Noise Reduction and Temperature Field Reconstruction of Flame Light Field Images Based on Improved U-network
-
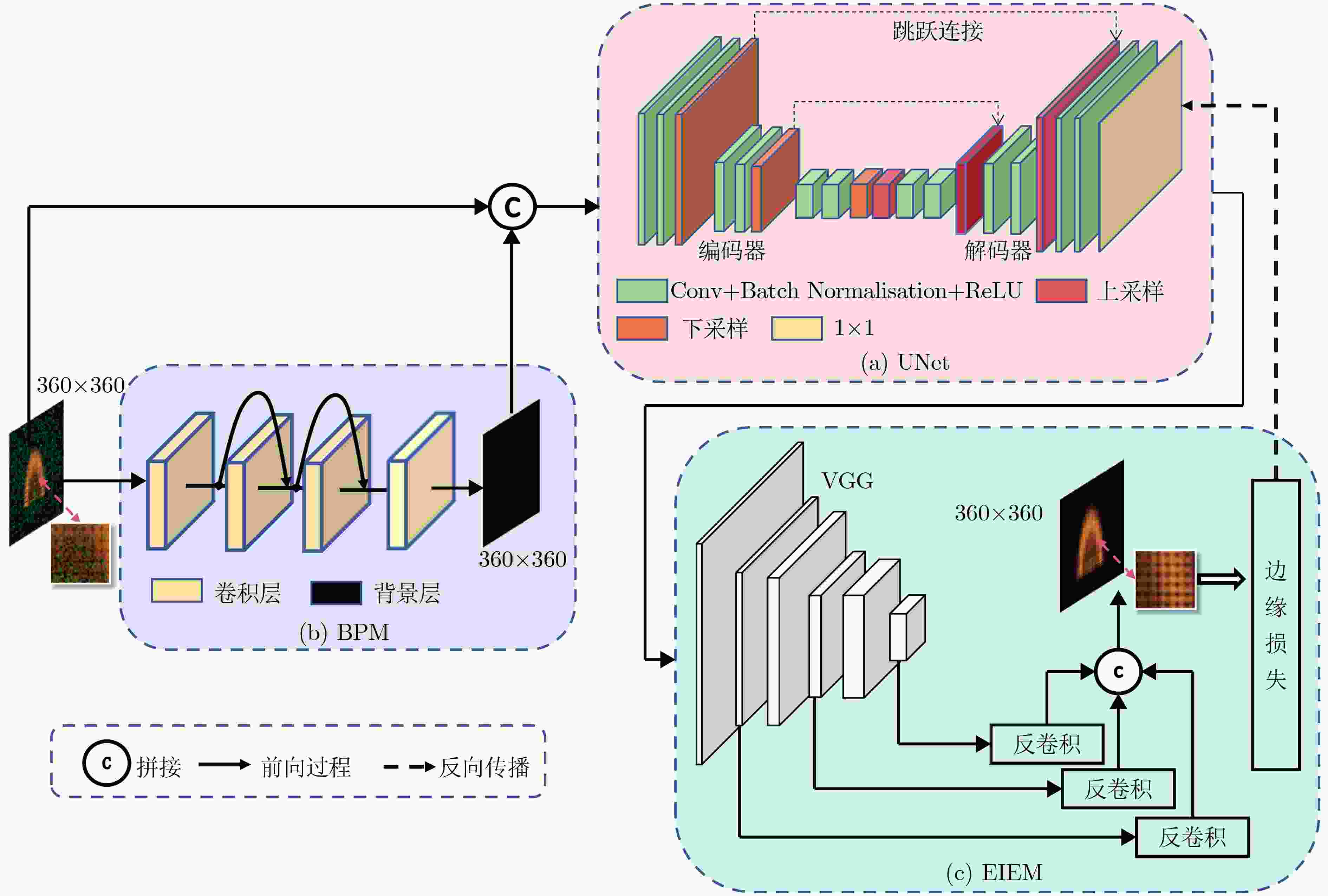
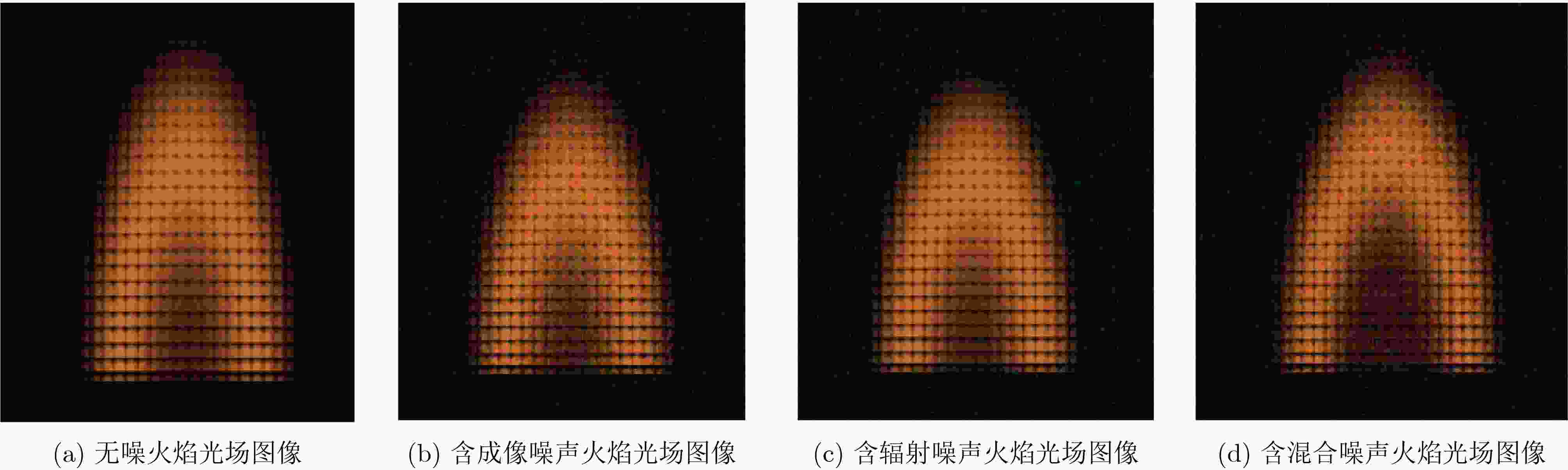
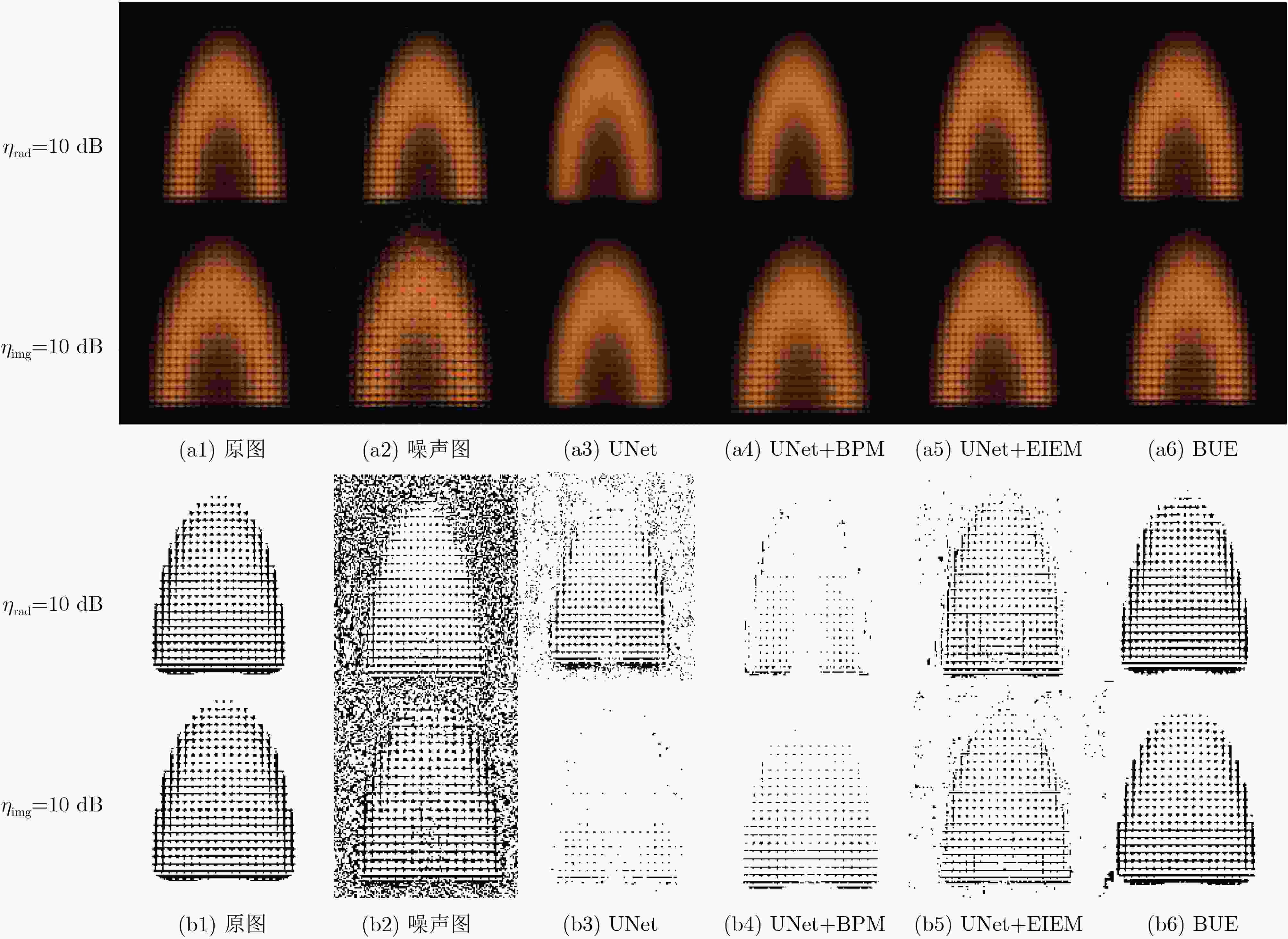
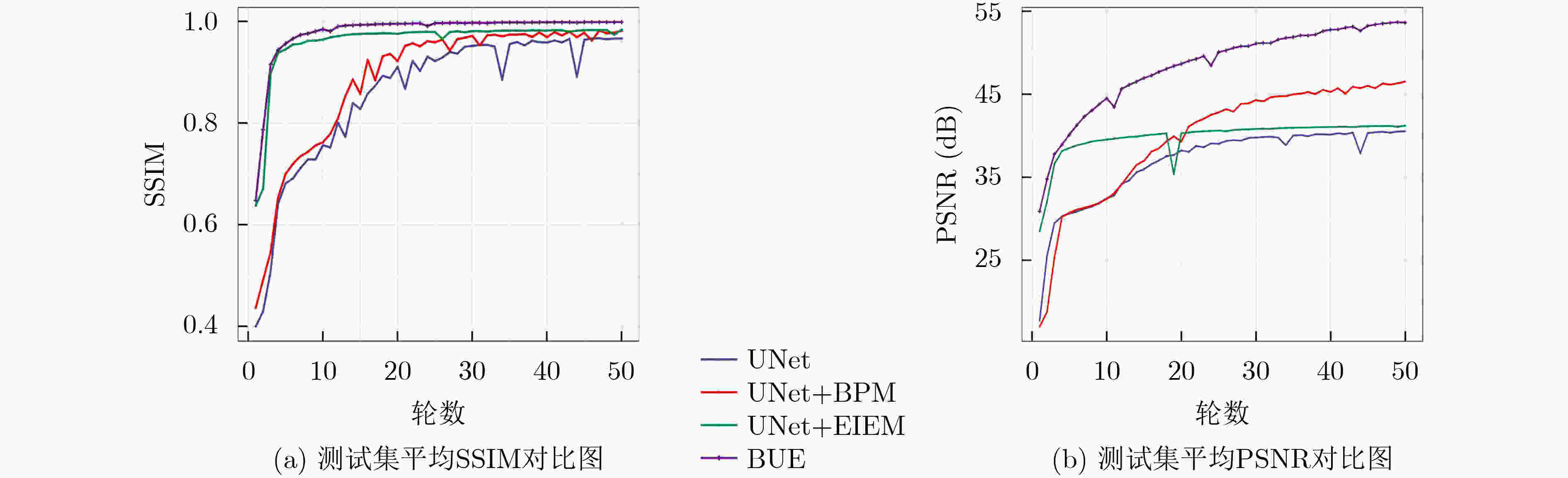
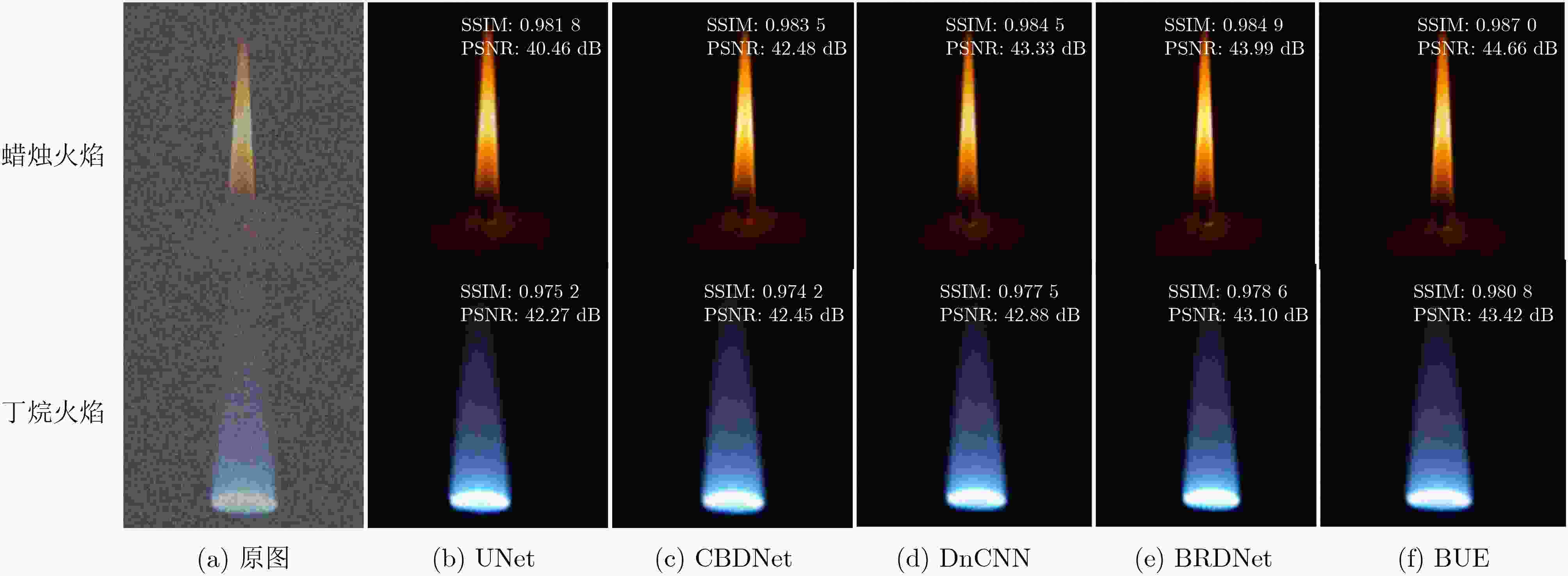
摘要: 火焰光场图像在形成过程中夹杂的辐射噪声和成像噪声会降低火焰温度场3维重建精度,该文提出一种基于改进U型网络(UNet)的降噪模型,该模型针对辐射噪声和成像噪声的特性以及复杂火焰图像的纹理信息设计了背景净化模块和边缘信息优化模块。通过密集卷积操作对图像背景层进行特征提取,着重净化夹杂在图像背景层的辐射噪声。通过UNet模块中对称的编码器-解码器网络结构和跳跃连接,对通道间的辐射噪声和表层的成像噪声降噪。最后利用边缘优化模块对图像细节信息进行提取,从而获得更高质量的火焰光场图像。数值模拟部分,在火焰光场图像上混合加入信噪比为10 dB的辐射噪声和成像噪声,经该文模型降噪后的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似指数(SSIM)高达47 dB和
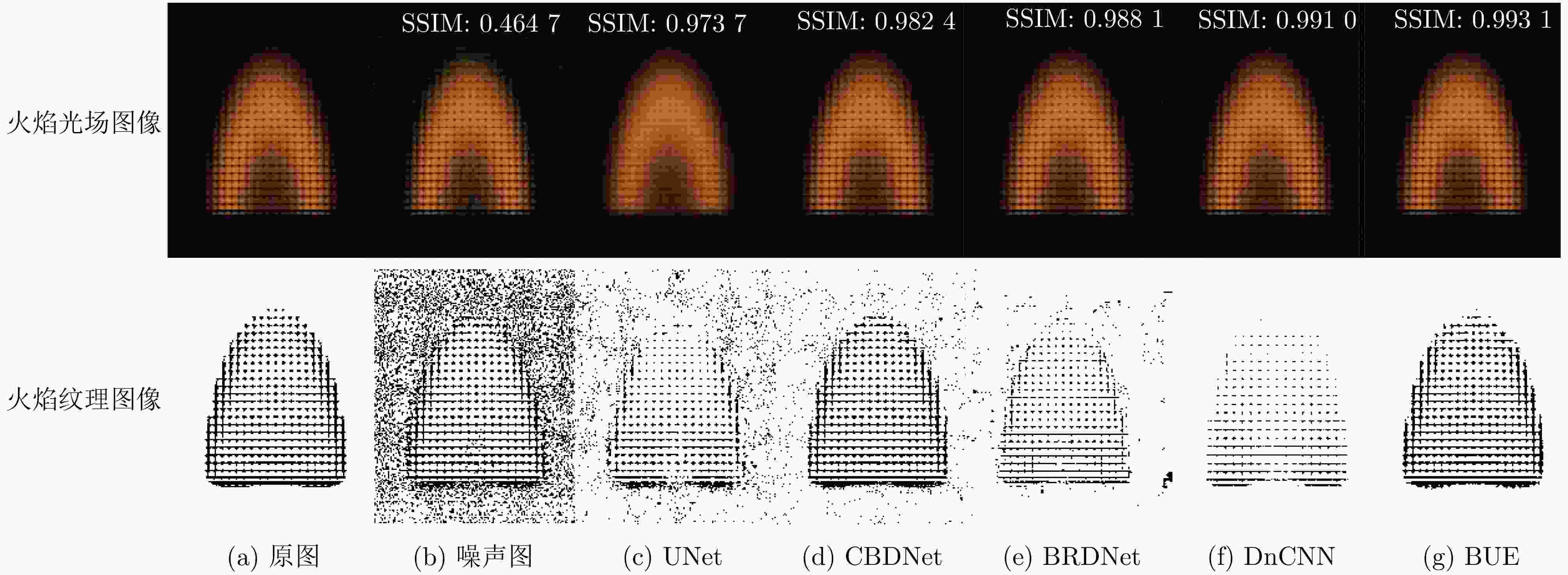
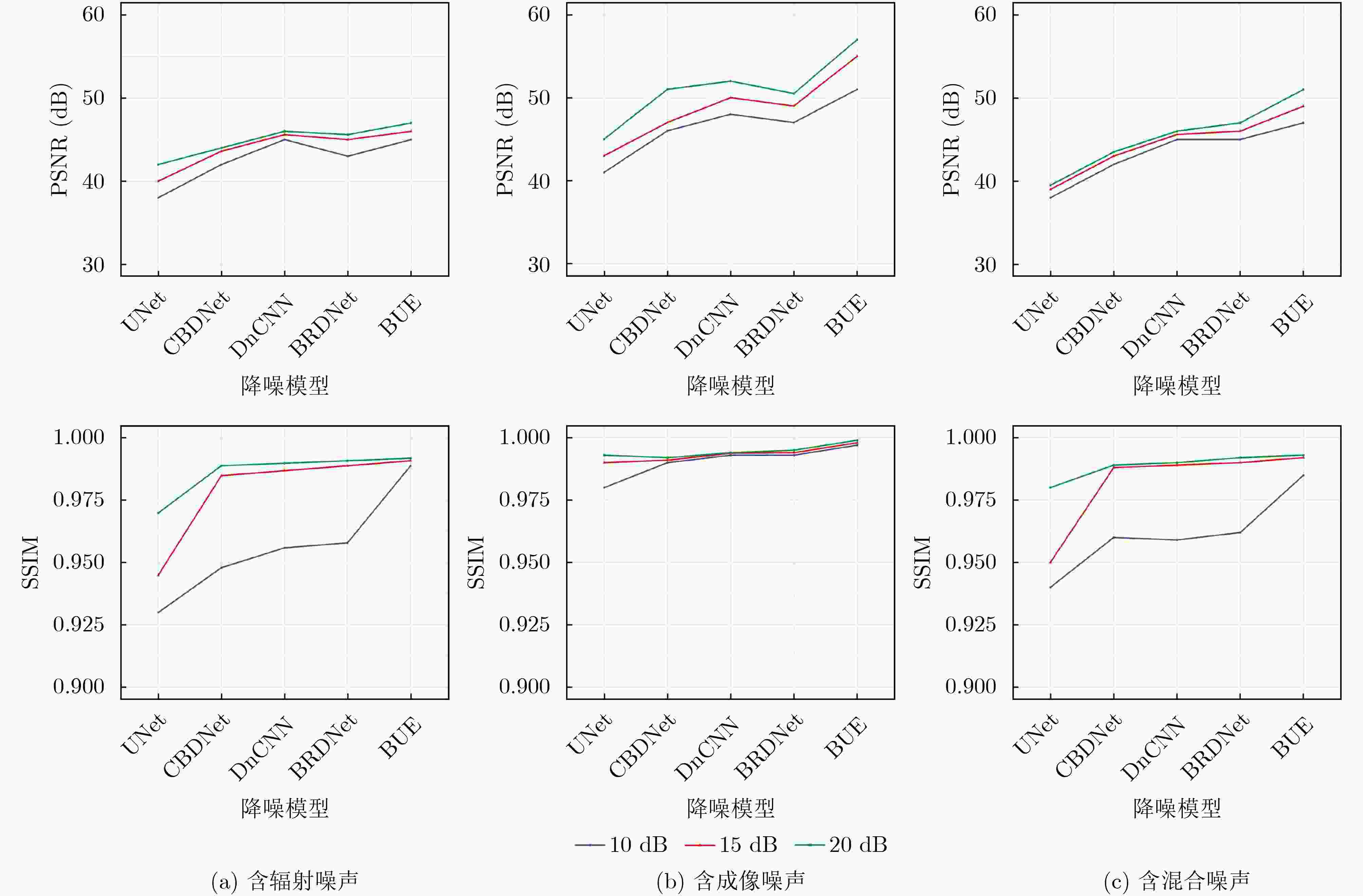
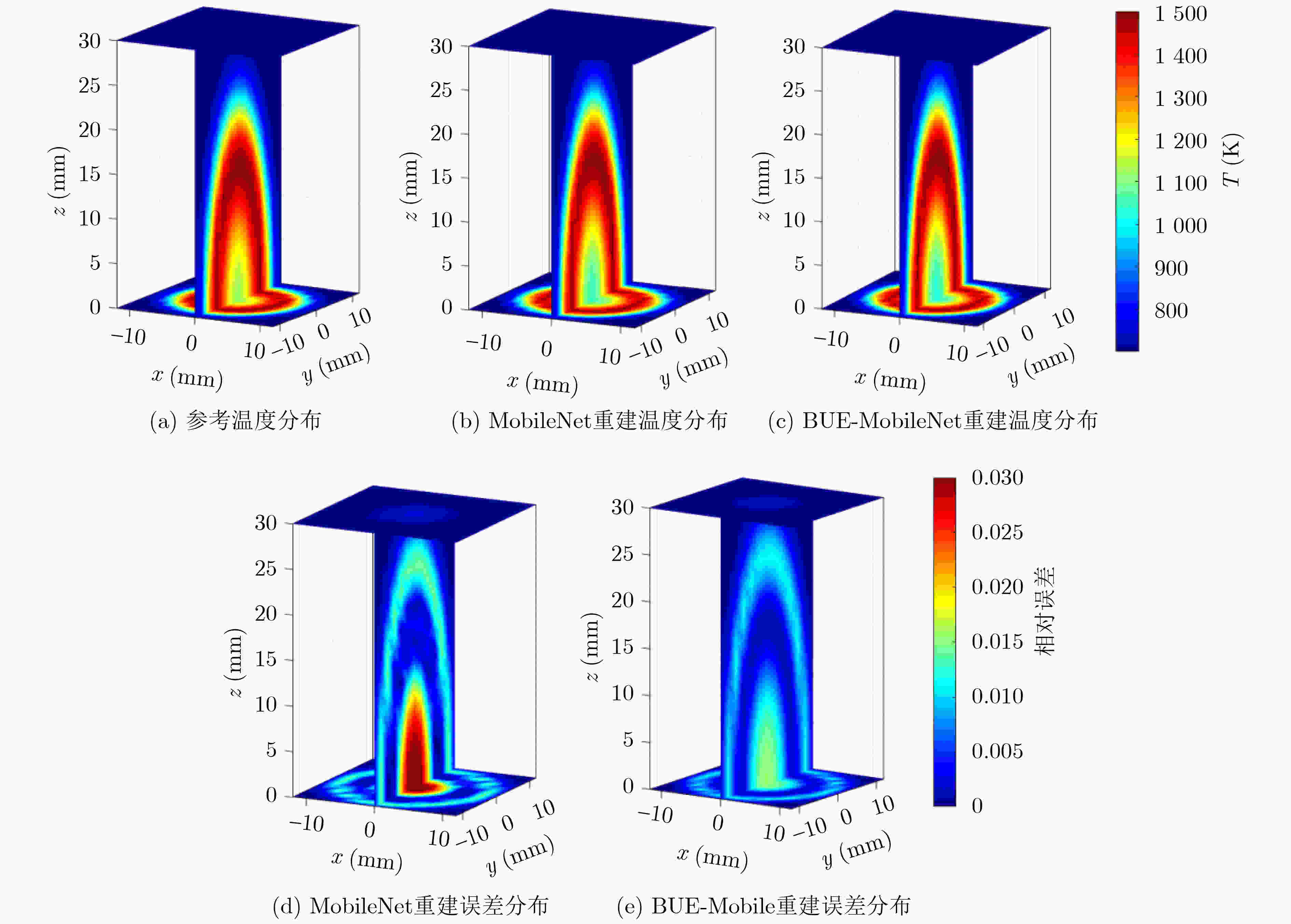
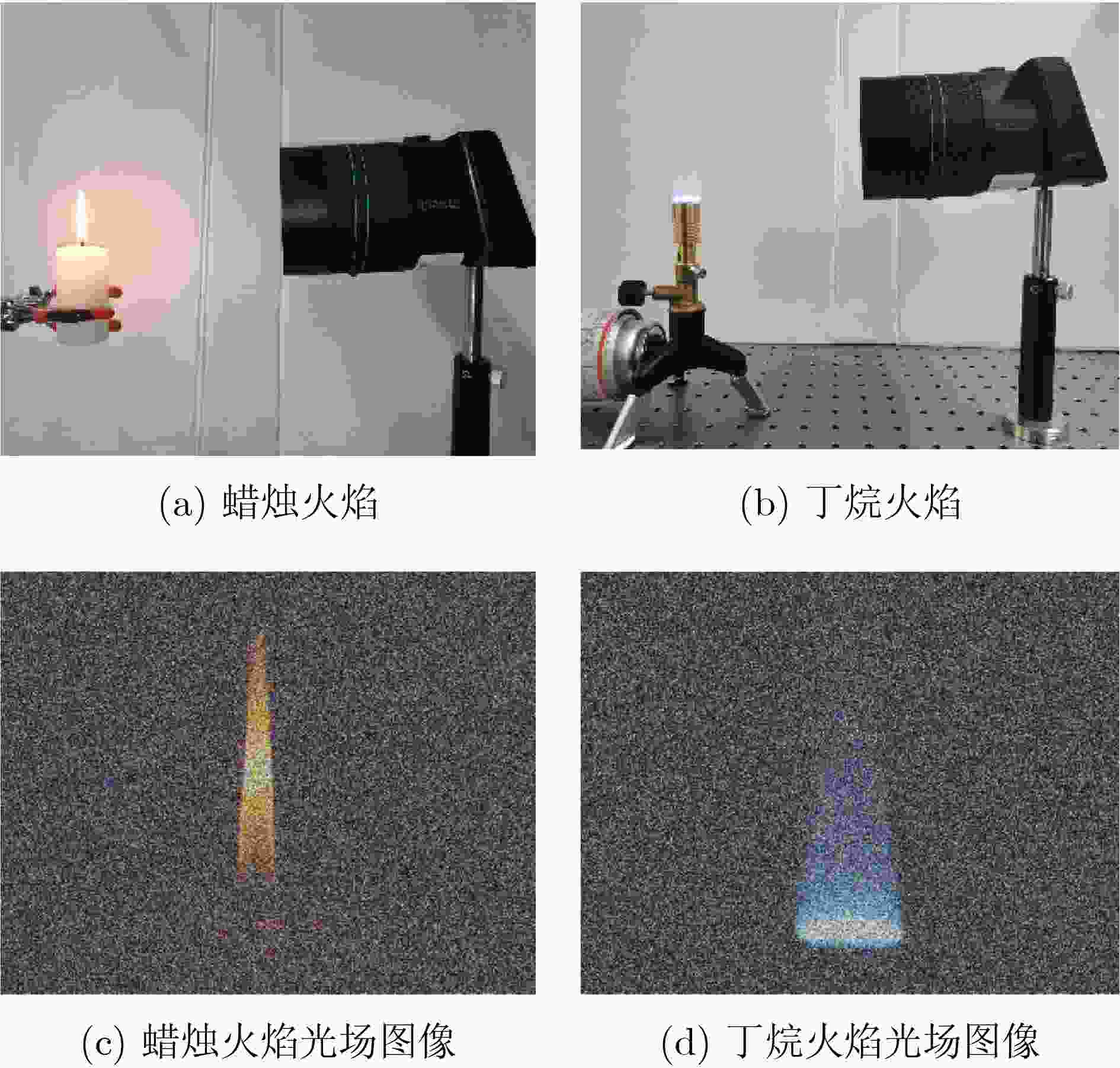
0.9931 ,与其他降噪模型相比有明显优势。随后,将火焰光场图像先经该文降噪模型降噪,再进行温度场重建,测得重建平均相对误差比未降噪时降低了约37%~57%,明显提升了火焰温度场3维重建的精度。实验部分,获取真实蜡烛火焰和丁烷火焰光场图像,经该文降噪模型降噪后的蜡烛火焰图像SSIM高达0.9870 ,降噪后的丁烷燃烧火焰图像SSIM为0.9808 。Abstract:Objective This study establishes the nonlinear relationship between flame light field images and the 3D temperature field using deep learning techniques, enabling rapid 3D reconstruction of the flame temperature field. However, light-field images are prone to radiation and imaging noise during transmission and imaging, which significantly degrades image quality and reduces the accuracy of temperature field reconstruction. Therefore, denoising of flame light field images, with maximum preservation of texture and edge details, is critical for high-precision 3D reconstruction. Deep learning-based denoising algorithms are capable of accommodating a broad range of noise distributions and are particularly effective in enhancing texture and contour information without requiring extensive prior knowledge. Given the complexity of noise in flame light field images, deep learning methods present an optimal solution for denoising. Methods This paper presents a denoising model based on an improved UNet network, designed to address radiation and imaging noise, as well as the texture information in complex flame images. The model reduces noise and optimizes the flame light field image through three modules: the background purification module, the UNet denoising module, and the edge optimization module. Feature extraction is performed on the image background layer using dense convolution operations, with a focus on purifying the radiated noise embedded in the background. The symmetrical encoder-decoder network structure and skip connections in the UNet module help to reduce both radiation noise between channels and imaging noise on the surface. The edge optimization module is tailored to extract detailed information from the image, aiming to enhance the quality of the flame light field images. Comparative and ablation experiments confirm the superior noise reduction performance and effectiveness of the proposed modules. Results and Discussions In the numerical simulation, radiation noise and imaging noise are added to the flame light field image, generating three types of datasets: single radiation noise, single imaging noise, and mixed noise. In the denoising experiment, the BUE denoising model is compared with UNet, CBDNet, DnCNN, and BRDNet. The denoising results ( Fig. 4 ) show that the PSNR and SSIM values of our BUE model exceed those of the other models, reaching 47 dB and0.9931 , respectively. Analysis of the four denoised texture images (Fig. 5 ) demonstrates that the BUE model effectively removes background noise while preserving internal details, such as texture and contour features. Ablation experiments are also conducted by adding the BPM and EIEM modules to the UNet benchmark model. The experimental results (Fig. 5 ,Fig. 6 ) confirm the effectiveness of the BPM and EIEM modules. Subsequently, the flame light field image is denoised using the proposed model, followed by reconstruction of the temperature field (Fig. 8 ). The average relative error of the reconstruction is reduced by approximately 37% to 57% compared to the non-denoised case, significantly improving the accuracy of the 3D flame temperature field reconstruction. In the real-world experiment, light field images of a candle flame and a butane flame are obtained. The SSIM values after denoising using the BUE model are0.9870 and0.9808 , respectively.Conclusions This paper presents a BUE denoising method based on the UNet model, incorporating a background purification module and an edge information enhancement module. This approach effectively extracts the background, reduces noise, and enhances contour and texture details in noisy flame light field images. The noise reduction performance of the model is evaluated through numerical simulations, and the results demonstrate the following: (1) Compared to UNet, CBDNet, DnCNN, and BRDNet, the proposed BUE denoising model shows significant advantages. Under mixed noise conditions with a signal-to-noise ratio of 10 dB, the model achieves a PSNR of 47 dB and an SSIM of 0.9931. Specifically, the PSNR improves by approximately 23.68% compared to UNet and 4.44% compared to DnCNN. (2) By integrating BUE as a denoising preprocessing module into the temperature field reconstruction model, the results show that incorporating denoising reduces the average relative error by approximately 37% to 57% compared to reconstruction without denoising. (3) Real candle flame and butane flame light field images are acquired, and the proposed noise reduction model achieves SSIM values of 0.9870 for the candle flame image and0.9808 for the butane flame image after denoising. -
表 1 合成数据集
数据集类型 噪声描述(dB) 数量 无噪图像 无 800 单辐射噪声图像 辐射噪声($ \eta_{\text{rad}} $=10, 15, 20) 800 单成像噪声图像 成像噪声 ($ \eta_{\text{img}} $=10, 15, 20) 800 混合噪声图像 等量辐射噪声和成像噪声($ \eta_{\text{rad}} $=$ \eta_{\text{img}} $=10, 15, 20) 800 表 2 MobileNet和BUE-MobileNet 重建火焰温度场的MRE和SSIM结果
噪声 $ \eta $(dB) MobileNet
(MRE(%)/SSIM)BUE-MobileNet
(MRE(%)/SSIM)辐射噪声 15 0.35/ 0.9990 0.16/0.999 7 成像噪声 15 0.33/ 0.9990 0.14/0.999 8 混合噪声 15 0.45/ 0.9943 0.28/0.998 5 -
[1] 张小雪, 王雨, 吴思远, 等. 基于级联稀疏查询机制的轻量化火灾检测算法[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(10): 230216. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230216.ZHANG Xiaoxue, WANG Yu, WU Siyuan, et al. An improved lightweight fire detection algorithm based on cascade sparse query[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2023, 50(10): 230216. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230216. [2] 王佳. 钙钛矿单探测器光谱测量方法及火焰温度探测研究[D]. [博士论文], 中北大学, 2023. doi: 10.27470/d.cnki.ghbgc.2023.000030.WANG Jia. Research on perovskite single detector spectrumeter for flame temperature detection[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], North University of China, 2023. doi: 10.27470/d.cnki.ghbgc.2023.000030. [3] 钟越, 蔡敏男, 徐文江, 等. 基于深度学习的湍流火焰三维羟基浓度场的时间超分辨率成像[J]. 航空动力学报, 2024, 39(12): 20230071. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20230071.ZHONG Yue, CAI Minnan, XU Wenjiang, et al. Temporal super-resolution imaging of 3D OH concentration field in turbulent flame based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2024, 39(12): 20230071. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20230071. [4] 张杰. 基于光场成像的火焰三维温度场测量方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 东南大学, 2018.ZHANG Jie. Three-dimensional temperature measurement of flame based on light field imaging[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Southeast University, 2018. doi: 10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2021.004361. [5] 张杰. 基于深度学习和光场成像的火焰三维温度场重建[D]. [硕士论文], 东南大学, 2021.ZHANG Jie. Rapid reconstruction of 3D flame temperature distribution based on deep learning and light field imaging[D]. [Master dissertation], Southeast University, 2021. doi: 10.27014/d.cnki.gdnau.2021.004361. [6] 孙安泰. 基于深度学习的火焰三维温度场层析重建及预测研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.003583.SUN Antai. Tomography reconstruction and prediction of three-dimensional temperature field of flame based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.003583. [7] TIAN Chunwei, FEI Lunke, ZHENG Wenxian, et al. Deep learning on image denoising: An overview[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 131: 251–275. doi: 10.1016/j.neUNet.2020.07.025. [8] CAI Minnan, LUO Weiyi, XU Wenjiang, et al. Development of learning-based noise reduction and image reconstruction algorithm in two dimensional Rayleigh thermometry[J]. Optik, 2021, 248: 168082. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168082. [9] 邓安东. 基于深度学习的火焰温度场重建及火焰图像降噪方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 上海交通大学, 2021. doi: 10.27307/d.cnki.gsjtu.2021.000774.DENG Andong. Research on temperature field reconstruction and image denoising of flame based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2021. doi: 10.27307/d.cnki.gsjtu.2021.000774. [10] NIU Zhitian, QI Hong, SHI Jingwen, et al. Three-dimensional rapid visualization of flame temperature field via compression and noise reduction of light field imaging[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 137: 106270. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2022.106270. [11] 李晓欢, 王霞, 王丛赫, 等. 基于残差UNet的水下Mueller矩阵图像去散射算法[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(24): 2410001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2410001.LI Xiaohuan, WANG Xia, WANG Conghe, et al. De-scattering algorithm for underwater mueller matrix images based on residual UNet[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(24): 2410001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2410001. [12] 李潇凡, 王胜强, 翁轩, 等. 基于UNet深度学习算法的东海大型漂浮藻类遥感监测[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(2): 0201002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0201002.LI Xiaofan, WANG Shengqiang, WENG Xuan, et al. Remote sensing of floating macroalgae blooms in the East China Sea based on UNet deep learning model[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(2): 0201002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0201002. [13] ZHANG Yulun, TIAN Yapeng, KONG Yu, et al. Residual dense network for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(7): 2480–2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2968521. [14] THECKEDATH D and SEDAMKAR R R. Detecting affect states using VGG16, ResNet50 and SE-ResNet50 networks[J]. SN Computer Science, 2020, 1(2): 79. doi: 10.1007/s42979-020-0114-9. [15] 寇旗旗, 程志威, 程德强, 等. 基于蓝图分离卷积的轻量化矿井图像超分辨率重建方法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(9): 4038–4050. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.1101.KOU Qiqi, CHENG Zhiwei, CHENG Deqiang, et al. Lightweight super resolution method based on blueprint separable convolution for mine image[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(9): 4038–4050. doi: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.1101. [16] 冯宇旭, 李裕梅. 深度学习优化器方法及学习率衰减方式综述[J]. 数据挖掘, 2018, 8(4): 186–200. doi: 10.12677/HJDM.2018.84020.FENG Yuxu and LI Yumei. An overview of deep learning optimization methods and learning rate attenuation methods[J]. Hans Journal of Data Mining, 2018, 8(4): 186–200. doi: 10.12677/HJDM.2018.84020. [17] LIU Jiaming, SUN Yu, XU Xiaojian, et al. Image restoration using total variation regularized deep image prior[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 2019: 7715–7719. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8682856. [18] 周成, 黄贺艳, 刘兵, 等. 基于混合散斑图的压缩计算鬼成像方法研究[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(9): 0911001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0911001.ZHOU Cheng, HUANG Heyan, LIU Bing, et al. Hybrid speckle-pattern compressive computational ghost imaging[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(9): 0911001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0911001. [19] 孙俊, 许传龙, 张彪, 等. 多焦距微透镜阵列光场成像火焰三维温度场测量[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2017, 38(10): 2164–2170.SUN Jun, XU Chuanlong, ZHANG Biao, et al. Three-dimensional temperature measurement of the flame using the light field camera with a multiple focus microlens array[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2017, 38(10): 2164–2170. [20] 龙超, 金恒, 黎玲, 等. 基于特征融合的非局部均值CT图像降噪[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1134024. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1134024.LONG Chao, JIN Heng, LI Ling, et al. CT Image denoising with non-local means based on feature fusion[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 1134024. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1134024. [21] SARA U, AKTER M, and UDDIN M S. Image quality assessment through FSIM, SSIM, MSE and PSNR—a comparative study[J]. Journal of Computer and Communications, 2019, 7(3): 8–18. doi: 10.4236/jcc.2019.73002. [22] GUO Shi, YAN Zifei, ZHANG Kai, et al. Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1712–1722. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00181. [23] MURALI V and SUDEEP P V. Image denoising using DnCNN: An exploration study[M]. JAYAKUMARI J, KARAGIANNIDIS G K, MA Maode, et al. Advances in Communication Systems and Networks: Select Proceedings of ComNet 2019. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 847–859. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3992-3_72. [24] TIAN Chunwei, XU Yong, and ZUO Wangmeng. Image denoising using deep CNN with batch renormalization[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 121: 461–473. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.08.022. [25] WEISS K, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M, and WANG Dingding. A survey of transfer learning[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2016, 3(1): 9. doi: 10.1186/s40537-016-0043-6. [26] SINHA D and EL-SHARKAWY M. Thin mobilenet: An enhanced mobilenet architecture[C]. The 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference, New York, USA, 2019: 280–285. doi: 10.1109/UEMCON47517.2019.8993089. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
