Membership Inference Attacks Based on Graph Neural Network Model Calibration
-
摘要: 针对图神经网络(GNN)模型在其预测中常处于欠自信状态,导致该状态下实施成员推理攻击难度大且攻击漏报率高的问题,该文提出一种基于GNN模型校准的成员推理攻击方法。首先,设计一种基于因果推断的GNN模型校准方法,通过基于注意力机制的因果图提取、因果图与非因果图解耦、后门路径调整策略和因果关联图生成过程,构建用于训练GNN模型的因果关联图。其次,使用与目标因果关联图在相同数据分布下的影子因果关联图构建影子GNN模型,模拟目标GNN模型的预测行为。最后,使用影子GNN模型的后验概率构建攻击数据集以训练攻击模型,根据目标GNN模型对目标节点的后验概率输出推断其是否属于目标GNN模型的训练数据。在4个数据集上的实验结果表明,该文方法在2种攻击模式下面对不同架构的GNN模型进行攻击时,攻击准确率最高为92.6%,性能指标优于基线攻击方法,可有效地实施成员推理攻击。Abstract:
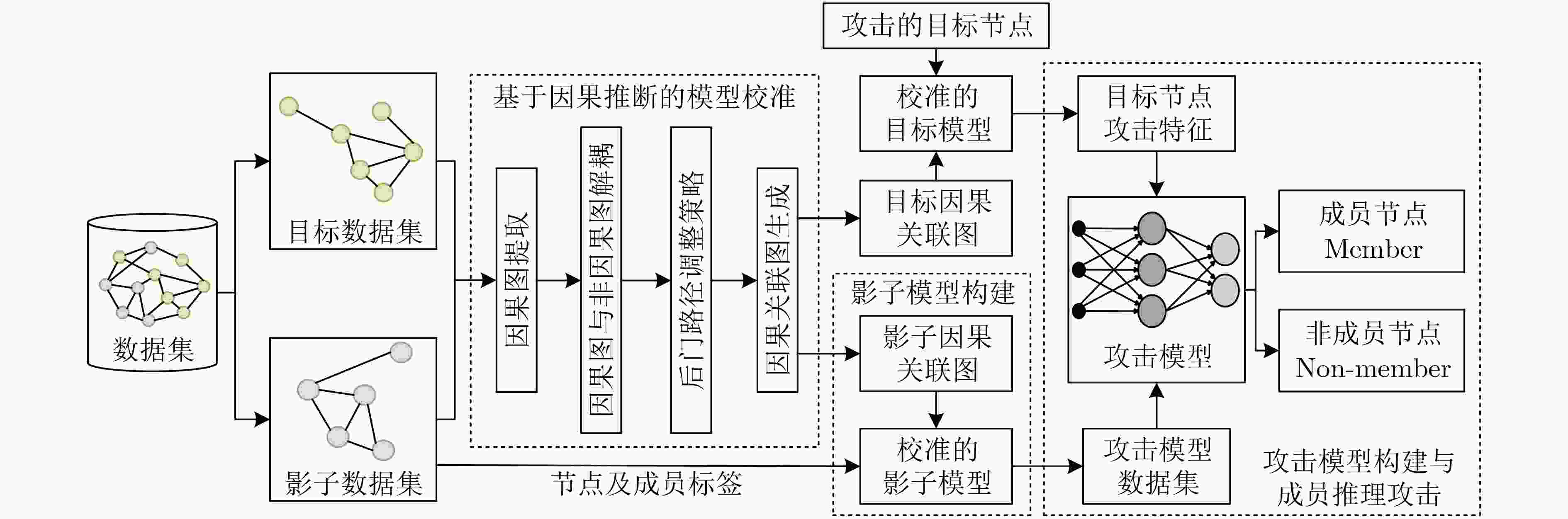
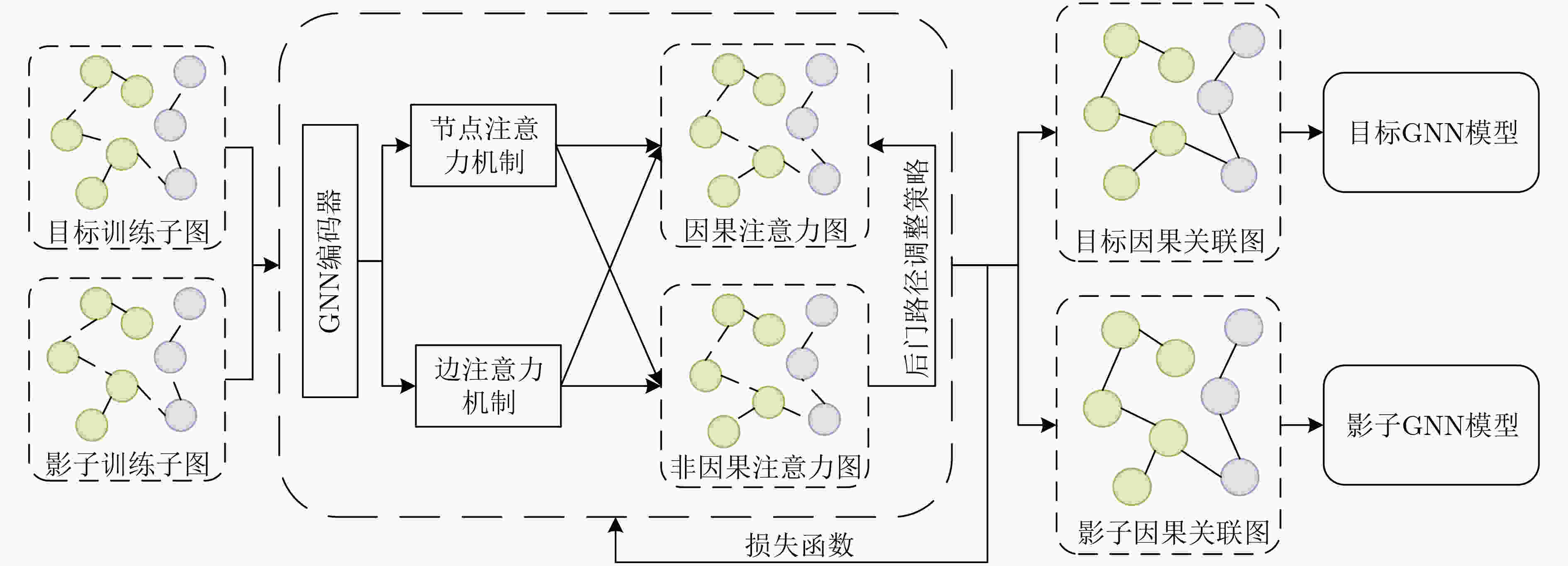
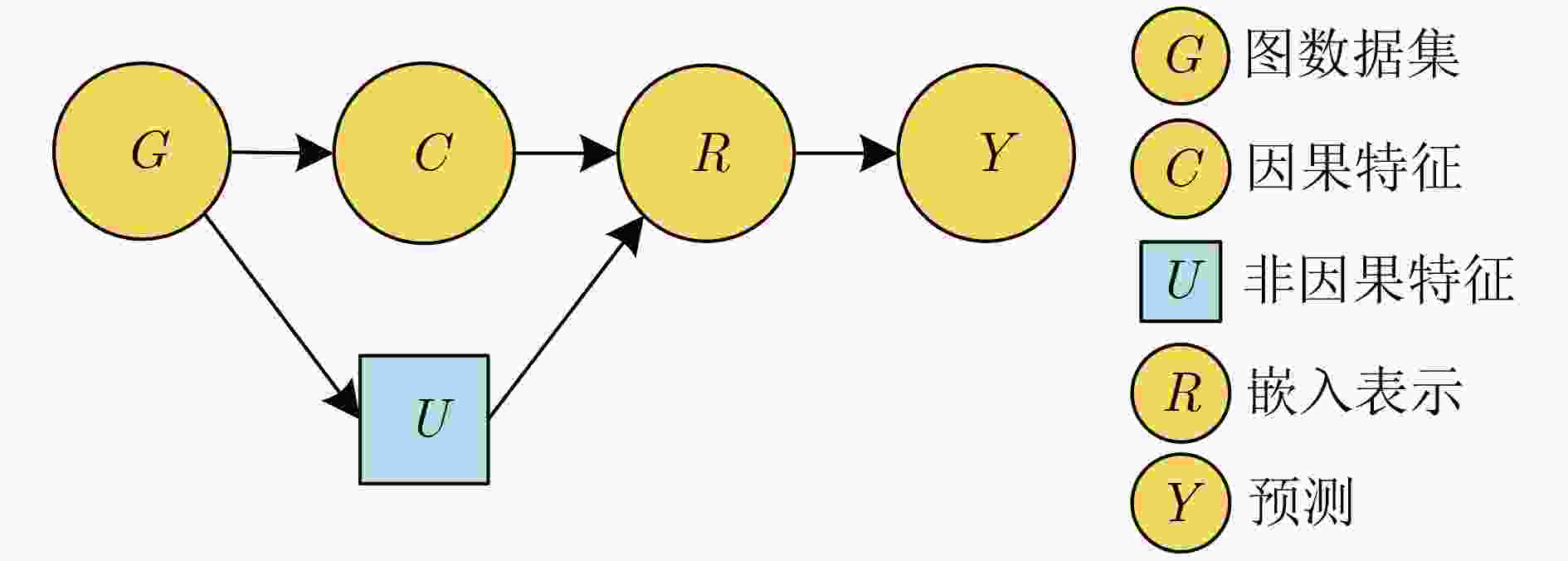
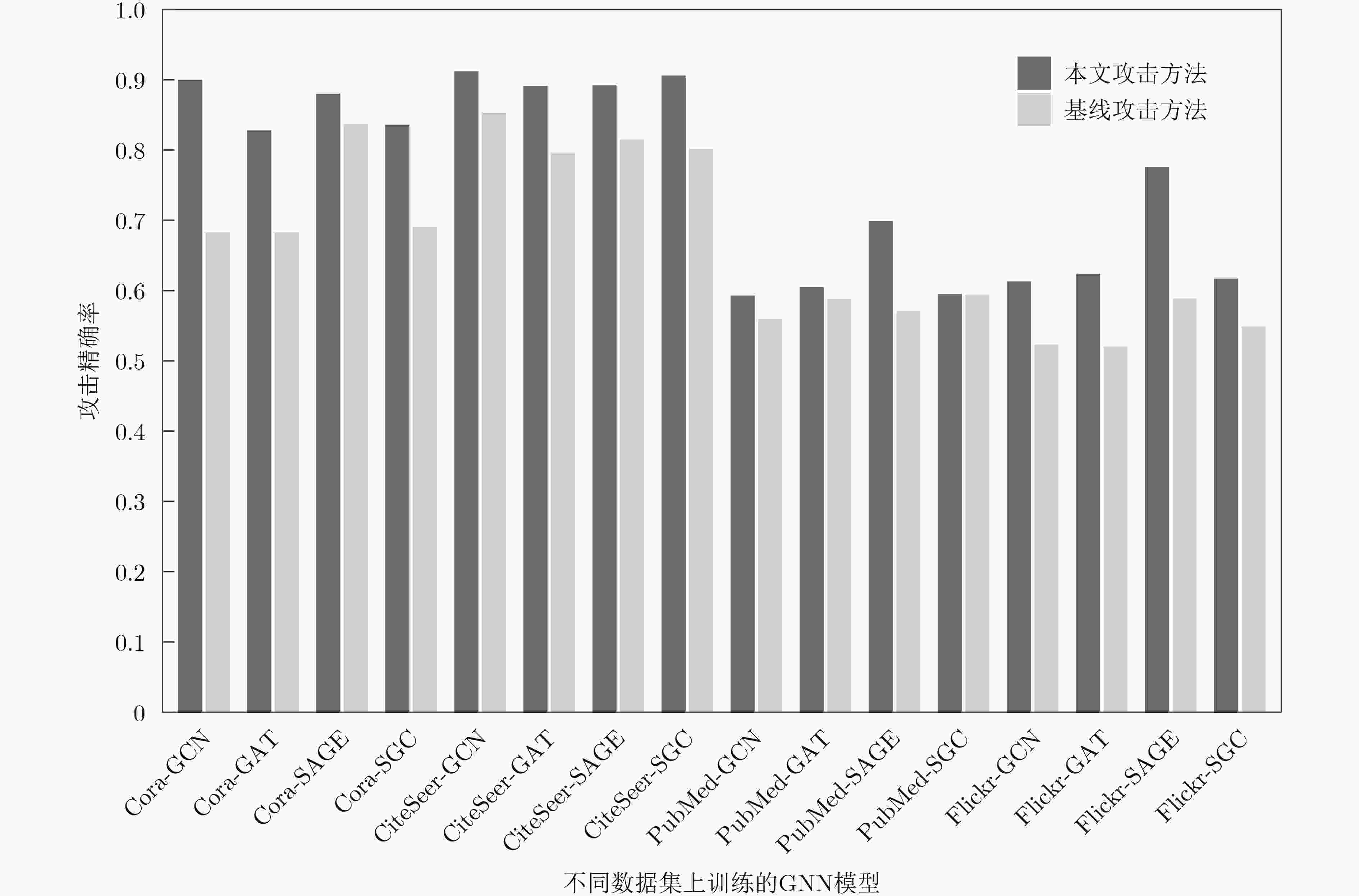
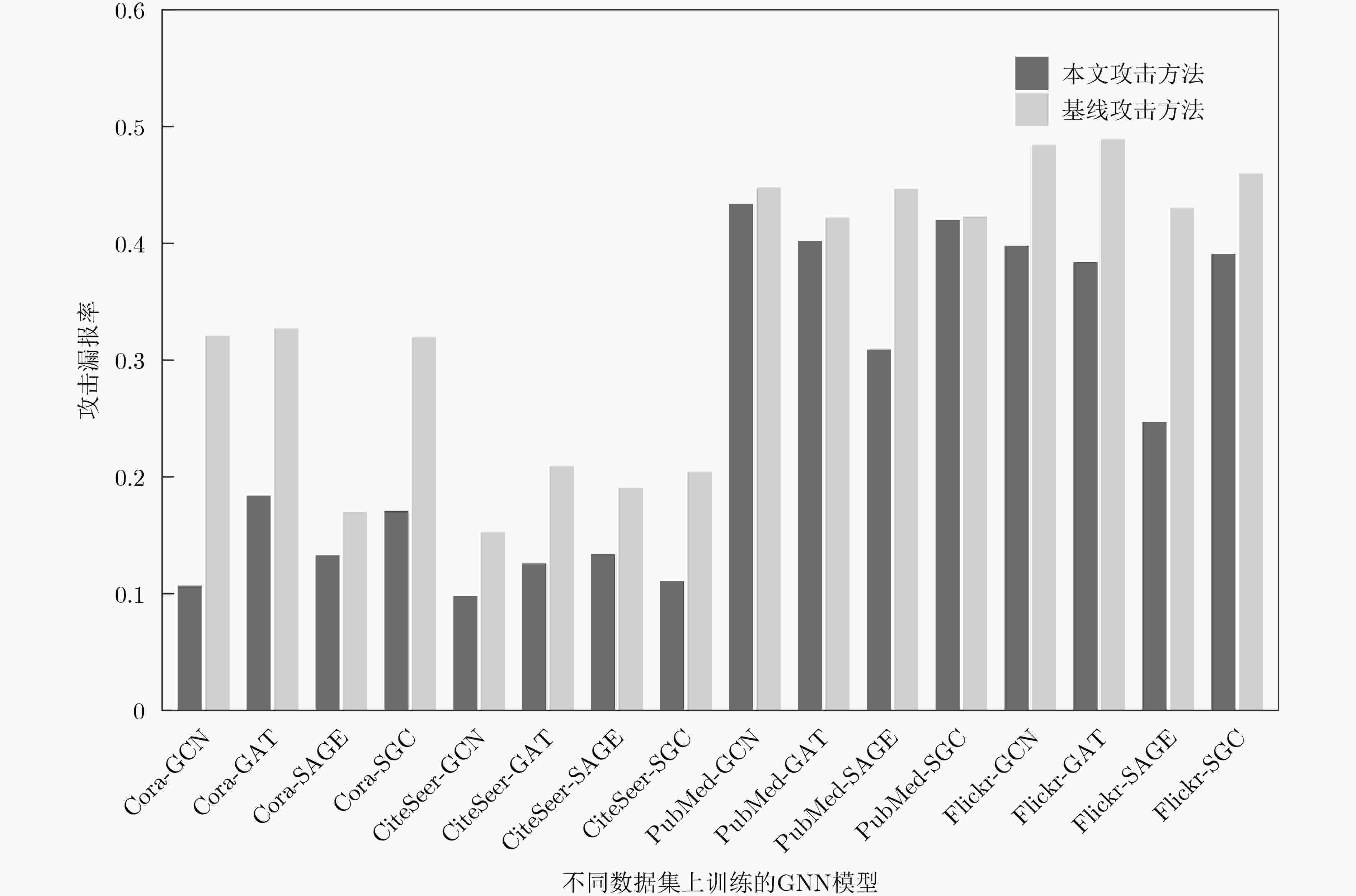
Objective Membership Inference Attacks (MIAs) against machine learning models represent a significant threat to the privacy of training data. The primary goal of MIAs is to determine whether specific data samples are part of a target model’s training set. MIAs reveal potential privacy vulnerabilities in artificial intelligence models, making them a critical area of research in AI security. Investigating MIAs not only helps security researchers assess model vulnerabilities to such attacks but also provides a theoretical foundation for establishing guidelines for the use of sensitive data and developing strategies to improve model security. In recent years, Graph Neural Network (GNN) models have become a key focus in MIAs research. However, GNN models often exhibit under-confidence in their predictions, marked by cautious probability distributions in model outputs. This issue prevents existing MIAs methods from fully utilizing posterior probability information, resulting in reduced attack accuracy and higher false negative rates. These challenges significantly limit the effectiveness and applicability of current attack methods. Therefore, addressing the under-confidence problem in GNN predictions and developing enhanced MIA approaches to improve attack performance has become both necessary and urgent. Methods Given that GNN models are often characterized by under-confidence in their predictions, which hampers the implementation of MIAs and resulting in high false negative rates, an MIAs method based on GNN Model Calibration (MIAs-MC) is proposed ( Fig. 1 ). First, a GNN model calibration method based on causal inference is designed and applied. This approach involves extracting causal graphs using an attention mechanism, decoupling causal and non-causal graphs, applying a backdoor adjustment strategy, and generating causal association graphs, which are then used to train the GNN model (Fig. 2 ). Next, a shadow GNN model is constructed using shadow causal association graphs that share the same data distribution as the target causal association graph, enabling the shadow models to mimic the performance of the target GNN model. Finally, posterior probabilities from the shadow GNN model are used to create an attack dataset, which is employed to train an attack model. This attack model is then used to infer whether a target node is part of the training data of the target GNN model, based on the posterior probabilities generated by the target GNN model.Results and Discussions To assess the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed attack method, two attack modes are implemented in the experiment, and MIAs are conducted under both modes. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms the baseline attack method across various metrics. In Attack Mode 1, the proposed method is evaluated on the Cora, CiteSeer, PubMed, and Flickr datasets, with comparative results presented against the baseline method ( Table 2 andTable 3 ). Compared to the baseline attack method, the proposed method achieves improvements in attack accuracy and attack precision for GCN, GAT, GraphSAGE, and SGC models, ranging from 3.4% to 35.0% and 1.2% to 34.6%, respectively. Furthermore, the results indicate that after GNN model calibration, the shadow model more effectively mimics the prediction behavior of the target model, contributing to an increased success rate of MIAs on the target model (Table 4 andTable 5 ). Notably, the GAT model exhibits high robustness against MIAs, both for the proposed and baseline methods. In Attack Mode 2, the attack performance of the proposed method is compared with the baseline method across the same datasets (Cora, CiteSeer, PubMed, and Flickr) (Fig. 4 ,Fig. 5 , andFig. 6 ). The proposed method improves attack accuracy by 0.4% to 32.1%, attack precision by 0.3% to 31.8%, and reduces the average attack false negative rate by 31.2%, compared to the baseline methods. Overall, the results from both attack modes indicate that calibrating the GNN model and training the attack model with the calibrated GNN posterior probabilities significantly enhances the performance of MIAs. However, the attack performance varies across different datasets and model architectures. Analysis of the experimental results reveals that the effectiveness of the proposed method is influenced by the structural characteristics of the graph datasets and the specific configurations of the GNN architectures.Conclusions The proposed MIAs method, based on GNN model calibration, constructs a causal association graph using a calibration technique rooted in causal inference. This causal association graph is subsequently used to build shadow GNN models and attack models, facilitating MIAs on target GNN models. The results verify that GNN model calibration enhances the effectiveness of MIAs. -
1 因果关联图生成算法
输入:GNN模型初始的训练子图G(Gt, Gs ∈ G),迭代次数T 输出:目标因果关联图Gtarget,影子因果关联图Gshadow (1) for t = 1 to T (2) Gc, Gu ← Attention(G) //因果图提取 (3) Lc, Lu ← Decouple(G) //因果图与非因果图解耦,生成对
应损失函数(4) Lcau ← Backdoor Adjustment(Gc, Gu) //后门路径调整,
生成后门路径调整损失函数(5) L ←Lc, Lu, Lcau //计算模型总损失函数 (6) θt+1 ← Update(θt) //更新模型参数 (7) Gt+1 ← Gt //迭代更新因果注意力图 (8) endfor (9) Gtarget, Gshadow ← GT //生成目标因果关联图和影子因果关
联图(10) 结束算法返回目标因果关联图Gtarget,影子因果关联图
Gshadow表 1 数据集的统计信息
数据集 类别数 节点数 边数 节点特征维度 使用节点数 Cora 7 2 708 5 429 1 433 2 520 CiteSeer 6 3 327 4 732 3 703 2 400 PubMed 3 19 717 44 338 500 18 000 Flickr 7 89 250 449 878 500 42 000 表 2 攻击模式1下MIAs-MC的攻击结果
数据集 GNN架构 Accuracy Precision AUC Recall F1-score Cora GCN 0.926 0.920 0.912 0.913 0.912 GAT 0.911 0.914 0.910 0.911 0.911 GraphSAGE 0.905 0.908 0.904 0.905 0.905 SGC 0.914 0.923 0.915 0.914 0.914 CiteSeer GCN 0.918 0.912 0.917 0.918 0.918 GAT 0.857 0.879 0.857 0.857 0.855 GraphSAGE 0.933 0.936 0.931 0.933 0.933 SGC 0.930 0.938 0.929 0.930 0.930 PubMed GCN 0.750 0.784 0.750 0.751 0.743 GAT 0.642 0.686 0.643 0.642 0.621 GraphSAGE 0.748 0.754 0.747 0.748 0.748 SGC 0.690 0.702 0.691 0.690 0.690 Flickr GCN 0.841 0.846 0.841 0.841 0.841 GAT 0.786 0.801 0.787 0.786 0.785 GraphSAGE 0.732 0.764 0.732 0.732 0.725 SGC 0.907 0.916 0.908 0.907 0.907 表 3 攻击模式1下基线攻击方法的攻击结果
数据集 GNN架构 Accuracy Precision AUC Recall F1-score Cora GCN 0.763 0.770 0.764 0.763 0.763 GAT 0.721 0.728 0.718 0.721 0.720 GraphSAGE 0.825 0.837 0.825 0.825 0.824 SGC 0.806 0.812 0.808 0.806 0.807 CiteSeer GCN 0.860 0.865 0.859 0.860 0.860 GAT 0.772 0.775 0.769 0.772 0.771 GraphSAGE 0.858 0.875 0.859 0.858 0.827 SGC 0.863 0.868 0.862 0.863 0.863 PubMed GCN 0.647 0.655 0.647 0.647 0.647 GAT 0.593 0.612 0.593 0.593 0.580 GraphSAGE 0.554 0.560 0.553 0.554 0.553 SGC 0.664 0.685 0.665 0.664 0.658 Flickr GCN 0.774 0.805 0.775 0.774 0.769 GAT 0.601 0.613 0.602 0.601 0.598 GraphSAGE 0.689 0.755 0.688 0.689 0.668 SGC 0.877 0.893 0.878 0.877 0.876 表 4 Cora数据集上影子模型与目标模型准确率差异(%)
GNN架构 基线攻击下训练准确率差值 基线攻击下测试准确率差值 模型校准后训练准确率差值 模型校准后测试准确率差值 GCN 0.32 3.97 0.79 0.95 GAT 3.65 1.99 1.91 2.22 GraphSAGE 0.32 4.92 0.16 0.80 SGC 0.66 0.47 1.11 1.70 表 5 PubMed数据集上影子模型与目标模型准确率差异(%)
GNN架构 基线攻击下训练准确率差值 基线攻击下测试准确率差值 模型校准后训练准确率差值 模型校准后测试准确率差值 GCN 1.45 0.75 1.15 0.14 GAT 0.36 1.15 0.82 0.51 GraphSAGE 0.20 5.12 0.13 3.15 SGC 1.58 0.60 0.73 0.56 -
[1] SHOKRI R, STRONATI M, SONG Congzheng, et al. Membership inference attacks against machine learning models[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, USA, 2017: 3–18. doi: 10.1109/SP.2017.41. [2] SALEM A, ZHANG Yang, HUMBERT M, et al. ML-Leaks: Model and data independent membership inference attacks and defenses on machine learning models[C]. The Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, USA, 2019: 24–27. [3] LONG Yunhui, WANG Lei, BU Diyue, et al. A pragmatic approach to membership inferences on machine learning models[C]. 2020 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Genoa, Italy, 2020: 521–534. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP48549.2020.00040. [4] KO M, JIN Ming, WANG Chenguang, et al. Practical membership inference attacks against large-scale multi-modal models: A pilot study[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023: 4848–4858. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00449. [5] CHOQUETTE-CHOO C A, TRAMER F, CARLINI N, et al. Label-only membership inference attacks[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 1964–1974. [6] LIU Han, WU Yuhao, YU Zhiyuan, et al. Please tell me more: Privacy impact of explainability through the lens of membership inference attack[C]. 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, USA, 2024: 120–120. doi: 10.1109/SP54263.2024.00120. [7] 吴博, 梁循, 张树森, 等. 图神经网络前沿进展与应用[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(1): 35–68. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.00035.WU Bo, LIANG Xun, ZHANG Shusen, et al. Advances and applications in graph neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(1): 35–68. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.00035. [8] OLATUNJI I E, NEJDL W, and KHOSLA M. Membership inference attack on graph neural networks[C]. 2021 Third IEEE International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Intelligent Systems and Applications (TPS-ISA), Atlanta, USA, 2021: 11–20. doi: 10.1109/TPSISA52974.2021.00002. [9] HE Xinlei, WEN Rui, WU Yixin, et al. Node-level membership inference attacks against graph neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05429, 2021. [10] WU Bang, YANG Xiangwen, PAN Shirui, et al. Adapting membership inference attacks to GNN for graph classification: Approaches and implications[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Auckland, New Zealand, 2021: 1421–1426. doi: 10.1109/ICDM51629.2021.00182. [11] WANG Xiuling and WANG W H. Link membership inference attacks against unsupervised graph representation learning[C]. The 39th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Austin, USA, 2023: 477–491. doi: 10.1145/3627106.3627115. [12] WANG Xiao, LIU Hongrui, SHI Chuan, et al. Be confident! Towards trustworthy graph neural networks via confidence calibration[C]. The 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 1820. [13] HSU H H H, SHEN Y, TOMANI C, et al. What makes graph neural networks miscalibrated?[C]. The 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1001. [14] LIU Tong, LIU Yushan, HILDEBRANDT M, et al. On calibration of graph neural networks for node classification[C]. 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Padua, Italy, 2022: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN55064.2022.9892866. [15] YANG Zhilin, COHEN W W, and SALAKHUTDINOV R. Revisiting semi-supervised learning with graph embeddings[C]. The 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 40–48. [16] ZENG Hanqing, ZHOU Hongkuan, SRIVASTAVA A, et al. GraphSAINT: Graph sampling based inductive learning method[C]. The 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 1–19. [17] KIPF T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]. The 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 1–14. [18] VELIČKOVIĆ P, CUCURULL G, CASANOVA A, et al. Graph attention networks[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1–12. [19] HAMILTON W, YING Z, and LESKOVEC J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs[C]. Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1025–1035. [20] WU F, SOUZA A, ZHANG Tianyi, et al. Simplifying graph convolutional networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6861–6871. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
