Adjacent Coordination Network for Salient Object Detection in 360 Degree Omnidirectional Images
-
摘要: 为解决360°全景图像显著目标检测(SOD)中的显著目标尺度变化和边缘不连续、易模糊的问题,该文提出一种基于相邻协调网络的360°全景图像显著目标检测方法(ACoNet)。首先,利用相邻细节融合模块获取相邻特征中的细节和边缘信息,以促进显著目标的精确定位。其次,使用语义引导特征聚合模块来聚合浅层特征和深层特征之间不同尺度上的语义特征信息,并抑制浅层特征传递的噪声,缓解解码阶段显著目标与背景区域不连续、边界易模糊的问题。同时构建多尺度语义融合子模块扩大不同卷积层的多尺度感受野,实现精确训练显著目标边界的效果。在2个公开的数据集上进行的大量实验结果表明,相比于其他13种先进方法,所提方法在6个客观评价指标上均有明显的提升,同时主观可视化检测的显著图边缘轮廓性更好,空间结构细节信息更清晰。Abstract: To address the issues of significant target scale variation, edge discontinuity, and blurring in 360° omnidirectional images Salient Object Detection (SOD), a method based on the Adjacent Coordination Network (ACoNet) is proposed. First, an adjacent detail fusion module is used to capture detailed and edge information from adjacent features, which facilitates accurate localization of salient objects. Then, a semantic-guided feature aggregation module is employed to aggregate semantic feature information from different scales between shallow and deep features, suppressing the noise transmitted by shallow features. This helps alleviate the problem of discontinuous salient objects and blurred boundaries between the object and background in the decoding stage. Additionally, a multi-scale semantic fusion submodule is constructed to enlarge the receptive field across different convolution layers, thereby achieving better training of the salient object boundaries. Extensive experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate that, compared to 13 other advanced methods, the proposed approach achieves significant improvements in six objective evaluation metrics. Moreover, the subjective visualized detection results show better edge contours and clearer spatial structural details of the salient maps.
-
表 1 360-SOD 数据集上不同方法客观指标对比
MAE↓ max-F↑ mean-F↑ max-Em↑ mean-Em↑ Sm↑ 360°SOD 本文方法 0.0181 0.7893 0.7815 0.9141 0.9043 0.8493 MPFRNet(2024) 0.0190 0.7653 0.7556 0.8854 0.8750 0.8416 LDNet(2023) 0.0289 0.6561 0.6414 0.8655 0.8437 0.7680 FANet(2020) 0.0208 0.7699 0.7485 0.9002 0.8729 0.8261 2D SOD MEANet(2022) 0.0243 0.7098 0.7016 0.8675 0.8398 0.7808 BSCGNet(2023) 0.0246 0.6795 0.6725 0.8666 0.8380 0.7844 SeaNet(2023) 0.0293 0.6080 0.5981 0.8611 0.8319 0.7374 AGNet(2022) 0.0221 0.7503 0.7410 0.8754 0.8574 0.8055 ACCoNet(res)(2023) 0.0243 0.6855 0.6735 0.8690 0.8159 0.7864 ACCoNet(vgg)(2023) 0.0245 0.6910 0.6782 0.8629 0.8060 0.7711 MSCNet(2023) 0.0247 0.7286 0.7162 0.8740 0.8672 0.8139 CorrNet(2022) 0.0474 0.2515 0.1673 0.5465 0.3867 0.5322 PGNet(2021) 0.0237 0.6944 0.6861 0.8625 0.8360 0.7895 CSDF(2023) 0.0275 0.6621 0.6433 0.8521 0.7829 0.7530 SwinNet(2022) 0.0240 0.7023 0.6818 0.8624 0.8315 0.7897 表 2 360-SSOD 数据集上不同方法客观指标对比
MAE↓ max-F↑ mean-F↑ max-Em↑ mean-Em↑ Sm↑ 360°SOD 本文方法 0.0288 0.6641 0.6564 0.8695 0.8632 0.7796 MPFRNet(2024) --- --- --- --- --- --- LDNet(2023) 0.0341 0.5868 0.5695 0.8415 0.8221 0.7252 FANet(2020) 0.0421 0.5939 0.5215 0.8426 0.7324 0.7186 2D SOD MEANet(2022) 0.0289 0.6343 0.6242 0.8578 0.8437 0.7479 BSCGNet(2023) 0.0316 0.5969 0.5832 0.8216 0.8079 0.7395 SeaNet(2023) 0.0383 0.3929 0.3432 0.7525 0.5695 0.5978 AGNet(2022) 0.0297 0.6371 0.6291 0.8409 0.8176 0.7701 ACCoNet(res)(2023) 0.0365 0.5752 0.5555 0.8312 0.7929 0.7341 ACCoNet(vgg)(2023) 0.0312 0.6043 0.5904 0.8297 0.7938 0.7358 MSCNet(2023) 0.0370 0.6239 0.6026 0.8512 0.8328 0.7613 CorrNet(2022) 0.0540 0.2586 0.0904 0.7046 0.3347 0.5006 PGNet(2021) 0.0946 0.0772 0.0545 0.5889 0.5613 0.4493 CSDF(2023) 0.0326 0.5490 0.5211 0.8117 0.7399 0.6942 SwinNet(2022) 0.0940 0.0772 0.0469 0.5877 0.5379 0.4482 表 3 本文模型与不同先进方法复杂度对比结果
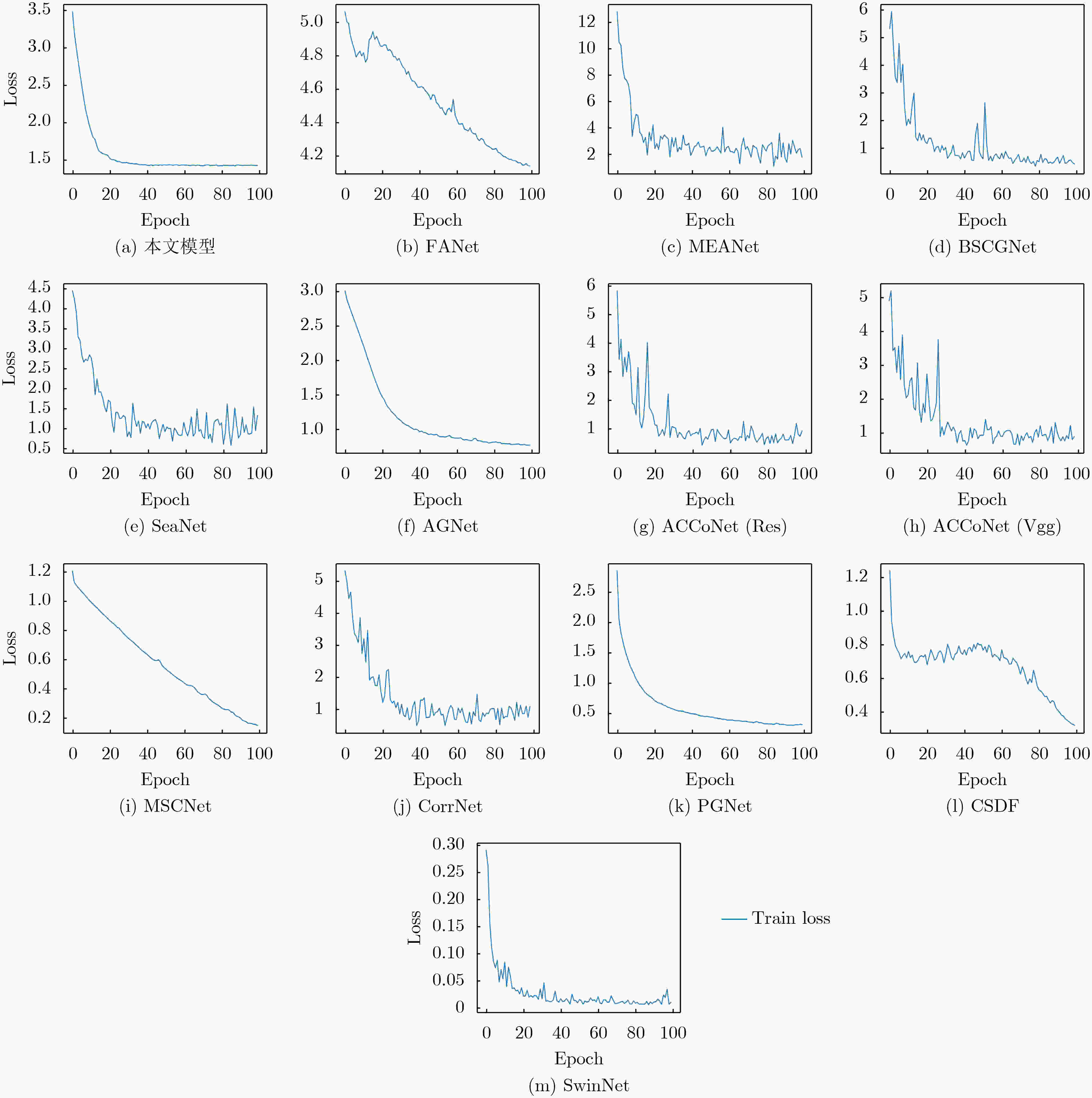
复杂度指标 本文模型 FANet MEANet BSCGNet SeaNet AGNet GFLOPs(G) 76.24 340.94 11.99 86.46 2.86 25.28 Params(M) 24.15 25.40 3.27 36.99 2.75 24.55 复杂度指标 ACCoNet MSCNet CorrNet PGNet CSDF SwinNet GFLOPs(G) 406.06 15.47 42.63 14.37 78.14 43.56 Params(M) 127.00 3.26 4.07 72.67 26.24 97.56 表 4 相关模块以及多分支结构的消融实验结果
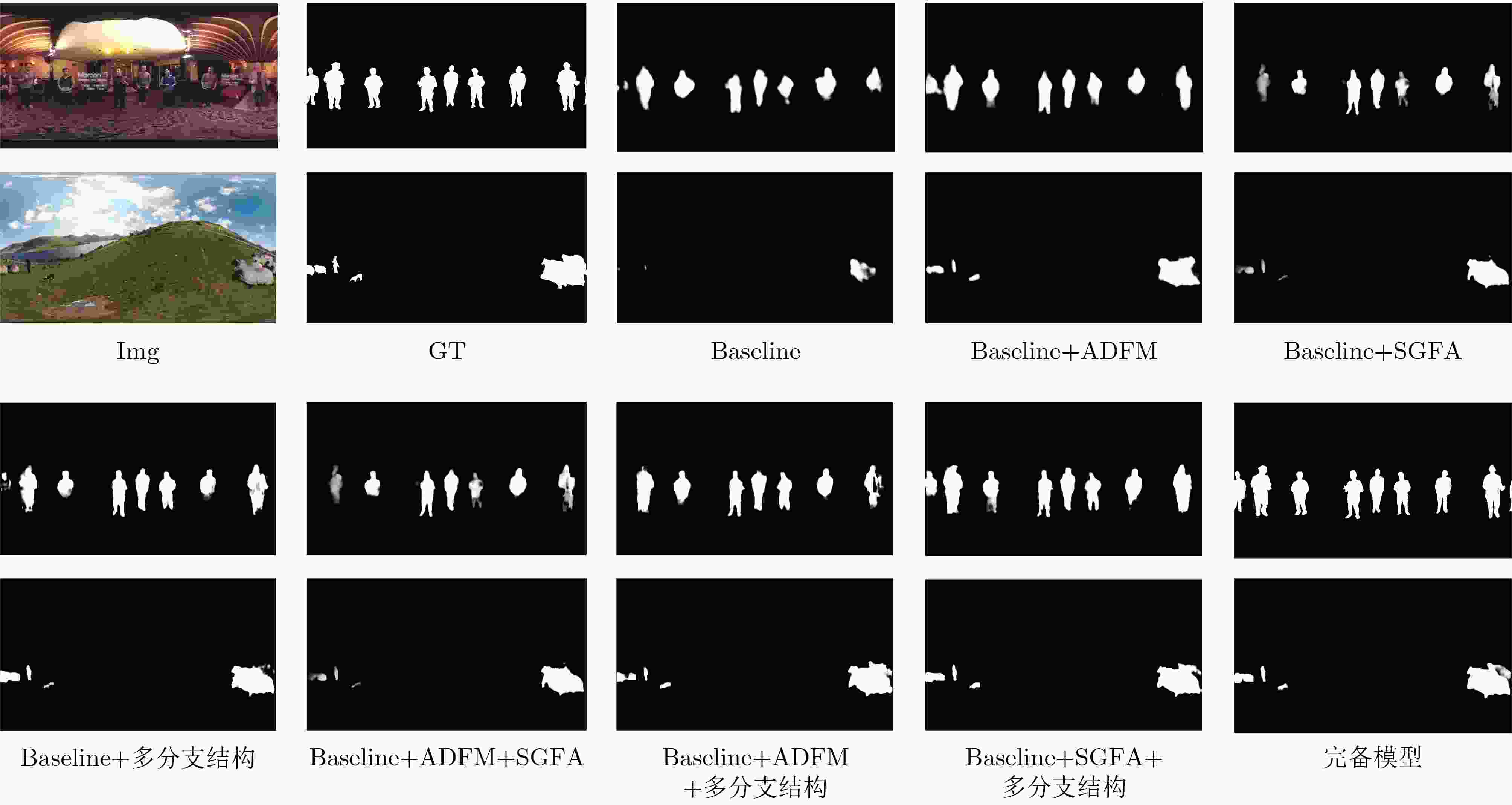
Baseline ADFM SGFA 多分支结构 MAE↓ max-F↑ mean-F↑ max-Em↑ mean-Em↑ Sm↑ √ 0.0238 0.7193 0.7107 0.8823 0.8525 0.7912 √ √ 0.0220 0.7580 0.7466 0.9133 0.8898 0.8185 √ √ 0.0209 0.7562 0.7517 0.8915 0.8796 0.8252 √ √ 0.0206 0.7584 0.7483 0.8959 0.8745 0.8304 √ √ √ 0.0207 0.7819 0.7642 0.9170 0.8650 0.8244 √ √ √ 0.0202 0.7704 0.7587 0.9007 0.8899 0.8322 √ √ √ 0.0184 0.7777 0.7660 0.9113 0.8878 0.8407 √ √ √ √ 0.0181 0.7893 0.7815 0.9141 0.9043 0.8493 -
[1] CONG Runmin, LEI Jianjun, FU Huazhu, et al. Review of visual saliency detection with comprehensive information[J]. IEEE Transactions on circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2019, 29(10): 2941–2959. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2870832. [2] 丁颖, 刘延伟, 刘金霞, 等. 虚拟现实全景图像显著性检测研究进展综述[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(7): 1575–1583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.07.024.DING Ying, LIU Yanwei, LIU Jinxia, et al. An overview of research progress on saliency detection of panoramic VR images[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(7): 1575–1583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.07.024. [3] GONG Xuan, XIA Xin, ZHU Wentao, et al. Deformable Gabor feature networks for biomedical image classification[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 4003–4011. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00405. [4] XU K, BA J, KIROS R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2048–2057. [5] 张德祥, 王俊, 袁培成. 基于注意力机制的多尺度全场景监控目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(9): 3249–3257. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210664.ZHANG Dexiang, WANG Jun, and YUAN Peicheng. Object detection method for multi-scale full-scene surveillance based on attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(9): 3249–3257. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210664. [6] GAO Yuan, SHI Miaojing, TAO Dacheng, et al. Database saliency for fast image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(3): 359–369. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2389616. [7] LI Jia, SU Jinming, XIA Changqun, et al. Distortion-adaptive salient object detection in 360°omnidirectional images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2020, 14(1): 38–48. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2957982. [8] MA Guangxiao, LI Shuai, CHEN Chenglizhao, et al. Stage-wise salient object detection in 360°omnidirectional image via object-level semantical saliency ranking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, 26(12): 3535–3545. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2020.3023636. [9] HUANG Mengke, LIU Zhi, LI Gongyang, et al. FANet: Features adaptation network for 360°omnidirectional salient object detection[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1819–1823. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3028192. [10] LIU Nian and HAN Junwei. DHSNet: Deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 678–686. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.80. [11] PANG Youwei, ZHAO Xiaoqi, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9410–9419. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00943. [12] ZENG Yi, ZHANG Pingping, LIN Zhe, et al. Towards high-resolution salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 7233–7242. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00733. [13] ZHANG Lu, DAI Ju, LU Huchuan, et al. A bi-directional message passing model for salient object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1741–1750. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00187. [14] FENG Mengyang, LU Huchuan, and DING E. Attentive feedback network for boundary-aware salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1623–1632. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00172. [15] WU Zhe, SU Li, and HUANG Qingming. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3902–3911. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00403. [16] MA Mingcan, XIA Changqun, and LI Jia. Pyramidal feature shrinking for salient object detection[C]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 2311–2318. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i3.16331. [17] QIN Xuebin, ZHANG Zichen, HUANG Chenyang, et al. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106: 107404. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404. [18] PAN Chen, LIU Jianfeng, YAN Weiqi, et al. Salient object detection based on visual perceptual saturation and two-stream hybrid networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4773–4787. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3074796. [19] MA Guangxiao, LI Shuai, CHEN Chenglizhao, et al. Rethinking image salient object detection: Object-level semantic saliency reranking first, pixelwise saliency refinement later[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4238–4252. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3068649. [20] REN Guangyu, XIE Yanchu, DAI Tianhong, et al. Progressive multi-scale fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection[J]. arXiv: 2106.03941, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2106.03941. [21] CHENG Mingming, MITRA N J, HUANG Xiaolei, et al. Global contrast based salient region detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 569–582. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345401. [22] LIU Qing, HONG Xiaopeng, ZOU Beiji, et al. Hierarchical contour closure-based holistic salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4537–4552. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2703081. [23] ZHAO Rui, OUYANG Wanli, LI Hongsheng, et al. Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1265–1274. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298731. [24] LIU Jiangjiang, HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, et al. A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3912–3921. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00404. [25] WU Yuhuan, LIU Yun, ZHANG Le, et al. EDN: Salient object detection via extremely-downsampled network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 3125–3136. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3164550. [26] ZHAO Jiaxing, LIU Jiangjiang, FAN Dengping, et al. EGNet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8778–8787. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00887. [27] LV Yunqiu, LIU Bowen, ZHANG Jing, et al. Semi-supervised active salient object detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 123: 108364. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108364. [28] WANG Tiantian, BORJI A, ZHANG Lihe, et al. A stagewise refinement model for detecting salient objects in images[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4039–4048. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.433. [29] HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, HU Xiaowei, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5300–5309. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.563. [30] LIU Nian, HAN Junwei, and YANG M H. PiCANet: Learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3089–3098. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00326. [31] OUYANG Wentao, ZHANG Xiuwu, ZHAO Lei, et al. MiNet: Mixed interest network for cross-domain click-through rate prediction[C/Ol]. The 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, 2020: 2669–2676. doi: 10.1145/3340531.3412728. [32] HUANG Tongwen, SHE Qingyun, WANG Zhiqiang, et al. GateNet: Gating-enhanced deep network for click-through rate prediction[J]. arXiv: 2007.03519, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2007.03519. [33] ZHANG Yi, ZHANG Lu, HAMIDOUCHE W, et al. A fixation-based 360° benchmark dataset for salient object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2020: 3458–3462. doi: 10.1109/ICIP40778.2020.9191158. [34] CONG Runmin, HUANG Ke, LEI Jianjun, et al. Multi-projection fusion and refinement network for salient object detection in 360° omnidirectional image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(7): 9495–9507. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3233883. [35] CHEN Dongwen, QING Chunmei, XU Xiangmin, et al. SalBiNet360: Saliency prediction on 360° images with local-global bifurcated deep network[C]. 2020 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces, Atlanta, USA, 2020: 92–100. doi: 10.1109/VR46266.2020.00027. [36] CHEN Gang, SHAO Feng, CHAI Xiongli, et al. Multi-stage salient object detection in 360° omnidirectional image using complementary object-level semantic information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(1): 776–789. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2023.3259433. [37] ZHANG Yi, HAMIDOUCHE W, and DEFORGES O. Channel-spatial mutual attention network for 360° salient object detection[C]. The 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Montreal, Canada, 2022: 3436–3442. doi: 10.1109/ICPR56361.2022.9956354. [38] WU Junjie, XIA Changqun, YU Tianshu, et al. View-aware salient object detection for 360° omnidirectional image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2023, 25: 6471–6484. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2022.3209015. [39] LIN Yuhan, SUN Han, LIU Ningzhong, et al. A lightweight multi-scale context network for salient object detection in optical remote sensing images[C]. The 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Montreal, Canada, 2022: 238–244. doi: 10.1109/ICPR56361.2022.9956350. [40] JIANG Yao, ZHANG Wenbo, FU Keren, et al. MEANet: Multi-modal edge-aware network for light field salient object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 491: 78–90. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.03.056. [41] LI Gongyang, LIU Zhi, ZHANG Xinpeng, et al. Lightweight salient object detection in optical remote-sensing images via semantic matching and edge alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5601111. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3235717. [42] LI Gongyang, LIU Zhi, BAI Zhen,et al. Lightweight Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images via Feature Correlation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60:5617712. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3145483. [43] FENG Dejun, CHEN Hongyu, LIU Suning, et al. Boundary-semantic collaborative guidance network with dual-stream feedback mechanism for salient object detection in optical remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4706317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3332282. [44] LIN Yuhan, SUN Han, LIU Ningzhong, et al. Attention guided network for salient object detection in optical remote sensing images[C]. The 31st International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Bristol, UK, 2022: 25–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-15919-0_3. [45] WANG Pengfei, ZHANG Chengquan, QI Fei, et al. PGNet: Real-time arbitrarily-shaped text spotting with point gathering network[C/OL]. The 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 2782–2790. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i4.16383. [46] LI Gongyang, LIU Zhi, ZENG Dan, et al. Adjacent context coordination network for salient object detection in optical remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(1): 526–538. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3162945. [47] SONG Yue, TANG Hao, SEBE N, et al. Disentangle saliency detection into cascaded detail modeling and body filling[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications, 2023, 19(1): 7. doi: 10.1145/3513134. [48] LIU Zhengyi, TAN Yacheng, HE Qian, et al. SwinNet: Swin transformer drives edge-aware RGB-D and RGB-T salient object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(7): 4486–4497. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3127149. [49] HUANG Mengke, LI Gongyang, LIU Zhi, et al. Lightweight distortion-aware network for salient object detection in omnidirectional images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(10): 6191–6197. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3253685. -






 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
