Differentially Private Federated Learning Based Wideband Spectrum Sensing for the Low-Altitude Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Swarm
-
摘要: 在低空智联网中,以无人机(UAV)为载体的宽带频谱感知技术在实现高效频谱监测与利用方面起着至关重要的作用。然而,以奈奎斯特速率采样需要很高的硬件和计算成本,无人机的高移动性也会使其处于不断变化的无线频谱环境,进而严重影响感知精度,无人机宽带频谱感知面临严峻挑战。针对上述问题,该文首先设计了一个低复杂度的特征拆分宽带频谱感知神经网络(FS-WSSNet),可在次奈奎斯特采样速率下实现高精度感知,以降低在无人机上的部署成本。随后,为充分整合利用低空智联网中多架无人机的频谱环境知识与计算资源,以适应其遇到的不同频谱环境,提出了一种基于差分隐私联邦迁移学习(DPFTL)的模型在线调整算法。该方法利用局部差分隐私,在协调多无人机上传模型参数至中心计算平台之前引入噪声,从而在无人机群体中同时实现频谱环境知识共享和数据隐私保护,使得其中每个无人机能够快速适应不断变化的频谱环境。仿真结果表明,同目前先进方案相比,FS-WSSNet在复杂度和感知性能方面均表现优越,使用所提的基于DPFTL的方案后,FS-WSSNet在无人机经历的多个新场景中无需模型调整,感知精度整体接近集中式训练。Abstract:
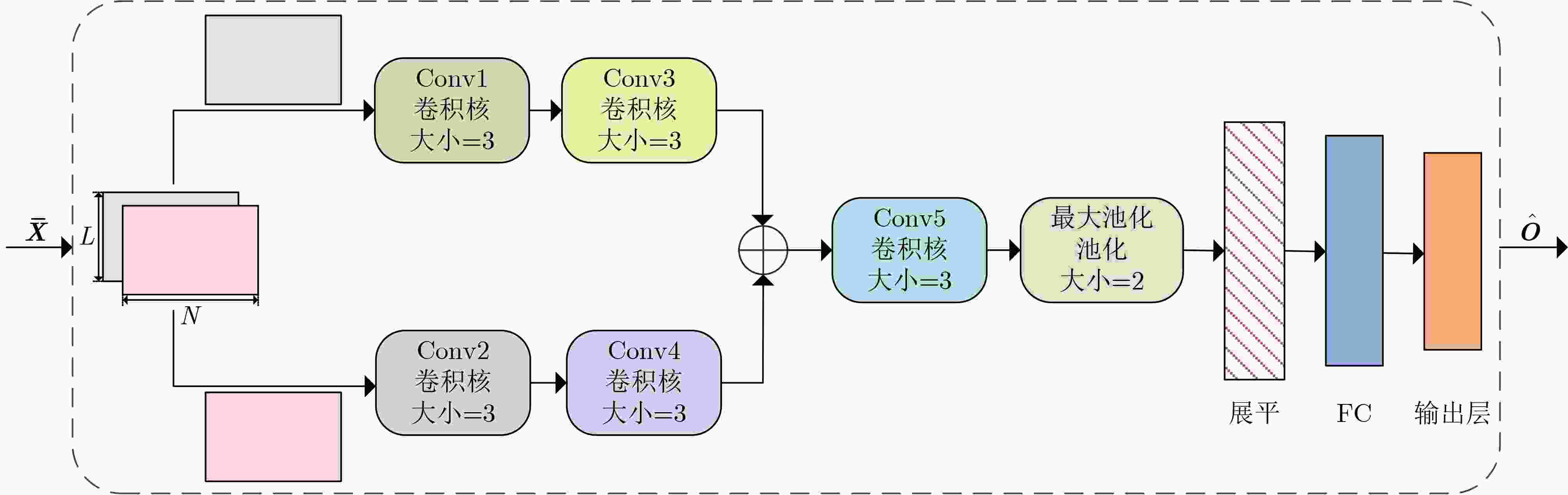
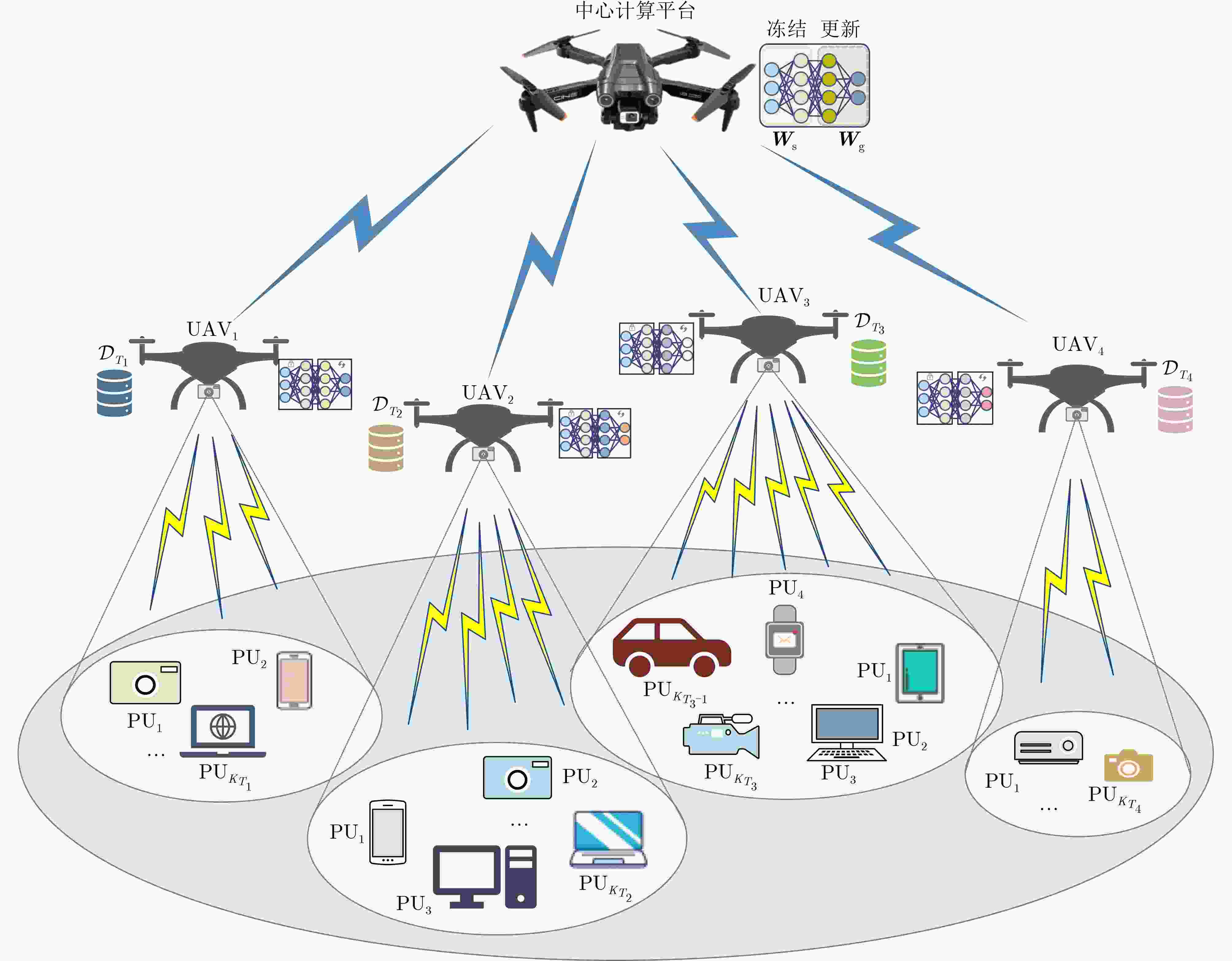
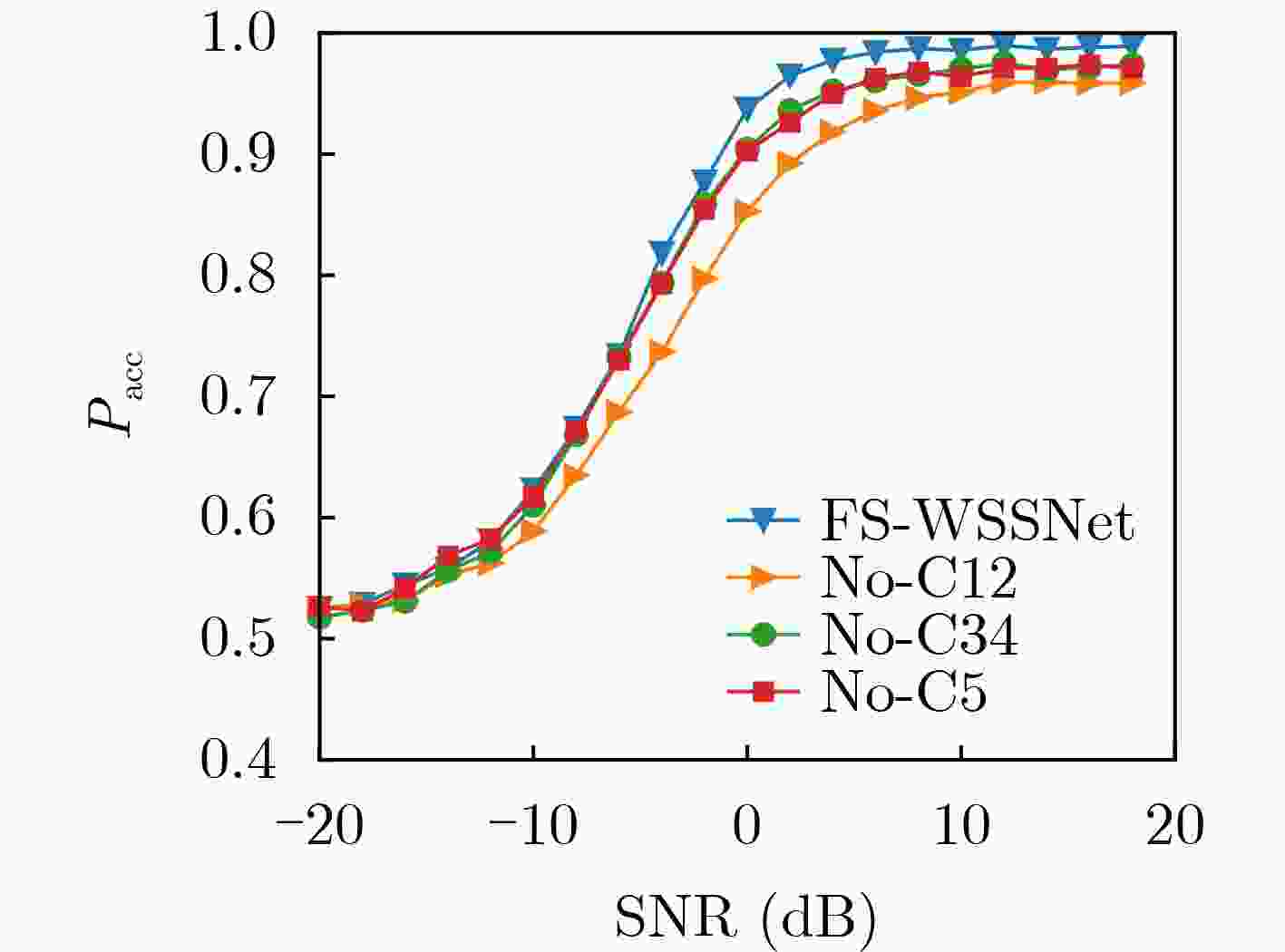
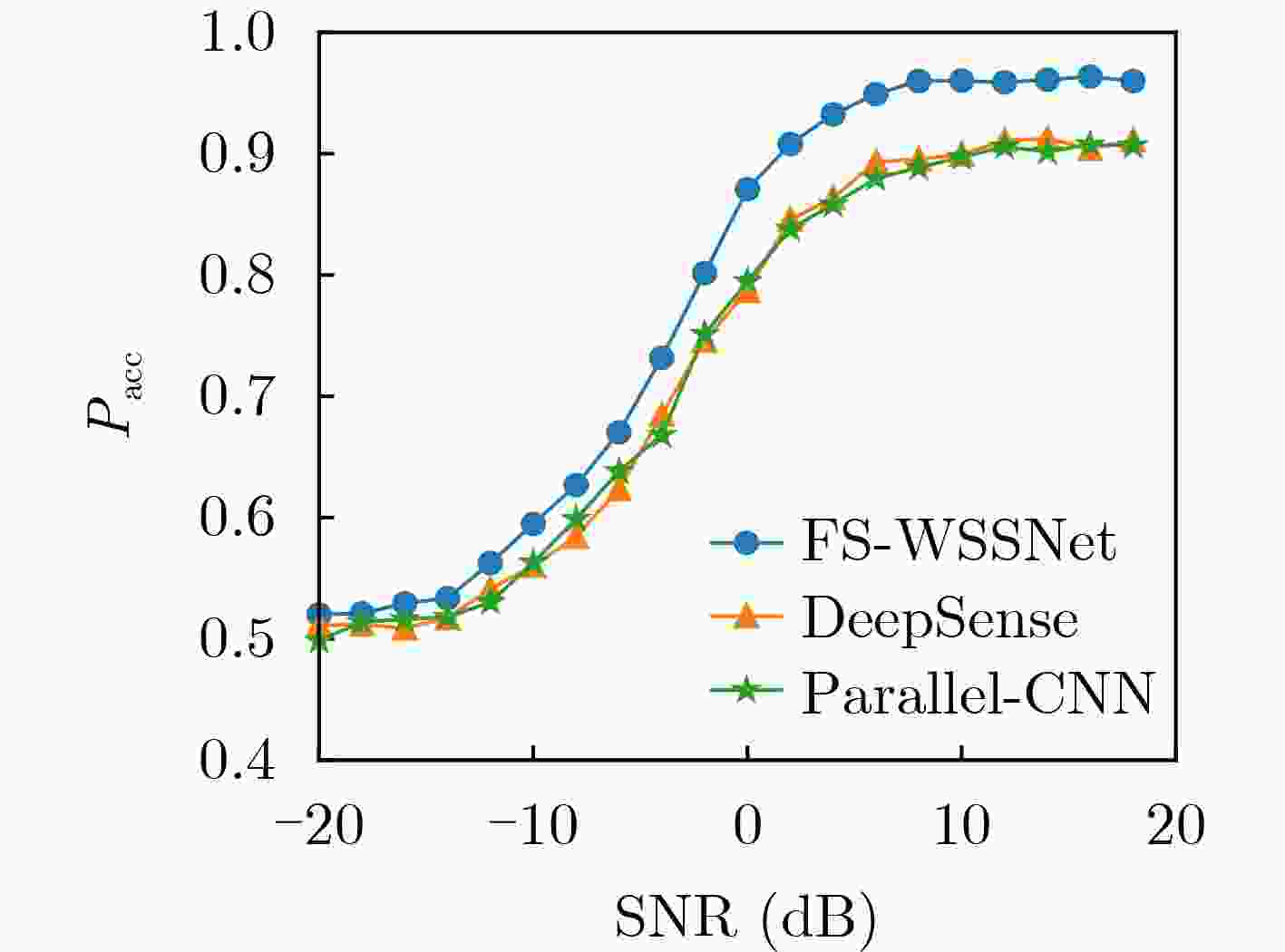
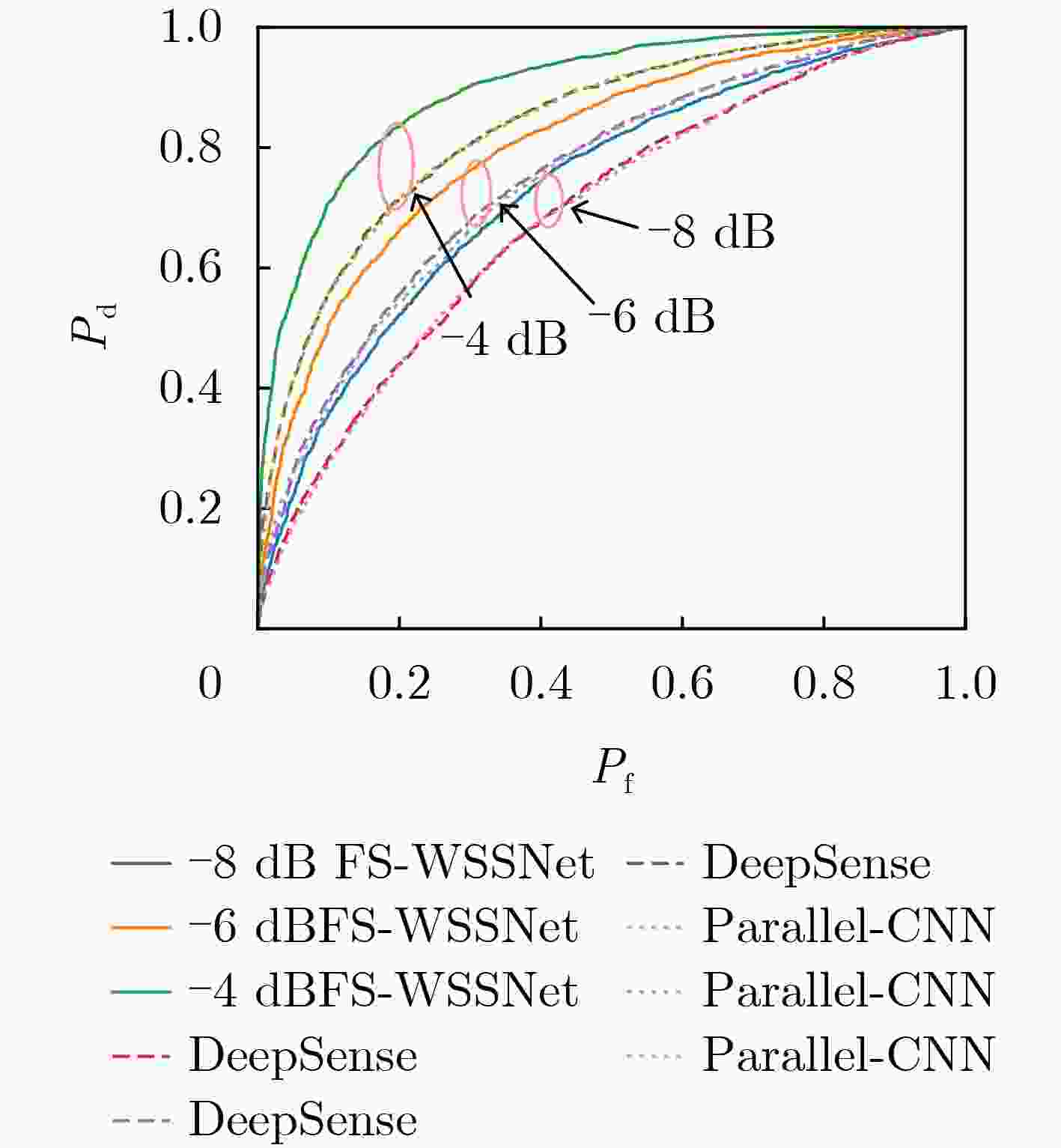
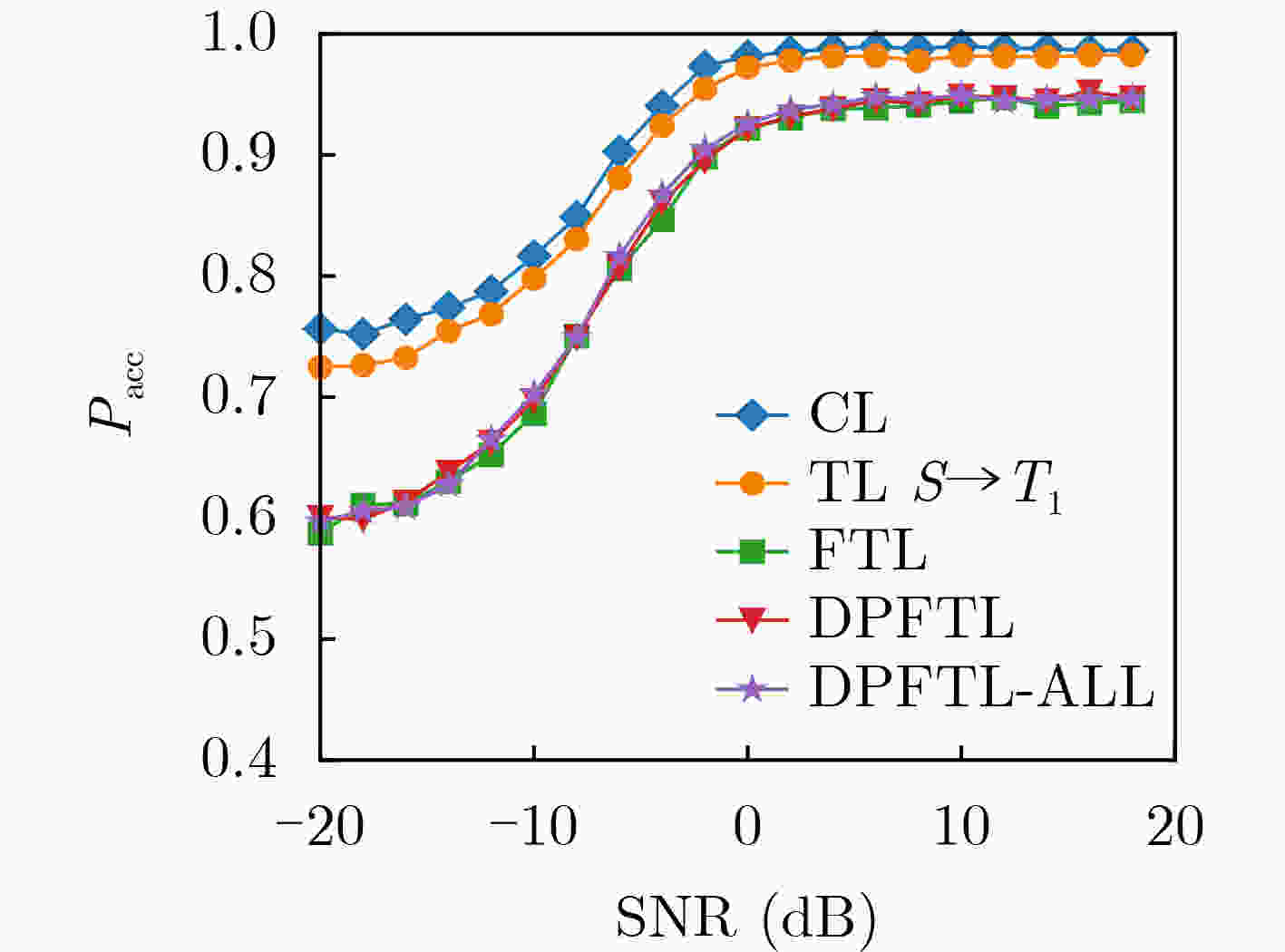
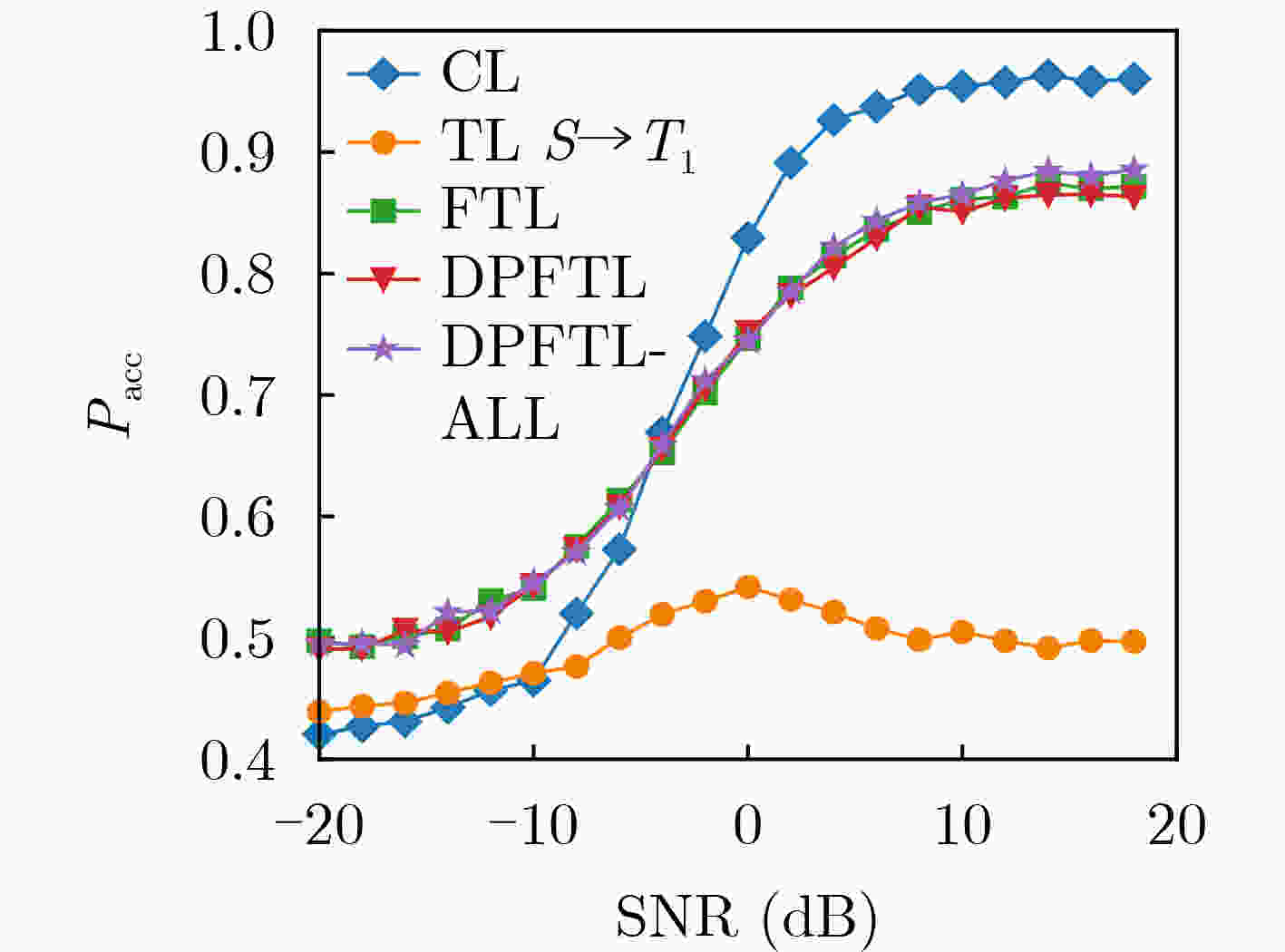
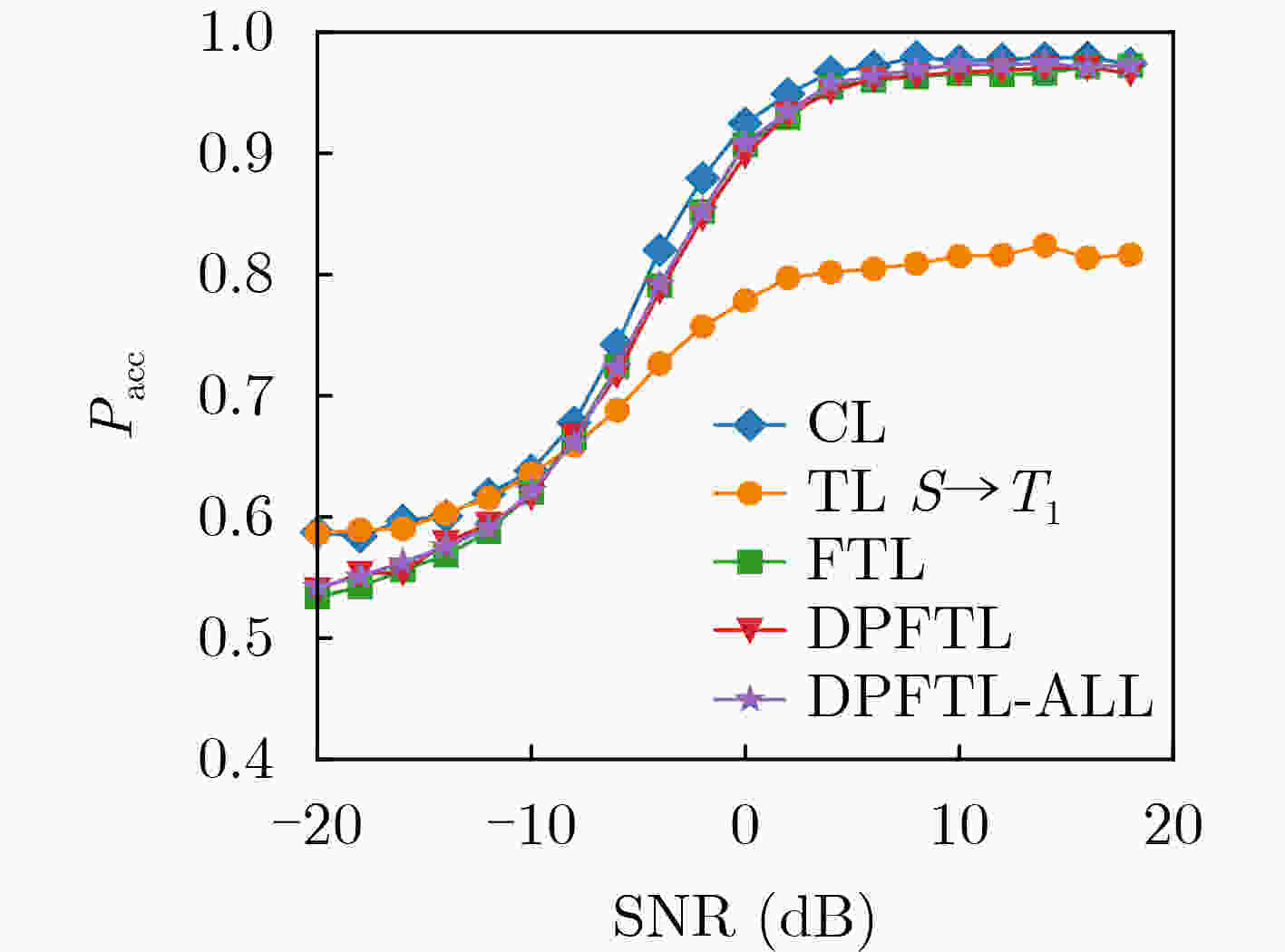
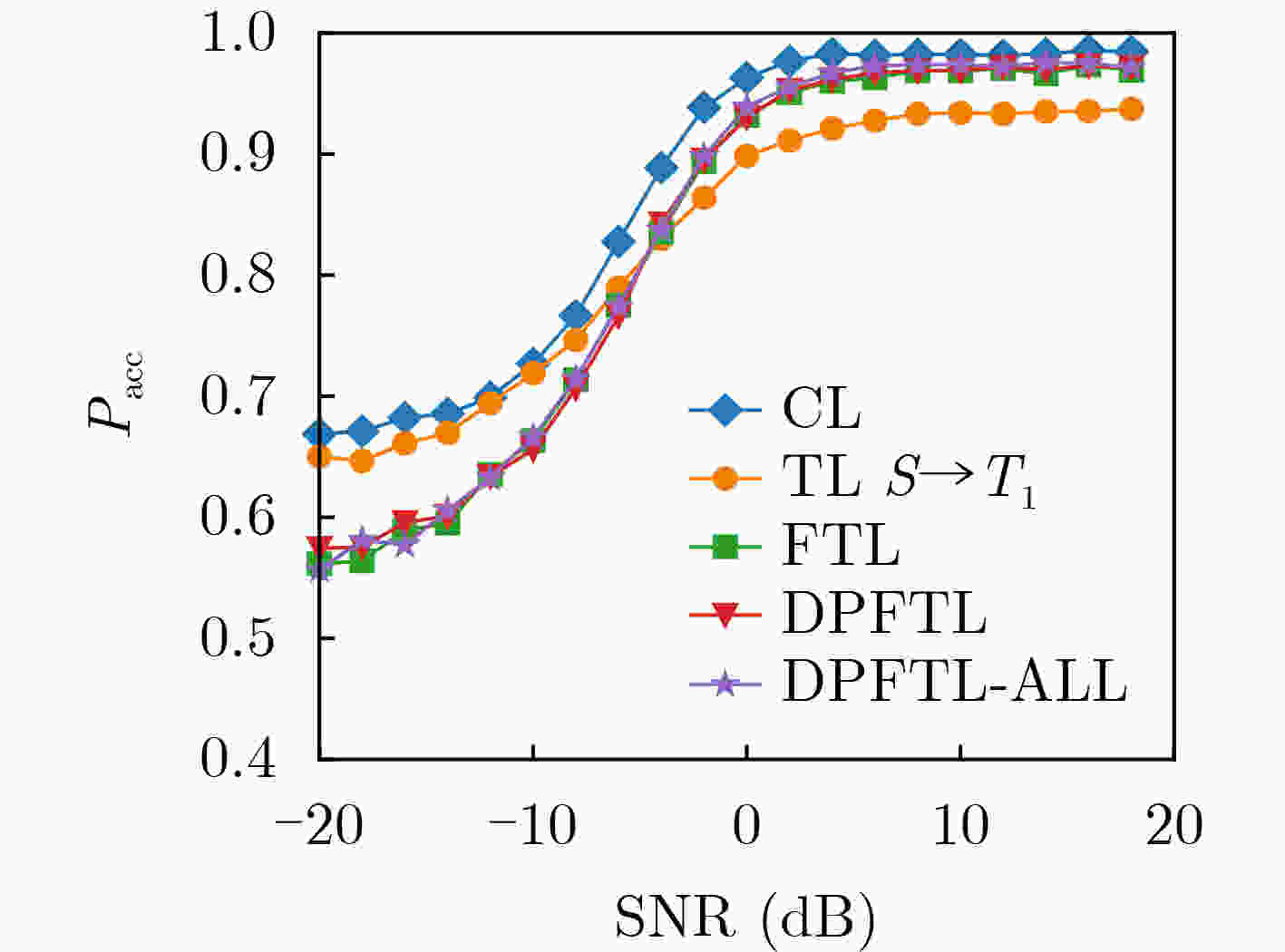
Objective Wideband Spectrum Sensing (WSS) for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in low-altitude intelligent networks is essential for efficient spectrum monitoring and utilization. However, sampling at the Nyquist rate incurs high hardware and computational costs. Moreover, the high mobility of UAVs subjects them to rapidly changing spectral environments, which significantly reduces sensing accuracy and presents major challenges for UAV-based WSS. Methods A low-complexity Feature-Splitting Wideband Spectrum Sensing neural Network (FS-WSSNet) is proposed to achieve high sensing accuracy while reducing the operational cost of UAVs through sub-Nyquist sampling. To integrate spectral knowledge and computational resources across multiple UAVs and enable adaptation to varying spectrum environments, an online model adaptation algorithm based on Differential Privacy Federated Transfer Learning (DPFTL) is further proposed. Before model parameters are uploaded to a central computation platform, noise is added according to local differential privacy constraints. This enables spectrum knowledge sharing while preserving data privacy within the UAV swarm, allowing FS-WSSNet on each UAV to rapidly adapt to dynamic spectral conditions. Results and Discussions Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed FS-WSSNet and the DPFTL-based online model adaptation algorithm. FS-WSSNet achieves substantially higher prediction accuracy than the comparison models, confirming that omitting convolutional layers degrades performance and supporting the design rationale of FS-WSSNet ( Fig. 3 ). In addition, FS-WSSNet consistently outperforms the baseline scheme across all Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) conditions (Fig. 4 ). Its Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve, which lies closer to the top-left corner, indicates improved detection performance across various thresholds (Fig. 5 ). FS-WSSNet also exhibits significantly lower computational complexity compared with the baseline (Table 1 ). Furthermore, under the proposed DPFTL-based scheme (Algorithm 1), FS-WSSNet maintains robust performance across different target scenarios without requiring local adaptation samples. This approach not only preserves data privacy but also improves the model’s generalization ability (Figs. 6 ~9 ).Conclusions This study proposes a cooperative WSS scheme based on DPFTL for low-altitude UAV swarms. First, data received by UAVs are processed using multicoset sampling to enable cost-efficient sub-Nyquist acquisition. The resulting signals are input into a low-complexity FS-WSSNet for accurate and efficient spectrum detection. An online model adaptation algorithm based on DPFTL is then developed, introducing noise to model parameters before upload to ensure data privacy. By supporting spectrum knowledge sharing and collaborative training, the algorithm effectively integrates the computational and data resources of multiple UAVs to construct a robust model adaptable to various scenarios. Simulation results confirm that the proposed scheme provides an efficient WSS solution for resource-constrained low-altitude UAV networks, achieving both privacy protection and adaptability across scenarios. -
1 基于DPFTL的模型在线调整算法
输入:目标域$ {T_i} $数据集$ {\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}} $,无人机数$ {N_{\text{u}}} $,通信轮次$ M $,学习
率$ \alpha $,源域模型参数$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^0} = {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{g}}^0 \cup {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^0 $输出:最优全局模型参数$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^M} $ (1)中心计算平台广播$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^0} $给所有无人机 (2)for $ t = 0,1, \cdots ,M - 1 $ do (3) for $ i = 1,2, \cdots ,{N_{\text{u}}} $ in parallel do (4) 无人机$ i $初始化本地模型$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{t,i}} = $$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^t} $,
$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{t,i}} = {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{g}}^{t,i} \cup {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{t,i} $(5) 计算梯度$ {{\boldsymbol{g}}^{t,i}}(\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}^n) = \nabla \mathcal{L}(\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}^n,{{\boldsymbol{W}}^{t,i}}) $,其中
$ n = 1,2, \cdots ,|{\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}}| $(6) $ {{\boldsymbol{g}}^{t,i}}(\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}^n) = {\boldsymbol{g}}_{\text{g}}^{t,i}(\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}^n) \cup {\boldsymbol{g}}_{\text{s}}^{t,i}(\mathcal{D}_{{T_i}}^n) $ (7) 根据式(9)进行梯度裁剪 (8) 根据式(10)进行本地模型更新 (9) 计算噪声标准差$ {\sigma _i} $ (10) 添加噪声$ {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{t,i} = {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{t,i} + \mathcal{N}(0,\sigma _i^2{\boldsymbol{I}}) $ (11) 含噪参数上传至中心计算平台 (12) end for (13) 根据式(13)进行全局特定任务层参数更新 (14) 中心计算平台广播全局特定任务层参数$ {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{t + 1} $ (15) $ {{\boldsymbol{W}}^{t + 1}} = {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{g}}^{t + 1} \cup {\boldsymbol{W}}_{\text{s}}^{t + 1} $ (16)end for 表 1 各方案参数量和Flops的对比
参数量 FLOPs FS-WSSNet 31 180 637 440 DeepSense 660 232 12 623 936 Parallel-CNN 165 080 1 099 072 -
[1] ADIL M, SONG Houbing, MASTORAKIS S, et al. UAV-assisted IoT applications, cybersecurity threats, AI-enabled solutions, open challenges with future research directions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(4): 4583–4605. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3309548. [2] SHARMA A, VANJANI P, PALIWAL N, et al. Communication and networking technologies for UAVs: A survey[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 168: 102739. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102739. [3] HU Hang, DA Xinyu, HUANG Yangchao, et al. SE and EE optimization for cognitive UAV network based on location information[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 162115–162126. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2951702. [4] DONG Peihao, HE Chaowei, GAO Shen, et al. Edge-learning-based collaborative automatic modulation classification for hierarchical cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(21): 34443–34454. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3431236. [5] FANG Jun, WANG Bin, LI Hongbin, et al. Recent advances on sub-Nyquist sampling-based wideband spectrum sensing[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(3): 115–121. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000353. [6] XU Weibo, WANG Shuo, YAN Shu, et al. An efficient wideband spectrum sensing algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle communication networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1768–1780. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2882532. [7] YANG Linxiao, FANG Jun, DUAN Huiping, et al. Fast compressed power spectrum estimation: Toward a practical solution for wideband spectrum sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(1): 520–532. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2946805. [8] WEI Ziping, ZHANG Han, ZHANG Yang, et al. Fast compressed wideband spectrum sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(2): 2924–2929. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3318217. [9] ZHANG Han, YANG Jian, and GAO Yue. Machine learning empowered spectrum sensing under a sub-sampling framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(10): 8205–8215. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3164800. [10] UVAYDOV D, D’ORO S, RESTUCCIA F, et al. DeepSense: Fast wideband spectrum sensing through real-time in-the-loop deep learning[C]. The IEEE INFOCOM 2021 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Vancouver, Canada, 2021: 1–10. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM42981.2021.9488764. [11] MEI Ruru and WANG Zhugang. Deep learning-based wideband spectrum sensing: A low computational complexity approach[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(10): 2633–2637. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3310715. [12] MEI Ruru and WANG Zhugang. Compressed spectrum sensing of sparse wideband signals based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(6): 8434–8444. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3358026. [13] LI Lusi, JIANG He, and HE Haibo. Deep transfer cooperative sensing in cognitive radio[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(6): 1354–1358. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3067508. [14] SOLANKI S, DEHALWAR V, CHOUDHARY J, et al. Spectrum sensing in cognitive radio using CNN-RNN and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 113482–113492. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3216877. [15] DONG Peihao, JIA Jibin, GAO Shen, et al. Pruned convolutional attention network based wideband spectrum sensing with sub-Nyquist sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(4): 6817–6822. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3507159. [16] WANG Zhibo, SONG Mengkai, ZHANG Zhifei, et al. Beyond inferring class representatives: User-level privacy leakage from federated learning[C]. The IEEE INFOCOM 2019 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 2512–2520. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2019.8737416. [17] DWORK C and ROTH A. The Algorithmic Foundations of Differential Privacy[M]. Boston: Now Publishers Inc. , 2014: 211–407. doi: 10.1561/0400000042. [18] MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
