A Novel Earth Surface Anomaly Detection Method Based on Collaborative Reasoning of Deep Learning and Remote Sensing Indexes
-
摘要: 地表异常检测是遥感图像处理领域颇具挑战的前沿问题。一方面,地表异常样本搜集困难,可训练样本稀缺。另一方面,地表异常场景类内差异大,类间相似性高,分类混淆问题突出。因此,该文提出一种融合遥感指数协同推理的地表异常检测方法(DeepIndex)。DeepIndex在大规模预训练视觉语言模型基础上,设计轻量级自适应微调模块,实现少样本高效学习。同时,DeepIndex引入具有物理机理的遥感指数先验辅助模型推理,改善分类混淆问题。为了验证方法有效性,该文构建了一个多光谱地表异常检测数据集(MS-ESAD),包含2 768张多光谱遥感图像,红、绿、蓝、红外等6个波段以及野火、绿潮、蓝藻3种地表异常类型。DeepIndex在MS-ESAD和NWPU45数据集上均表现优异,在少量样本训练(20%)条件下,分别取得92.36%和94.39%的分类精度。同时,消融实验表明,融合遥感指数协同推理能够显著改善模型分类混淆问题。Abstract:
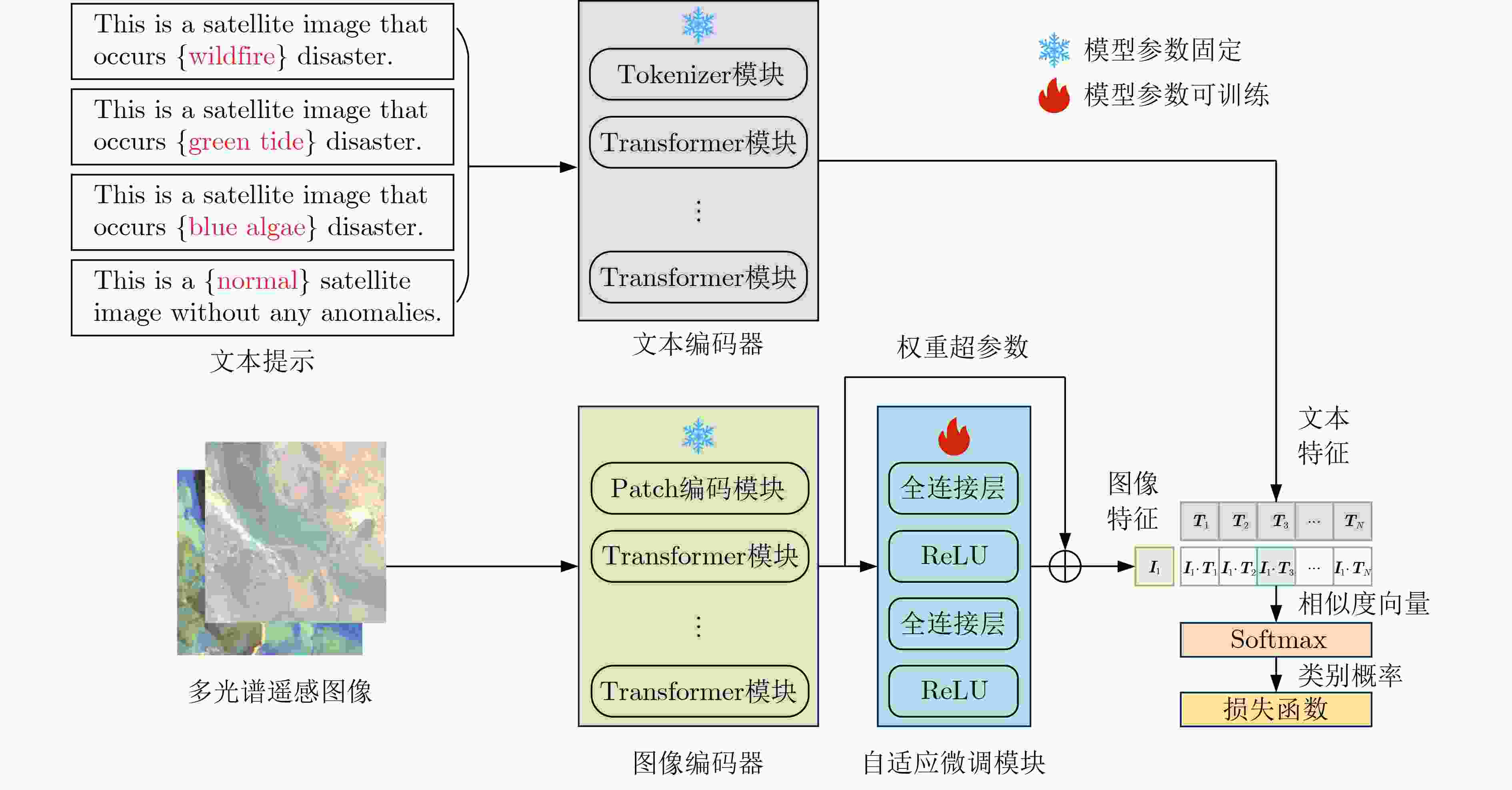
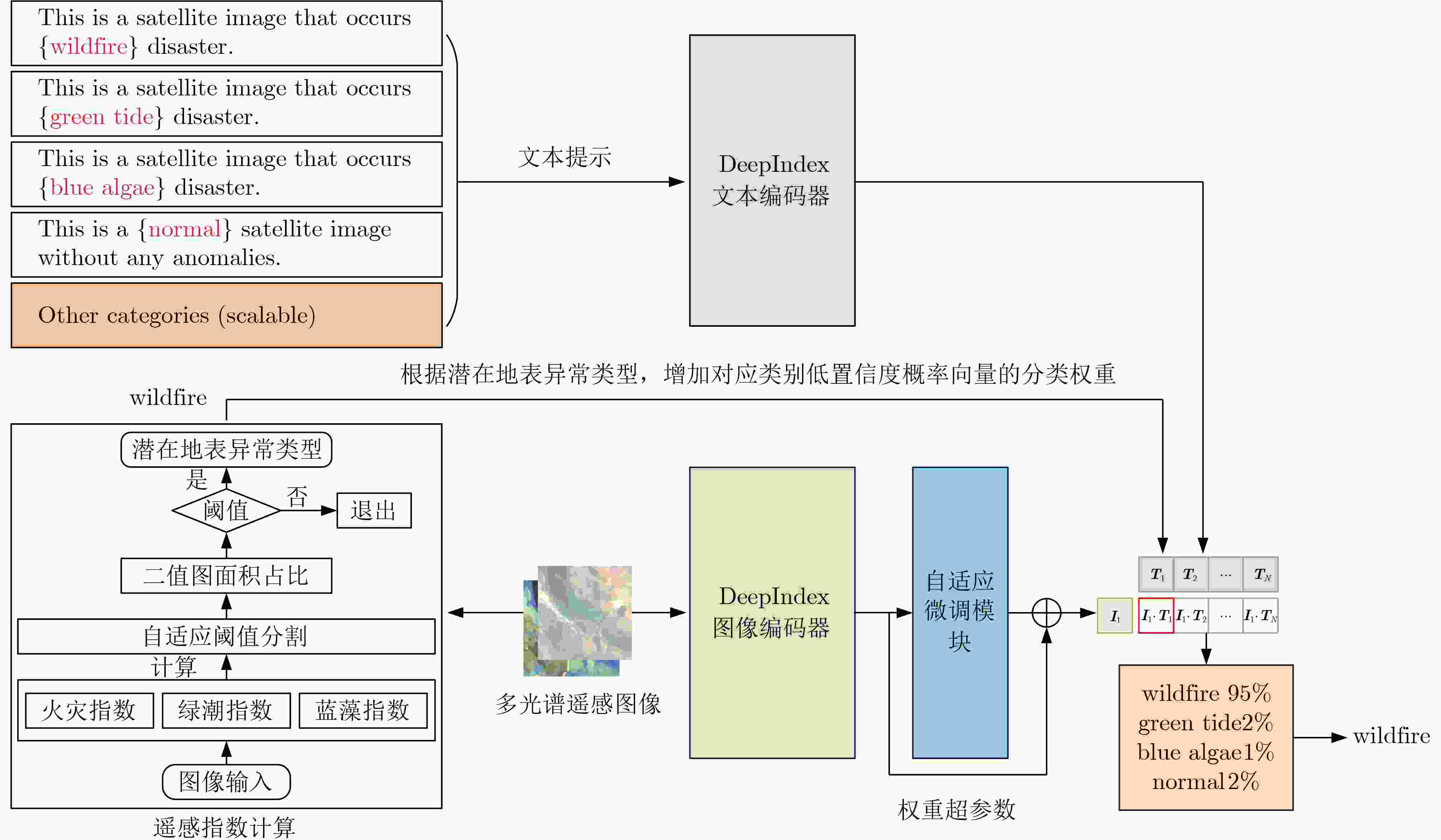
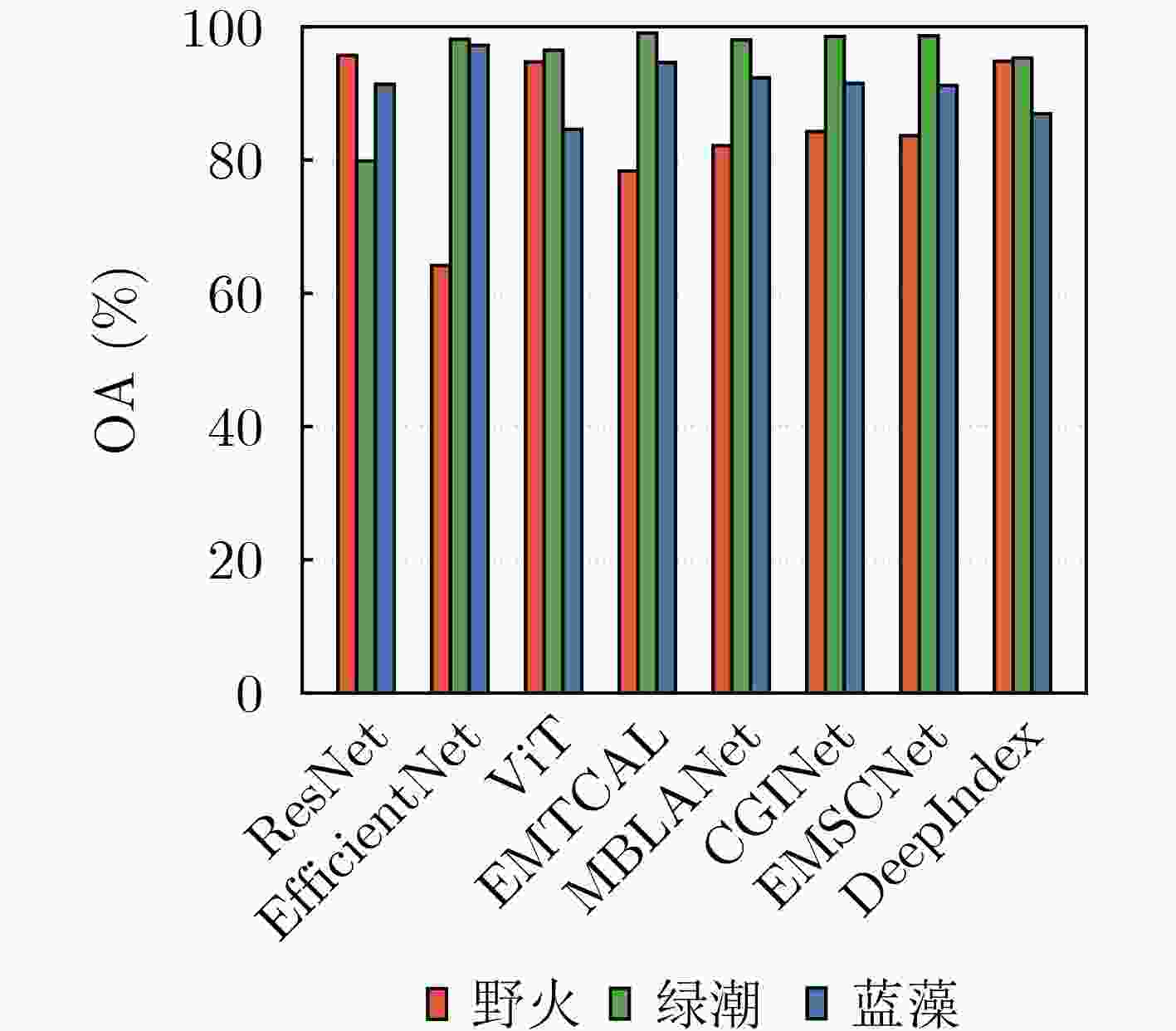
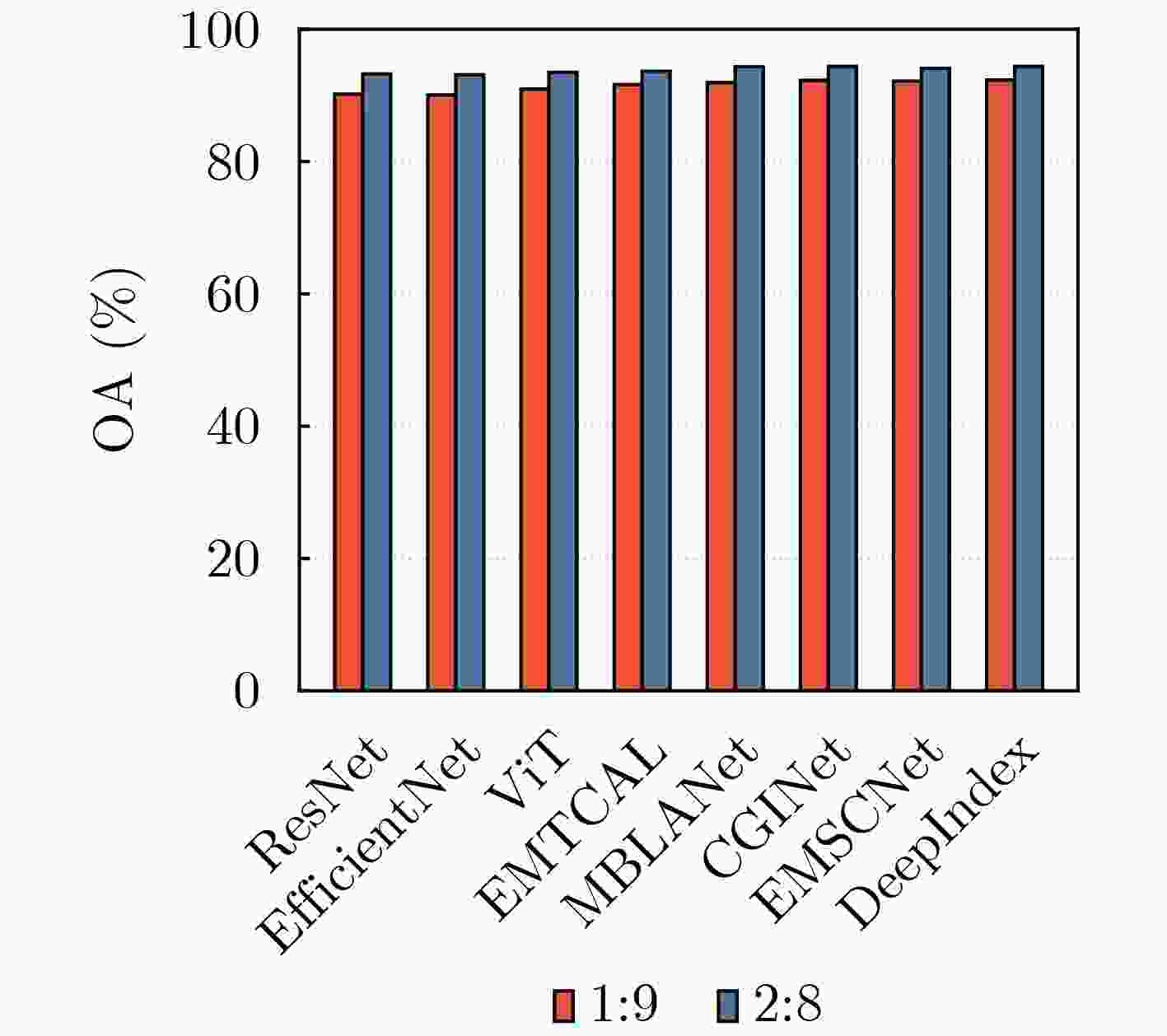
Objective Earth Surface Anomalies (ESAs) refer to geographical phenomena that deviate from the normal state. They are characterized by wide distribution, high occurrence frequency, rapid evolution, and a large impact range. In recent years, sudden surface anomalies have occurred frequently, making remote sensing surface anomaly detection a prominent research topic. Although deep learning-based anomaly detection methods have made substantial progress, they still face two challenges: (1) limited learning ability under conditions of few samples, and (2) unreliable reasoning when identifying surface anomaly scenes with high inter-class similarity. To address these challenges, a novel surface anomaly detection method, DeepIndex, is proposed. This method leverages prior knowledge from large vision-language models to enhance few-sample learning and integrates remote sensing indexes to improve the reliability of identifying complex and similar surface anomaly scenes. Methods A novel scheme of “large-scale pre-trained foundational model + efficient fine-tuning” is employed to construct the entire network and implement training, thereby enabling efficient learning of surface anomaly features under conditions with few samples. Specifically, the foundational vision-language model, Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP), is selected as the backbone of DeepIndex, with an efficient fine-tuning module developed to enhance few-sample learning. Leveraging the vision-language structure, DeepIndex can simultaneously encode image and text features, with the output category determined by text input, granting it open-set classification capability. Furthermore, DeepIndex innovatively integrates remote sensing indexes and physical mechanisms into the reasoning process, improving both interpretability and generalization performance. Specifically, DeepIndex first computes remote sensing indexes and applies an adaptive threshold segmentation method to generate binary segmentation maps. These maps are then processed to output the area ratio of the anomalous region. Based on the area ratio (with a default threshold of 0.1), potential surface anomaly categories are identified. The classification weights of these potential categories are then increased by 20%. Finally, DeepIndex uses the increased weights for classification, improving the identification of surface anomaly scenes with high inter-class similarity and enhancing reasoning reliability. Notably, DeepIndex increases weights only for categories with lower original confidence (<0.5), achieving a balance between regular and confused samples for stable classification. In summary, DeepIndex utilizes vision-language representation learning to develop a collaborative reasoning framework that integrates remote sensing indexes for surface anomaly detection. This framework improves the deep network’s reasoning capabilities and realizes the complementary advantages of deep learning and remote sensing indexes. Results and Discussions The effectiveness and superiority of the proposed DeepIndex are demonstrated using a self-constructed dataset, MultiSpectral Earth Surface Anomaly Detection (MS-ESAD), and the public dataset, NWPU45. The MS-ESAD dataset is challenging, containing 2,768 multispectral remote sensing images across six bands (red, green, blue, infrared, and two short infrared bands) and three types of surface anomalies (wildfire, green tide, and blue algae). This dataset provides a foundation for surface anomaly detection research. For evaluation, class Average Accuracy (AA) and Overall Accuracy (OA) metrics are used for both datasets. The ablation study ( Tables 2 and3 ) shows that the proposed DeepIndex collaborative reasoning framework significantly enhances zero-shot classification performance (9.84%) and improves the identification of confusing samples (7.39%). Quantitative and qualitative comparisons (Fig. 4 ,Table 4 ) further illustrate that DeepIndex achieves the best class AA (92.36%), which is 3.38% higher than the classic convolutional neural network ResNet and 0.42% higher than ViT. Additionally, compared to recent remote sensing scene classification networks, DeepIndex demonstrates more stable performance, owing to the integration of remote sensing index priors. For the NWPU45 dataset, experimental results (Fig. 5 ,Table 5 ) further highlight the advantages of DeepIndex under conditions with few samples (10% and 20% for training). Compared with advanced remote sensing image scene classification methods (e.g., EMSCNet) from the past two years, DeepIndex shows a slight accuracy advantage of 0.17% and 0.31%, respectively. These results demonstrate the strong application potential of DeepIndex for remote sensing image scene classification tasks, especially with limited training samples.Conclusions This paper combines physically constrained remote sensing indexes with deep networks and proposes a collaborative reasoning deep framework for Earth surface anomaly detection, named DeepIndex. Through large-scale pre-training and adaptive fine-tuning strategies, DeepIndex effectively learns highly generalized features from scarce samples. Additionally, DeepIndex adopts a unique reasoning pattern that utilizes remote sensing index priors to assist network discrimination, enhancing its ability to recognize complex and ambiguous surface anomaly scenes. Furthermore, this paper constructs a multispectral surface anomaly dataset that provides valuable data support for related research. The experimental results demonstrate that the integration of remote sensing indexes significantly improves classification performance under conditions with limited training samples. Compared with other advanced remote sensing scene classification methods, DeepIndex shows notable advantages in both accuracy and stability. -
表 1 MS-ESAD数据集概览
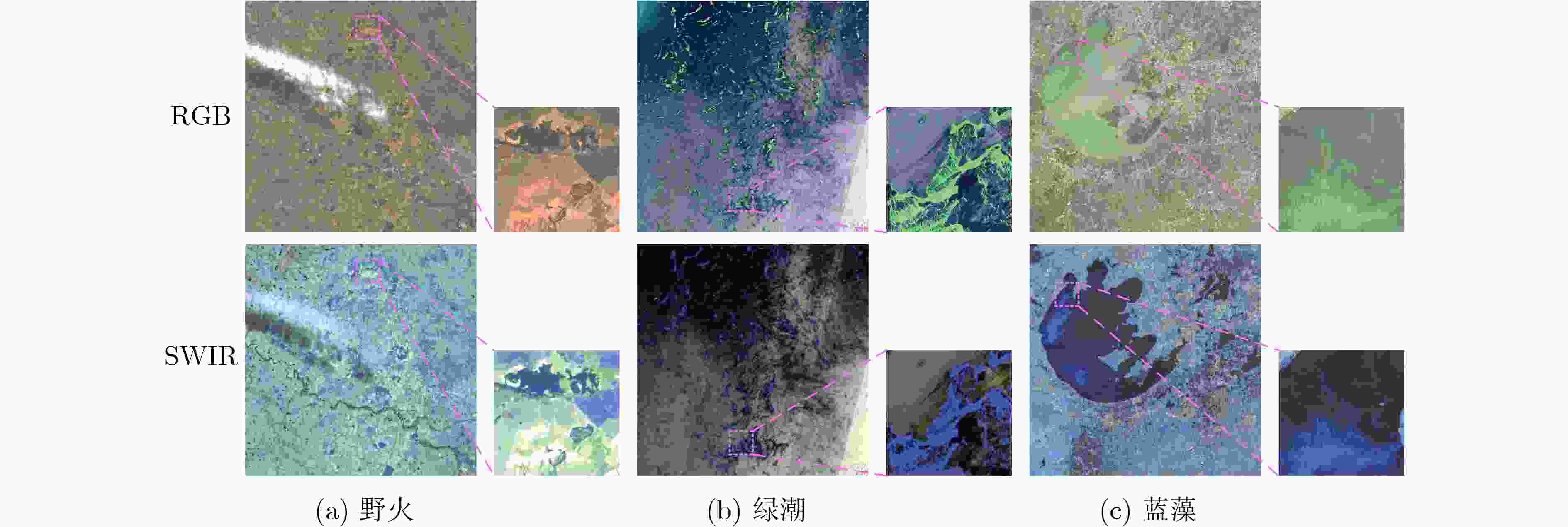
属性 描述 波段 蓝、绿、红、近红外、短波红外1、短波红外2 波段号 B02, B03, B04, B08, B11, B12 合成图像 RGB可见光图像、SWIR红外图像 图像分辨率 10 m 图像大小 512×512添加单位 地表异常类型 野火、绿潮、蓝藻 样本数量 野火:1 110,绿潮:1 048,蓝藻:610 表 2 DeepIndex零样本推理消融实验结果(%)
方法 MS-ESAD训练 野火 绿潮 蓝藻 AA DeepIndex 否 0.0 0.0 26.11 8.70 DeepIndex+遥感指数 否 1.75 6.55 47.31 18.54 表 3 DeepIndex在混淆样本上的消融实验结果(%)
方法 MS-ESAD训练 野火 绿潮 蓝藻 AA DeepIndex 是 52.63 72.91 25.92 50.49 DeepIndex+遥感指数 是 60.00 72.92 40.74 57.88 表 4 DeepIndex与其他方法在MS-ESAD数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
-
[1] 王桥. 地表异常遥感探测与即时诊断方法研究框架[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1141–1152. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220124.WANG Qiao. Research framework of remote sensing monitoring and real-time diagnosis of earth surface anomalies[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1141–1152. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220124. [2] WEI Haishuo, JIA Kun, WANG Qiao, et al. Real-time remote sensing detection framework of the earth’s surface anomalies based on a priori knowledge base[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2023, 122: 103429. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2023.103429. [3] REN Shoujia, PAN Yaozhong, ZHU Xiufang, et al. A general and simple automated impervious surface mapping approach based on three-dimensional texture features (3DTF) using fine spatial resolution remotely sensed imagery[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 923: 171181. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171181. [4] WU Hanyi, ZHAO Chuanwu, ZHU Yu, et al. A multiscale examination of heat health risk inequality and its drivers in mega-urban agglomeration: A case study in the Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 458: 142528. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142528. [5] ZHAO Chuanwu, PAN Yaozhong, REN Shoujia, et al. Accurate vegetation destruction detection using remote sensing imagery based on the three-band difference vegetation index (TBDVI) and dual-temporal detection method[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2024, 127: 103669. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2024.103669. [6] ZHU Wenquan, YANG Xinyi, LIU Ruoyang, et al. A new feature extraction algorithm for measuring the spatial arrangement of texture Primitives: Distance coding diversity[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2024, 127: 103698. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2024.103698. [7] LIU Ruoyang, ZHU Wenquan, and YANG Xinyi. Screening image features of collapsed buildings for operational and rapid remote sensing identification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(24): 5747. doi: 10.3390/rs15245747. [8] ROY D P, JIN Yufang, LEWIS P E, et al. Prototyping a global algorithm for systematic fire-affected area mapping using MODIS time series data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 97(2): 137–162. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2005.04.007. [9] YANG Fan, GUO Jianhua, TAN Hai, et al. Automated extraction of urban water bodies from ZY-3 multi-spectral imagery[J]. Water, 2017, 9(2): 144. doi: 10.3390/w9020144. [10] FAN Jiahui, YAO Yunjun, TANG Qingxin, et al. A hybrid index for monitoring burned vegetation by combining image texture features with vegetation indices[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(9): 1539. doi: 10.3390/rs16091539. [11] WEI Haishuo, JIA Kun, WANG Qiao, et al. A remote sensing index for the detection of multi-type water quality anomalies in complex geographical environments[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2024, 17(1): 2313695. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2024.2313695. [12] ZHAO Chuanwu, PAN Yaozhong, WU Hanyi, et al. A novel spectral index for vegetation destruction event detection based on multispectral remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 11290–11309. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3412737. [13] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539. [14] JIAO Licheng, HUANG Zhongjian, LIU Xu, et al. Brain-inspired remote sensing interpretation: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 2992–3033. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3247455. [15] ZHU Xiaoxiang, TUIA D, MOU Lichao, et al. Deep learning in remote sensing: A comprehensive review and list of resources[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2017, 5(4): 8–36. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2017.2762307. [16] WANG Libo, LI Rui, ZHANG Ce, et al. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 190: 196–214. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.06.008. [17] HONG Danfeng, ZHANG Bing, LI Xuyang, et al. SpectralGPT: Spectral remote sensing foundation model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(8): 5227–5244. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3362475. [18] SU Hongjun, WU Zhaoyue, ZHANG Huihui, et al. Hyperspectral anomaly detection: A survey[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(1): 64–90. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2021.3105440. [19] XU Yichu, ZHANG Lefei, DU Bo, et al. Hyperspectral anomaly detection based on machine learning: An overview[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 3351–3364. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3167830. [20] LI Chenyu, ZHANG Bing, HONG Danfeng, et al. LRR-Net: An interpretable deep unfolding network for hyperspectral anomaly detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5513412. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3279834. [21] LI Jingtao, WANG Xinyu, ZHAO Hengwei, et al. Anomaly segmentation for high-resolution remote sensing images based on pixel descriptors[C]. The 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 4426–4434. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i4.25563. [22] CHEN Boan, GAO Zhi, LI Ziyao, et al. Hierarchical GNN framework for earth’s surface anomaly detection in single satellite imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5627314. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3408330. [23] XU Jianming, YAN Kai, FAN Zaiwang, et al. Toward a novel method for general on-orbit earth surface anomaly detection leveraging large vision models and lightweight priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4706321. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3432749. [24] GAO Peng, GENG Shijie, ZHANG Renrui, et al. CLIP-Adapter: Better vision-language models with feature adapters[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2024, 132(2): 581–595. doi: 10.1007/s11263-023-01891-x. [25] RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 8748–8763. [26] SCHUHMANN C, BEAUMONT R, VENCU R, et al. LAION-5B: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1833. [27] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Austria, 2021. [28] ZHANG Hailong, QIU Zhongfeng, DEVRED E, et al. A simple and effective method for monitoring floating green macroalgae blooms: A case study in the Yellow Sea[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(4): 4528–4548. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.004528. [29] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [30] TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114. [31] TANG Xu, LI Mingteng, MA Jingjing, et al. EMTCAL: Efficient multiscale transformer and cross-level attention learning for remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5626915. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3194505. [32] CHEN Sibao, WEI Qingsong, WANG Wenzhong, et al. Remote sensing scene classification via multi-branch local attention network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 99–109. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3127851. [33] ZHAO Yichen, CHEN Yaxiong, XIONG Shengwu, et al. Co-enhanced global-part integration for remote-sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4702114. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3367877. [34] ZHAO Yibo, LIU Jianjun, YANG Jinlong, et al. EMSCNet: Efficient multisample contrastive network for remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5605814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3262840. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
