Left Atrial Scar Segmentation Method Combining Cross-Modal Feature Excitation and Dual Branch Cross Attention Fusion
-
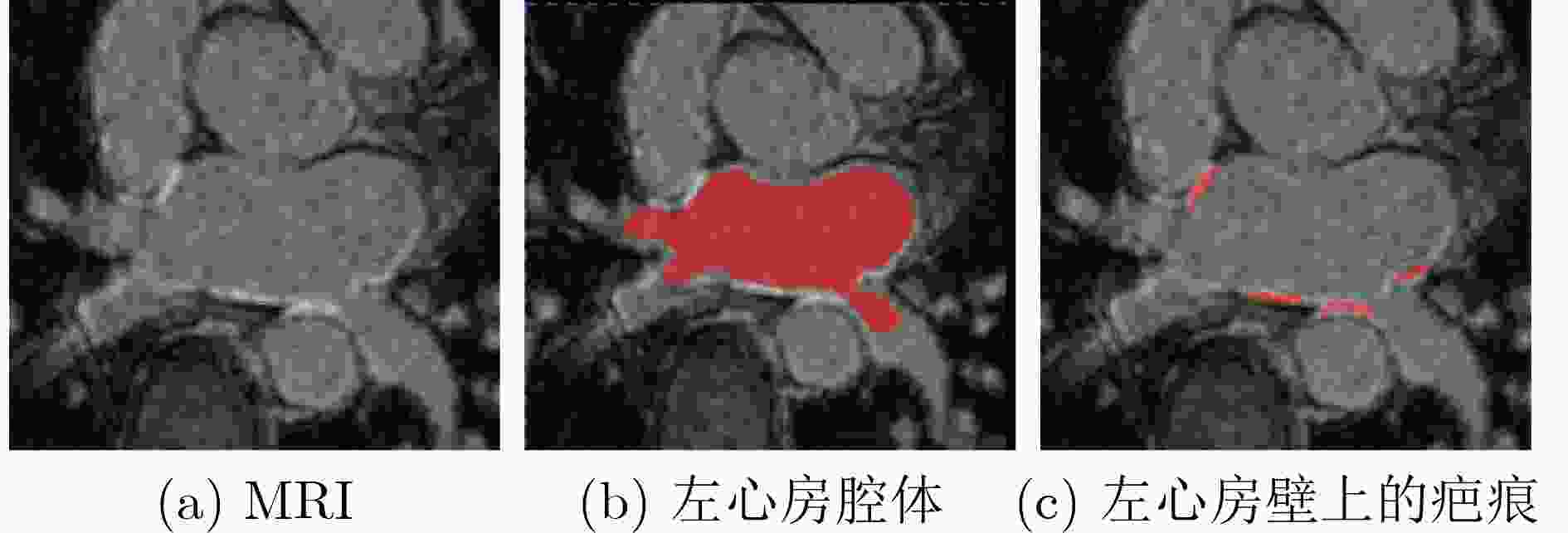
摘要: 左心房疤痕的分布情况与严重程度能够为房颤的生理病理学研究提供重要信息,因此,实现左心房疤痕的自动化分割对房颤的临床诊断与治疗有着重要意义。但由于左心房疤痕具有形状多样化、目标小、分布离散等特点,现有的左心房疤痕分割方法往往难以取得好的分割效果。该文利用疤痕通常分布在左心房壁上的先验知识,提出一种基于左心房边界特征增强的左心房疤痕分割方法,通过提出的跨模态特征激励模块与双分支交叉注意力融合模块在U型网络的编码器与瓶颈层分别对核磁共振图像与左心房边界符号距离图进行特征增强引导与深层语义信息融合增强,实现从特征层面提高模型对左心房边界特性信息的关注度。该文所提分割模型在LAScarQS2022数据集上进行验证,分割结果评估明显优于当前主流的分割方法。Dice分数和准确率相比基线网络分别提升了4.14%和6.37%。Abstract:
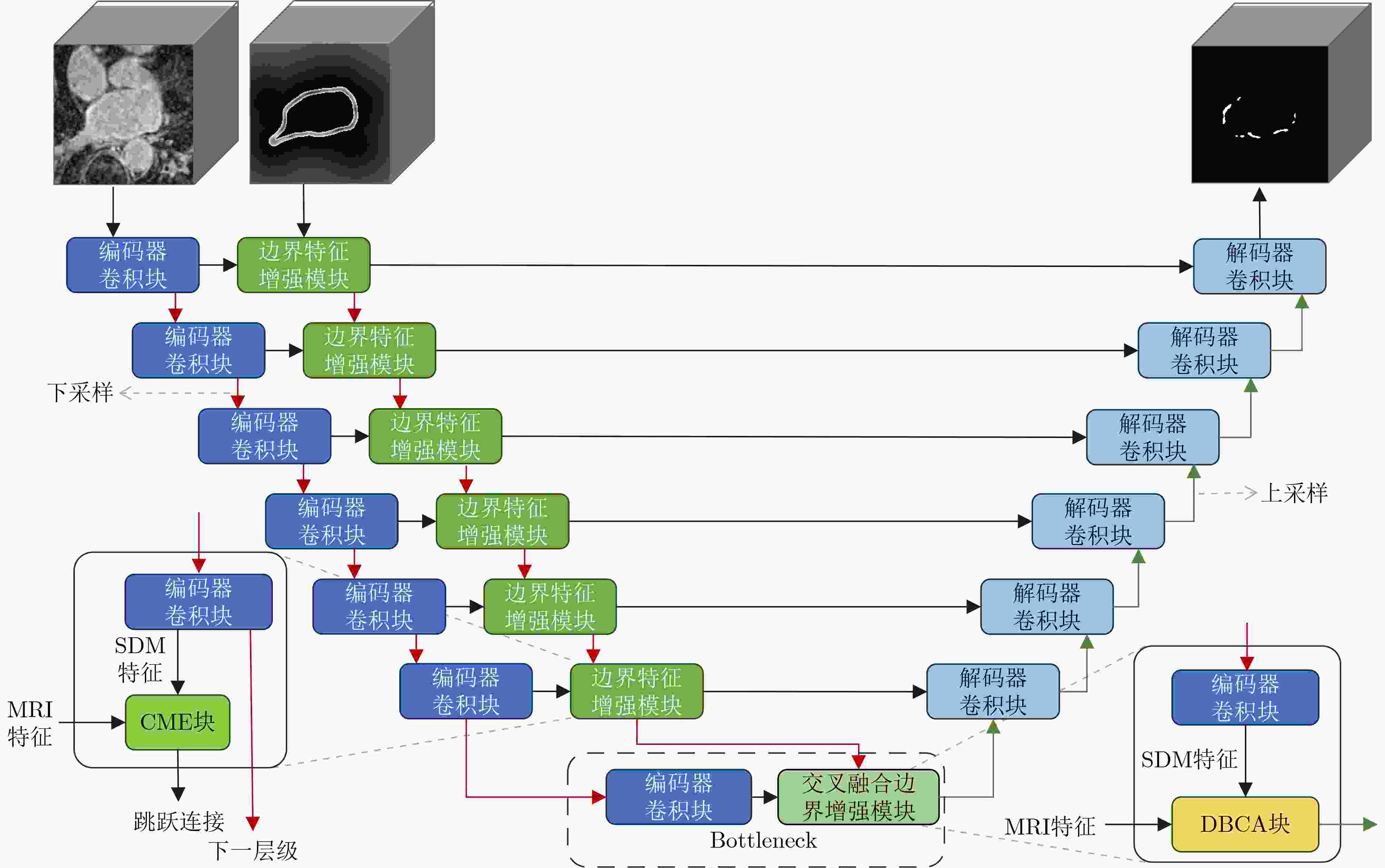
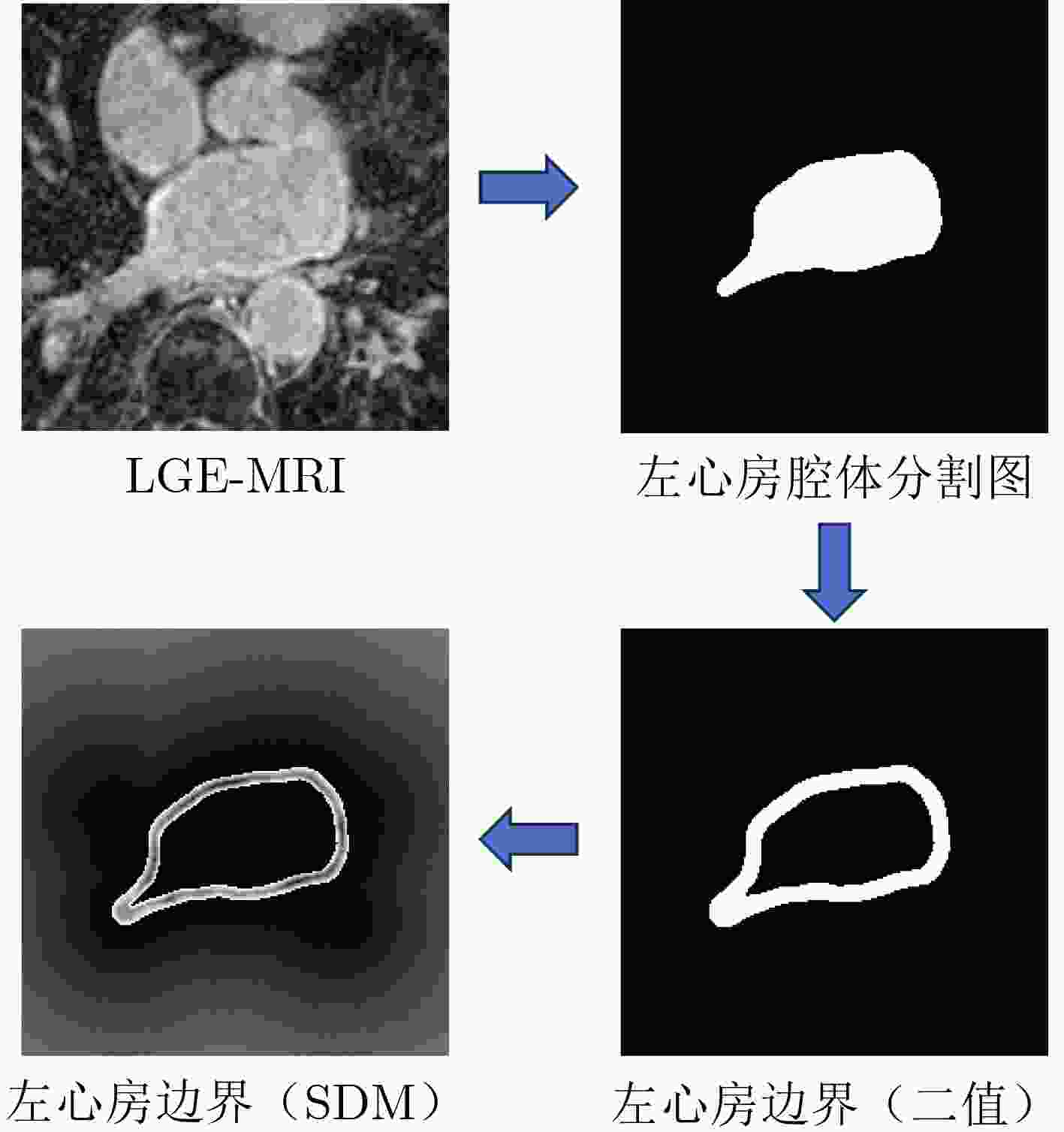
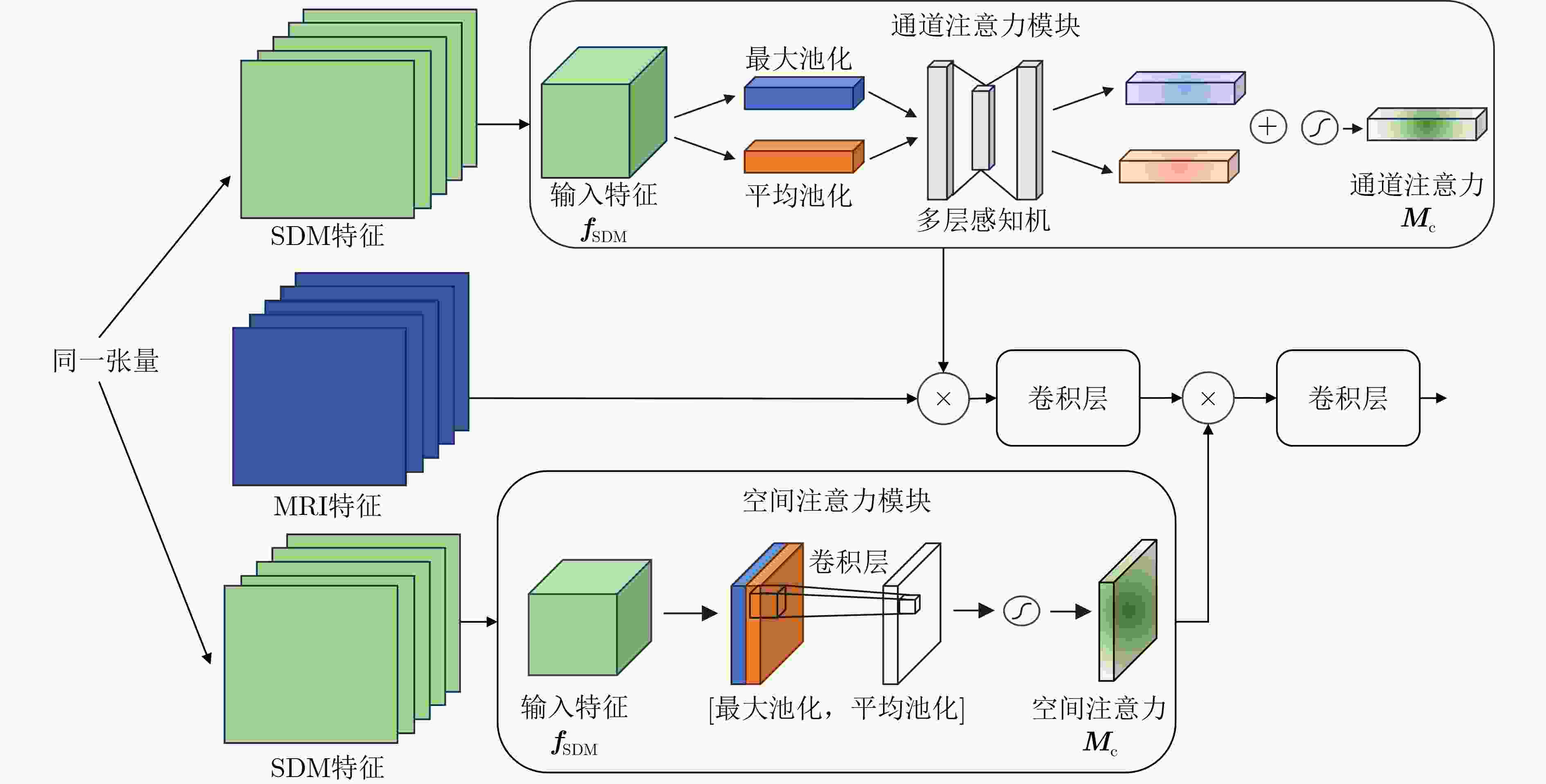
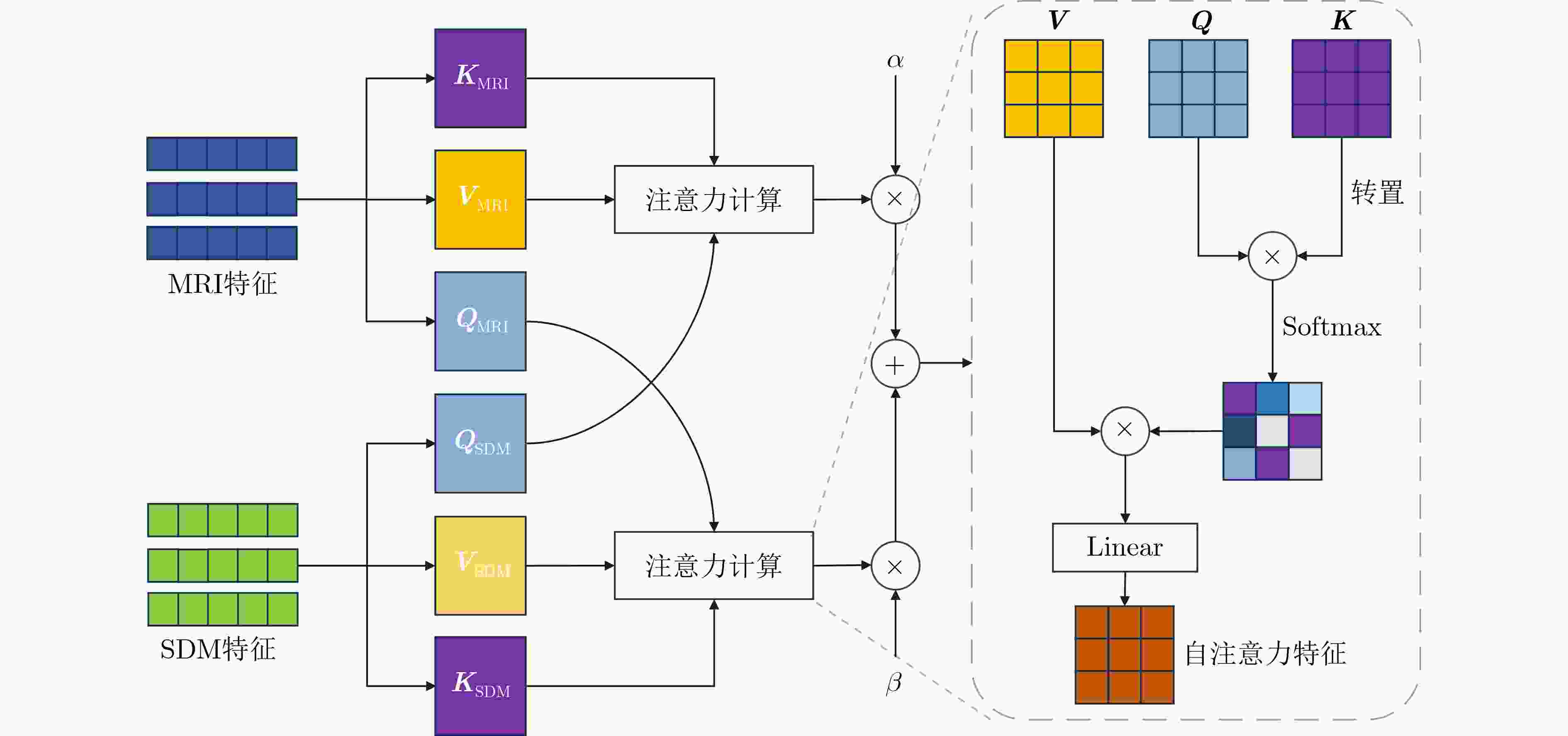
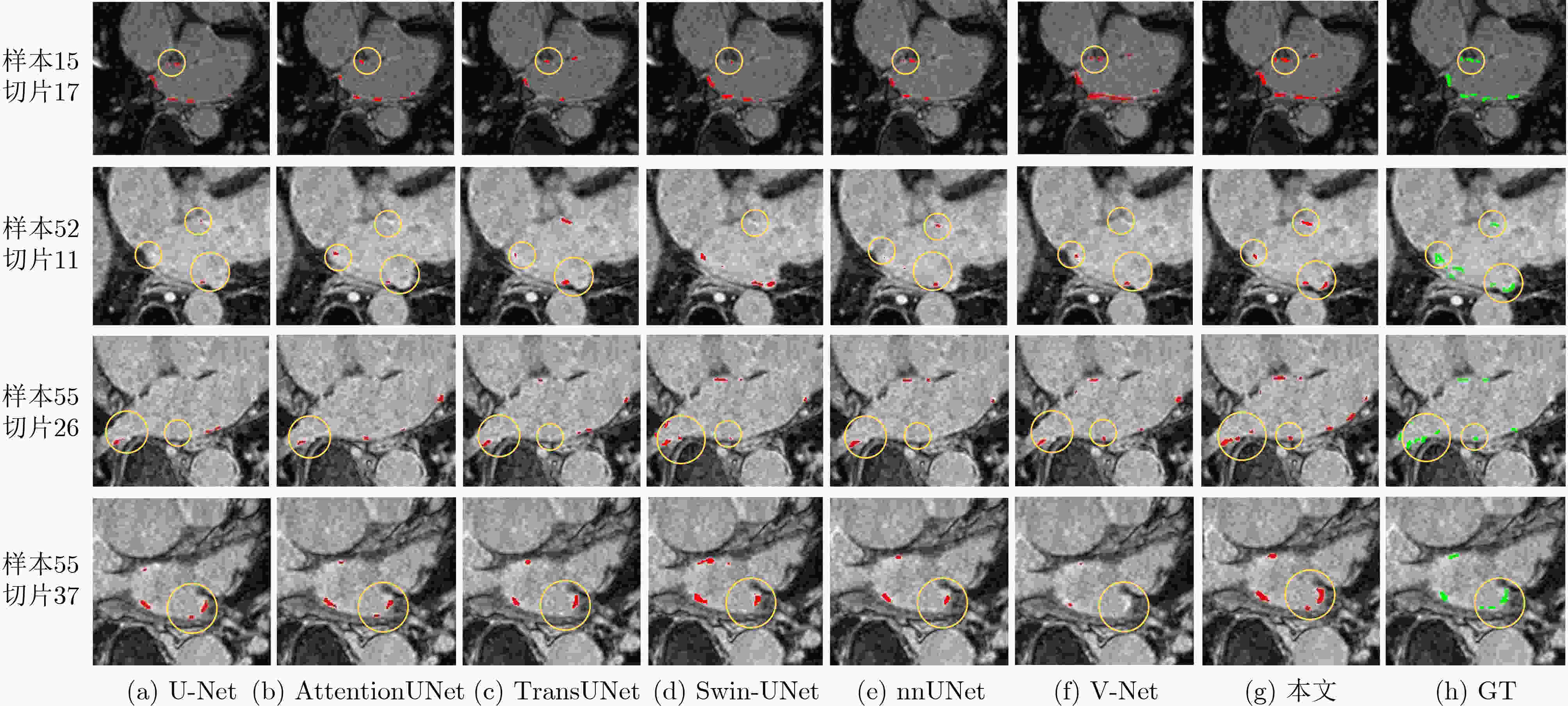
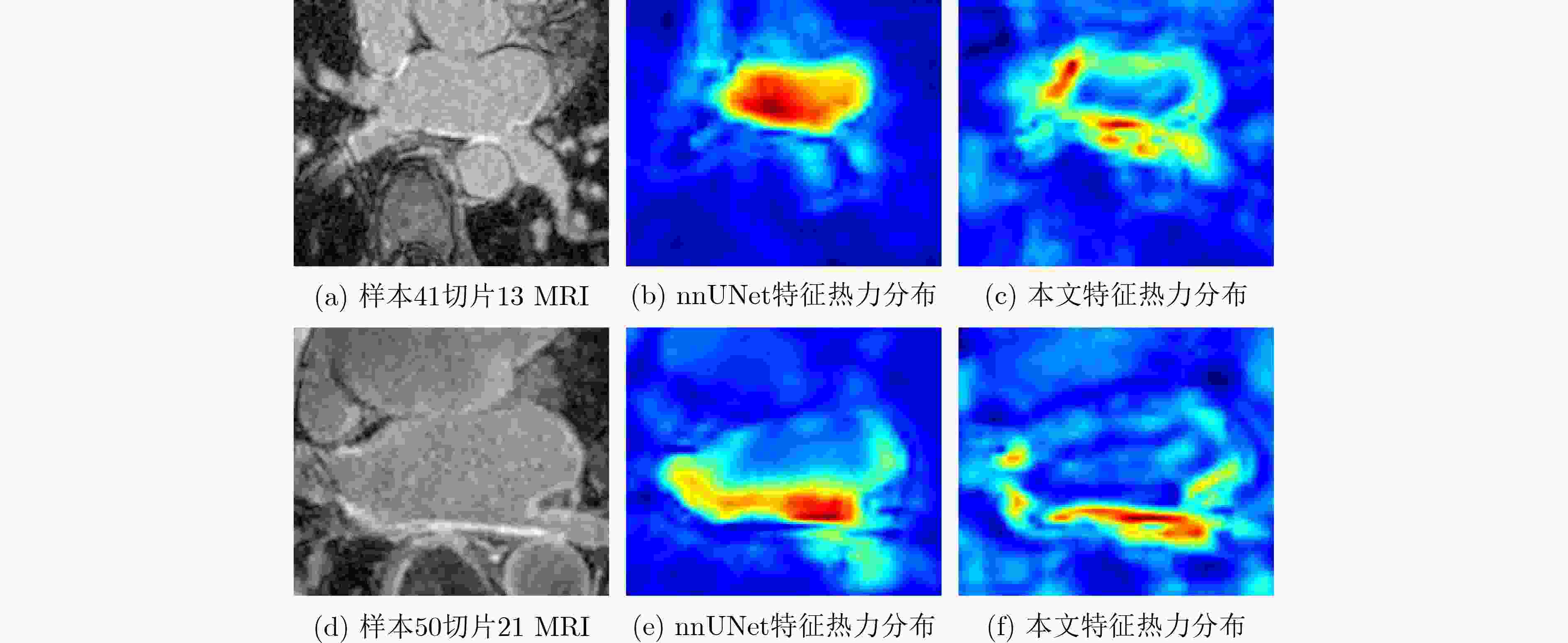
Objective Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a common arrhythmia associated with increased mortality. The distribution and extent of left atrial fibrosis are critical for predicting the onset and persistence of AF, as fibrotic tissue alters cardiac electrical conduction. Accurate segmentation of left atrial scars is essential for identifying fibrotic lesions and informing clinical diagnosis and treatment. However, this task remains challenging due to the irregular morphology, sparse distribution, and small size of scars. Deep learning models often perform poorly in scar feature extraction owing to limited supervision of atrial boundary information, which results in detail loss and reduced segmentation accuracy. Although increasing dataset size can improve performance, medical image acquisition is costly. To address this, the present study integrates prior knowledge that scars are generally located on the atrial wall to enhance feature extraction while reducing reliance on large labeled datasets. Two boundary feature enhancement modules are proposed. The Cross-Modal feature Excitation (CME) module encodes atrial boundary features to guide the network’s attention to atrial structures. The Dual-Branch Cross-Attention (DBCA) fusion module combines Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and boundary features at a deeper level to enhance boundary scar representation and improve segmentation accuracy. Methods This study proposes an enhanced U-shaped encoder–decoder framework for left atrial scar segmentation, incorporating two modules: the CME module and the DBCA module. These modules are embedded within the encoder to strengthen attention on atrial boundary features and improve segmentation accuracy. First, left atrial cavity segmentation is performed on cardiac MRI using a pre-trained model to obtain a binary mask. This binary map undergoes dilation and erosion to generate a Signed Distance Map (SDM), which is then used together with the MRI as input to the model. The SDM serves as an auxiliary representation that introduces boundary constraints. The CME module, integrated within the encoder’s convolutional blocks, applies channel and spatial attention mechanisms to both MRI and SDM features, thereby enhancing boundary information and guiding attention to scar regions. To further reinforce boundary features at the semantic level, the DBCA module is positioned at the bottleneck layer. This module employs a two-branch cross-attention mechanism to facilitate deep interaction and fusion of MRI and boundary features. The bidirectional cross-attention enables SDM and MRI features to exchange cross-modal information, reducing feature heterogeneity and generating semantically enriched and robust boundary fusion features. A combined Dice and cross-entropy loss function is used during training to improve segmentation precision and scar region identification. Results and Discussions This study uses a dataset of 60 left atrial scar segmentations from the LAScarQS 2022 Task 1. The dataset is randomly divided into 48 training and 12 test cases. Several medical image segmentation models, including U-Net, nnUNet, and TransUNet, are evaluated. Results show that three-dimensional segmentation consistently outperforms two-dimensional approaches. The proposed method exceeds the baseline nnUNet, with a 4.14% improvement in Dice score and a 6.37% increase in accuracy ( Table 1 ). Visual assessments confirm improved sensitivity to small scar regions and enhanced attention to boundaries (Fig. 6 ,Fig. 7 ). To assess model performance, comparative and ablation experiments are conducted. These include evaluations of encoder configurations (shared vs independent), feature fusion strategies (CME, DBCA, and CBAM), and fusion weight parameters α and β. An independent encoder incorporating both CME and DBCA modules achieves the highest performance (Table 3 ), with the optimal weight configuration at α = 0.7 and β = 0.3 (Table 5 ). The effect of different left atrial border widths 2.5 mm, 5.0 mm, and 7.5 mm is also analyzed. A 5.0 mm width provides the best segmentation results, whereas 7.5 mm may extend beyond the relevant region and reduce accuracy (Table 6 ).Conclusions This study integrates the proposed CME and DBCA modules into the nnUNet framework to address detail loss and feature extraction limitations in left atrial scar segmentation. The findings indicate that: (1) The CME module enhances MRI feature representation by incorporating left atrial boundary information across spatial and channel dimensions, improving the model’s focus on scar regions; (2) The DBCA module enables effective learning and fusion of boundary and MRI features, further improving segmentation accuracy; (3) The proposed model outperforms existing medical image segmentation methods on the LAScarQS2022 dataset, achieving a 4.14% increase in Dice score and a 6.37% gain in accuracy compared to the baseline nnUNet. Despite these improvements, current deep learning models remain limited in their sensitivity to small and poorly defined scars, which often results in segmentation omissions. Challenges persist due to the limited dataset size and the relatively small proportion of scar tissue within each image. These factors constrain the training process and model generalizability. Future work should focus on optimizing scar segmentation under small-sample conditions and addressing sample imbalance to improve overall performance. -
表 1 对比实验结果
方法 Dice(%) 95HD(voxel) ASD(voxel) Sensitivity(%) Accuracy(%) 2D U-Net 42.64 11.23 2.47 37.85 68.90 AttentionUNet 43.22 10.85 2.59 39.03 69.48 TransUNet 47.44 9.10 1.83 44.18 72.06 Swin-UNet 48.62 9.13 1.83 48.01 73.96 3D V-Net 49.48 10.03 2.27 54.50 77.17 nnUNet 52.41 9.05 1.79 51.34 75.62 本文 54.58 6.59 1.41 61.02 80.44 表 2 与不同规模的基线网络对比
模型 评价指标 参数量(M) Dice(%) 95HD(voxel) ASD(voxel) Sensitivity(%) Accuracy(%) nnUNet 52.41 9.05 1.79 51.34 75.62 126.22 nnUNet-L 52.48 9.32 1.85 51.87 75.93 189.33 本文 54.58 6.59 1.41 61.02 80.44 166.53 表 3 不同模型结构消融实验结果
模型 评价指标 参数量(M) Dice (%) 95HD (voxel) ASD (voxel) Sensitivity (%) Accuracy (%) Share encoder +CME+DBCA 53.72 7.09 1.61 53.80 76.85 127.67 Independent encoder +conv+conv 53.33 9.16 1.73 53.20 76.55 165.87 Independent encoder +CME+conv 53.21 8.68 1.69 52.72 76.31 165.91 Independent encoder +conv+DBCA 53.17 9.17 1.74 52.71 76.31 166.48 Independent encoder +CME+DBCA 54.58 6.59 1.41 61.02 80.44 166.53 表 4 CBAM模块、CME模块与DBCA模块不同位置组合消融实验结果
编码器 瓶颈层 评价指标 CBAM CME CBAM CME DBCA Dice (%) 95HD (voxel) ASD (voxel) Sensitivity (%) Accuracy (%) √ 53.28 8.95 1.65 55.71 77.80 √ 53.73 7.60 1.53 58.46 79.17 √ 53.23 9.64 1.82 52.61 76.26 √ 52.17 9.65 1.85 50.45 75.18 √ 53.33 9.03 1.83 54.41 77.15 √ √ 53.64 8.64 1.64 53.30 76.60 √ √ 52.88 9.33 1.80 51.15 75.53 √ √ 50.50 9.85 1.80 45.86 72.89 √ √ 54.58 6.59 1.41 61.02 80.44 表 5 $ \alpha $和$ \beta $取值消融实验结果
$ \alpha $ $ \beta $取值 评价指标 Dice(%) 95HD(voxel) ASD(voxel) Sensitivity(%) Accuracy(%) $ \alpha $= 0.1, $ \beta $ = 0.9 52.72 9.73 1.84 50.98 75.45 $ \alpha $= 0.3, $ \beta $ = 0.7 53.82 8.43 1.65 54.11 77.01 $ \alpha $ = 0.5, $ \beta $ = 0.5 53.48 9.26 1.74 53.47 76.69 $ \alpha $ = 0.7, $ \beta $ = 0.3 54.58 6.59 1.41 61.02 80.44 $ \alpha $ = 0.9, $ \beta $ = 0.1 54.47 7.51 1.49 56.09 77.99 表 6 左心房边界宽度取值对模型效果影响结果
边界宽度(mm) 评价指标 Dice(%) 95HD(voxel) ASD(voxel) Sensitivity(%) Accuracy(%) 2.5 54.59 7.09 1.43 59.06 79.47 5.0 54.58 6.59 1.41 61.02 80.44 7.5 53.40 8.47 1.67 54.40 77.15 -
[1] LIPPI G, SANCHIS-GOMAR F, and CERVELLIN G. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: An increasing epidemic and public health challenge[J]. International Journal of Stroke, 2021, 16(2): 217–221. doi: 10.1177/1747493019897870. [2] AKOUM N, DACCARETT M, MCGANN C, et al. Atrial fibrosis helps select the appropriate patient and strategy in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A DE-MRI guided approach[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 2011, 22(1): 16–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2010.01876.x. [3] 谷祥婷, 黄锐. 心房颤动发病机制和维持机制的研究进展[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2019, 27(1): 112–115,120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2019.01.025.GU Xiangting and HUANG Rui. Research progress on pathogenesis and maintaining mechanism of atrial fibrillation[J]. Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease, 2019, 27(1): 112–115,120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2019.01.025. [4] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [5] ISENSEE F, JAEGER P F, KOHL S A A, et al. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation[J]. Nature Methods, 2021, 18(2): 203–211. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z. [6] 孙军梅, 葛青青, 李秀梅, 等. 一种具有边缘增强特点的医学图像分割网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(5): 1643–1652. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210784.SUN Junmei, GE Qingqing, LI Xiumei, et al. A medical image segmentation network with boundary enhancement[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(5): 1643–1652. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210784. [7] 周涛, 刘赟璨, 陆惠玲, 等. ResNet及其在医学图像处理领域的应用: 研究进展与挑战[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 149–167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210914.ZHOU Tao, LIU Yuncan, LU Huiling, et al. ResNet and its application to medical image processing: Research progress and challenges[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 149–167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210914. [8] SHOTTON J, JOHNSON M, and CIPOLLA R. Semantic texton forests for image categorization and segmentation[C]. 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587503. [9] 周涛, 侯森宝, 陆惠玲, 等. C2 Transformer U-Net: 面向跨模态和上下文语义的医学图像分割模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1807–1816. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220445.ZHOU Tao, HOU Senbao, LU Huiling, et al. C2 Transformer U-Net: A medical image segmentation model for cross-modality and contextual semantics[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1807–1816. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220445. [10] ALBAWI S, MOHAMMED T A, and AL-ZAWI S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network[C]. 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICEngTechnol.2017.8308186. [11] NIYAS S, PAWAN S J, ANAND KUMAR M, et al. Medical image segmentation with 3D convolutional neural networks: A survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 493: 397–413. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.04.065. [12] 张淑军, 彭中, 李辉. SAU-Net: 基于U-Net和自注意力机制的医学图像分割方法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(10): 2433–2442. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200984.ZHANG Shujun, PENG Zhong, and LI Hui. SAU-Net: Medical image segmentation method based on U-Net and self-attention[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(10): 2433–2442. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20200984. [13] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [14] ÇİÇEK Ö, ABDULKADIR A, LIENKAMP S S, et al. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation[C]. The 19th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2016, Athens, Greece, 2016: 424–432. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49. [15] MILLETARI F, NAVAB N, and AHMADI S A. V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C]. 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, USA, 2016: 565–571. doi: 10.1109/3DV.2016.79. [16] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [17] OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, LE FOLGOC L, et al. Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas[C]. The 1st Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning (MIDL 2018), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [18] CHEN Jieneng, LU Yongyi, YU Qihang, et al. TransUNet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation[C]. PThe 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021. [19] CAO Hu, WANG Yueyue, CHEN J, et al. Swin-Unet: UNet-Like pure transformer for medical image segmentation[C]. Computer Vision – ECCV 2022 Workshops, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 205–218. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-25066-8_9. [20] PERRY D, MORRIS A, BURGON N, et al. Automatic classification of scar tissue in late gadolinium enhancement cardiac MRI for the assessment of left-atrial wall injury after radiofrequency ablation[C]. Medical Imaging 2012: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, San Diego, USA, 2012: 83151D. doi: 10.1117/12.910833. [21] KARIM R, ARUJUNA A, BRAZIER A, et al. Automatic segmentation of left atrial scar from delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging[C]. The 6th International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart, New York City, USA, 2011: 63–70. [22] LI Lei, ZIMMER V A, SCHNABEL J A, et al. AtrialJSQnet: A new framework for joint segmentation and quantification of left atrium and scars incorporating spatial and shape information[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 76: 102303. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102303. [23] LIU Tianyi, HOU Size, ZHU Jiayuan, et al. UGformer for robust left atrium and scar segmentation across scanners[C]. Proceedings of the 1st Challenge on Left Atrial and Scar Quantification and Segmentation, Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 36–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-31778-1_4. [24] OGBOMO-HARMITT S, GRZELAK J, QURESHI A, et al. TESSLA: Two-Stage ensemble scar segmentation for the left atrium[C]. Proceedings of the 1st Challenge on Left Atrial and Scar Quantification and Segmentation, Singapore, 2022: 106–114. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-31778-1_10. [25] KHAN A, ALWAZZAN O, BENNING M, et al. Sequential segmentation of the left atrium and atrial scars using a multi-scale weight sharing network and boundary-based processing[C]. The 1st Challenge on Left Atrial and Scar Quantification and Segmentation, Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 69–82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-31778-1_7. [26] DANGI S, LINTE C A, and YANIV Z. A distance map regularized CNN for cardiac cine MR image segmentation[J]. Medical Physics, 2019, 46(12): 5637–5651. doi: 10.1002/mp.13853. [27] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. [28] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]. Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2017–2025. [29] ROMBACH R, BLATTMANN A, LORENZ D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10674–10685. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01042. [30] LI Lei, ZIMMER V A, SCHNABEL J A, et al. Medical image analysis on left atrial LGE MRI for atrial fibrillation studies: A review[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 77: 102360. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102360. [31] LI Lei, ZIMMER V A, SCHNABEL J A, et al. AtrialGeneral: Domain generalization for left atrial segmentation of multi-center LGE MRIs[C]. The 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021, Strasbourg, France, 2021: 557–566. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_54. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
