Energy Aware Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Age of Information Enabled Data Collection Policies
-
摘要: 为了应对智能反射面(RIS)辅助的无人机(UAV)在物联网数据收集过程中能量高效利用与信息收集时效性之间的均衡问题,该文提出一种基于深度强化学习的数据收集优化策略。针对无人机在数据采集过程中的飞行能耗、通信复杂性及采集信息时效性(AoI)约束,设计了一种基于双深度Q网络(DDQN)的联合优化方案,涵盖无人机轨迹规划、物联网设备调度以及智能反射面相位调整。该方案有效缓解了传统Q学习方法中Q值过估计的问题,使无人机能够根据实时环境动态调整飞行轨迹和通信策略,从而在提升数据传输效率的同时降低能量消耗。仿真结果表明,与传统方法相比,所提方案能够显著提高数据收集效率。此外,通过合理分配能量与通信资源,所提方案能够动态适应不同通信环境参数变化,确保系统在能耗与AoI之间达到最佳均衡。Abstract:
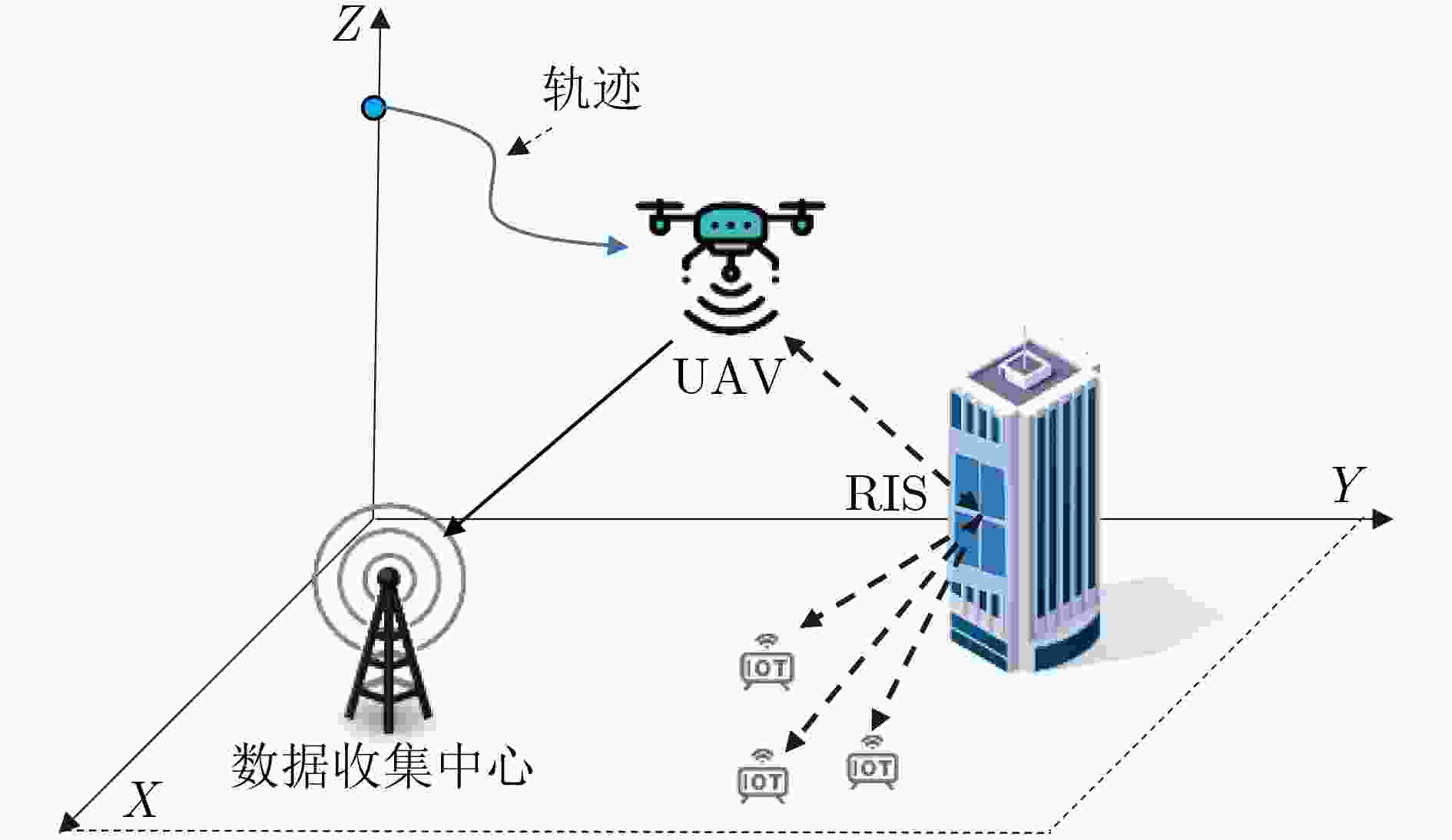
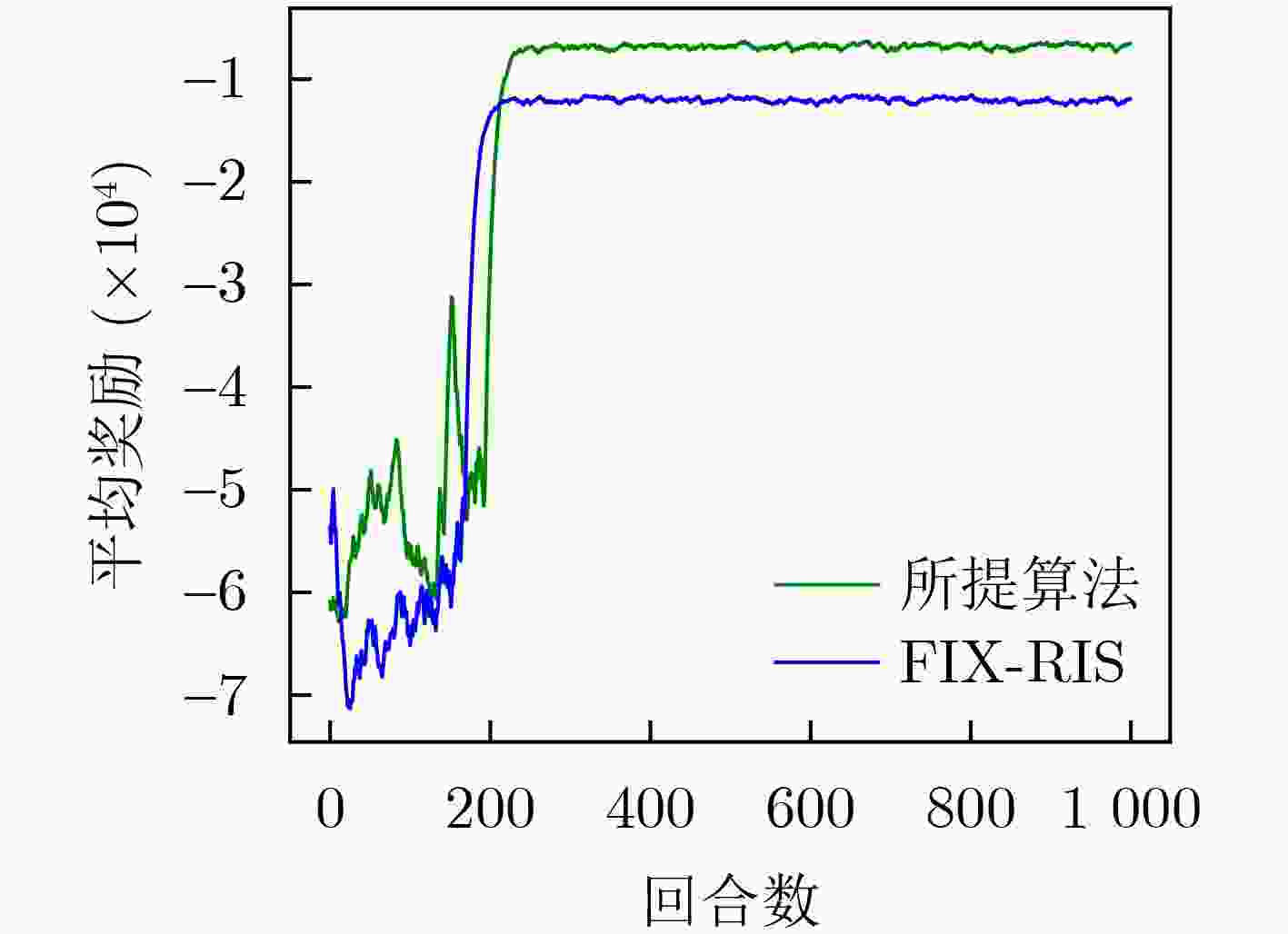
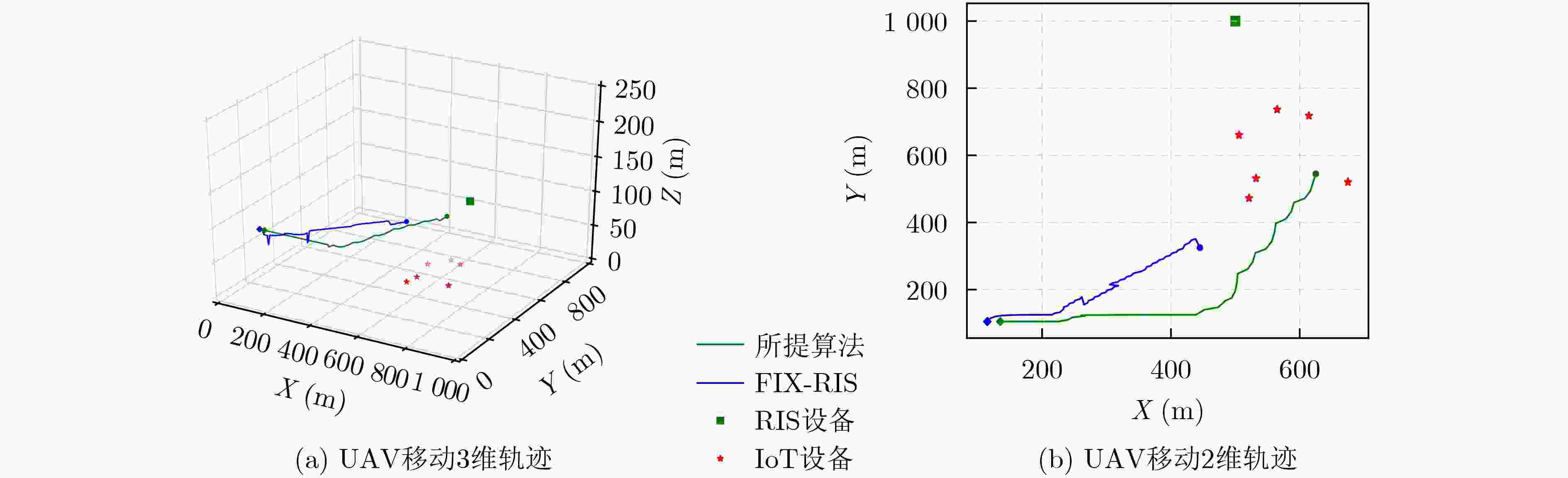
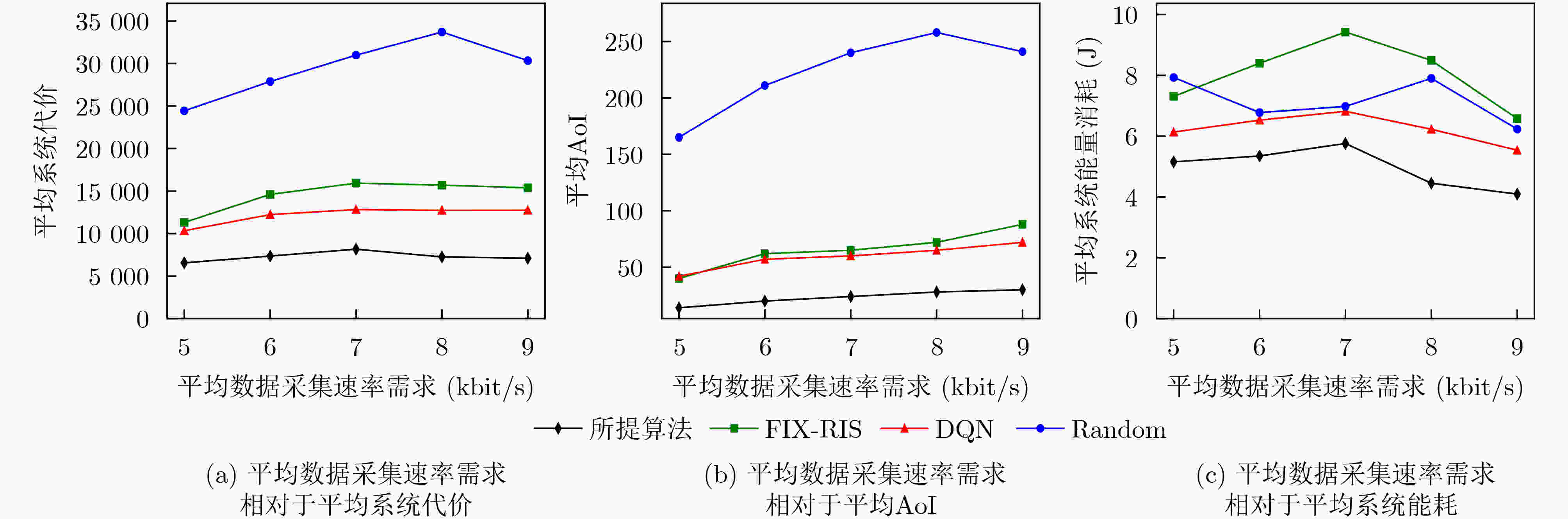
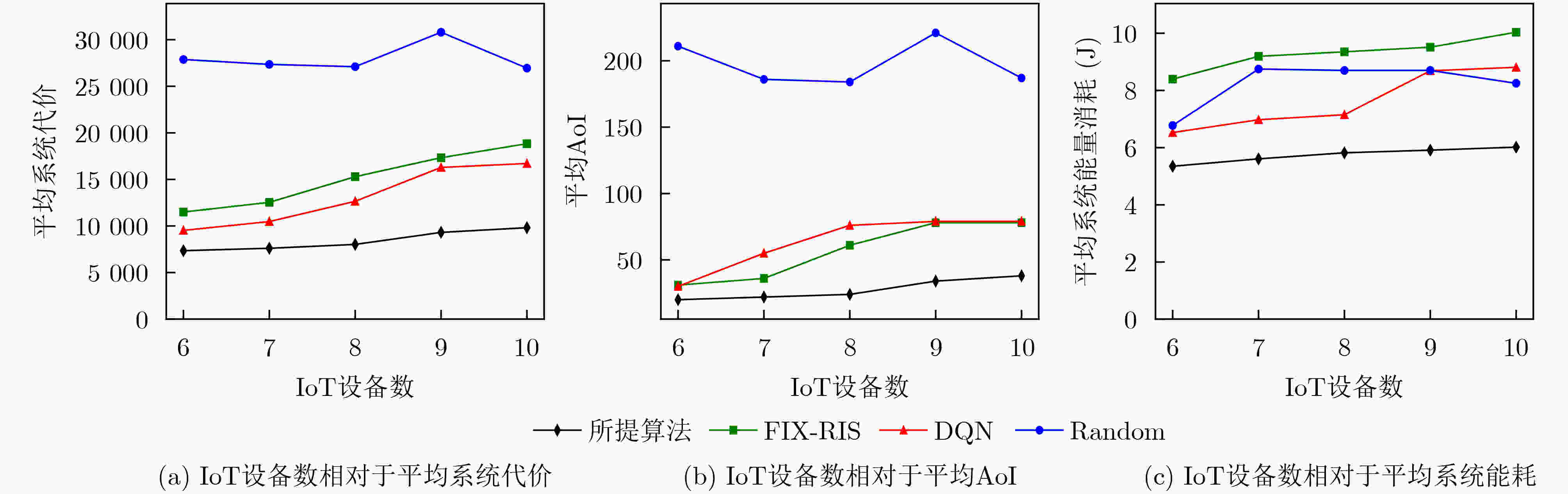
Objective This study aims to develop and implement an optimization framework that addresses the critical balance between energy consumption and information freshness in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-assisted Internet of Things (IoT) data collection systems, enhanced by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS). In complex urban environments, traditional line-of-sight communication between UAVs and ground-based IoT devices is often obstructed by buildings and infrastructure, hindering comprehensive coverage and efficient data collection. While RIS technology offers promising solutions by dynamically adjusting signal reflection directions, optimizing communication signal coverage, and enhancing quality, it introduces additional complexity in system design and resource allocation, requiring sophisticated adaptive optimization techniques. The integration of RIS enables stable communication connections across various UAV flight heights and angles, mitigating disruptions caused by obstacles or signal interference, thus improving data collection efficiency and reliability. However, this integration must account for multiple factors, including UAV energy consumption, communication complexity, and Age of Information (AoI) constraints. These approaches must adapt to the dynamic nature of UAV operations and fluctuating communication conditions, ensuring optimal performance in terms of energy efficiency and data freshness. The research also addresses several key challenges, including real-time adaptation to environmental changes, optimal scheduling of IoT device interactions, dynamic adjustment of RIS phase configurations, efficient trajectory planning, and the maintenance of data freshness under various system constraints. The proposed framework establishes a robust foundation for next-generation IoT data collection systems that can adapt to diverse operational conditions while maintaining high performance standards. This is achieved through the implementation of advanced deep reinforcement learning techniques, specifically designed to manage the complex interplay between UAV mobility, RIS configuration, and IoT device scheduling, ensuring efficient and timely data collection while optimizing system resources. Methods A comprehensive data collection optimization strategy is proposed, based on deep reinforcement learning principles, specifically designed to address the complex challenges in UAV-assisted IoT data collection systems enhanced by RIS technology. The methodology employs a Double Deep Q-Network (DDQN) architecture, integrating UAV trajectory planning, IoT device scheduling, and RIS phase adjustment within a three-dimensional grid-based movement space. The system incorporates a channel model that accounts for both direct and RIS-assisted communication paths, including a probabilistic path loss model for direct links and Rician fading for RIS-assisted links. The optimization problem is formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), where the state space includes the UAV position, previous movement information, and average AoI, while the action space involves 3D movement decisions and IoT device scheduling. The reward function is designed to balance multiple performance metrics, including system AoI, UAV flight energy consumption, data collection energy, data upload energy, and penalties for boundary violations. The DDQN implementation utilizes two Q-networks—the current and target networks—separating action selection from action evaluation, effectively addressing the issue of Q-value overestimation. The training process incorporates experience replay for sample storage and periodic updates to the target network to enhance learning stability. Additionally, the RIS phase shift optimization is derived through geometric relationships, considering both direct and RIS-assisted communication paths. This comprehensive approach enables the joint optimization of UAV trajectory, IoT device scheduling, and RIS phase adjustment, while ensuring energy efficiency and timely data collection in complex communication environments. Results and Discussions The proposed method enables the UAV to dynamically adjust its flight trajectory and communication strategy based on real-time environmental conditions, enhancing data transmission efficiency while reducing energy consumption. Extensive simulation experiments comprehensively evaluate the performance of the DDQN-based optimization framework. Convergence analysis demonstrates that the method achieves faster and more stable convergence compared to traditional DQN approaches. The average reward steadily increases and stabilizes after approximately 200 episodes, while baseline methods exhibit slower convergence and higher performance variance ( Fig. 3 ). The optimized UAV trajectory visualization shows that the method effectively guides the UAV to collect data efficiently from all IoT devices while avoiding unnecessary detours. The trajectory strikes a balance between visiting high-priority devices (those with higher AoI) and maintaining energy-efficient flight paths, clearly illustrating the effectiveness of the joint optimization of movement and device scheduling decisions (Fig. 4 ). Energy consumption analysis reveals that the proposed method achieves superior energy efficiency, with a 15% reduction in total energy consumption while maintaining comparable data collection performance. This improvement results from the intelligent integration of RIS-assisted communication and optimal trajectory planning, which reduces the need for energy-intensive maneuvers and prolonged hovering periods (Fig. 5 ) (Fig. 6 ). The AoI performance evaluation further confirms the method’s effectiveness in maintaining data freshness. The average AoI across all IoT devices remains consistently lower than in baseline methods, with a 20% improvement in worst-case AoI values. This demonstrates the method’s ability to balance the trade-off between visiting different devices and maintaining acceptable AoI levels, even under challenging network conditions. The framework’s adaptive nature is evident in its capacity to prioritize devices with critical AoI values while maintaining overall system efficiency, showing robust performance across varying network densities and device distributions (Fig. 5 ) (Fig. 6 ).Conclusions The proposed deep reinforcement learning-based optimization policy effectively addresses the complex challenges in UAV-assisted IoT data collection systems enhanced by RIS technology, demonstrating significant improvements in both energy efficiency and information freshness. The integration of advanced learning techniques with RIS-assisted communication provides a robust and adaptive solution for practical deployment in urban IoT environments. The comprehensive evaluation framework and detailed performance analysis offer valuable insights for system designers and practitioners. The superior performance in terms of convergence speed, trajectory optimization, energy efficiency, and AoI management confirms the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Future research will focus on extending the framework to multi-UAV coordination scenarios, exploring the impact of dynamic environmental changes, and developing more sophisticated reward mechanisms to address additional operational constraints, such as security and airspace restrictions. The promising results also indicate potential applications in emergency response systems, smart city infrastructure, and environmental monitoring networks. -
1 基于DDQN的UAV数据采集算法
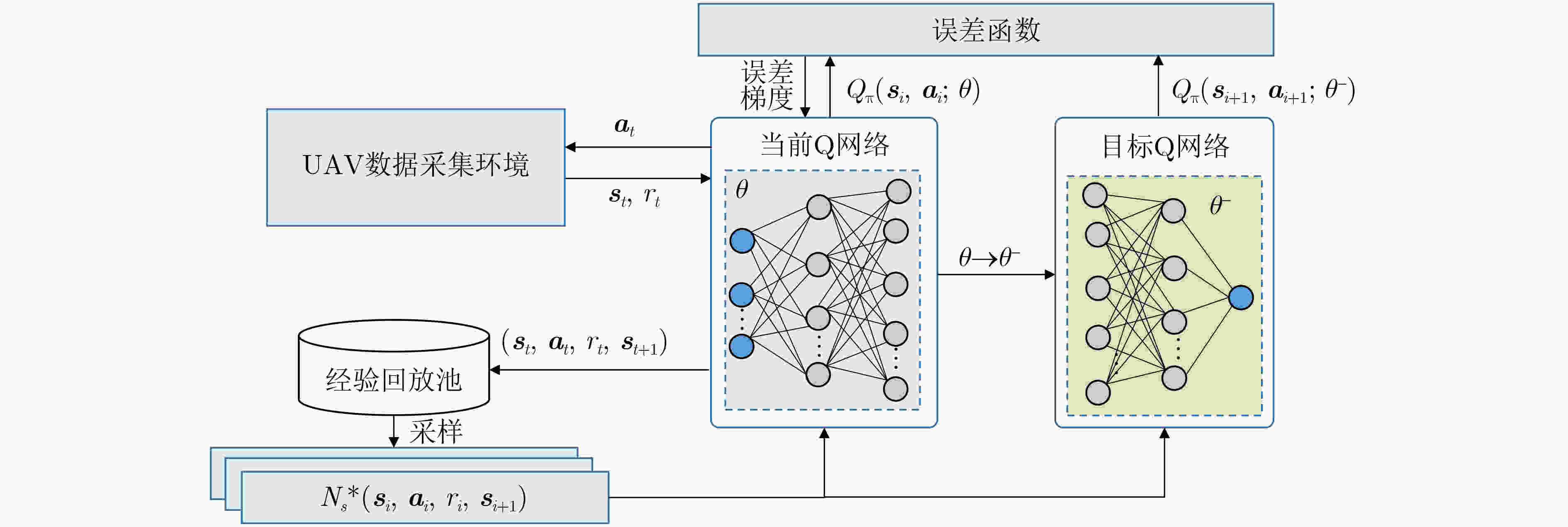
输入:UAV观测到的环境状态 输出:UAV轨迹和IoT设备调度策略 (1) 随机初始化神经网络参数 (2) for episode = 1,2,···,NEP do (3) 初始化仿真环境参数 (4) for t = 1,2,···,T do (5) 根据$ {Q_\pi }({\boldsymbol{s}},{\boldsymbol{a}};\theta ) $选取状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}} $对应的动作a; (6) 根据式(31)获得RIS的相位偏移; (7) 执行动作控制UAV飞行和IoT调度后,使用式(23)计算
瞬时奖励$ r $并获得下一时刻的状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}' $;(8) if UAV移动跃出边界 do (9) 状态回滚$ {\boldsymbol{s}}' \leftarrow {\boldsymbol{s}} $,为$ r $添加惩罚项; (10) 将环境数据$ ({\boldsymbol{s}},{\boldsymbol{a}},{{r}},{\boldsymbol{s}}') $存入经验池; (11) if 经验池存满数据 do (12) 从经验池取出Ns个样本; (13) 对于每个样本,用目标值网络计算式(29); (14) 更新当前Q网络以最小化损失式(30); (15) 每隔一定步长$ {\theta ^ - } \leftarrow \theta $; (16) end (17) end 表 1 主要仿真参数
参数 数值 $ {x^{{\text{MAX}}}} $, $ {y^{{\text{MAX}}}} $(m) 1 000, 1 000 $ L $,$ {z^{{\text{MIN}}}} $, $ {z^{{\text{MAX}}}} $(m) 10, 60, 80 $ {l_t} $(m) {0, 1, 2} $ {c_1} $, $ {c_2} $ 12.081, 0.113 95[7] $ {\mu ^{{\text{LoS}}}} $ , $ {\mu ^{{\text{NLoS}}}} $ 1.445 44, 199.526[7] $ {K_1} $, $ {K_2} $ 3, 4 $ \rho $, $ \beta $ (dBm) –30, –50[8] $ {\delta _1} $, $ {\delta _2} $(dBm/Hz) –174, –174 $ {B_1} $, $ {B_2} $(MHz) 2, 2 $ {P_1} $, $ {P_2} $(W) 0.5, 0.8 $ {P_{\mathrm{B}}} $, $ {P_{\mathrm{I}}} $, $ {P_{\mathrm{V}}} $ 88.63, 79.85, 11.46 $ {\zeta _1} $, $ {\zeta _2} $, $ {\zeta _3} $, $ {\zeta _4} $ 100, 1, 10, 10 $ \varLambda $, $ \varXi $ 0.6, 0.05 $ {U_{{\text{tip}}}} $(m/s) 120[29] $ \varUpsilon $(kg/m3) 1.225[29] $ G $(m2) 0.503[29] $ \chi $(bit) 1 000 -
[1] 段洁, 胡显静, 林欢, 等. 面向物联网数据特征的信息中心网络缓存方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2240–2248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200631.DUAN Jie, HU Xianjing, LIN Huan, et al. Information-centric networking caching scheme for data characteristics of internet of things[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2240–2248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200631. [2] JAVAID S, SAEED N, QADIR Z, et al. Communication and control in collaborative UAVs: Recent advances and future trends[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(6): 5719–5739. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3248841. [3] 刘志新, 赵松晗, 杨毅, 等. 智能反射面辅助的无人机无线携能通信网络吞吐量最大化算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2325–2331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220195.LIU Zhixin, ZHAO Songhan, YANG Yi, et al. Throughput maximization algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-aided unmanned aerial vehicle communication networks with wireless energy transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2325–2331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220195. [4] 张在琛, 江浩. 智能超表面使能无人机高能效通信信道建模与传输机理分析[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(10): 2623–2634. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221352.ZHANG Zaichen and JIANG Hao. Channel modeling and characteristics analysis for high energy-efficient RIS-assisted UAV communications[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(10): 2623–2634. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221352. [5] SAVKIN A V, HUANG Chao, and NI Wei. Joint multi-UAV path planning and LoS communication for mobile-edge computing in IoT networks with RISs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(3): 2720–2727. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3215255. [6] SAVKIN A V, HUANG Chao, and NI Wei. Collision-free 3-D navigation of a UAV team for optimal data collection in Internet-of-Things networks with reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(3): 4070–4077. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2023.3269095. [7] LIN Xinzhong, XIE Cong, XIE Wenwu, et al. Security performance analysis of RIS-assisted UAV wireless communication in industrial IoT[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2022, 78(4): 5957–5973. doi: 10.1007/s11227-021-04095-7. [8] ZHAI Liangsen, ZOU Yulong, ZHU Jia, et al. RIS-assisted UAV-enabled wireless powered communications: System modeling and optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(5): 5094–5108. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3324500. [9] RANJHA A and KADDOUM G. URLLC facilitated by mobile UAV relay and RIS: A joint design of passive beamforming, blocklength, and UAV positioning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(6): 4618–4627. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3027149. [10] ESKANDARI M, HUANG Hailong, SAVKIN A V, et al. Model predictive control-based 3D navigation of a RIS-equipped UAV for LoS wireless communication with a ground intelligent vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(3): 2371–2384. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3232890. [11] LI Linpei, GUAN Wanqing, ZHAO Chuan, et al. Trajectory planning, phase shift design, and IoT devices association in flying-RIS-assisted mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(1): 147–157. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3300700. [12] AL-HILO A, SAMIR M, ELHATTAB M, et al. RIS-assisted UAV for timely data collection in IoT networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2023, 17(1): 431–442. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2022.3215279. [13] TYROVOLAS D, MEKIKIS P V, TEGOS S A, et al. Energy-aware design of UAV-mounted RIS networks for IoT data collection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(2): 1168–1178. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3229672. [14] LIU Jianghu and ZHANG Hongtao. Height-fixed UAV enabled energy-efficient data collection in RIS-aided wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(11): 7452–7463. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3250988. [15] ALMASOUD A M. Robust anti-jamming technique for UAV data collection in IoT using landing platforms and RIS[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 70635–70651. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3294596. [16] YANG Bowen, YU Yao, LI Jianqi, et al. An AoI-guaranteed sensor data collection strategy for RIS-assisted UAV communication system[C]. 2023 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Dalian, China, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCC57788.2023.10233285. [17] SAMIR M, ELHATTAB M, ASSI C, et al. Optimizing age of information through aerial reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(4): 3978–3983. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3063953. [18] HUANG Hongli, LIU Juan, and XIE Lingfu. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted fresh data collection in UAV communications[C]. The 11th International Conference in Communications, Signal Processing, and Systems, Singapore, 2022: 189–197. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-2362-5_24. [19] XIAO Xiongbing, WANG Xiumin, and LIN Weiwei. Joint AoI-aware UAVs trajectory planning and data collection in UAV-based IoT systems: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2024, 70(4): 6484–6495. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2024.3440406. [20] JIANG Wenwen, AI Bo, LI Mushu, et al. Average age-of-information minimization in aerial IRS-assisted data delivery[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(17): 15133–15146. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3264618. [21] CHEN Zhen, GUO Yeyong, ZHANG Peichang, et al. Physical layer security improvement for hybrid RIS-assisted MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2024, 28(11): 2493–2497. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2024.3427010. [22] RUAN Chengyao, ZHANG Zaichen, JIANG Hao, et al. Wideband near-field channel covariance estimation for XL-MIMO systems in the face of beam split[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3471733. [23] QIU Chen, WEI Zhiqing, YUAN Xin, et al. Multiple UAV-mounted base station placement and user association with joint fronthaul and backhaul optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(9): 5864–5877. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3001136. [24] SHI Wangqi, JIANG Hao, XIONG Baiping, et al. RIS-empowered V2V communications: Three-dimensional beam domain channel modeling and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(11): 15844–15857. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3434568. [25] WEI Zhiqiang, CAI Yuanxin, SUN Zhuo, et al. Sum-rate maximization for IRS-assisted UAV OFDMA communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(4): 2530–2550. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3042977. [26] XU Peng, NIU Wenqi, CHEN Gaojie, et al. Performance analysis of RIS-assisted systems with statistical channel state information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(1): 1089–1094. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3126374. [27] JIANG Hao, SHI Wangqi, ZHANG Zaichen, et al. Large-scale RIS enabled air-ground channels: Near-field modeling and analysis[J]. arXiv: 2403.12781, 2024. [28] LIN Na, TANG Hailun, ZHAO Liang, et al. A PDDQNLP algorithm for energy efficient computation offloading in UAV-assisted MEC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 8876–8890. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3266497. [29] CHEN Guqiao, CHENG Changjun, XU Xiaoli, et al. Minimizing the age of information for data collection by cellular-connected UAV[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(7): 9631–9635. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3249747. [30] WANG Xu, WANG Sen, LIANG Xingxing, et al. Deep reinforcement learning: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(4): 5064–5078. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3207346. [31] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236. [32] VAN HASSELT H, GUEZ A, and SILVER D. Deep reinforcement learning with double q-learning[C]. The 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 2094–2100. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v30i1.10295. [33] WANG Liang, WANG Kezhi, PAN Cunhua, et al. Joint trajectory and passive beamforming design for intelligent reflecting surface-aided UAV communications: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2023, 22(11): 6543–6553. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3200998. [34] MEI Haibo, YANG Kun, LIU Qiang, et al. 3D-trajectory and phase-shift design for RIS-assisted UAV systems using deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 3020–3029. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3143839. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
