Mixture Distribution-Based Truth Discovery Algorithm under Local Differential Privacy
-
摘要: 移动群智感知是收集数据的重要手段之一,其中一个基本的问题就是如何从众多质量不同的感知数据中发现“真值”。为解决真值发现过程中可能存在的隐私泄露问题,现有方法通常结合本地差分隐私技术来对工人提交数据进行保护。然而这些方法往往没有充分考虑到数据中存在的表示工人质量的高斯噪音对噪音“真值”的准确度带来的负面影响。此外,直接采用拉普拉斯机制进行隐私保护会由于拉普拉斯分布的随机性和无界性导致大量噪音注入。为解决上述问题,该文提出一种基于混合分布的本地差分隐私真值发现算法(MOON)。该算法结合了工人质量的高斯噪音和隐私保护的拉普拉斯噪音,通过优化混合噪音模型,设计求解算法以提高“真值”精度。理论分析表明,MOON在保证隐私保护的同时,具有较低的计算和通信复杂度。在两个真实数据集上实验结果表明,相对于最新成果,在增加较少计算开销的前提下,MOON在求得的“真值”精度上提高了20%。Abstract:
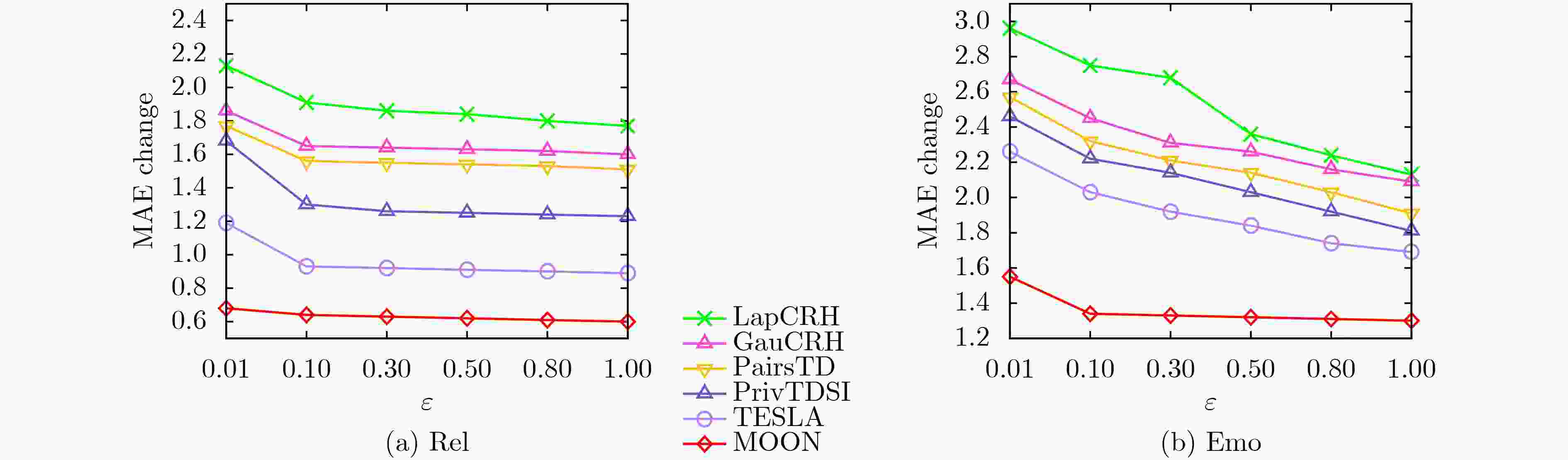
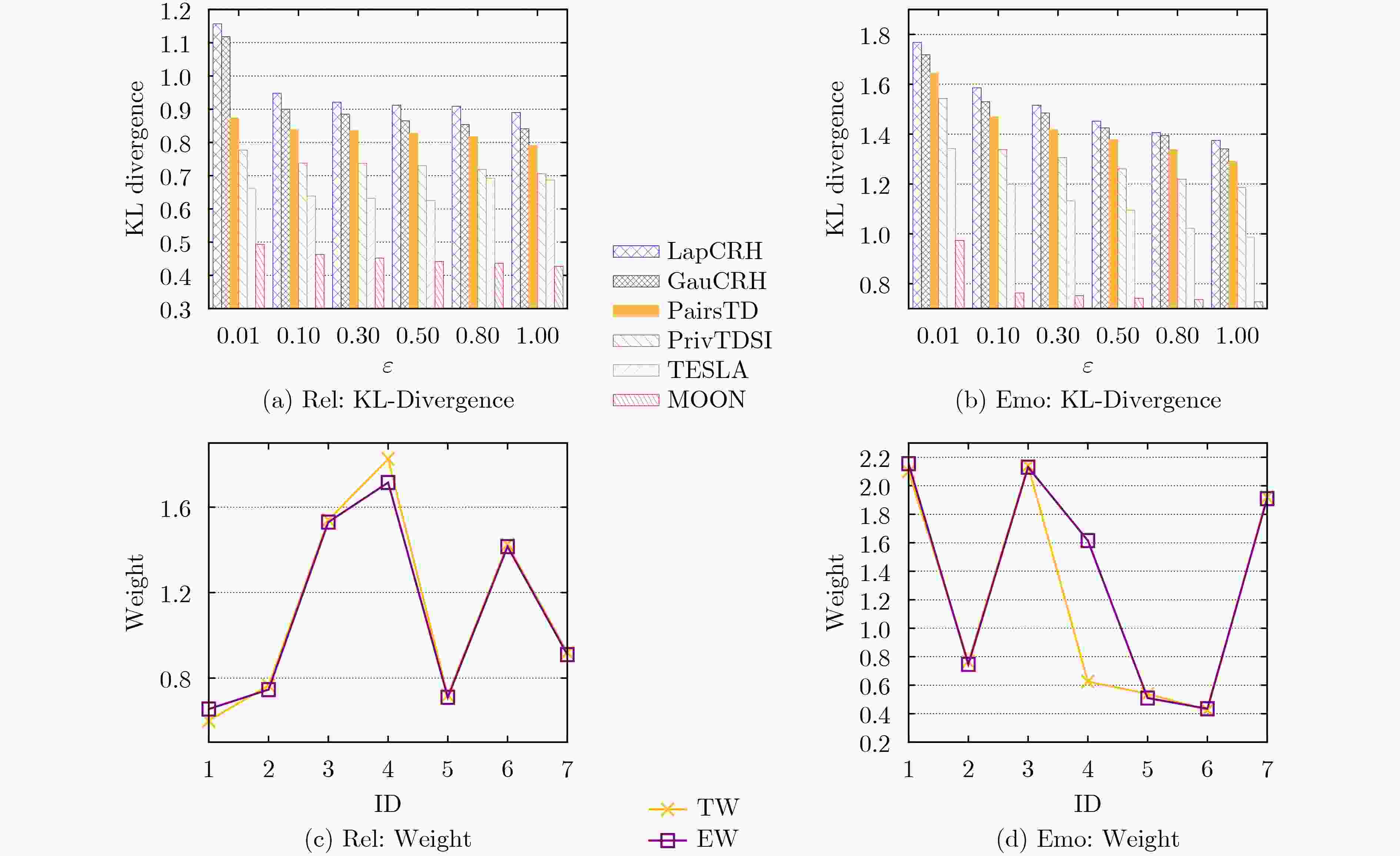
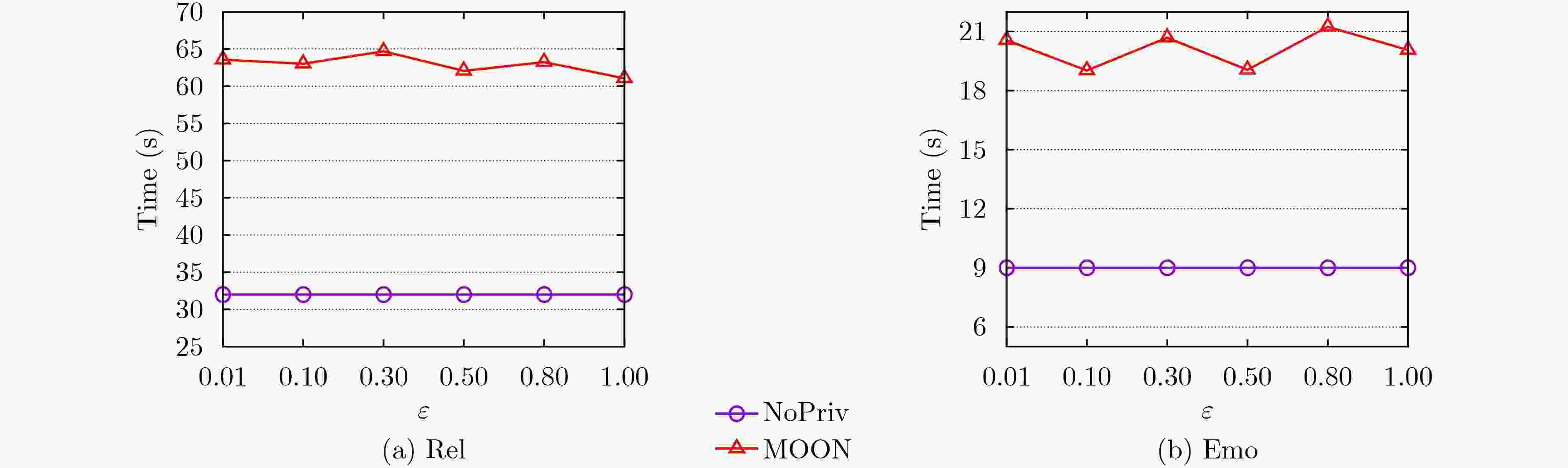
Objective Mobile crowd sensing is recognized as one of the significant means for data collection, wherein a fundamental challenge lies in discovering the “truth” from a multitude of sensing data of varying quality. To address potential privacy leakage issues during the truth discovery process, existing methods often incorporate local differential privacy techniques to protect the data submitted by workers. However, these methods fail to adequately consider the negative impact of Gaussian noise, which reflects worker quality, on the accuracy of the noise “truth”. Moreover, directly applying the Laplace mechanism for privacy protection introduces excessive noise due to the randomness and unbounded nature of the Laplace distribution, resulting in poor precision and utility of truth discovery. Additionally, existing truth discovery methods are either designed for discrete value scenarios or often fail to strictly satisfy Local Differential Privacy (LDP). Therefore, designing a truth discovery algorithm based on mixed distributions that strictly adheres to LDP poses a significant challenge. This is particularly true in continuous value scenarios, where balancing privacy protection with the accuracy of truth discovery, as well as efficiently optimizing the complexity of mixed distribution models to enhance algorithm precision and efficiency, remains a critical issue to be resolved. Methods A novel algorithm, termed Mixture distributiOn-based truth discOvery under local differeNtial privacy (MOON), is proposed. This algorithm primarily considers both the Gaussian noise inherent in the data uploaded by workers, which reflects their quality, and the exogenous Laplace noise injected to protect private data. Based on the mixed noise distribution, new iterative equations for truth discovery are designed. Specifically, each worker first injects Laplace noise into their sensed data and uploads the noise-added data to the server. Subsequently, a probabilistic model combining Gaussian and Laplace noise is constructed and jointly estimated. Finally, the constrained optimization problem is solved using the Lagrange multiplier method to derive iterative equations for worker quality and the “true value” of the noise. Results and Discussions Experimental results demonstrate that, across two real-world datasets, as the privacy budget ε increases, the MOON algorithm exhibits the least impact on utility compared to other benchmark algorithms. Furthermore, when compared to the state-of-the-art TESLA algorithm, MOON achieves at least a 20% improvement in precision ( Fig.3 ). In the context of truth discovery, weight updating is a critical component. Therefore, the experiments also validate the differences between the mixed noise weight distribution derived by the MOON algorithm and the true weight distribution across different datasets (Fig.4 ). The results indicate that the weight distribution obtained by MOON is closer to the true distribution, aligning with the utility analysis presented in the algorithm analysis section. This is attributed to the smaller scale of noise added to high-quality data. Additionally, the runtime of the MOON algorithm is generally higher than that of the non-privacy-preserving truth discovery algorithm NoPriv, being approximately twice as long (Fig.5 ), which is consistent with the theoretical analysis. This is due to the injection of Laplace noise into the data uploaded by workers in MOON, necessitating more iterations to converge to the final truth. However, since both runtimes are measured in seconds, this discrepancy is considered acceptable in practical applications.Conclusions Existing truth discovery algorithms that satisfy local differential privacy (LDP) fail to adequately account for the negative impact of Gaussian noise, which reflects worker quality, on the accuracy of the noise "truth." Moreover, while directly applying the Laplace mechanism for noise addition strictly ensures LDP compliance, the randomness and unbounded nature of the Laplace distribution result in excessive noise injection. To address these issues, the MOON algorithm is proposed in this work. Theoretical analysis demonstrates that MOON achieves privacy protection while maintaining low computational and communication complexity. Experimental results on two real-world datasets show that, compared to the latest advancements, MOON improves the precision of the derived "truth" by 20% with minimal additional computational overhead. In future work, the potential social relationships among workers, which may lead to similarities in the data submitted by certain workers, as well as functional dependencies among task attributes, will be leveraged to further enhance the accuracy of truth discovery under local differential privacy. -
表 1 常用符号
符号 符号定义 M, N 工人数、任务数 $ {w_s} $ 第s个工人的质量 $ x_n^s $ 第s个工人所做第n个任务的值 $ x_n^* $ 第n个任务的真值 U, T 工人集合、任务集合 $ \stackrel \frown{x} _n^ * $ 噪音真值 $ x_n^{\prime s} $ 噪音值 Un 做了第n个任务的工人集合 $\tau $ 迭代阈值 1 MOON算法
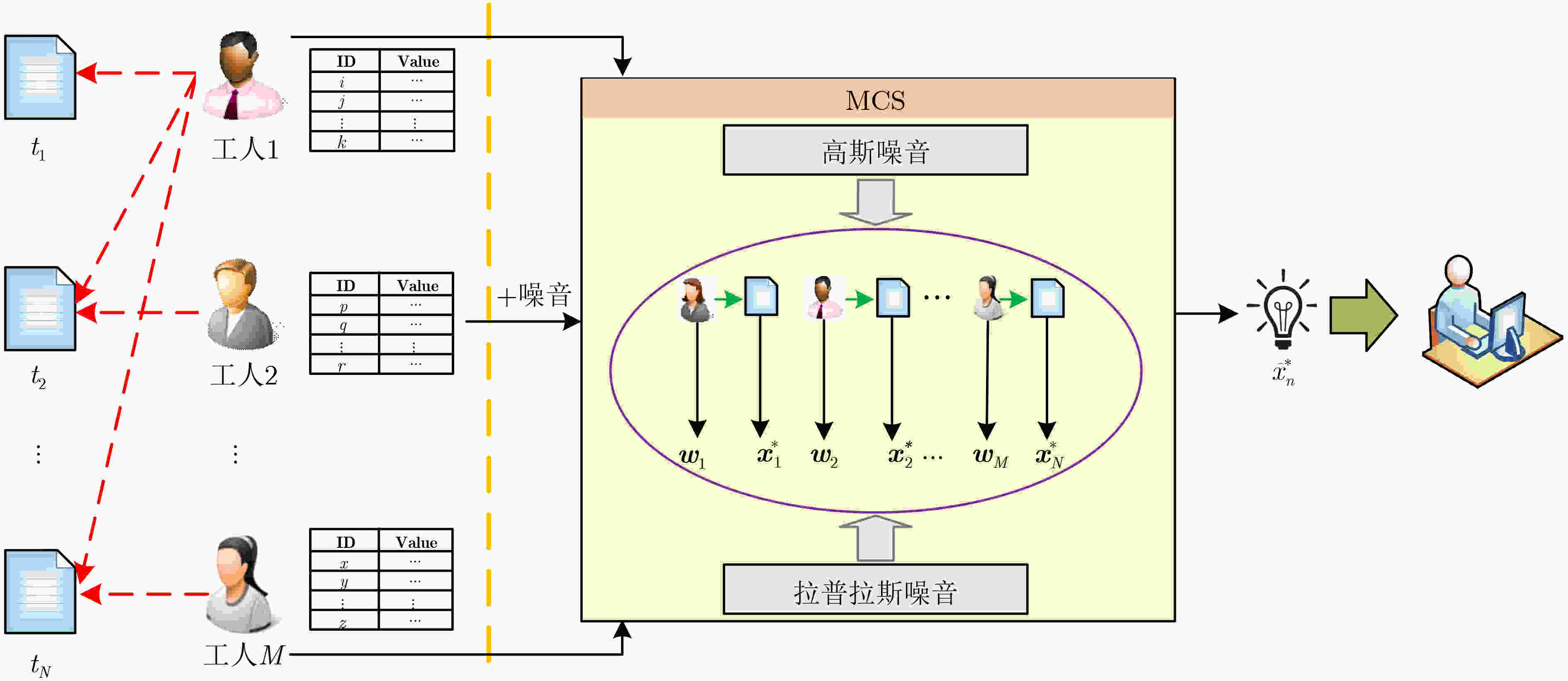
输入:工人的感知值$ x_n^s $;迭代阈值$\tau $; 输出:工人的质量(权重)$ {w_s} $;任务噪音真值$ \stackrel \frown{x}{}_n^ * $; /*本地端*/ 1. for $ s = 1,2, \cdots ,M $ do; 2. for $ n = 1,2, \cdots ,N $do; 3. 调用Laplace机制对感知值进行加噪; 4. 工人将加噪后的感知值$ x_n^{\prime s} $上传给服务器; 5. end for 6. end for /*服务器端*/ 7.初始化$ {w_s} $,$ \stackrel \frown{x}{}_n^ * $; 8. repeat 9. 根据式(18)更新工人质量$ {w_s} $; 10. 根据式(24)更新加噪真值$ \stackrel \frown{x}{}_n^ * $; 11. until 达到迭代次数或者满足迭代阈值$\tau $; 12. return $ {w_s} $, $ \stackrel \frown{x}{}_n^ * $; -
[1] 吕翊, 王燕, 崔亚平, 等. 考虑工人培养的移动群智感知任务分配机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1505–1513. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220249.LÜ Yi, WANG Yan, CUI Yaping, et al. Worker development-aware task allocation strategy in mobile crowd sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(4): 1505–1513. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220249. [2] LIU Yutong, KONG Linghe, and CHEN Guihai. Data-oriented mobile crowdsensing: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(3): 2849–2885. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2910855. [3] 蒋伟进, 陈萍萍, 张婉清, 等. 基于组合多臂赌博机的移动群智感知用户招募算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 1119–1128. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210119.JIANG Weijin, CHEN Pingping, ZHANG Wanqing, et al. Mobile crowdsensing user recruitment algorithm based on combination multi-armed bandit[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 1119–1128. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210119. [4] ZHANG Daqing, WANG Leye, XIONG Haoyi, et al. 4W1H in mobile crowd sensing[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(8): 42–48. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6871668. [5] 熊金波, 毕仁万, 田有亮, 等. 移动群智感知安全与隐私: 模型、进展与趋势[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(9): 1949–1966. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01949.XIONG Jinbo, BI Renwan, TIAN Youliang, et al. Security and privacy in mobile crowdsensing: Model, progresses, and trends[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(9): 1949–1966. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01949. [6] MA Huadong, ZHAO Dong, and YUAN Peiyan. Opportunities in mobile crowd sensing[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(8): 29–35. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6871666. [7] FANG Xiu, SHEN Chenling, SHENG Q Z, et al. A multi-truth discovery approach based on confidence interval estimation of truths[C]. The 19th International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications, Shenyang, China, 2023: 599–615. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-46677-9_41. [8] XIAO Houping and WANG Shiyu. A joint maximum likelihood estimation framework for truth discovery: A Unified Perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(6): 5521–5533. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2022.3173911. [9] MO Wen, LI Zeyuan, ZENG Zhiwen, et al. SCTD: A spatiotemporal correlation truth discovery scheme for security management of data platform[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2023, 139: 109–125. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2022.09.022. [10] LIANG Tingxuan, CHEN Lingyi, HUANG Mingfeng, et al. RLTD: A reinforcement learning-based truth data discovery scheme for decision support systems under sustainable environments[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 143: 110369. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110369. [11] XIAN Youquan, LIU Peng, LI Dongcheng, et al. Safeguarding the truth of high-value price oracle task: A dynamically adjusted truth discovery method[J]. arXiv: 2402.02543, 2024. [12] WANG Han, LIU Anfeng, XIONG N N, et al. TVD-RA: A truthful data value discovery-based reverse auction incentive system for mobile crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(4): 5826–5839. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3308072. [13] KANG Yunchuan, LIU Anfeng, XIONG N N, et al. DTD: An intelligent data and bid dual truth discovery scheme for MCS in IIoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(2): 2507–2519. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3292920. [14] LI Qi, LI Yaliang, GAO Jing, et al. Resolving conflicts in heterogeneous data by truth discovery and source reliability estimation[C]. 2014 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Snowbird Utah, USA, 2014: 1187–1198. doi: 10.1145/2588555.2610509. [15] ERLINGSSON Ú, PIHUR V, and KOROLOVA A. RAPPOR: Randomized aggregatable privacy-preserving ordinal response[C]. 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Scottsdale Arizona, USA, 2014: 1054–1067. doi: 10.1145/2660267.2660348. [16] TANG Jun, KOROLOVA A, BAI Xiaolong, et al. Privacy loss in apple’s implementation of differential privacy on MaCOS 10.12[J]. arXiv: 1709.02753, 2017. [17] DING Bolin, KULKARNI J, and YEKHANIN S. Collecting telemetry data privately[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 3574–3583. [18] HUSAIN H, BALLE B, CRANKO Z, et al. Local differential privacy for sampling[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Palermo, Italy, 2020: 3404–3413. [19] LIU Yuxian, LIU Fagui, WU Haotian, et al. RPTD: Reliability-enhanced privacy-preserving truth discovery for mobile crowdsensing[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2022, 207: 103484. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2022.103484. [20] TANG Jianchao, FU Shaojing, LIU Ximeng, et al. Achieving privacy-preserving and lightweight truth discovery in mobile crowdsensing (Extended abstract)[C]. The IEEE 39th International Conference on Data Engineering, Anaheim, USA, 2023: 3797–3798. doi: 10.1109/ICDE55515.2023.00325. [21] CHENG Yudan, MA Jianfeng, LIU Zhiquan, et al. A privacy-preserving and reputation-based truth discovery framework in mobile crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2023, 20(6): 5293–5311. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2023.3276976. [22] LIU Xingting, ZHOU Siwang, ZHANG Wei, et al. Privacy-preserving truth discovery for collaborative-cloud encryption in mobile crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(3): 4990–5001. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2023.3274812. [23] XIONG Ping, LI Guirong, LIU Hengzhu, et al. Decentralized privacy-preserving truth discovery for crowd sensing[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 632: 730–741. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.03.046. [24] WANG Leye, FAN Guanghong, and HAN Xiao. Federated truth discovery for mobile crowdsensing with privacy-preserving trustworthiness assessment[J]. IEEE Data Engineering Bulletin, 2023, 46(1): 124–144. [25] LIU Rui and PAN Jianping. Lightweight privacy-preserving truth discovery for vehicular air quality monitoring[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2023, 9(1): 280–291. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2022.03.021. [26] AGATE V, FERRARO P, RE G L, et al. BLIND: A privacy preserving truth discovery system for mobile crowdsensing[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2024, 223: 103811. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2023.103811. [27] SUN Peng, WANG Zhibo, FENG Yunhe, et al. Towards personalized privacy-preserving incentive for truth discovery in crowdsourced binary-choice question answering[C]. The IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, Canada, 2020: 1133–1142. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM41043.2020.9155429. [28] LI Yaliang, MIAO Chenglin, SU Lu, et al. An efficient two-layer mechanism for privacy-preserving truth discovery[C]. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 2018: 1705–1714. doi: 10.1145/3219819.3219998. [29] WANG Di and XU Jinhui. Inferring ground truth from crowdsourced data under local attribute differential privacy[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2021, 865: 85–98. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2021.02.039. [30] SUN Haipei, DONG Boxiang, WANG Hui, et al. Truth inference on sparse crowdsourcing data with local differential privacy[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Seattle, USA, 2018: 488–497. doi: 10.1109/BigData.2018.8622635. [31] LI Yaliang, XIAO Houping, QIN Zhan, et al. Towards differentially private truth discovery for crowd sensing systems[C]. The 40th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, Singapore, 2020: 1156–1166. doi: 10.1109/ICDCS47774.2020.00037. [32] SUN Peng, WANG Zhibo, WU Liantao, et al. Towards personalized privacy-preserving incentive for truth discovery in mobile crowdsensing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(1): 352–365. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.3003673. [33] XU Guowen, LI Hongwei, XU Shengmin, et al. Catch you if you deceive me: Verifiable and privacy-aware truth discovery in crowdsensing systems[C]. The 15th ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Taipei, China, 2020: 178–192. doi: 10.1145/3320269.3384720. [34] ZHANG Pengfei, CHENG Xiang, SU Sen, et al. PrivTDSI: A local differentially private approach for truth discovery via sampling and inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023, 9(2): 471–484. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2022.3186175. [35] ZHANG Pengfei, CHENG Xiang, SU Sen, et al. Effective truth discovery under local differential privacy by leveraging noise-aware probabilistic estimation and fusion[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 261: 110213. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.110213. [36] BUCKLEY C, LEASE M, SMUCKER M D, et al. Overview of the TREC 2010 relevance feedback track (notebook)[C]. The 19th Text Retrieval Conference (TREC) Notebook, Gaithersburg, USA, 2010. [37] XU Guowen, LI Hongwei, LIU Sen, et al. Efficient and privacy-preserving truth discovery in mobile crowd sensing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3854–3865. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2895834. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
