Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method Against Spectrum Sensing Data Falsification Attacks Based on Multiscale Entropy
-
摘要: 针对协作频谱感知易遭受频谱感知数据篡改(SSDF)攻击导致无法准确识别恶意用户的问题,该文提出一种基于多尺度熵的协作频谱感知方法。该方法通过滑动窗对用户进行多次本地感知以获取信誉值。随后引入多尺度熵算法,对用户的感知结果进一步实施多尺度分析,利用分析结果作为权重更新信誉值,归一化处理后对用户进行判定并做出最终全局判决。仿真结果表明,对于不同的攻击策略,在攻击概率超过0.4的情况下,所提算法与其它对比算法相比恶意用户检测率分别平均提升3.56%, 0.77%和6.45%, 36.92%,具有良好的抗攻击能力。且与熵加权算法相比,其复杂度更低。
-
关键词:
- 协作频谱感知 /
- 频谱感知数据篡改攻击 /
- 信誉值 /
- 多尺度熵
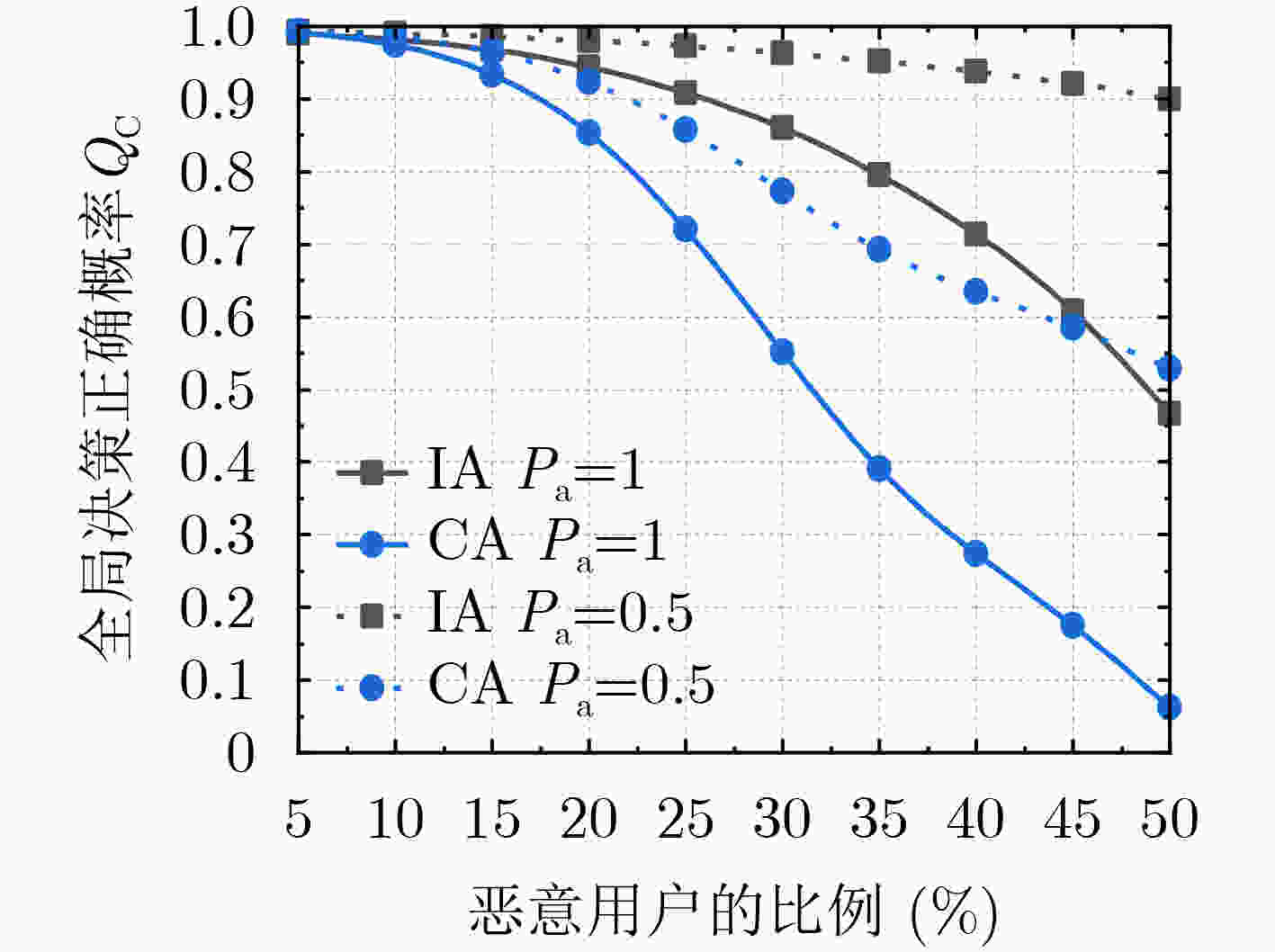
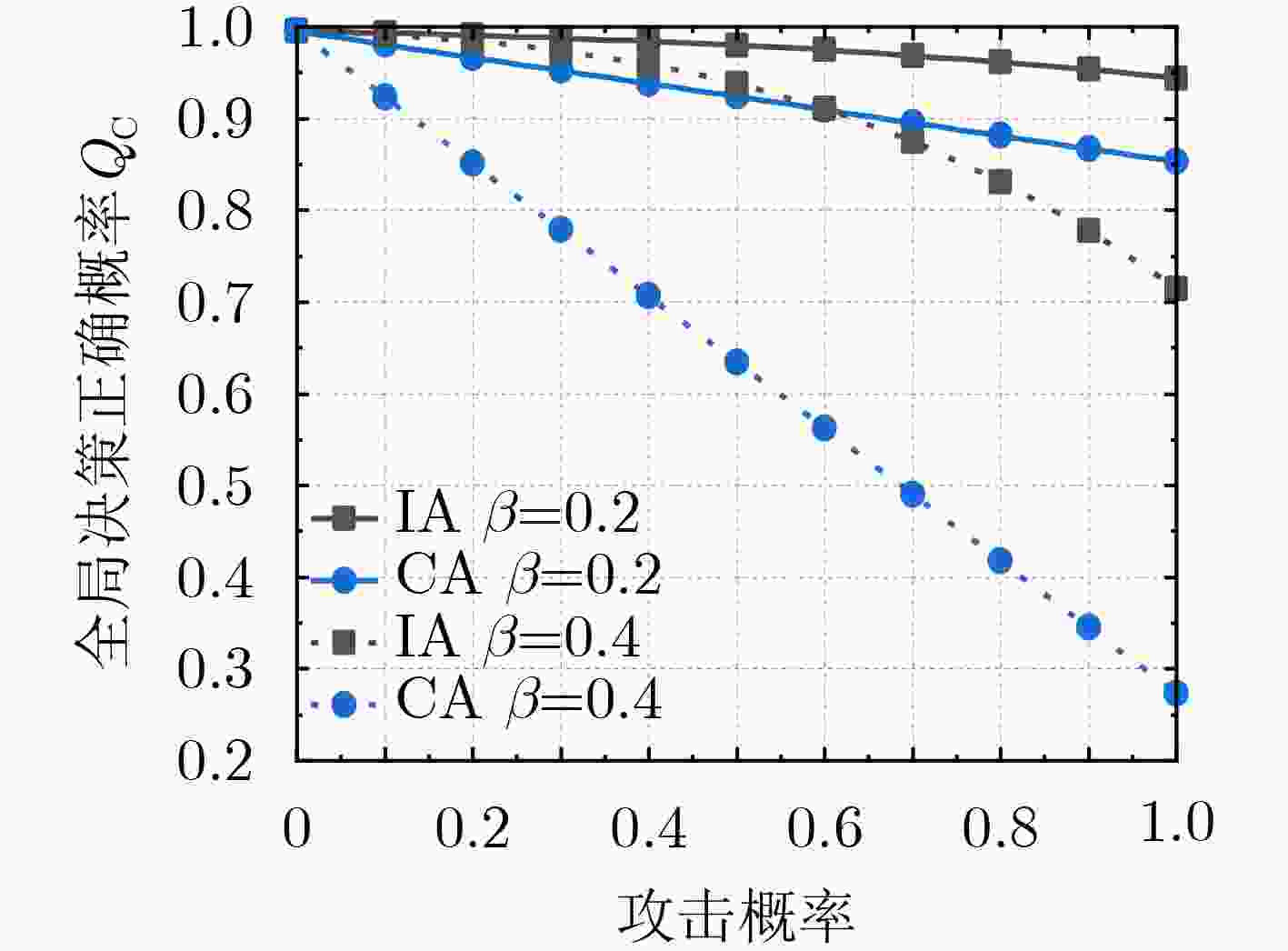
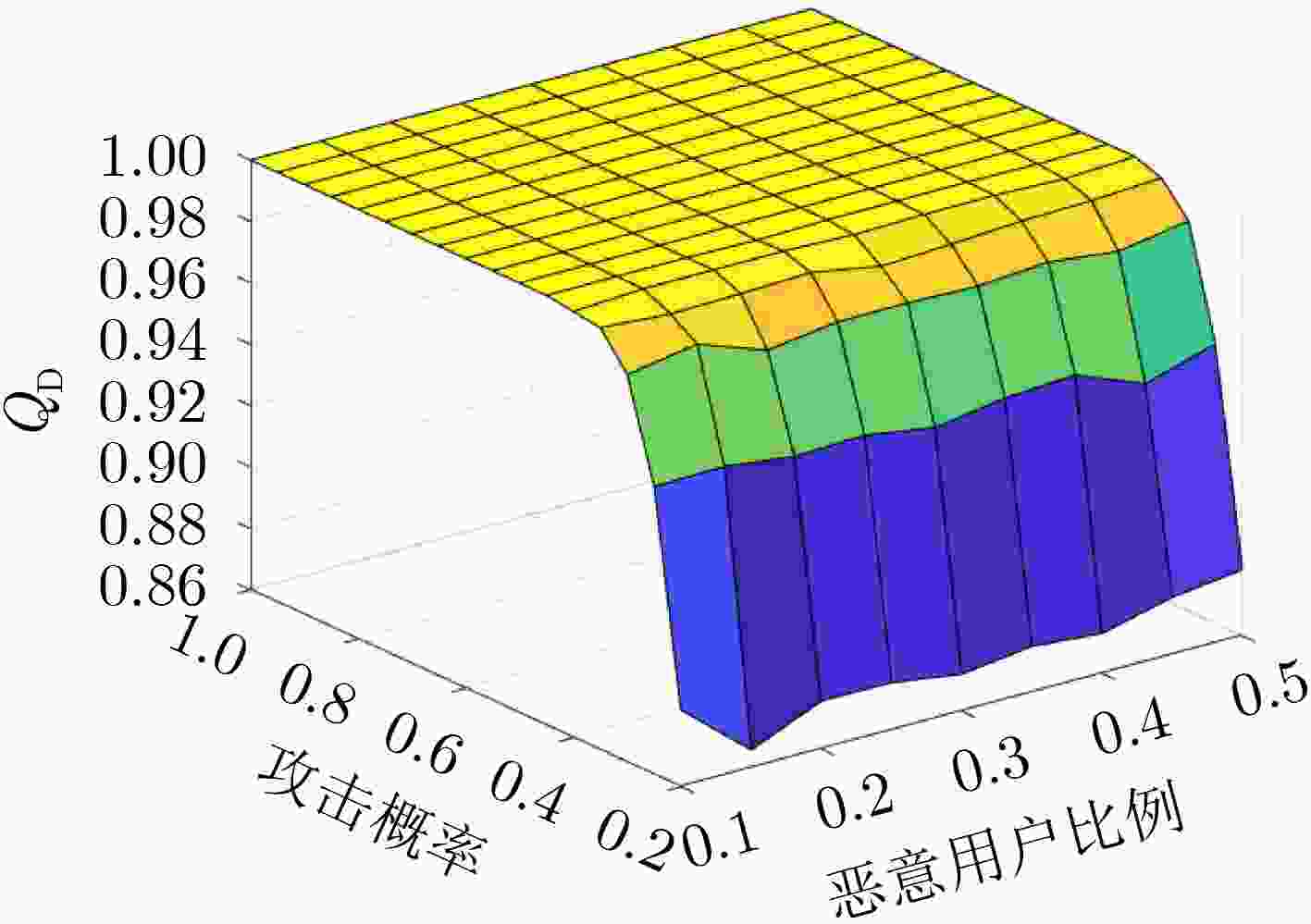
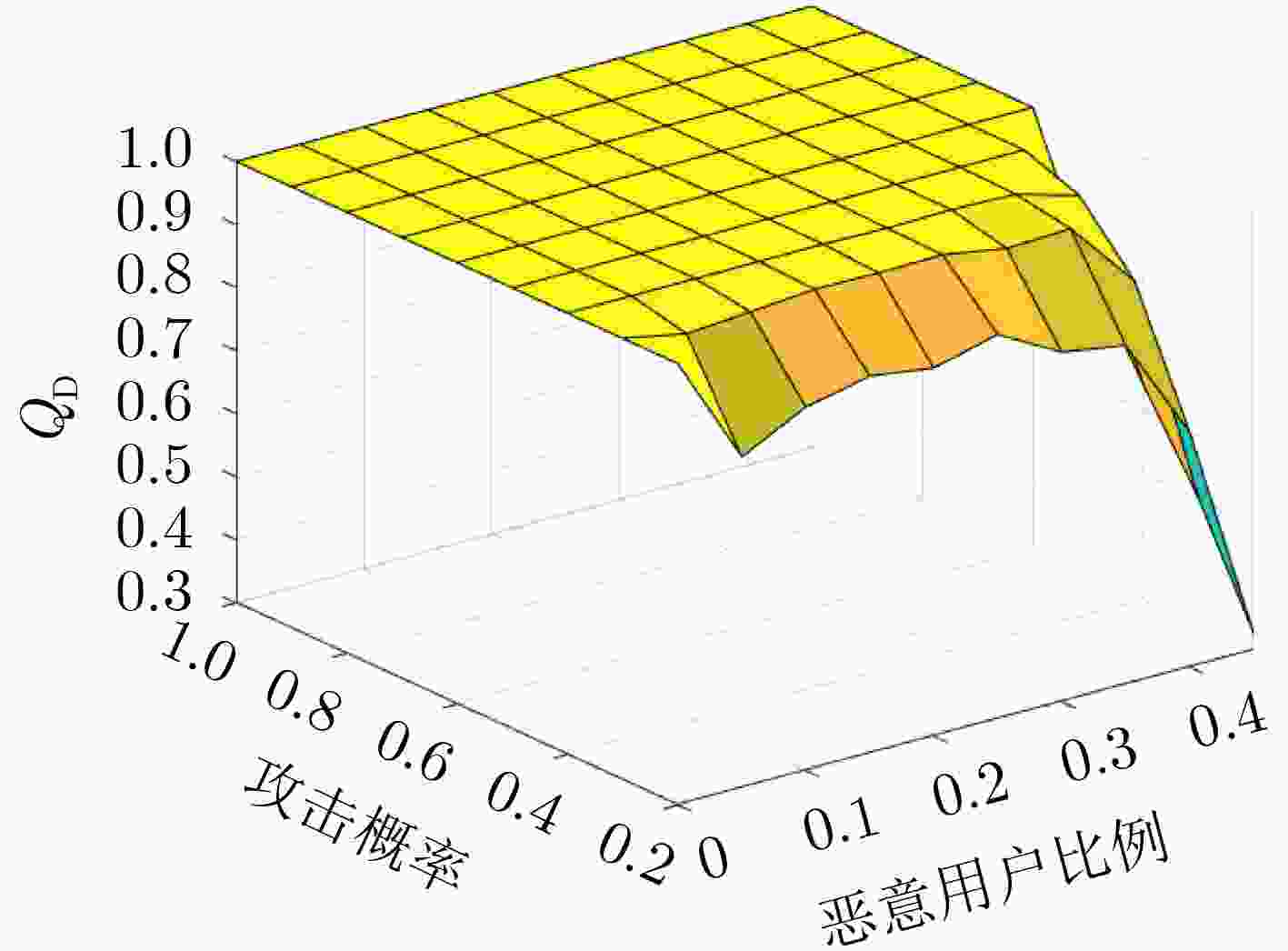
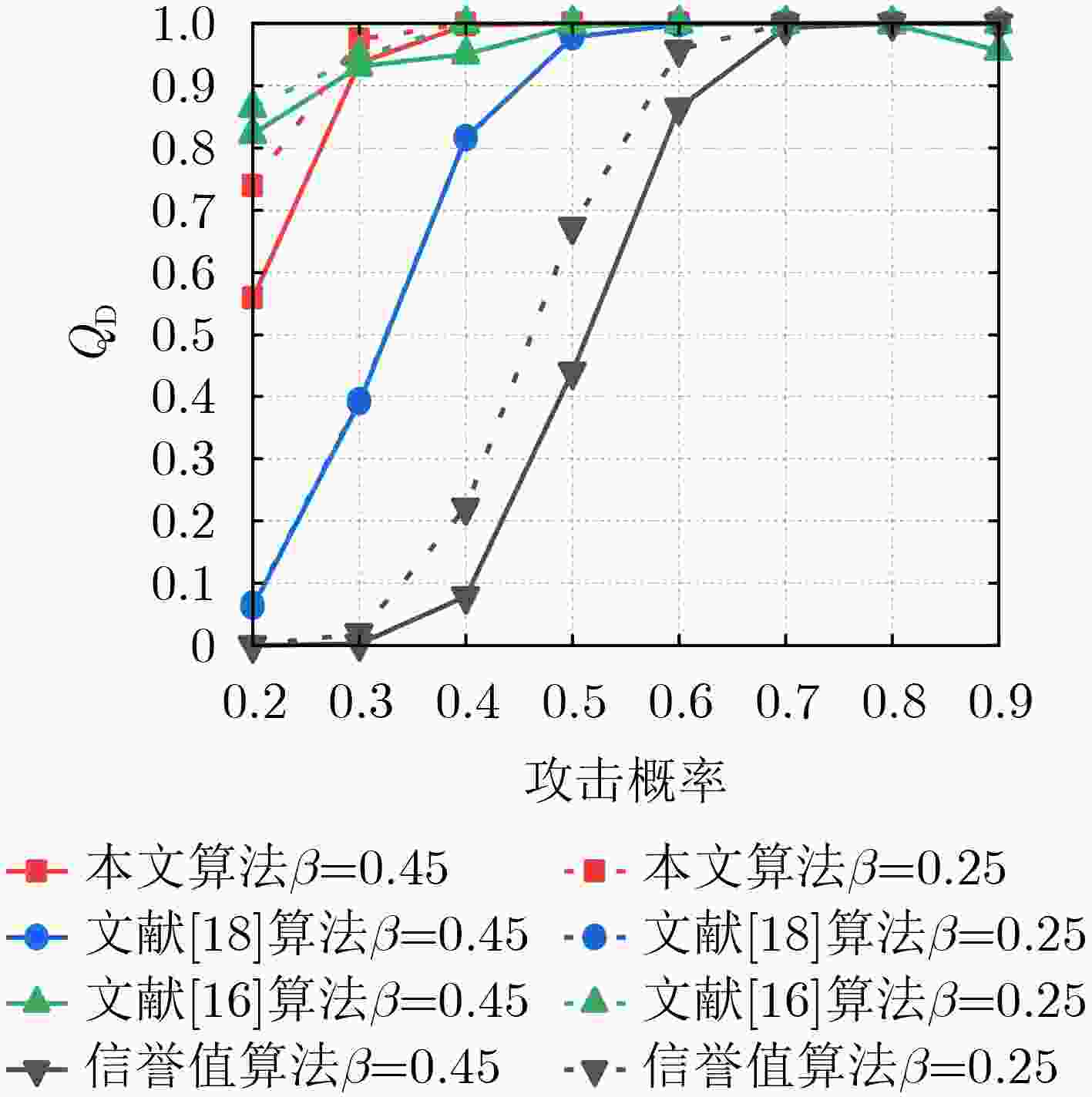
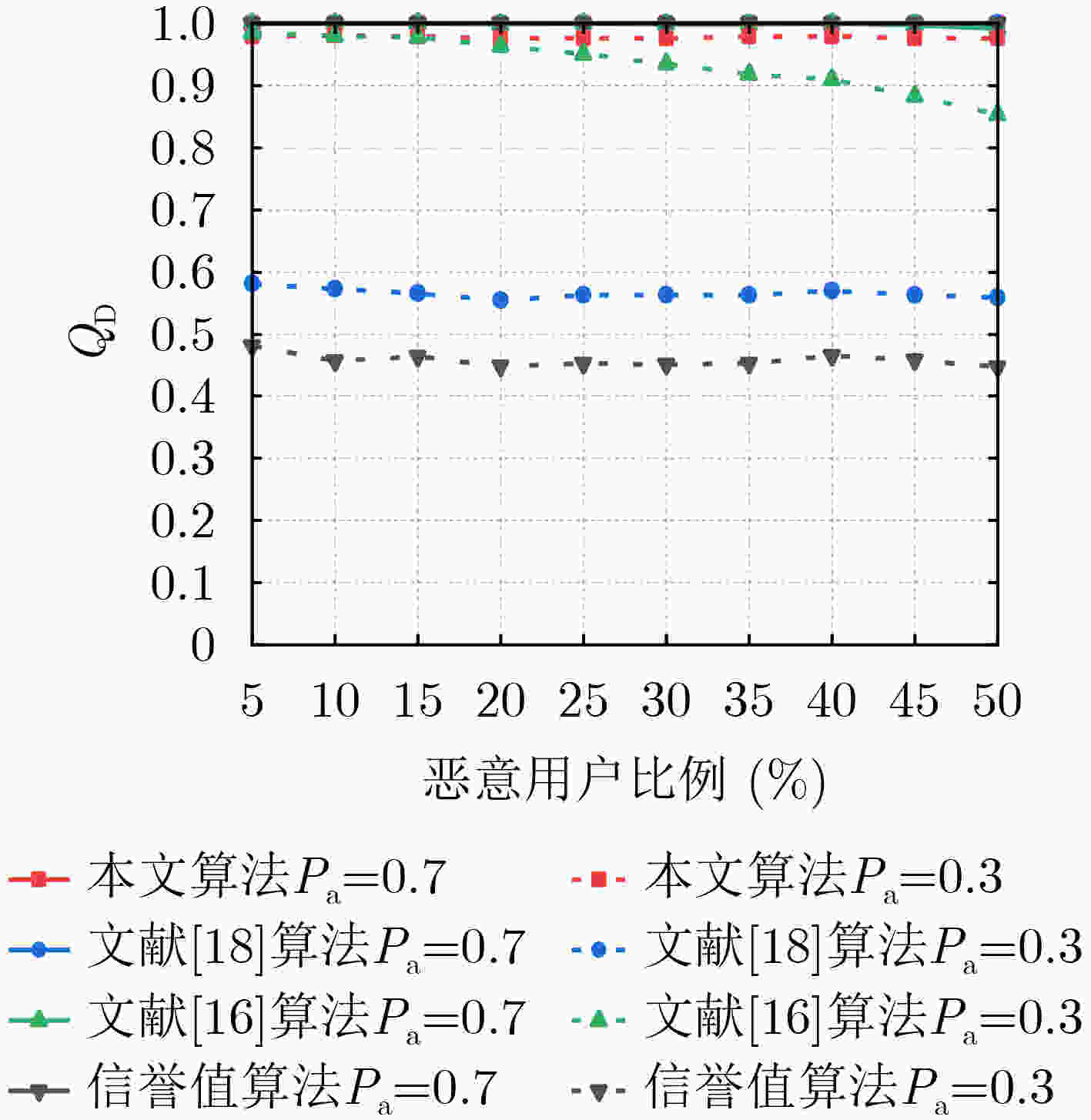
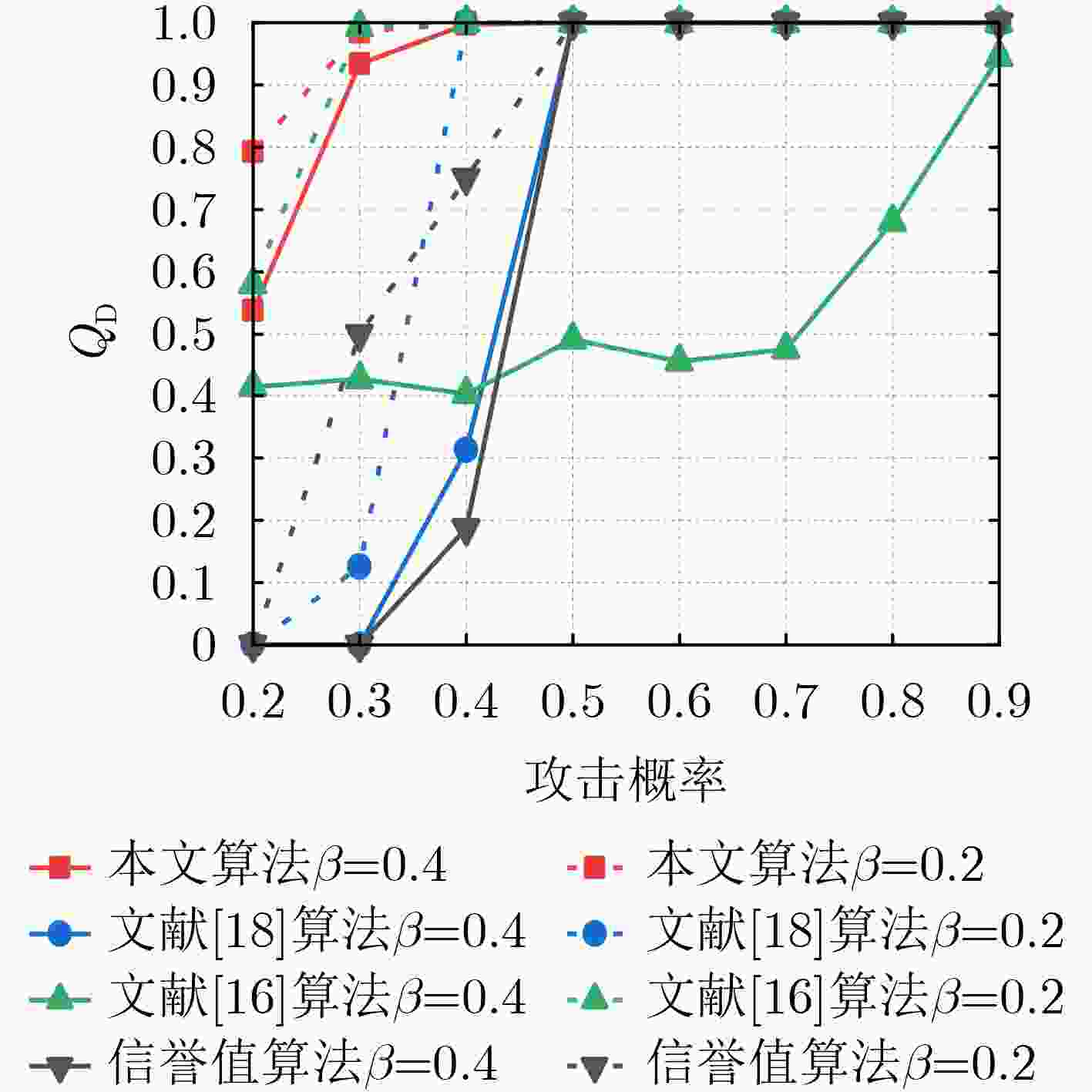
Abstract:Objective With the rapid development of 5G and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and the increasing number of devices accessing wireless networks, Cognitive Radio (CR) technology offers an effective solution to alleviate spectrum resource scarcity. CR allows Secondary Users (SU) to perform spectrum sensing and share the Primary User (PU) frequency band. However, Cooperative Spectrum Sensing (CSS) is vulnerable to Spectrum Sensing Data Falsification (SSDF) attacks by Malicious Users (MU), which degraded sensing performance. Existing anti-SSDF algorithms, while reducing the effects of SSDF attacks, face challenges in detecting MU under complex attack strategies. This study proposes the use of multiscale entropy to enhance anti-SSDF attack schemes. By updating the reputation value of SU sensing results through multiscale analysis, the detection performance and MU detection rate of the CSS algorithm under various attack strategies are significantly improved. This work provides a solution to the problem of SSDF attacks under complex strategies and offers a theoretical foundation for CSS technology in areas with scarce spectrum resources. Methods The multiscale entropy algorithm calculates the reputation value of the SU using a sliding window model. It extracts effective features from the local sensing results of the SU and converts them into weights, which are then used to update the SU’s reputation value. The final reputation value is compared with a threshold to identify MU. The sliding window model collects SU sensing results from different time slots and computes the reputation value by comparing them with the Fusion Center (FC) judgment results. A normalization function processes the updated reputation value to derive the final global decision. A higher reputation value indicates that the SU’s local sensing result is more reliable, while a lower reputation value suggests the user may be an MU. Results and Discussions The multiscale entropy algorithm performs multiscale analysis of the SU perception results based on a sliding window model. This approach mitigates the impact of MU on CSS system performance by extracting effective features to counter Independent Attacks (IA) and Collaborative Attacks (CA). Simulation results show that CA affects CSS performance more significantly than IA ( Fig. 3 ,Fig. 4 ). The proposed algorithm effectively identifies MUs under both attack strategies (Fig. 7 ,Fig. 9 ), demonstrating its effectiveness. Additionally, the algorithm exhibits low complexity (Table 1 ). Under both IA and CA, when the attack probability exceeds 0.4, the MU detection rate improves by an average of 3.56%, 0.77%, and 6.45%, 36.92%, respectively, compared to the baseline algorithms. These results highlight the strong anti-attack capability of the proposed algorithm.Conclusions This paper addresses the SSDF attacks problem in CSS. The detection capability of MU is constrained by the reliability of the global decision. To mitigate this issue, a CSS method based on multiscale entropy is proposed. The method, built on the sliding window model, utilizes multiscale entropy to extract feature information that enhances judgment accuracy, thereby updating the reputation value and improving the global decision. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm exhibits strong resistance to SSDF attacks and performs well in MU detection under both IA and CA, with lower complexity. This approach is particularly suitable for regions with scarce spectrum resources, ensuring the reliable operation of CR systems and enabling efficient spectrum utilization by effectively identifying MU. Future work will explore the application of deep learning techniques in CSS against SSDF attacks, aiming to further enhance network performance. -
Key words:
- Cooperative spectrum sensing (CSS) /
- SSDF attacks /
- Reputation value /
- Multiscale entropy
-
1 多尺度熵算法
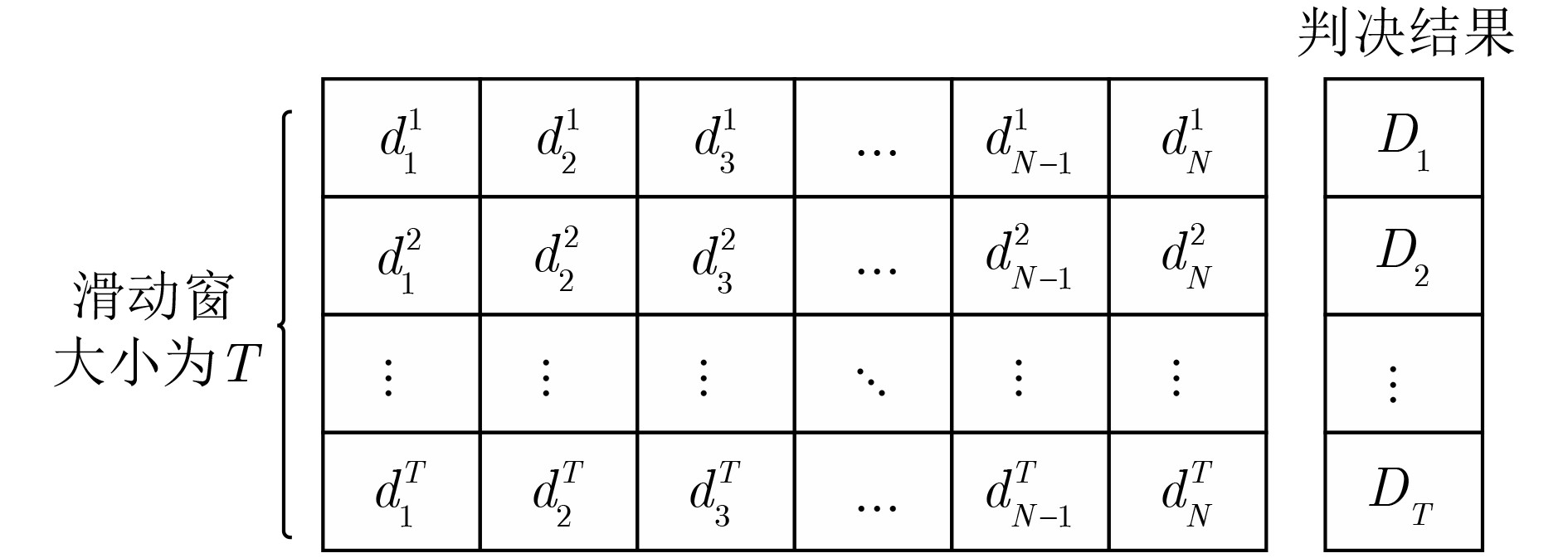
初始化:恶意用户集合$M$为空 (1) for$t = 1:T$do (2) for$i = 1:N$do (3) SU进行本地频谱感知,将结果上传至FC; (4) FC根据上传结果${r_i}$,通过式(16)获得全局决策${D_t}$; (5) 计算信誉值${R_i} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{t = 1}^T {{\tau _i}(t)/T} $; (6) end for (7) end for (8) for$i = 1:N$do (9) 根据式(17)–式(21),计算多尺度熵$ {{{M}}_{{\mathrm{SE}}}} $; (10) 按照式(22)将式(21)化为权重,计算调整后的信誉值${h_i}$; (11) 对${h_i}$归一化处理,得到最终信誉值${H_i}$; (12) If ${H_i} < \varLambda $ then (13) ${{M}} \leftarrow {{M}} + \left\{ i \right\}$; (14) end if (15) end for (16) 通过式(25),做出最终全局决策$D_t^{'}$; 表 1 算法数学运算次数与复杂度对比
运算 所提算法 文献[16]算法 所提算法复杂度 文献[16]算法复杂度 $ + / - $ $\begin{gathered} (m + 2){(L - m + {\text{1}})^2} \\ + {\text{3(}}G - L{\text{)}} + T + 1 \\ \end{gathered} $ $NT + 2N + l - 1$ $ \begin{array}{c}{O}(N\cdot ((m+2){(}{L-m+1)^2}\\ +\text{3(}G-L\text{)}+T+1))\end{array} $ $ \begin{array}{c}{ O}(N\cdot (NT+2N+l)\\ +2N-2)\end{array} $ $ \times $ 1 2 ${O}(N)$ ${O}(N + {\text{1}})$ $ \div $ $L + {\text{7}}$ 3 $ {O}(N\cdot(L+\text{7})) $ ${O}(N + {\text{2}})$ -
[1] SHAFIQUE K, KHAWAJA B A, SABIR F, et al. Internet of Things (IoT) for next-generation smart systems: a review of current challenges, future trends and prospects for emerging 5G-IoT scenarios[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 23022–23040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970118. [2] KHASAWNEH M, AZAB A, ALRABAEE S, et al. Convergence of IoT and cognitive radio networks: a survey of applications, techniques, and challenges[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 71097–71112. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3294091. [3] DAI M Y, WU J, LIANG X S, et al. A self-correcting cooperative spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks in low SNR region[C]. 2023 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT). Wuxi, China, 2023: 1385–1389. doi: 10.1109/ICCT59356.2023.10419802. [4] XU Z Y, SUN Z G, GUO L L, et al. Joint spectrum sensing and spectrum access for defending massive SSDF attacks: a novel defense framework[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2022, 31(2): 240–254. doi: 10.1049/cje.2021.00.090. [5] FRAGKIADAKIS A G, TRAGOS E Z, and ASKOXYLAKIS I G. A survey on security threats and detection techniques in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2013, 15(1): 428–445. doi: 10.1109/SURV.2011.122211.00162. [6] 郭文祥, 余志勇, 逄晨, 等. 认知无线电频谱感知技术综述[J]. 通信技术, 2018, 51(2): 261–265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2018.02.001.GUO Wenxiang, YU Zhiyong, PANG Chen, et al. Overview on cognitive radio spectrum sensing technology[J]. Communications Technology, 2018, 51(2): 261–265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2018.02.001. [7] WU J, SONG T C, YU Y, et al. Generalized byzantine attack and defense in cooperative spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 53272–53286. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2866485. [8] CHOUHAN A, PARMAR A, CAPTAIN K, et al. Defending against byzantine attacks in CRNs: PCA-based malicious user detection and weighted cooperative spectrum Sensing[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024, 13(5): 1488–1492. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2024.3377275. [9] WU J, LI P, CHEN Y, et al. Analysis of byzantine attack strategy for cooperative spectrum sensing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(8): 1631–1635. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2990869. [10] PARMAR A, SHAH K, CAPTAIN K M, et al. Gaussian mixture model-based anomaly detection for defense against byzantine attack in cooperative spectrum sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(2): 499–509. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3342409. [11] BENEDETTO F, CORONAS P, GIUNTA G, et al. A reputation-based cooperative spectrum sensing in the presence of malicious byzantine users[C]. 2018 IEEE 87th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring). Porto, Portugal, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2018.8417486. [12] REN J, ZHANG Y X, YE Q, et al. Exploiting secure and energy-efficient collaborative spectrum sensing for cognitive radio sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(10): 6813–6827. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2591006. [13] ZHANG Q Y, ZENG W H, QIN Z J, et al. TaP2-CSS: A trustworthy and privacy-preserving cooperative spectrum sensing solution based on blockchain[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(8): 14634–14646. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3344648. [14] CHATTERJEE P S. Systematic survey on SSDF attack and detection mechanism in cognitive wireless sensor network[C]. 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT). Hubli, India, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CONIT51480.2021.9498386. [15] XIAO S F, WU J, LIN P Y, et al. Reputation-based self-differential sequential mechanism for collaborative spectrum sensing against byzantine attack in cognitive wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2024, 8(10): 1–4. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2024.3454708. [16] CHOUHAN A, CAPTAIN K, PARMAR A, et al. Defending cooperative spectrum sensing from byzantine attacks: An effective entropy-based weighted algorithm[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(12): 2063–2067. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3306814. [17] MA L C, XIANG Y, PEI Q Q, et al. Robust reputation-based cooperative spectrum sensing via imperfect common control channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(5): 3950–3963. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2763980. [18] FU Y H and HE Z M. Bayesian-inference-based sliding window trust model against probabilistic SSDF attack in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 1764–1775. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2936263. [19] 宋铁成, 吴俊, 梁浩宇, 等. 基于滑动窗口的协作频谱感知对抗拜占庭攻击[J]. 信息对抗技术, 2024, 3(3): 63–78. doi: 10.12399/j.issn.2097-163x.2024.03.004.SONG Tiecheng, WU Jun, LIANG Haoyu, et al. Sliding window-based cooperative spectrum sensing against byzantine attack[J]. Information Countermeasure Technology, 2024, 3(3): 63–78. doi: 10.12399/j.issn.2097-163x.2024.03.004. [20] 孙志国, 王钊, 陈增茂, 等. 基于双重信誉值与多角度权值的抗SSDF攻击协作频谱感知方法[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(12): 134–145. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023213.SUN Zhiguo, WANG Zhao, CHEN Zengmao, et al. Double reputation and multi-angle weight-based cooperative spectrum sensing method against SSDF attacks[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(12): 134–145. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023213. [21] ZHANG L Y, DING G R, WU Q H, et al. Byzantine attack and defense in cognitive radio networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(3): 1342–1363. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2422735. [22] 尹洪梅. 基于多尺度熵的水热型地热可持续取热理论及实验研究[D]. [博士论文], 天津大学, 2022. doi: 10.27356/d.cnki.gtjdu.2022.000056.YIN Hongmei. Theoretical and experimental study on hydrothermal geothermal sustainable heat extraction based on multi-scale entropy[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Tianjin University, 2022. doi: 10.27356/d.cnki.gtjdu.2022.000056. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
