Research on Security, Privacy, and Energy Efficiency in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Assisted Federal Edge Learning Communication Systems
-
摘要: 无人机(UAV)辅助联邦边缘学习的通信能够有效解决终端设备数据孤岛问题和数据泄露风险。然而,窃听者可能利用联邦边缘学习中的模型更新来恢复终端设备的原始隐私数据,从而对系统的隐私安全构成极大威胁。为了克服这一挑战,该文在无人机辅助联邦边缘学习通信系统提出一种有效的安全聚合和资源优化方案。具体来说,终端设备利用其本地数据进行局部模型训练来更新参数,并将其发送给全局无人机,无人机据此聚合出新的全局模型参数。窃听者试图通过窃听终端设备发送的模型参数信号来恢复终端设备的原始数据。该文通过联合优化终端设备的传输带宽、CPU频率、发送功率以及无人机的CPU频率,最大化安全隐私能效。为了解决该优化问题,该文提出一种演进深度确定性策略梯度(DDPG)算法,通过和系统智能交互,在保证基本时延和能耗需求的情况下获得安全聚合和资源优化方案。最后,通过和基准方案对比,验证了所提方案的有效性。Abstract:
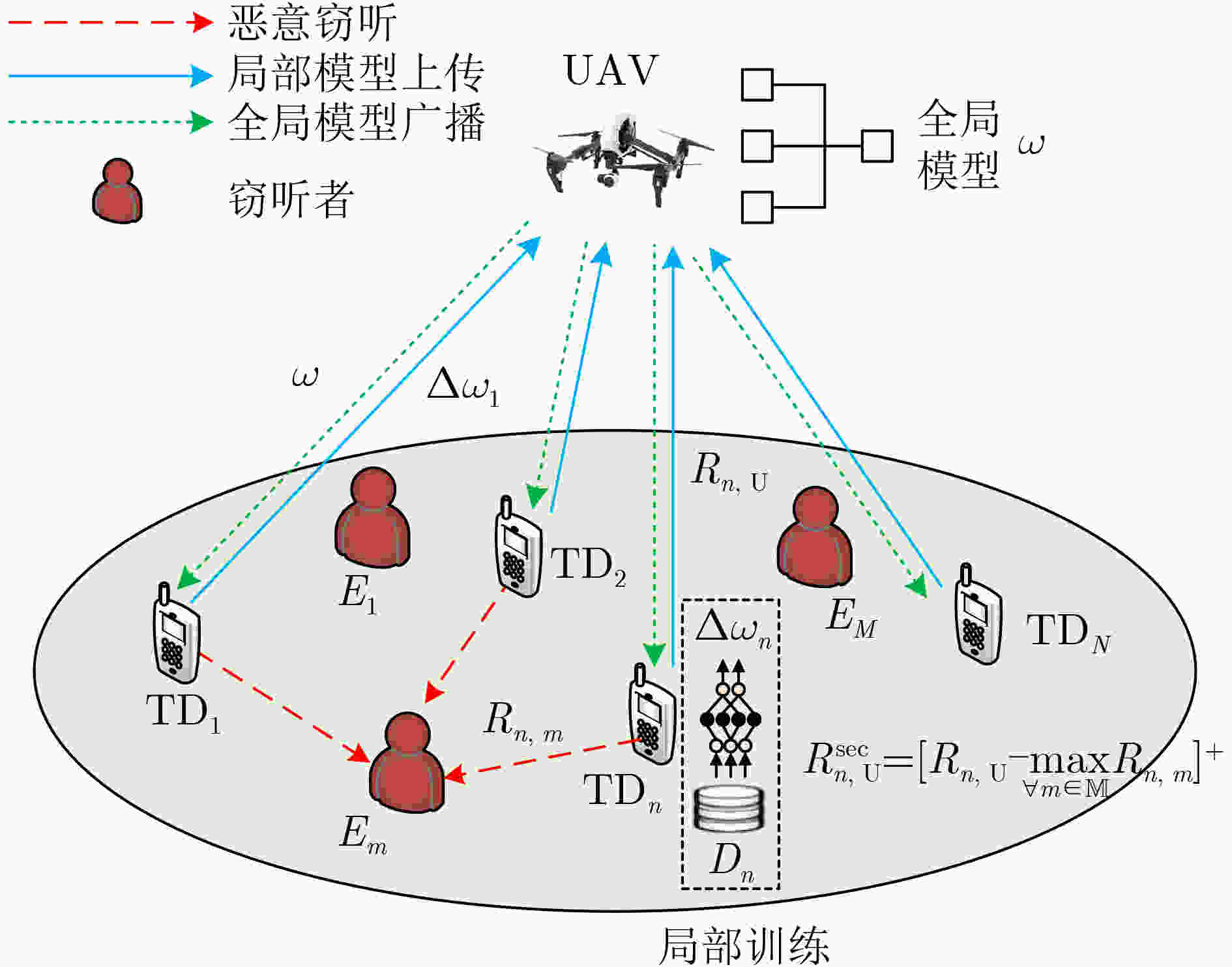
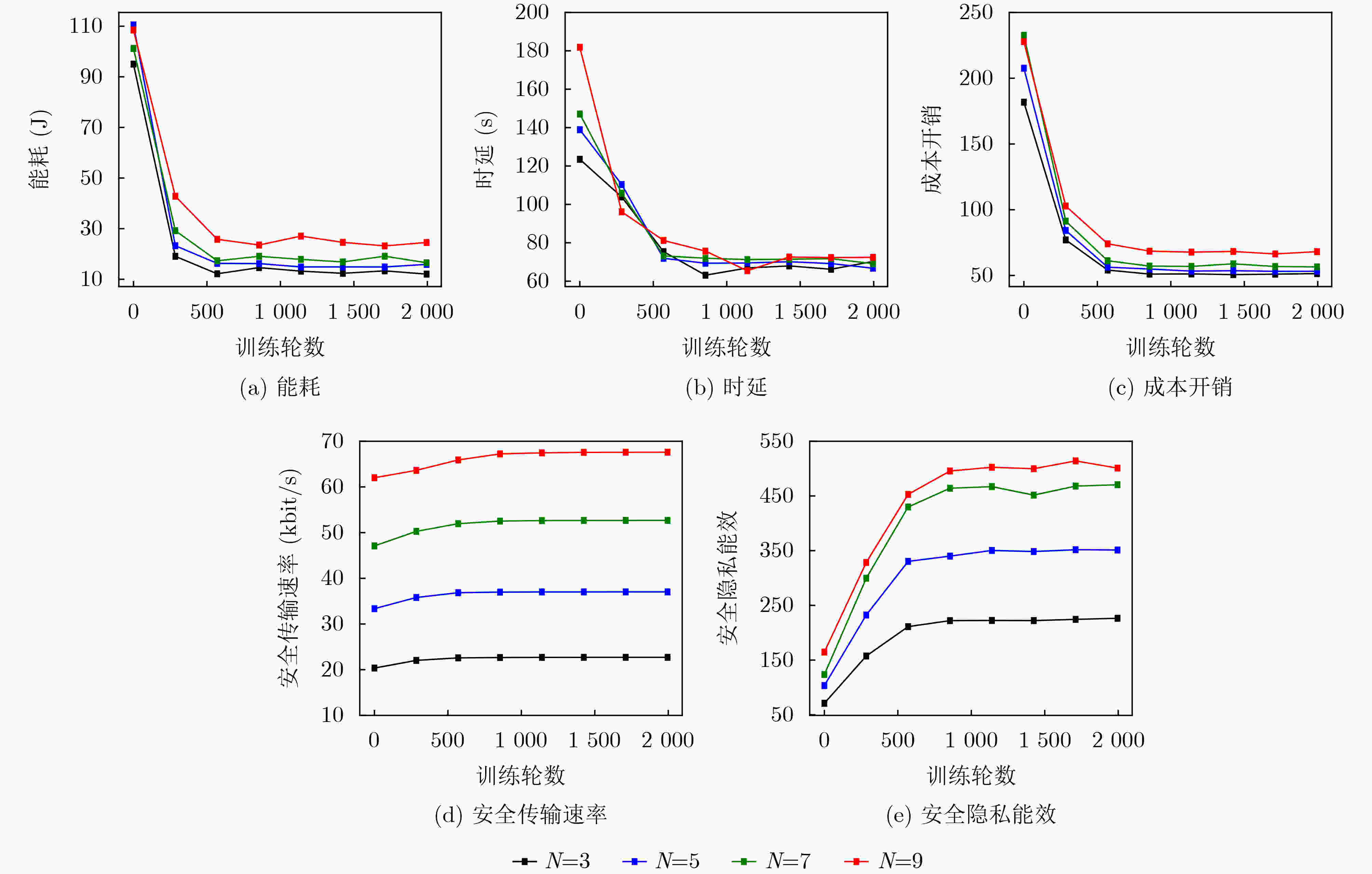
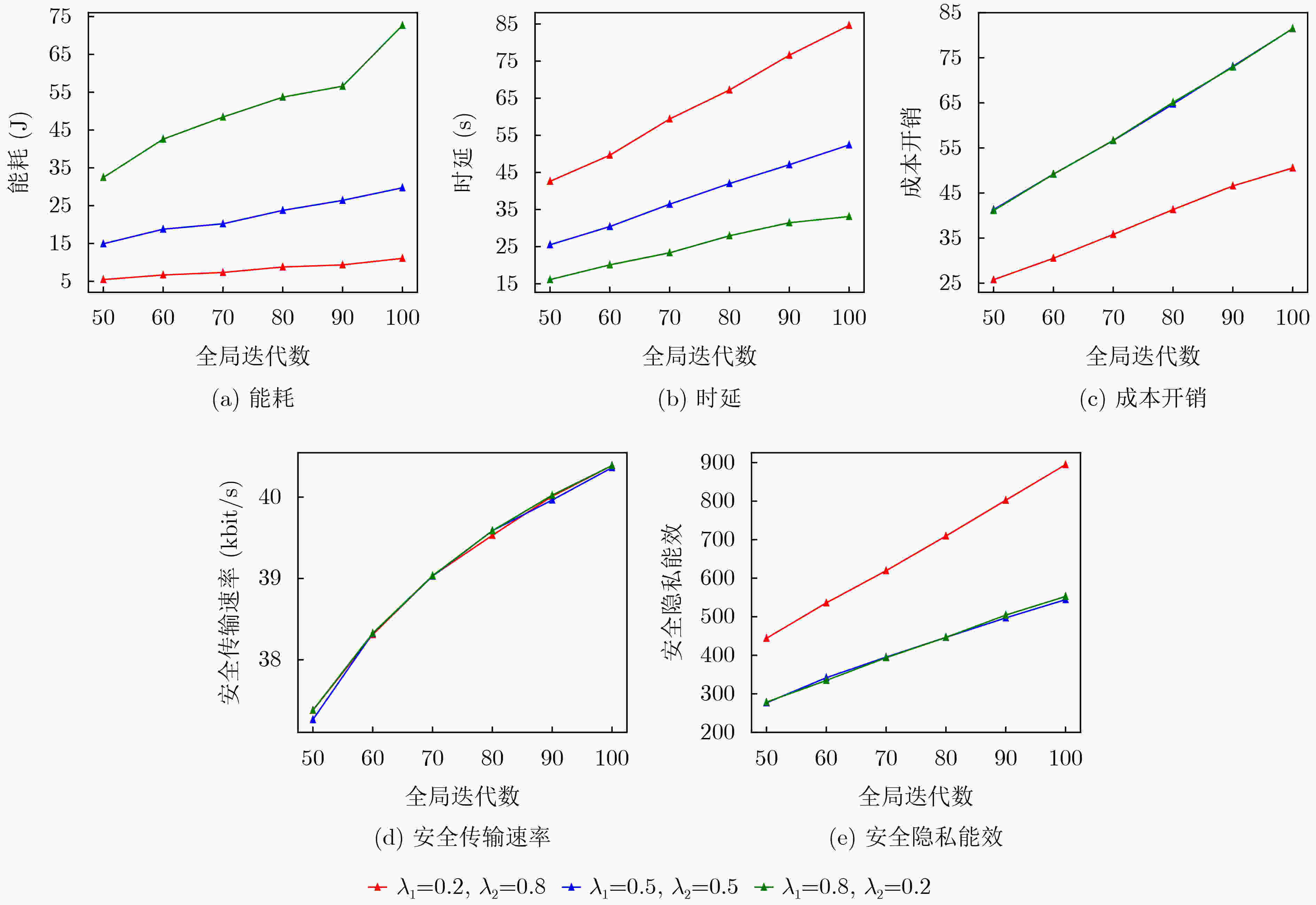
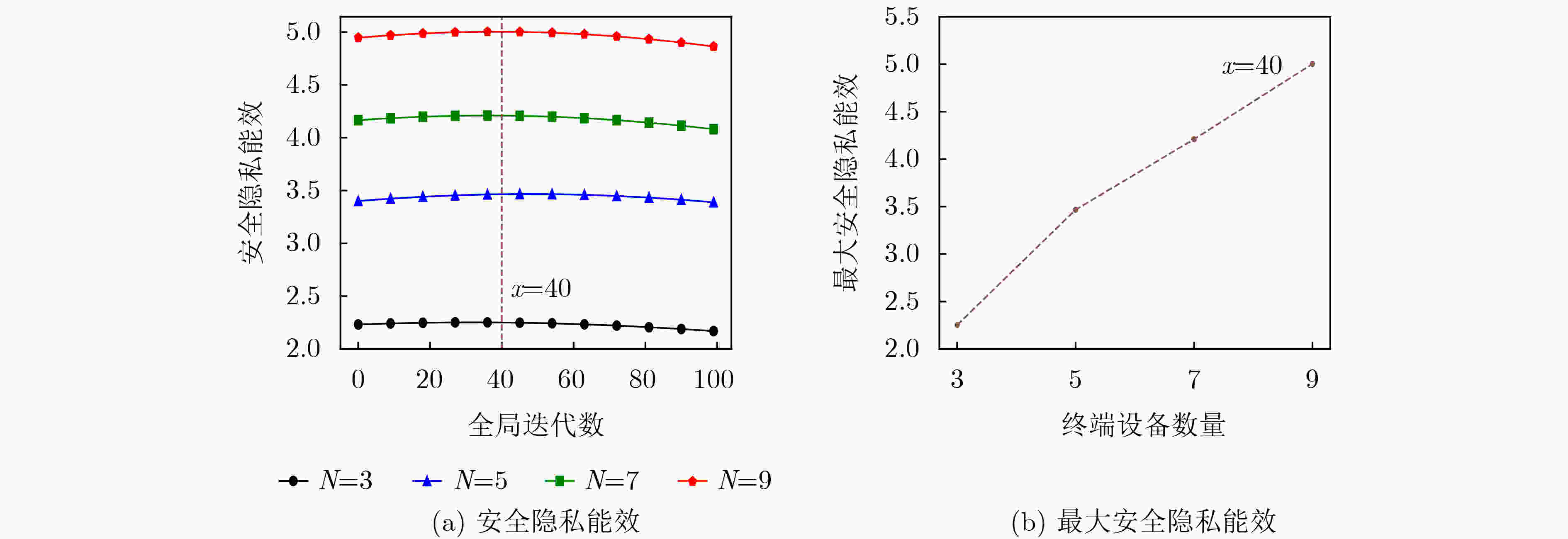
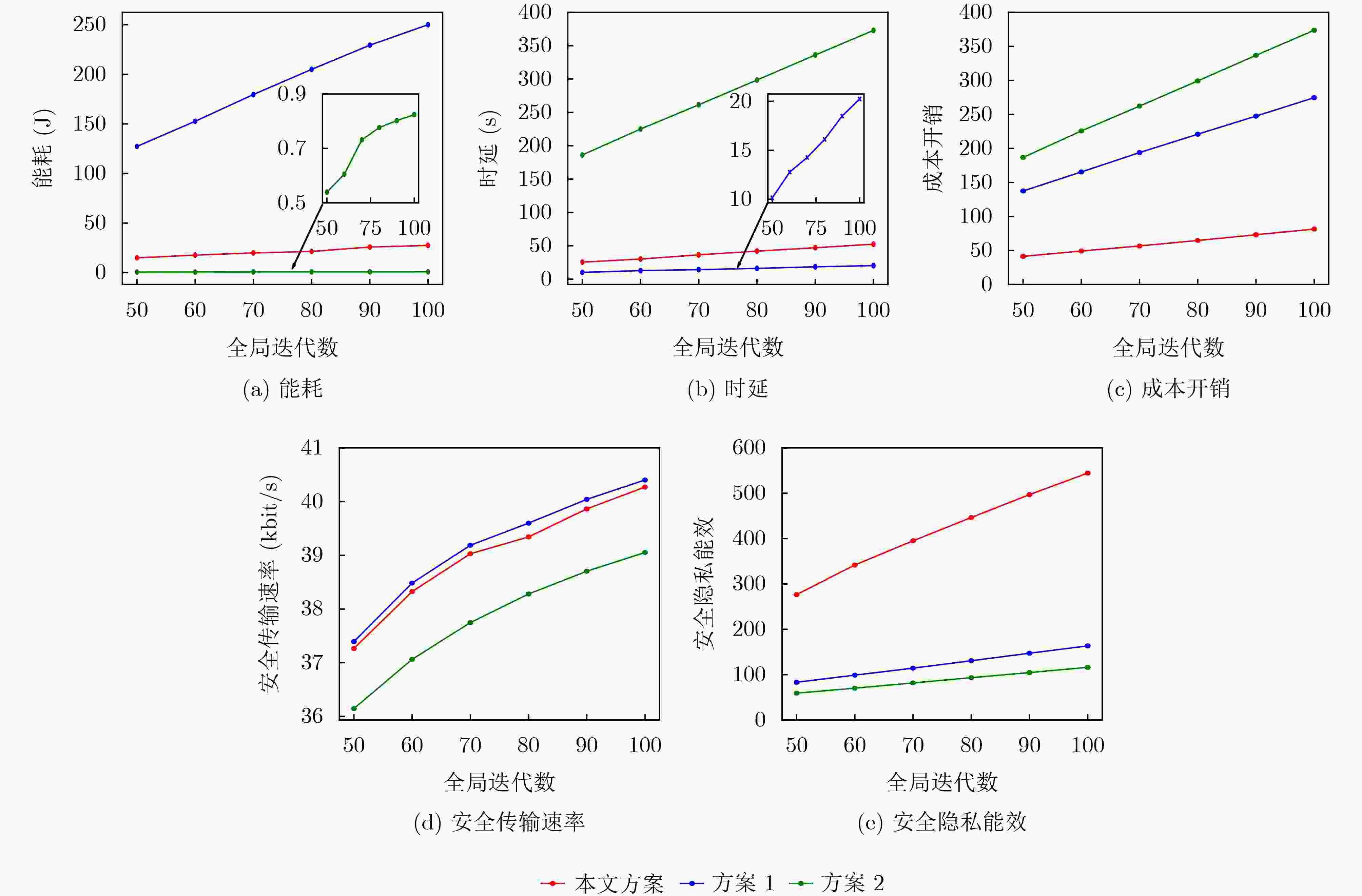
Objective Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Assisted Federal Edge Learning (UAV-Assisted FEL) communication addresses the data isolation problem and mitigates data leakage risks in terminal devices. However, eavesdroppers may exploit model updates in FEL to recover original private data, significantly threatening the system’s privacy and security. Methods To address this issue, this study proposes a secure aggregation and resource optimization scheme for UAV-Assisted FEL communication systems. Terminal devices train local models using local data and update parameters, which are transmitted to a global UAV. The UAV aggregates these parameters to generate new global model parameters. Eavesdroppers attempt to intercept the transmitted parameters to reconstruct the original data. To enhance security-privacy energy efficiency, the transmission bandwidth, CPU frequency, and transmit power of terminal devices, along with the CPU frequency of the UAV, are jointly optimized. An evolutionary Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm is proposed to solve this optimization problem. The algorithm intelligently interacts with the system to achieve secure aggregation and resource optimization while meeting latency and energy consumption requirements. Results and Discussions The simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme. The experiments evaluate the effects of the scheme on key performance metrics, including system cost, secure transmission rate, and secure privacy energy efficiency, from multiple perspectives. As shown in ( Fig. 2 ), with an increasing number of terminal devices, system cost, secure transmission rate, and secure privacy energy efficiency all increase. These results indicate that the proposed scheme ensures system security and enhances energy efficiency, even in multi-device scenarios. As shown in (Fig. 3 ), under varying global iteration counts, the system balances latency and energy consumption by either extending the duration to lower energy consumption or increasing energy consumption to reduce latency. The secure transmission rate rises with the number of global iterations, as fewer iterations allow the system to tolerate higher energy consumption and latency per iteration, leading to reduced transmission power from terminal devices to meet system constraints. Additionally, secure privacy energy efficiency improves with increasing global iterations, further demonstrating the scheme’s capacity to ensure system security and reduce system cost as global iterations increase. As shown in (Fig. 4 ), during UAV flight, secure privacy energy efficiency fluctuates, with higher secure transmission rates observed when the communication environment between terminal devices and the UAV is more favorable. As shown in (Fig. 5 ), the proposed scheme is compared with two baseline schemes: Scheme 1, which minimizes system latency, and Scheme 2, which minimizes system energy consumption. The proposed scheme significantly outperforms both baselines in cost overhead. Scheme 1 achieves a slightly higher secure transmission rate than the proposed scheme due to its focus on minimizing latency at the expense of higher energy consumption. Conversely, Scheme 2 shows a considerably lower secure transmission rate as it prioritizes minimizing energy consumption, resulting in lower transmission power and compromised secure transmission rates. The results indicate that the secure privacy energy efficiency of the proposed scheme significantly exceeds that of the baseline schemes, further demonstrating its effectiveness.Conclusions To enhance data transmission security and reduce system costs, this paper proposes a secure aggregation and resource optimization scheme for UAV-Assisted FEL. Under constraints of limited computational and communication resources, the scheme jointly optimizes the transmission bandwidth, CPU frequency, and transmission power of terminal devices, along with the CPU frequency of the UAV, to maximize the secure privacy energy efficiency of the UAV-Assisted FEL system. Given the complexity of the time-varying system and the strong coupling of multiple optimization variables, an advanced DDPG algorithm is developed to solve the optimization problem. The problem is first modeled as a Markov Decision Process, followed by the construction of a reward function positively correlated with the secure privacy energy efficiency objective. The proposed DDPG network then intelligently generates joint optimization variables to obtain the optimal solution for secure privacy energy efficiency. Simulation experiments evaluate the effects of the proposed scheme on key system performance metrics from multiple perspectives. The results demonstrate that the proposed scheme significantly outperforms other benchmark schemes in improving secure privacy energy efficiency, thereby validating its effectiveness. -
表 1 仿真参数设置
参数 值 参数 值 参数 值 $ \left| {{D_n}} \right| $ 600 $ {p^{\max }}\left( {{\text{dBm}}} \right) $ 20 $ {c_0}\left( {{\text{cycle/bit}}} \right) $ 1 500 $ \eta $ 0.005 $ {f^{\min }}\left( {{\text{MHz}}} \right) $ 100 $ {c_n}\left( {{\text{cycle/sample}}} \right) $ $ {\mathcal{U}}\left[ {{{10}^4},3 \times {{10}^4}} \right] $ ${\varepsilon _g}$ 0.01 $ {f^{\max }}\left( {{\text{GHz}}} \right) $ 2 $ {\mathrm{BW}}\left( {{\text{MHz}}} \right) $ 3 $ a $ 11.95 $ F_U^{\min }\left( {{\text{GHz}}} \right) $ 1 $ \psi \left( {{\text{kbit}}} \right) $ 21.84 $ b $ 0.14 $ F_{\text{U}}^{\max }\left( {{\text{GHz}}} \right) $ 6 $ N $ 3~9 $ {\beta _0} $ $ 7 \times {10^{ - 5}} $ $ \delta _0^2 = \delta _1^2\left( {{\text{dBm}}} \right) $ –90 $ E_n^{\max }\left( {\text{J}} \right) $ 20 $ {p^{\min }}\left( {{\text{dBm}}} \right) $ 10 $ \sigma _{n,m}^2\left( {{\text{dBm}}} \right) $ –70 $ E_U^{\max }\left( {\text{J}} \right) $ 30 -
[1] BASHIR A K, VICTOR N, BHATTACHARYA S, et al. Federated learning for the healthcare metaverse: Concepts, applications, challenges, and future directions[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(24): 21873–21891. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3304790. [2] ZHANG Shiying, LI Jun, SHI Long, et al. Federated learning in intelligent transportation systems: Recent applications and open problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(5): 3259–3285. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3324962. [3] ZHAO Yang, ZHAO Jun, JIANG Linshan, et al. Privacy-preserving blockchain-based federated learning for IoT devices[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(3): 1817–1829. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3017377. [4] KURUNATHAN H, HUANG Hailong, LI Kai, et al. Machine learning-aided operations and communications of unmanned aerial vehicles: A contemporary survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2024, 26(1): 496–533. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3312221. [5] BAI Yang, CHEN Lixing, LI Jianhua, et al. Multicore federated learning for mobile-edge computing platforms[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(7): 5940–5952. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3224239. [6] WANG Xiaofei, HAN Yiwen, WANG Chenyang, et al. In-edge AI: Intelligentizing mobile edge computing, caching and communication by federated learning[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(5): 156–165. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2019.1800286. [7] SUN Wen, ZHAO Yong, MA Wenqiang, et al. Accelerating convergence of federated learning in MEC with dynamic community[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(2): 1769–1784. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3241770. [8] LIM W Y B, NG J S, XIONG Zehui, et al. Decentralized edge intelligence: A dynamic resource allocation framework for hierarchical federated learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2022, 33(3): 536–550. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2021.3096076. [9] 陈卓, 江辉, 周杨. 一种面向联邦学习对抗攻击的选择性防御策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 1119–1127. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230137.CHEN Zhuo, JIANG Hui, and ZHOU Yang. A selective defense strategy for federated learning against attacks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 1119–1127. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230137. [10] YAN Kang, SHU Nina, WU Tao, et al. A survey of energy-efficient strategies for federated learning inmobile edge computing[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2024, 25(5): 645–663. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2300181. [11] LIU Tianyu, DI Boya, and SONG Lingyang. Privacy-preserving federated edge learning: Modeling and optimization[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(7): 1489–1493. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3167088. [12] DAO N N, PHAM Q V, TU N H, et al. Survey on aerial radio access networks: Toward a comprehensive 6G access infrastructure[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 1193–1225. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059644. [13] HOU Peng, JIANG Xiaohan, WANG Zongshan, et al. Federated deep reinforcement learning-based intelligent dynamic services in UAV-assisted MEC[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(23): 20415–20428. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3284450. [14] NEHRA A, CONSUL P, BUDHIRAJA I, et al. Federated learning based trajectory optimization for UAV enabled MEC[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 2023: 1640–1645. doi: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10278857. [15] TANG Shunpu, ZHOU Wenqi, CHEN Lunyuan, et al. Battery-constrained federated edge learning in UAV-enabled IoT for B5G/6G networks[J]. Physical Communication, 2021, 47: 101381. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2021.101381. [16] SEID A M, ERBAD A, ABISHU H N, et al. Multiagent federated reinforcement learning for resource allocation in UAV-enabled internet of medical things networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(22): 19695–19711. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3283353. [17] GEIPING J, BAUERMEISTER H, DRöGE H, et al. Inverting gradients-how easy is it to break privacy in federated learning?[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1421. [18] YAO Jingjing and ANSARI N. Secure federated learning by power control for internet of drones[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(4): 1021–1031. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2021.3076167. [19] POPOSKA M, PEJOSKI S, RAKOVIC V, et al. Delay minimization of federated learning over wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2024, 28(1): 108–112. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3337320. [20] YAO Jingjing and ANSARI N. Enhancing federated learning in fog-aided IoT by CPU frequency and wireless power control[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(5): 3438–3445. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3022590. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
