.781 0.601 0.679 DeepFool 0.913 0.668 0.725 0.696 AdvGAN 0.972 0.925 0.871 0.898 -
[1] 李树涛, 李聪妤, 康旭东. 多源遥感图像融合发展现状与未来展望[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(1): 148–166. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210259.LI Shutao, LI Congyu, and KANG Xudong. Development status and future prospects of multi-source remote sensing image fusion[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(1): 148–166. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210259. [2] 付琨, 卢宛萱, 刘小煜, 等. 遥感基础模型发展综述与未来设想[J]. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(7): 1667–1680. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20233313.FU Kun, LU Wanxuan, LIU Xiaoyu, et al. A comprehensive survey and assumption of remote sensing foundation modal[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(7): 1667–1680. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20233313. [3] WANG Yu, SHAO Zhenfeng, LU Tao, et al. Remote sensing image super-resolution via multiscale enhancement network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 5000905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3248069. [4] YAO Xudong, GUO Qing, and LI An. Cloud detection in optical remote sensing images with deep semi-supervised and active learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 6006805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3287537. [5] BANIECKI H and BIECEK P. Adversarial attacks and defenses in explainable artificial intelligence: A survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 107: 102303. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102303. [6] SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014: 1–11. [7] GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, and SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–11. [8] LI Yanjie, LI Yiquan, DAI Xuelong, et al. Physical-world optical adversarial attacks on 3D face recognition[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 24699–24708. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.02366. [9] CARRARA F, FALCHI F, AMATO G, et al. Detecting adversarial inputs by looking in the black box[J]. ERCIM News, 2019, 116: 16–17. [10] MA Xingjun, NIU Yuhao, GU Lin, et al. Understanding adversarial attacks on deep learning based medical image analysis systems[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 110: 107332. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107332. [11] 郭凯威, 杨奎武, 张万里, 等. 面向文本识别的对抗样本攻击综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2024, 29(9): 2672–2691. doi: 10.11834/jig.230412.GUO Kaiwei, YANG Kuiwu, ZHANG Wanli, et al. A review of adversarial examples for optical character recognition[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2024, 29(9): 2672–2691. doi: 10.11834/jig.230412. [12] XU Weilin, EVANS D, and QI Yanjun. Feature squeezing: Detecting adversarial examples in deep neural networks[C]. Network and Distributed Systems Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, USA, 2018. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2018.23198. [13] HENDRYCKS D and GIMPEL K. Early methods for detecting adversarial images[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2016. [14] FEINMAN R, CURTIN R R, SHINTRE S, et al. Detecting adversarial samples from artifacts[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.00410, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1703.00410. [15] LEE K, LEE K, LEE H, et al. A simple unified framework for detecting out-of-distribution samples and adversarial attacks[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 7167–7177. [16] CHEN Kejiang, CHEN Yuefeng, ZHOU Hang, et al. Adversarial examples detection beyond image space[C]. ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, Canada, 2021: 3850–3854. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414008. [17] METZEN J H, GENEWEIN T, FISCHER V, et al. On detecting adversarial perturbations[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 1–12. [18] KENDALL A and GAL Y. What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision?[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5580–5590. [19] MA Chenxi. Uncertainty-aware GAN for single image super resolution[C]. The 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 4071–4079. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v38i5.28201. [20] BUDDENKOTTE T, SANCHEZ L E, CRISPIN-ORTUZAR M, et al. Calibrating ensembles for scalable uncertainty quantification in deep learning-based medical image segmentation[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2023, 163: 107096. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107096. [21] KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I J, and BENGIO S. Adversarial examples in the physical world[M]. YAMPOLSKIY R V. Artificial Intelligence Safety and Security. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2018: 99–112. doi: 10.1201/9781351251389. [22] MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, and FROSSARD P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2574–2582. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.282. [23] XIAO Chaowei, LI Bo, ZHU Junyan, et al. Generating adversarial examples with adversarial networks[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3905–3911. [24] 刘帅威, 李智, 王国美, 等. 基于Transformer和GAN的对抗样本生成算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2024, 50(2): 180–187. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0067077.LIU Shuaiwei, LI Zhi, WANG Guomei, et al. Adversarial example generation algorithm based on transformer and GAN[J]. Computer Engineering, 2024, 50(2): 180–187. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0067077. [25] GONG Zhitao and WANG Wenlu. Adversarial and clean data are not twins[C]. The Sixth International Workshop on Exploiting Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Data Management, Seattle, USA, 2023: 6. doi: 10.1145/3593078.3593935. [26] LU Yunfei, CHANG Chenxia, GAO Song, et al. Boosting adversarial example detection via local histogram equalization and spectral feature analysis[J]. The Visual Computer, 2024: 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s00371-024-03734-3. [27] BISHOP C M. Mixture density networks[R]. Birmingham, UK: Aston University, 1994. [28] DEVRIES T and TAYLOR G W. Learning confidence for out-of-distribution detection in neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.04865, 2018. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1802.04865. [29] HERNÁNDEZ-LOBATO J M and ADAMS R P. Probabilistic backpropagation for scalable learning of Bayesian neural networks[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 1861–1869. [30] GAL Y and GHAHRAMANI Z. Dropout as a Bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning[C]. The 33nd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 1050–1059. [31] KAR A and BISWAS P K. Fast Bayesian uncertainty estimation and reduction of batch normalized single image super-resolution network[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 4957–4966. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00492. [32] LIU Tao, CHENG Jun, and TAN Shan. Spectral Bayesian uncertainty for image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 18166–18175. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01742. [33] BELHASIN O, ROMANO Y, FREEDMAN D, et al. Principal uncertainty quantification with spatial correlation for image restoration problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(5): 3321–3333. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3343031. [34] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [35] KIM J, LEE J K, and LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646–1654. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.182. [36] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2014. [37] GHAHRAMANI Z. Probabilistic machine learning and artificial intelligence[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 452–459. doi: 10.1038/nature14541. [38] LI Ke, WAN Gang, CHENG Gong, et al. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 296–307. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.023. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
