Model and Data Dual-driven Joint Limited-Angle CT Reconstruction and Metal Artifact Reduction Method
-
摘要: 有限角度计算机断层扫描(LACT)旨在通过减少扫描角度的范围来减少辐射剂量。由于投影数据是不完备的且未考虑联合有限角度和金属伪影校正(LAMAR)任务,传统方法重建的CT图像往往存在伪影,特别是当患者携带金属植入物时,伪影将进一步加重,影响后期医疗诊断及下游任务的精度。为解决这一问题,该文利用双域知识和深度展开技术,融合Transformer的非局部特性捕获能力和卷积神经网络(CNN)的局部特征提取能力,提出了能够联合解决LAMAR和LACT任务的模型与数据双驱动双域重建网络,记为MD3Net。该文首先构建了双域优化模型,使用邻近梯度下降算法对优化模型进行求解,并将其展开成模型驱动的CT重建网络。其次,设计了任务选择(TS)模块,通过判断初始估计CT图像中有无金属以利用同一模型同时处理有金属和无金属的重建任务。在数据驱动网络中,构建了融合Transformer和CNN的双分支的迹感知投影域邻近子网络和结合通道注意力、空间注意力的图像域邻近子网络,进而提升网络表示能力。实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,所提算法在联合LACT和LAMAR任务上重建效果更好。Abstract:
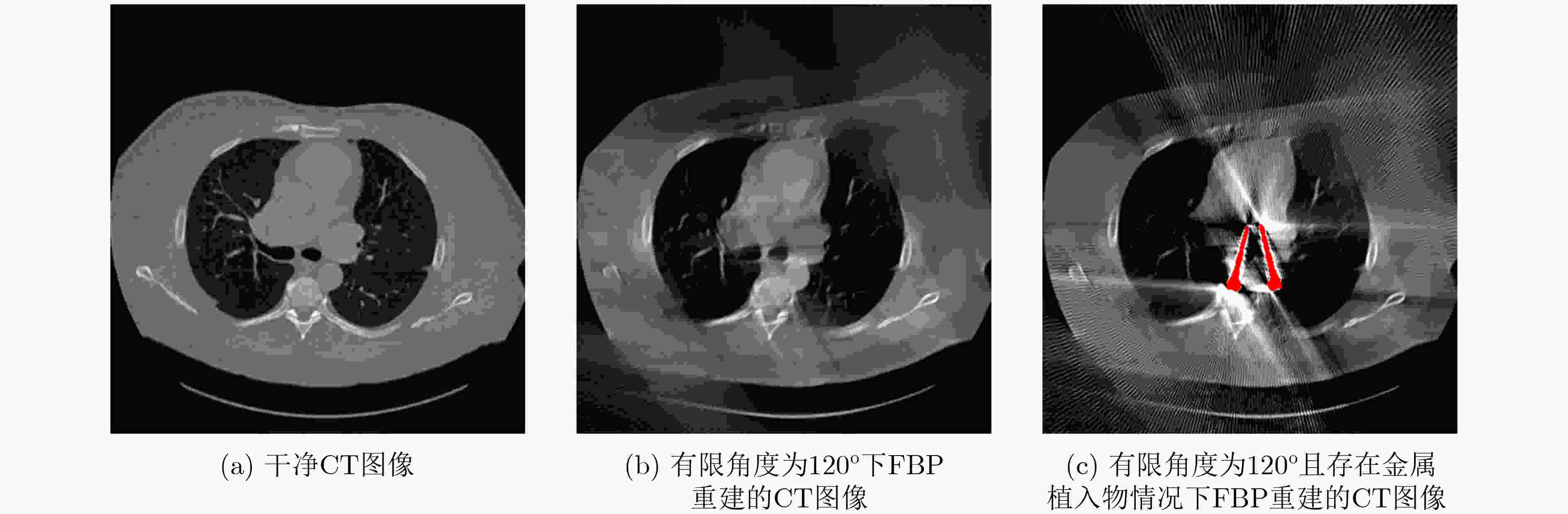
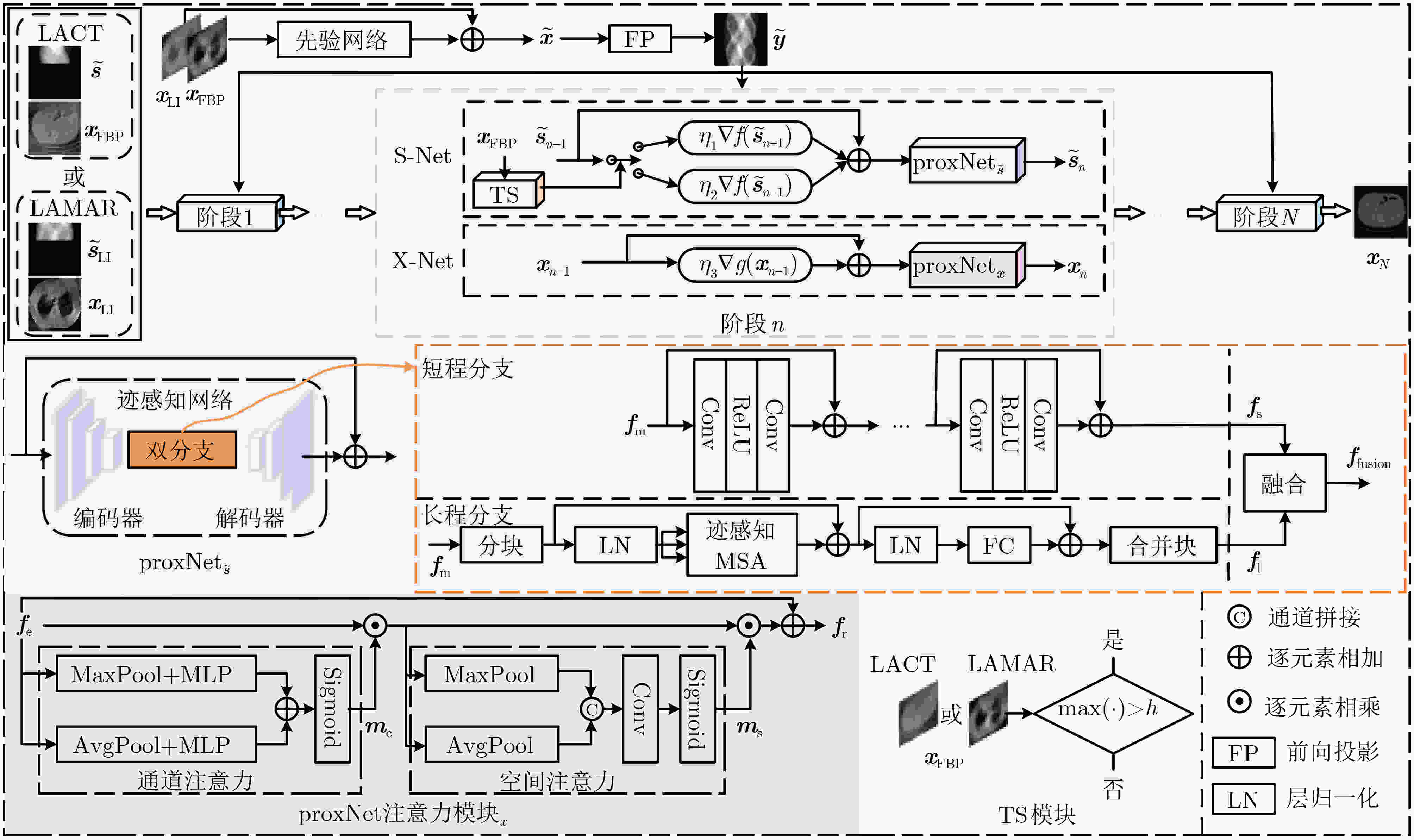
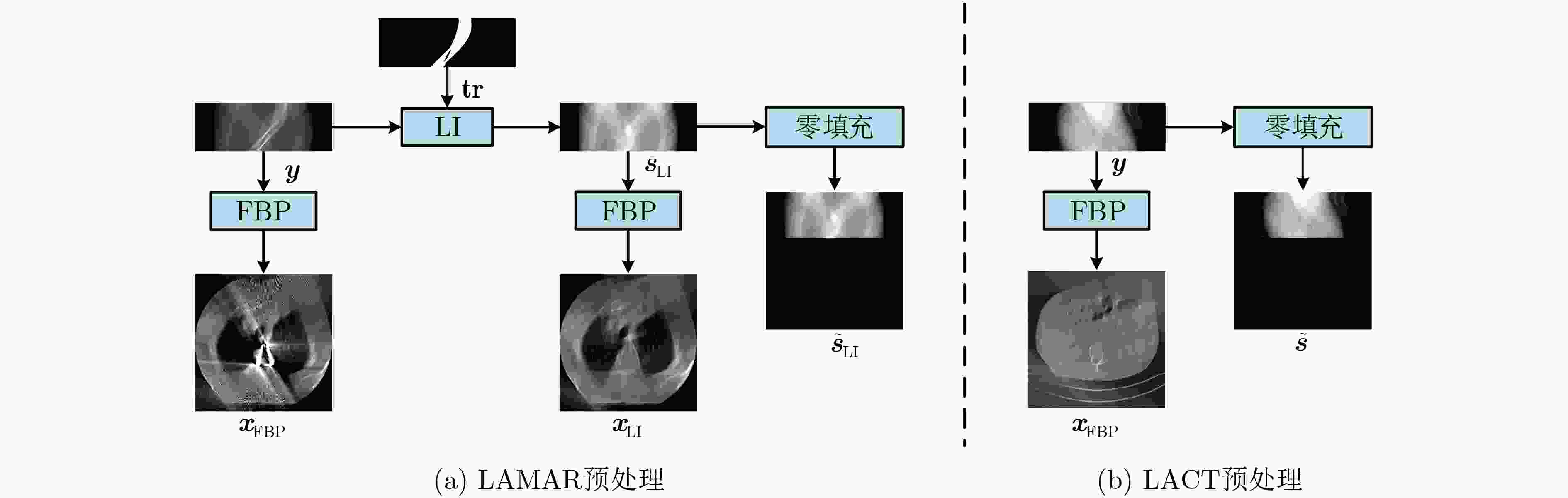
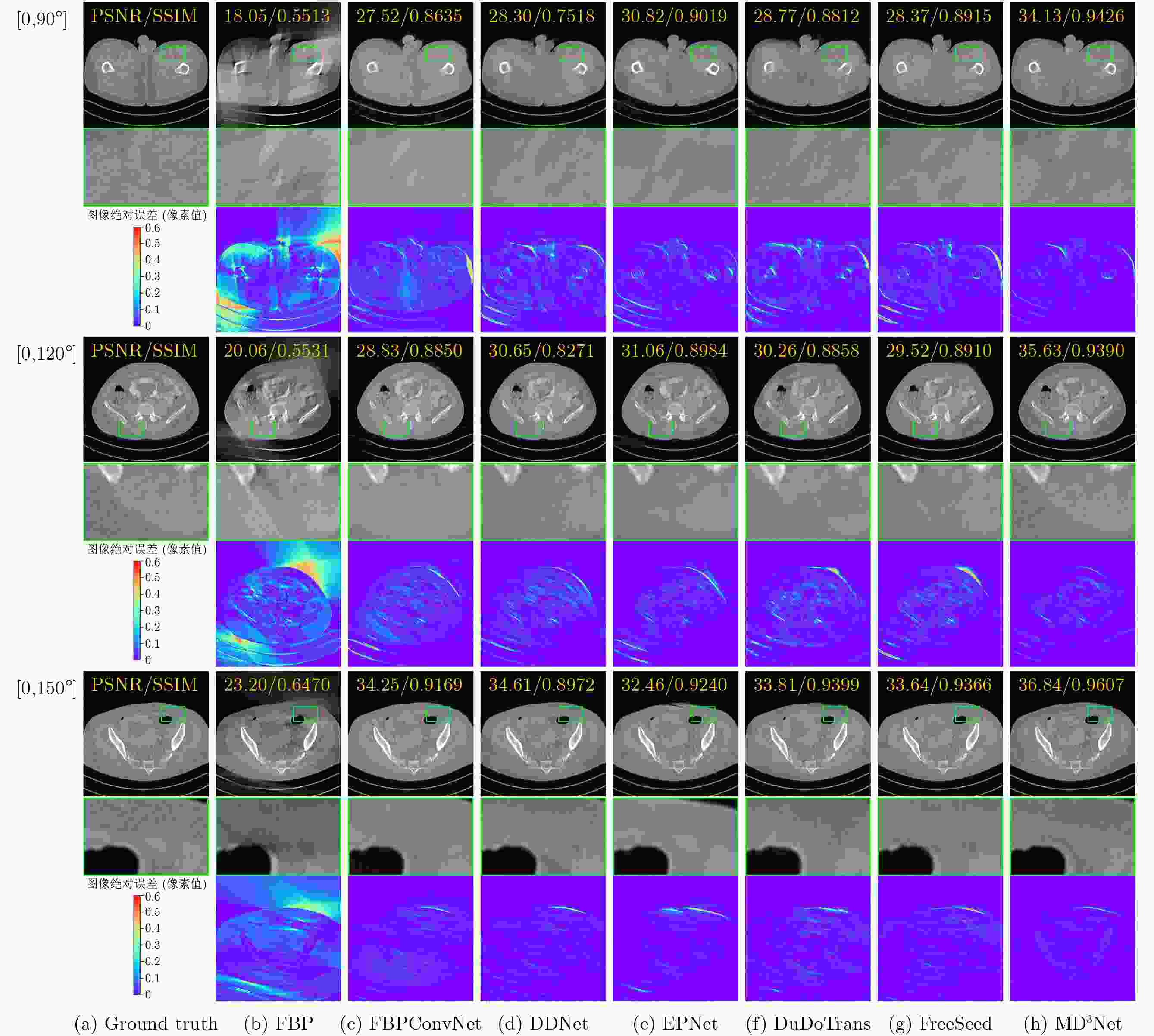
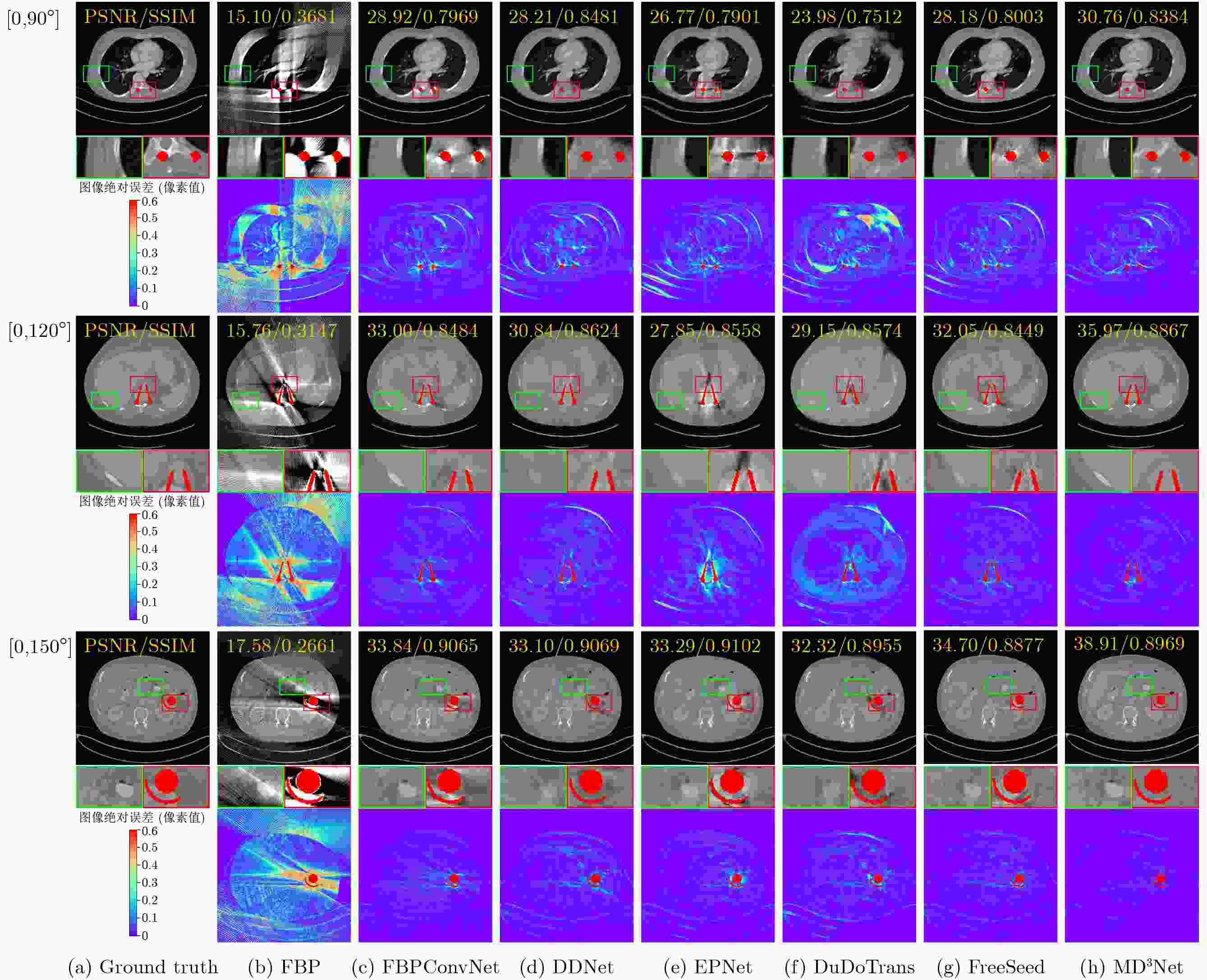
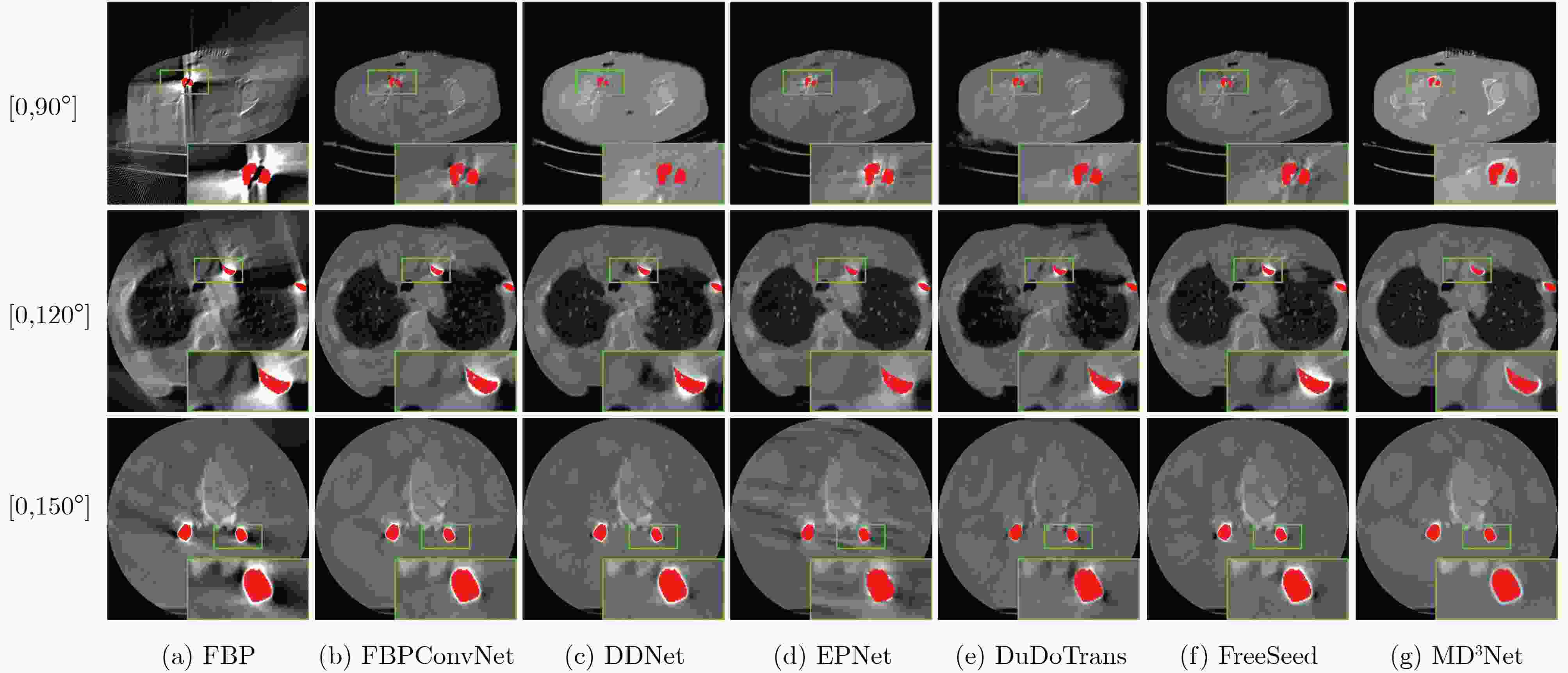
Objective Computed Tomography (CT) is widely used in medical diagnostics due to its non-destructive, non-contact imaging capabilities. To lower cancer risk from radiation exposure, clinical practice often limits scanning angles, referred to as Limited-Angle CT (LACT). Incomplete projection data in LACT leads to wedge-shaped artifacts in reconstructions using Filtered Back-Projection (FBP) algorithms. These artifacts worsen in the presence of metallic implants. Although LACT reconstruction without metal and full-angle CT Metal Artifact Reduction (MAR) have been extensively studied, the joint task of Limited-Angle and Metal Artifact Reduction (LAMAR) has received limited attention. This study proposes a model- and data-driven CT network that integrates a Task Selection (TS) module to apply appropriate gradient descent steps for different tasks. This enables simultaneous processing of LACT and LAMAR. The network also incorporates dual-domain information interaction during alternating iterations to reconstruct high-quality CT images. Methods First, a dual-domain reconstruction model integrating both model- and data-driven model is constructed to address the joint task of LACT reconstruction and LAMAR. The model comprises four components: an image-domain data fidelity term, a projection-domain data fidelity term, an image-domain regularization term, and a projection-domain regularization term. These terms are solved using an alternating iteration strategy. The image- and projection-domain subproblems are addressed using the proximal gradient descent algorithm, with the iterative process unrolled into a Deep Neural Network (DNN). Each stage of the deep unrolling network includes three components: a TS module, a projection-domain subnetwork, and an image-domain subnetwork. The TS module dynamically determines gradient descent step sizes for the LACT and LAMAR tasks by comparing image-domain FBP reconstruction results with predefined thresholds. The projection-domain subnetwork is shared by both tasks. Finally, the data-driven proximal network comprises the projection-domain and image-domain subnetworks. The projection-domain subnetwork includes an encoder, a dual-branch structure, and a decoder. The encoder has two stages, each consisting of a convolutional layer followed by an activation function; the decoder mirrors this architecture. A Transformer-based long-range branch incorporates non-metal trace information into a self-attention mechanism to guide correction of metal trace data using contextual information from non-metal regions. A short-range branch, composed of six residual blocks, extracts local features. The outputs of the two branches are fused using a weighted strategy before being passed to the decoder. The image-domain subnetwork is implemented as an attention-based U-Net. Channel and spatial attention mechanisms are applied before each of the four downsampling operations in the U-Net encoder. This design allows the decoder to more effectively leverage encoded information for high-quality CT image reconstruction without increasing the number of network parameters. Results and Discussions Experimental results on both LACT reconstruction and LAMAR tasks show that the proposed method outperforms existing CT reconstruction algorithms in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Quantitative comparisons ( Table 1 ) indicate that the proposed method achieves higher average Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and lower Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) for both tasks across three angular ranges. Specifically, average PSNR improvements for the LAMAR and LACT tasks reach 2.78 dB, 2.88 dB, and 2.32 dB, respectively, compared with the best-performing baseline methods. Qualitative comparisons (Fig 4 andFig 5 ) show that reconstructing CT images and projection data through alternating iterations, combined with dual-domain information interaction, enables the network to effectively suppress composite artifacts and improve the reconstruction of soft tissue regions and fine structural details. These results consistently exceed those of existing approaches. Visual assessment of reconstruction performance on the clinical dataset for the LAMAR task (Fig 6 ) further demonstrates the method’s effectiveness in reducing metal artifacts around implants. The reconstructed images exhibit clearer structural boundaries and improved tissue visibility, indicating strong generalization to previously unseen clinical data.Conclusions To address the combined task of LACT reconstruction and LAMAR, this study proposes a dual-domain, model- and data-driven reconstruction framework. The optimization problem is solved using an alternating iteration strategy and unfolded into a model-driven CT reconstruction network, with each subnetwork trained in a data-driven manner. In the projection-domain network, a TS module identifies the presence of metallic implants in the initial CT estimates, allowing a single model to simultaneously handle cases with and without metal. A trace-aware projection-domain proximal subnetwork, integrating Transformer and convolutional neural network architectures, is designed to capture both local and non-local contextual features for restoring metal-corrupted regions. In the image-domain network, a U-Net architecture enhanced with channel and spatial attention mechanisms is used to maximize spatial feature utilization and improve reconstruction quality. Experimental results on the AAPM and DeepLesion datasets confirm that the proposed method consistently outperforms existing algorithms under various limited-angle conditions and in the presence of metal artifacts. Further evaluation on the SpineWeb dataset demonstrates the network’s generalization capability across clinical scenarios. -
表 1 使用PSNR(dB), SSIM和RMSE对3种有限角度设置下的LACT及LAMAR任务进行定量比较
方法 $ [0,{90^ \circ }] $ $ [0,{120^ \circ }] $ $ [0,{150^ \circ }] $ LACT LAMAR Average LACT LAMAR Average LACT LAMAR Average FBP[2] 17.27 0.5317 0.0688 14.82 0.3739 0.0927 16.05 0.4528 0.0808 19.51 0.5881 0.0532 17.16 0.3448 0.0709 18.34 0.4665 0.0621 22.97 0.6453 0.0358 19.68 0.2939 0.0533 21.33 0.4969 0.0446 FBPConvNet[16] 25.64 0.8431 0.0268 29.11 0.7877 0.0180 27.38 0.8154 0.0224 27.11 0.8822 0.0231 32.50 0.8575 0.0121 29.81 0.8699 0.0176 32.59 0.9141 0.0126 34.94 0.9224 0.0093 33.77 0.9183 0.0110 DDNet[17] 26.29 0.7397 0.0247 29.33 0.8688 0.0174 27.81 0.8043 0.0211 29.42 0.8301 0.0175 31.13 0.8745 0.0141 30.28 0.8523 0.0158 34.23 0.8878 0.0101 33.28 0.9131 0.0111 33.76 0.9005 0.0106 EPNet[10] 27.85 0.8359 0.0211 28.63 0.8368 0.0189 28.24 0.8364 0.0200 29.59 0.8818 0.0172 30.14 0.8635 0.0160 29.87 0.8727 0.0166 34.31 0.9312 0.0105 33.43 0.9156 0.0111 33.87 0.9234 0.0108 DuDoTrans[8] 26.65 0.8542 0.0236 25.48 0.7717 0.0272 26.07 0.8130 0.0254 29.09 0.8896 0.0181 28.17 0.8492 0.0199 28.63 0.8694 0.0190 32.83 0.9268 0.0119 31.34 0.8866 0.0139 32.09 0.9067 0.0129 FreeSeed[5] 26.05 0.8606 0.0254 29.55 0.8051 0.0170 27.80 0.8329 0.0212 28.58 0.8861 0.0192 32.03 0.8674 0.0128 30.31 0.8768 0.0160 33.78 0.9284 0.0108 34.88 0.9044 0.0092 34.33 0.9164 0.0100 MD3Net 30.39 0.9142 0.0162 31.45 0.8404 0.0139 30.92 0.8773 0.0151 32.25 0.9309 0.0137 34.12 0.8625 0.0100 33.19 0.8967 0.0119 35.20 0.9507 0.0099 38.09 0.8934 0.0064 36.65 0.9221 0.0082 表 2 本文方法各个模块3个角度下对联合LACT和LAMAR任务的平均PSNR(dB)/SSIM
方法 X-Net S-Net S-Net w/o L X-Net w/o A $ [0,{90^ \circ }] $ $ [0,{120^ \circ }] $ $ [0,{150^ \circ }] $ Average PSNR/SSIM PSNR/SSIM PSNR/SSIM PSNR/SSIM M1 √ × × × 30.78/ 0.8698 32.83/ 0.8668 35.56/ 0.9183 33.09/ 0.8850 M2 × √ × × 26.67/ 0.6737 27.95/ 0.6934 30.18/ 0.7616 28.27/ 0.7096 M3 √ × √ × 30.66/ 0.8721 32.97/ 0.8927 36.26/ 0.9120 33.30/ 0.8923 M4 × √ × √ 30.83/ 0.8639 33.11/ 0.8878 36.49/ 0.9171 33.48/ 0.8896 M5 √ √ × × 30.92/ 0.8773 33.19/ 0.8967 36.65/ 0.9221 33.59/ 0.8987 表 3 MD3Net关于阈值h的性能分析
阈值h LACT LAMAR Average PSNR(dB)/
SSIMPSNR(dB)/
SSIMPSNR(dB)/
SSIM1 30.70/ 0.9133 30.64/ 0.7999 30.67/ 0.8566 1.5 30.39/ 0.9142 31.45/ 0.8404 30.92/ 0.8773 2 30.67/ 0.9124 30.99/ 0.7894 30.83/ 0.8509 1.5(可学习的) 30.87/ 0.9115 30.93/ 0.8111 30.90/ 0.8613 -
[1] DE BASEA M B, THIERRY-CHEF I, HARBRON R, et al. Risk of hematological malignancies from CT radiation exposure in children, adolescents and young adults[J]. Nature Medicine, 2023, 29(12): 3111–3119. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02620-0. [2] PAN Xiaochuan, SIDKY E Y, and VANNIER M. Why do commercial CT scanners still employ traditional, filtered back-projection for image reconstruction?[J]. Inverse Problems, 2009, 25(12): 123009. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/25/12/123009. [3] YOO S, YANG Xiaogang, WOLFMAN M, et al. Sinogram image completion for limited angle tomography with generative adversarial networks[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, China, 2019: 1252–1256. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2019.8804416. [4] ZHANG Yanbo and YU Hengyong. Convolutional neural network based metal artifact reduction in x-ray computed tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1370–1381. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2823083. [5] MA Chenglong, LI Zilong, ZHANG Junping, et al. FreeSeed: Frequency-band-aware and self-guided network for sparse-view CT reconstruction[C]. 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 250–259. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-43999-5_24. [6] SHI Baoshun, ZHANG Shaolei, and FU Zhaoran. Artifact region-aware transformer: Global context helps CT metal artifact reduction[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024, 31: 1249–1253. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2024.3393355. [7] 于佳弘, 张昆鹏, 靳爽, 等. 弦图插值结合UNIT网络图像转换的CT金属伪影校正[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1214–1223. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.07.18.YU Jiahong, ZHANG Kunpeng, JIN Shuang, et al. Sinogram interpolation combined with unsupervised image-to-image translation network for CT metal artifact correction[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1214–1223. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.07.18. [8] WANG Ce, SHANG Kun, ZHANG Haimiao, et al. DuDoTrans: Dual-domain transformer for sparse-view CT reconstruction[C]. 5th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Medical Image Reconstruction, Singapore, 2022: 84–94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-17247-2_9. [9] LIN Weian, LIAO Haofu, PENG Cheng, et al. DuDoNet: Dual domain network for CT metal artifact reduction[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 10504–10513. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.01076. [10] WANG Ce, ZHANG Haimiao, LI Qian, et al. Improving generalizability in limited-angle CT reconstruction with sinogram extrapolation[C]. 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 2021: 86–96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_9. [11] WAGN Hong, LI Yuexiang, MENG Deyu, et al. Adaptive convolutional dictionary network for CT metal artifact reduction[C]. Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, 2022: 1401–1407. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2022/195. [12] 袁伟, 席雅睿, 谭川东, 等. 基于Swin-Transformer迭代展开的有限角CT图像重建用于PTCT成像[J]. 光学学报, 2024, 44(8): 0834001. doi: 10.3788/AOS231823.YUAN Wei, XI Yarui, TAN Chuandong, et al. Limited-angle CT image reconstruction based on Swin-Transformer iterative unfolding for PTCT imaging[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(8): 0834001. doi: 10.3788/AOS231823. [13] 赵云松, 李宏伟, 张朋. 有限角CT成像研究进展[J]. 中国体视学与图像分析, 2022, 27(4): 436–446. doi: 10.13505/j.1007-1482.2022.27.04.010.ZHAO Yunsong, LI Hongwei, and ZHANG Peng. Development of limited-angle CT imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Stereology and Image Analysis, 2022, 27(4): 436–446. doi: 10.13505/j.1007-1482.2022.27.04.010. [14] YAZDANPANAH A P and REGENTOVA E E. Sparse-view CT reconstruction using curvelet and TV-based regularization[C]. 13th International Conference on Image Analysis and Recognition, Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal, 2016: 672–677. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41501-7_75. [15] XU Moran, HU Dianlin, LUO Fulin, et al. Limited-angle X-ray CT reconstruction using image gradient l0-norm with dictionary learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2021, 5(1): 78–87. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2020.2991887. [16] JIN K H, MCCANN M T, FROUSTEY E, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4509–4522. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2713099. [17] ZHANG Zhicheng, LIANG Xiaokun, DONG Xu, et al. A sparse-view CT reconstruction method based on combination of DenseNet and deconvolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1407–1417. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2823338. [18] GAO Yuan, ZHANG Liu, YU Wenxue, et al. Cas-PRED: A limited-angle cone beam CT reconstruction research based on prior information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 4504117. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3335513. [19] HU Dianlin, ZHANG Yikun, QUAN Guotao, et al. CROSS: Cross-domain residual-optimization-based structure strengthening reconstruction for limited-angle CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2023, 7(5): 521–531. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2023.3242662. [20] CHENG Weiting, HE Jichun, LIU Yi, et al. CAIR: Combining integrated attention with iterative optimization learning for sparse-view CT reconstruction[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2023, 163: 107161. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107161. [21] VERBURG J M and SECO J. CT metal artifact reduction method correcting for beam hardening and missing projections[J]. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 2012, 57(9): 2803–2818. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/9/2803. [22] KALENDER W A, HEBEL R, and EBERSBERGER J. Reduction of CT artifacts caused by metallic implants[J]. Radiology, 1987, 164(2): 576–577. doi: 10.1148/radiology.164.2.3602406. [23] MEYER E, RAUPACH R, LELL M, et al. Normalized metal artifact reduction (NMAR) in computed tomography[J]. Medical Physics, 2010, 37(10): 5482–5493. doi: 10.1118/1.3484090. [24] ZHANG Haimiao, DONG Bin, and LIU Baodong. A reweighted joint spatial-radon domain CT image reconstruction model for metal artifact reduction[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2018, 11(1): 707–733. doi: 10.1137/17M1140212. [25] WANG Hong, LI Yuexiang, ZHANG Haimiao, et al. InDuDoNet: An interpretable dual domain network for CT metal artifact reduction[C]. 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 2021: 107–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_11. [26] WANG Hong, LI Yuexiang, ZHANG Haimiao, et al. InDuDoNet+: A deep unfolding dual domain network for metal artifact reduction in CT images[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2023, 85: 102729. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102729. [27] SHI Baoshun, JIANG Ke, ZHANG Shaolei, et al. Mud-Net: Multi-domain deep unrolling network for simultaneous sparse-view and metal artifact reduction in computed tomography[J]. Machine Learning: Science and Technology, 2024, 5(1): 015010. doi: 10.1088/2632-2153/ad1b8e. [28] SHI Baoshun, ZHANG Shaolei, JIANG Ke, et al. Coupling model-and data-driven networks for CT metal artifact reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2024, 10: 415–428. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2024.3369408. [29] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [30] LIU Xiangbin, LIU Ying, FU Weina, et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: SCTV-UNet: A COVID-19 CT segmentation network based on attention mechanism[J]. Soft Computing, 2024, 28(2): 473. doi: 10.1007/s00500-023-07991-7. [31] MCCOLLOUGH C. TU-FG-207A-04: Overview of the low dose CT grand challenge[J]. Medical Physics, 2016, 43(6Part35): 3759–3760. doi: 10.1118/1.4957556. [32] YAN Ke, WANG Xiaosong, LU Le, et al. Deep lesion graphs in the wild: Relationship learning and organization of significant radiology image findings in a diverse large-scale lesion database[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9261–9270. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00965. [33] GLOCKER B, ZIKIC D, KONUKOGLU E, et al. Vertebrae localization in pathological spine CT via dense classification from sparse annotations[C]. 16th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Nagoya, Japan, 2013: 262–270. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5_33. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
