Research on Combined Navigation Algorithm Based on Adaptive Interactive Multi-Kalman Filter Modeling
-
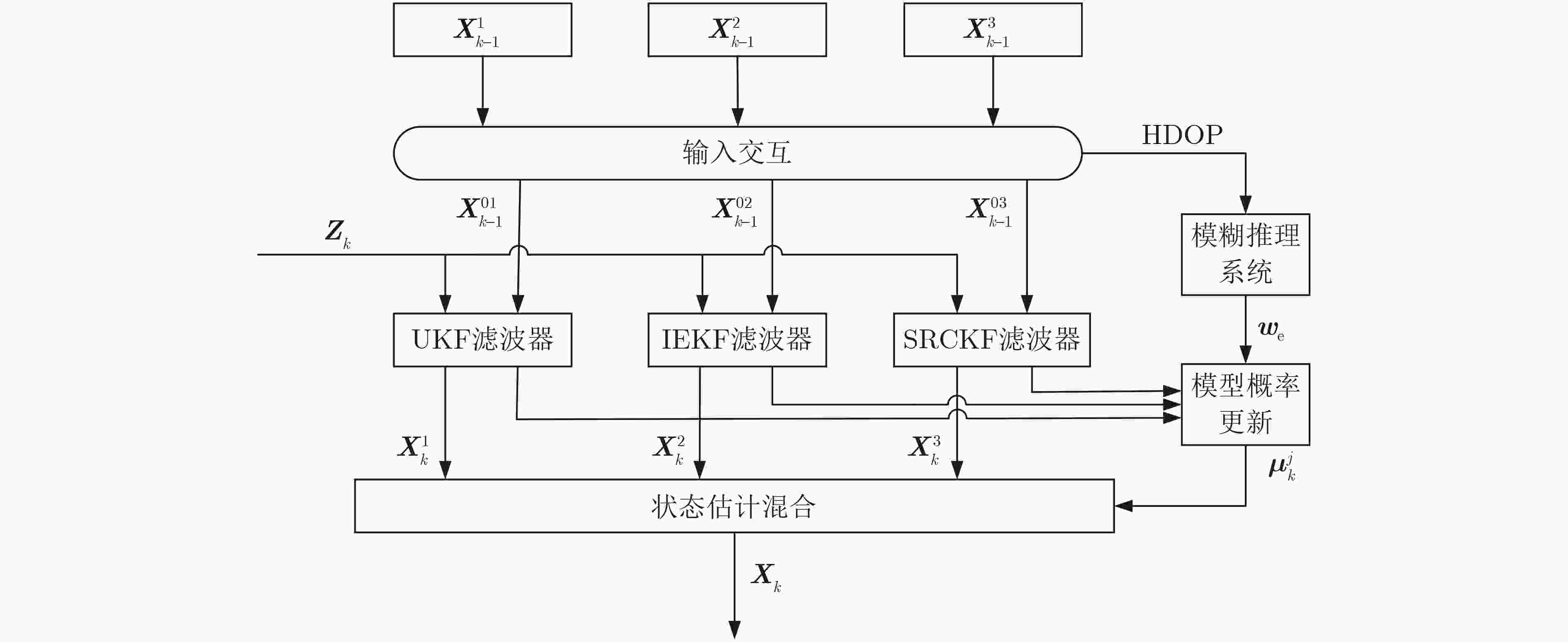
摘要: 在组合导航系统中,信息融合和定位精度取决于惯性系统和传感器的特性,然而在实际应用中获取先验知识仍然具有挑战性。为解决车辆导航中卫星信号质量的变化及系统非线性降低组合导航系统性能的问题,该文提出一种基于多卡尔曼滤波器的模糊自适应交互式多模型算法(FAIMM-MKF),将基于卫星信号质量的模糊控制器(Fuzzy Controller)与自适应交互多模型(AIMM)相结合,通过组合无迹卡尔曼滤波(UKF)、迭代扩展卡尔曼滤波(IEKF)和平方根容积卡尔曼滤波(SRCKF)3种不同的滤波器,适配车辆动力学模型,并通过车载半实物仿真实验验证该方法的性能。结果表明,在卫星信号质量发生改变的情况下,与传统的交互式多模型算法相比,该方法显著提高了车辆在复杂环境中的定位精度。Abstract: Practical applications struggle to obtain prior knowledge about inertial systems and sensors, affecting information fusion and positioning accuracy in combined navigation systems. To address the degradation of integrated navigation performance due to satellite signal quality changes and system nonlinearity in vehicle navigation, a Fuzzy Adaptive Interactive Multi-Model algorithm based on Multiple Kalman Filters (FAIMM-MKF) is proposed. It integrates a Fuzzy Controller based on satellite signal quality (Fuzzy Controller) and an Adaptive Interactive Multi-Model (AIMM). Improved Kalman filters such as Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF), Iterated Extended Kalman Filter (IEKF), and Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter (SRCKF) are designed to match vehicle dynamics models. The method’s performance is verified through in-vehicle semi-physical simulation experiments. Results show that the method significantly improves vehicle positioning accuracy in complex environments with varying satellite signal quality compared to traditional interactive multi-model algorithms.
-
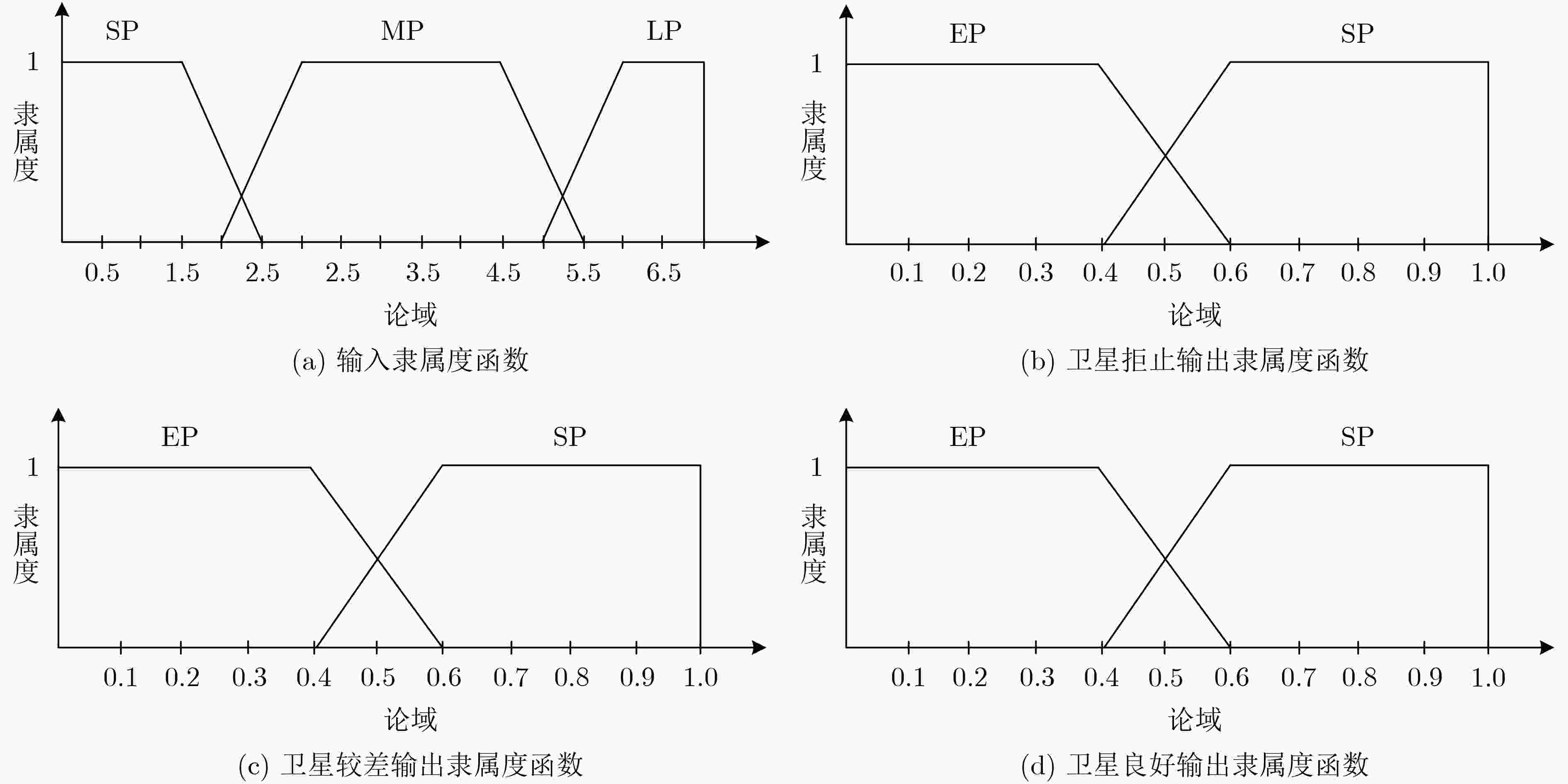
表 1 模糊规则表
HDOP 模型权重调整因子 卫星拒止 卫星较差 卫星良好 SP SP SP EP MP SP EP SP LP EP SP SP 表 2 传感器误差参数
性能指标 陀螺仪 加速度计 零偏 随机游走 零偏 随机游走 更新频率 参数 5°/h 0.15°/$ \sqrt h $ 0.2 mg 800 ug/$ \sqrt {{\mathrm{Hz}}} $ 125 Hz 表 3 最大误差和标准误差对比
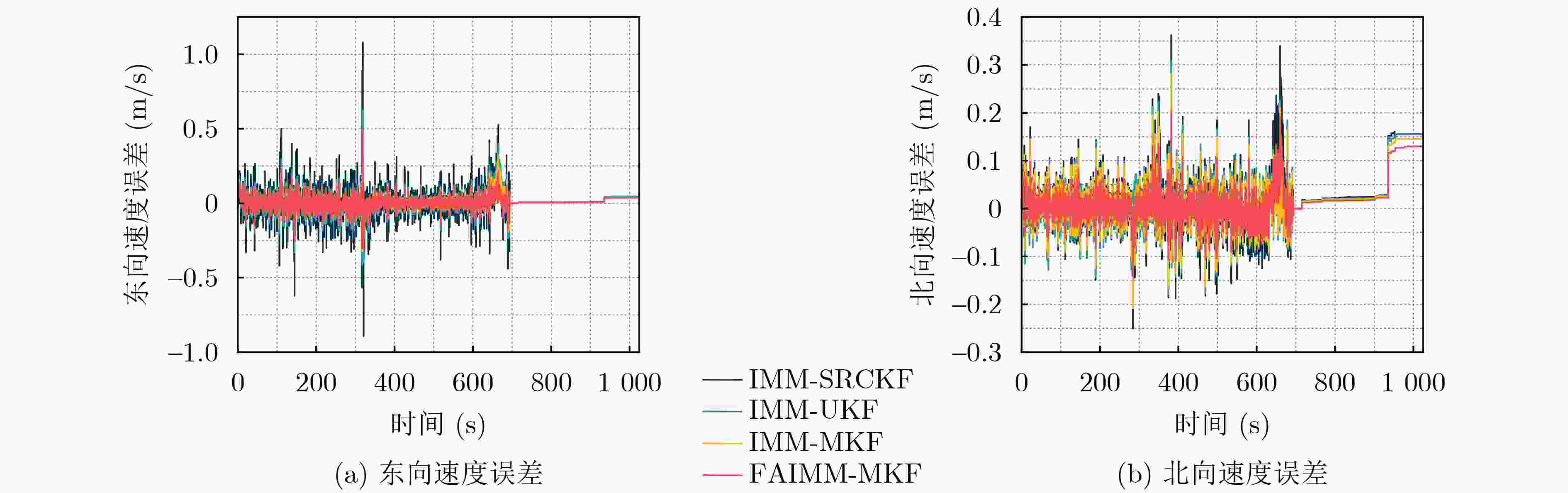
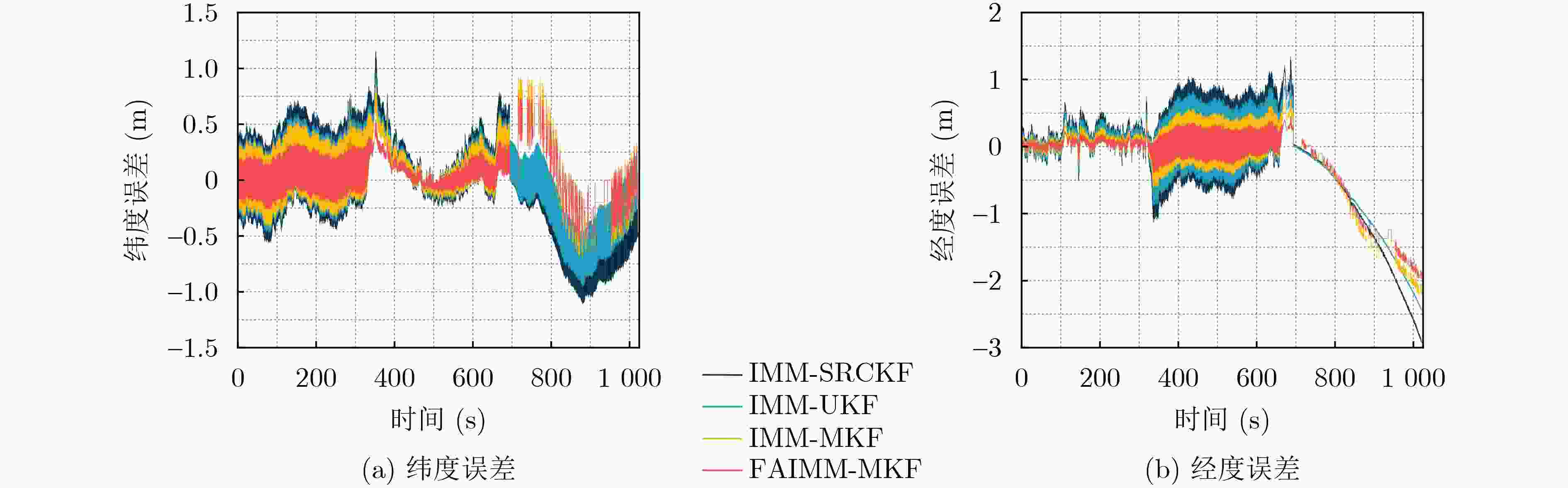
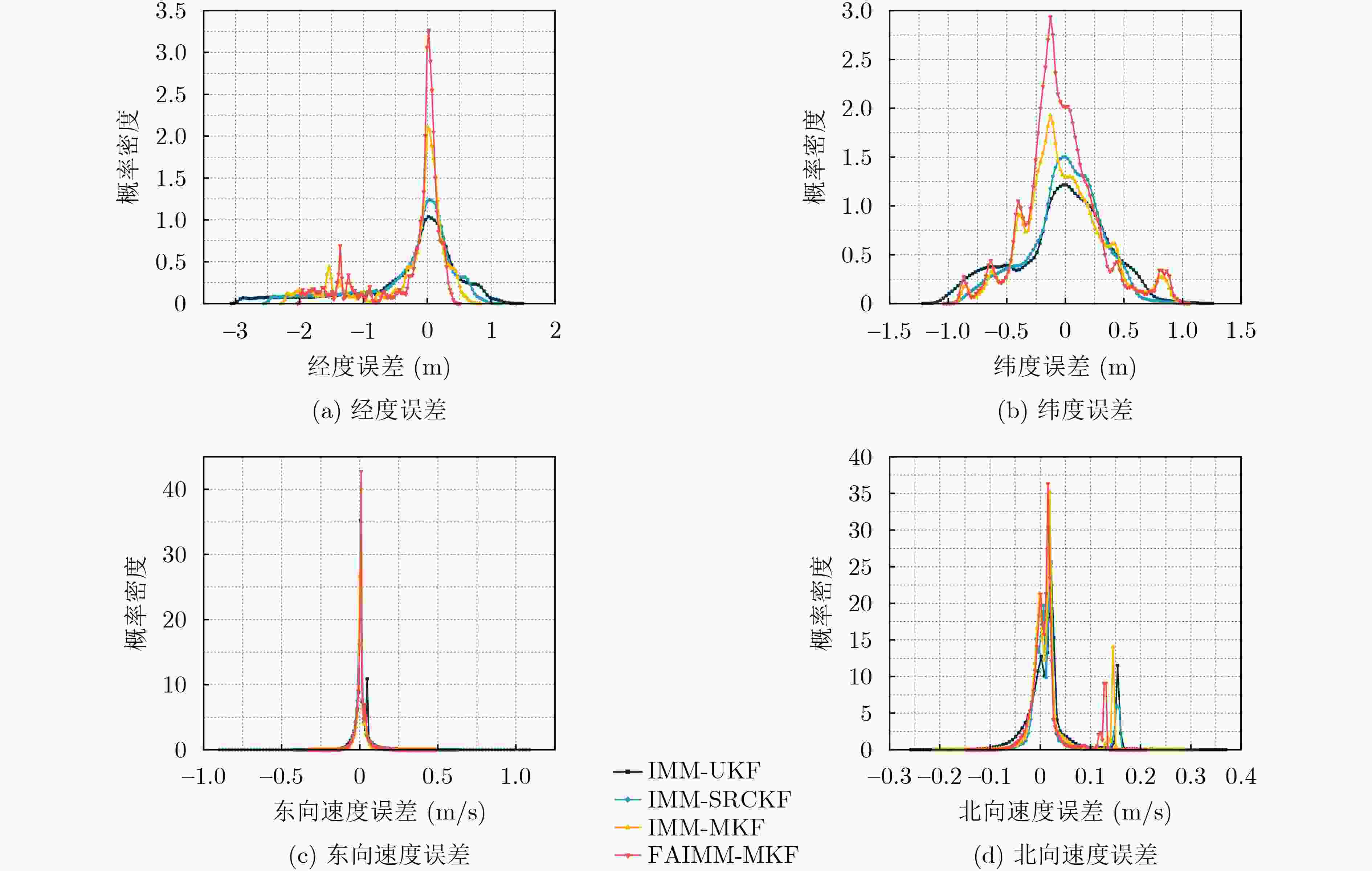
算法 东向速度(m/s) 北向速度(m/s) 纬度误差(m) 经度误差(m) 最大误差 标准差 最大误差 标准差 最大误差 标准差 最大误差 标准差 IMM-UKF 1.080 0 0.048 5 0.347 1 0.055 2 1.151 5 0.395 6 –2.919 1 0.835 6 IMM-SRCKF 0.623 7 0.042 4 0.288 3 0.045 1 0.974 2 0.311 6 –2.439 4 0.705 3 IMM-MKF 0.483 5 0.038 6 0.280 6 0.043 8 0.941 0 0.291 5 –2.193 6 0.678 7 FAIMM-MKF 0.467 1 0.028 4 0.205 3 0.040 2 0.760 8 0.220 1 –1.962 5 0.589 3 表 4 平均绝对误差和均方根误差对比
算法 东向速度(m/s) 北向速度(m/s) 纬度(m) 经度(m) MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE MAE RMSE IMM-UKF 0.030 2 0.055 0 0.038 1 0.059 6 0.309 3 0.397 1 0.568 3 0.873 6 IMM-SRCKF 0.024 9 0.043 0 0.027 9 0.048 8 0.235 2 0.311 7 0.481 5 0.743 3 IMM-MKF 0.024 6 0.039 9 0.026 1 0.047 6 0.190 4 0.303 4 0.440 1 0.729 5 FAIMM-MKF 0.018 3 0.029 1 0.025 6 0.043 6 0.164 5 0.226 9 0.364 0 0.642 0 -
[1] 徐晓苏, 仲灵通. 一种基于M估计的抗差自适应多模型组合导航算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2021, 29(4): 482–490. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2021.04.009.XU Xiaosu and ZHONG Lingtong. Robust adaptive multiple model integrated navigation algorithm based on M-estimation[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2021, 29(4): 482–490. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2021.04.009. [2] ZHAO Huijun, LIU Jun, CHEN Xuemei, et al. Information monitoring and adaptive information fusion of multisource fusion navigation systems in complex environments[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(14): 25047–25056. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3391872. [3] JWO D J and CHANG W Y. Variational Bayesian based IMM robust GPS navigation filter[J]. Computers, Materials and Continua, 2022, 72(1): 755–773. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2022.025040. [4] HAN Bo, HUANG Hanqiao, LEI Lei, et al. An improved IMM algorithm based on STSRCKF for maneuvering target tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 57795–57804. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2912983. [5] MA Jian and GUO Xiaoting. Combination of IMM algorithm and ASTRWCKF for maneuvering target tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 143095–143103. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3013561. [6] 王常虹, 张大力, 夏红伟, 等. GEO混合推力机动目标跟踪IMM算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2023, 44(3): 443–453. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2023.03.013.WANG Changhong, ZHANG Dali, XIA Hongwei, et al. An IMM algorithm for tracking GEO maneuvering target with hybrid thrust[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2023, 44(3): 443–453. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2023.03.013. [7] 李俊. 基于联邦卡尔曼滤波器的容错多传感器组合导航算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2023. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2023.000673.LI Jun. Research on fault tolerant multi-sensor integrated navigation algorithm based on federated Kalman filter[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023. doi: 10.27251/d.cnki.gnjdc.2023.000673. [8] HWANG I, SEAH C E, and LEE S. A study on stability of the interacting multiple model algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(2): 901–906. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2558156. [9] XIE Guo, SUN Lanlan, WEN Tao, et al. Adaptive transition probability matrix-based parallel IMM algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(5): 2980–2989. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2922305. [10] 陈维义, 何凡, 刘国强, 等. 变结构交互式多模型滤波和平滑算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(12): 4005–4012. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.12.31.CHEN Weiyi, HE Fan, LIU Guoqiang, et al. Variable structure interactive multiple model filtering and smoothing algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(12): 4005–4012. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.12.31. [11] 曾浩, 母王强, 杨顺平. 高机动目标跟踪ATPM-IMM算法[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(7): 93–101. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022135.ZENG Hao, MU Wangqiang, and YANG Shunping. High maneuvering target tracking ATPM-IMM algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(7): 93–101. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2022135. [12] FAN Peirong, CUI Xiaowei, ZHAO Sihao, et al. A two-step stochastic hybrid estimation for GNSS carrier phase tracking in urban environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 8503718. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3095062. [13] 王伟, 刘萌, 薛冰. GPS辅助的SINS系统快速动基座初始对准[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2020, 52(12): 49–57. doi: 10.11918/201905245.WANG Wei, LIU Meng, and XUE Bing. Fast initial alignment of GPS-assisted SINS system on moving base[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020, 52(12): 49–57. doi: 10.11918/201905245. [14] JIA Di, JIANG Lu, CHEN Tianhua, et al. IMM based sequential fault-tolerant fusion estimation with heavy-tailed noises[C]. The 2022 34th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Hefei, China, 2022: 499–504. doi: 10.1109/CCDC55256.2022.10033545. [15] 王振峰, 李飞, 王新宇, 等. 基于交互式多模型无迹卡尔曼滤波的悬架系统状态估计[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(2): 242–253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.02.003.WANG Zhenfeng, LI Fei, WANG Xinyu, et al. State estimation of suspension system based on interacting multiple model unscented Kalman filter[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(2): 242–253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.02.003. [16] 焦鹏悦, 杨德友, 蔡国伟. 基于Koopman算子与卡尔曼滤波的同步发电机动态状态估计[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2024, 52(9): 27–35. doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.231088.JIAO Pengyue, YANG Deyou, and CAI Guowei. Dynamic state estimation for a synchronous generator based on the Koopman operator and Kalman filter[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2024, 52(9): 27–35. doi: 10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.231088. [17] 卢道华, 宋世磊, 王佳, 等. SINS/DVL水下组合导航技术发展综述[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(7): 1159–1170. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10229.LU Daohua, SONG Shilei, WANG Jia, et al. Review on the development of SINS/DVL underwater integrated navigation technology[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(7): 1159–1170. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2021.10229. [18] SEO J W, KIM J S, KIM D J, et al. Vehicle localization using convolutional neural networks with IMM-EKF for automated vertical parking[C]. The 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 2022: 1976–1981. doi: 10.1109/ITSC55140.2022.9922403. [19] WU Qingdong, LI Chenxi, SHEN Tao, et al. Improved adaptive iterated extended Kalman filter for GNSS/INS/UWB-integrated fixed-point positioning[J]. CMES-Computer Modeling in Engineering and Sciences, 2022, 134(3): 1761–1772. doi: 10.32604/cmes.2022.020545. [20] HU Gaoge, GAO Bingbing, ZHONG Yongmin, et al. Unscented Kalman filter with process noise covariance estimation for vehicular ins/gps integration system[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 64: 194–204. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.08.005. [21] SONG Rui, CHEN Xiyuan, FANG Yongchun, et al. Integrated navigation of GPS/INS based on fusion of recursive maximum likelihood IMM and square-root cubature Kalman filter[J]. ISA Transactions, 2020, 105: 387–395. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2020.05.049. [22] SUN Sibo, ZHANG Xinyu, ZHENG Ce, et al. Underwater acoustical localization of the black box utilizing single autonomous underwater vehicle based on the second-order time difference of arrival[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(4): 1268–1279. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2950954. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
