Federated Learning Technologies for 6G Industrial Internet of Things: From Requirements, Vision to Challenges, Opportunities
-
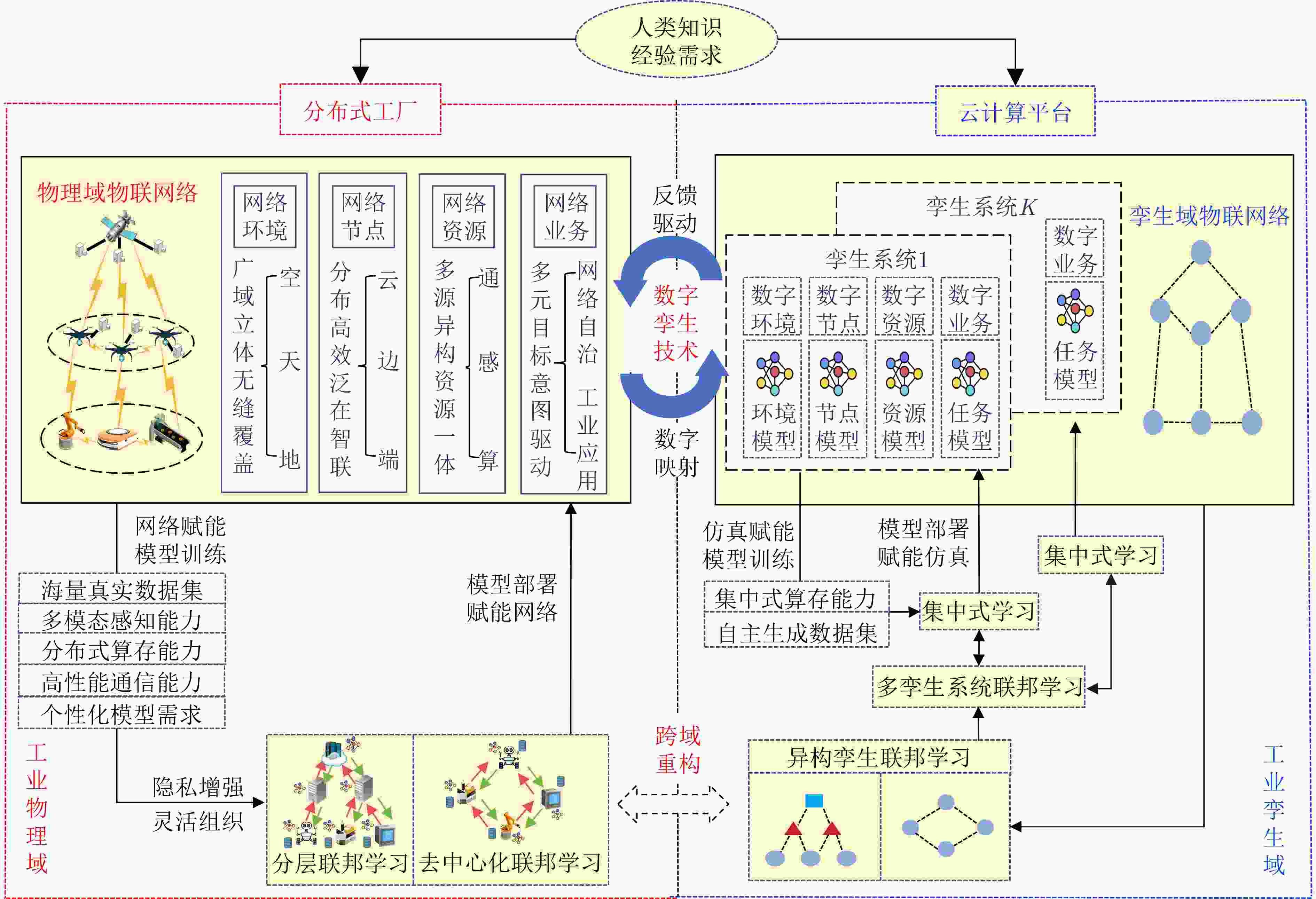
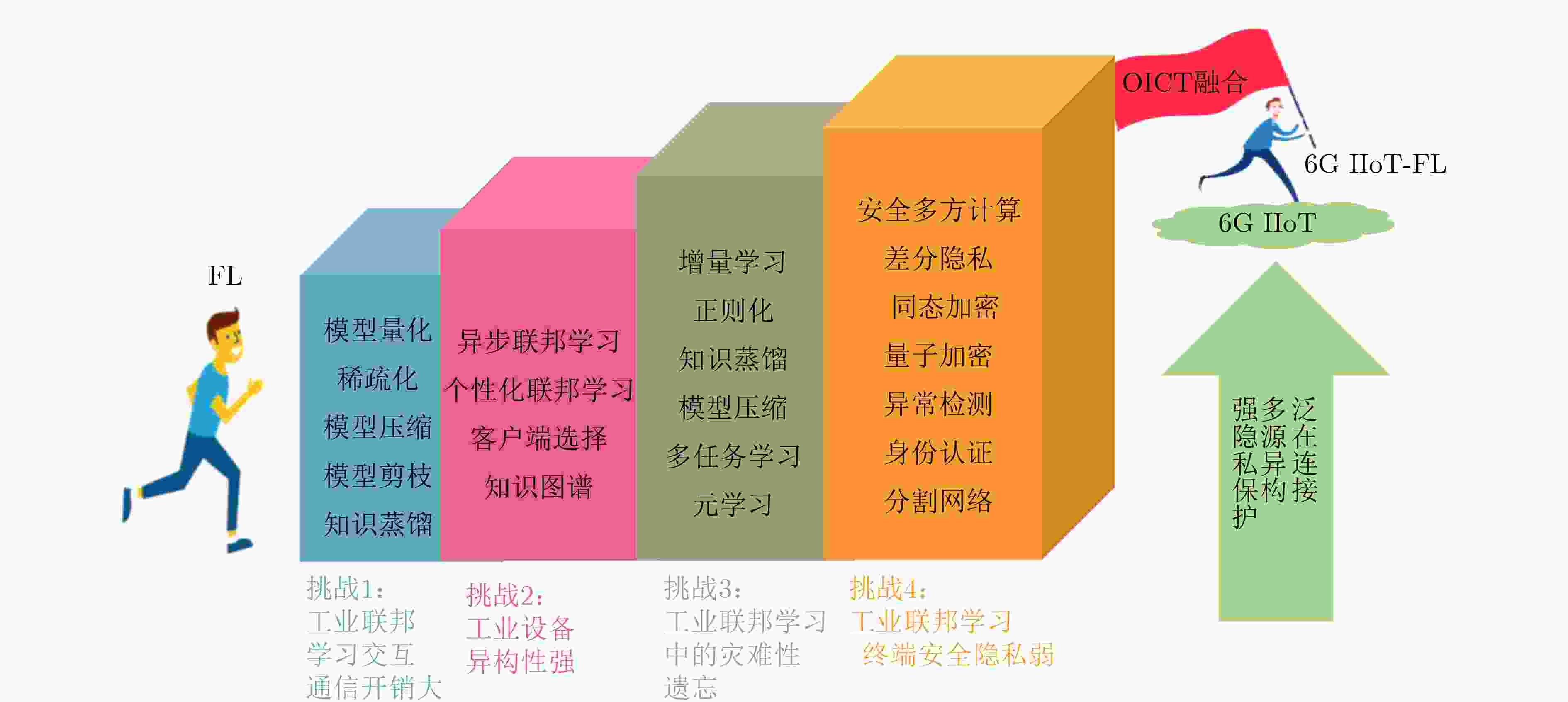
摘要: 随着6G技术的蓬勃发展和工业物联网的不断演进,联邦学习在工业领域的应用备受关注。因此,该文专注于探讨6G推动下工业物联网中联邦学习的发展与应用潜力,分析6G在工业物联网的应用前景,探索如何结合6G特性利用联邦学习技术满足数据隐私保护、资源优化和智能决策需求。首先,调研总结了现有相关工作,提出了联邦学习技术面向6G工业物联网应用场景的发展需求与愿景。在此基础上,构建了一种基于分层跨域架构的工业联邦学习新范式,旨在融合6G与数字孪生技术赋能实现泛在、灵活、层次化的联邦学习,以支撑典型工业物联网场景中按需、可靠的分布式智能业务,实现运营信息通信技术(OCIT)的融合。其次,分析归纳了面向6G工业物联网的联邦学习(6G IIoT-FL)可能面临的研究挑战,并提出了潜在的解决方案或建议。最后,指出了该技术未来值得关注的相关方向,旨在一定程度上为后续研究开拓思路。Abstract: With the rapid development of 6G technology and the evolution of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), federated learning has gained significant attention in the industrial sector. This paper explores the development and application potential of federated learning in 6G-driven IIoT, analyzing 6G’s prospects and how its high speed, low latency, and reliability can support data privacy, resource optimization, and intelligent decision-making. First, existing related work is summarized, and the development requirements along with the vision for applying federated learning technology in 6G industrial IoT scenarios are outlined. Based on this, a new paradigm for industrial federated learning, featuring a hierarchical cross-domain architecture, is proposed to integrate 6G and digital twin technologies, enabling ubiquitous, flexible, and layered federated learning. This supports on-demand and reliable distributed intelligent services in typical Industrial IoT scenarios, achieving the integration of Operational and Communication Information Technology (OCIT). Next, the potential research challenges that federated learning might face towards 6G industrial IoT(6G IIoT-FL) are analyzed and summarized, followed by potential solutions or recommendations. Finally, relevant future directions worth attention in this field are highlighted in the study, with the aim of providing insights for subsequent research to some extent.
-
表 1 相关工作调研
参考文献 主题 贡献 尚未考虑 [11] 面向6G通信技术的工业5.0和
信息物理系统分析了6G技术在工业物联网和智能信息物理系统中存在的挑战与机遇,提出了相关解决方案 没有讨论联邦学习在其中的应用 [12] 面向联邦学习的工业物联网 具体介绍了无线联邦学习在工业物联网中的应用场景和方法,并分析了其优势和局限性 没有涉及6G技术部分的探讨 [13] 面向联邦学习的工业物联网 讨论了无线联邦学习和工业物联网的融合应用,包括架构、算法和安全等方面,为实现6G无线联邦学习
技术提供基础没有重点讨论6G无线联邦学习技术 [14] 面向联邦学习的工业物联网 对联邦学习在工业物联网状态监测中的应用进行了
全面的综述未涉及6G网络的发展及其对联邦学习和工业过程状态监测的潜在影响 [15] 面向6G通信技术的联邦学习 分析了在6G通信场景下,如何利用无线联邦学习解决数据隐私和安全等问题,并探讨了未来发展方向 缺少讨论具体工业物联网应用场景 -
[1] MUMTAZ S, BO A, AL-DULAIMI A, et al. Guest editorial 5G and beyond mobile technologies and applications for industrial IoT (IIoT)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(6): 2588–2591. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2823311. [2] LU Yang and ZHENG Xianrong. 6G: A survey on technologies, scenarios, challenges, and the related issues[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2020, 19: 100158. doi: 10.1016/j.jii.2020.100158. [3] GUI Guan, LIU Miao, TANG Fengxiao, et al. 6G: Opening new horizons for integration of comfort, security, and intelligence[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(5): 126–132. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900516. [4] LETAIEF K B, CHEN Wei, SHI Yuanming, et al. The roadmap to 6G: AI empowered wireless networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(8): 84–90. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1900271. [5] AMBIKA P. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)[J]. Advances in Computers, 2020, 117(1): 321–338. doi: 10.1016/BS.ADCOM.2019.10.007. [6] QVIST-SØRENSEN P. Applying IIoT and AI–Opportunities, requirements and challenges for industrial machine and equipment manufacturers to expand their services[J]. Central European Business Review, 2020, 9(2): 46–77. doi: 10.18267/j.cebr.234. [7] MAO Yuyi, YU Xianghao, HUANG Kaibin, et al. Green edge AI: A contemporary survey[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2024, 112(7): 880–911. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2024.3437365. [8] ZHU Ligeng, LIU Zhijian, and HAN Song. Deep leakage from gradients[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 1323. [9] ZHOU Tailin, ZHANG Jun, and TSANG D H K. FedFA: Federated learning with feature anchors to align features and classifiers for heterogeneous data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(6): 6731–6742. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3325366. [10] 范绍帅, 吴剑波, 田辉. 面向能量受限工业物联网设备的联邦学习资源管理[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(8): 65–77. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2022126.FAN Shaoshuai, WU Jianbo, and TIAN Hui. Federated learning resource management for energy-constrained industrial IoT devices[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(8): 65–77. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2022126. [11] BASU D, GHOSH U, and DATTA R. 6G for industry 5.0 and smart CPS: A journey from challenging hindrance to opportunistic future[C]. 2022 IEEE Silchar Subsection Conference, Silchar, India, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/SILCON55242.2022.10028927. [12] NGUYEN D C, DING M, PATHIRANA P N, et al. Federated learning for industrial internet of things in future industries[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(6): 192–199. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100102. [13] BOOBALAN P, RAMU S P, PHAM Q V, et al. Fusion of federated learning and industrial internet of things: A survey[J]. Computer Networks, 2022, 212: 109048. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109048. [14] BERGHOUT T, BENBOUZID M, BENTRCIA T, et al. Federated learning for condition monitoring of industrial processes: A review on fault diagnosis methods, challenges, and prospects[J]. Electronics, 2022, 12(1): 158. doi: 10.3390/electronics12010158. [15] LIU Yi, YUAN Xingliang, XIONG Zehui, et al. Federated learning for 6G communications: Challenges, methods, and future directions[J]. China Communications, 2020, 17(9): 105–118. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2020.09.009. [16] GHILDIYAL Y, SINGH R, ALKHAYYAT A, et al. An imperative role of 6G communication with perspective of industry 4.0: Challenges and research directions[J]. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2023, 56: 103047. doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2023.103047. [17] ZHU Guangxu, LYU Zhonghao, JIAO Xiang, et al. Pushing AI to wireless network edge: An overview on integrated sensing, communication, and computation towards 6G[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(3): 130301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3652-2. [18] GONG Yongkang, YAO Haipeng, WANG Jingjing, et al. Edge intelligence-driven joint offloading and resource allocation for future 6G industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024, 11(6): 5644–5655. doi 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3141728. [19] HIESSL T, SCHALL D, KEMNITZ J, et al. Industrial federated learning–requirements and system design[C]. The International Conference on Practical Applications of Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, L’Aquila, Italy, 2020: 42–53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51999-5_4. [20] MAKKAR A, KIM T W, SINGH A K, et al. SecureIIoT environment: Federated learning empowered approach for securing IIoT from data breach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(9): 6406–6414. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3149902. [21] YE Mang, FANG Xiuwen, DU Bo, et al. Heterogeneous federated learning: State-of-the-art and research challenges[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2024, 56(3): 79. doi: 10.1145/3625558. [22] TANG Fengxiao, CHEN Xuehan, RODRIGUES T K, et al. Survey on Digital Twin Edge Networks (DITEN) toward 6G[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 1360–1381. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3197811. [23] LIN Xingqin, KUNDU L, DICK C, et al. 6G digital twin networks: From theory to practice[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(11): 72–78. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2200830. [24] LU Yunlong, HUANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Ke, et al. Communication-efficient federated learning for digital twin edge networks in industrial IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(8): 5709–5718. doi: 10.1109/tii.2020.3010798. [25] LU Yunlong, HUANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Ke, et al. Communication-efficient federated learning and permissioned blockchain for digital twin edge networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(4): 2276–2288. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3015772. [26] PRAHARAJ L, GUPTA M, and GUPTA D. Hierarchical federated transfer learning and digital twin enhanced secure cooperative smart farming[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Sorrento, Italy, 2023: 3304–3313. doi: 10.1109/BigData59044.2023.10386345. [27] TAO Fei, ZHANG He, and ZHANG Chenyuan. Advancements and challenges of digital twins in industry[J]. Nature Computational Science, 2024, 4(3): 169–177. doi: 10.1038/s43588-024-00603-w. [28] RAMU S P, BOOPALAN P, PHAM Q V, et al. Federated learning enabled digital twins for smart cities: Concepts, recent advances, and future directions[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022, 79: 103663. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.103663. [29] GUO Jingjing, LIU Zhiquan, TIAN Siyi, et al. TFL-DT: A trust evaluation scheme for federated learning in digital twin for mobile networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(11): 3548–3560. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3310094. [30] HE Yejun, YANG Mengna, ZHOU He, et al. Computation offloading and resource allocation based on DT-MEC-assisted federated learning framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2023, 9(6): 1707–1720. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2023.3298926. [31] QADIR Z, LE K N, SAEED N, et al. Towards 6G Internet of Things: Recent advances, use cases, and open challenges[J]. ICT Express, 2023, 9(3): 296–312. doi: 10.1016/j.icte.2022.06.006. [32] QUY V K, NGUYEN D C, VAN ANH D, et al. Federated learning for green and sustainable 6G IIoT applications[J]. Internet of Things, 2024, 25: 101061. doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2024.101061. [33] YANG Wei, XIANG Wei, YANG Yuan, et al. Optimizing Federated Learning With Deep Reinforcement Learning for Digital Twin Empowered Industrial IoT [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(2): 1884-1893. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3183465. [34] FARAHANI B and MONSEFI A K. Smart and collaborative industrial IoT: A federated learning and data space approach[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2023, 9(2): 436–447. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2023.01.022. [35] CHEN Jianrui, WANG Jingjing, JIANG Chunxiao, et al. Trustworthy semantic communications for the metaverse relying on federated learning[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 30(4): 18–25. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2200587. [36] OOI M P L, SOHAIL S, HUANG V G, et al. Measurement and applications: Exploring the challenges and opportunities of hierarchical federated learning in sensor applications[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2023, 26(9): 21–31. doi: 10.1109/MIM.2023.10328671. [37] ZHU Juncen, CAO Jiannong, SAXENA D, et al. Blockchain-empowered federated learning: Challenges, solutions, and future directions[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(11): 240. doi: 10.1145/3570953. [38] LIU Shimin, LU Yuqian, SHEN Xingwang, et al. A digital thread-driven distributed collaboration mechanism between digital twin manufacturing units[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2023, 68: 145–159. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2023.02.014. [39] CRONIN C, CONWAY A, and WALSH J. Flexible manufacturing systems using IIoT in the automotive sector[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 38: 1652–1659. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.01.119. [40] TSAI Y H, CHANG D M, and HSU T C. Edge computing based on federated learning for machine monitoring[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(10): 5178. doi: 10.3390/app12105178. [41] GUO Sheng, LI Zengxiang, LIU Hui, et al. Personalized federated learning for multi-task fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2211.09406, 2022. [42] CHEN Baotong, WAN Jiafu, LAN Yanting, et al. Improving cognitive ability of edge intelligent IIoT through machine learning[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 33(5): 61–67. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1800505. [43] GUO Qi, TANG Fengxiao, and KATO N. Federated reinforcement learning-based resource allocation for D2D-aided digital twin edge networks in 6G industrial IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(5): 7228–7236. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3227655. [44] SUN Fanglei and DIAO Zhifeng. Federated learning and blockchain-enabled intelligent manufacturing for sustainable energy production in industry 4.0[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(5): 1482. doi: 10.3390/pr11051482. [45] TARIQ M, ALI M, NAEEM F, et al. Vulnerability assessment of 6G-enabled smart grid cyber–physical systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(7): 5468–5475. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3042090. [46] BOUZINIS P S, DIAMANTOULAKIS P D, and KARAGIANNIDIS G K. Wireless federated learning (WFL) for 6G networks Part I: Research challenges and future trends[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3121071. [47] CHAUDHARY R, AUJLA G S, GARG S, et al. SDN-enabled multi-attribute-based secure communication for smart grid in IIoT environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(6): 2629–2640. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2789442. [48] WEN Mi, XIE Rong, LU Kejie, et al. FedDetect: A novel privacy-preserving federated learning framework for energy theft detection in smart grid[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(8): 6069–6080. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3110784. [49] XIAO Lijun, HAN Dezhi, YANG Ce, et al. TS-DP: An efficient data processing algorithm for distribution digital twin grid for industry 5.0[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2024, 70(1): 1983–1994. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2023.3332099. [50] PÉREZ S, PÉREZ J, ARROBA P, et al. Predictive GPU-based ADAS management in energy-conscious smart cities[C]. 2019 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, Casablanca, Morocco, 2019: 349–354. doi: 10.1109/ISC246665.2019.9071685. [51] TAÏK A and CHERKAOUI S. Electrical load forecasting using edge computing and federated learning[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9148937. [52] CAO Hui, LIU Shubo, ZHAO Renfang, et al. IFed: A novel federated learning framework for local differential privacy in power internet of things[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2020, 16(5): 1550147720919698. doi: 10.1177/1550147720919698. [53] BOUACHIR O, ALOQAILY M, ÖZKASAP Ö, et al. FederatedGrids: Federated learning and blockchain-assisted P2P energy sharing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2022, 6(1): 424–436. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2022.3140978. [54] SHAHID O, POURIYEH S, PARIZI R M, et al. Communication efficiency in federated learning: Achievements and challenges[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2107.10996, 2021. [55] SHLEZINGER N, CHEN Mingzhe, ELDAR Y C, et al. Federated learning with quantization constraints[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 8851–8855. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054168. [56] HUANG Anbu, CHEN Yuanyuan, LIU Yang, et al. RPN: A residual pooling network for efficient federated learning[C]. Proceedings of the 24th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2020: 1223–1229. [57] IMTEAJ A, THAKKER U, WANG Shiqiang, et al. A survey on federated learning for resource-constrained IoT devices[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(1): 1–24. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3095077. [58] JIANG Yuang, WANG Shiqiang, VALLS V, et al. Model pruning enables efficient federated learning on edge devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(12): 10374–10386. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3166101. [59] WU Chuhan, WU Fengzhao, LYU Lingjuan, et al. Communication-efficient federated learning via knowledge distillation[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2032. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29763-x. [60] XIA Dan, JIANG Chun, WAN Jiafu, et al. Heterogeneous network access and fusion in smart factory: A survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(6): 113. doi: 10.1145/3530815. [61] PRAKASH S and AVESTIMEHR A S. Mitigating byzantine attacks in federated learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010.07541, 2020. [62] XU Chenhao, QU Youyang, XIANG Yong, et al. Asynchronous federated learning on heterogeneous devices: A survey[J]. Computer Science Review, 2023, 50: 100595. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2023.100595. [63] SUN Wen, LEI Shiyu, WANG Lu, et al. Adaptive federated learning and digital twin for industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(8): 5605–5614. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3034674. [64] ABDELMONIEM A M, SAHU A N, CANINI M, et al. REFL: Resource-efficient federated learning[C]. The Eighteenth European Conference on Computer Systems, Rome Italy, 2023: 215–232. doi: 10.1145/3552326.3567485. [65] CAO Mei, ZHANG Yujie, MA Zezhong, et al. C2S: Class-aware client selection for effective aggregation in federated learning[J]. High-Confidence Computing, 2022, 2(3): 100068. doi: 10.1016/j.hcc.2022.100068. [66] TAN A Z, HAN Yu, CUI Lizhen, et al. Towards personalized federated learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(12): 9587–9603. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3160699. [67] DENG Yongheng, CHEN Weining, REN Ju, et al. TailorFL: Dual-personalized federated learning under system and data heterogeneity[C]. The 20th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Boston, USA, 2022: 592–606. doi: 10.1145/3560905.3568503. [68] REN Lei, LI Yingjie, WANG Xiaokang, et al. An ABGE-aided manufacturing knowledge graph construction approach for heterogeneous IIoT data integration[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2023, 61(12): 4102–4116. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2022.2042416. [69] ZHANG Kai, WANG Yu, WANG Hongyi, et al. Efficient federated learning on knowledge graphs via privacy-preserving relation embedding aggregation[C]. The Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022: 613–621. doi: 10.18653/v1/2022.findings-emnlp.43. [70] ZHU Xiangrong, LI Guangyao, and HU Wei. Heterogeneous federated knowledge graph embedding learning and unlearning[C]. The ACM Web Conference 2023, Austin, USA, 2023: 2444–2454. doi: 10.1145/3543507.3583305. [71] EK K, PORTET F, LALANDA P, et al. A federated learning aggregation algorithm for pervasive computing: Evaluation and comparison[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Kassel, Germany, 2021: 1–10. doi: 10.1109/PERCOM50583.2021.9439129. [72] SEN S, NIELSEN S M, HUSOM E J, et al. Replay-driven continual learning for the industrial internet of things[C]. The 2023 IEEE/ACM 2nd International Conference on AI Engineering–Software Engineering for AI, Melbourne, Australia, 2023: 43–55. doi: 10.1109/CAIN58948.2023.00014. [73] LIU Yongxin, WANG Jian, LI Jianqiang, et al. Class-incremental learning for wireless device identification in IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(23): 17227–17235. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3078407. [74] JIN Zhigang, ZHOU Junyi, LI Bing, et al. FL-IIDS: A novel federated learning-based incremental intrusion detection system[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2024, 151: 57–70. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2023.09.019. [75] JIN Hai, BAI Dongshan, YAO Dezhong, et al. Personalized edge intelligence via federated self-knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2023, 34(2): 567–580. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2022.3225185. [76] ZHANG Yu and YANG Qiang. A survey on multi-task learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34(12): 5586–5609. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2021.3070203. [77] WANG Bokun, YUAN Zhuoning, YING Yiming, et al. Memory-based optimization methods for model-agnostic meta-learning and personalized federated learning[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2023, 24(1): 145. [78] RAO Bosen, ZHANG Jiale, WU Di, et al. Privacy inference attack and defense in centralized and federated learning: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2024. doi: 10.1109/TAI.2024.3363670. [79] ZHAO Bin, FAN Kai, YANG Kan, et al. Anonymous and Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning With Industrial Big Data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(9): 6314-6323. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3052183. [80] NGUYEN V L, LIN P C, CHENG Bochao, et al. Security and privacy for 6G: A survey on prospective technologies and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(4): 2384–2428. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3108618. [81] KADHE S, RAJARAMAN N, KOYLUOGLU O O, et al. FastSecAgg: Scalable secure aggregation for privacy-preserving federated learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2009.11248, 2020. [82] EL OUADRHIRI A and ABDELHADI A. Differential privacy for deep and federated learning: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 22359–22380. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3151670. [83] HARDY S, HENECKA W, IVEY-LAW H, et al. Private federated learning on vertically partitioned data via entity resolution and additively homomorphic encryption[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1711.10677, 2017. [84] ZHAO Ping, CAO Zhikui, JIANG Jin, et al. Practical private aggregation in federated learning against inference attack[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(1): 318–329. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3201231. [85] REN Chao, YAN Rudai, XU Minrui, et al. QFDSA: A quantum-secured federated learning system for smart grid dynamic security assessment[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(5): 8414–8426. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3321793. [86] WANG Xiaoding, GARG S, LIN Hui, et al. Toward accurate anomaly detection in industrial internet of things using hierarchical federated learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(10): 7110–7119. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3074382. [87] XIONG Hu, WU Yan, JIN Chuanjie, et al. Efficient and privacy-preserving authentication protocol for heterogeneous systems in IIoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(12): 11713–11724. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2999510. [88] WU Tianyu, HE Shizhu, LIU Jingping, et al. A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(5): 1122–1136. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123618. [89] SUN Yu, WANG Shuohuan, FENG Shikun, et al. ERNIE 3.0: Large-scale knowledge enhanced pre-training for language understanding and generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2107.02137, 2021. [90] ZHOU Ce, LI Qian, LI Chen, et al. A comprehensive survey on pretrained foundation models: A history from BERT to ChatGPT[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2024. [91] KASNECI E, SESSLER K, KÜCHEMANN S, et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education[J]. Learning and Individual Differences, 2023, 103: 102274. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274. [92] YANG Hanqing, SIEW M, and JOE-WONG C. An LLM-based digital twin for optimizing human-in-the loop systems[C]. 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Foundation Models for Cyber-Physical Systems & Internet of Things, Hong Kong, China, 2024. doi: 10.1109/FMSys62467.2024.00009. [93] CHEN Jiayuan, YI Changyan, DU Hongyang, et al. A revolution of personalized healthcare: Enabling human digital twin with mobile AIGC[J]. IEEE Network, 2024, 38(6): 234–242. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2024.3366560. [94] CHEN Xuehan, LUO Linfeng, TANG Fengxiao, et al. AIGC-based evolvable digital twin networks: A road to the intelligent metaverse[J]. IEEE Network, 2024, 38(6): 370–379. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2024.3411008. [95] WU Xingjiao, XIAO Luwei, SUN Yixuan, et al. A survey of human-in-the-loop for machine learning[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2022, 135: 364–381. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2022.05.014. [96] TURNER C J, MA Ruidong, CHEN Jingyu, et al. Human in the loop: Industry 4.0 technologies and scenarios for worker mediation of automated manufacturing[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 103950–103966. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3099311. [97] HIRAI R, SAITO Y, and SARUWATARI H. Federated learning for human-in-the-loop many-to-many voice conversion[C]. The 12th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop, Grenoble, France, 2023. [98] WU Wen, LI Mushu, QU Kaige, et al. Split learning over wireless networks: Parallel design and resource management[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(4): 1051–1066. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3242704. [99] HAFI H, BRIK B, FRANGOUDIS P A, et al. Split federated learning for 6G enabled-networks: Requirements, challenges, and future directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 9890–9930. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3351600. [100] THAPA C, CHAMIKARA M A P, and CAMTEPE S A. Advancements of federated learning towards privacy preservation: From federated learning to split learning[M]. UR REHMAN M H and GABER M M. Federated Learning Systems: Towards Next-Generation AI. Cham: Springer, 2021: 79–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-70604-3_4. [101] LI Weikang, LU Sirui, and DENG Dongling. Quantum federated learning through blind quantum computing[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 2021, 64(10): 100312. doi: 10.1007/s11433-021-1753-3. [102] CHEN S Y C and YOO S. Federated quantum machine learning[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23(4): 460. doi: 10.3390/e23040460. [103] YUN W J, KIM J P, JUNG S, et al. Slimmable quantum federated learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.10221, 2022. [104] XIA Qi and LI Qun. QuantumFed: A federated learning framework for collaborative quantum training[C]. 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Madrid, Spain, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM46510.2021.9685012. [105] ŞAHIN A and YANG Rui. A Survey on over-the-air computation[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(3): 1877–1908. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3264649. [106] ZHANG Deyou, XIAO Ming, PANG Zhibo, et al. Broadband over-the-air computation for federated learning in industrial IoT[C]. The 48th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Brussels, Belgium, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/IECON49645.2022.9968873. [107] YANG Kai, JIANG Tao, SHI Yuanming, et al. Federated learning via over-the-air computation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(3): 2022–2035. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2961673. [108] RATHI N, CHAKRABORTY I, KOSTA A, et al. Exploring neuromorphic computing based on spiking neural networks: Algorithms to hardware[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(12): 243. doi: 10.1145/3571155. [109] NUNES J D, CARVALHO M, CARNEIRO D, et al. Spiking neural networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 60738–60764. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3179968. [110] SKATCHKOVSKY N, JANG H, and SIMEONE O. Federated neuromorphic learning of spiking neural networks for low-power edge intelligence[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 8524–8528. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053861. [111] WANG Huan, LI Yanfu, and GRYLLIAS K. Brain-inspired spiking neural networks for industrial fault diagnosis: A survey, challenges, and opportunities[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2401.02429, 2023. [112] ZHU Zhengyu, LI Zheng, CHU Zheng, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted wireless powered heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 9881–9892. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3274220. [113] ZHU Zhengyu, XU Jinlei, SUN Gangcan, et al. Robust beamforming design for IRS-aided secure SWIPT terahertz systems with non-linear EH model[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(4): 746–750. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3142098. [114] 王平, 杨志伟, 李贺举. 智能反射面赋能的联邦边缘学习及其在车联网中的应用[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(10): 46–57. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023192.WANG Ping, YANG Zhiwei, and LI Heju. Federated edge learning with reconfigurable intelligent surface and its application in internet of vehicles[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(10): 46–57. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023192. [115] ZHENG Jie, ZHANG Haijun, KANG Jiawen, et al. Covert federated learning via intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(8): 4591–4604. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3281880. [116] ZHANG Yutong, DI Boya, ZHANG Hongliang, et al. Meta-wall: Intelligent omni-surfaces aided multi-cell MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(9): 7026–7039. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3154041. [117] MAHMOOD A, BELTRAMELLI L, ABEDIN S F, et al. Industrial IoT in 5G-and-beyond networks: Vision, architecture, and design trends[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(6): 4122–4137. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3115697. [118] ELHOUSHY S, IBRAHIM M, and HAMOUDA W. Cell-free massive MIMO: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(1): 492–523. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3123267. [119] ZHAO Chen, GAO Zhipeng, WANG Qian, et al. AFL: An adaptively federated multitask learning for model sharing in industrial IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(18): 17080–17088. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3125989. [120] VU T T, NGO D T, TRAN N H, et al. Cell-free massive MIMO for wireless federated learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6377–6392. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3002988. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
