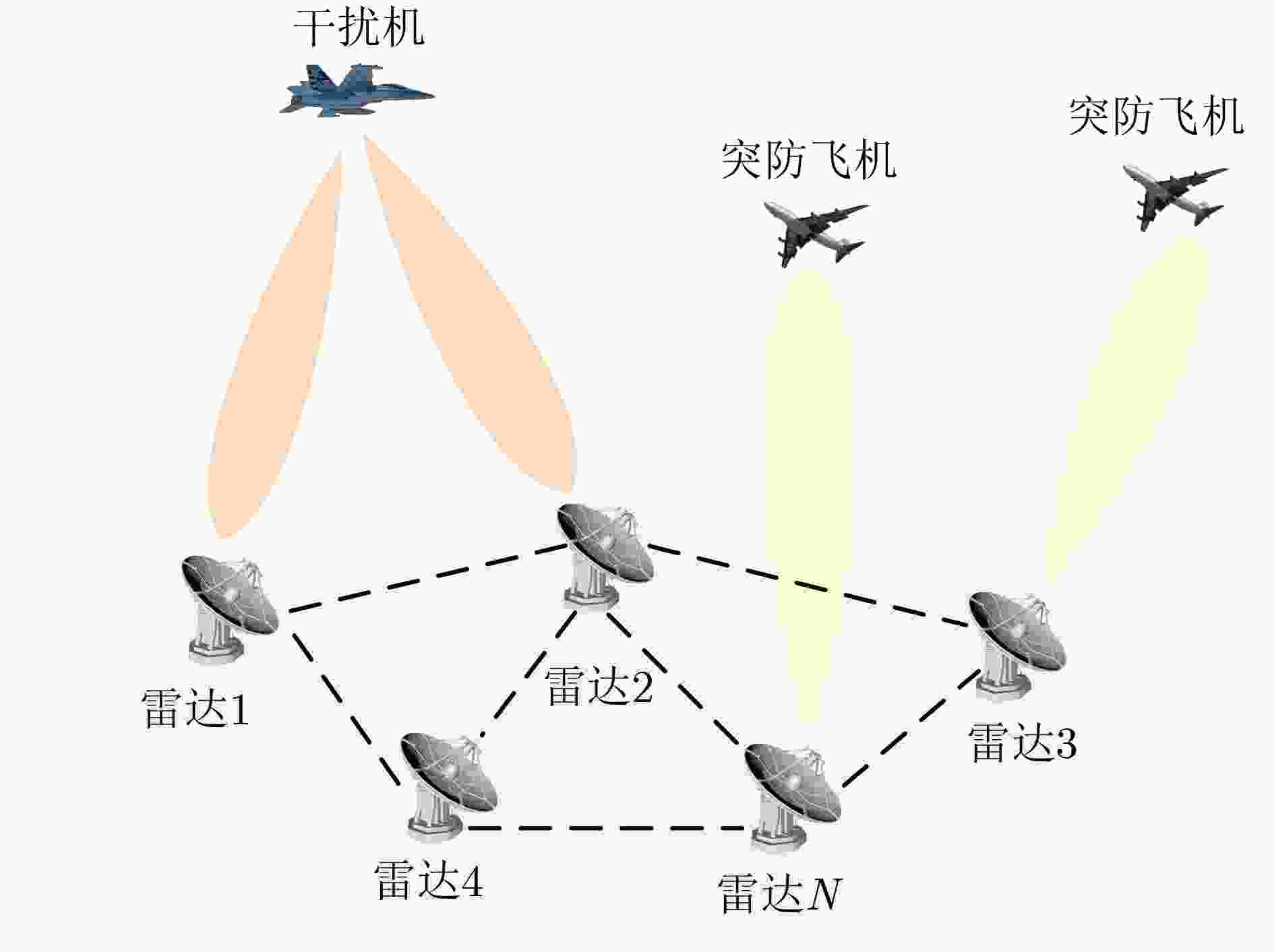
Collaborative Interference Resource Allocation Method Based on Improved Secretary Bird Algorithm
-
摘要: 在战场环境中,针对多波束干扰系统突防组网雷达场景下干扰资源分配的问题,该文提出一种引入柯西变异和全局协同控制策略的改进秘书鸟算法(ISBOA)对战场上的干扰资源进行优化分配。首先,建立突防场景下的多波束干扰系统模型,并将组网雷达检测融合概率作为多干扰机协同压制干扰组网雷达的性能评估指标;其次,以最小化检测概率为目标函数,对多干扰机干扰样式、干扰波束和功率资源进行联合优化分配;最后,利用ISBOA进行求解。实验结果经过对比表明,ISBOA算法搜索能力更强,收敛精度更高,具有更强的稳定性,能够更加合理地分配战场上的干扰资源。Abstract:
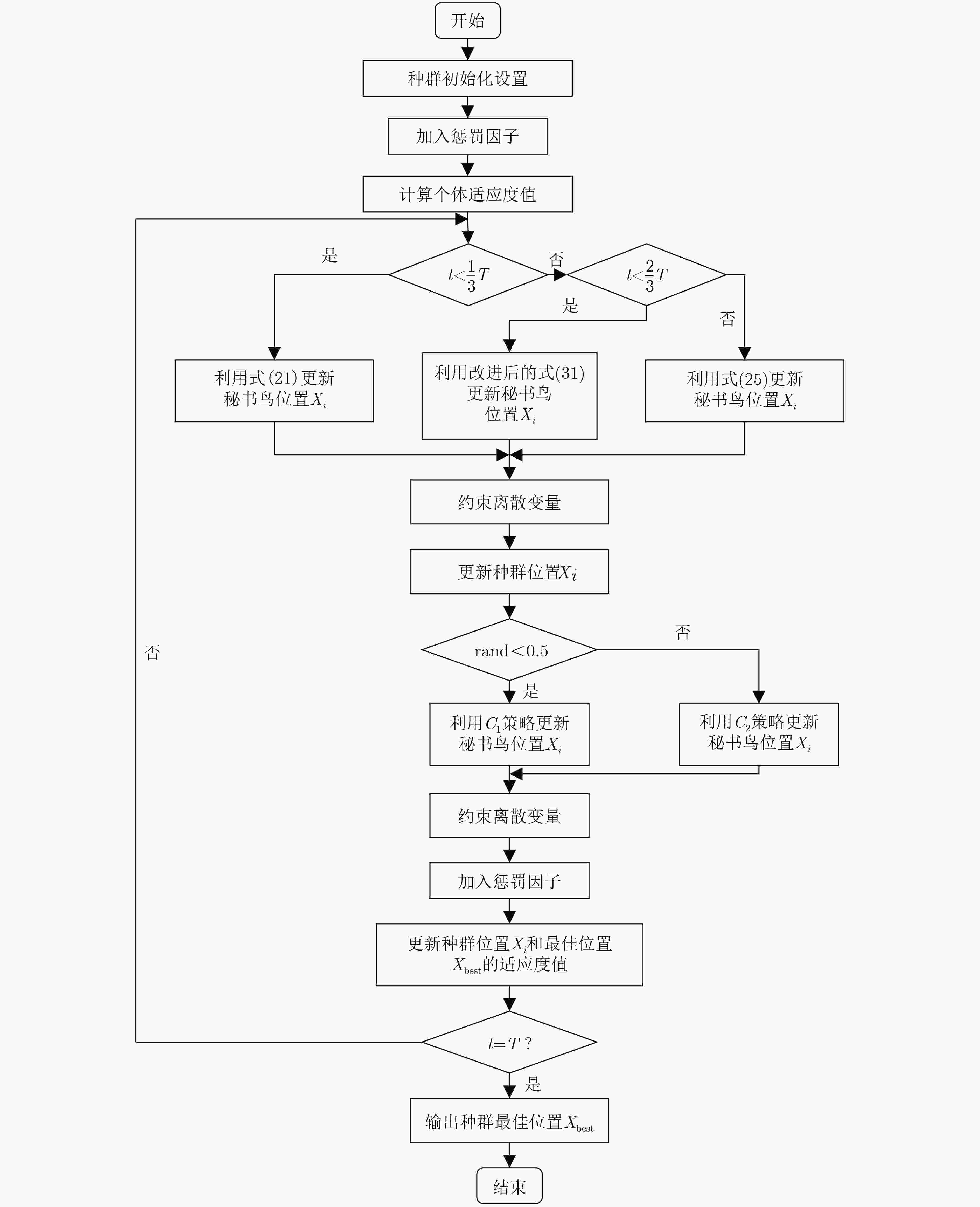
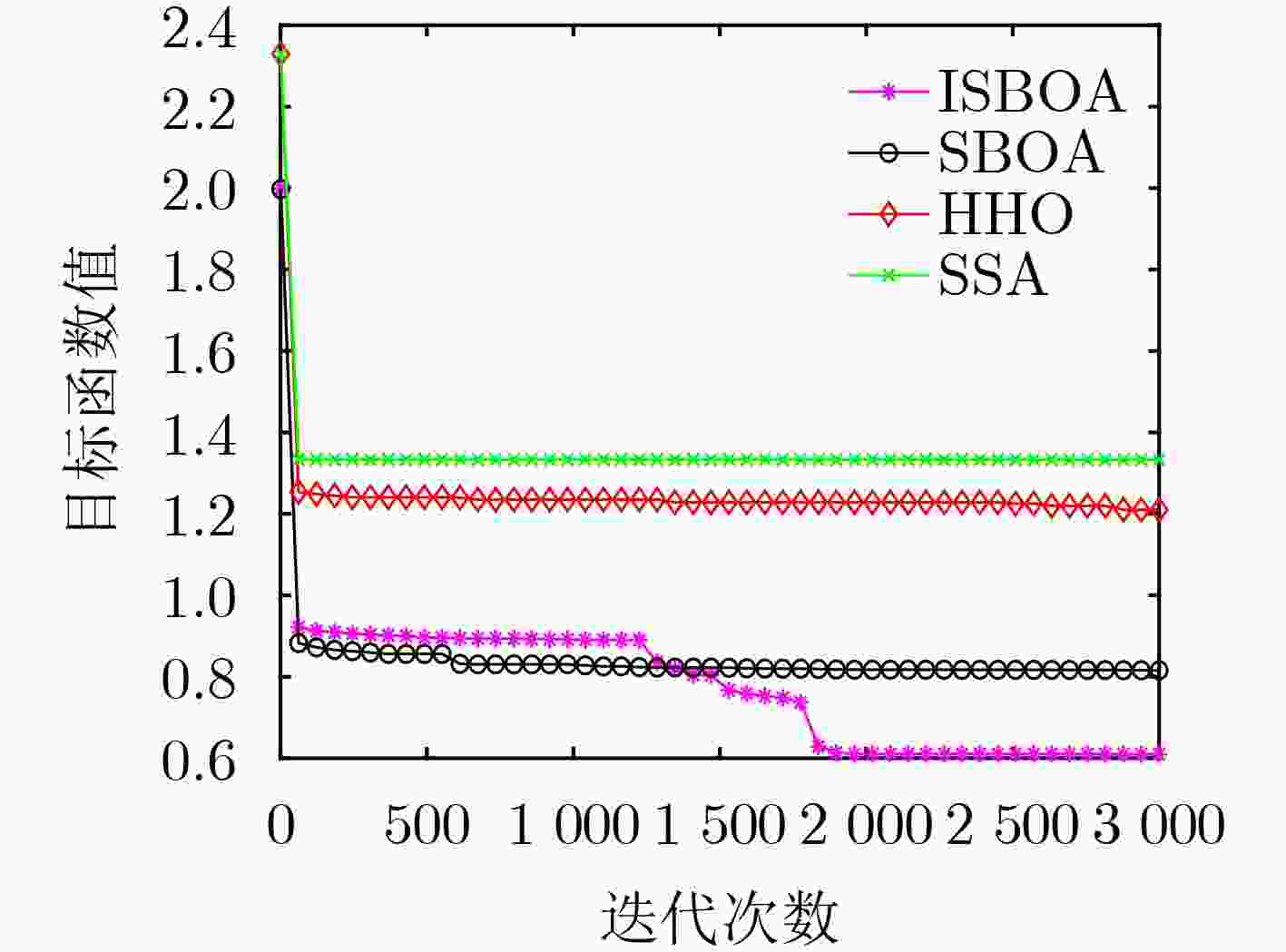
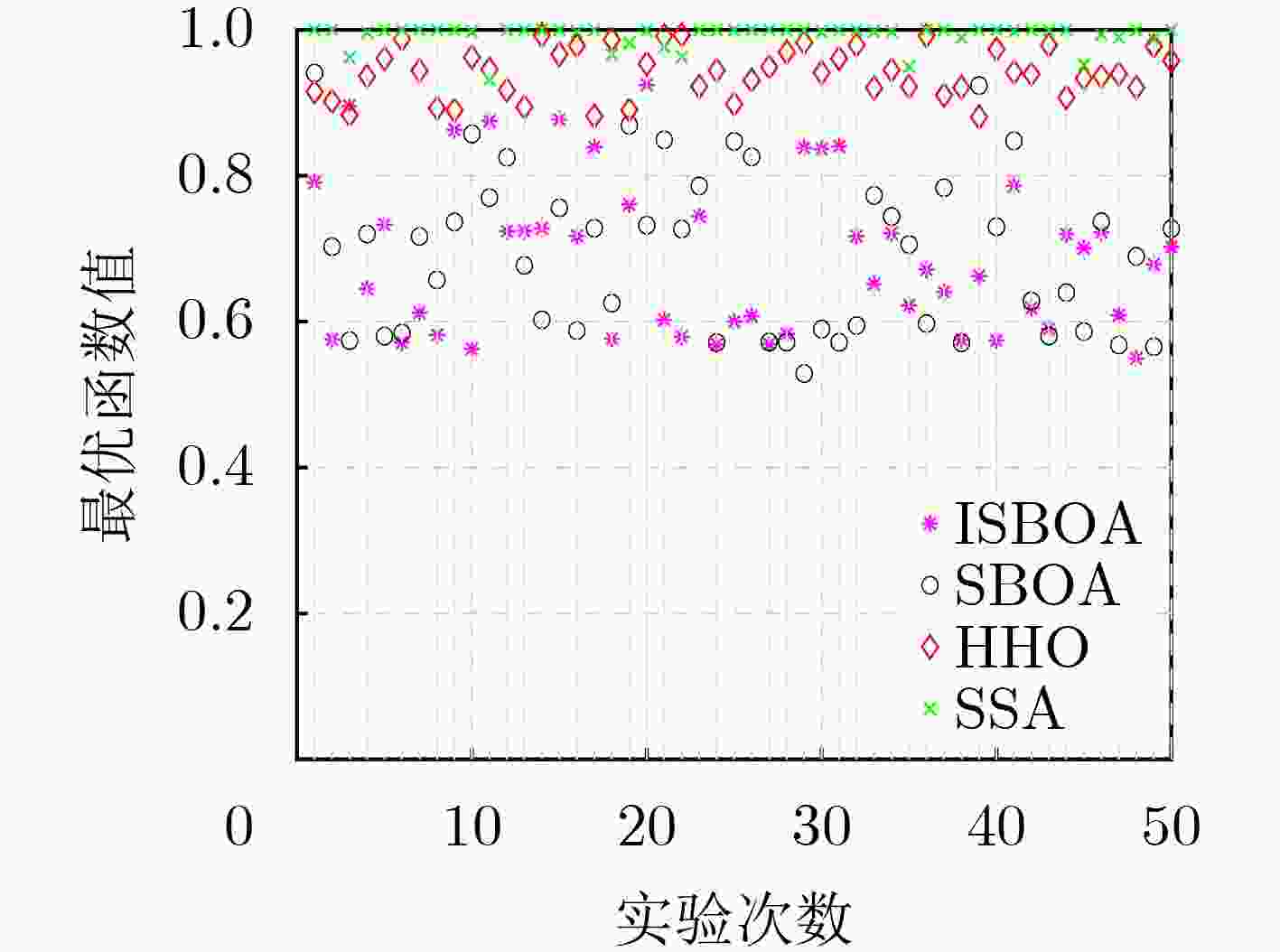
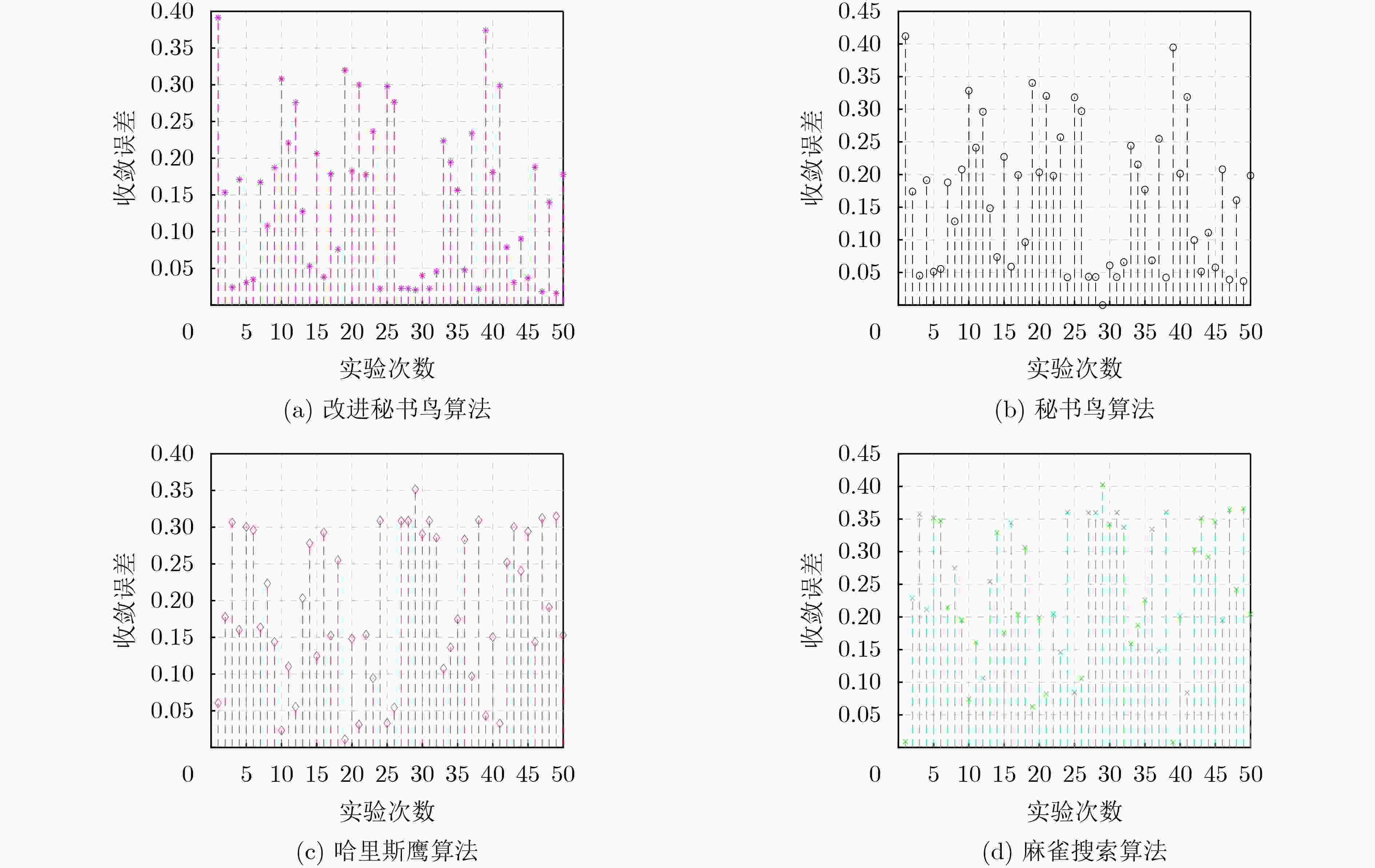
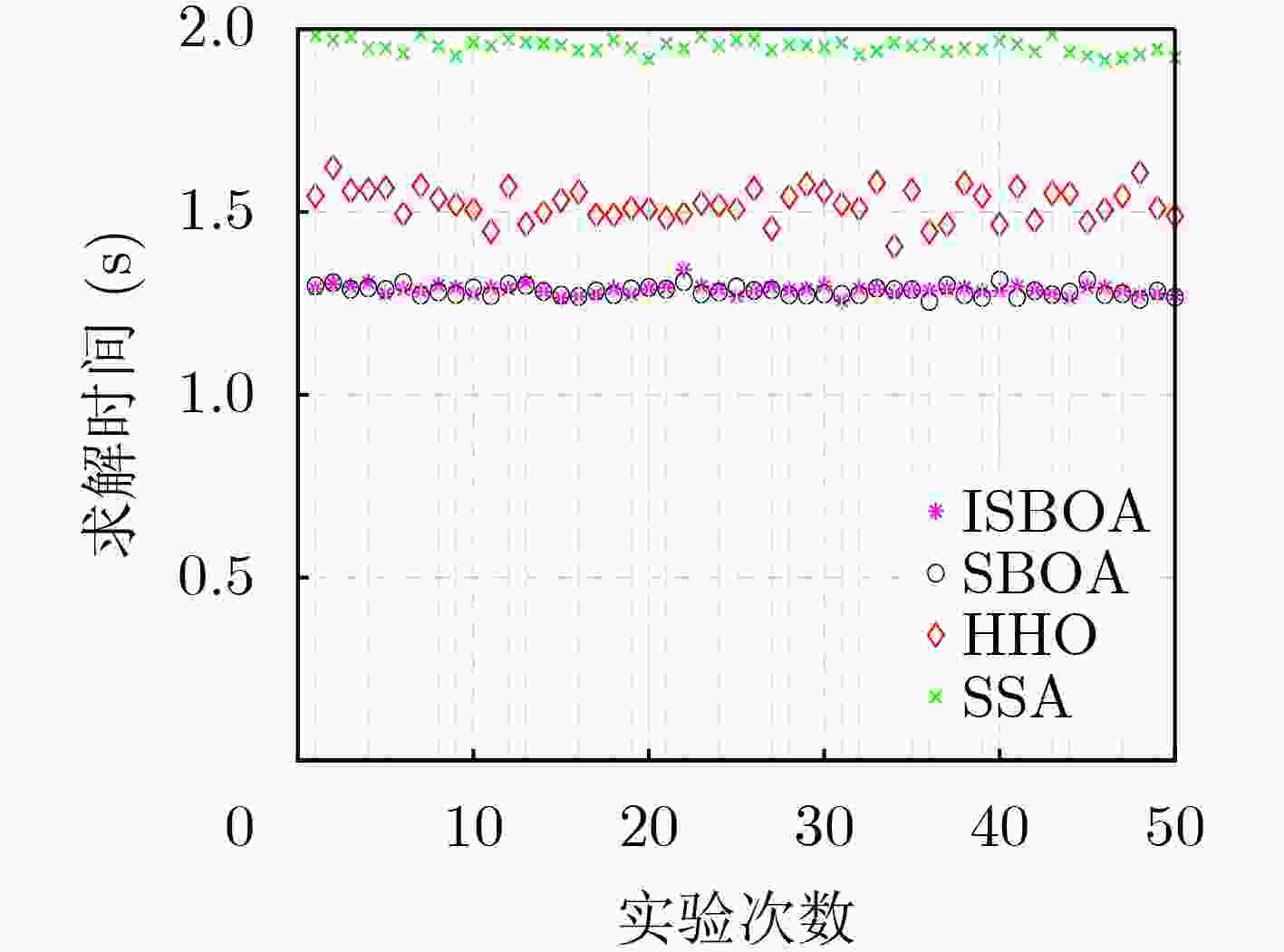
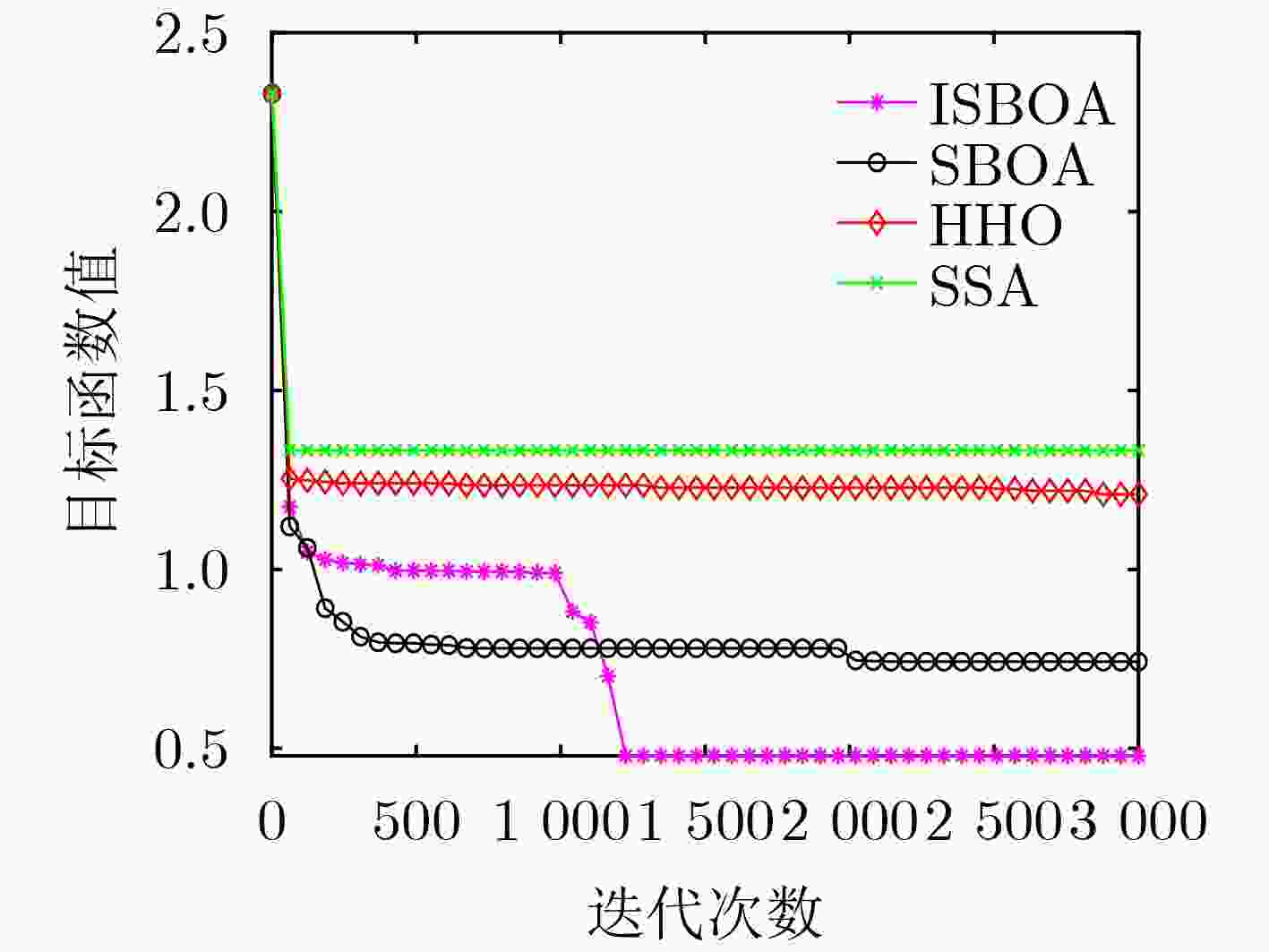
Objective In the complex electromagnetic environment of Networked Radars (NR), efficiently utilizing limited interference resources to reduce enemy detection capabilities and support successful penetration remains a critical challenge. Existing heuristic algorithms, while partially effective, do not jointly optimize interference patterns, beams, and power resources in multi-beam systems, limiting their applicability in penetration scenarios. To address this limitation, this study proposes an interference resource allocation strategy based on the Improved Secretary Bird Optimization Algorithm (ISBOA). The proposed strategy minimizes detection probability by integrating Cauchy mutation and global collaborative control, enabling the joint optimization of interference patterns, beams, and power across multiple jammers. This approach ensures rational resource allocation, enhances search capability, and improves convergence accuracy, thereby meeting the demands of penetration scenarios. The findings provide a novel solution for interference resource allocation in multi-beam systems against NR. Methods This study models the complex interference resource allocation problem as a multi-constrained nonlinear mixed-integer programming problem and addresses it using an improved intelligent optimization algorithm. A mixed-integer programming model incorporating interference patterns, beams, and power resources is established, with the detection and fusion probability of networked radar as the performance evaluation metric. The model accounts for the dynamic interactions between radars and jammers, as well as the pulse compression gains of various interference patterns. To overcome the limitations of the traditional Secretary Bird Optimization Algorithm (SBOA) in handling discrete variables and complex constraints, the study integrates Cauchy mutation and global collaborative control strategies. Cauchy mutation leverages its long-tail characteristics to enhance the algorithm’s global search capability, reducing the risk of convergence to local optima. The global collaborative control strategy incorporates penalty factors to ensure compliance with multi-variable constraints, enabling the simultaneous optimization of discrete and continuous variables. Results and Discussions This study presents an innovative interference resource allocation method for multi-beam jamming systems targeting networked radar, leveraging the ISBOA. By integrating Cauchy mutation and global cooperative control strategies, ISBOA significantly enhances optimization performance. Simulation results indicate that ISBOA outperforms other algorithms, including the original SBOA, Harris Hawks Optimizer (HHO), and Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA). In a scenario with six jammers and eight radars, ISBOA achieved an optimal function value of 0.6095 , which is notably lower than0.8158 (SBOA),1.2666 (HHO), and1.3679 (SSA) (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, ISBOA demonstrated faster convergence and greater stability across 50 independent experiments, yielding an average optimal function value of0.6892 (Fig. 5 ) and a convergence error of0.1449 (Fig. 6 ). ISBOA’s joint optimization of interference patterns, beams, and power resources enables more efficient allocation of jamming resources and reduces the detection probability of networked radar. This advantage is further validated across various scenarios, where ISBOA consistently outperformed other algorithms in solution quality and computational efficiency (Fig. 8 ). The experimental results highlight ISBOA’s robustness and adaptability, demonstrating its potential for application in complex battlefield environments.Conclusions This study proposes an optimization method for interference resource allocation in multi-beam jamming systems targeting networked radar scenarios, utilizing ISBOA. A mixed-integer programming model integrating interference patterns, beams, and power resources is developed. ISBOA incorporates Cauchy mutation and global cooperative control strategies to enhance global search capability and stability. Simulation results demonstrate that ISBOA outperforms the original SBOA, HHO, and SSA in terms of convergence speed and search efficiency. ISBOA exhibits superior stability and enables more rational allocation of interference resources, effectively reducing the detection probability of networked radar. Moreover, ISBOA demonstrates strong adaptability and robustness across various scenarios, providing an effective solution for interference resource allocation in complex battlefield environments. -
表 1 干扰信号脉压增益
干扰样式 脉压增益 参数说明 随机移频干扰 ${\left(1 - \dfrac{{|\zeta |}}{B}\right)^2}B\tau $ $\zeta $为移频宽度
$B$为信号宽度
$\tau $为信号时宽卷积灵巧噪声干扰 $\dfrac{{\tau + {\tau _n}}}{{1/B + {\tau _n}}}$ ${\tau _n}$为噪声时宽 间歇采样重复转发干扰 $\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\eta ^2} + 2\dfrac{{{{\sin }^2}\left( {\pi \eta } \right)}}{{{\pi ^2}}}} \end{array}} \right)B\tau $ $\eta $为间隙采样占空比 表 2 不同融合准则对应的检测概率
融合准则 检测概率 AND准则(K=N) $ {\rm{P d}}_{q}^{t}=\displaystyle\prod_{n=1}^{N} {\rm{P d}}_{n, A}^{t} $ OR准则(K=1) ${\mathrm{Pb}}_q^t=1-\displaystyle\prod_{n=1}^N(1-{\mathrm{Pd}}_{n,q}^t) $ 秩K准则 ${\mathrm{Pd}}_q^t = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{f = K}^N {\left\{ {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{\forall \left\{ {\displaystyle\sum {{h_n}} = f} \right\}} {\left( {\displaystyle\prod\limits_n {{{\left( {{\mathrm{Pd}}_{n,q}^t} \right)}^{{h_n}}}} {{\left( {1 - {\mathrm{Pd}}_{n,q}^t} \right)}^{1 - {h_n}}}} \right)} } \right\}} $ 表 3 雷达的仿真参数设置
参数名称 参数值 雷达功率(kW) 200 天线增益(dB) 45 脉冲宽度(μs) 1 工作波长(m) 0.1 虚警概率 ${10^{ - 6}}$ 目标雷达散射截面(m2) 1 有效噪声温度(K) 290 噪声系数(dB) 3 表 4 干扰机及干扰信号参数设置
参数名称 参数值 干扰总功率(W) 600 单机最小发射功率(W) 0 单机最大发射功率(W) 100 天线增益(dB) 10 极化失配损失 0.5 间歇转发占空比 0.5 移频最大带宽(MHz) 2.5 卷积视频噪声宽度(μs) 0.2 表 5 干扰样式分配结果
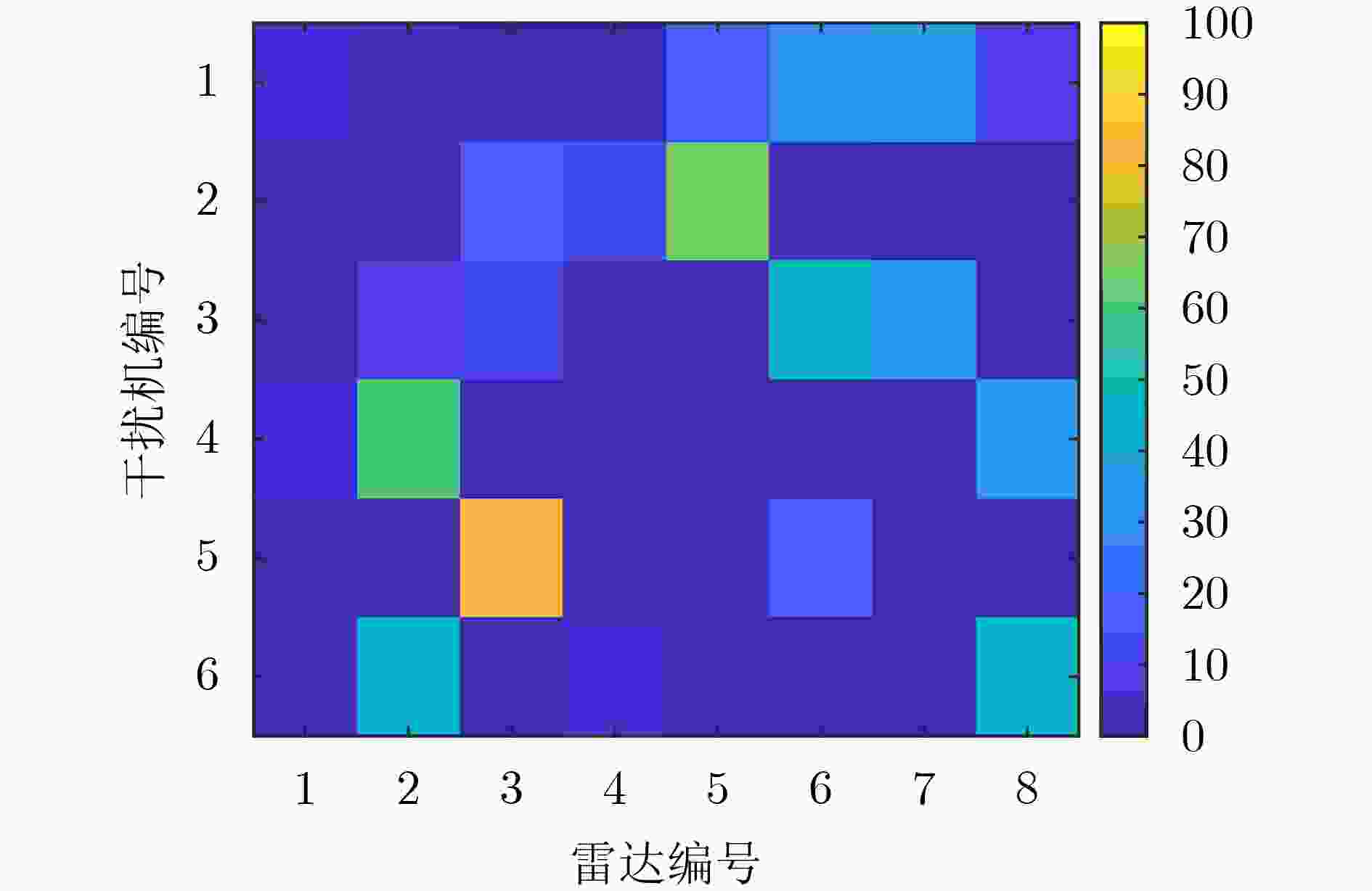
干扰机编号 干扰样式 1 间歇采样重复转发干扰 2 随机移频干扰 3 灵巧噪声卷积干扰 4 随机移频干扰 5 间歇采样重复转发干扰 6 间歇采样重复转发干扰 表 6 算法总体性能对比
算法名称 最优目标函数平均值 收敛误差平均值 ISBOA 0.6892 0.1449 SBOA 0.6936 0.1647 HHO 0.9409 0.1911 SSA 0.9924 0.2384 -
[1] 张养瑞, 高梅国, 罗皓月, 等. 基于检测概率的雷达网协同干扰效果评估方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(8): 1778–1786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.08.10.ZHANG Yangrui, GAO Meiguo, LUO Haoyue, et al. Evaluation method of cooperative jamming effect on radar net based on detection probability[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(8): 1778–1786. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.08.10. [2] 胡莹, 黄永明, 俞菲, 等. 多用户大规模MIMO系统能效资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(9): 2198–2203. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150088.HU Ying, HUANG Yongming, YU Fei, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation based on multi-user massive MIMO system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2015, 37(9): 2198–2203. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150088. [3] 赵忠凯, 王鸿. 组网雷达协同干扰资源分配模型及算法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2019, 44(5): 85–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2019.05.019.ZHAO Zhongkai and WANG Hong. Model and algorithm of cooperative jamming resource allocation for network radar[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2019, 44(5): 85–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2019.05.019. [4] WU Jiale, SHI Chenguang, ZHANG Weiwei, et al. Power control game between a distributed radar network and a smart jammer[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2024, 18(1): 61–72. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2023.3334759. [5] 王跃东, 顾以静, 梁彦, 等. 伴随压制干扰与组网雷达功率分配的深度博弈研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023.WANG Yuedong, GU Yijing, LIANG Yan, et al. Deep game of escorting suppressive jamming and networked radar power allocation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023. [6] 韩鹏, 张龙. 雷达干扰资源优化分配博弈模型和算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(2): 78–83,90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.02.018.HAN Peng and ZHANG Long. Game model and algorithm of radar jamming resources optimization allocation[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(2): 78–83,90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.02.018. [7] 王书剑, 李惠东. 改进灰狼算法在干扰资源分配中的应用[J]. 应用科技, 2021, 48(2): 54–57,99. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202007006.WANG Shujian and LI Huidong. Research on improved gray wolf algorithm in interference resource allocation[J]. Applied Science and Technology, 2021, 48(2): 54–57,99. doi: 10.11991/yykj.202007006. [8] HE Bin and SU Hongtao. Joint power allocation and beamforming between a multistatic radar and jammer based on game theory[C]. 2019 IEEE 11th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks (ICCSN), Chongqing, China, 2019: 337–341. doi: 10.1109/ICCSN.2019.8905330. [9] 邢怀玺, 吴华, 陈游, 等. 基于多目标灰狼算法的干扰资源多效能优化方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(10): 1990–1998. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0559.XING Huaixi, WU Hua, CHEN You, et al. Multi-efficiency optimization method of jamming resource based on multi-objective grey wolf optimizer[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(10): 1990–1998. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0559. [10] 陈琳, 薛青, 张俊峰, 等. 基于频段覆盖率的协同空战干扰资源分配研究[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(1): 164–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2020.01.033.CHEN Lin, XUE Qing, ZHANG Junfeng, et al. Jamming resources allocation in cooperative air combat based on frequency coverage[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2020, 45(1): 164–168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2020.01.033. [11] 陈振坤, 程嗣怡, 刘丹, 等. 基于改进蝴蝶算法的协同干扰资源分配方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2023, 45(3): 98–106. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.03.016.CHEN Zhenkun, CHENG Siyi, LIU Dan, et al. A method of cooperative interference resource allocation based on improved butterfly optimization algorithm[J]. Modern Radar, 2023, 45(3): 98–106. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.03.016. [12] 尧泽昆, 王超, 施庆展, 等. 基于改进离散模拟退火遗传算法的雷达网协同干扰资源分配模型[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(3): 824–830. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.03.07.YAO Zekun, WANG Chao, SHI Qingzhan, et al. Cooperative jamming resource allocation model for radar network based on improved discrete simulated annealing genetic algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(3): 824–830. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.03.07. [13] 柳向, 李东生, 吴世俊. 改进布谷鸟算法在协同干扰资源分配中的应用[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(2): 84–90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.02.019.LIU Xiang, LI Dongsheng, and WU Shijun. Application of improved cuckoo search algorithm in optimization assignment for cooperative jamming resources[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(2): 84–90. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.02.019. [14] 陆德江, 王星, 陈游, 等. 联合多种资源协同干扰组网雷达系统的自适应调度方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(9): 2744–2754. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.09.12.LU Dejiang, WANG Xing, CHEN You, et al. Adaptive scheduling method of joint multi-resource for cooperative interference of networked radar system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(9): 2744–2754. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.09.12. [15] 孟超普, 程林, 王秀锦. 对线性调频脉压雷达的改进移频干扰研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2016, 39(3): 1–6. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2016.03.001.MENG Chaopu, CHENG Lin, and WANG Xiujin. Research into improved frequency-shift jamming to linear frequency modulation pulse compression radar[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2016, 39(3): 1–6. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2016.03.001. [16] 吕波, 冯起, 袁乃昌. 对LFM脉压雷达的移频压制干扰技术研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2009, 31(1): 9–12,17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2009.01.003.LV Bo, FENG Qi, and YUAN Naichang. A study on frequency-shifting blanket jamming to LFM pulse-compression radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2009, 31(1): 9–12,17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2009.01.003. [17] 张煜, 杨绍全. 对线性调频雷达的卷积干扰技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(6): 1408–1411. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.01388.ZHANG Yu and YANG Shaoquan. Convolution jamming technique countering LFM radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2007, 29(6): 1408–1411. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.01388. [18] JIANG Haiqing, ZHANG Yangrui, and XU Hongyi. Optimal allocation of cooperative jamming resource based on hybrid quantum-behaved particle swarm optimisation and genetic algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(1): 185–192. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0119. [19] GAO Xiangqiang, LIU Rongke, and KAUSHIK A. Hierarchical multi-agent optimization for resource allocation in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32(3): 692–707. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2020.3030920. [20] FU Youfa, LIU Dan, CHEN Jiadui, et al. Secretary bird optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic for solving global optimization problems[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2024, 57(5): 123. doi: 10.1007/s10462-024-10729-y. [21] 李楠, 薛建凯, 舒慧生. 基于自适应t分布变异麻雀搜索算法的无人机航迹规划[J]. 东华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 48(3): 69–74. doi: 10.19886/j.cnki.dhdz.2021.0223.LI Nan, XUE Jiankai, and SHU Huisheng. A sparrow search algorithm with adaptive t distribution mutation-based path planning of unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Donghua University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 48(3): 69–74. doi: 10.19886/j.cnki.dhdz.2021.0223. [22] HEIDARI A A, MIRJALILI S, FARIS H, et al. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 97: 849–872. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.02.028. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
