Distributionally Robust Task Offloading for Low-Altitude Intelligent Networks
-
摘要: 作为新质生产力的低空智联网(LAIN),主要由低空各类飞行器组成,可辅助实现空基多接入边缘计算(MEC)功能,能够有效应对实时数据处理和超低时延通信的挑战。考虑到任务的数据量大小具有随机性,该文聚焦研究基于LAIN的MEC网络中任务的卸载决策问题,以优化最差情况下的系统时延,保障服务的鲁棒性。首先,为刻画任务量的不确定性,利用历史数据构建基于概率距离度量的不确定集合,并建模了相应的分布鲁棒优化问题,以最小化最差任务大小概率分布情况下的系统时延。然后,为求解该最小化最大混合整数规划问题,将问题分解为嵌套的内层问题和外层问题,并基于分支定界法和二进制鲸鱼算法机制,设计了一种基于不确定任务大小的分布式鲁棒任务卸载优化算法(DRTOOA)。最后,通过仿真验证,结果表明所提DRTOOA能够优化系统时延,且具有较高的求解效率。Abstract:
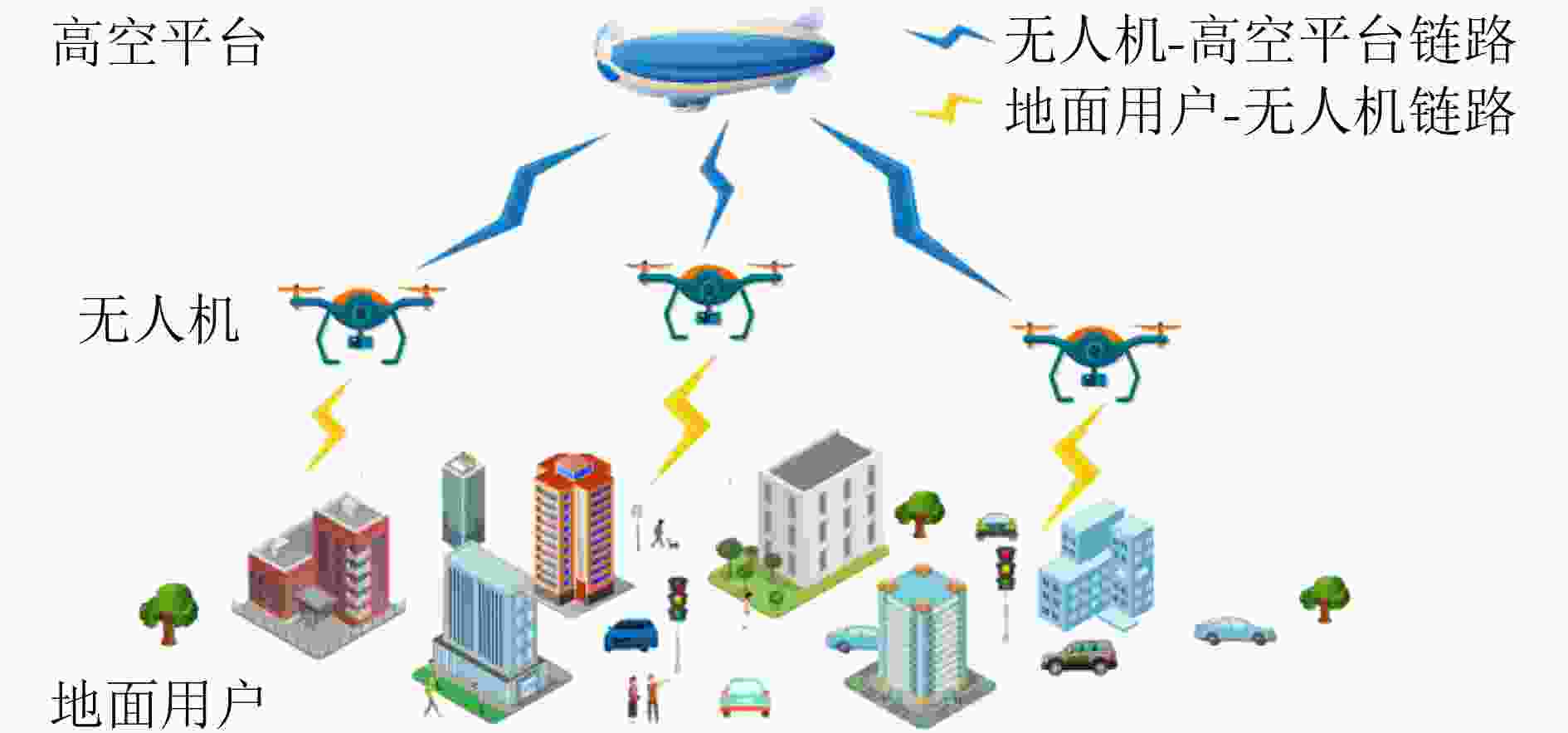
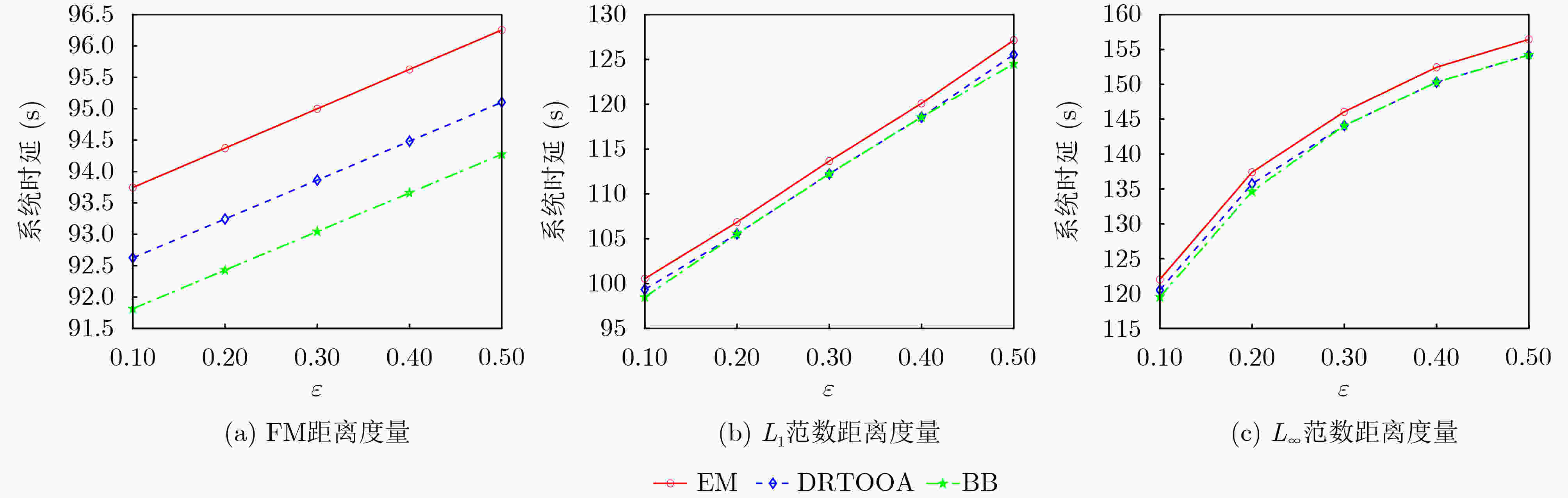
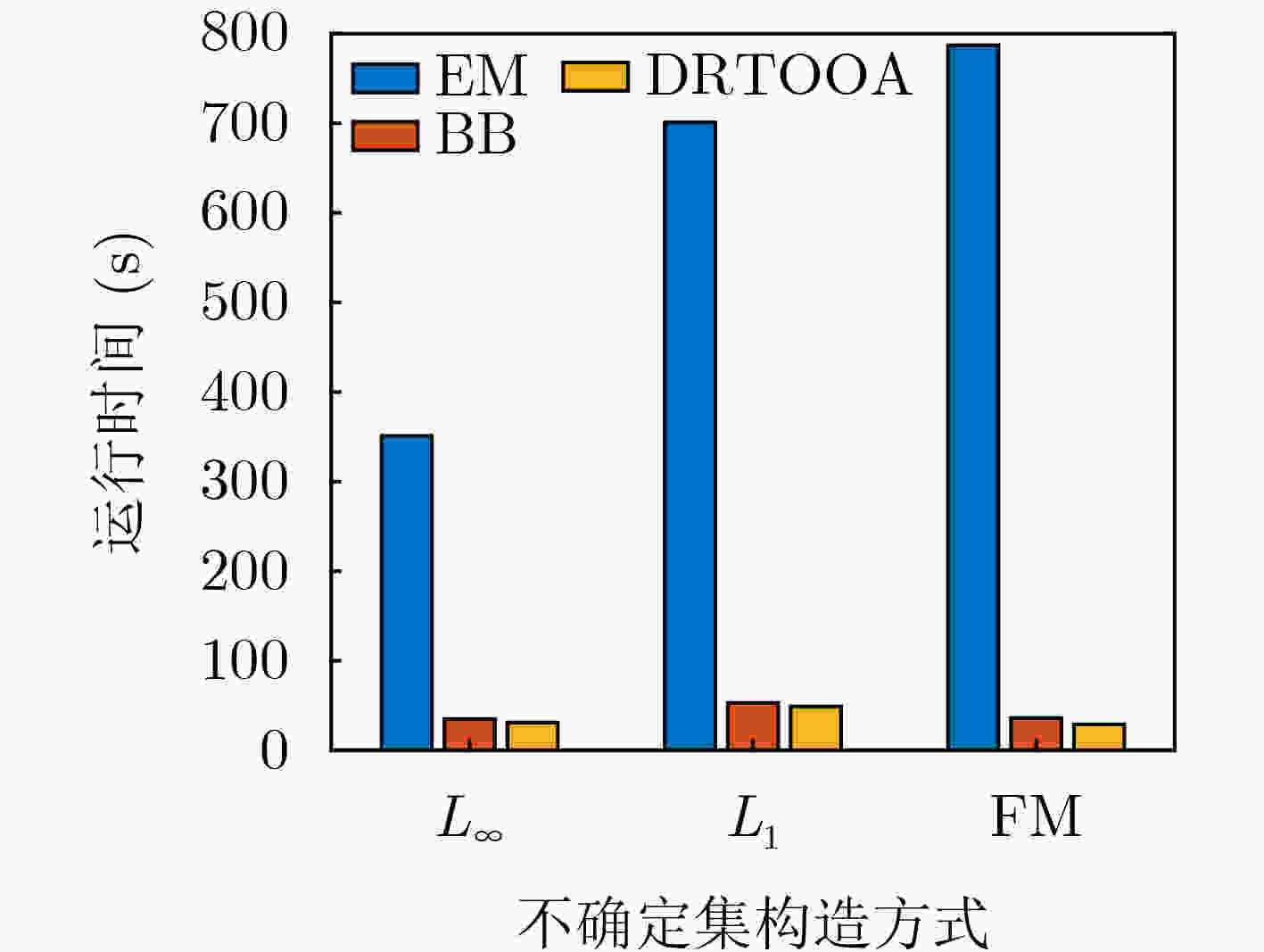
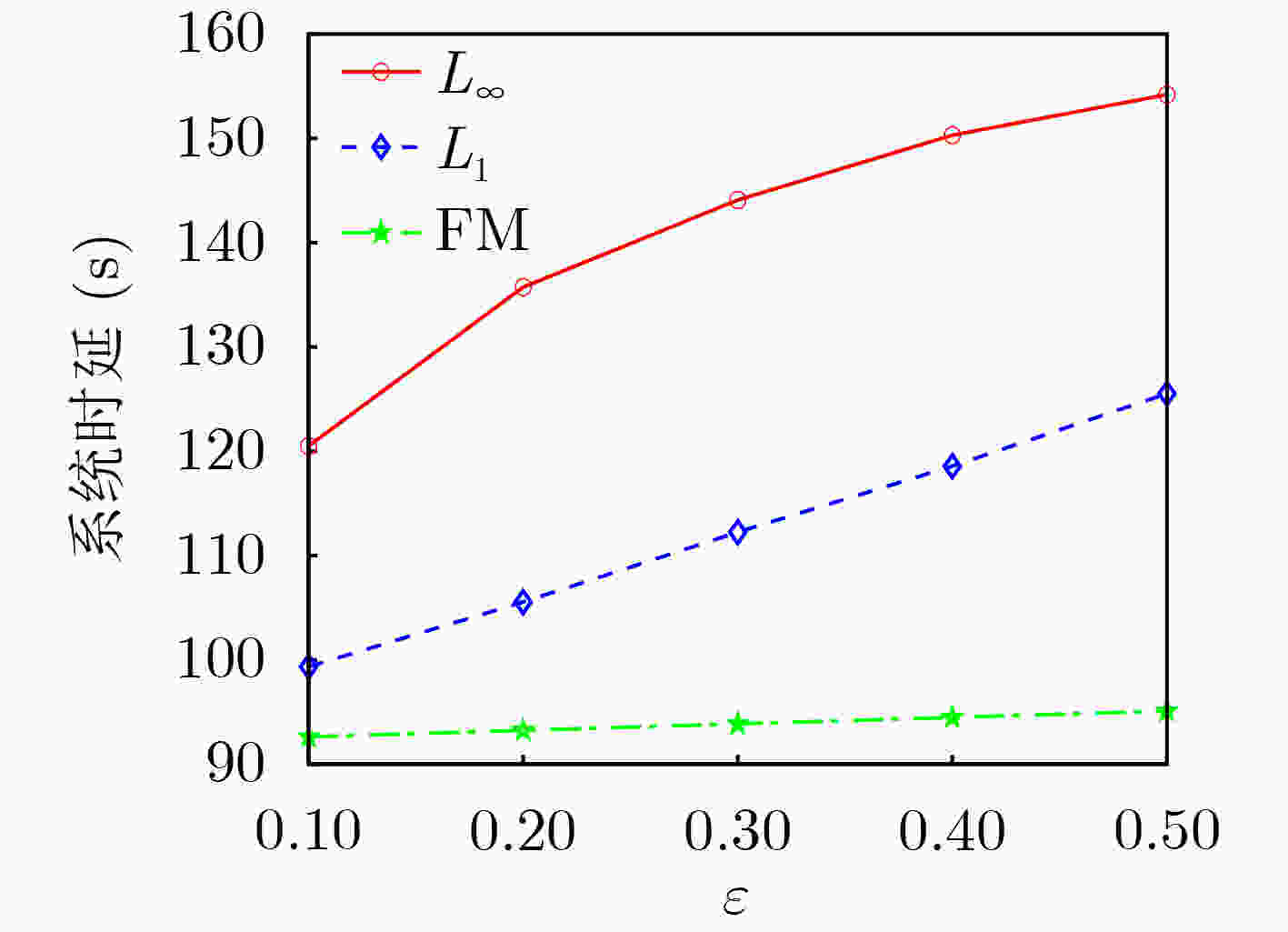
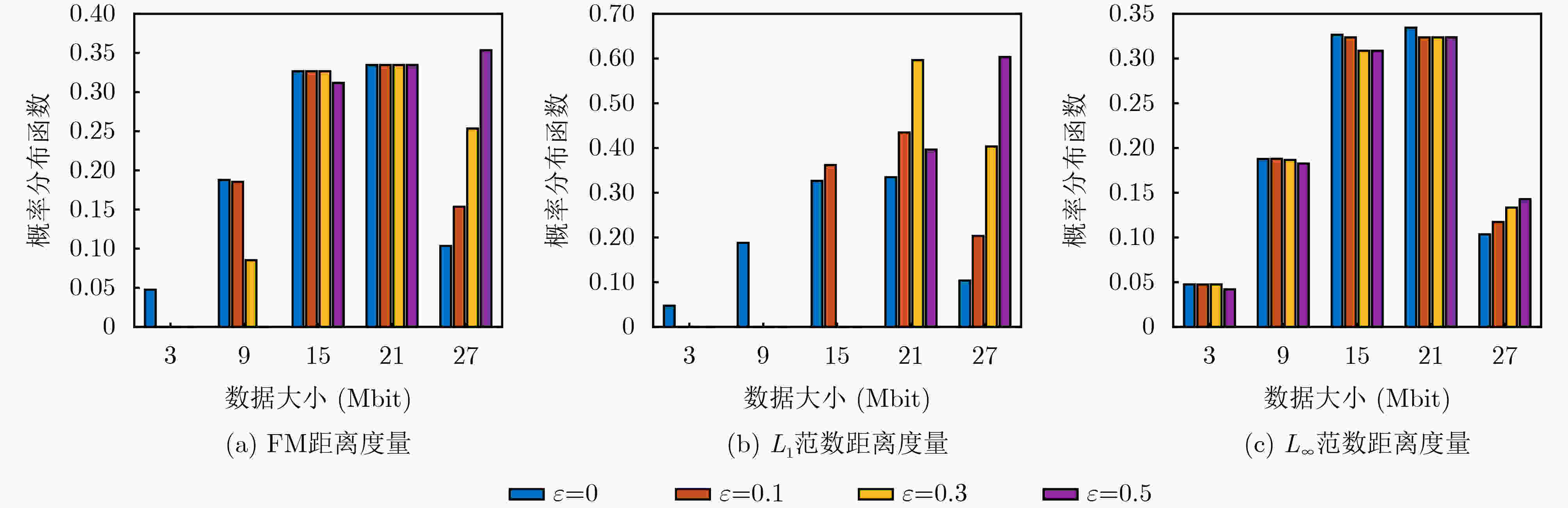
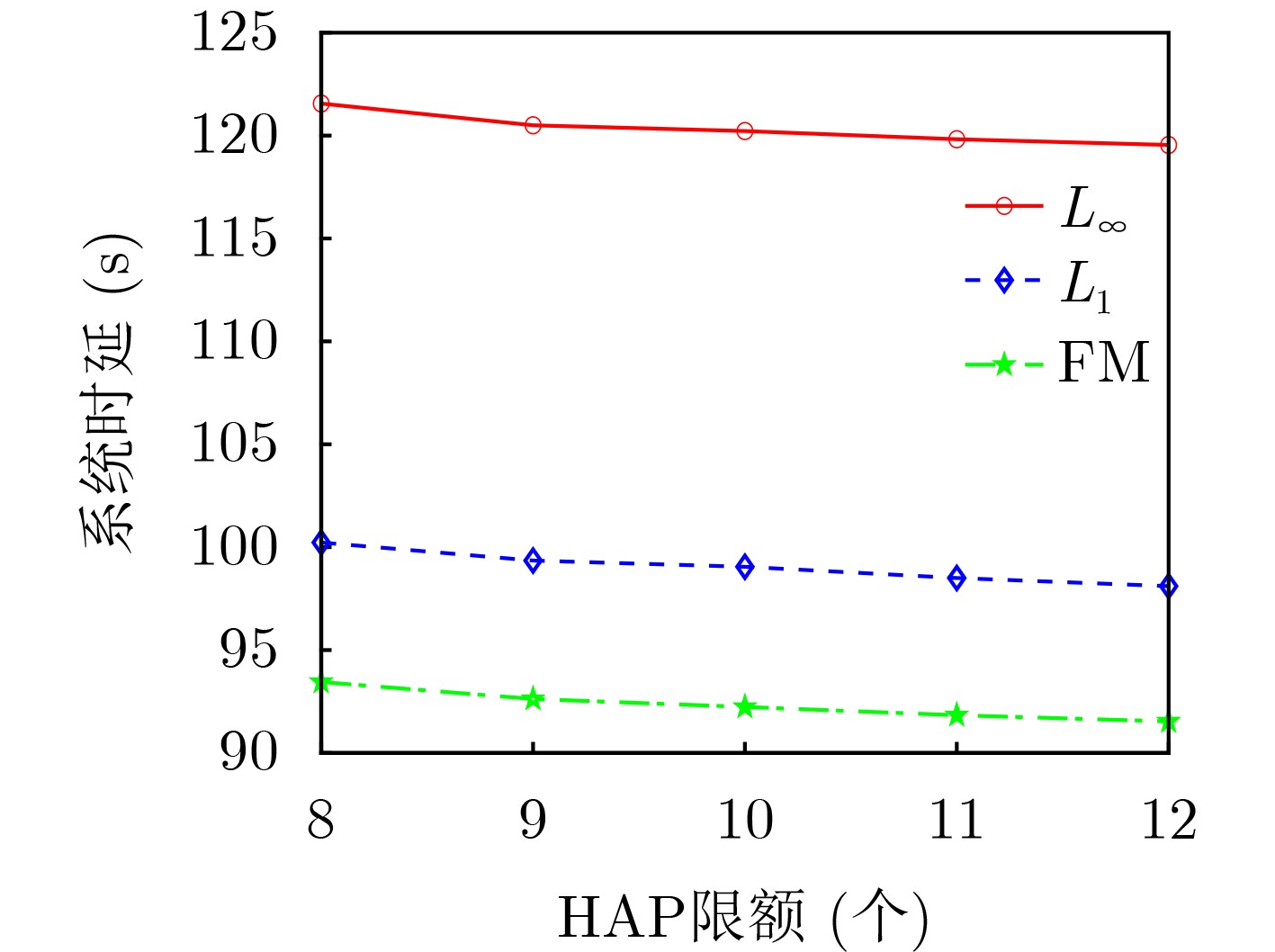
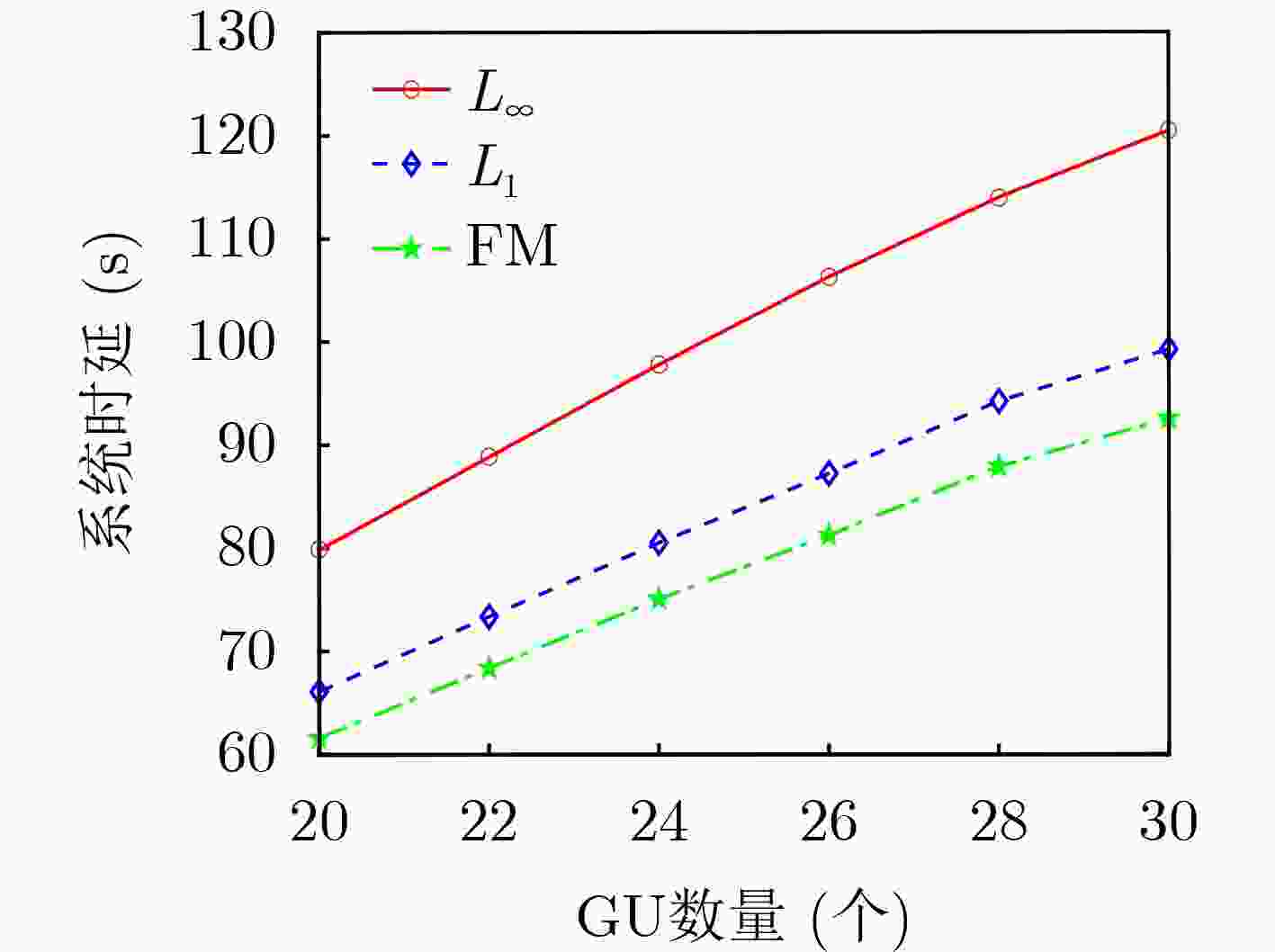
Objective The rapid development of Low-Altitude Intelligent Networks (LAINs) and the widespread adoption of Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC) have introduced challenges related to the random variability in task data sizes, which constrains the efficiency of LAIN-assisted MEC networks. Although task offloading has been extensively studied, most existing research overlooks the uncertainty in task sizes. This randomness can lead to unexpected outages and inefficient resource utilization, making it difficult to meet quality-of-service requirements. Distributionally Robust Optimization (DRO) based on uncertainty sets is a promising approach to addressing these challenges. By formulating and solving a DRO problem that accounts for task uncertainties, this study provides a robust and conservative solution applicable to various LAIN-related scenarios. Methods This study proposes an LAIN-assisted MEC network comprising multiple hovering Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), a High-Altitude Platform (HAP), and Ground Users (GUs). To accurately model task size randomness, three probabilistic distance metrics—L1, L∞ and Fortet-Mourier (FM)—are introduced to construct uncertainty sets based on historical data. A DRO problem is then formulated using these uncertainty sets to optimize task offloading decisions within the proposed network. The objective is to minimize system latency under the worst-case probability distribution of task sizes, thereby enhancing system robustness. The proposed DRO problem, structured as a minimization-maximization mixed-integer programming model, is solved iteratively through decomposition into an inner and an outer problem. The inner problem, a linear programming problem, is addressed using standard solvers such as GUROBI. For the outer problem, the low-complexity Branch and Bound (BB) method is employed to solve the integer programming component efficiently by systematically exploring subsets of the solution space and pruning infeasible regions using upper and lower bounds. To handle large-scale and multi-constraint scenarios, a heuristic Binary Whale Optimization Algorithm (BWOA) is further integrated to accelerate convergence. Therefore, the Distributionally Robust Task Offloading Optimization Algorithm (DRTOOA) is developed by combining BB and BWOA. Initially, BB determines a subset of binary variables, followed by BWOA optimization for the remaining variables. This process is repeated iteratively until convergence is achieved. Results and Discussions The performance of the proposed DRTOOA is evaluated through numerical simulations. System latency is analyzed under three probabilistic distance metrics used for constructing uncertainty sets ( Fig. 3 ). As the tolerance of the uncertainty sets increases, system latency rises across all metrics. Notably, the latency achieved via DRTOOA is lower than that obtained using the Exhaustive Method (EM) but higher than that using the BB method, demonstrating its robustness against uncertainties. In terms of computational efficiency, DRTOOA outperforms other benchmark algorithms by achieving the shortest latency, highlighting its effectiveness in solving large-scale problems (Fig. 4 ). Among the three probabilistic distance metrics, the FM metric yields the lowest system latency with relatively stable performance as the tolerance changes (Fig. 5 ). Additionally, the impact of uncertainty set tolerance on the probability distribution of task sizes is examined (Fig. 6 ). As the tolerance decreases, the task size distribution aligns more closely with the reference distribution. Conversely, increasing the tolerance results in a higher probability of larger task sizes. Notably, optimization based on the FM probabilistic distance metric exhibits greater stability under varying tolerances. Furthermore, the impact of HAP quota limitations and the number of GUs on system latency are analyzed (Figs. 7 and8 ). System latency decreases as HAP quotas increase, indicating that additional HAP resources alleviate task processing pressure. Conversely, an increase in the number of GUs leads to higher system latency due to the greater computational demand. Overall, DRTOOA effectively optimizes system latency and demonstrates superior performance compared with other baseline algorithms in terms of robustness and computational efficiency.Conclusions This study addresses the task offloading problem in LAIN-assisted MEC networks, considering the uncertainty in task sizes. By constructing uncertainty sets based on different probabilistic distance metrics and formulating a DRO problem, the DRTOOA is proposed, effectively integrating the BB method with the BWOA. Simulation results demonstrate that: (1) Compared with the BB method and the EM, DRTOOA effectively reduces system latency, demonstrating higher efficiency in problem-solving. (2) Among the three probabilistic distance metrics—FM distance, L1 norm distance, and L∞ norm distance—the FM metric exhibits the most stability, yielding the lowest system latency under the same conditions. (3) System latency is influenced by factors such as the tolerance of uncertainty sets, HAP quota limitations, and the number of GUs. However, this study assumes static or quasi-static network nodes for simplification, limiting the consideration of UAV flexibility and dynamicity. Future research should explore the impact of UAV and HAP mobility, as well as real-world factors such as communication interference and equipment failures, on task offloading decisions and overall system performance. -
1 整体算法
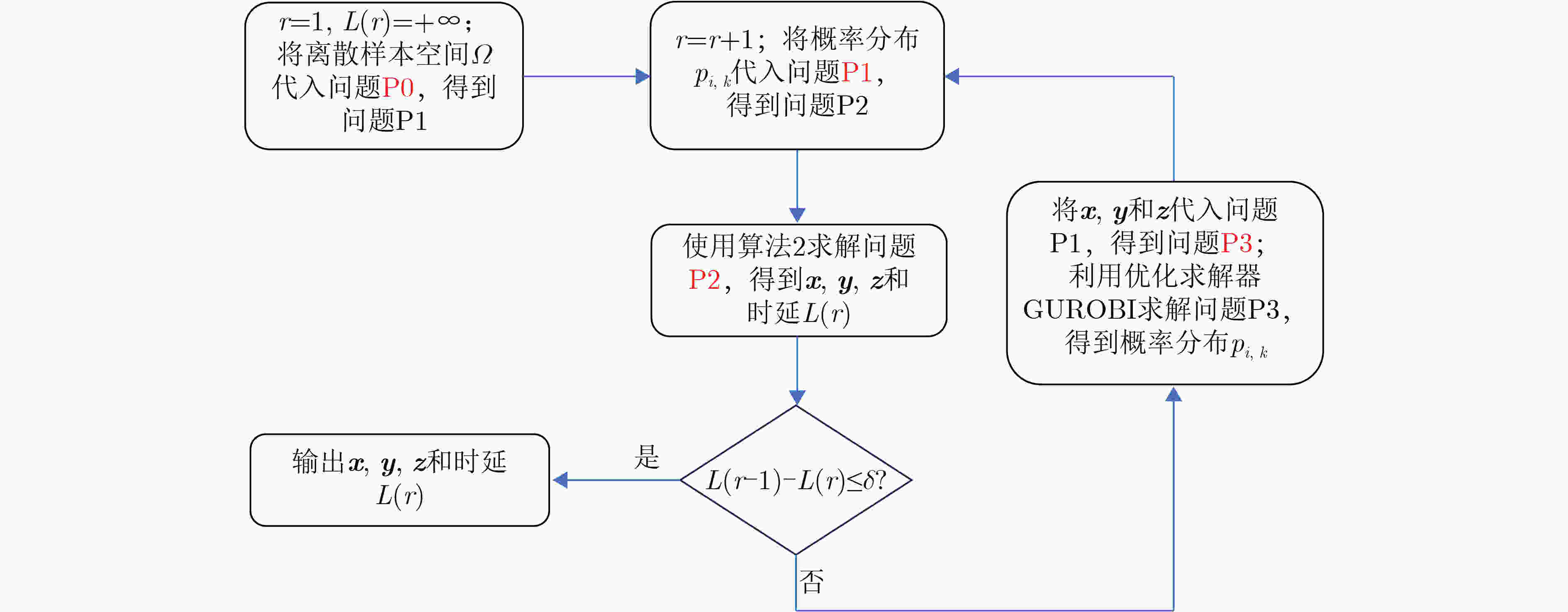
(1) 初始化参数:$ r = 1 $,$ L(r) = + \infty $; (2) 将参考分布$ \mathbb{P}_i^0 $赋值给最差分布$ {\mathbb{P}_i} $; (3) repeat (4) $ r = r + 1 $; (5) 将最差分布$ {\mathbb{P}_i} $带入问题$ {\text{P1}} $,得到问题$ {\text{P2}} $,利用算法2求解问题$ {\text{P2}} $,得到$ {\boldsymbol{x}} $, $ {\boldsymbol{y}} $, $ {\boldsymbol{z}} $和最小时延$ L(r) $; (6) 将$ {\boldsymbol{x}} $, $ {\boldsymbol{y}} $和$ {\boldsymbol{z}} $带入问题$ {\text{P1}} $,得到问题$ {\text{P3}} $,利用优化求解器GUROBI求解问题$ {\text{P3}} $,得到最差分布$ {\mathbb{P}_i} $; (7) until $ L(r - 1) - L(r) \le \delta $ 2 整数问题求解
(1) 将问题$ {\text{P2}} $的整数变量$ {\boldsymbol{x }}$, $ {\boldsymbol{y}} $和$ {\boldsymbol{z}} $松弛为0~1的连续变量$ {\boldsymbol{x}}' $, $ {\boldsymbol{y}}' $和$ {\boldsymbol{z}}' $,得到问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,利用问题求解器求解问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,得到0~1的连续值$ \hat {\boldsymbol{x}} $; (2) repeat (3) 在$ \hat {\boldsymbol{x}} $中选择第1个出现的非整数值作为分支变量$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* $; (4) 添加约束 $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* = {{\textit{0}}} $到问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,求解得到优化结果$ {\text{LAT0}} $; (5) 添加约束 $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* = {{\textit{1}}} $到问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,求解得到优化结果$ {\text{LAT1}} $; (6) if $ {\text{LAT0 < LAT1}} $ (7) $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* ={{\textit{0}}} $; (8) 添加约束 $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* = {{\textit{0}}} $到问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,并更新问题$ {\text{P2}}' $; (9) else (10) $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* = {{\textit{1}}} $; (11) 添加约束 $ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{}^* = {{\textit{1}}} $到问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,并更新问题$ {\text{P2}}' $; (12) endif (13) 利用优化求解器GUROBI求解问题$ {\text{P2}}' $,得到0~1的连续值$ \hat {\boldsymbol{x}} $; (14) until$ \hat {\boldsymbol{x }}$中全为整数 (15) $ {\boldsymbol{x}} = \hat {\boldsymbol{x}} $ ,将$ {\boldsymbol{x}} $代入问题$ {\text{P2}} $; (16) 初始化:鲸鱼数量,最大迭代次数,鲸鱼位置($ {\boldsymbol{y}} $和$ {\boldsymbol{z}} $取值); (17) 根据式(50)计算每只鲸鱼适应度值,选出最优鲸鱼的位置(最优$ {\boldsymbol{y}} $和$ {\boldsymbol{z}} $取值); (18) repeat (19) 更新鲸鱼位置 ; (20) 计算每只鲸鱼适应度值; (21) 更新最优鲸鱼的位置; (22) until达到收敛条件或最大迭代次数 -
[1] 樊邦奎, 李云, 张瑞雨. 浅析低空智联网与无人机产业应用[J]. 地理科学进展, 2021, 40(9): 1441–1450. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.09.001.FAN Bangkui, LI Yun, and ZHANG Ruiyu. Initial analysis of low-altitude internet of intelligences (IOI) and the applications of unmanned aerial vehicle industry[J]. Progress in Geography, 2021, 40(9): 1441–1450. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.09.001. [2] MOZAFFARI M, SAAD W, BENNIS M, et al. A tutorial on UAVs for wireless networks: Applications, challenges, and open problems[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(3): 2334–2360. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2902862. [3] 吴启晖, 董超, 贾子晔, 等. 低空智联网组网与控制理论方法[J]. 航空学报, 2024, 45(3): 028809. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28809.WU Qihui, DONG Chao, JIA Ziye, et al. Networking and control mechanism for low-altitude intelligent networks[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(3): 028809. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28809. [4] CHEN Shanzhi, LIANG Yingchang, SUN Shaohui, et al. Vision, requirements, and technology trend of 6G: How to tackle the challenges of system coverage, capacity, user data-rate and movement speed[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(2): 218–228. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900333. [5] AZARI M M, SOLANKI S, CHATZINOTAS S, et al. Evolution of non-terrestrial networks from 5G to 6G: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(4): 2633–2672. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3199901. [6] PREMSANKAR G, DI FRANCESCO M, and TALEB T. Edge computing for the internet of things: A case study[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(2): 1275–1284. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2805263. [7] JIA Ziye, YOU Jiahao, DONG Chao, et al. Cooperative cognitive dynamic system in UAV swarms: Reconfigurable mechanism and framework[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2024, 19(3): 90–101. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2024.3404391. [8] DONG Chao, ZHANG Yifan, JIA Ziye, et al. Three-dimension collision-free trajectory planning of UAVs based on ADS-B information in low-altitude urban airspace[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2025, 38: 103170. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2024.08.001. [9] 朱奕安, 何佳, 贾子晔, 等. 基于ADS-B与Remote ID的低空智联网无人机监视性能分析[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2025, 40(1): 27–44. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2025.01.003.ZHU Yian, HE Jia, JIA Ziye, et al. ADS-B and Remote ID based performance analysis for UAV surveillance in low-altitude intelligent networks[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2025, 40(1): 27–44. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2025.01.003. [10] JIA Ziye, SHENG Min, LI Jiandong, et al. LEO-satellite-assisted UAV: Joint trajectory and data collection for internet of remote things in 6G aerial access networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(12): 9814–9826. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3021255. [11] LU Zhuo, JIA Ziye, WU Qihui, et al. Joint trajectory planning and communication design for multiple UAVs in intelligent collaborative air-ground communication systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(19): 31053–31067. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3415076. [12] HOSSAIN M A, HOSSAIN A R, and ANSARI N. Numerology-capable UAV-MEC for future generation massive IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(23): 23860–23868. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3189945. [13] WU Qihui, CHEN Jiaxin, XU Yuhua, et al. Joint computation offloading, role, and location selection in hierarchical multicoalition UAV MEC networks: A Stackelberg game learning approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(19): 18293–18304. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3158489. [14] CUI Can, JIA Ziye, DONG Chao, et al. Distributionally robust chance-constrained optimization for hierarchical UAV-based MEC[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2023 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Hoboken, USA, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOMWKSHPS57453.2023.10226027. [15] ALAM M S, KURT G K, YANIKOMEROGLU H, et al. High altitude platform station based super macro base station constellations[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(1): 103–109. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000542. [16] LIU Shasha, DAHROUJ H, and ALOUINI M S. Joint user association and beamforming in integrated satellite-HAPS-ground networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(4): 5162–5178. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3329168. [17] KURT G K, KHOSHKHOLGH M G, ALFATTANI S, et al. A vision and framework for the high altitude platform station (HAPS) networks of the future[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 729–779. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3066905. [18] JIANG Guanwang, JIA Ziye, HE Lijun, et al. Distributionally robust optimization for computation offloading in aerial access networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.02037, 2024. [19] CAO Huijuan, YU Genghua, and CHEN Zhigang. Cooperative task offloading and dispatching optimization for large-scale users via UAVs and HAP[C]. 2023 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Glasgow, United Kingdom, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC55385.2023.10118722. [20] JIA Ziye, WU Qihui, DONG Chao, et al. Hierarchical aerial computing for internet of things via cooperation of HAPs and UAVs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(7): 5676–5688. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3151639. [21] HE Yixin, NIE Laisen, GUO Tan, et al. A NOMA-enabled framework for relay deployment and network optimization in double-layer airborne access VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(11): 22452–22466. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3139888. [22] YE Neng, CHEN Lu, OUYANG Qiaolin, et al. Time-efficient data download for emergency UAV: Joint optimization of on-board computation and communication under energy constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(10): 13718–13722. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3276866. [23] HAMMOUTI H E, BENJILLALI M, SHIHADA B, et al. Learn-as-you-fly: A distributed algorithm for joint 3d placement and user association in multi-UAVs networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(12): 5831–5844. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2939315. [24] LI Liang, SHI Dian, HOU Ronghui, et al. Energy-efficient proactive caching for adaptive video streaming via data-driven optimization[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(6): 5549–5561. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2981250. [25] CHEN Yali, AI Bo, NIU Yong, et al. Energy-constrained computation offloading in space-air-ground integrated networks using distributionally robust optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(11): 12113–12125. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3116593. [26] LIBERTI L. Undecidability and hardness in mixed-integer nonlinear programming[J]. RAIRO-Operations Research, 2019, 53(1): 81–109. doi: 10.1051/ro/2018036. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
