Performance and Optimal Placement Analysis of Intelligent Reflecting Surface-assisted Wireless Networks
-
摘要: 当基站(BS)和用户的位置固定,基站到智能反射面(IRS)与IRS到用户的距离和一定时,该文在视距信道和瑞利信道下基于最大化系统可达速率准则对无源和有源IRS的最优放置位置进行分析。首先,运用相位对齐和大数定律推导了无源和有源IRS辅助无线网络可达速率的闭合表达式;然后,分析了基站到IRS的路径损耗指数${\beta _1}$和IRS到用户的路径损耗指数${\beta _2}$对IRS最优部署位置的影响,即当${\beta _{\text{1}}} \gt {\beta _{\text{2}}}$时,无源IRS的最优部署位置始终靠近基站,随着${\beta _1}$和${\beta _2}$的差距逐渐增大,有源IRS的最优部署位置逐渐靠近基站;当${\beta _1} \lt {\beta _2}$时,则得到相反的结论。仿真结果表明:当${\beta _1} = {\beta _2}$且无源IRS到基站和到用户的距离相等时,系统的可达速率性能最差。当固定有源IRS处的噪声功率且增加用户处的噪声功率时,IRS的最优部署位置始终靠近用户;当固定后者增大前者时,IRS的最优部署位置逐渐靠近基站。Abstract:
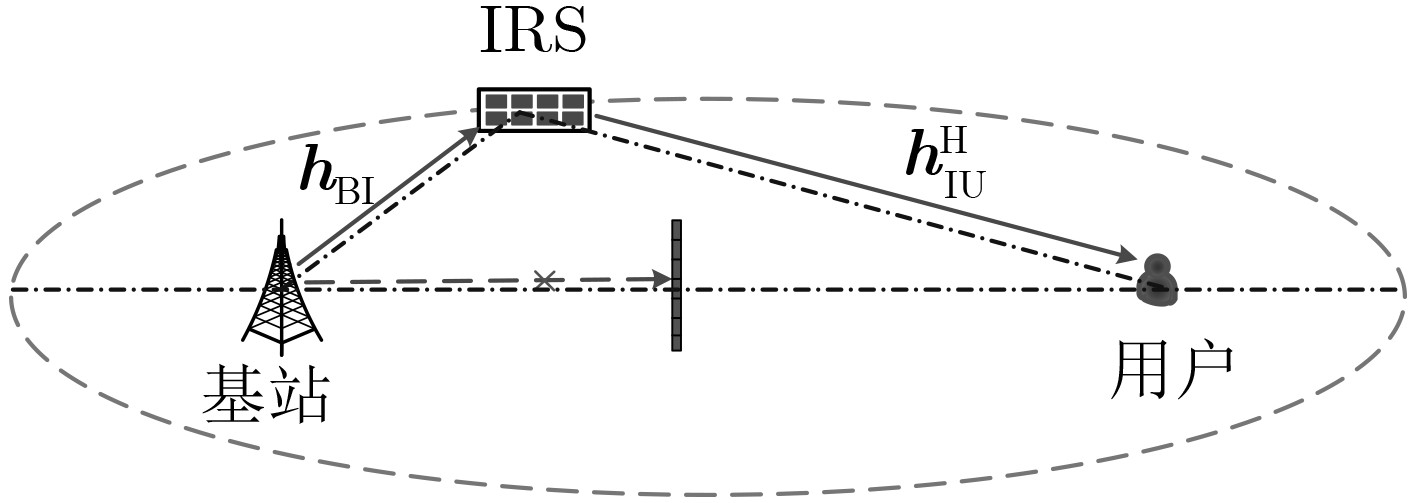
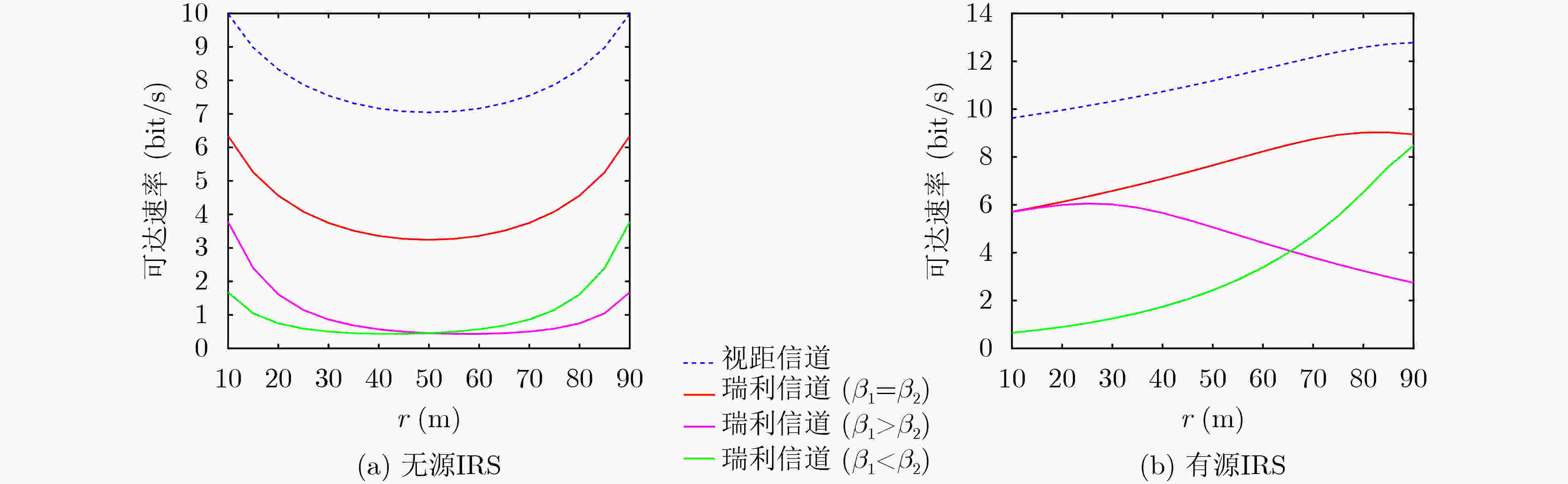
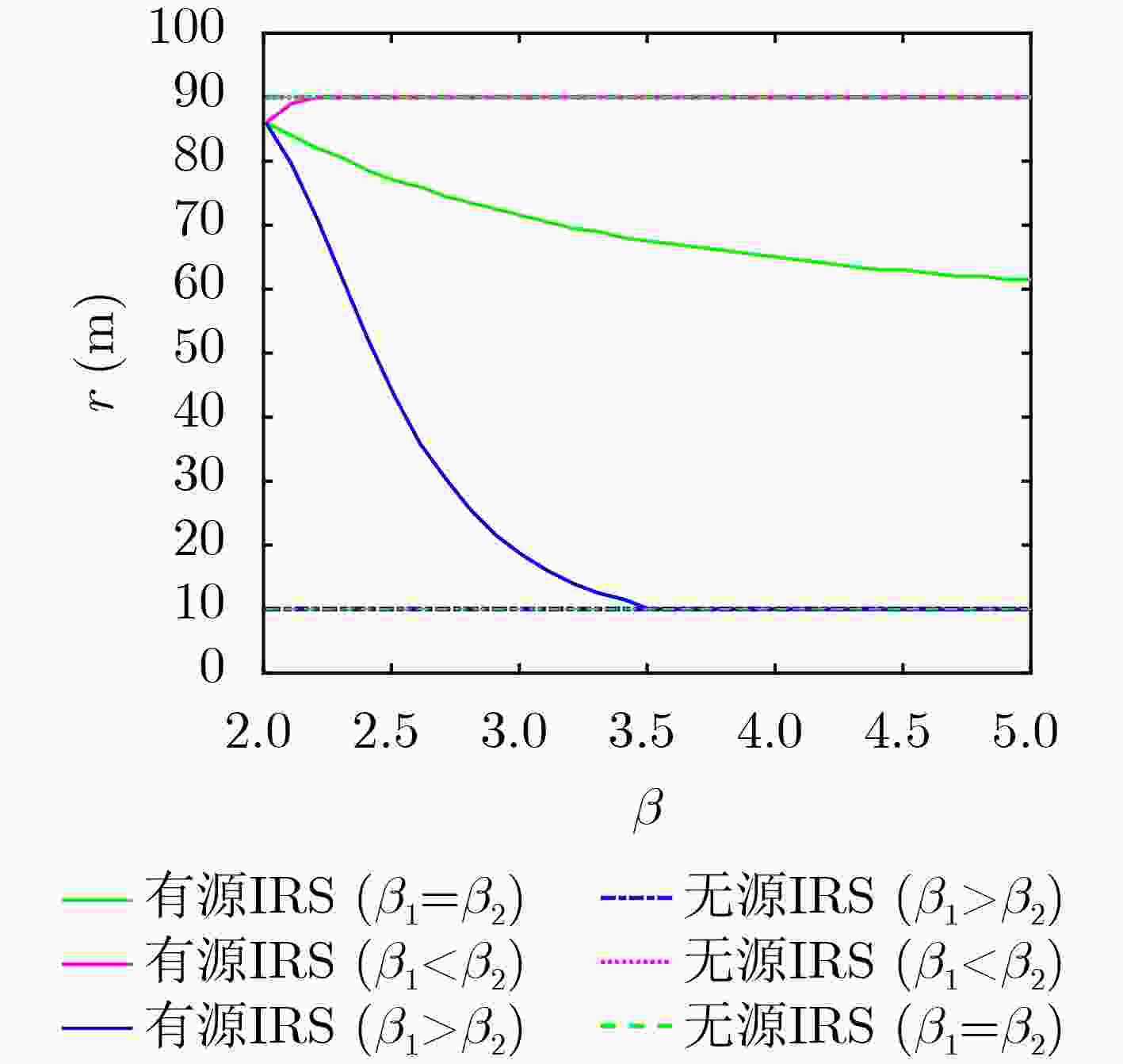
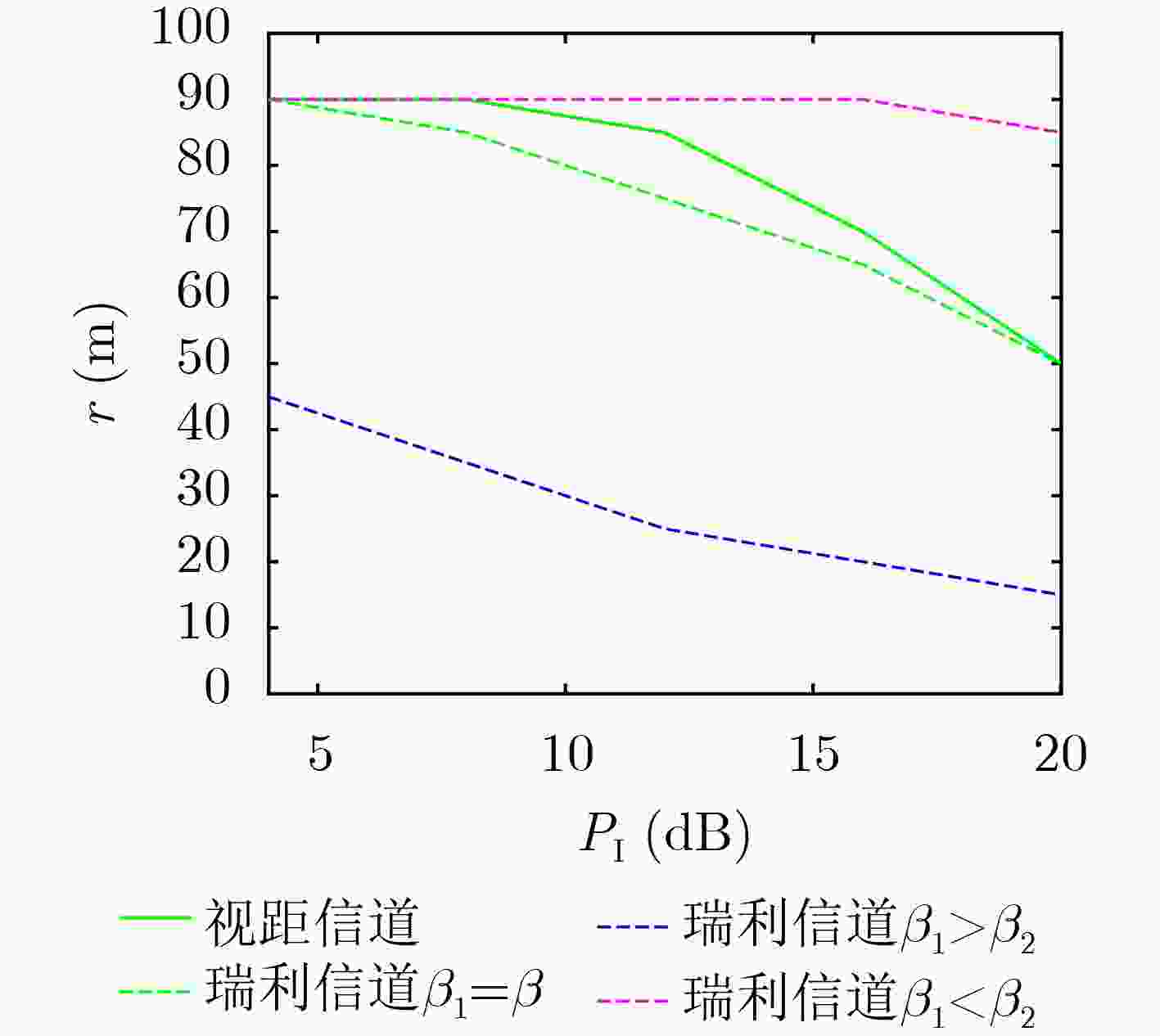
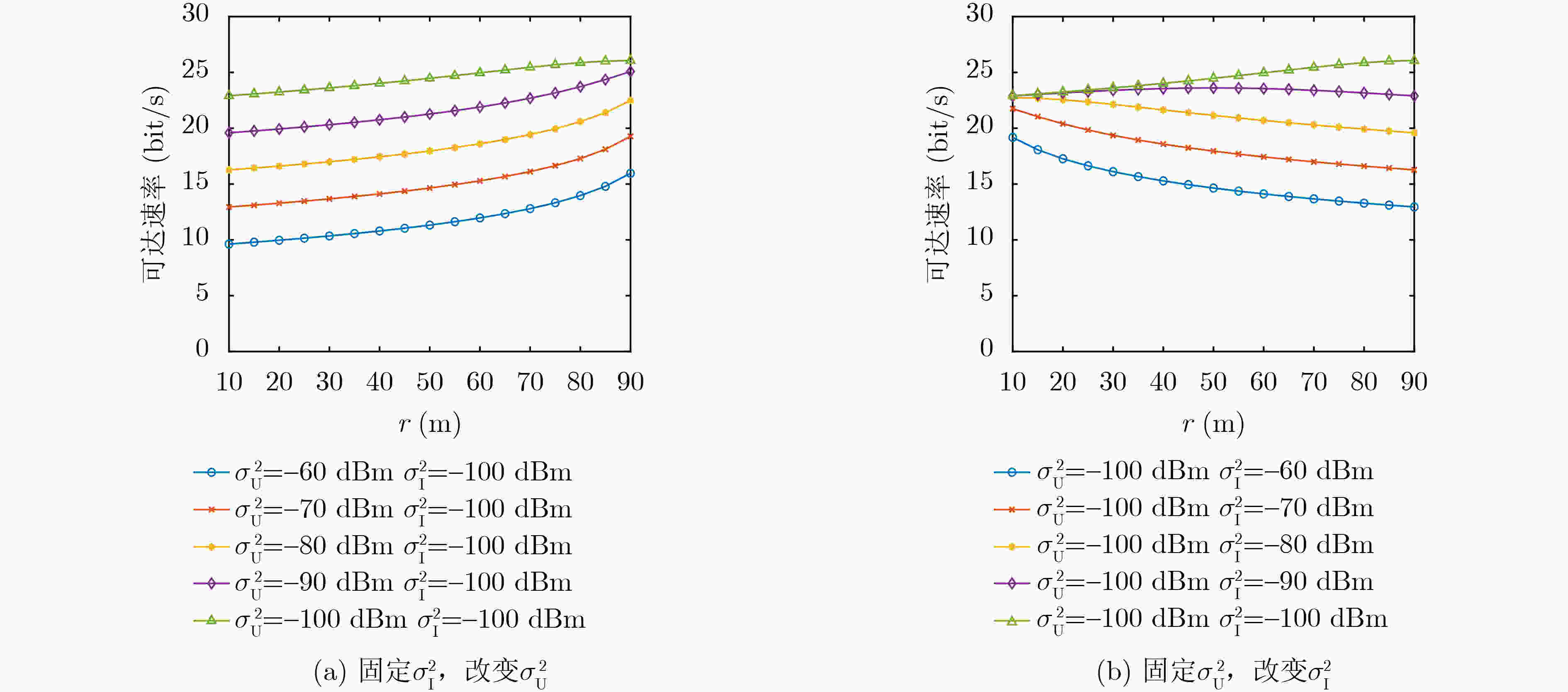
Objective: Previous studies have extensively examined the performance of Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS)-assisted wireless communications by varying the location of the IRS. However, relocating the IRS alters the sum of the distances between the IRS and the base station, as well as the distances to users, leading to discrepancies in reflective channel transmission distances, which introduces a degree of unfairness. Additionally, the assumption that the path loss indices for the base station-to-IRS and IRS-to-user channels are equal is overly idealistic. In practical scenarios, the user’s height is typically much lower than that of the base station, and the IRS may be positioned closer to either the base station or the user. This disparity results in significantly different path loss indices for the two channels. Consequently, this paper focuses on identifying the optimal deployment location of the IRS while keeping the total distance fixed. The IRS is modeled to move along an ellipsoid or ellipsoidal plane defined by the base station and the user as focal points. The analysis provides insights into the optimal deployment of the IRS while taking into account a broader range of application scenarios, specifically addressing different path loss indices for the base station-to-IRS and IRS-to-user channels given a predetermined sum of the transmitting powers. Methods: Utilizing concepts of phase alignment and the law of large numbers, closed-form expressions for the reachability rate of both passive and active IRS-assisted wireless networks are initially derived for two scenarios: the line-of-sight channel and the Rayleigh channel. Following this, the study analyzes how the path loss exponents from the base station to the IRS and from the IRS to the user impact the optimal deployment location of the IRS. Results and Discussions: The reachability rate of a passive IRS-assisted wireless network, considering IRS locations under both line-of-sight and Rayleigh channels, is illustrated. It is evident that the optimal deployment location of the IRS is nearest to either the base station or the user when β1=β2. When β1>β2, the optimal deployment location of the IRS is obtained solely at the base station, while the least effective deployment location shifts progressively closer to the user. Conversely, a contrasting result is obtained when β1<β2. The above results verify the correctness of the theoretical derivation in Section 3.1.3. The reachability rate of an active IRS-assisted wireless network as a function of IRS location under line-of-sight and Rayleigh channels is depicted. The figure indicates that when β1=β2, the system’s reachability rate under the line-of-sight channel exceeds that of the Rayleigh channel, with the optimal deployment location of the active IRS positioned in proximity to the user. When β1>β2 (fixed β2, increasing β1), the optimal deployment location of the active IRS progressively approaches the base station. And when β1<β2, the optimal deployment location shifts closer to the user. The optimal deployment location of the IRS for IRS-assisted wireless networks operating under a Rayleigh channel, reflecting variations in the path loss index β, is portrayed. Notably, for passive IRS systems, regardless of the path loss index variations, the optimal deployment locations across three different cases yield consistent conclusions with those derived. For the active IRS, when β1=β2=β1, the optimal deployment location gradually distances itself from the user ultimately approaching the IRS location at m (directly above the midpoint of the line connecting the base station and user). Conversely, when β1>β2, the optimal deployment position of the IRS increasingly aligns with the base station along an elliptical trajectory; conversely, when β1<β2, it shifts towards the user. The optimal deployment location of the active IRS under both line-of-sight and Rayleigh channels as a function of Igressively approaches the base station. And wRS reflected power PI is displayed. The analysis indicates that in both channel conditions, as the IRS reflected power increases, the optimal deployment location for the active IRS progressively moves closer to the base station along an elliptical trajectory as PI gradually increases. And at β1=β2 and PI=PB, the optimal deployment location of the active IRS maintains an equal distance from both the base station and the user. The system’s reachability rate in relation to the distance r from the base station to the active IRS, accounting for different user noise $\sigma_{\mathrm{U}}^2 $ and amplified noise $\sigma_{\mathrm{I}}^2 $ of the active IRS, is presented. When fixing $\sigma_{\mathrm{I}}^2 $ and gradually increasing $\sigma_{\mathrm{U}}^2 $, the optimal deployment location of the active IRS is situated closer to the user. Conversely, when fixing $\sigma_{\mathrm{U}}^2 $ and gradually increasing $\sigma_{\mathrm{U}}^2 $, the optimal deployment location gradually approaches the base station. Additionally, irrespective of increased noise levels, the system’s reachability rate demonstrates a tendency to decline. Conclusions: This paper examines the maximization of system reachable rates by varying the deployment locations of passive and active IRSs in line-of-sight and Rayleigh channel transmission scenarios. In the analysis, fixed positions are assumed for both the base station and the user, with the sum of the base station-to-IRS and IRS-to-user distances kept constant. Phase alignment and the law of large numbers are employed to derive a closed-form expression for the reachable rate. Theoretical analysis and simulation results provide several key insights: When β1<β2, the optimal deployment locations for both passive and active IRS are close to the user, the least favorable deployment locations for passive IRS move progressively closer to the base station as the difference between β1 and β2 increases. When β1=β2, the optimal deployment location for the active IRS remains near the user, while the passive IRS can be effectively placed near either the base station or the user. When β1>β2, the optimal deployment location of the passive IRS remains close to the base station. As the difference between β1 and β2 ncreases, the optimal deployment location of the active IRS gradually shifts closer to the base station. Additionally, as the amplified noise of the active IRS increases, its optimal deployment location moves closer to the base station. Conversely, when the noise at the user increases, the optimal deployment location of the active IRS is always closer to the user. -
表 1 路径损耗指数设置表
无源IRS 有源IRS ${\beta _1}$ ${\beta _2}$ ${\beta _1}$ ${\beta _2}$ ${\beta _1} \gt {\beta _2}$ 3.0 2.2 3.5 2.5 ${\beta _1} = {\beta _2}$ 2.2 2.2 2.5 2.5 ${\beta _1} \lt {\beta _2}$ 2.2 3.0 2.5 3.5 -
[1] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107. [2] 朱秋明, 倪浩然, 华博宇, 等. 无人机毫米波信道测量与建模研究综述[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(12): 2–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20221114-0001.ZHU Qiuming, NI Haoran, HUA Boyu, et al. A survey of UAV millimeter-wave channel measurement and modeling[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(12): 2–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20221114-0001. [3] ZHENG Beixiong, YOU Changsheng, MEI Weidong, et al. A survey on channel estimation and practical passive beamforming design for intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless communications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(2): 1035–1071. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3155305. [4] WANG Xuehui, SHU Feng, SHI Weiping, et al. Beamforming design for IRS-aided decode-and-forward relay wireless network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2022, 6(1): 198–207. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2022.3145031. [5] 张在琛, 江浩. 智能超表面使能无人机高能效通信信道建模与传输机理分析[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(10): 2623–2634. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221352.ZHANG Zaichen and JIANG Hao. Channel modeling and characteristics analysis for high energy-efficient RIS-assisted UAV communications[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(10): 2623–2634. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221352. [6] DONG Limeng and WANG Huiming. Enhancing secure MIMO transmission via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7543–7556. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3012721. [7] ZHENG Beixiong and ZHANG Rui. Simultaneous transmit diversity and passive beamforming with large-scale intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(2): 920–933. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3199426. [8] YU Xianghao, JAMALI V, XU Dongfang, et al. Smart and reconfigurable wireless communications: From IRS modeling to algorithm design[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(6): 118–125. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100145. [9] WEI Wenjing, PANG Xiaowei, TANG Jie, et al. Secure transmission design for aerial IRS assisted wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(6): 3528–3540. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3257387. [10] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A, PAN Cunhua, ELBIR E, et al. Coverage probability of distributed IRS systems under spatially correlated channels[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(8): 1722–1726. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3077991. [11] ZENG Piao, QIAO Deli, WU Qingqing, et al. Throughput maximization for active intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless powered communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(5): 992–996. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3152563. [12] MIAO Jiansong, LI Tongjie, BAI Shanling, et al. Secrecy capacity enhancement in active IRS-assisted UAV communication system[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(9): 4377. doi: 10.3390/s23094377. [13] LI Yunli, YOU Changsheng, and CHUN Y J. Active-IRS aided wireless network: System modeling and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(2): 487–491. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3221116. [14] GE Yimeng, FAN Jiancun, LI G Y, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-enhanced UAV communications: Advances, challenges, and prospects[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 30(6): 119–126. doi: 10.1109/MWC.008.2200124. [15] SHI Weiping, WU Qingqing, WU Di, et al. Joint transmit and reflective beamforming design for active IRS-aided SWIPT systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2024, 33(2): 536–548. doi: 10.23919/cje.2022.00.287. [16] LONG Ruizhe, LIANG Yingchang, PEI Yiyang, et al. Active reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(8): 4962–4975. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3064024. [17] DI RENZO M, NTONTIN K, SONG Jian, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces vs. relaying: Differences, similarities, and performance comparison[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2020, 1: 798–807. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.3002955. [18] YANG Liang, YANG Yin, HASNA M O, et al. Coverage, probability of SNR gain, and DOR analysis of RIS-aided communication systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(8): 1268–1272. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2987798. [19] DONG Rongen, TENG Yin, SUN Zhongwen, et al. Performance analysis of wireless network aided by discrete-phase-shifter IRS[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2022, 24(5): 603–612. doi: 10.23919/JCN.2022.000029. [20] KANG Zhenyu, YOU Changsheng, and ZHANG Rui. IRS-aided wireless relaying: Deployment strategy and capacity scaling[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(2): 215–219. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3123075. [21] YOU Changsheng and ZHANG Rui. Wireless communication aided by intelligent reflecting surface: Active or passive?[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(12): 2659–2663. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3111044. [22] WASSERMAN L. All of Statistics: A Concise Course in Statistical Inference[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2004. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
