Service Caching and Task Migration Mechanism Based on Internet of Vehicles
-
摘要: 近年来,随着车联网(IoV)应用的迅猛增长,为满足其对低时延和高效率计算服务需求,并缓解回程链路的传输压力,移动边缘计算(MEC)技术被广泛应用于车联网领域。然而,车辆高移动性使得边缘服务缓存和任务迁移的实现具有很强的挑战性。为此,针对车联网动态环境的特点,该文提出一种适应车联网动态环境特性的服务缓存和任务迁移联合优化算法(SCTMA),基于多智能体深度确定性策略梯度方法,在考虑车辆用户与路边单元(RSU)及基站之间交互不确定性的前提下,对边缘服务缓存和任务迁移进行联合优化。仿真结果表明,所提算法能降低缓存和任务迁移成本,提高缓存命中率。
-
关键词:
- 车联网 /
- 服务缓存 /
- 任务迁移 /
- 多智能体深度强化学习
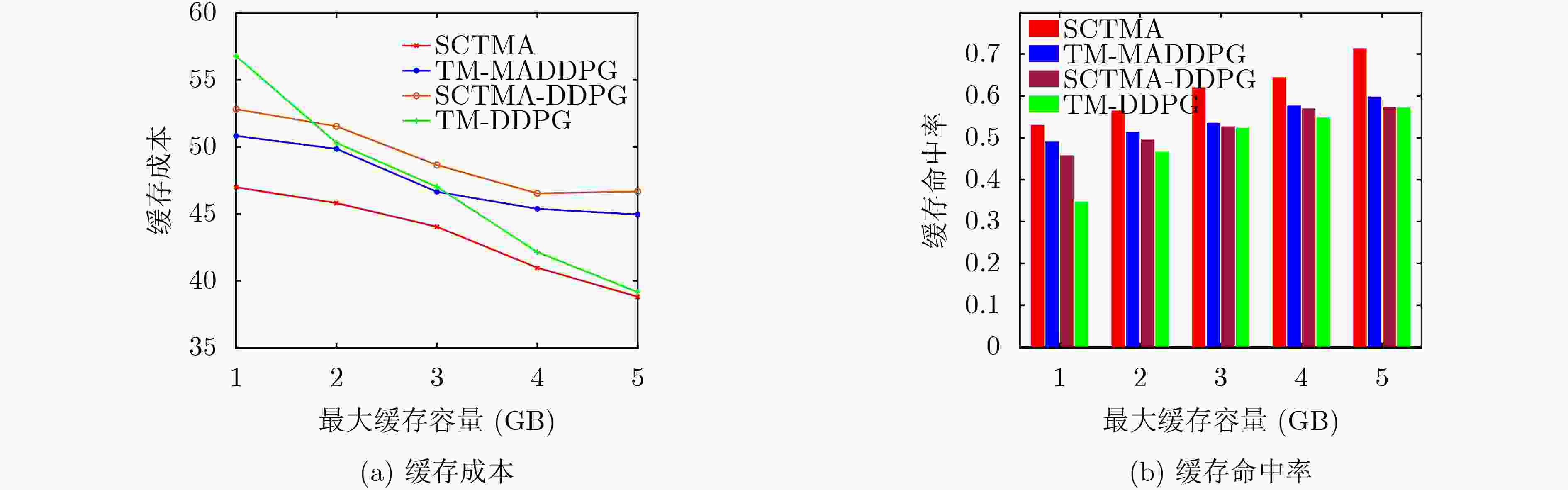
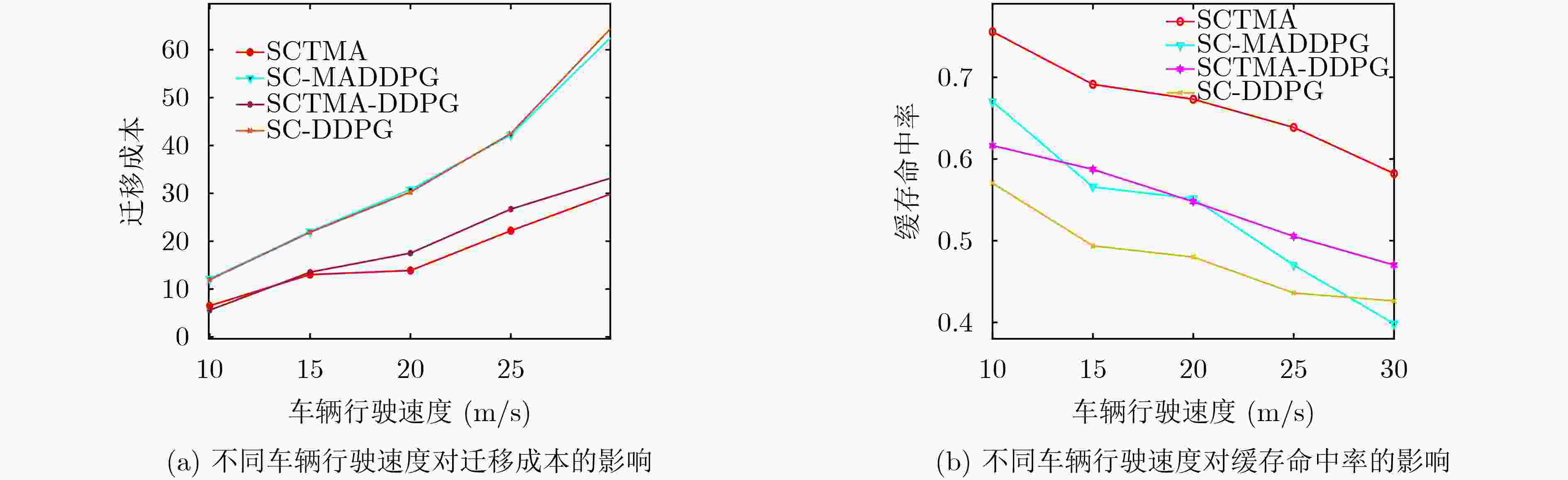
Abstract:Objective In the era of digital transformation and smart mobility, the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) has emerged as a transformative paradigm reshaping transportation systems and vehicle-related services. In recent years, the proliferation of IoV applications has led to the generation and processing of large volumes of real-time data, requiring ultra-low latency and high-efficiency computation to maintain seamless functionality and ensure high-quality user experiences. To meet these demands, Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) has been widely adopted in the IoV domain, effectively reducing the load on backhaul links. However, the dynamic and mobile nature of vehicular networks poses significant challenges to the effective deployment of edge services and the efficient management of task migration. Vehicles continuously move across regions with heterogeneous network conditions, edge node coverage, and service availability. Conventional static or rule-based approaches for service caching and task migration often fail to adapt to these environmental dynamics, leading to degraded performance, frequent service interruptions, and elevated energy consumption. This study proposes a Joint Service Caching and Task Migration Algorithm (SCTMA) tailored to the dynamic characteristics of the IoV environment. By incorporating machine learning, optimization techniques, and context-aware decision-making, SCTMA dynamically adjusts caching and migration strategies to ensure that appropriate services are delivered to suitable edge nodes at the optimal time, thereby minimizing latency and improving resource utilization. Methods This study systematically considers multiple constraints within the IoV system, including caching decisions, the number of cached services, cache capacity, CPU resource consumption, and task migration policies at edge nodes. To jointly optimize service caching and task migration under these constraints, a Markov Decision Process (MDP) model is constructed. The MDP framework captures the temporal dynamics of the IoV environment, wherein system states, such as vehicle location, service demand, and cache status evolve over time. The reward function is formulated to balance competing objectives, including minimizing latency, reducing energy consumption, and improving the cache hit ratio. To address inefficient utilization of Base Station (BS) caching resources and mitigate storage waste, the concept of a service hit ratio is introduced. Based on this ratio, BSs proactively cache frequently requested services, thereby reducing latency and energy usage during Vehicle User (VU) service requests and enhancing overall caching efficiency. A task migration algorithm is also developed, incorporating vehicle velocity to estimate the remaining dwell time of a VU within the coverage area of a RoadSide Unit (RSU). This estimation is used to compute the associated service data migration volume and assess migration costs. Building on this framework, a Joint SCTMA is proposed. SCTMA employs the Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MADDPG) method to address uncertainties in multi-agent settings. This approach reduces system communication and computation costs, optimizes migration notification strategies, and improves the cache hit ratio. Results and Discussions Simulation results indicate that the proposed SCTMA algorithm effectively reduces caching and task migration costs while improving the cache hit ratio. Following training, the system’s long-term average reward under SCTMA markedly exceeds that of baseline algorithms ( Fig. 3 ). Specifically, SCTMA maintains the long-term average reward at approximately –30, whereas the best-performing comparative method stabilizes at around –38, corresponding to an improvement of at least 21.05%. Further analysis of edge device caching performance (Fig. 5(a) ,Fig. 5(b) ) shows that as the maximum cache capacity increases, the system using SCTMA consistently achieves the highest cache hit ratio across all tested scenarios.Conclusions In edge computing-enabled IoV ecosystems, where vehicles interact with infrastructure and peer nodes through interconnected edge networks, this study examines decision-making mechanisms for service hit rate optimization and task migration. By formulating the joint optimization of service caching and task migration as A MDP, a Joint SCTMA is proposed. Simulation results show that SCTMA reduces service caching and task migration costs, shortens service request latency for VU, and improves overall system performance. However, the current study assumes an idealized IoV environment. Future research should evaluate the algorithm’s robustness and efficiency under real-world conditions. -
表 1 仿真参数
参数 值 BS数量 3 MEC服务器数量 3 RSU数量 10 车辆数量 15 服务类型数量 10 服务大小 100~600 MB 车辆速度 30 m/s RSU覆盖半径 150 m BS覆盖半径 500 m MEC服务器最大缓存容量 2 GB MEC服务器的CPU频率 $5 \times {10^6}$ cycle/s -
[1] WU Ziying and YAN Danfeng. Deep reinforcement learning-based computation offloading for 5G vehicle-aware multi-access edge computing network[J]. China Communications, 2021, 18(11): 26–41. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2021.11.003. [2] 李智勇, 王琦, 陈一凡, 等. 车辆边缘计算环境下任务卸载研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(5): 963–982. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00963.LI Zhiyong, WANG Qi, CHEN Yifan, et al. A survey on task offloading research in vehicular edge computing[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(5): 963–982. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00963. [3] WU Qiong, ZHAO Yu, FAN Qiang, et al. Mobility-aware cooperative caching in vehicular edge computing based on asynchronous federated and deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2023, 17(1): 66–81. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3221271. [4] LING Chen, ZHANG Weizhe, FAN Qingyang, et al. Cooperative service caching in vehicular edge computing networks based on transportation correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(12): 22754–22767. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3382723. [5] WANG Ruyan, KAN Zunwei, CUI Yaping, et al. Cooperative caching strategy with content request prediction in internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(11): 8964–8975. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3056084. [6] ZENG Feng, ZHANG Kanwen, WU Lin, et al. Efficient caching in vehicular edge computing based on edge-cloud collaboration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(2): 2468–2481. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3213130. [7] SHEN Qiaoqiao, HU Binjie, and XIA Enjun. Dependency-aware task offloading and service caching in vehicular edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(12): 13182–13197. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3196544. [8] NGUYEN T V, DAO N N, TUONG V D, et al. User-aware and flexible proactive caching using LSTM and ensemble learning in IoT-MEC networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(5): 3251–3269. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3097768. [9] LIU Wenjie, ZHANG Haixia, DING Hui, et al. Mobility-aware coded edge caching in vehicular networks with dynamic content popularity[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC49053.2021.9417383. [10] PENG Yan, TANG Xiaogang, ZHOU Yiqing, et al. Computing and communication cost-aware service migration enabled by transfer reinforcement learning for dynamic vehicular edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(1): 257–269. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3225239. [11] LABRIJI I, MENEGHELLO F, CECCHINATO D, et al. Mobility aware and dynamic migration of MEC Services for the Internet of Vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2021, 18(1): 570–584. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2021.3052808. [12] WANG Haipeng, LV Tiejun, LIN Zhipeng, et al. Energy-delay minimization of task migration based on game theory in MEC-assisted vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(8): 8175–8188. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3175238. [13] LABRIJI I, STRINATI E C, PERRAUD E, et al. Dynamic migration strategy for mobile multi-access edge computing services[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, USA, 2022: 710–715. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771612. [14] WU Qiong, WANG Siyuan, GE Hongmei, et al. Delay-sensitive task offloading in vehicular fog computing-assisted platoons[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2024, 21(2): 2012–2026. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2023.3322881. [15] YU Genghua, HE Yixin, WU Jian, et al. Mobility-aware proactive edge caching for large files in the internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(13): 11293–11305. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3240423. [16] 杨守义, 韩昊锦, 郝万明, 等. 边缘计算中面向缓存的迁移决策和资源分配[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(12): 4391–4398. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240427.YANG Shouyi, HAN Haojin, HAO Wanming, et al. Cache oriented migration decision and resource allocation in edge computing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(12): 4391–4398. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240427. [17] GAN Jiongpeng, LI Shen, LIN Xianke, et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning-based multi-objective cooperative control strategy for hybrid electric vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(8): 11123–11135. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3373906. [18] ZHOU Huan, ZHANG Zhenyu, WU Yuan, et al. Energy efficient joint computation offloading and service caching for mobile edge computing: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2023, 7(2): 950–961. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2022.3186403. [19] LIU Yan, LIN Peng, ZHANG Mengya, et al. Mobile-aware service offloading for UAV-assisted IoV: A multiagent tiny distributed learning approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(12): 21191–21201. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3373225. [20] 黄思进, 文佳, 陈哲毅. 面向边缘车联网系统的智能服务迁移方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2025, 37(2): 379–391. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-1142.HUANG Sijin, WEN Jia, and CHEN Zheyi. Intelligent service migration towards MEC-based IoV systems[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2025, 37(2): 379–391. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-1142. -





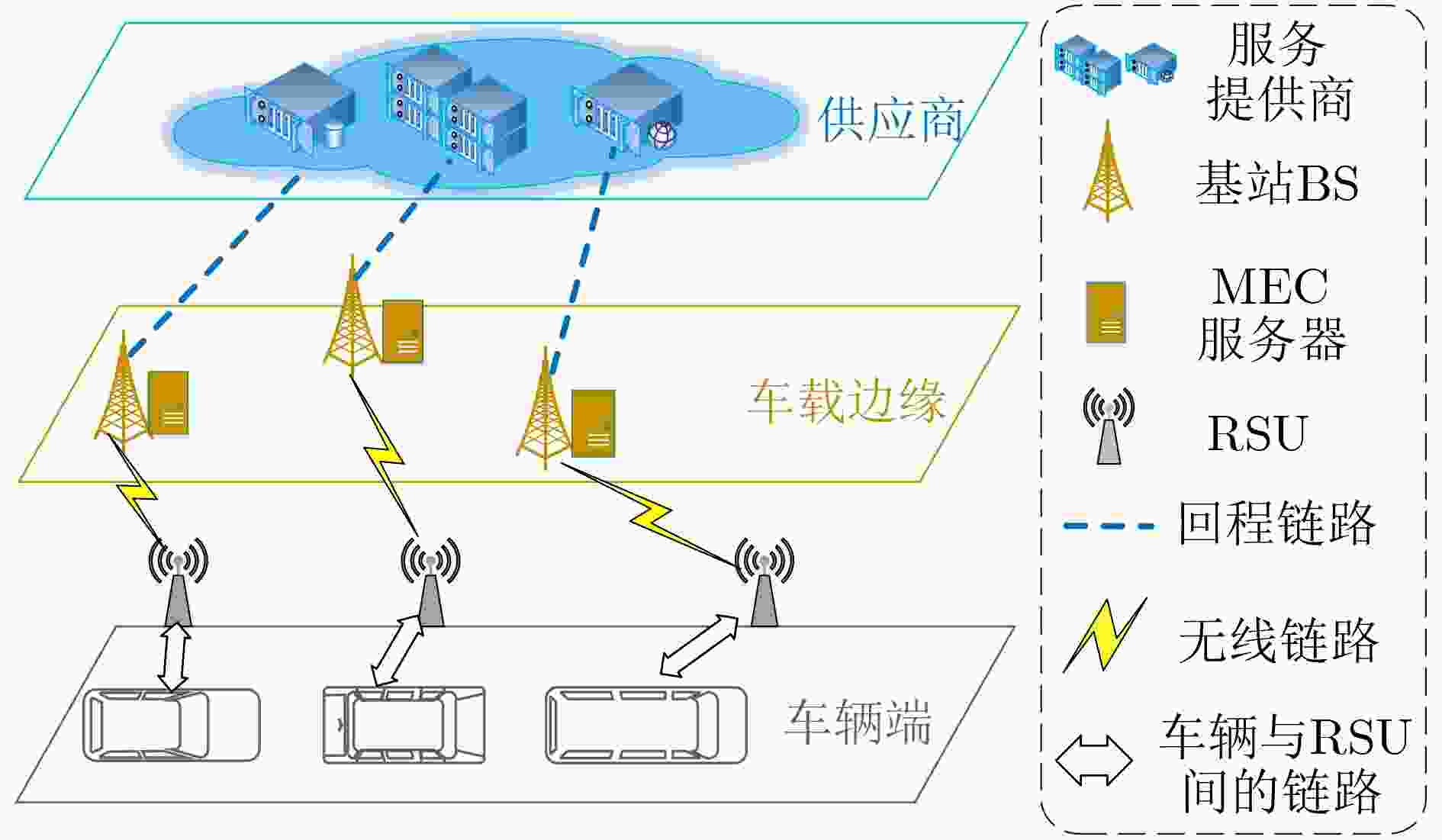
 下载:
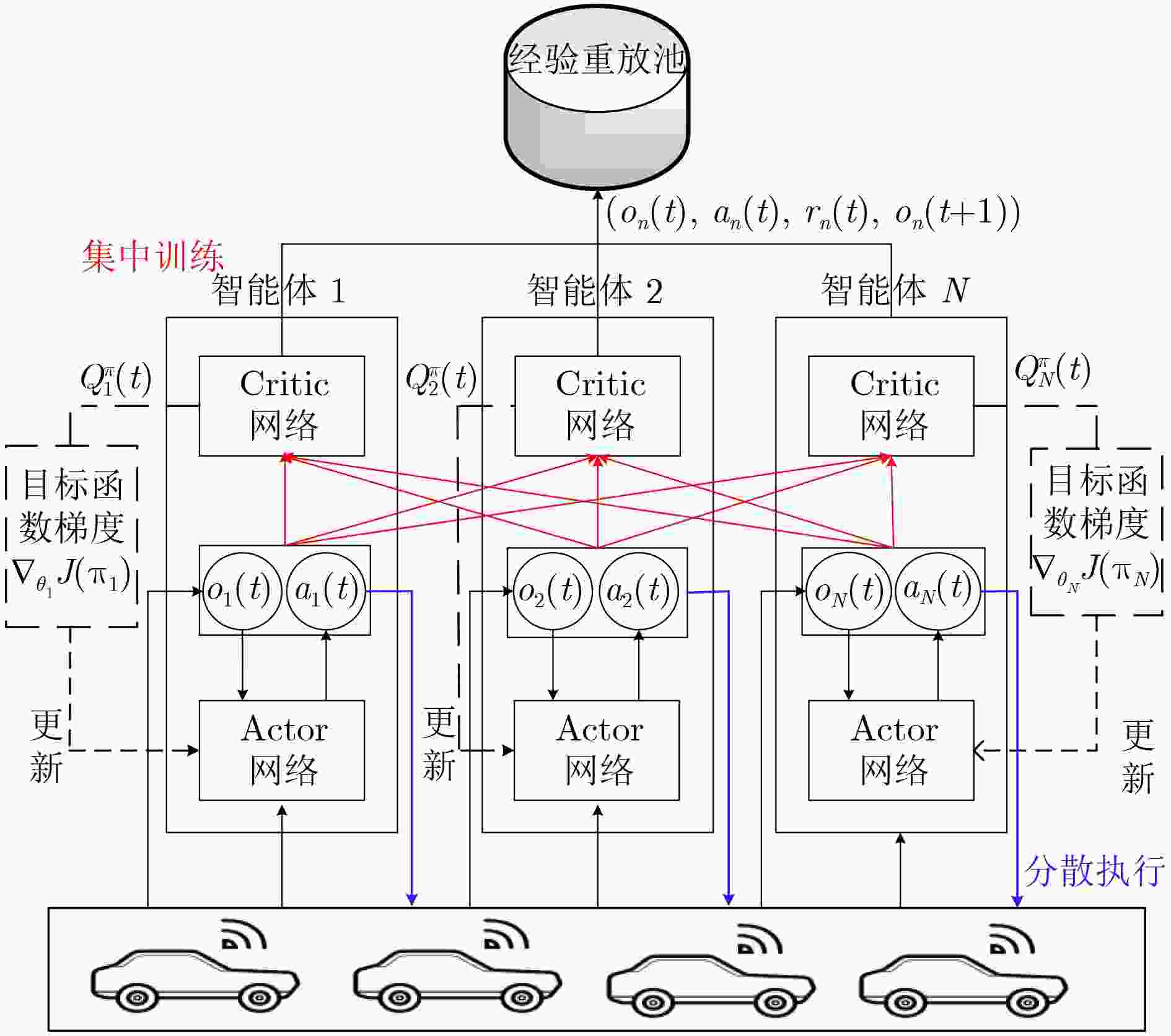
下载:
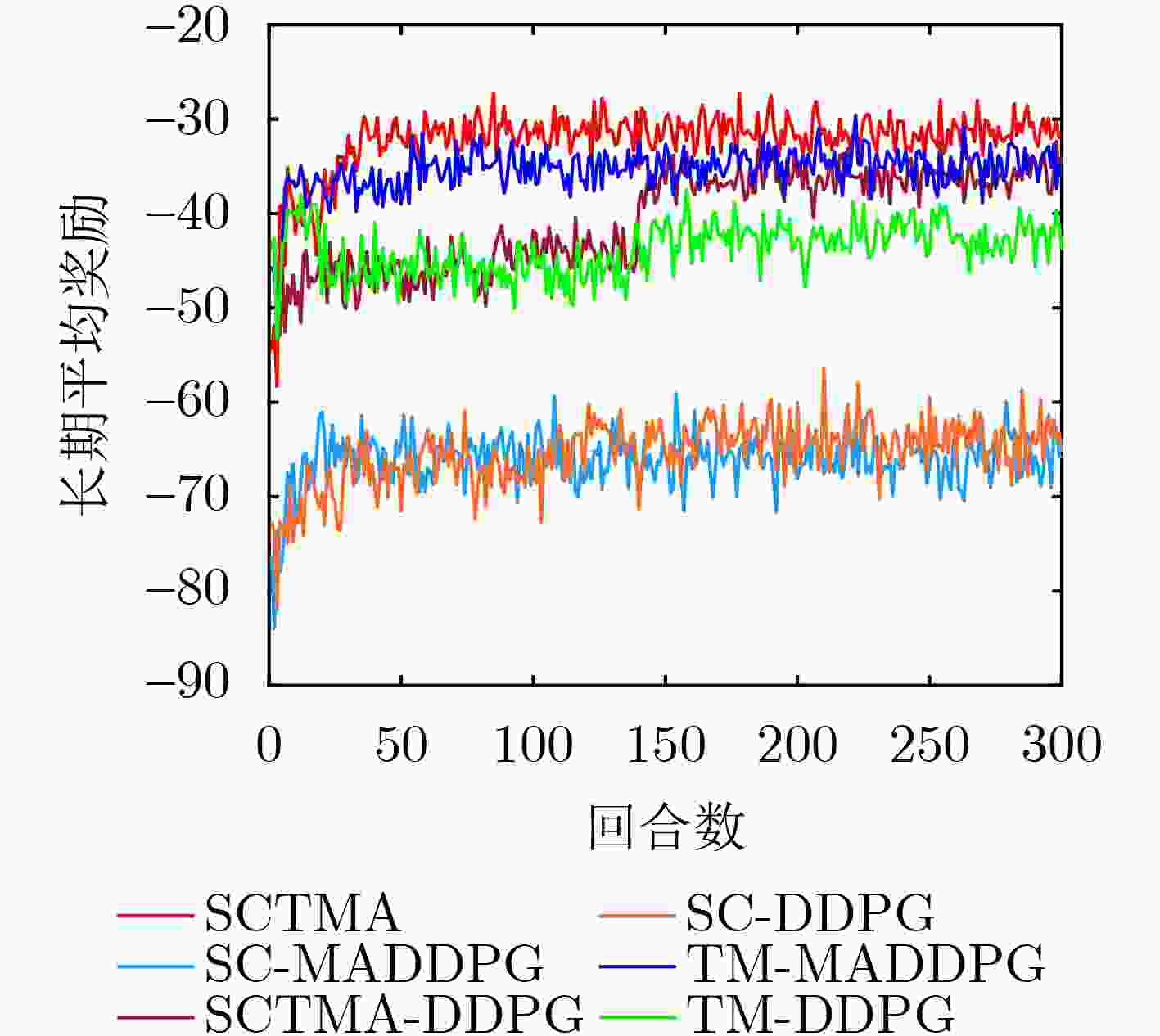
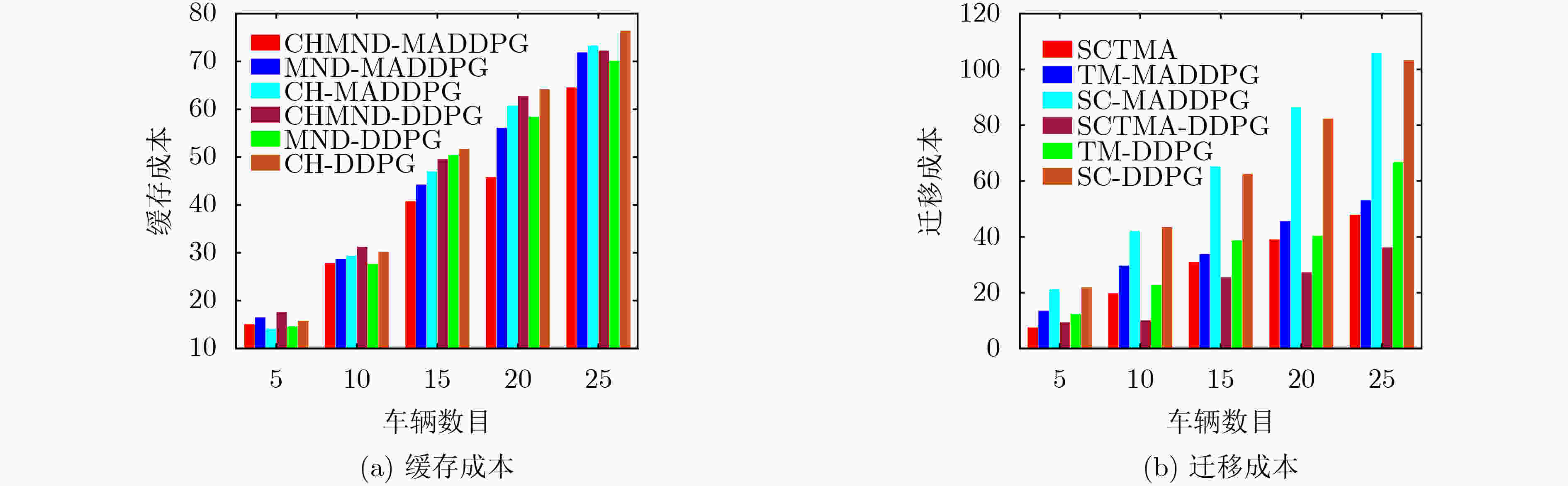


 下载:
下载:
