Wire Length Driven Tension Refine Based Macro Placer
-
摘要: 随着重用方法学被引入到超大规模集成电路设计中,宏单元的使用率大幅提高。宏单元与标准单元之间巨大的尺寸差异给电路布局器带来了严峻的挑战。该文提出并实现了基于张力微调和线长驱动的宏单元布局器 WIMPlace。该文方法结合了基于权重的分割方法和受液体表面张力原理启发的宏单元微调技术,以实现有效的宏放置。WIMPlace算法采用4步流程:预处理、预布局、宏微调和宏合法化,并在其中宏微调阶段合理利用标准单元密度和线长函数进行优化。该文采用DREAMPlace2.0布局工具作为后端布局器,并在现代混合尺寸(MMS)测试集上进行实验。实验结果表明,与学术界领先的混合尺寸布局器ePlace-MS和最新的DREAMPlace4.0结果相比,在总共16个案例中的15个中,该文所提的WIMPlace算法都实现了最短的线长(HPWL),这表明该文方法在优化线长方面非常有效。Abstract:
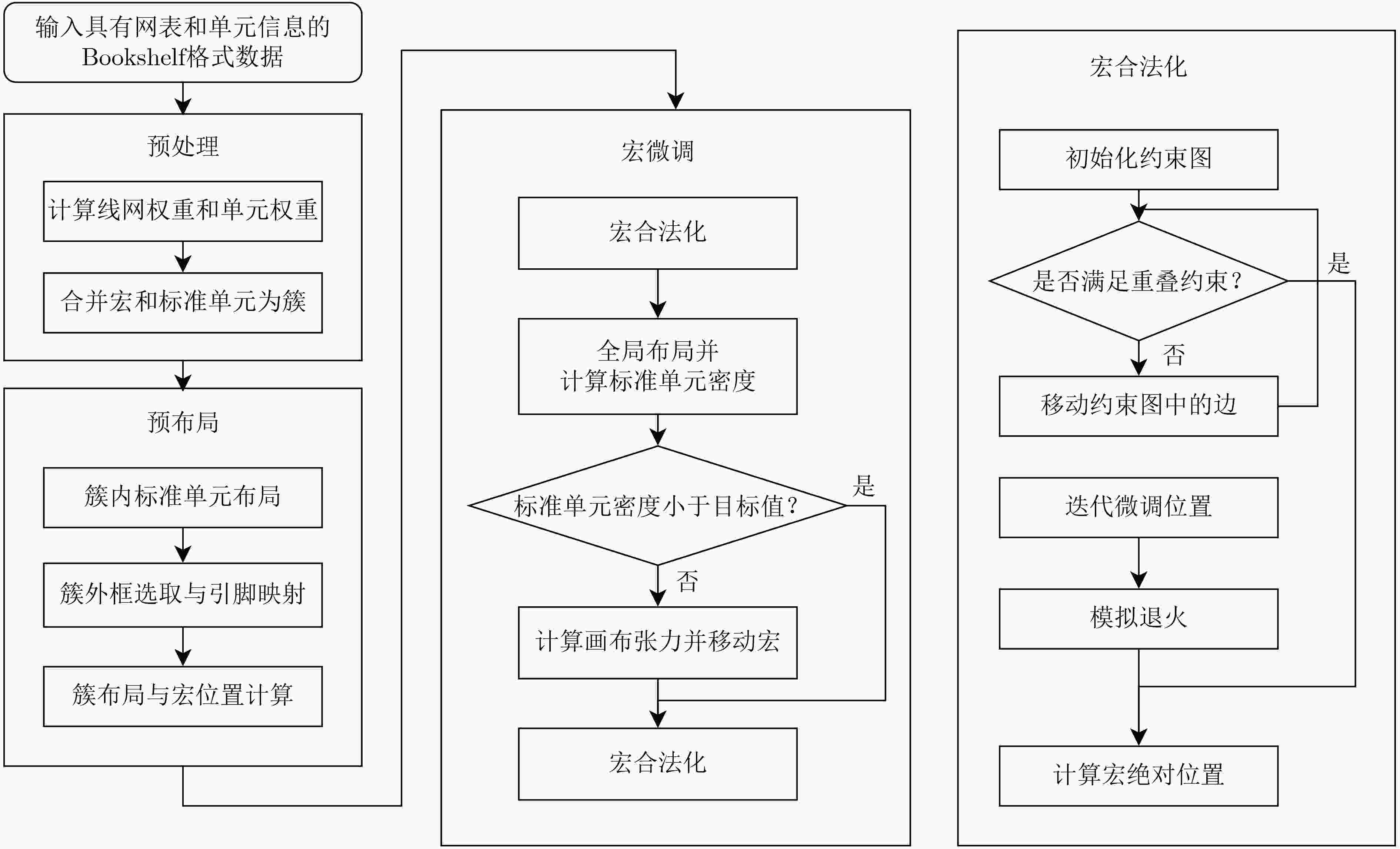
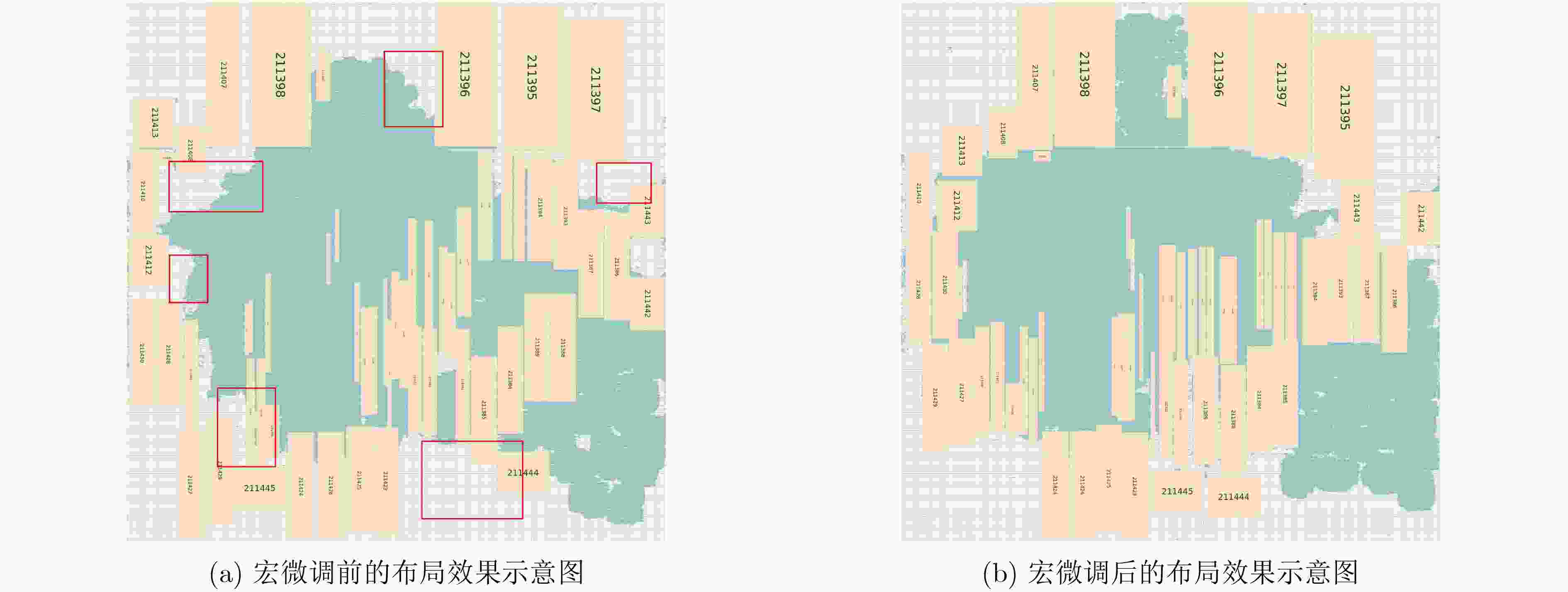
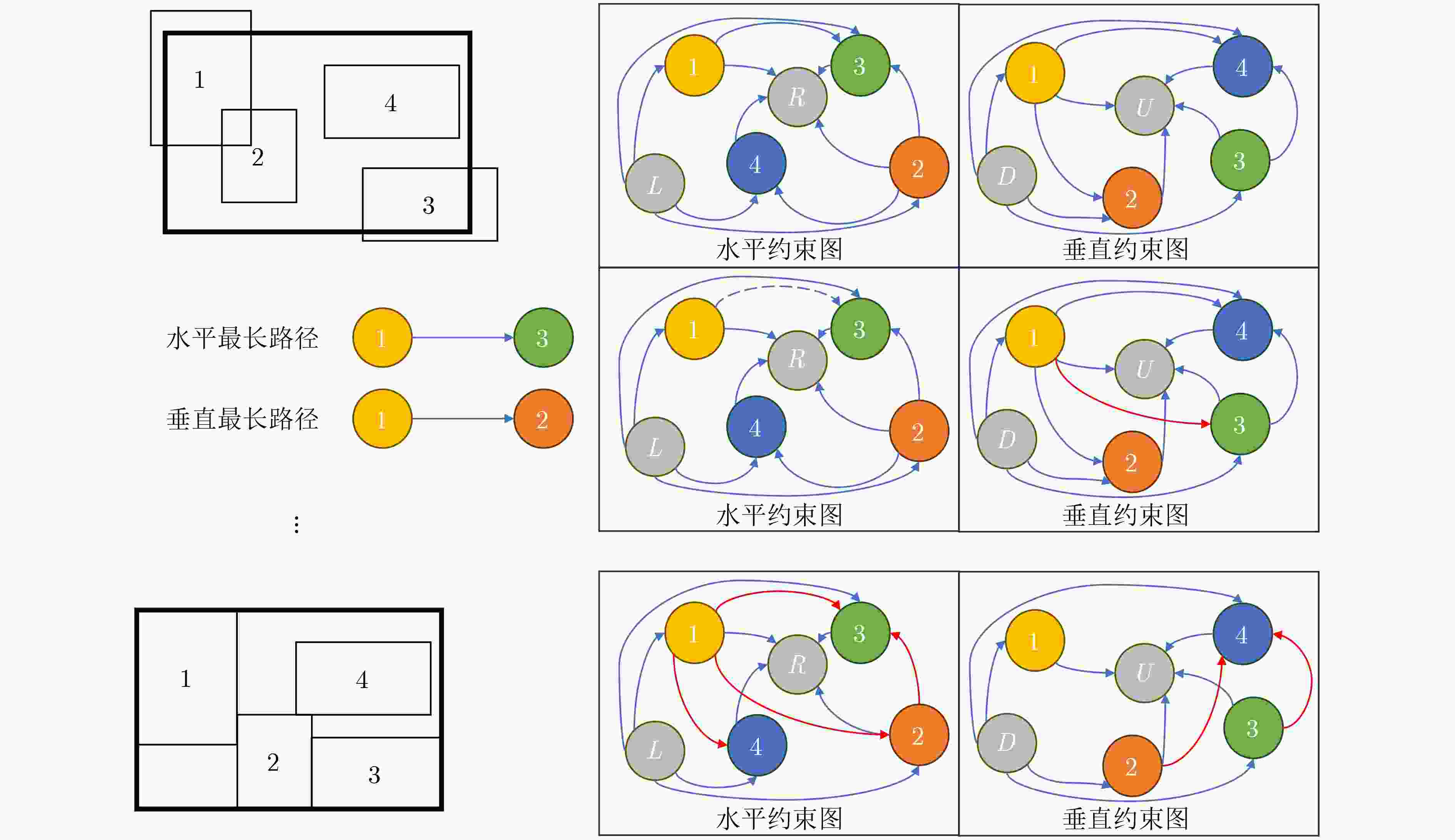
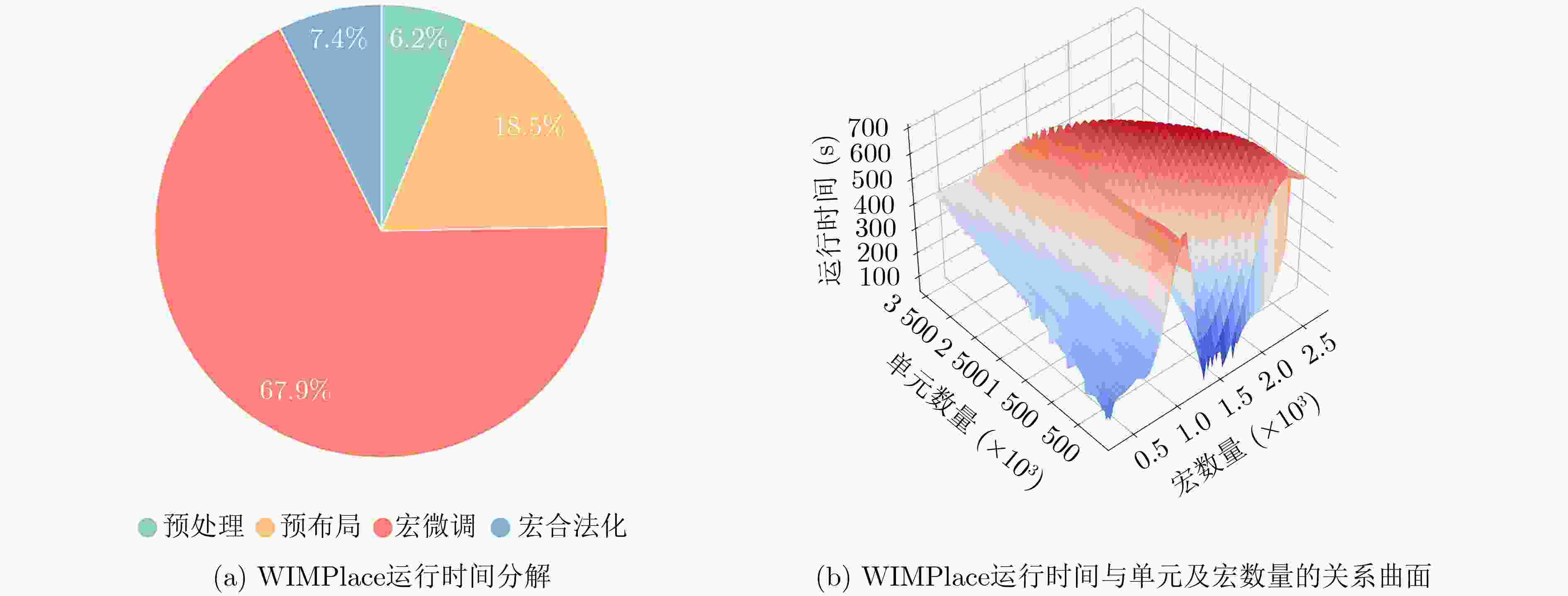
Objective With the introduction of reuse methodologies in integrated circuit design, the utilization of macro cells in Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) has significantly increased. However, the considerable size difference between macro cells and standard cells presents a significant challenge for circuit placers. This study proposes a novel macro placer, WIMPlace, based on tension fine-tuning and wirelength-driven approaches. The aim is to address issues such as density imbalance and degradation of solution quality observed in existing mixed-size placers, thereby providing a more effective solution for VLSI design. Methods The proposed method in this paper consists of four stages: preprocessing, pre-placement, macro cell fine-tuning, and macro legalization. Initially, a weight-based partitioning approach is employed to group standard cells with macro into supersets, addressing density issues during the initial placement (Section 3.1). In the pre-placement stage, the DREAMPlace 2.0 tool is used for placing standard cells, and the initial positions of macro cells are determined based on the locations of these clusters (Section 3.2). A local tension model, inspired by the principle of surface tension in liquids, is then adopted to fine-tune the positions of macros, ensuring that connections between standard cells and macros are as compact as possible (Section 3.3, Fig. 2 ). Finally, a constraint graph-based macro legalization strategy is applied to prevent overlaps between macros (Section 3.4,Fig. 3 ).Results and Discussions Experimental results demonstrate that the WIMPlace achieves exceptional performance on the MMS benchmark, outperforming other advanced mixed-size placers, such as ePlace-MS and DREAMPlace 4.0. Specifically, in 15 out of 16 cases, it achieved the shortest wirelength, with average reductions of 4.31% and 2.39%, respectively (Section 4, Table 2 ). Additionally, WIMPlace exhibits excellent solution stability, particularly showing a linear increase in runtime as the number of cells increases (Section 4,Fig. 4 ), indicating that the algorithm not only optimizes wirelength effectively but also demonstrates high computational efficiency. Notably, in the newblue3 case, despite the macro cells occupying a significant portion of the chip area, WIMPlace still demonstrated strong adaptability.Conclusions In summary, WIMPlace, as proposed in this paper, is an efficient macro cell placer that achieves gradual fine-tuning optimization of macro cells by combining gradient field movements based on a surface tension analogy and employing preprocessing techniques to balance macros with their associated standard cells. Compared to existing mixed-size placers, WIMPlace demonstrates superior performance across multiple key metrics, particularly in wirelength optimization. Future work could focus on integrating additional design objectives, such as timing, congestion, and thermal management, to enhance the applicability and flexibility of WIMPlace. This study provides new perspectives and technical approaches for VLSI design. -
1 单元预处理算法
输入:待布局的线网集合E和单元集合V。 输出:分块后的结果P。 步骤1 初始化所有单元和线网权重为0; 步骤2 遍历所有宏单元N; 步骤2.1 更新宏单元权重; 步骤2.2 遍历下一层驱动单元直到达到设定值; 步骤2.2.1 根据式(4)更新驱动线网权重; 步骤2.2.2 根据式(5)更新驱动单元权重; 步骤3 遍历所有宏单元N,若单元对当前宏权重最大则加入组P。 表 1 MMS测试套件统计数据
电路 单元总数 可移动单元数量 标准单元数量 宏数量 端子数量 线网数量 目标密度(%) ADAPTEC1 211 447 210 967 210 904 63 480 221 142 100 ADAPTEC2 255 023 254 584 254 457 127 439 266 009 100 ADAPTEC3 451 650 450 985 450 927 58 665 466 758 100 ADAPTEC4 496 054 494 785 494 716 69 1 260 515 951 100 ADAPTEC5 843 128 842 558 842 482 76 570 867 798 50 BIGBLUE1 278 164 277 636 277 604 32 528 284 479 100 BIGBLUE2 557 866 535 741 534 782 959 22 125 577 235 100 BIGBLUE3 1 096 812 1 095 583 1 093 034 2 549 1 229 1 123 170 100 BIGBLUE4 2 177 353 2 169 382 2 169 183 199 7 970 2 229 886 100 NEWBLUE1 330 474 330 137 330 073 64 337 338 901 80 NEWBLUE2 441 516 440 264 436 516 3 748 1 252 465 219 90 NEWBLUE3 494 011 482 884 482 833 51 11 127 552 199 80 NEWBLUE4 646 139 642 798 642 717 81 3 341 637 051 50 NEWBLUE5 1 233 058 1 228 268 1 228 177 91 4 790 1 284 251 50 NEWBLUE6 1 255 039 1 248 224 1 248 150 74 6 815 1 288 443 80 NEWBLUE7 2 507 954 2 481 533 2 481 372 161 26 421 2 636 820 80 表 2 MMS基准测试套件的HPWL和sHPWL(×106)测试结果
基准 FLOP FP3.0 CPx POLAR mPL6 NP3U DP2.0 ePlace-MS DP4.0 本文 ADAPTEC1 76.83 82.39 79.05 92.17 77.84 75.55 67.68 66.99 65.75 65.71 ADAPTEC2 84.14 88.53 99.11 149.43 88.40 78.50 83.62 76.76 76.78 73.55 ADAPTEC3 175.99 187.98 175.18 170.48 180.40 169.74 174.63 161.55 157.47 156.93 ADAPTEC4 161.68 187.50 156.75 175.19 162.02 166.68 143.44 147.04 144.40 142.96 ADAPTEC5 357.83 338.74 338.67 340.45 336.30 294.24 368.45 312.86 307.25 291.99 BIGBLUE1 94.92 104.91 96.18 99.12 99.36 96.57 85.75 86.29 85.80 85.67 BIGBLUE2 153.02 145.89 147.19 157.72 144.37 147.17 137.67 130.06 125.49 123.14 BIGBLUE3 346.24 400.40 344.63 420.28 319.63 338.47 280.5 284.39 277.55 276.15 BIGBLUE4 777.84 775.43 772.53 814.07 804.00 799.66 654.54 656.68 647.21 645.98 NEWBLUE1 67.97 73.91 65.26 70.68 66.93 61.25 66.62 61.87 60.95 56.27 NEWBLUE2 187.40 197.15 187.87 197.65 179.18 163.76 159.79 162.68 159.25 150.40 NEWBLUE3 345.99 325.72 269.47 601.17 415.86 280.92 351.25 304.16 281.57 274.49 NEWBLUE4 256.54 270.70 256.97 277.60 277.69 229.36 261.2 229.20 225.34 220.91 NEWBLUE5 510.83 500.09 453.05 450.69 515.49 420.46 458.31 392.93 390.97 390.03 NEWBLUE6 493.64 512.19 452.83 475.78 482.44 474.86 461.8 409.28 414.17 393.59 NEWBLUE7 1078.18 1016.10 1010.00 1107.59 1038.66 1100.84 946.3 895.11 886.18 883.51 平均sHPWL 20.37% 24.72% 16.83% 36.04% 21.44% 12.67% 11.38% 4.31% 2.39% 0% -
[1] CHENG C K, KAHNG A B, KUNDU S, et al. Assessment of reinforcement learning for macro placement[C]. The 2023 International Symposium on Physical Design, New York, USA, 2023: 158–166. doi: 10.1145/3569052.3578926. [2] LANIUS C, LOU Jie, LOH J, et al. Automatic generation of structured macros using standard cells‒application to CIM[C]. The 2023 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, Vienna, Austria, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ISLPED58423.2023.10244608. [3] YU Shenglu and DU Shimin. VLSI floorplanning algorithm based on reinforcement learning with obstacles[M]. SAMSONOVICH A V and LIU Tingting. Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures 2023. Cham: Springer, 2024: 1034–1043. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-50381-8_110. [4] CHANG Y C, CHANG Yaowen, WU Guangming, et al. B*-Trees: A new representation for non-slicing floorplans[C]. The 37th Annual Design Automation Conference, Los Angeles, USA, 2000: 458–463. doi: 10.1145/337292.337541. [5] HONG Xianlong, HUANG Gang, CAI Yici, et al. Corner block list: An effective and efficient topological representation of non-slicing floorplan[C]. IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design, San Jose, USA, 2000: 8–12. doi: 10.1109/ICCAD.2000.896442. [6] YAN J Z, VISWANATHAN N, and CHU C. Handling complexities in modern large-scale mixed-size placement[C]. Proceedings of the 46th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2009: 436–441. doi: 10.1145/1629911.1630028. [7] KIM M C and MARKOV I L. ComPLx: A competitive primal-dual Lagrange optimization for global placement[C]. The 49th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2012: 747–752. doi: 10.1145/2228360.2228496. [8] LIN Tao, CHU C, SHINNERL J R, et al. POLAR: Placement based on novel rough legalization and refinement[C]. 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, USA, 2013: 357–362. doi: 10.1109/ICCAD.2013.6691143. [9] CHEN T C, JIANG Zhewei, HSU T C, et al. NTUplace3: An analytical placer for large-scale mixed-size designs with preplaced blocks and density constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2008, 27(7): 1228–1240. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2008.923063. [10] CHAN T F, CONG J, SHINNERL J R, et al. mPL6: Enhanced multilevel mixed-size placement[C]. The 2006 International Symposium on Physical Design, San Jose, USA, 2006: 212–214. doi: 10.1145/1123008.1123055. [11] LU Jingwei, ZHUANG Hao, CHEN Pengwen, et al. ePlace-MS: Electrostatics-based placement for mixed-size circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2015, 34(5): 685–698. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2391263. [12] AGNESINA A, RAJVANSHI P, YANG Tian, et al. AutoDMP: Automated DREAMPlace-based macro placement[C]. The 2023 International Symposium on Physical Design, 2023: 149–157. doi: 10.1145/3569052.3578923. [13] YU Tao, GAO Peng, WANG Fei, et al. Non‐overlapping placement of macro cells based on reinforcement learning in chip design[J]. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 2025, 53(2): 1159–1170. doi: 10.1002/cta.4235. [14] SCHLAG S, HEUER T, GOTTESBÜREN L, et al. High-quality hypergraph partitioning[J]. ACM Journal of Experimental Algorithmics, 2022, 27: 1.9. doi: 10.1145/3529090. [15] CHEON Y and WONG D F. Design hierarchy guided multilevel circuit partitioning[C]. The 2002 International Symposium on Physical Design, San Diego, USA, 2002: 30–35. doi: 10.1145/505388.505398. [16] LIN Yibo, PAN D Z, REN Haoxing, et al. DREAMPlace 2.0: Open-source GPU-accelerated global and detailed placement for large-scale VLSI designs[C]. 2020 China Semiconductor Technology International Conference, Shanghai, China, 2020: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/CSTIC49141.2020.9282573. [17] CONG J and XIE Min. A robust detailed placement for mixed-size IC designs[C]. The 2006 Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 2006: 188–194. doi: 10.1145/1118299.1118353. [18] VISWANATHAN N, PAN Min, and CHU C. FastPlace 3.0: A fast multilevel quadratic placement algorithm with placement congestion control[C]. 2007 Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 2007: 135–140. doi: 10.1109/ASPDAC.2007.357975. [19] HSU M K and CHANG Yaowen. Unified analytical global placement for large-scale mixed-size circuit designs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2012, 31(9): 1366–1378. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2012.2193582. [20] LIAO Peiyu, GUO Dawei, GUO Zizheng, et al. DREAMPlace 4.0: Timing-driven placement with momentum-based net weighting and Lagrangian-based refinement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2023, 42(10): 3374–3387. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2023.3240132. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
