LGDNet: Table Detection Network Combining Local and Global Features
-
摘要: 在大数据时代,表格广泛存在于各类文档图像中,进行表格检测对于表格信息再利用具有重要意义。针对现有的基于卷积神经网络的表格检测算法存在感受野受限、依赖于预设的候选区域以及表格边界定位不准确等问题,该文提出一种基于 DINO模型的表格检测网络。首先,设计一种图像预处理方法,旨在增强表格的角点和线特征,以更好地区分表格与文本等其他文档元素。其次,设计一种主干网络SwTNet-50,通过在ResNet中引入Swin Transformer Blocks (STB),有效地进行局部-全局特征信息的提取,提高模型的特征提取能力以及对表格边界的检测准确性。最后,为了弥补DINO模型在1对1匹配中编码器特征学习不足问题,采用协同混合匹配训练策略,提高编码器的特征学习能力,提升模型检测精度。与多种基于深度学习的表格检测方法进行对比,该文模型在表格检测数据集TNCR上优于对比算法,在IoU阈值为0.5, 0.75和0.9时F1-Score分别达到98.2%, 97.4%和93.3%。在IIIT-AR-13K数据集上,IoU阈值为0.5时F1-Score为98.6%。
-
关键词:
- 表格检测 /
- 卷积神经网络 /
- Transformer /
- 特征提取
Abstract: In the era of big data, table widely exists in various document images, and table detection is of great significance for the reuse of table information. In response to issues such as limited receptive field, reliance on predefined proposals, and inaccurate table boundary localization in existing table detection algorithms based on convolutional neural network, a table detection network based on DINO model is proposed in this paper. Firstly, an image preprocessing method is designed to enhance the corner and line features of table, enabling more precise table boundary localization and effective differentiation between table and other document elements like text. Secondly, a backbone network SwTNet-50 is designed, and Swin Transformer Blocks (STB) are introduced into ResNet to effectively combine local and global features, and the feature extraction ability of the model and the detection accuracy of table boundary are improved. Finally, to address the inadequacies in encoder feature learning in one-to-one matching and insufficient positive sample training in the DINO model, a collaborative hybrid assignments training strategy is adopted to improve the feature learning ability of the encoder and detection precision. Compared with various table detection methods based on deep learning, our model is better than other algorithms on the TNCR table detection dataset, with F1-Scores of 98.2%, 97.4%, and 93.3% for IoU thresholds of 0.5, 0.75, and 0.9, respectively. On the IIIT-AR-13K dataset, the F1-Score is 98.6% when the IoU threshold is 0.5.-
Key words:
- Table detection /
- Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) /
- Transformer /
- Feature extraction
-
表 1 辅助头信息
辅助头i 匹配方式Ai {pos}, {neg}生成规则 Pi生成规则 $B_i^{\left\{ {{\text{pos}}} \right\}}$生成规则 Faster R-CNN {pos}:IoU(proposal, gt)>0.5
{neg}:IoU(proposal, gt)<0.5{pos}:gt labels, offset(proposal, gt)
{neg}:gt labelspositive proposals
$\left( {{x_1}, {y_1}, {x_2}, {y_2}} \right)$ATSS {pos}:IoU(anchor, gt)>(mean+std)
{neg}:IoU(anchor, gt)<(mean+std){pos}:gt labels, offset(anchor, gt), centerness
{neg}:gt labelspositive anchors
$\left( {{x_1}, {y_1}, {x_2}, {y_2}} \right)$表 2 TNCR, IIIT-AR-13K数据集上的对比实验结果(%)
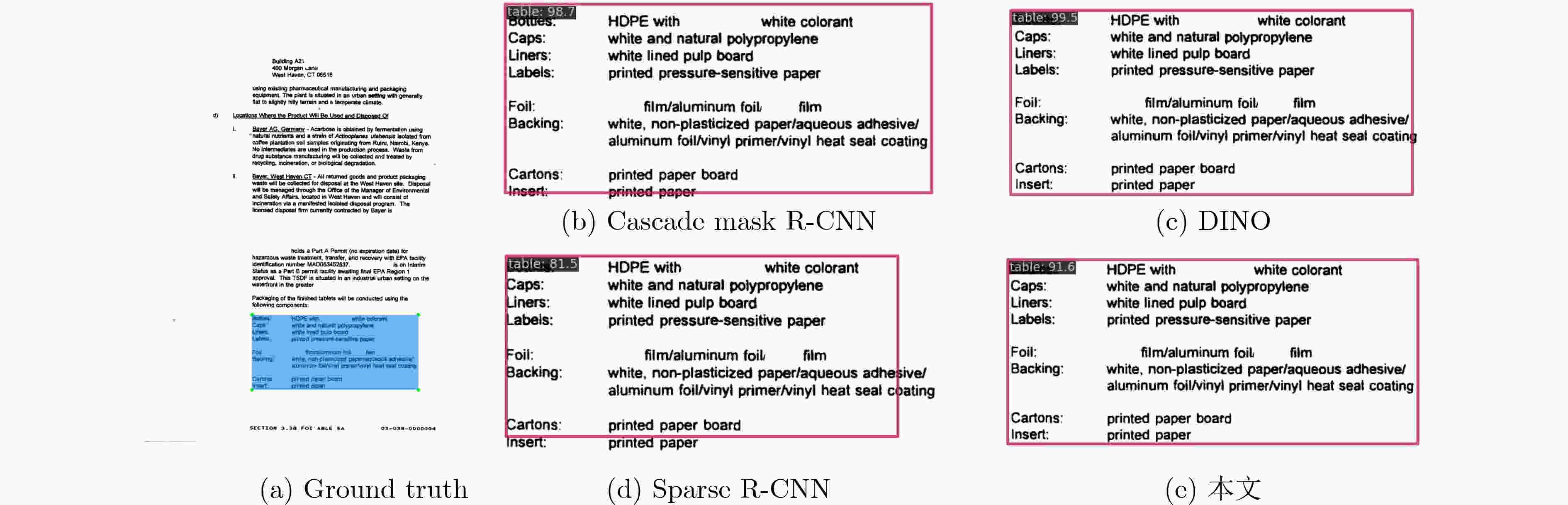
数据集 网络模型 F1-Score IoU@0.5 IoU@0.75 IoU@0.9 TNCR Cascade Mask R-CNN[12] 93.1 92.1 86.6 DiffusionDet[20] 95.5 93.9 88.5 Deformable DETR[17] 94.5 93.7 89.3 DINO[21] 94.6 91.4 90.1 Sparse R-CNN[19] 95.2 94.8 90.9 本文 98.2 97.4 93.3 IIIT-AR-13K Faster R-CNN[8] 93.7 – – Mask R-CNN[25] 97.1 – – DINO[21] 97.4 – – 本文 98.6 – – 表 3 主干网络对比实验结果(%)
网络模型 主干网络 F1-Score IoU@0.5 IoU@0.75 IoU@0.9 DINO[21] ResNet50 93.5 90.6 89.7 Swin Transformer 94.6 91.4 90.1 本文 SwTNet-50 95.8 93.6 91.1 表 4 消融实验结果(%)
序号 网络模型 F1-Score IoU@0.5 IoU@0.75 IoU@0.9 1 DINO[21] 94.6 91.4 90.1 2 DINO+文档图像预处理(DINO_DIP) 95.2 92.0 90.5 3 DINO_DIP+SwTNet-50 96.8 94.2 91.7 4 DINO_DIP+一对多匹配辅助分支 97.5 96.7 92.8 5 LGDNet(DINO_DIP+SwTNet-50+一对多匹配辅助分支) 98.2 97.4 93.3 -
[1] 高良才, 李一博, 都林, 等. 表格识别技术研究进展[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(6): 1898–1917. doi: 10.11834/jig.220152.GAO Liangcai, LI Yibo, DU Lin, et al. A survey on table recognition technology[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(6): 1898–1917. doi: 10.11834/jig.220152. [2] WATANABE T, LUO Qin, and SUGIE N. Structure recognition methods for various types of documents[J]. Machine Vision and Applications, 1993, 6(2/3): 163–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01211939. [3] GATOS B, DANATSAS D, PRATIKAKIS I, et al. Automatic table detection in document images[C]. The Third International Conference on Advances in Pattern Recognition, Bath, UK, 2005: 609–618. doi: 10.1007/11551188_67. [4] KASAR T, BARLAS P, ADAM S, et al. Learning to detect tables in scanned document images using line information[C]. 2013 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Washington, USA, 2013: 1185–1189. doi: 10.1109/ICDAR.2013.240. [5] ANH T, IN-SEOP N, and SOO-HYUNG K. A hybrid method for table detection from document image[C]. 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2015: 131–135. doi: 10.1109/ACPR.2015.7486480. [6] LEE K H, CHOY Y C, and CHO S B. Geometric structure analysis of document images: A knowledge-based approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1224–1240. doi: 10.1109/34.888708. [7] SCHREIBER S, AGNE S, WOLF I, et al. DeepDeSRT: Deep learning for detection and structure recognition of tables in document images[C]. 2017 14th IAPR International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Kyoto, Japan, 2017: 1162–1167. doi: 10.1109/ICDAR.2017.192. [8] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. [9] ARIF S and SHAFAIT F. Table detection in document images using foreground and background features[C]. 2018 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Canberra, Australia, 2018: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/DICTA.2018.8615795. [10] SIDDIQUI S A, MALIK M I, AGNE S, et al. DeCNT: Deep deformable CNN for table detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 74151–74161. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2880211. [11] SUN Ningning, ZHU Yuanping, and HU Xiaoming. Faster R-CNN based table detection combining corner locating[C]. 2019 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Sydney, Australia, 2019: 1314–1319. doi: 10.1109/ICDAR.2019.00212. [12] CAI Zhaowei and VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6154–6162. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00644. [13] PRASAD D, GADPAL A, KAPADNI K, et al. CascadeTabNet: An approach for end to end table detection and structure recognition from image-based documents[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2439–2447. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW50498.2020.00294. [14] AGARWAL M, MONDAL A, and JAWAHAR C V. CDeC-Net: Composite deformable cascade network for table detection in document images[C]. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 9491–9498. doi: 10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9411922. [15] HUANG Yilun, YAN Qinqin, LI Yibo, et al. A YOLO-based table detection method[C]. 2019 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Sydney, Australia, 2019: 813–818. doi: 10.1109/ICDAR.2019.00135. [16] SHEHZADI T, HASHMI K A, STRICKER D, et al. Towards end-to-end semi-supervised table detection with deformable transformer[C]. The 17th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition-ICDAR 2023, San José, USA, 2023: 51–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-41679-8_4. [17] ZHU Xizhou, SU Weijie, LU Lewei, et al. Deformable DETR: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2021. [18] XIAO Bin, SIMSEK M, KANTARCI B, et al. Table detection for visually rich document images[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 282: 111080. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2023.111080. [19] SUN Peize, ZHANG Rufeng, JIANG Yi, et al. Sparse R-CNN: End-to-end object detection with learnable proposals[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 14449–14458. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01422. [20] CHEN Shoufa, SUN Peize, SONG Yibing, et al. DiffusionDet: Diffusion model for object detection[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 19773–19786. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01816. [21] ZHANG Hao, LI Feng, LIU Shilong, et al. DINO: DETR with improved DeNoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.03605, 2022. [22] ZONG Zhuofan, SONG Guanglu, and LIU Yu. DETRs with collaborative hybrid assignments training[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 6748–6758. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00621. [23] ABDALLAH A, BERENDEYEV A, NURADIN I, et al. TNCR: Table net detection and classification dataset[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 473: 79–97. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.11.101. [24] MONDAL A, LIPPS P, and JAWAHAR C V. IIIT-AR-13K: A new dataset for graphical object detection in documents[C]. The 14th IAPR International Workshop, DAS 2020, Wuhan, China, 2020: 216-230. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-57058-3_16. [25] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.322. -






 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:
