A Self-distillation Object Segmentation Method Based on Transformer Feature Pyramid
-
摘要: 为在不增加网络参数规模的情况下提升目标分割性能,该文提出一种基于Transformer特征金字塔的自蒸馏目标分割方法,提升了Transformer分割模型的实用性。首先,以Swin Transformer为主干网构建了像素级的目标分割模型;然后,设计了适合Transformer的蒸馏辅助分支,该分支由密集连接空间空洞金字塔(DenseASPP)、相邻特征融合模块(AFFM)和得分模块构建而成,通过自蒸馏方式指导主干网络学习蒸馏知识;最后,利用自上而下的学习策略指导模型学习,以保证自蒸馏学习的一致性。实验表明,在4个公开数据集上所提方法均能有效提升目标分割精度,在伪装目标检测(COD)数据集上比次优的Transformer知识蒸馏(TKD)方法的Fβ值提高了约1.57%。
-
关键词:
- 自蒸馏 /
- Transformer /
- 目标分割 /
- 特征金字塔
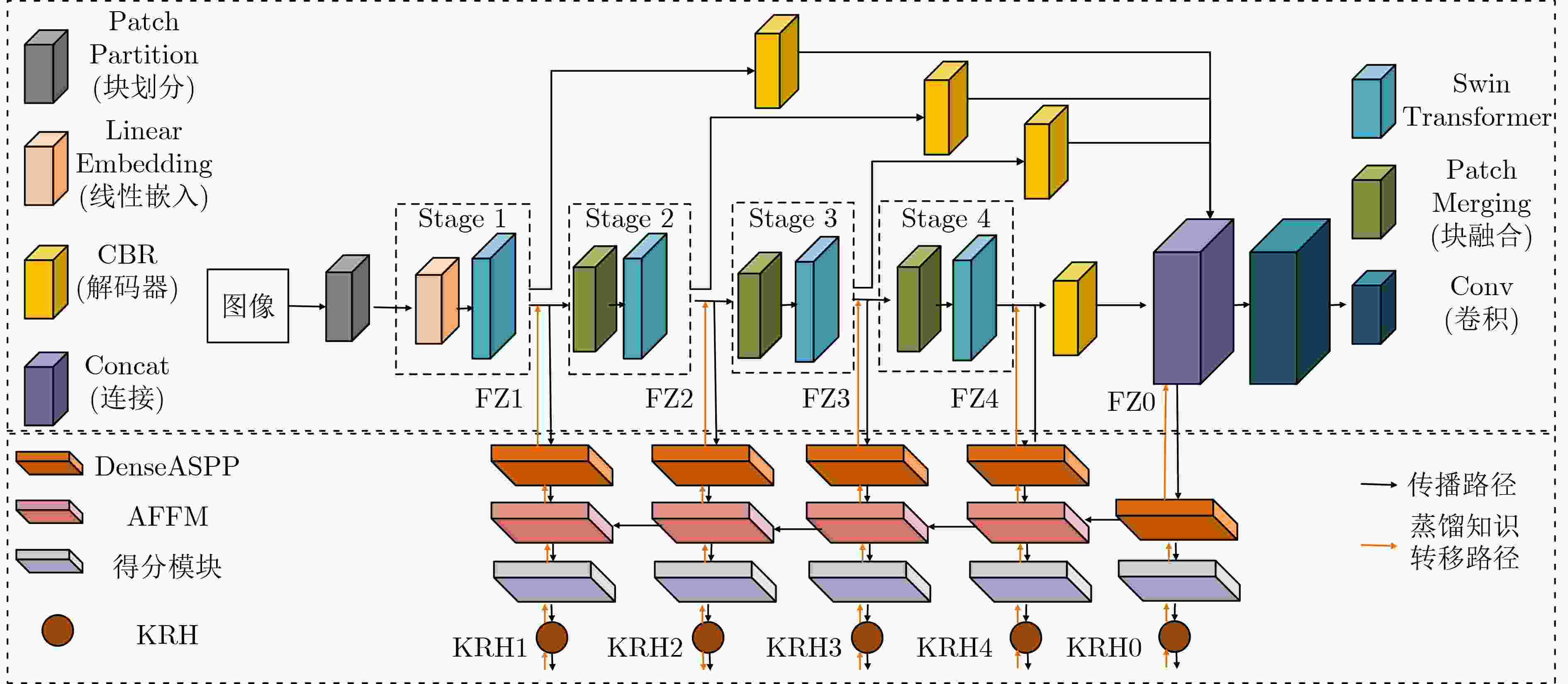
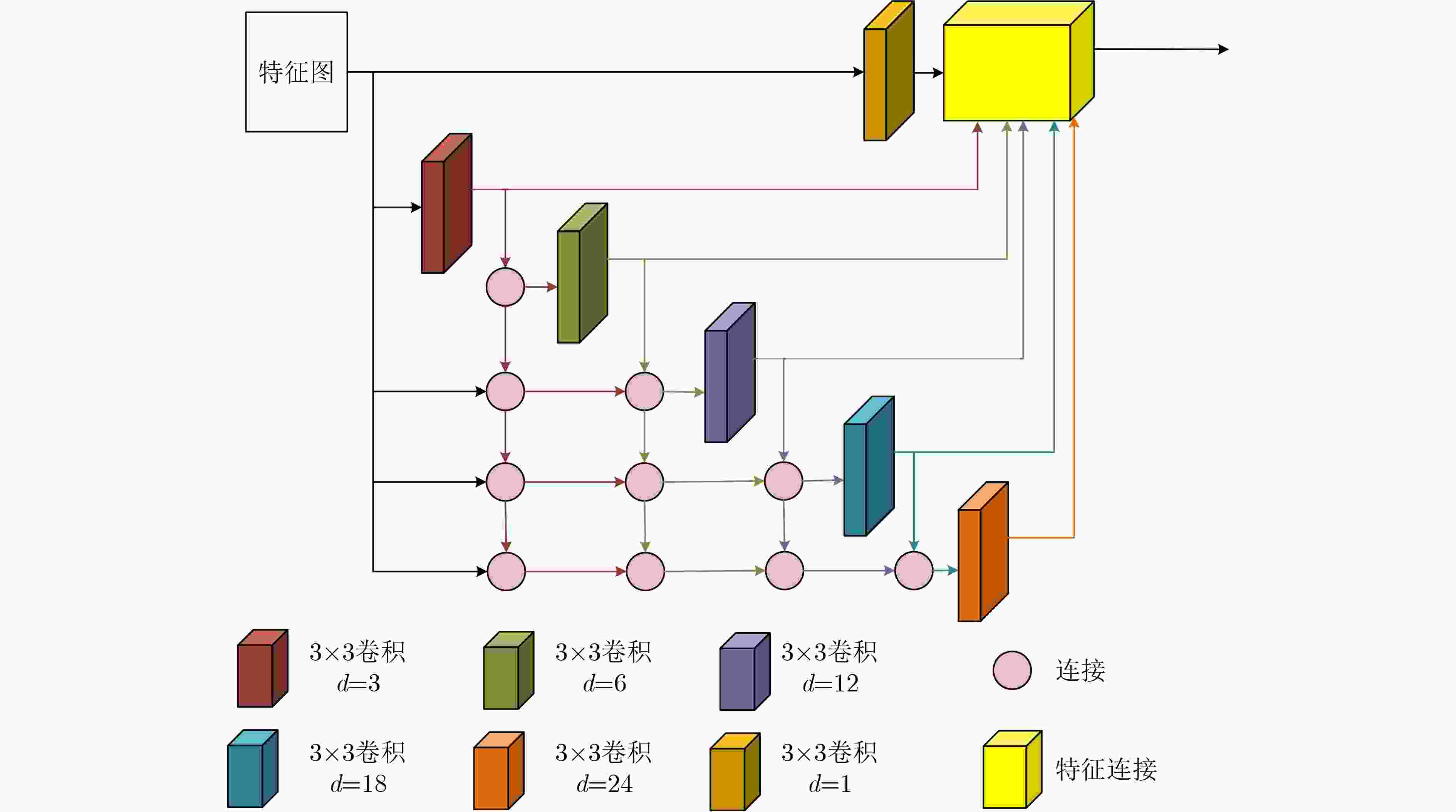
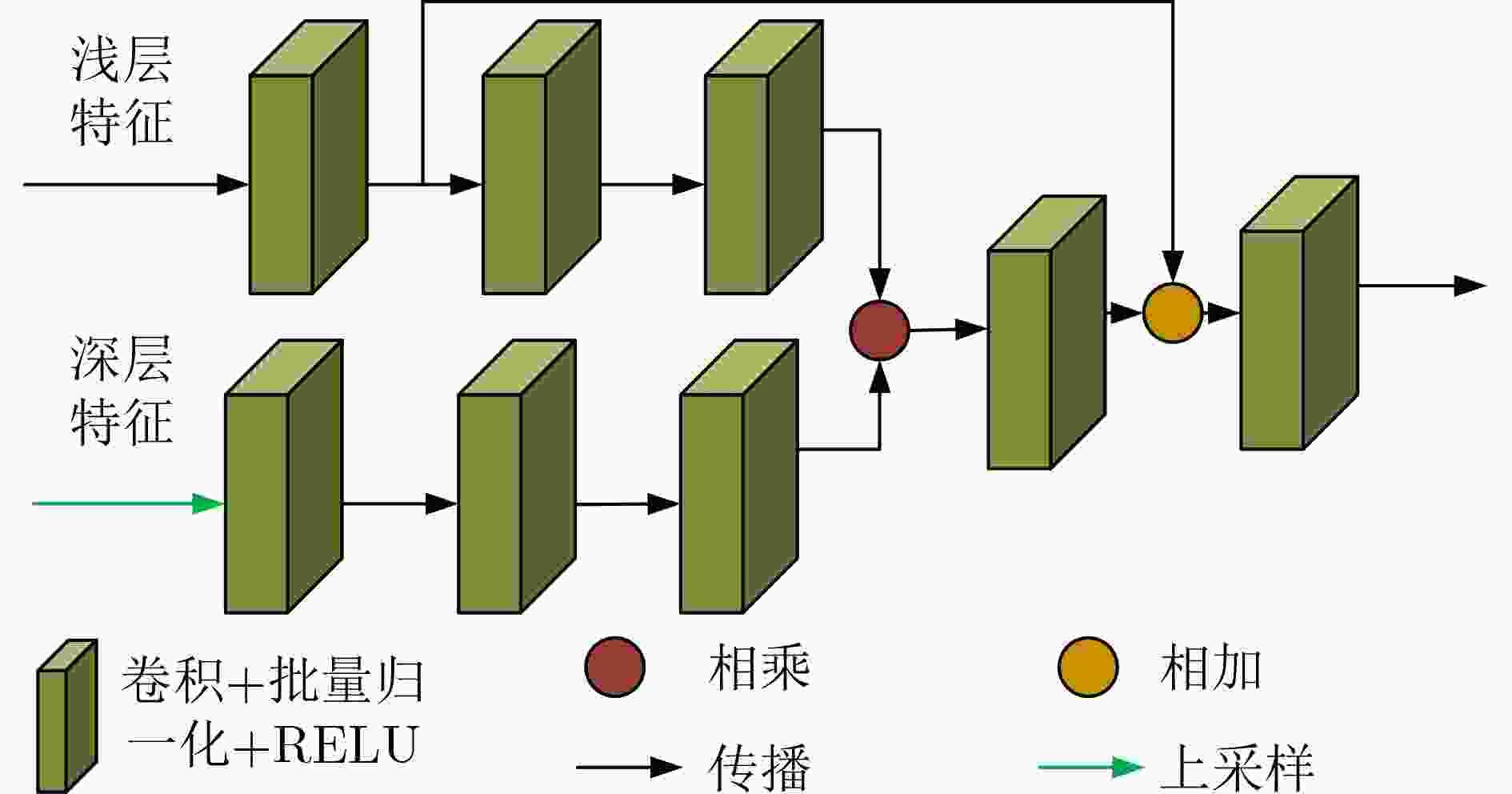
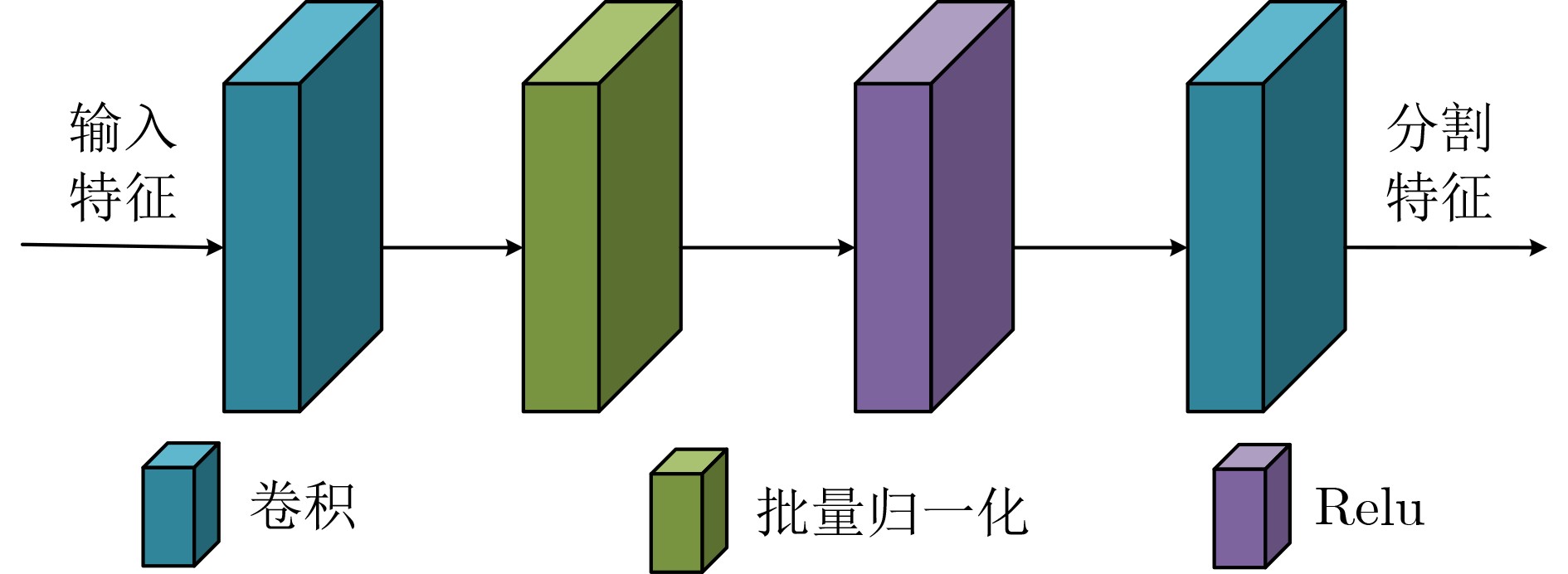
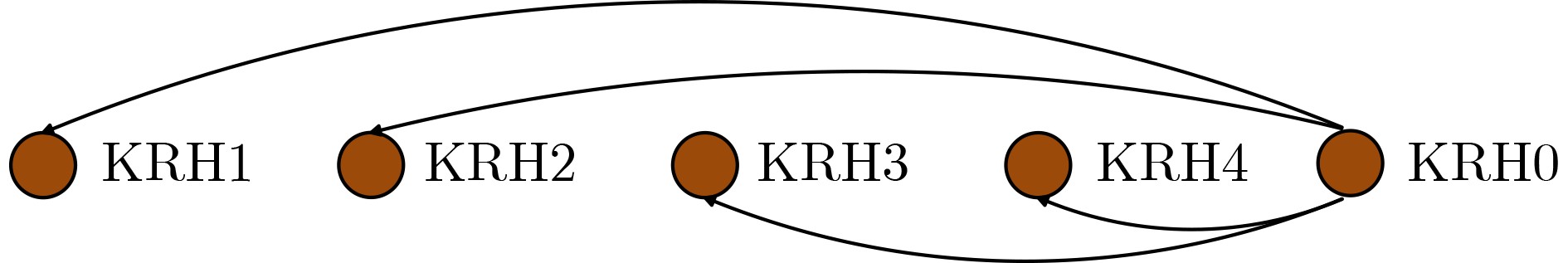
Abstract:Objective Neural networks that demonstrate superior performance often necessitate complex architectures and substantial computational resources, thereby limiting their practical applications. Enhancing model performance without increasing network parameters has emerged as a significant area of research. Self-distillation has been recognized as an effective approach for simplifying models while simultaneously improving performance. Presently, research on self-distillation predominantly centers on models with Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures, with less emphasis on Transformer-based models. It has been observed that due to their structural differences, different network models frequently extract varied semantic information for the same spatial locations. Consequently, self-distillation methods tailored to specific network architectures may not be directly applicable to other structures; those designed for CNNs are particularly challenging to adapt for Transformers. To address this gap, a self-distillation method for object segmentation is proposed, leveraging a Transformer feature pyramid to improve model performance without increasing network parameters. Methods First, a pixel-wise object segmentation model is developed utilizing the Swin Transformer as the backbone network. In this model, the Swin Transformer produces four layers of features. Each layer of mapped features is subjected to Convolution-Batch normalization-ReLU (CBR) processing to ensure that the backbone features maintain a uniform channel size. Subsequently, all backbone features are concatenated along the channel dimension, after which convolution operations are performed to yield pixel-wise feature representations. In the next phase, an auxiliary branch is designed that integrates Densely connected Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (DenseASPP), Adjacent Feature Fusion Modules (AFFM), and a scoring module, facilitating self-distillation to guide the main network. The specific architecture is depicted. The self-distillation learning framework consists of four sub-branches, labeled FZ1 to FZ4, alongside a main branch labeled FZ0. Each auxiliary sub-branch is connected to different layers of the backbone network to extract layer-specific features and produce a Knowledge Representation Header (KRH) that serves as the segmentation result. The main branch is linked to the fully connected layer to extract fused features and optimize the mixed features from various layers of the backbone network. Finally, a top-down learning strategy is employed to guide the model’s training, ensuring consistency in self-distillation. The KRH0 derived from the main branch FZ0 integrates the knowledge KRH1-KRH4 obtained from each sub-branch FZ1–FZ4, steering the overall optimization direction for self-distillation learning. Consequently, the main branch and sub-branches can be regarded as teacher and student entities, respectively, forming four distillation pairs, with FZ0 directing FZ1–FZ4. This top-down distillation strategy leverages the main branch to instruct the sub-branches to learn independently, thereby enabling the sub-branches to acquire more discriminative features from the main branch while maintaining consistency in the optimization direction between the sub-branches and the main branch. Results and Discussions The results quantitatively demonstrate the segmentation performance of the proposed method. The data indicates that the proposed method consistently achieves superior segmentation results across all four datasets. On average, the metric Fβ of the proposed method exceeds that of the suboptimal method, Transformer Knowledge Distillation (TKD), by 0.98%. Additionally, the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) metric of the proposed method is 0.86% higher than that of the suboptimal method, Target-Aware Transformer (TAT). These results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively addresses the challenge of camouflage target segmentation. Notably, on the Camouflage Object Detection (COD) dataset, the proposed method improves Fβ by 1.57% compared to TKD, while achieving an enhancement of 0.81% in mIoU relative to TAT. Among CNN methods, Poolnet+ (POOL+) attained the highest average Fβ, yet it falls short of the proposed method by 4.22%. This difference can be attributed to the Transformer’s capability to overcome the limitations of the restricted receptive field inherent in CNNs, thereby extracting a greater amount of semantic information from images. The results also show that the self-distillation method is similarly effective within the Transformer framework, significantly enhancing the segmentation performance of the Transformer model. The proposed method outperforms other self-distillation strategies, achieving the best segmentation results across all four datasets. When compared to the baseline model, the average metrics for Fβ and mIoU exhibit increases of 1.98% and 2.40%, respectively. Conclusions The proposed self-distillation algorithm enhances object segmentation performance and demonstrates the efficacy of self-distillation within the Transformer architecture. -
Key words:
- Self-distillation /
- Transformer /
- Object segmentation /
- Feature pyramid
-
表 1 不同分割方法的分割结果(%)
方法 COD DUT-O THUR SOC 平均值 Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU EMANet 63.07 26.42 78.38 59.86 82.60 62.70 86.83 71.63 74.02 51.61 CCNet 64.44 41.27 79.70 63.15 84.80 70.10 87.27 77.79 74.90 56.91 GateNet 65.81 46.11 82.22 70.04 87.59 78.60 88.20 79.71 78.40 64.33 CPD 60.42 42.94 83.38 72.33 87.90 79.38 83.59 71.42 76.53 62.46 DSR 54.68 36.25 80.63 66.83 84.04 72.25 82.44 73.04 69.69 55.24 EDN 65.27 46.04 84.23 75.38 88.71 83.31 74.89 63.94 78.71 68.40 POOL+ 61.55 45.39 82.95 70.84 85.25 74.74 87.92 79.39 79.42 67.59 TAT 67.95 47.05 84.28 71.65 88.65 78.34 89.45 80.36 82.58 69.35 TKD 68.46 46.83 83.96 71.27 88.86 78.35 89.35 80.06 82.66 69.13 所提方法 70.03 47.86 85.34 71.87 89.54 79.78 89.64 81.34 83.64 70.21 表 2 不同自蒸馏方法的分割结果(%)
方法 COD DUT-0 THUR SOC 平均值 Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU Fβ mIoU BL 67.34 46.09 83.03 68.25 88.24 77.54 88.03 79.34 81.66 67.81 BL+DKS 68.45 47.26 84.78 70.37 88.62 78.52 89.26 80.54 82.78 69.17 BL+BYOT 68.38 46.32 85.03 70.34 88.57 77.83 88.36 80.37 82.58 68.72 BL+DHM 67.52 45.67 84.23 69.53 89.32 76.97 88.75 81.13 82.45 68.33 BL+SA 69.21 46.23 84.16 69.30 89.24 78.24 88.69 80.24 82.83 68.50 所提方法 70.03 47.86 85.34 71.87 89.54 79.78 89.64 81.34 83.64 70.21 表 3 不同目标分割方法效率
EMANet CCNet GateNet CPD DSR POOL+ TAT 所提方法 参数(MB) 34.80 52.10 128.63 47.85 75.29 70.50 140.21 132.25 速度(fps) 37.59 35.34 33.03 32.60 8.80 21.53 18.54 36.15 表 4 消融实验结果
序号 自蒸馏模块 学习策略 结果(%) DenseASPP AFFM 自上而下 Fβ mIoU 1 × × × 67.34 46.09 2 × × √ 67.53 46.28 3 √ × √ 69.03 47.11 4 × √ √ 68.34 46.84 5 √ √ × 69.23 46.96 6 √ √ √ 70.03 47.86 -
[1] 吕岳, 周浙泉, 吕淑静. 基于双层解耦策略和注意力机制的遮挡目标分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(1): 335–343. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211288.LÜ Yue, ZHOU Zhequan and LÜ Shujing. Occluded object segmentation based on bilayer decoupling strategy and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(1): 335–343. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211288. [2] ZHENG Yunfei, ZHANG Xiongwei, WANG Feng, et al. Detection of people with camouflage pattern via dense deconvolution network[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(1): 29–33. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2825959. [3] 任莎莎, 刘琼. 小目标特征增强图像分割算法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(8): 1894–1904. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211123.REN Shasha and LIU Qiong. A tiny target feature enhancement algorithm for semantic segmentation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(8): 1894–1904. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211123. [4] 梁新宇, 权冀川, 杨辉, 等. 多尺度特征提取和多层次注意力机制的迷彩伪装目标分割算法[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2022, 34(5): 683–692. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2022.19000.LIANG Xinyu, QUAN Jichuan, YANG Hui, et al. Camouflage target segmentation algorithm using multi-scale feature extraction and multi-level attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2022, 34(5): 683–692. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2022.19000. [5] LI Xiangtai, DING Henghui, YUAN Haobo, et al. Transformer-based visual segmentation: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(12): 10138–10163. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3434373. [6] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986. [7] CHEN Lei, CAO Tieyong, ZHENG Yunfei, et al. A self‐distillation object segmentation method via frequency domain knowledge augmentation[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2023, 17(3): 341–351. doi: 10.1049/cvi2.12170. [8] 邵仁荣, 刘宇昂, 张伟, 等. 深度学习中知识蒸馏研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(8): 1638–1673. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01638.SHAO Renrong, LIU Yuang, ZHANG Wei, et al. A survey of knowledge distillation in deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computer, 2022, 45(8): 1638–1673. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01638. [9] WU Di, CHEN Pengfei, YU Xuehui, et al. Spatial self-distillation for object detection with inaccurate bounding boxes[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 6832–6842. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00631. [10] LIN Sihao, XIE Hongwei, WANG Bing, et al. Knowledge distillation via the target-aware transformer[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10905–10914. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01064. [11] LIU Ruiping, YANG Kailun, ROITBERG A, et al. TransKD: Transformer knowledge distillation for efficient semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(12): 20933–20949. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3455416. [12] YANG Maoke, YU Kun, ZHANG Chi, et al. DenseASPP for semantic segmentation in street scenes[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3684–3692. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00388. [13] ZHENG Yunfei, SUN Meng, WANG Xiaobing, et al. Self-distillation object segmentation via pyramid knowledge representation and transfer[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2023, 29(5): 2615–2631. doi: 10.1007/s00530-023-01121-x. [14] ZHANG Linfeng, SONG Jiebo, GAO Anni, et al. Be your own teacher: Improve the performance of convolutional neural networks via self‐distillation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3712–3721. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00381. [15] CHENG Mingming, MITRA N J, HUANG Xiaolei, et al. SalientShape: Group saliency in image collections[J]. The Visual Computer, 2014, 30(4): 443–453. doi: 10.1007/s00371-013-0867-4. [16] ZHAI Qiang, LI Xin, YANG Fan, et al. Mutual graph learning for camouflaged object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA 2021: 12992–13002. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01280. [17] WANG Yangtao, SHEN Xi, YUAN Yuan, et al. TokenCut: Segmenting objects in images and videos with self-supervised transformer and normalized cut[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(12): 15790–15801. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3305122. [18] KIRILLOV A, MINTUN E, RAVI N, et al. Segment anything[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023: 3992–4003. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00371. [19] JI Wei, LI Jingjing, BI Qi, et al. Segment anything is not always perfect: An investigation of SAM on different real-world applications[J]. Machine Intelligence Research, 2024, 21(4): 617–630. doi: 10.1007/s11633-023-1385-0. [20] YANG Chuanguang, AN Zhulin, ZHOU Helong, et al. Online knowledge distillation via mutual contrastive learning for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(8): 10212–10227. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3257878. [21] CHEN Lei, CAO Tieyong, ZHENG Yunfei, et al. A non-negative feedback self-distillation method for salient object detection[J]. PeerJ Computer Science, 2023, 9: e1435. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1435. [22] FAN Dengping, JI Gepeng, SUN Guolei, et al. Camouflaged object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2774–2784. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00285. [23] YANG Chuan, ZHANG Lihe, LU Huchuan, et al. Saliency detection via graph based manifold ranking[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3166–3173. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.407. [24] FAN Dengping, CHENG Mingming, LIU Jiangjiang, et al. Salient objects in clutter: Bringing salient object detection to the foreground[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 186–202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01267-0_12. [25] LI Xia, ZHONG Zhisheng, WU Jianlong, et al. Expectation‐maximization attention networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9166–9175. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00926. [26] HUANG Zilong, WANG Xinggang, HUANG Lichao, et al. CCNeT: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 603–612. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00069. [27] ZHAO Xiaoqi, PANG Youwei, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Suppress and balance: A simple gated network for salient object detection[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 35–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58536-5_3. [28] WU Zhe, SU Li and HUANG Qingming. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3902–3911. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00403. [29] WANG Liansheng, CHEN Rongzhen, ZHU Lei, et al. Deep sub-region network for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(2): 728–741. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2988768. [30] WU Yuhuan, LIU Yun, ZHANG Le, et al. EDN: Salient object detection via extremely-downsampled network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3125–3136. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3164550. [31] LIU Jiangjiang, HOU Qibin, LIU Zhiang, et al. PoolNet+: Exploring the potential of pooling for salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(1): 887–904. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3140168. [32] HOU Yuenan, MA Zheng, LIU Chunxiao, et al. Learning lightweight lane detection CNNs by self‐attention distillation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1013–1021. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00110. [33] SUN Dawei, YAO Anbang, ZHOU Aojun, et al. Deeply‐supervised knowledge synergy[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6990–6999. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00716. [34] LI Duo and CHEN Qifeng. Dynamic hierarchical mimicking towards consistent optimization objectives[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 7639–7648. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00766. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
