Cache Oriented Migration Decision and Resource Allocation in Edge Computing
-
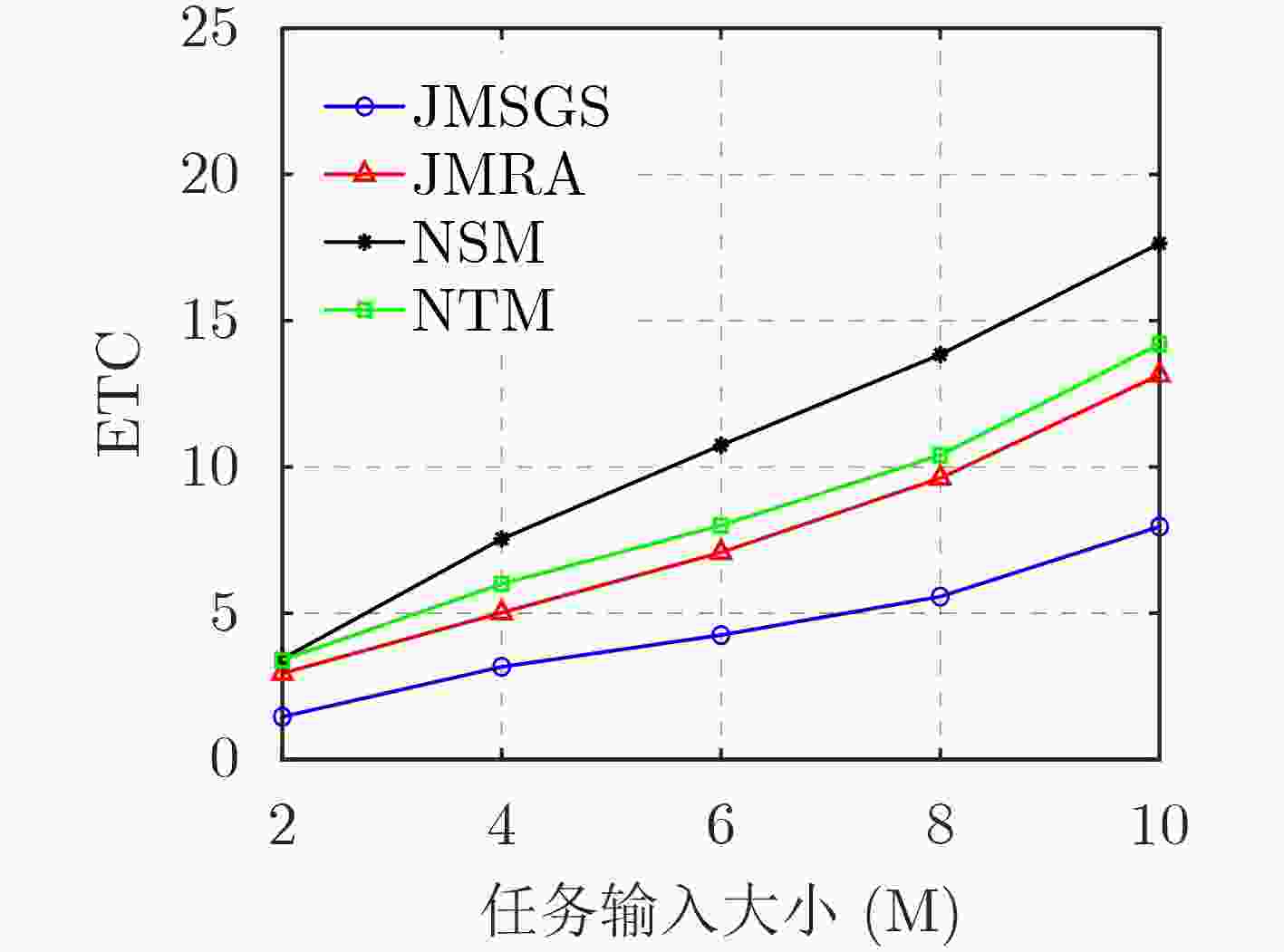
摘要: 边缘计算通过在网络边缘侧为用户提供计算资源和缓存服务,可以有效降低执行时延和能耗。由于用户的移动性和网络的随机性,缓存服务和用户任务会频繁地在边缘服务器之间迁移,增加了系统成本。该文构建了一种基于预缓存的迁移计算模型,研究了资源分配、服务缓存和迁移决策的联合优化问题。针对这一混合整数非线性规划问题,通过分解原问题,分别采用库恩塔克条件和二分搜索法对资源分配进行优化,并提出一种基于贪婪策略的迁移决策和服务缓存联合优化算法(JMSGS)获得最优迁移决策和缓存决策。仿真结果验证了所提算法的有效性,实现系统能耗和时延加权和最小。Abstract: Edge computing provides computing resources and caching services at the network edge, effectively reducing execution latency and energy consumption. However, due to user mobility and network randomness, caching services and user tasks frequently migrate between edge servers, increasing system costs. The migration computation model based on pre-caching is constructed and the joint optimization problem of resource allocation, service caching and migration decision-making is investigated. To address this mixed-integer nonlinear programming problem, the original problem is decomposed to optimize the resource allocation using Karush-Kuhn-Tucker condition and bisection search iterative method. Additionally, a Joint optimization algorithm for Migration decision-making and Service caching based on a Greedy Strategy (JMSGS) is proposed to obtain the optimal migration and caching decisions. Simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in minimizing the weighted sum of system energy consumption and latency.
-
Key words:
- Edge computing /
- Migrate strategy /
- Service cache /
- Resource allocation
-
1 二分搜索的上行传输功率分配算法
初始化:传输功率$ {p_i} $范围,收敛阈值$r$ (1) 根据式(21)计算得出$ \phi (p_i^{{\text{max}}}) $ (2) if $ \phi (p_i^{{\text{max}}}) \lt 0 $ then (3) $ p_i^* = p_i^{{\text{max}}} $ (4) else (5) 初始化参数$ {p_l} = p_i^{{\text{min}}} $, $ {p_h} = p_i^{{\text{max}}} $ (6) end if (7) if $ \phi ({p_m}) < 0 $ then (8) ${p_l} = {p_m}$ (9) else (10) $ {p_h} = {p_m} $ (11) end if (12) until $({p_h} - {p_l}) \le r$ (13) $ p_i^* = ({p_l} + {p_h})/2 $ 2 基于贪婪决策的迁移缓存联合优化算法
初始化:${N_{{\text{local}}}}{\text{ = }}{N_{\text{0}}}$, ${N_{{\text{mec}}}} = \phi $ (1) for $i{\text{ = 1:}}N$ (2) for $m{\text{ = 1:}}M_i^{{\text{sort}}}$ (3) 计算用户的代价增益函数$\Delta C(m)$ (4) end for (5) 将每个用户的代价增益函数倒序排列,加入序列$N_i^{{\text{sort}}}$ (6) for $ i{\text{ = 1:}}N_i^{{\text{sort}}} $ 计算目标函数值 (7) if ${\text{ET}}{{\text{C}}_{o + i}}{\text{ \lt ET}}{{\text{C}}_o}$ (8) $ \alpha = 1 $, $ \vartheta = 1 $ or $ \varpi $=1 (9) else (10) 保持原有模式 (11) end if (12) if $ \varpi = 1 $, $ C_m^{\text{b}} + C_m^{\text{a}} \le C_m^{\max } $ (13) 将应用程序缓存至服务器 (14) else if $ X_m^{\min } < {X_i} $ (15) 更新服务器状态 (16) else (17) 本地执行 (18) end if 表 1 仿真参数
参数 数值 任务大小$\lambda $(Mb) 10~20 应用程序大小$b$(Gb) 1~5 本地计算能力${f_{{\text{loc}}}}$(GHz) 0.5~1.5 边缘服务器数目(个) 5~20 噪声功率谱密度${N_{\text{0}}}$(dBm/Hz) –174 系统带宽B(MHz) 1~2 服务器计算能力${f_{{\text{es}}}}$(GHz) 15~25 服务器缓存容量(Gb) 20~30 -
[1] SHEN Xuemin, GAO Jie, WU Wen, et al. Holistic network virtualization and pervasive network intelligence for 6G[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(1): 1–30. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3135829. [2] OKEGBILE S D, CAI Jun, NIYATO D, et al. Human digital twin for personalized healthcare: Vision, architecture and future directions[J]. IEEE Network, 2023, 37(2): 262–269. doi: 10.1109/MNET.118.2200071. [3] CAI Qing, ZHOU Yiqing, LIU Ling, et al. Collaboration of heterogeneous edge computing paradigms: How to fill the gap between theory and practice[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2024, 31(1): 110–117. doi: 10.1109/MWC.014.2200283. [4] LI Zhuo, ZHOU Xu, and QIN Yifang. A survey of mobile edge computing in the industrial internet[C]. 2019 7th International Conference on Information, Macao, China, 2019: 94–98. doi: 10.1109/ICICN.2019.8834959. [5] MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHANG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201. [6] CHEN Xiangyi, BI Yuanguo, CHEN Xueping, et al. Dynamic service migration and request routing for microservice in multicell mobile-edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(15): 13126–13143. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3140183. [7] CHEN Jiayuan, YI Changyan, WANG Ran, et al. Learning aided joint sensor activation and mobile charging vehicle scheduling for energy-efficient WRSN-based industrial IoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(4): 5064–5078. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3224443. [8] LIANG Zezu, LIU Yuan, LOK T M, et al. Multi-cell mobile edge computing: Joint service migration and resource allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5898–5912. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3070974. [9] LIANG Zezu, LIU Yuan, LOK T M, et al. Multiuser computation offloading and downloading for edge computing with virtualization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(9): 4298–4311. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922613. [10] SHI You, YI Changyan, WANG Ran, et al. Service migration or task rerouting: A two-timescale online resource optimization for MEC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(2): 1503–1519. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3290005. [11] XIA Zhuoqun, MAO Xiaoxiao, GU Ke, et al. Dual-mode data forwarding scheme based on interest tags for fog computing-based SIoVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2022, 19(3): 2780–2797. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2022.3161539. [12] HU Yi, WANG Hao, WANG Liangyuan, et al. Joint deployment and request routing for microservice call graphs in data centers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2023, 34(11): 2994–3011. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2023.3311767. [13] CHEN Long, ZHENG Shaojie, WU Yalan, et al. Resource and fairness-aware digital twin service caching and request routing with edge collaboration[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(11): 1881–1885. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3298200. [14] FENG Hao, GUO Songtao, YANG Li, et al. Collaborative data caching and computation offloading for multi-service mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(9): 9408–9422. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3099303. [15] SHEN Qiaoqiao, HU Binjie, and XIA Enjun. Dependency-aware task offloading and service caching in vehicular edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(12): 13182–13197. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3196544. [16] HE Ting, KHAMFROUSH H, WANG Shiqiang, et al. It’s hard to share: Joint service placement and request scheduling in edge clouds with sharable and non-sharable resources[C]. 2018 IEEE 38th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems, Vienna, Austria, 2018: 365–375. doi: 10.1109/ICDCS.2018.00044. [17] WANG Shiqiang, URGAONKAR R, HE Ting, et al. Dynamic service placement for mobile micro-clouds with predicted future costs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2017, 28(4): 1002–1016. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2016.2604814. [18] 杨守义, 成昊泽, 党亚萍. 基于集群协作的云雾混合计算资源分配和负载均衡策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(7): 2423–2431. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220719.YANG Shouyi, CHENG Haoze, and DANG Yaping. Resource allocation and load balancing strategy in cloud-fog hybrid computing based on cluster-collaboration[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(7): 2423–2431. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220719. [19] 杨守义, 李富康, 任瑞敏. 信任环境下考虑系统公平性的边缘计算卸载策略和资源分配[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(3): 142–154. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024030.YANG Shouyi, LI Fukang, and REN Ruimin. Edge computing offloading policies and resource allocation considering system fairness in trusted environments[J]. Journal on Communications, 2024, 45(3): 142–154. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024030. [20] LYU Xinchen, TIAN Hui, SENGUL C, et al. Multiuser joint task offloading and resource optimization in proximate clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(4): 3435–3447. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2593486. -






 下载:
下载:
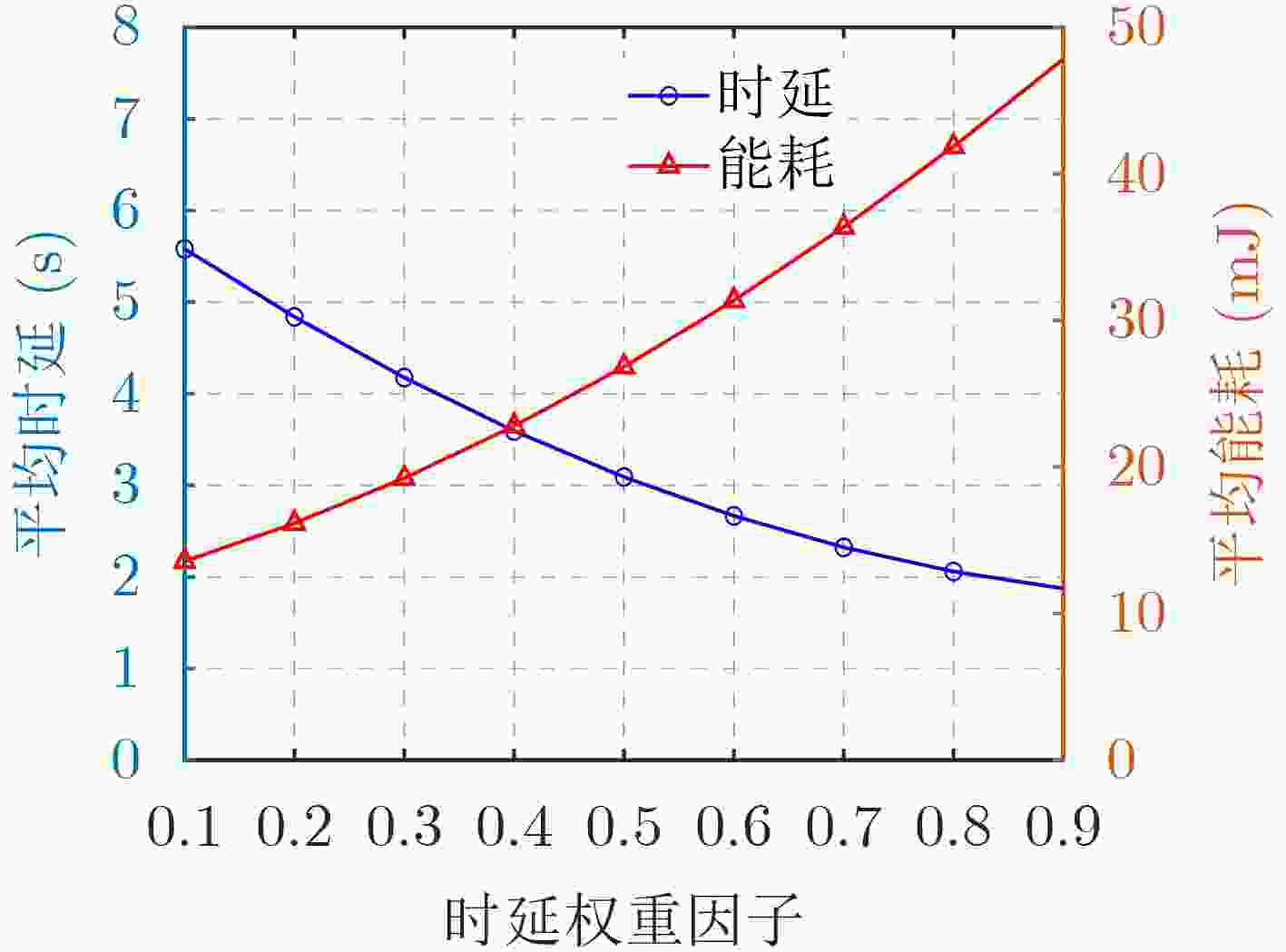
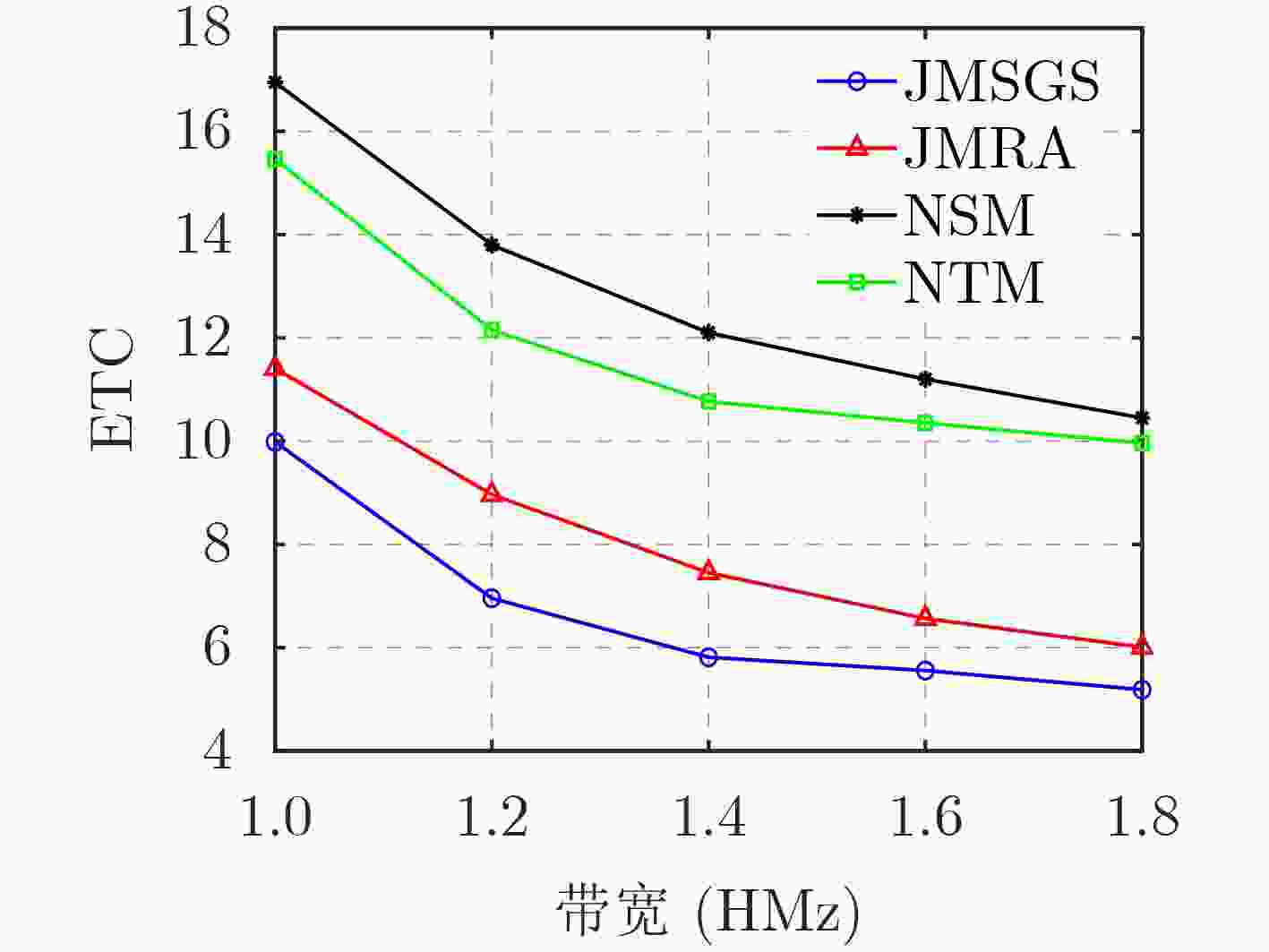
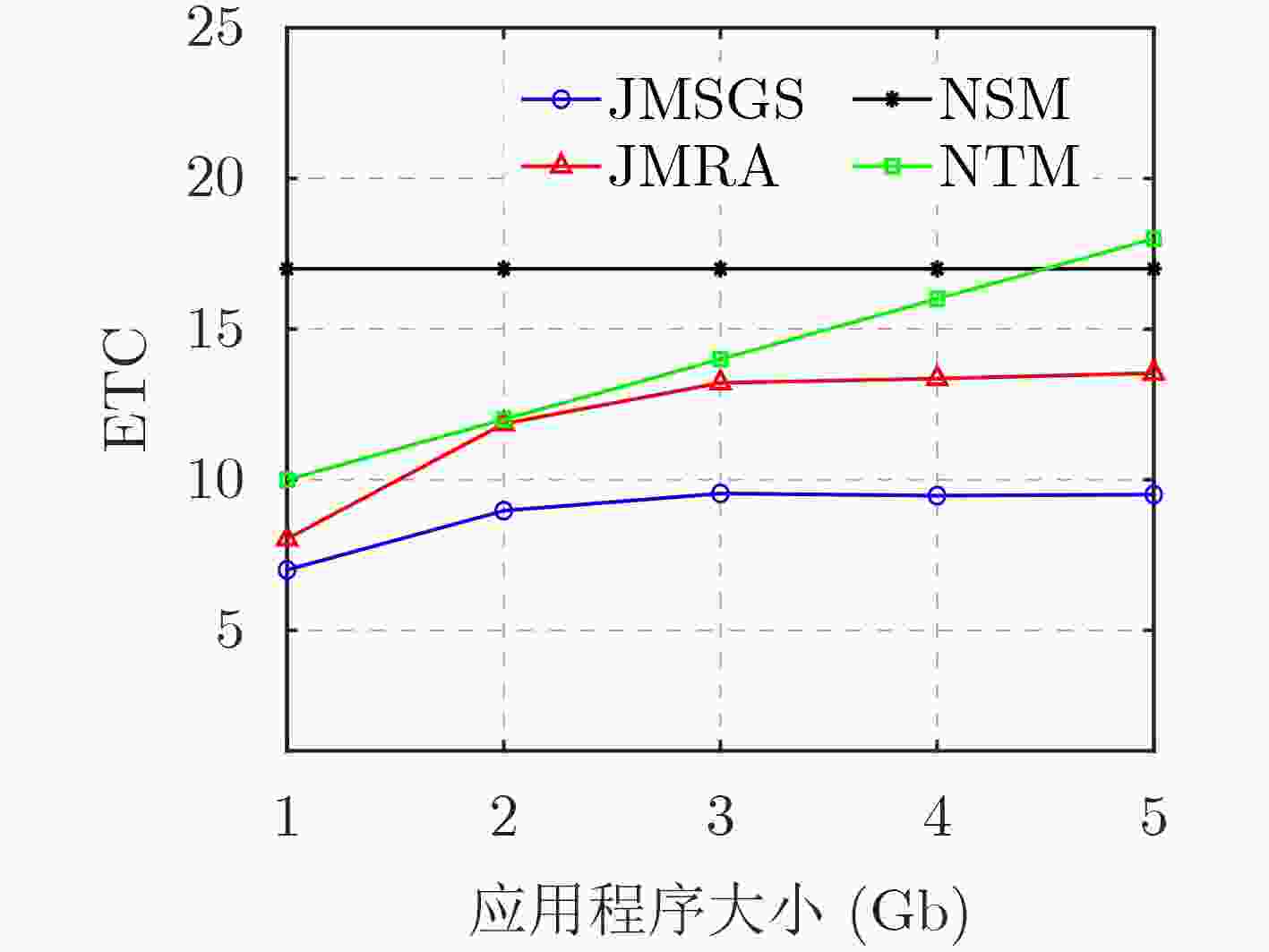
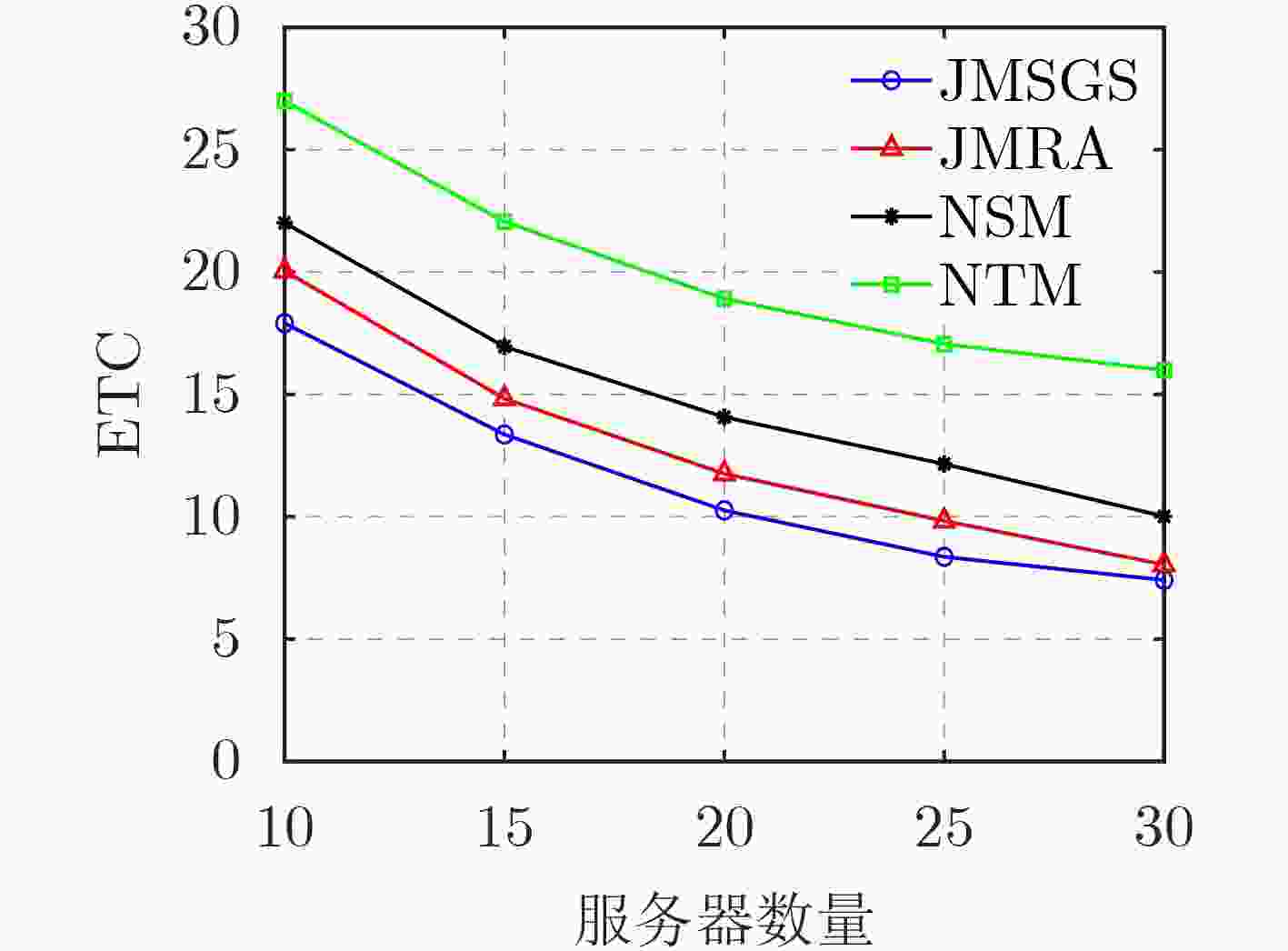


 下载:
下载:
