Scene-adaptive Knowledge Distillation-based Fusion of Infrared and Visible Light Images
-
摘要: 红外与可见光图像融合的目的是将这两种异模态图像信息整合成场景细节信息更全面的融合图像。现有的一些融合算法仅关注评价指标的提升,而忽略了其在现实应用中的模型轻量性和场景泛化性的需求。为了解决该问题,该文提出一种基于场景自适应知识蒸馏的红外与可见光图像融合方法。首先,将领先的融合算法作为教师网络得到白天场景的学习样本,用低光增强算法继续处理得到黑夜场景的学习样本;然后,通过光照感知网络预测可见光图像的白天黑夜场景概率,从而指导学生网络实现对教师网络的场景自适应知识蒸馏;最后,引入基于结构重参数化的视觉变换器(RepViT)进一步降低模型的计算资源消耗。在MSRS和LLVIP数据集上与7种主流的深度学习融合算法进行了定性与定量的实验对比,所提融合方法能够在更低的计算资源消耗下,实现多个评价指标的提升,并在白天黑夜场景均能实现较好的融合视觉效果。
-
关键词:
- 红外与可见光图像融合 /
- 场景自适应 /
- 知识蒸馏 /
- 结构重参数化 /
- 深度学习
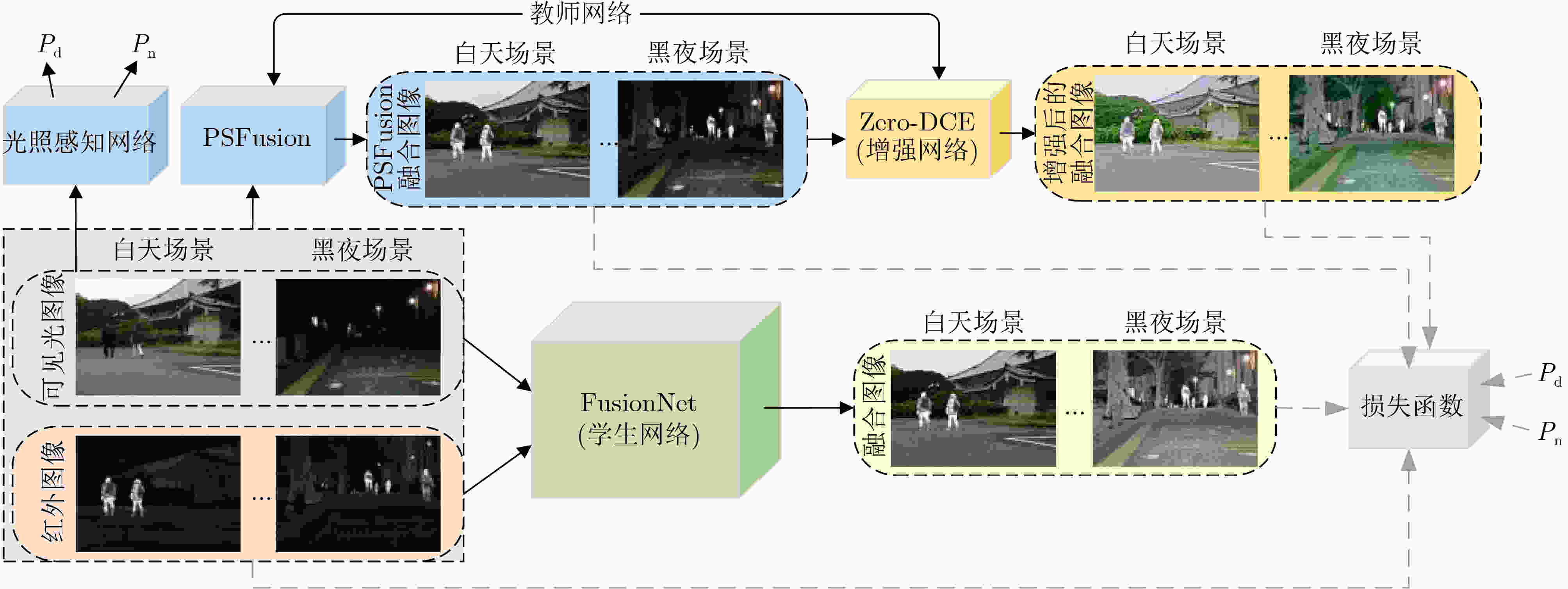
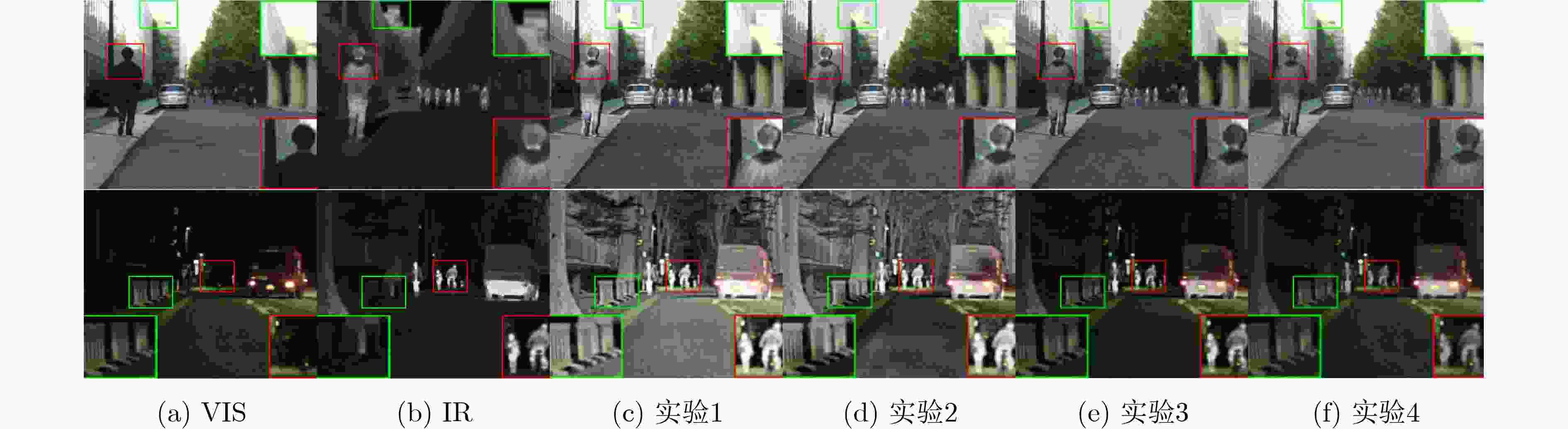
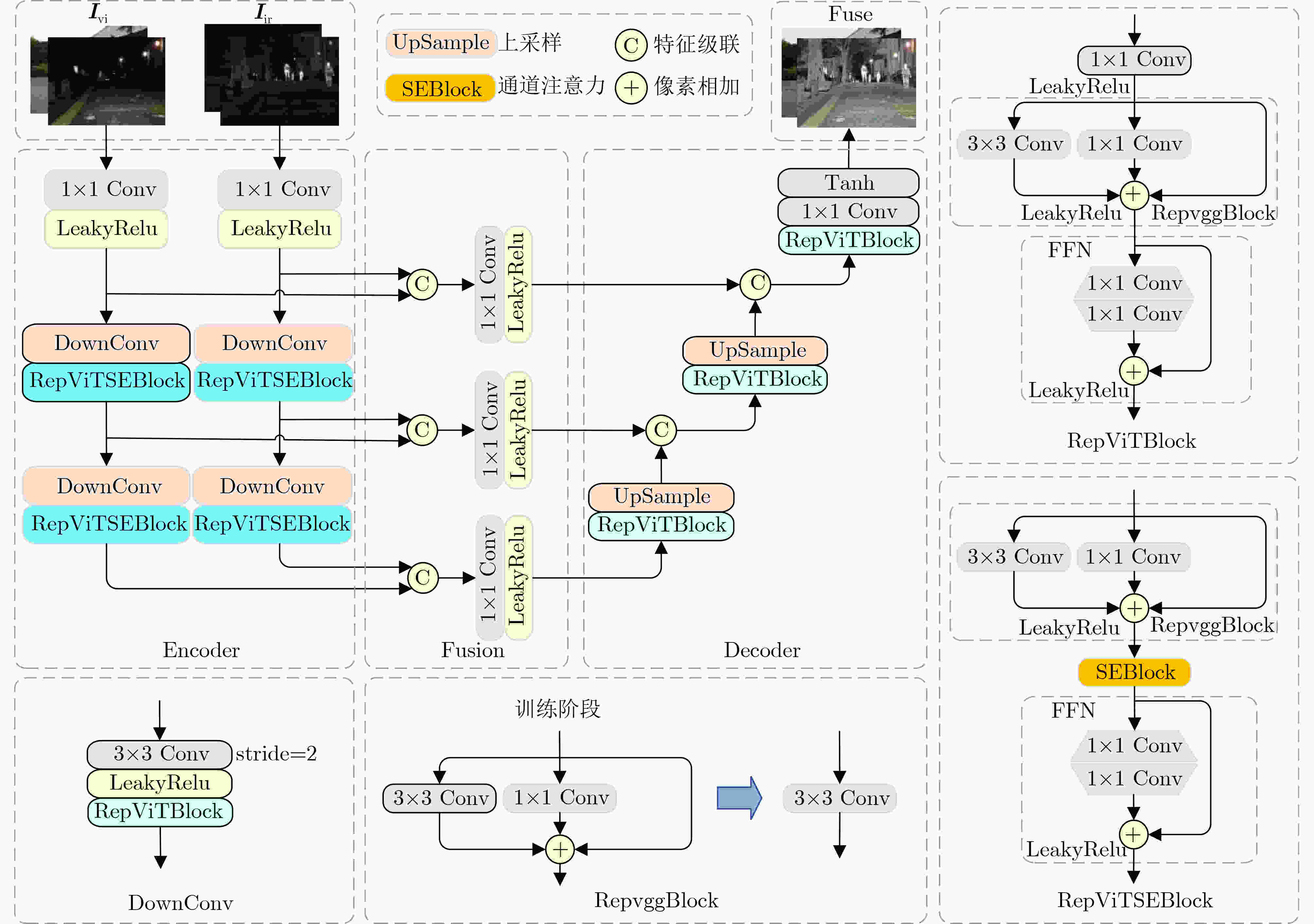
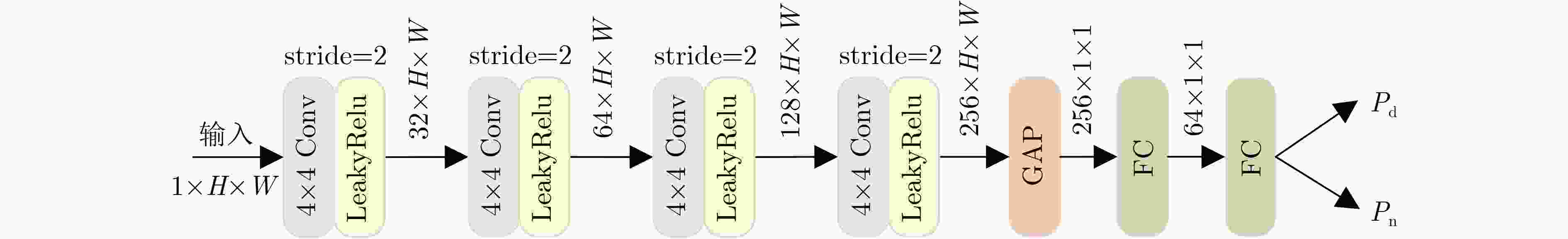
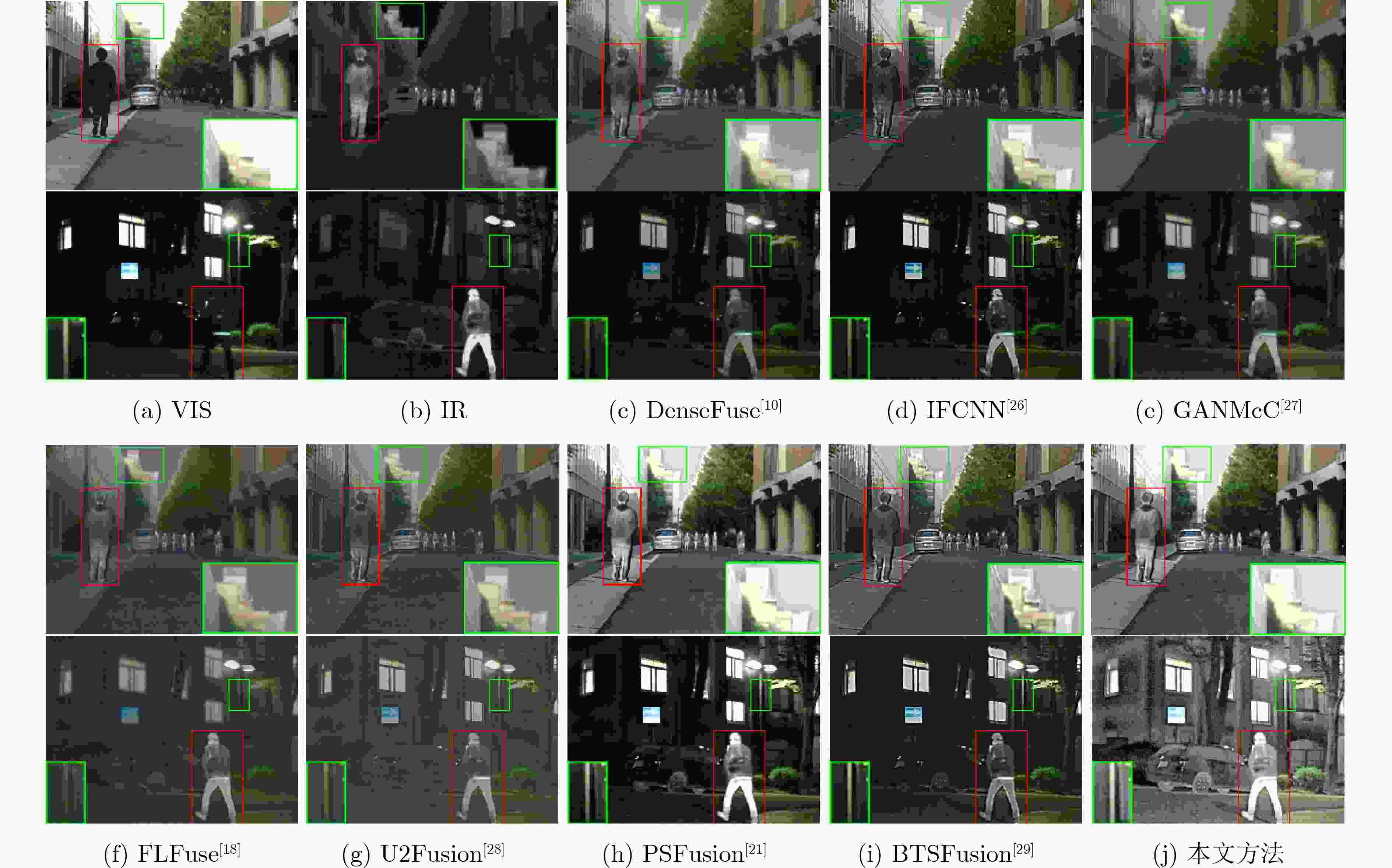
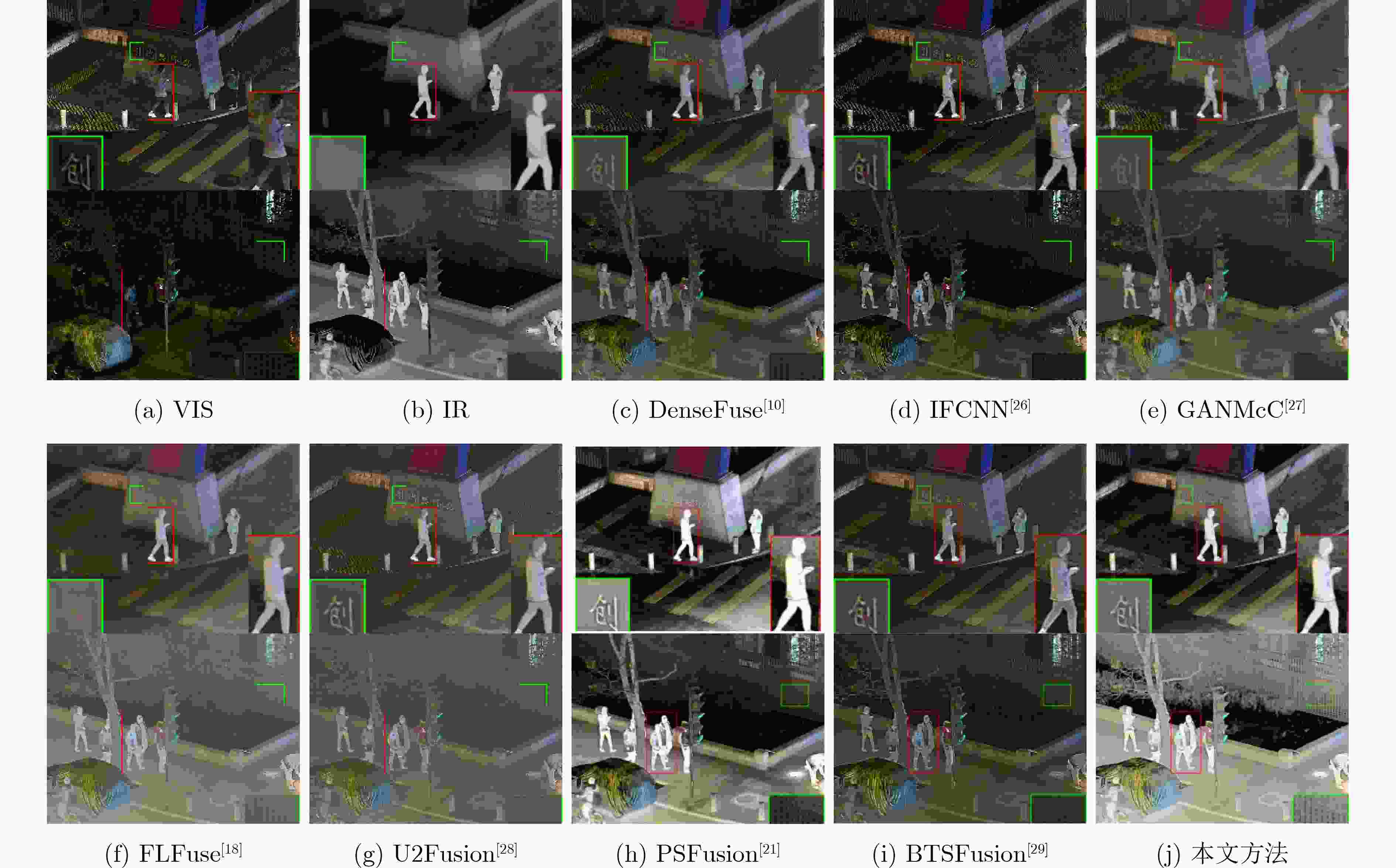
Abstract:Objective The fusion of InfRared (IR) and VISible light (VIS) images is critical for enhancing visual perception in applications such as surveillance, autonomous navigation, and security monitoring. IR images excel in highlighting thermal targets under adverse conditions (e.g., low illumination, occlusions), while VIS images provide rich texture details under normal lighting. However, existing fusion methods predominantly focus on optimizing performance under uniform illumination, neglecting challenges posed by dynamic lighting variations, particularly in low-light scenarios. Additionally, computational inefficiency and high model complexity hinder the practical deployment of state-of-the-art fusion algorithms. To address these limitations, this study proposes a scene-adaptive knowledge distillation framework that harmonizes fusion quality across daytime and nighttime conditions while achieving lightweight deployment through structural re-parameterization. The necessity of this work lies in bridging the performance gap between illumination-specific fusion tasks and enabling resource-efficient models for real-world applications. Methods The proposed framework comprises three components: a teacher network for pseudo-label generation, a student network for lightweight inference, and a light perception network for dynamic scene adaptation ( Fig. 1 ). The teacher network integrates a pre-trained progressive semantic injection fusion network (PSFusion) to generate high-quality daytime fusion results and employs Zero-reference Deep Curve Estimation (Zero-DCE) to enhance nighttime outputs under low-light conditions. The light perception network, a compact convolutional classifier, dynamically adjusts the student network’s learning objectives by outputting probabilistic weights (Pd, Pn) based on VIS input categories (Fig. 3 ). The student network, constructed with structurally Re-parameterized Vision Transformer (RepViT) blocks, utilizes multi-branch architectures during training that collapse into single-path networks during inference, significantly reducing computational overhead (Fig. 2 ). A hybrid loss function combines Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) and adaptive illumination losses (Eq. 8–15), balancing fidelity to source images with scene-specific intensity and gradient preservation.Results and Discussions Qualitative analysis on the MSRS and LLVIP datasets demonstrates that the proposed method preserves IR saliency (highlighted in red boxes) and VIS textures (green boxes) more effectively than seven benchmark methods, including DenseFuse and PSFusion, particularly in low-light scenarios ( Fig. 4 ,Fig. 5 ). Quantitative evaluation reveals superior performance in six metrics: the method achieves SD scores of 9.728 7 (MSRS) and 10.006 7 (LLVIP), AG values of 6.5477 (MSRS) and 4.7956 (LLVIP), and SF scores of 0.0670 (MSRS) and 0.0648 (LLVIP), outperforming existing approaches in contrast, edge sharpness, and spatial detail preservation (Table 1 ). Computational efficiency is markedly improved, with the student network requiring only 0.76 MB parameters and 4.49 ms runtime on LLVIP, representing a 98.8% reduction in runtime compared to PSFusion (380.83 ms) (Table 2 ). Ablation studies confirm the necessity of RepViT blocks and adaptive illumination loss, as removing these components degrades SD by 16.2% and AG by 60.8%, with other evaluation metrics also experiencing varying degrees of decline,respectively (Table 3 ,Fig. 6 ).Conclusions This work introduces a scene-adaptive knowledge distillation framework that unifies high-performance IR-VIS fusion with computational efficiency. Key innovations include teacher knowledge distillation for illumination-specific pseudo-label generation, RepViT-based structural re-parameterization for lightweight inference, and probabilistic weighting for dynamic illumination adaptation. Experimental results validate the framework’s superiority in perceptual quality and operational efficiency across benchmark datasets. Future work will extend the architecture to multispectral fusion and real-time video applications. -
表 1 本文方法与 7 种对比算法的评价指标结果
数据集 算法 评价指标 SD VIF AG SCD EN SF MSRS DenseFuse[10] 7.5 090 0.7 317 2.2 024 1.4 668 6.0 225 0.0 255 IFCNN[26] 6.6 247 0.6 904 3.6 574 1.4 483 5.8 457 0.0 450 GANMcC[27] 8.0 840 0.6 283 1.9 036 1.4 622 6.0 204 0.0 212 FLFuse[18] 6.6 117 0.4 791 1.7 241 1.1 108 5.5 299 0.0 189 U2Fusion[28] 5.7 280 0.3 902 1.8 871 0.9 897 4.7 535 0.0 243 PSFusion[21] 8.2 107 1.0 638 4.4 334 1.8 315 6.7 084 0.0 519 BTSFusion[29] 7.3 536 0.5 342 3.9 851 1.4 804 6.1 631 0.0 525 本文方法 9.7 287 1.0 010 6.5 477 1.5 573 7.3 170 0.0 670 LLVIP DenseFuse[10] 9.2 490 0.8 317 2.7 245 1.4 190 6.8 727 0.0 363 IFCNN[26] 8.6 038 0.8 094 4.1 833 1.3 853 6.7 336 0.0 565 GANMcC[27] 9.0 244 0.7 155 2.1 196 1.2 786 6.6 894 0.0 267 FLFuse[18] 8.8 942 0.6 337 1.2 916 0.8 539 6.4 600 0.0 162 U2Fusion[28] 7.7 951 0.5 631 2.2 132 0.8 092 5.9 464 0.0 287 PSFusion[21] 9.9 358 1.1 044 5.5 673 1.6 784 7.6 017 0.0 754 BTSFusion[29] 8.8 164 0.6 736 4.5 411 1.2 510 6.7 583 0.0 617 本文方法 10.0 067 1.0 436 4.7 956 1.7 005 7.4 720 0.0 648 表 2 模型参数与运行效率的对比结果
算法 模型参数 MSRS(480×640) LLVIP( 1024 ×1280 )参数量 权重(MB) 运行时间(ms) FLOPs(G) 运行时间(ms) FLOPs(G) DenseFuse[10] 88 225 0.34 165.52 27.03 459.54 115.32 IFCNN[26] 129 987 0.50 19.21 40.05 45.52 170.87 GANMcC[27] 1 864 129 7.11 260.48 572.96 734.13 / FLFuse[18] 14 328 0.05 1.10 4.36 1.34 18.59 U2Fusion[28] 659 217 2.51 169.93 202.36 482.12 863.41 PSFusion[21] 45 899 360 175.09 171.23 180.86 380.83 / BTSFusion[29] 55 444 0.21 153.91 15.73 160.11 67.11 本文方法* 200 689 0.77 4.30 1.87 6.80 7.97 本文方法 199 457 0.76 2.40 1.86 4.49 7.93 表 3 消融实验的客观评价指标结果
消融实验 评价指标 实验编号 RVB Lauto SD VIF AG SCD EN SF 1 √ √ 9.7 287 1.0 010 6.5 477 1.5 573 7.3 170 0.0 670 2 × √ 8.9 909 0.8 988 6.2 219 1.2 732 7.1 821 0.0 625 3 √ × 7.8 663 0.9 494 3.2 929 1.7 506 6.3 839 0.0 403 4 × × 8.1 535 0.8 838 2.5 674 1.6 765 6.4 347 0.0 339 -
[1] ZHANG Xingchen and DEMIRIS Y. Visible and infrared image fusion using deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(8): 10535–10554. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3261282. [2] 唐霖峰, 张浩, 徐涵, 等. 基于深度学习的图像融合方法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(1): 3–36. doi: 10.11834/jig.220422.TANG Linfeng, ZHANG Hao, XU Han, et al. Deep learning-based image fusion: A survey[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2023, 28(1): 3–36. doi: 10.11834/jig.220422. [3] ZHANG Hao, XU Han, TIAN Xin, et al. Image fusion meets deep learning: A survey and perspective[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 76: 323–336. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.06.008. [4] KARIM S, TONG Grng, LI Jinyang, et al. Current advances and future perspectives of image fusion: A comprehensive review[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 90: 185–217. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.09.019. [5] LI Hui, WU Xiaojun, and KITTLER J. MDLatLRR: A novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4733–4746. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2975984. [6] LIU Yu, CHEN Xun, WARD R K, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1882–1886. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2618776. [7] FU Zhizhong, WANG Xue, XU Jin, et al. Infrared and visible images fusion based on RPCA and NSCT[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 77: 114–123. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2016.05.012. [8] MA Jinlei, ZHOU Zhiqiang, WANG Bo, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 82: 8–17. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2017.02.005. [9] ZHAO Wenda, LU Huimin, and WANG Dong. Multisensor image fusion and enhancement in spectral total variation domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 20(4): 866–879. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2760100. [10] LI Hui and WU Xiaojun. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614–2623. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342. [11] LI Hui, WU Xiaojun, and DURRANI T. NestFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(12): 9645–9656. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3005230. [12] LI Hui, WU Xiaojun, and KITTLER J. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 72–86. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.023. [13] LONG Yongzhi, JIA Haitao, ZHONG Yida, et al. RXDNFuse: A aggregated residual dense network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 69: 128–141. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.11.009. [14] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. [15] XIE Saining, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5987–5995. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.634. [16] MA Jiayi, TANG Linfeng, XU Meilong, et al. STDFusionNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5009513. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3075747. [17] MA Jiayi, YU Wei, LIANG Pengwei, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11–26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004. [18] XUE Weimin, WANG Anhong, and ZHAO Lijun. FLFuse-Net: A fast and lightweight infrared and visible image fusion network via feature flow and edge compensation for salient information[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2022, 127: 104383. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2022.104383. [19] 陈昭宇, 范洪博, 马美燕, 等. 基于结构重参数化的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(7): 2275–2283. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.2003.CHEN Zhaoyu, FAN Hongbo, MA Meiyan, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on structural re-parameterization[J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(7): 2275–2283. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.2003. [20] 马美燕, 陈昭宇, 刘海鹏. 基于差分融合与边缘增强的轻量级红外与可见光图像融合算法[J]. 化工自动化及仪表, 2024, 51(4): 644–651. doi: 10.20030/j.cnki.1000-3932.202404013.MA Meiyan, CHEN Zhaoyu, and LIU Haipeng. A lightweight infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on difference fusion and edge enhancement[J]. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2024, 51(4): 644–651. doi: 10.20030/j.cnki.1000-3932.202404013. [21] TANG Linfeng, ZHANG Hao, XU Han, et al. Rethinking the necessity of image fusion in high-level vision tasks: A practical infrared and visible image fusion network based on progressive semantic injection and scene fidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 99: 101870. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.101870. [22] GUO Chunle, LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, et al. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1777–1786. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00185. [23] WANG Ao, CHEN Hui, LIN Zijia, et al. Rep ViT: Revisiting mobile CNN from ViT perspective[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 15909–15920. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01506. [24] TANG Linfeng, YUAN Jiteng, ZHANG Hao, et al. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 83/84: 79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.03.007. [25] LIU Jinyuan, FAN Xin, HUANG Zhanbo, et al. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 5792–5801. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00571. [26] ZHANG Yu, LIU Yu, SUN Peng, et al. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 54: 99–118. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.07.011. [27] MA Jiayi, ZHANG Hao, SHAO Zhenfeng, et al. GANMcC: A generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 5005014. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3038013. [28] XU Han, MA Jiayi, JIANG Junjun, et al. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(1): 502–518. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548. [29] QIAN Yao, LIU Gang, TANG Haojie, et al. BTSFusion: Fusion of infrared and visible image via a mechanism of balancing texture and salience[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2024, 173: 107925. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107925. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
