3D Model Classification Based on Central Anchor Hard Triplet Loss and Multi-view Feature Fusion
-
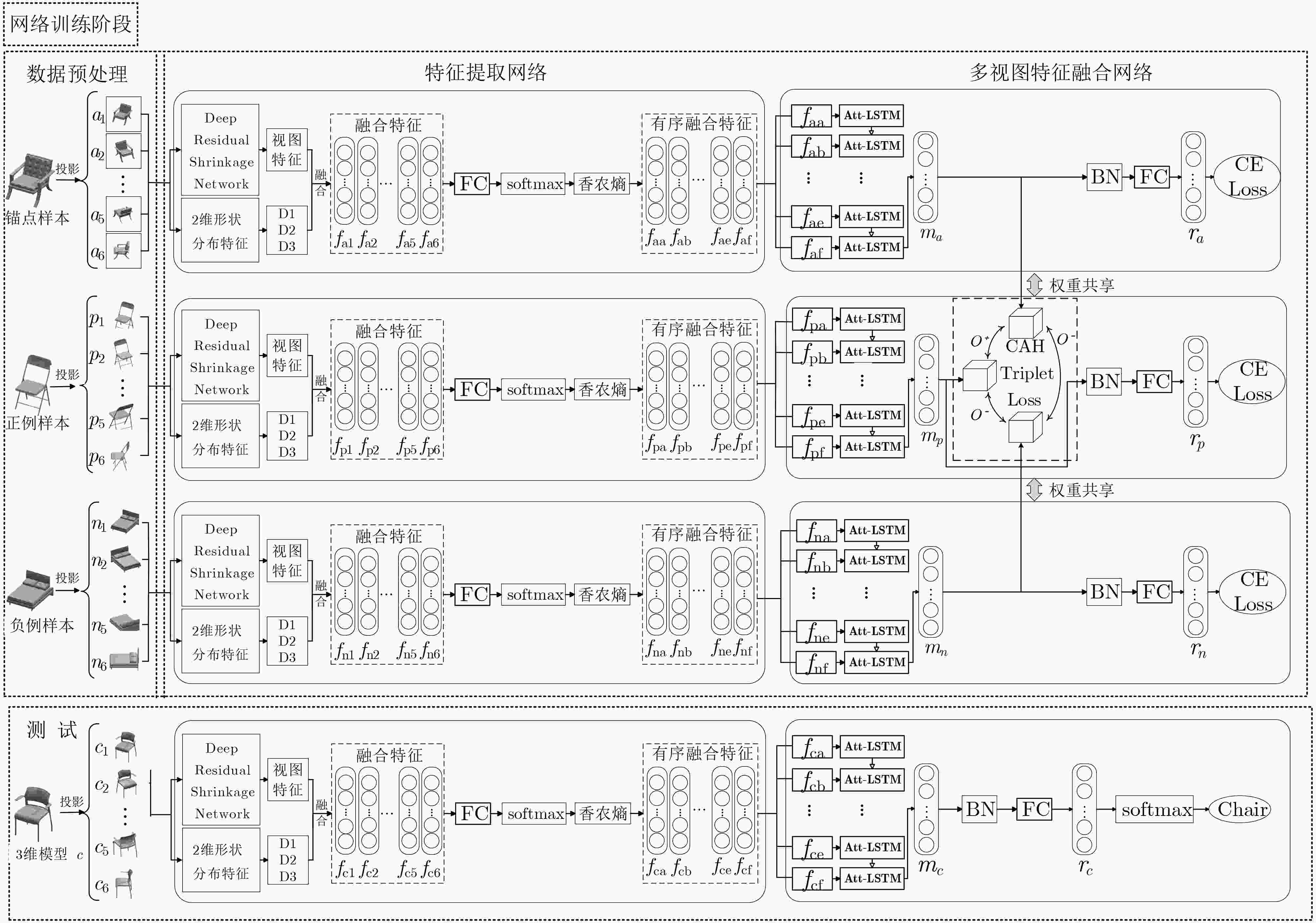
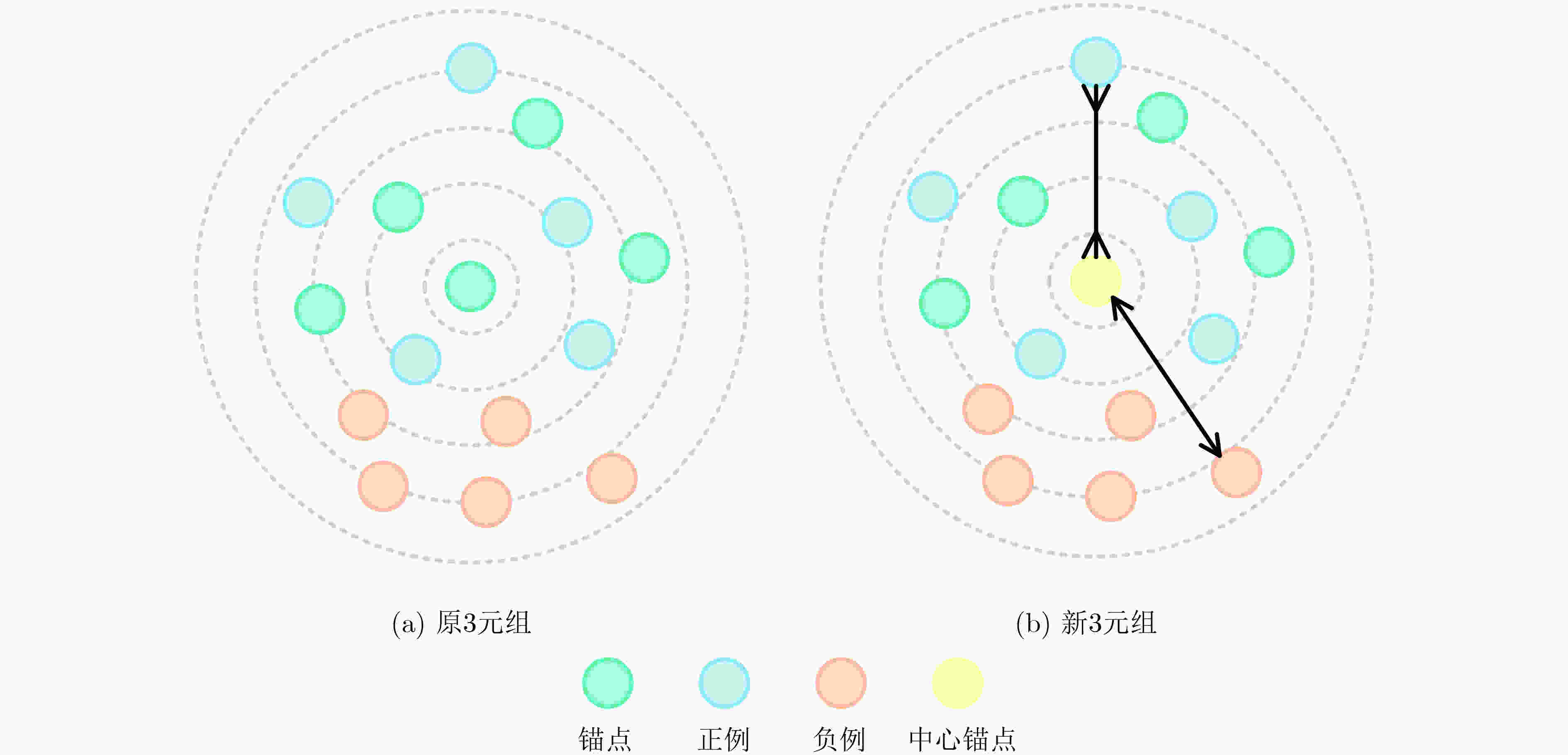
摘要: 多视图可以全面表征3维模型的视觉特性以及潜在的空间结构信息,但现有方法容易忽视不同视图间的差异性和互补性。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于中心锚困难3元组损失和多视图特征融合的3维模型分类方法。首先,以3维模型的多视图集为输入,利用深度残差收缩网络(DRSN)提取视图特征并融合2维形状分布特征D1, D2和D3得到视图融合特征;其次,根据3维模型视图融合特征,通过香农熵来衡量视图分类的不确定性,并将3维模型的多视图按视图显著性由高到低排序;然后,搭建基于注意力-长短期记忆网络(Att-LSTM)的3元组多视图特征融合网络,利用LSTM学习多视图之间的上下文信息,并融入多头注意力机制充分捕捉多视图间的相关信息;最后,引入度量学习并提出了一种新颖的中心锚困难3元组损失(CAH Triplet Loss),并联合交叉熵损失(CE Loss)来优化多视图特征融合网络,减小同类样本、增大异类样本在特征空间上的距离,加强网络对3维模型区分性特征的学习。实验表明:该方法在3维模型数据集ModelNet10上的分类准确率达到93.83%,分类性能突出。Abstract:
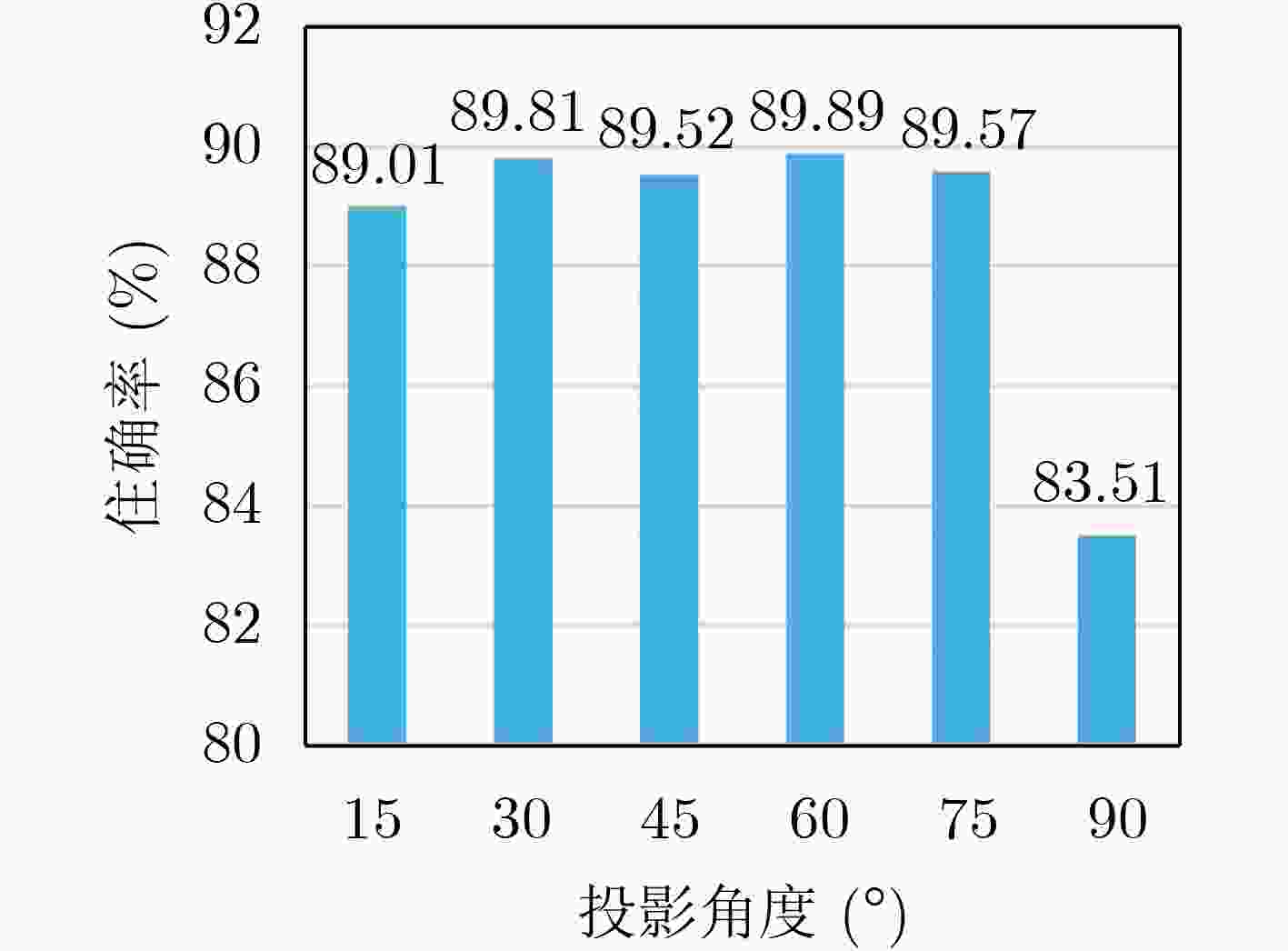
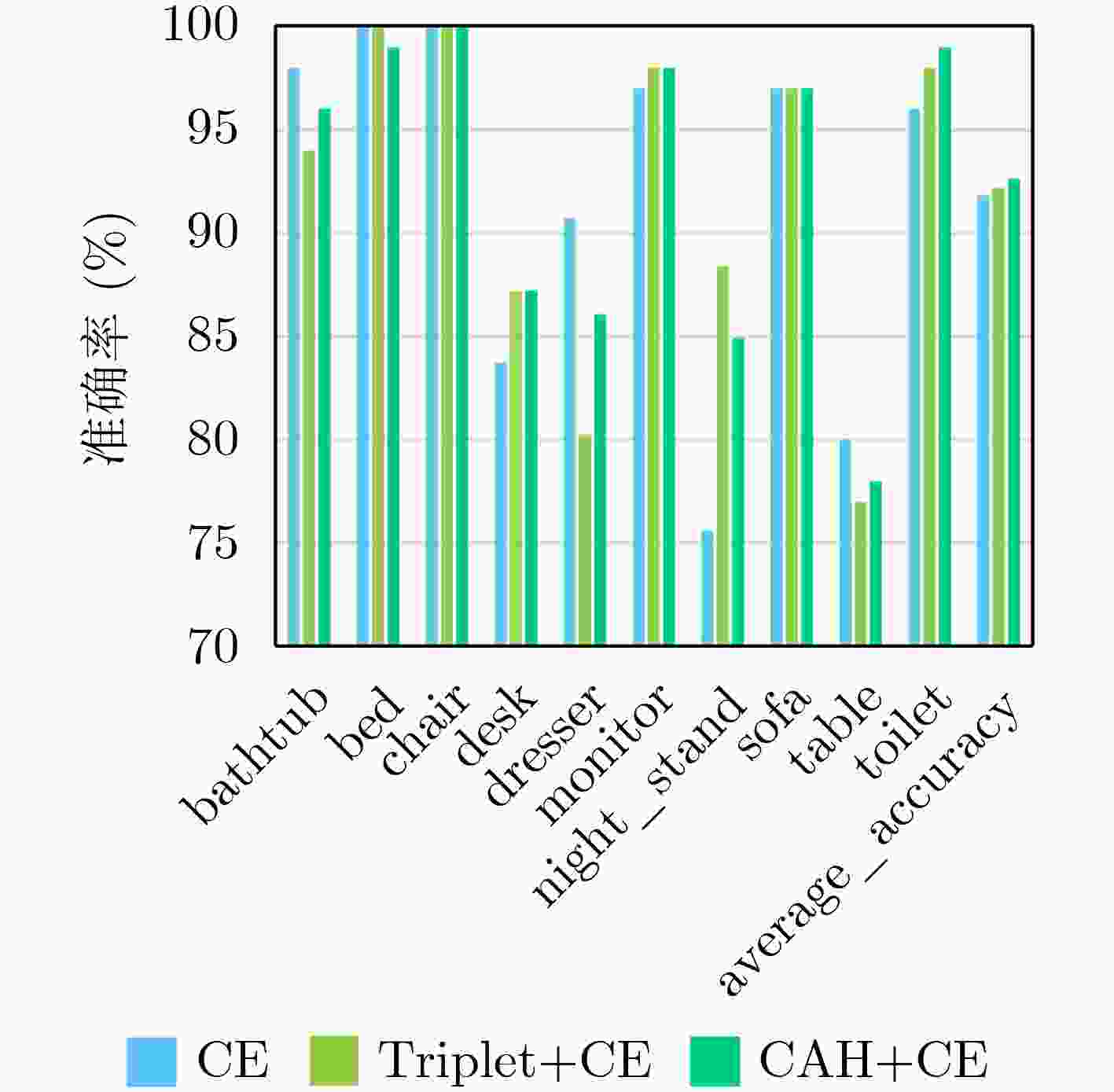
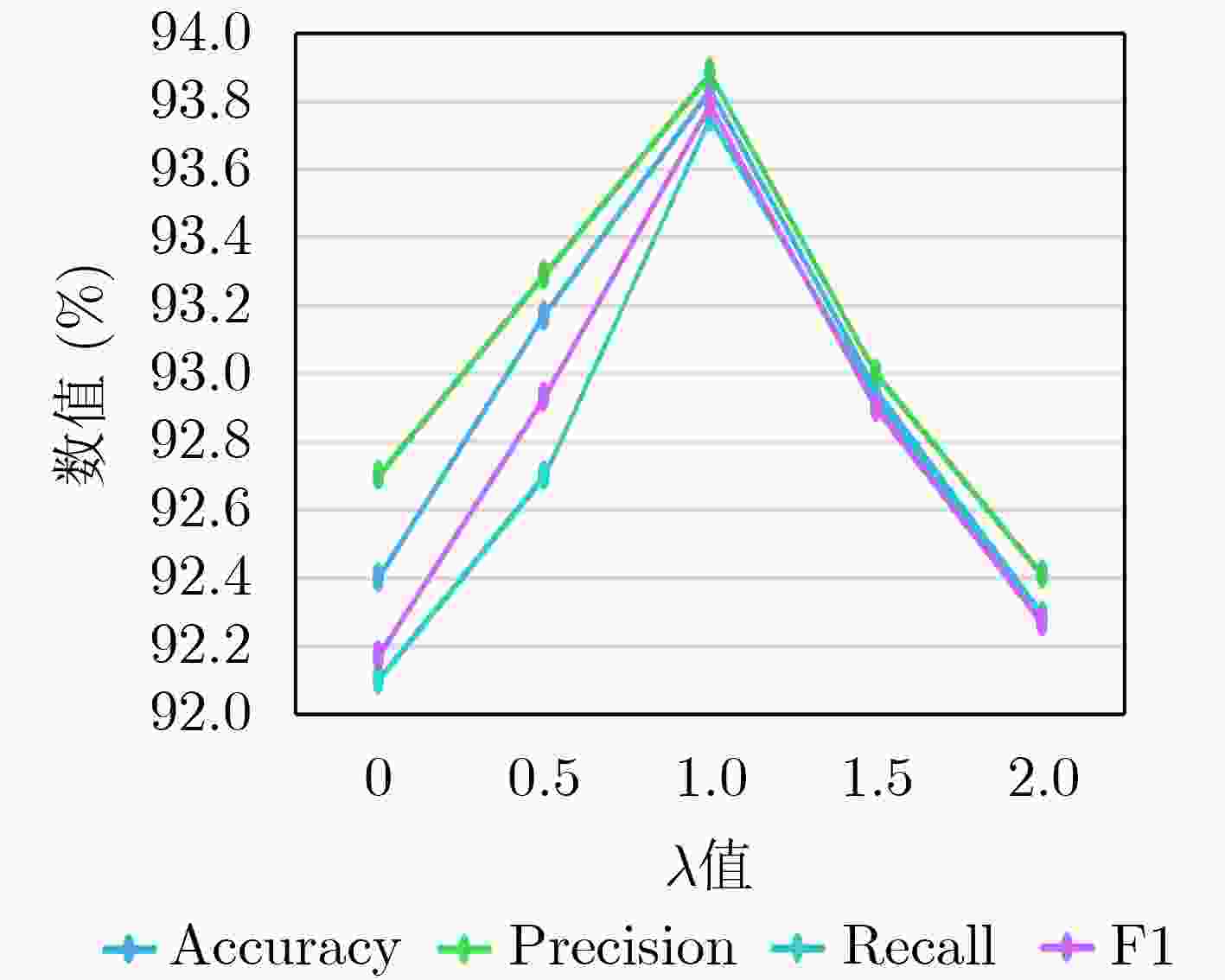
Objective In view-based 3D model classification, deep learning algorithms extract more representative features from 2D projections to improve classification accuracy. However, several challenges remain. A single view captures information only from a specific perspective, often leading to the omission of critical features. To address this, multiple views are generated by projecting the 3D model from various angles. These multi-view representations provide more comprehensive information through fusion. Nonetheless, the feature content of each view differs, and treating all views equally may obscure discriminative information. Moreover, inter-view complementarity and correlations may be overlooked. Effective utilization of multi-view information is therefore essential to enhance the accuracy of 3D model classification. Methods A 3D model classification method based on Central Anchor Hard Triplet Loss (CAH Triplet Loss) and multi-view feature fusion is proposed. Firstly, multi-view sets of 3D models are used as input, and view features are extracted using a Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN). These features are then fused with the 2D shape distribution features D1, D2, and D3 to obtain fused features of the 2D views. Secondly, Shannon entropy is applied to evaluate the uncertainty of view classification based on the fused features. The multiple views of each 3D model are then ranked in descending order of view saliency. Thirdly, triple network based on an Attention-enhanced Long Short-Term Memory (Att-LSTM) architecture is constructed for multi-view feature fusion. The LSTM component captures contextual dependencies among views, while a multi-head attention mechanism is integrated to fully capture inter-view relevance. Fourth, metric learning is applied by combining CAH Triplet Loss with Cross-Entropy Loss (CE Loss) to optimize the fusion network. This combined loss function is designed to reduce the feature-space distance between similar samples while increasing the distance between different samples, thereby enhancing the network’s capacity to learn discriminative features from 3D models. Results and Discussions When DRSN is used to extract view features from 2D projections and softmax is applied for classification, the 3D model classification achieves the highest accuracy, as shown in Table 1 . The integration of shape distribution features D1, D2, and D3 with view features yields a more comprehensive representation of the 3D model, which significantly improves classification accuracy (Table 2 ). Incorporating CAH Triplet Loss reduces intra-class distances and increases inter-class distances in the feature space. This guides the network to learn more discriminative feature representations, further improving classification accuracy, as illustrated inFigure 4 . The application of Shannon entropy to rank view saliency enables the extraction of complementary and correlated information across multiple views. This ranking strategy enhances the effective use of multi-view data, resulting in improved classification performance, as shown inTable 3 .Conclusions This study presents a novel multi-view 3D model classification framework that achieves improved performance through 3 key innovations. Firstly, a hybrid feature extraction strategy is proposed, combining view features extracted by the DRSN with 2D shape distribution features D1, D2, and D3. This fusion captures both high-level semantic and low-level geometric characteristics, enabling a comprehensive representation of 3D objects. Secondly, a view saliency evaluation mechanism based on Shannon entropy is introduced. This approach dynamically assesses and ranks views according to their classification uncertainty, ensuring that the most informative views are prioritized and that the complementarity among views is retained. At the core of the architecture lies a feature fusion module that integrates Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks with multi-head attention mechanisms. This dual-path structure captures sequential dependencies across ordered views through LSTM and models global inter-view relationships through attention, thereby effectively leveraging view correlation and complementarity. Thirdly, the proposed CAH Triplet Loss combines center loss and hard triplet loss to simultaneously minimize intra-class variation and maximize inter-class separation. Together with cross-entropy loss, this joint optimization enhances the network’s ability to learn discriminative features for robust 3D model classification. -
Key words:
- 3D model classification /
- Multi-view feature fusion /
- Attention mechanism /
- Triplet loss
-
表 1 不同网络下的3维模型分类结果(%)
模型 Accuracy Precision Recall F1 Alexnet 89.63 89.59 89.13 89.26 Shuffenet 89.39 89.35 88.95 89.04 Resnet 89.52 89.47 89.08 89.18 DRSN 89.89 89.77 89.64 89.66 表 2 不同形状分布特征下的3维模型分类结果(%)
特征 Accuracy Precision Recall F1 View feature 89.89 89.77 89.64 89.66 View feature+D1 90.23 90.20 90.14 90.09 View feature+D2 90.31 90.26 90.07 90.12 View feature+D3 90.35 90.42 90.03 90.10 View feature+D1+D2+D3 90.79 90.83 90.65 90.65 表 3 不同视图顺序下的各类别分类准确率(%)
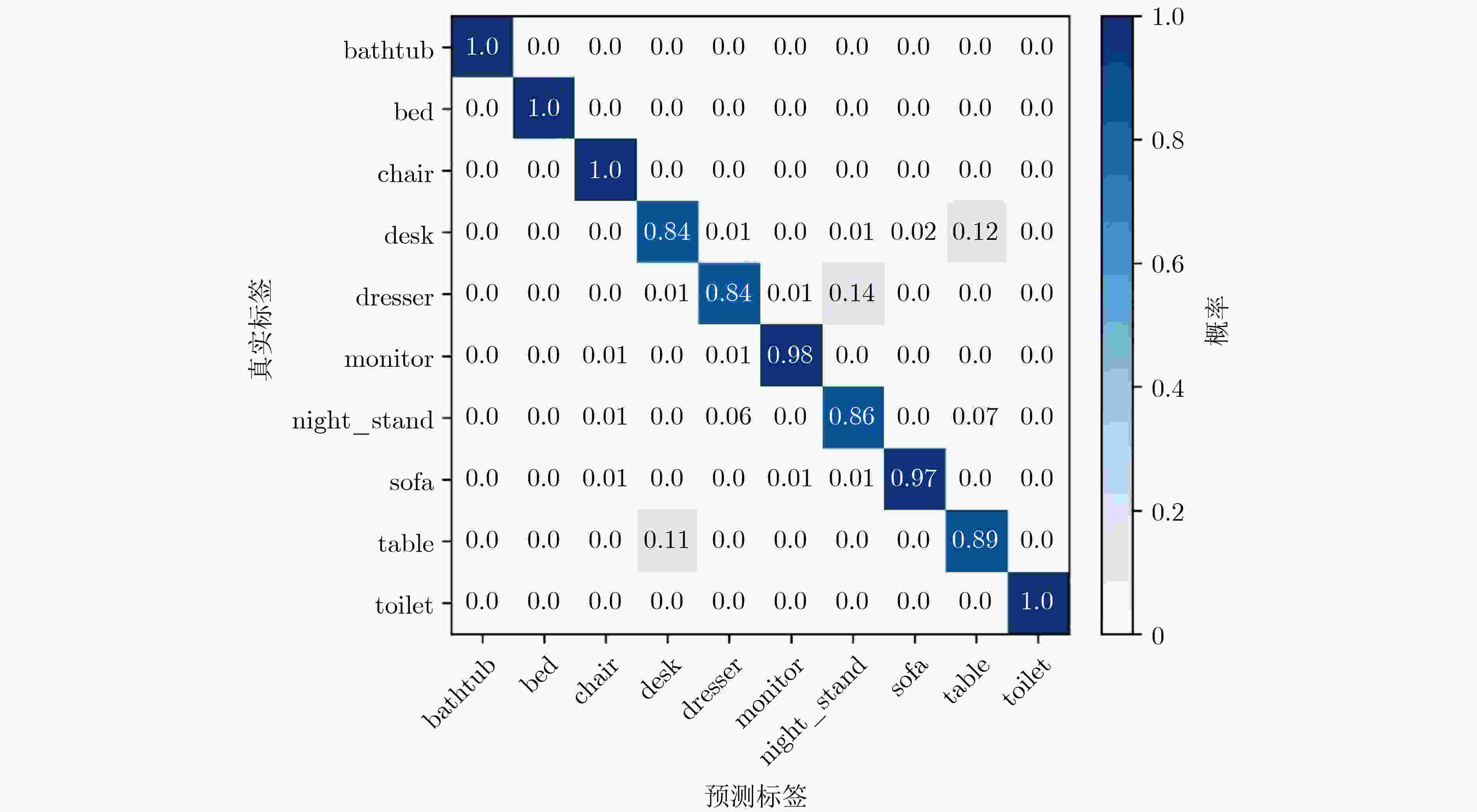
类别 默认顺序 降序 升序 bathtub 84.00 98.00 100.00 bed 100.00 99.00 100.00 chair 100.00 99.00 100.00 desk 79.07 89.53 83.72 dresser 86.05 84.88 83.72 monitor 97.00 98.00 98.00 night_stand 82.56 84.88 86.05 sofa 96.00 97.00 97.00 table 87.00 78.00 89.00 toilet 98.00 98.00 100.00 average_accuracy 91.74 92.73 93.83 表 4 不同方法下的各类别分类准确率(%)
类别 LSTM+
CELSTM+
CE+
CAHSE+LSTM+
CE+CAHSE+Att-
LSTM+CE+
CAHbathtub 98.00 96.00 96.00 100.00 bed 100.00 99.00 100.00 100.00 chair 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 desk 83.72 87.21 93.02 83.72 dresser 90.70 86.05 82.56 83.72 monitor 97.00 98.00 98.00 98.00 night_stand 75.58 84.88 88.37 86.05 sofa 97.00 97.00 97.00 97.00 table 80.00 78.00 77.00 89.00 toilet 96.00 99.00 100.00 100.00 Average accuracy 91.85 92.62 93.28 93.83 表 5 基于视图的分类方法的准确率对比
表 6 ModelNet10和ModelNet40的实验结果比较
数据集 准确率(%) ModelNet 10 93.83 ModelNet 40 91.09 -
[1] 周燕, 李文俊, 党兆龙, 等. 深度学习的三维模型识别研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2024, 18(4): 916–929. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2309010.ZHOU Yan, LI Wenjun, DANG Zhaolong, et al. Survey of 3D model recognition based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science & Technology, 2024, 18(4): 916–929. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2309010. [2] QI C R, SU Hao, MO Kaichun, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77–85. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.16. [3] QI C R, YI Li, SU Hao, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105–5114. [4] YAN Xu, ZHENG Chaoda, LI Zhen, et al. PointASNL: Robust point clouds processing using nonlocal neural networks with adaptive sampling[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 5588–5597. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00563. [5] YU Ying and ZHANG Jun. Classification model of 3D point cloud based on linked adaptive graph convolution[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2303(1): 012003. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2303/1/012003. [6] HUANG Changqin, JIANG Fan, HUANG Qionghao, et al. Dual-graph attention convolution network for 3-D point cloud classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(4): 4813–4825. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3162301. [7] XUE Jiaming, MEN Chaoguang, LIU Yongmei, et al. Adaptive neighbourhood recovery method for machine learning based 3D point cloud classification[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 44(1): 311–340. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2022.2162354. [8] HASSAN R, FRAZ M M, RAJPUT A, et al. Residual learning with annularly convolutional neural networks for classification and segmentation of 3D point clouds[J]. Neurocomputing, 2023, 526: 96–108. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.01.026. [9] MATURANA D and SCHERER S. VoxNet: A 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition[C]. 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 2015: 922–928. doi: 10.1109/IROS.2015.7353481. [10] WU Zhirong, SONG Shuran, KHOSLA A, et al. 3D ShapeNets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1912–1920. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298801. [11] WANG Cheng, CHENG Ming, SOHEL F, et al. NormalNet: A voxel-based CNN for 3D object classification and retrieval[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 323: 139–147. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.075. [12] HE Yunqian, XIA Guihua, LUO Yongkang, et al. DVFENet: Dual-branch voxel feature extraction network for 3D object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459: 201–211. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.06.046. [13] CAI Weiwei, LIU Dong, NING Xin, et al. Voxel-based three-view hybrid parallel network for 3D object classification[J]. Displays, 2021, 69: 102076. doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2021.102076. [14] WANG Bingxu, LAN Jinhui, and LI Feifan. MSG-voxel-GAN: Multi-scale gradient voxel GAN for 3D object generation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 83(10): 88505–88522. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-17116-9. [15] LIU Daikun, WANG Teng, and SUN Changyin. Voxel-based multi-scale transformer network for event stream processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(4): 2112–2124. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3301176. [16] MA Ziping, ZHOU Jie, MA Jinlin, et al. A novel 3D shape recognition method based on double-channel attention residual network[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(22): 32519–32548. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12041-9. [17] SHI Baoguang, BAI Song, ZHOU Zhichao, et al. DeepPano: Deep panoramic representation for 3-D shape recognition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(12): 2339–2343. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2480802. [18] GAO Xueyao, YANG Boyu, and ZHANG Chunxiang. Combine EfficientNet and CNN for 3D model classification[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2023, 20(5): 9062–9079. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023398. [19] 王鹏宇, 水盼盼, 余锋根, 等. 基于多视角卷积神经网络的三维模型分类方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(4): 436–449. doi: 10.1360/N112018-00254.WANG Pengyu, SHUI Panpan, YU Fenggen, et al. 3D shape classification based on convolutional neural networks fusing multi-view information[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(4): 436–449. doi: 10.1360/N112018-00254. [20] SU Hang, MAJI S, KALOGERAKIS E, et al. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 945–953. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.114. [21] 白静, 姬卉, 邵会会, 等. 基于深度集成及细节感知的细粒度三维模型分类[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2022, 34(10): 1580–1589. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2022.19180.BAI Jing, JI Hui, SHAO Huihui, et al. Fine-grained 3D model classification based on deep ensemble and detail awareness[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2022, 34(10): 1580–1589. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2022.19180. [22] LIU Anan, GUO Fubin, ZHOU Heyu, et al. Semantic and context information fusion network for view-based 3D model classification and retrieval[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 155939–155950. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3018875. [23] LIANG Qi, WANG Yixin, NIE Weizhi, et al. MVCLN: Multi-view convolutional LSTM network for cross-media 3D shape recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 139792–139802. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012692. [24] 白静, 司庆龙, 秦飞巍. 基于卷积神经网络和投票机制的三维模型分类与检索[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(2): 303–314. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17160.BAI Jing, SI Qinglong, and QIN Feiwei. 3D model classification and retrieval based on CNN and voting scheme[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2019, 31(2): 303–314. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1089.2019.17160. [25] LIU Anan, ZHOU Heyu, LI Mengjie, et al. 3D model retrieval based on multi-view attentional convolutional neural network[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(7): 4699–4711. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-7521-8. [26] WEI Xin, YU Ruixuan, and SUN Jian. View-GCN: View-based graph convolutional network for 3D shape analysis[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1847–1856. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00192. [27] WEI Xin, YU Ruixuan, and SUN Jian. Learning view-based graph convolutional network for multi-view 3D shape analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(6): 7525–7541. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3221785. [28] SHI Shaojun, NIE Feiping, WANG Rong, et al. When multi-view classification meets ensemble learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 490: 17–29. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.02.052. [29] HAN Zongbo, ZHANG Changqing, FU Huazhu, et al. Trusted multi-view classification with dynamic evidential fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(2): 2551–2566. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3171983. [30] SCHROFF F, KALENICHENKO D, and PHILBIN J. FaceNet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 815–823. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298682. [31] WANG Jian, ZHOU Feng, WEN Shilei, et al. Deep metric learning with angular loss[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2612–2620. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.283. [32] HERMANS A, BEYER L, and LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.07737, 2017. [33] WEN Yandong, ZHANG Kaipeng, LI Zhifeng, et al. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 499–515. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46478-7_31. [34] QIU Yuan, LIU Hongli, LIU Jianwei, et al. Center-triplet loss for railway defective fastener detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(3): 3180–3190. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3339883. [35] FARZANEH A H and QI Xiaojun. Facial expression recognition in the wild via deep attentive center loss[C]. The 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 2401–2410. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00245. [36] JIAO Jinyue, GONG Zhiqiang, and ZHONG Ping. Triplet spectralwise transformer network for hyperspectral target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5519817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3306084. [37] CHEN Kanghao, LEI Weixian, ZHAO Shen, et al. PCCT: Progressive class-center triplet loss for imbalanced medical image classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2023, 27(4): 2026–2036. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2023.3240136. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
