Nested Tensor-based Simultaneous Localization and Communication Method for RIS-assisted Near-field Integrated Sensing And Communication Systems
-
摘要: 可重构智能表面(RIS)因其能够智能配置无线传输环境而成为增强通信和感知的革新技术。随着RIS孔径的增加,电磁场特性发生根本性变化,近场范围扩大。与远场通信和感知不同,近场通信和感知需要考虑更为复杂的信道结构特性,这使得RIS辅助的毫米波系统在近场通信和感知方面更具挑战。基于此,该文研究一种RIS辅助通信感知一体化(ISAC)的近场传输系统。首先,利用所考虑的ISAC场景的多维度资源和Khatri-Rao空时编码方法,将接收到的ISAC信号构造为4阶嵌套张量。然后,利用嵌套张量的代数结构和对近场信道模型的2阶菲涅耳近似,设计一种基于嵌套张量的同时定位和通信方案,在不发送专用导频的情况下实现近场环境散射点和用户定位以及信息符号检测。仿真结果表明,提出的方案具有较好的ISAC性能并优于现有方案。此外,即使是在高阶调制情况下,所提方案也有良好的定位精度和的误码率性能。Abstract:
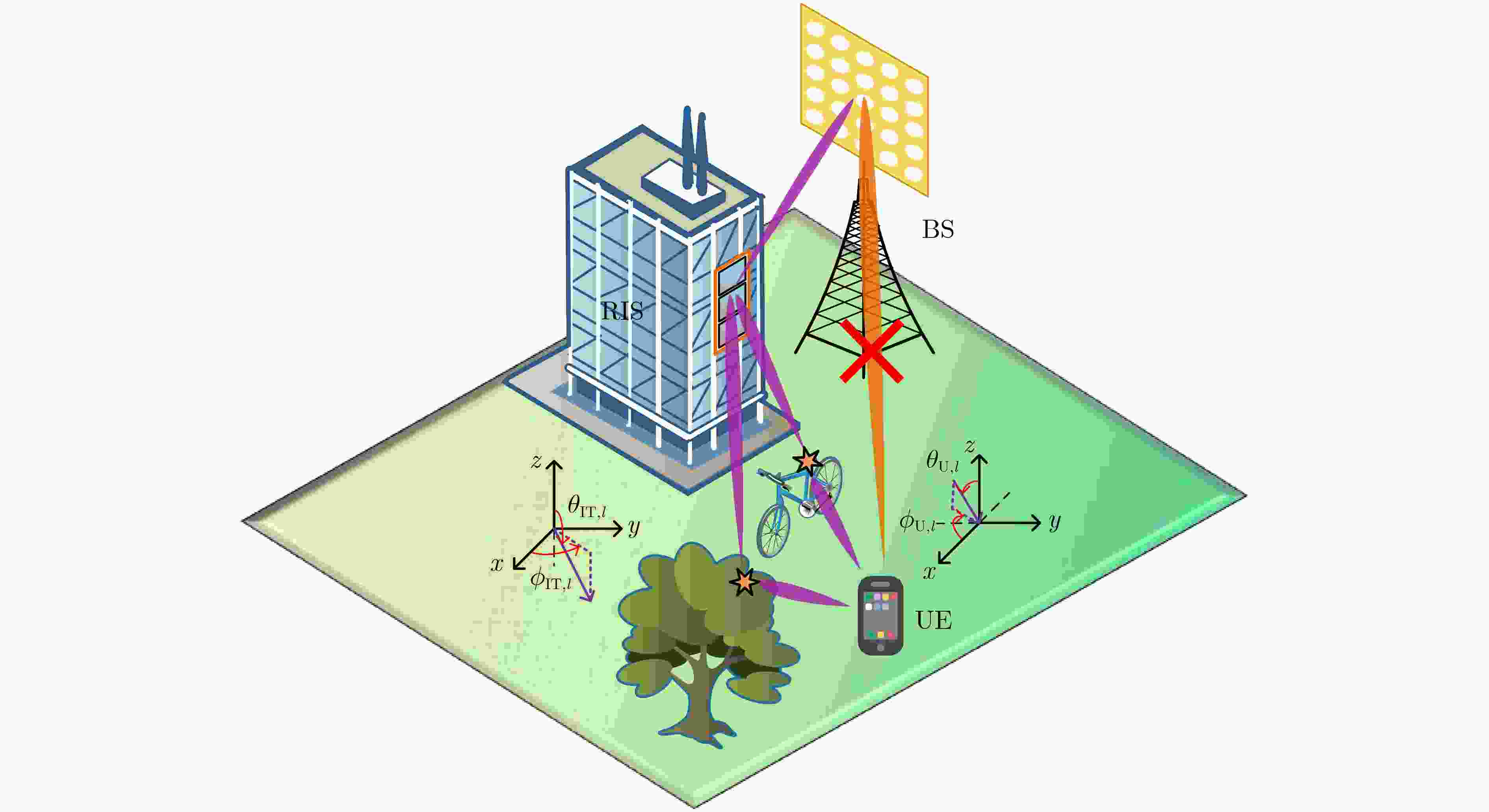
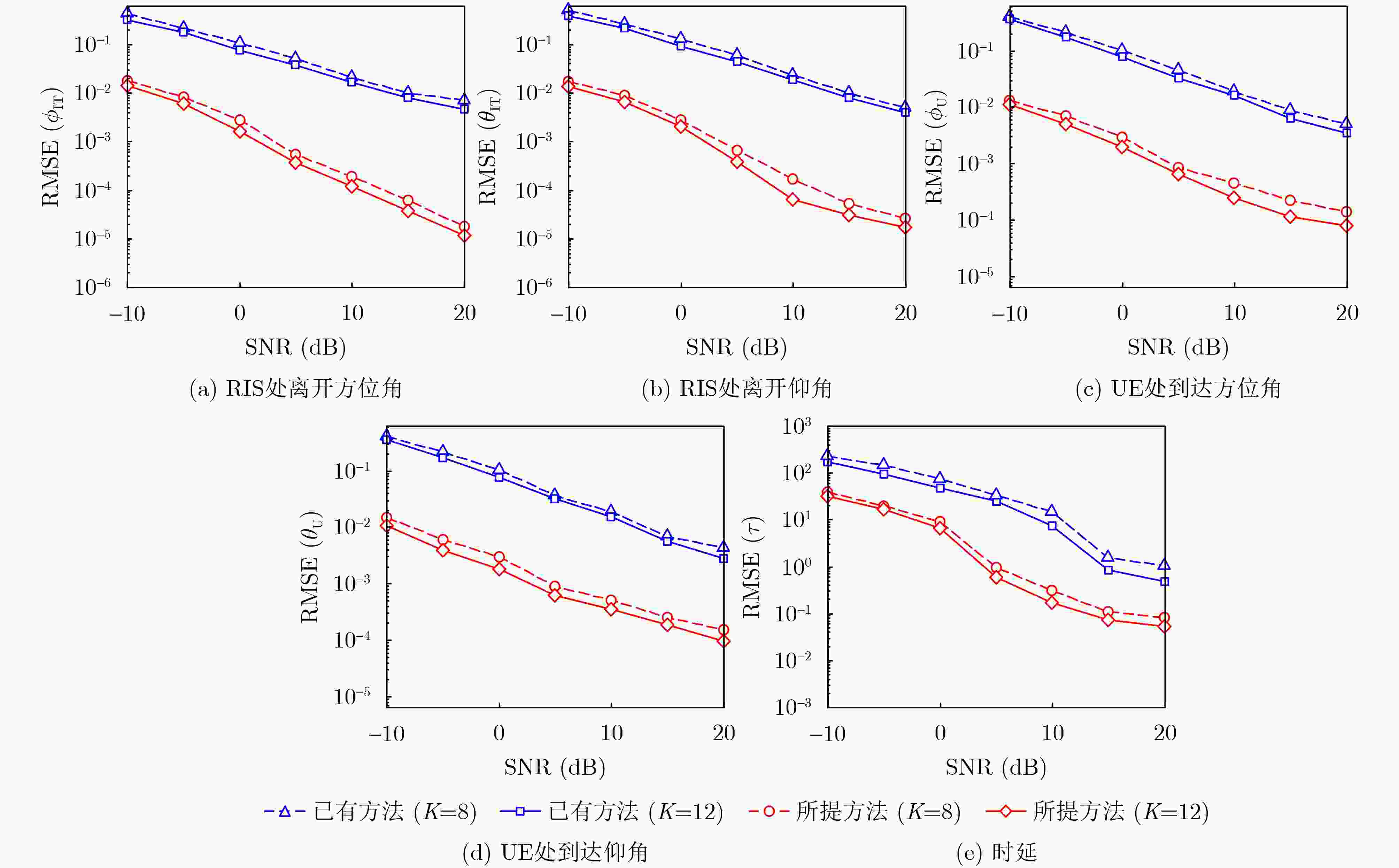
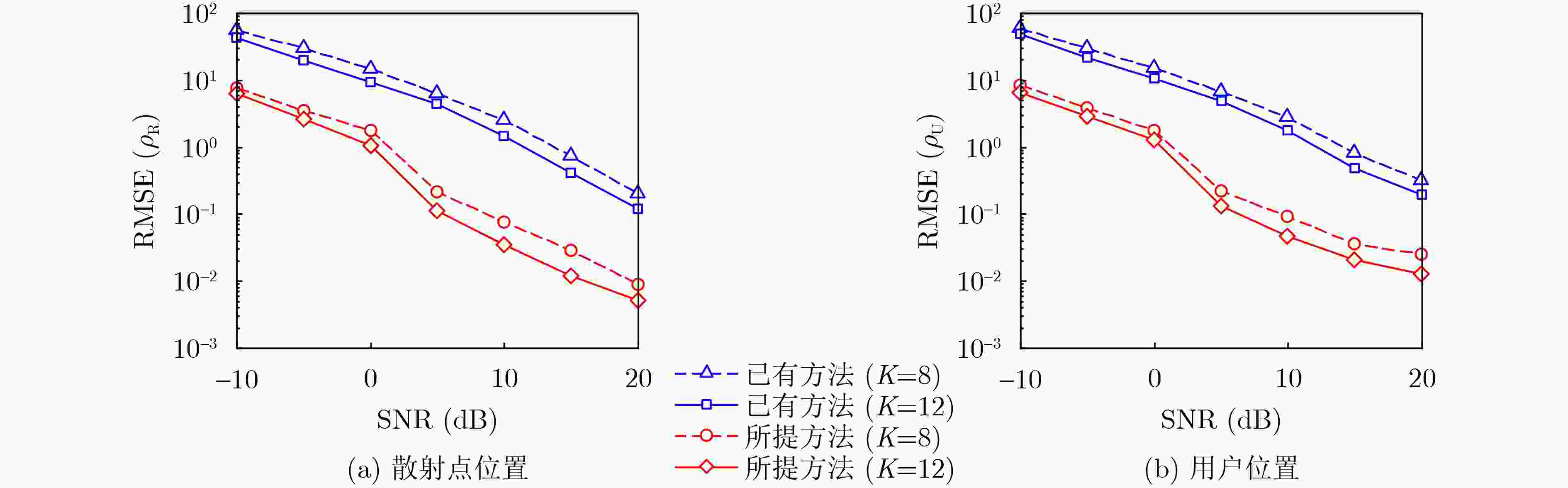
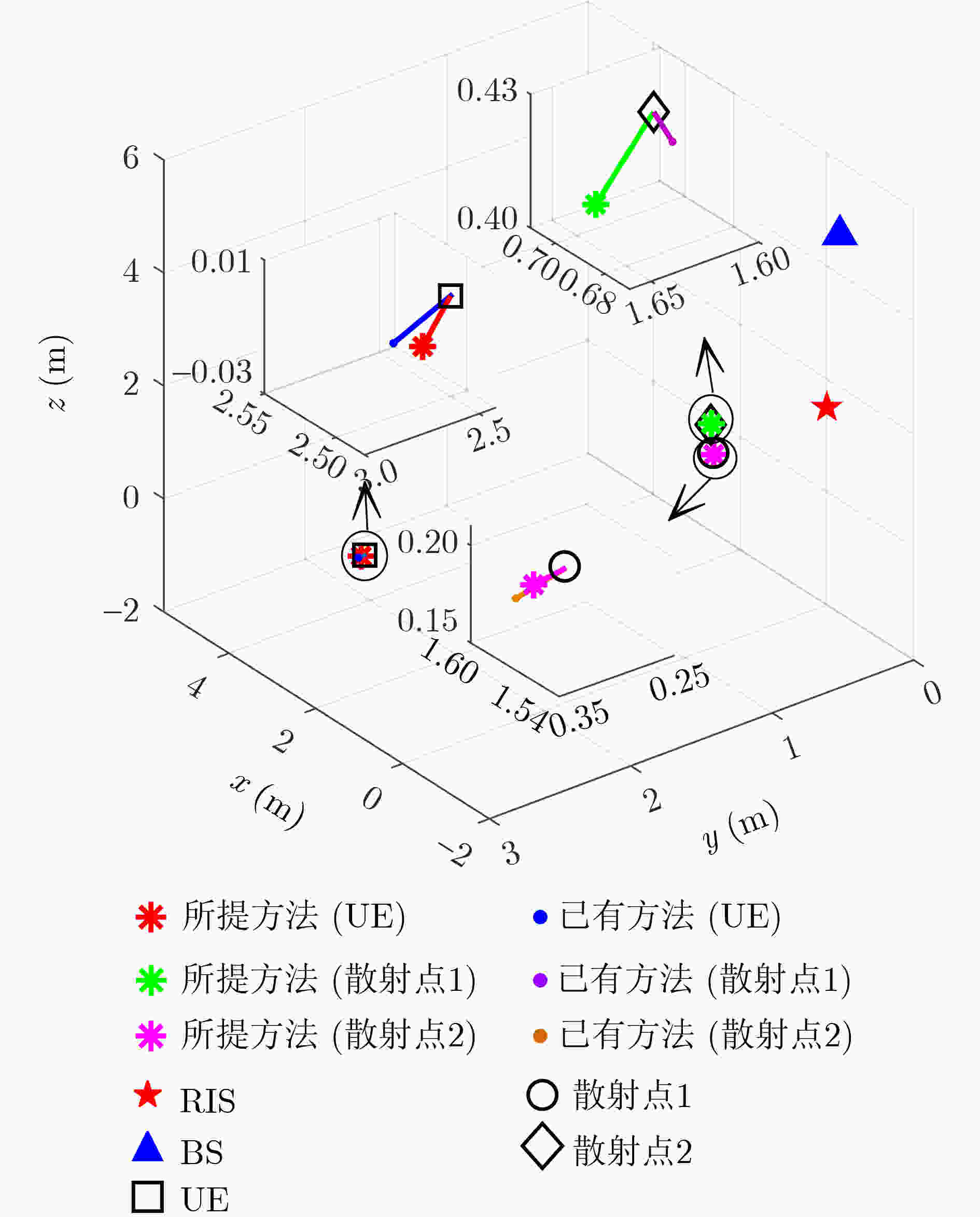
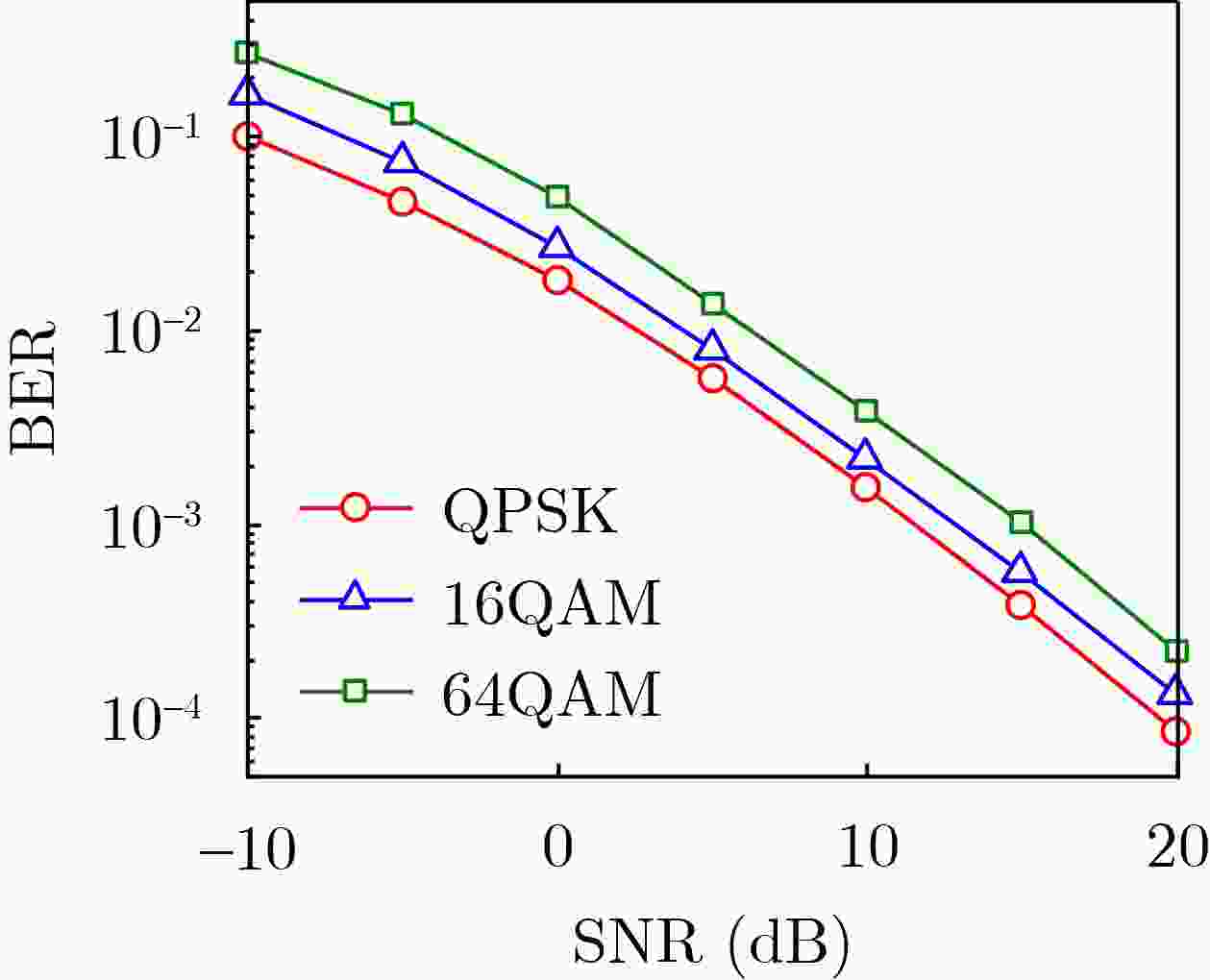
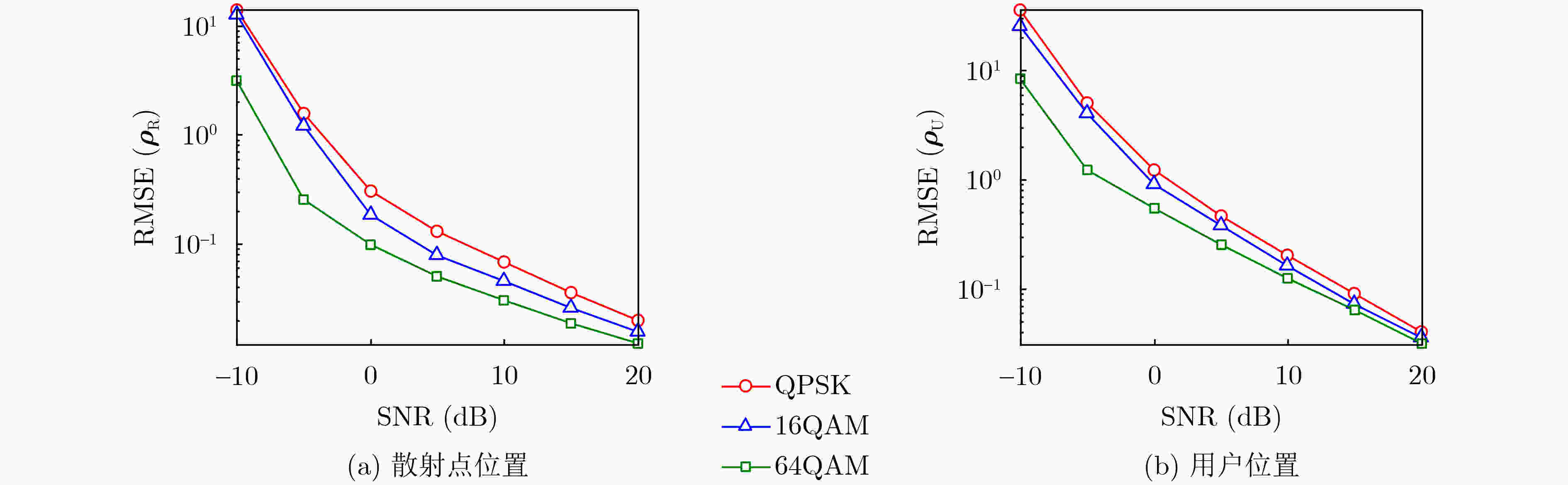
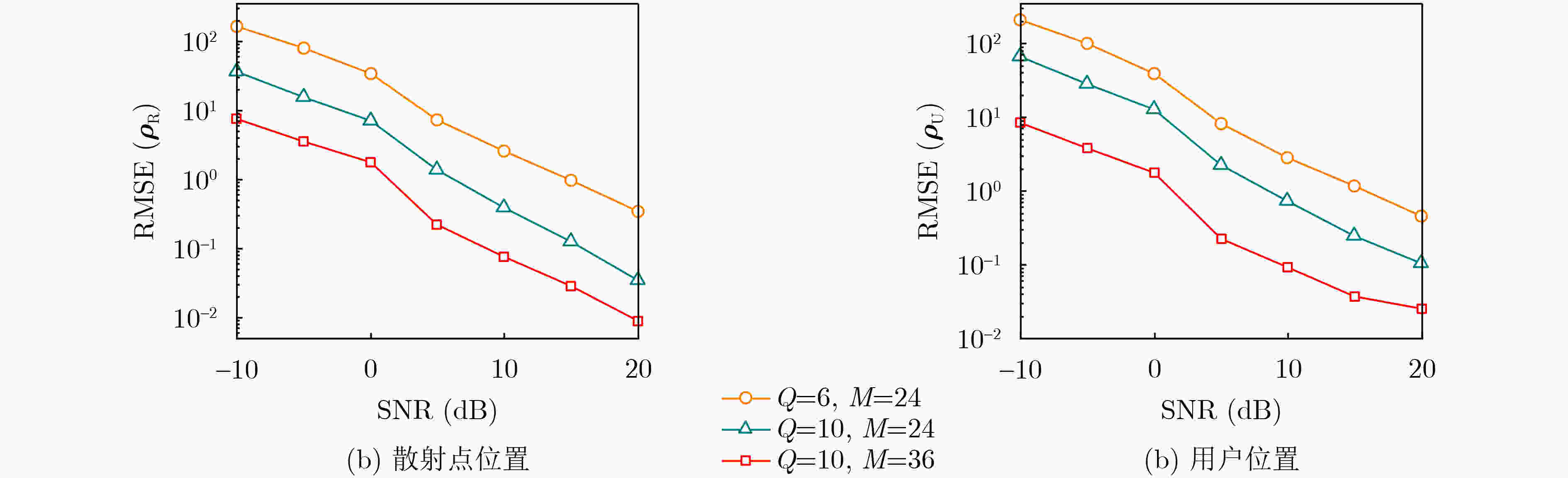
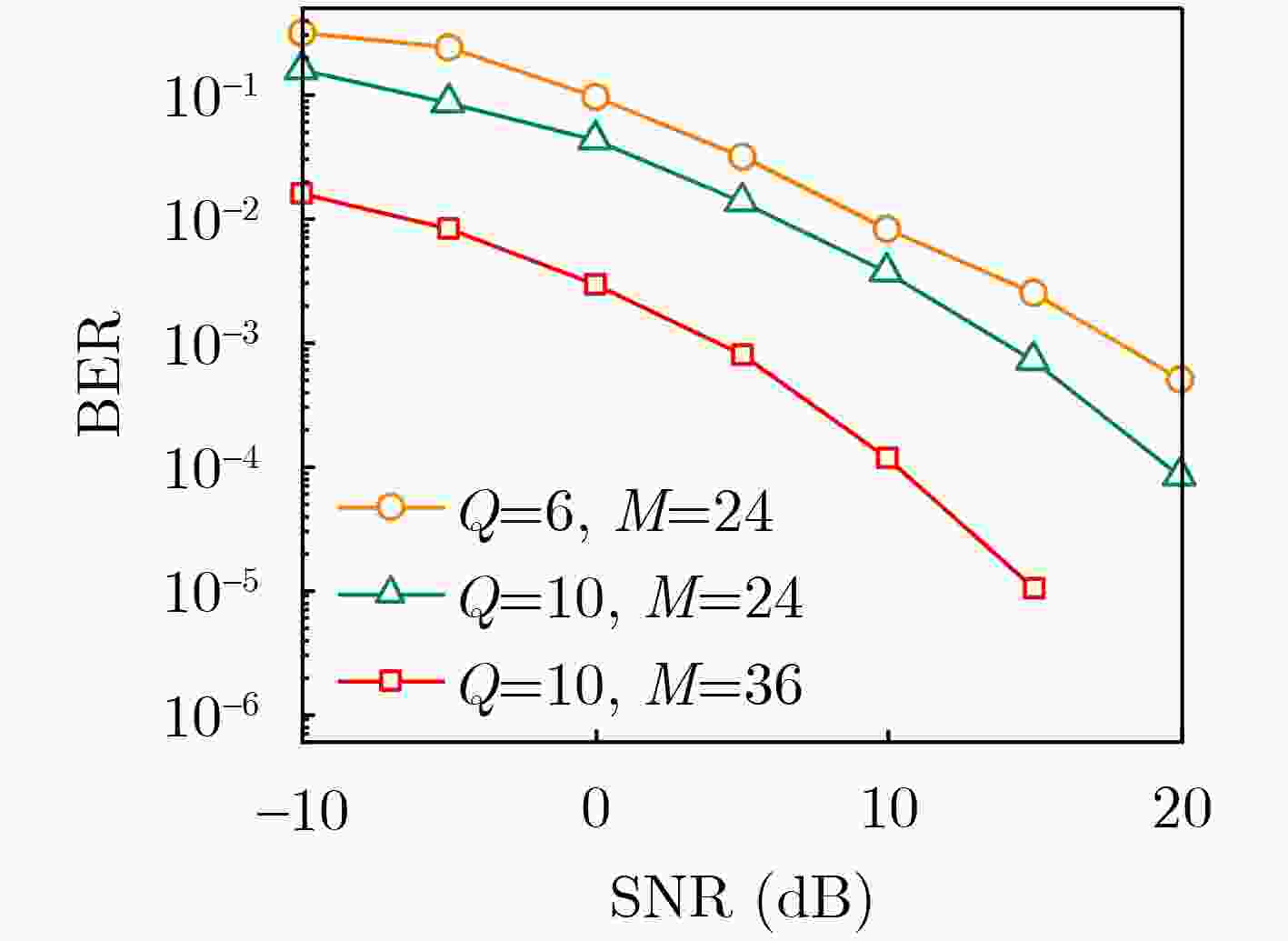
Objective As wireless communication technology advances, sensing and communication systems are shifting toward higher frequency bands, larger antenna arrays, and miniaturization. This integration of hardware architecture, channel characteristics, and signal processing enables wireless infrastructure to support environmental sensing in addition to communication. Technologies such as millimeter-wave communication, Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS), and Integrated Sensing And Communication (ISAC) facilitate this development. Although extensive research has examined RIS applications in ISAC systems, expanding the RIS aperture fundamentally alters electromagnetic field characteristics, extending the near-field range. Unlike far-field scenarios, near-field communication and sensing exhibit more complex channel structures, posing challenges for RIS-assisted millimeter-wave systems. To address these challenges, this study proposes an ISAC framework and develops a nested tensor-based Simultaneous Localization And Communication (SLAC) scheme. This approach localizes scattering points and users while detecting information symbols in near-field environments, eliminating the need for dedicated pilot signals. Methods First, a near-field spherical wave transmission model is established. To mitigate the complexity introduced by spatial path variations across reflection units, a channel model based on the second-order Taylor approximation is derived, incorporating distance, direction of arrival, and angle of arrival. Next, to fully utilize the time redundancy of Khatri-Rao Space-Time (KRST) coding, the received signal is formulated as a nested tensor model comprising outer and inner PARAFAC tensors, enabling the development of a nested tensor-based SLAC scheme. For the outer PARAFAC tensor, an Alternating Least Squares (ALS) algorithm is employed for channel matrix estimation and information symbol detection. For the inner PARAFAC model, a two-stage algorithm is used for channel parameter estimation and User Equipment (UE) and scatterer localization. The Minimum Description Length (MDL) method determines the number of transmission channel paths. In the first stage, the ALS method decomposes the PARAFAC model to estimate channel parameters. In the second stage, the ESPRIT algorithm is applied to refine parameter estimation and perform localization. Finally, the estimated channel parameters are used to determine the locations of the UE and scatterer points. Results and Discussions The proposed scheme first utilizes the multi-dimensional resources of the ISAC scenario and the KRST coding method to structure the received ISAC signals into a fourth-order nested tensor. Leveraging the algebraic properties of the nested tensor and the second-order Fresnel approximation of the near-field channel model, the nested tensor-based SLAC scheme is designed to enable near-field localization of scattering points and UE, as well as information symbol detection. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme achieves superior ISAC performance compared with existing methods ( Fig. 2 ,Fig. 3 ,Fig. 4 ). Performance improves as the number of subcarriers increases (Fig. 2 ,Fig. 3 ). Additionally, the scheme maintains high localization accuracy and symbol detection performance even under higher-order modulation (Fig. 5 ,Fig. 6 ). Further improvements in ISAC performance are observed with an increased number of time slots and coding length (Fig. 7 ,Fig. 8 ). The results also indicate good convergence across various parameter configurations.Conclusions This paper proposes an RIS-assisted ISAC millimeter-wave near-field transmission scheme based on a nested tensor model and develops a nested tensor-based SLAC scheme leveraging the second-order Fresnel approximation of the near-field channel model. The constructed nested tensor model exhibits an algebraic structure, enabling the proposed scheme to operate without dedicated pilot signals. Moreover, the model integrates multiple dimensions of sensing and communication signals, enhancing information symbol detection and target localization accuracy by extracting additional useful information. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves good convergence across various parameter configurations. Compared with existing methods, it exhibits superior sensing performance. Under higher-order modulation, it maintains excellent information symbol detection and achieves high-precision channel state information recovery, providing centimeter-level localization accuracy. Furthermore, the method is scalable and can be applied to larger-scale systems, such as expanding RIS or increasing the number of antennas. However, system scalability increases computational complexity, particularly for higher-order tensor models. To address this, optimizing the algorithm structure, such as introducing tensor-based closed-form algorithms (e.g., higher-order singular value decomposition), is a promising approach. -
1 基于嵌套张量的SLAC算法
初始化:相移矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} _k} $,编码矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{C}} $,信道矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\text{BI,}}k}} $,接收信
号$ {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{k,p,q}} $(1)将接收信号$ {{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{k,p,q}} $构造成张量$ {\mathcal{Y}_{k,q}} $ (2)借助张量$ {\mathcal{Y}_{k,q}} $,使用ALS算法求解$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{S}}_k} $和$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{H}}_k} $ (3)将$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{H}}_k} $构造张量$ {\hat {\mathcal{H}}_k} $,通过伪逆计算未知信道矩阵$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\text{IU,}}k}} $ (4)将$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{H}}_{{\text{IU,}}k}} $构造张量$ {\hat {\mathcal{H}}_{{\text{IU}}}} $,使用ALS算法分解因子矩阵得到
$ \left\{ {{{\hat {\boldsymbol{A}}}_{{\text{IT}}}},{{\hat {\boldsymbol{A}}}_{\text{U}}},\hat {\boldsymbol{B}}} \right\} $(5)使用MDL算法求解路径数目$ L $ (6)通过下采样方法得到$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{A}}_{{\text{IT}}}} $和$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{A}}_{\text{U}}} $对应的协方差矩阵 (7)使用ESPRIT算法和基于相关的算法估计信道参数
$ \left\{ {{{\hat \phi }_{{\text{U}},l}},{{\hat \theta }_{{\text{U}},l}},{{\hat \phi }_{{\text{IT}},l}},{{\hat \theta }_{{\text{IT}},l}},{{\hat \tau }_l}} \right\}_{l = 1}^L $(8)使用已估计的信道参数进行定位得到$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{\rho}} _{\text{U}}} $和$ \left\{ {{{\hat{\boldsymbol{ \rho}} }_{{\text{R,}}l}}} \right\}_{l = 1}^L $ 输出:发送信息符号$ {\hat S_k} $,信道参数
$ \left\{ {{{\hat \phi }_{{\text{U}},l}},{{\hat \theta }_{{\text{U}},l}},{{\hat \phi }_{{\text{IT}},l}},{{\hat \theta }_{{\text{IT}},l}},{{\hat \tau }_l}} \right\}_{l = 1}^L $,用户和散射点位置$ {\hat {\boldsymbol{\rho}} _{\text{U}}} $和
$ \left\{ {{{\hat {\boldsymbol{\rho }}}_{{\text{R,}}l}}} \right\}_{l = 1}^L $ -
[1] CHEN Shanzhi, SUN Shaohui, and KANG Shaoli. System integration of terrestrial mobile communication and satellite communication—the trends, challenges and key technologies in B5G and 6G[J]. China Communications, 2020, 17(12): 156–171. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2020.12.011. [2] CHEN Wanshi, LIN Xingqin, LEE J, et al. 5G-advanced toward 6G: Past, present, and future[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(6): 1592–1619. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3274037. [3] HAN Chong, WANG Yiqin, LI Yuanbo, et al. Terahertz wireless channels: A holistic survey on measurement, modeling, and analysis[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(3): 1670–1707. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3182539. [4] 褚宏云, 杨梦瑶, 黄航, 等. 混合智能反射面辅助的通信感知一体化: 高能效波束成形设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(6): 2462–2469. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230699.CHU Hongyun, YANG Mengyao, HUANG Hang, et al. Hybrid reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted integrated sensing and communication: Energy efficient beamforming design[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(6): 2462–2469. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230699. [5] HU Xiaoling, LIU Chenxi, PENG Mugen, et al. IRS-based integrated location sensing and communication for mmWave SIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(6): 4132–4145. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3223428. [6] YANG Runruo, WANG Chengxiang, HUANG Jie, et al. A novel 6G ISAC channel model combining forward and backward scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(11): 8050–8065. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3258150. [7] PAN Yijin, PAN Cunhua, and JIN Shi. Localization in the near field of a RIS-assisted mmWave/subTHz system[C]. 2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022: 3905–3910. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM48099.2022.10001107. [8] 李兴旺, 田志发, 张建华, 等. IRS辅助NOMA网络下隐蔽通信性能研究[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(6): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174.LI Xingwang, TIAN Zhifa, ZHANG Jianhua, et al. Performance analysis of covert communication in IRS-assisted NOMA networks[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2024, 54(6): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174. [9] LIN Zhi, NIU Hehao, AN Kang, et al. Refracting RIS-aided hybrid satellite-terrestrial relay networks: Joint beamforming design and optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3717–3724. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3155711. [10] AN Kang, SUN Yifu, LIN Zhi, et al. Exploiting multi-layer refracting RIS-assisted receiver for HAP-SWIPT networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(10): 12638–12657. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3394214. [11] LIN Zhi, NIU Hehao, AN Kang, et al. Pain without gain: Destructive beamforming from a malicious RIS perspective in IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(5): 7619–7629. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3316830. [12] XIONG Baiping, ZHANG Zaichen, JIANG Hao, et al. A 3D non-stationary MIMO channel model for reconfigurable intelligent surface auxiliary UAV-to-ground mmWave communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(7): 5658–5672. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3142437. [13] DARDARI D, DECARLI N, GUERRA A, et al. LOS/NLOS near-field localization with a large reconfigurable intelligent surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(6): 4282–4294. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3128415. [14] SAVKIN A V, HUANG Chao, and NI Wei. Joint multi-UAV path planning and LoS communication for mobile-edge computing in IoT networks with RISs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(3): 2720–2727. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3215255. [15] ZHU Qi, LI Ming, LIU Rang, et al. Joint transceiver beamforming and reflecting design for active RIS-aided ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(7): 9636–9640. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3249752. [16] LE Q N, NGUYEN V D, DOBRE O A, et al. RIS-assisted full-duplex integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(10): 1677–1681. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3285391. [17] LYU Wanting, YANG Songjie, XIU Yue, et al. CRB Minimization for RIS-aided mmWave integrated sensing and communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(10): 18381–18393. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3361939. [18] ALKHATEEB A, El AYACH O, LEUS G, et al. Channel estimation and hybrid precoding for millimeter wave cellular systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(5): 831–846. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2014.2334278. [19] JIANG Fan, WEN Fuxi, GE Yu, et al. Beamspace multidimensional ESPRIT approaches for simultaneous localization and communications[J]. 2021. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2111.07450. [20] NAKAMURA M, HASHIZUME H, and SUGIMOTO M. Simultaneous localization and communication method using short-time and narrow-band dual-carrier acoustic signals[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5163–5172. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3107849. [21] WEI Xiuhong and DAI Linglong. Channel estimation for extremely large-scale massive MIMO: Far-field, near-field, or hybrid-field?[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(1): 177–181. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3124927. [22] LU Yu and DAI Linglong. Near-field channel estimation in mixed LoS/NLoS environments for extremely large-scale MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(6): 3694–3707. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3260242. [23] WEI Xiuhong, DAI Linglong, ZHAO Yajun, et al. Codebook design and beam training for extremely large-scale RIS: Far-field or near-field?[J]. China Communications, 2022, 19(6): 193–204. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2022.06.015. [24] EMENONYE D R, DHILLON H S, and BUEHRER R M. RIS-aided localization under position and orientation offsets in the near and far field[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 9327–9345. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3270029. [25] YANG Songjie, XIE Chenfei, LYU Wanting, et al. Near-field channel estimation for extremely large-scale reconfigurable intelligent surface (XL-RIS)-aided wideband mmWave systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2024, 42(6): 1567–1582. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2024.3389120. [26] XIAO Jian, WANG Ji, WANG Zhaolin, et al. Multi-task learning for near/far field channel estimation in STAR-RIS networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(10): 6344–6359. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3402619. [27] ZUO Weiliang, XIN Jingmin, OHMORI H, et al. Subspace-based algorithms for localization and tracking of multiple near-field sources[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(1): 156–171. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2897953. [28] XIMENES L R, FAVIER G, and DE ALMEIDA A L F. Semi-blind receivers for non-regenerative cooperative MIMO communications based on nested PARAFAC modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(18): 4985–4998. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2454473. [29] LIN Yuxing, JIN Shi, MATTHAIOU M, et al. Tensor-based channel estimation for millimeter wave MIMO-OFDM with dual-wideband effects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(7): 4218–4232. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2983673. [30] ZHOU Zhou, FANG Jun, YANG Linxiao, et al. Low-rank tensor decomposition-aided channel estimation for millimeter wave MIMO-OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(7): 1524–1538. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2699338. [31] DU Jianhe, CHENG Yuan, JIN Libiao, et al. Nested tensor-based integrated sensing and communication in RIS-assisted THz MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 1141–1157. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3359323. [32] NION D and SIDIROPOULOS N D. Tensor algebra and multidimensional harmonic retrieval in signal processing for MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(11): 5693–5705. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2058802. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
