Design of Rotation Invariant Model Based on Image Offset Angle and Multibranch Convolutional Neural Networks
-
摘要: 卷积神经网络(CNN)具有平移不变性,但缺乏旋转不变性。近几年,为卷积神经网络进行旋转编码已成为解决这一技术痛点的主流方法,但这需要大量的参数和计算资源。鉴于图像是计算机视觉的主要焦点,该文提出一种名为图像偏移角和多分支卷积神经网络(OAMC)的模型用于实现旋转不变。首先检测输入图像的偏移角,并根据偏移角反向旋转图像;将旋转后的图像输入无旋转编码的多分支结构卷积神经网络,优化响应模块,以输出最佳分支作为模型的最终预测。OAMC模型在旋转后的手写数字数据集上以最少的8 k参数量实现了96.98%的最佳分类精度。与在遥感数据集上的现有研究相比,模型仅用前人模型的1/3的参数量就可将精度最高提高8%。Abstract: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) exhibit translation invariance but lack rotation invariance. In recent years, rotating encoding for CNNs becomes a mainstream approach to address this issue, but it requires a significant number of parameters and computational resources. Given that images are the primary focus of computer vision, a model called Offset Angle and Multibranch CNN (OAMC) is proposed to achieve rotation invariance. Firstly, the model detect the offset angle of the input image and rotate it back accordingly. Secondly, feed the rotated image into a multibranch CNN with no rotation encoding. Finally, Response module is used to output the optimal branch as the final prediction of the model. Notably, with a minimal parameter count of 8 k, the model achieves a best classification accuracy of 96.98% on the rotated handwritten numbers dataset. Furthermore, compared to previous research on remote sensing datasets, the model achieves up to 8% improvement in accuracy using only one-third of the parameters of existing models.
-
表 1 旋转MNIST数据集测试精度
-
[1] MO Hanlin and ZHAO Guoying. RIC-CNN: Rotation-invariant coordinate convolutional neural network[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 146: 109994. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109994. [2] ZHU Tianyu, FERENCZI B, PURKAIT P, et al. Knowledge combination to learn rotated detection without rotated annotation[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 15518–15527. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01489. [3] HAN Jiaming, DING Jian, XUE Nan, et al. ReDet: A rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2785–2794. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00281. [4] LI Feiran, FUJIWARA K, OKURA F, et al. A closer look at rotation-invariant deep point cloud analysis[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 16198–16207. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01591. [5] MARCOS D, VOLPI M, KOMODAKIS N, et al. Rotation equivariant vector field networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5058–5067. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.540. [6] EDIXHOVEN T, LENGYEL A, and VAN GEMERT J C. Using and abusing equivariance[C]. Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Paris, France, 2023: 119–128. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW60793.2023.00019. [7] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791. [8] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Spatial transformer networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2017–2025. [9] LAPTEV D, SAVINOV N, BUHMANN J M, et al. TI-POOLING: Transformation-invariant pooling for feature learning in convolutional neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 289–297. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.38. [10] ZHOU Yanzhao, YE Qixiang, QIU Qiang, et al. Oriented response networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4961–4970. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.527. [11] WORRALL D E, GARBIN S J, TURMUKHAMBETOV D, et al. Harmonic networks: Deep translation and rotation equivariance[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7168–7177. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.758. [12] WEILER M, HAMPRECHT F A, and STORATH M. Learning steerable filters for rotation equivariant CNNs[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 849–858. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00095. [13] FIRAT H. Classification of microscopic peripheral blood cell images using multibranch lightweight CNN-based model[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2024, 36(4): 1599–1620. doi: 10.1007/s00521-023-09158-9. [14] WEI Xuan, SU Shixiang, WEI Yun, et al. Rotational convolution: Rethinking convolution for downside fisheye images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 4355–4364. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3298475. [15] COHEN T S, GEIGER M, KOEHLER J, et al. Spherical CNNs[C]. The Sixth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018. [16] WEILER M and CESA G. General e(2)-equivariant steerable cnns[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32. [17] CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, ZHOU Peicheng, et al. Multi-class geospatial object detection and geographic image classification based on collection of part detectors[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 98: 119–132. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.10.002. [18] WU Zhize, WAN Shouhong, WANG Xiaofeng, et al. A benchmark data set for aircraft type recognition from remote sensing images[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 89: 106132. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106132. [19] XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945. [20] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. -





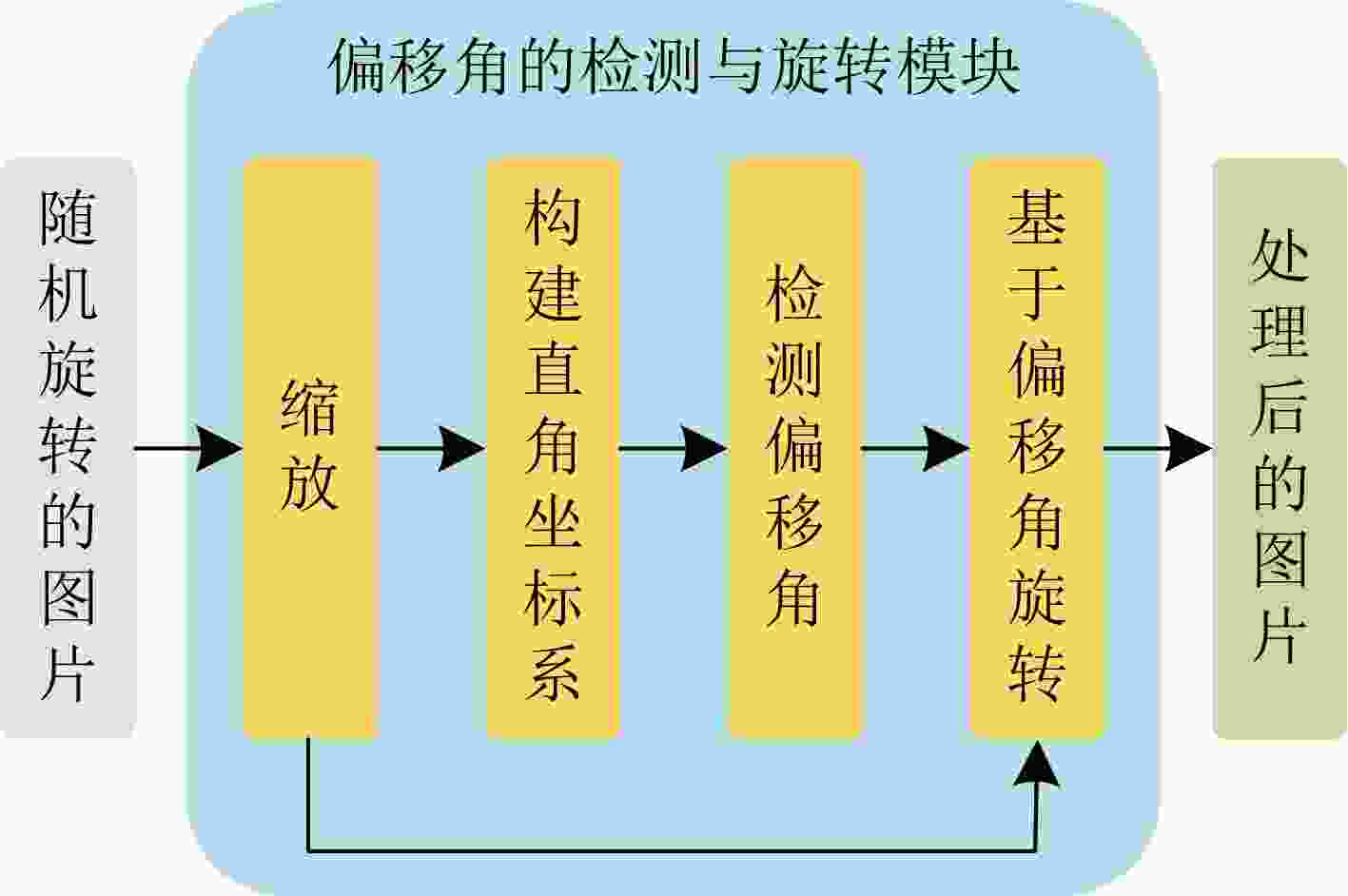
 下载:
下载:
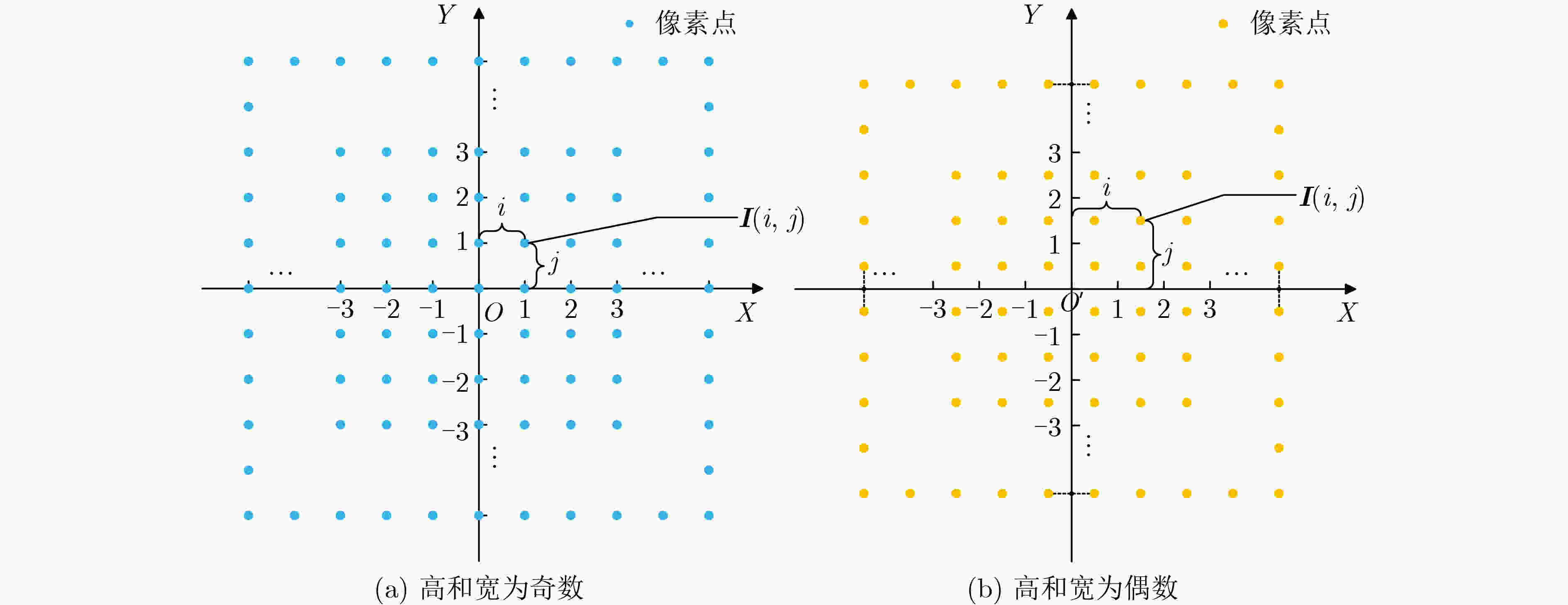

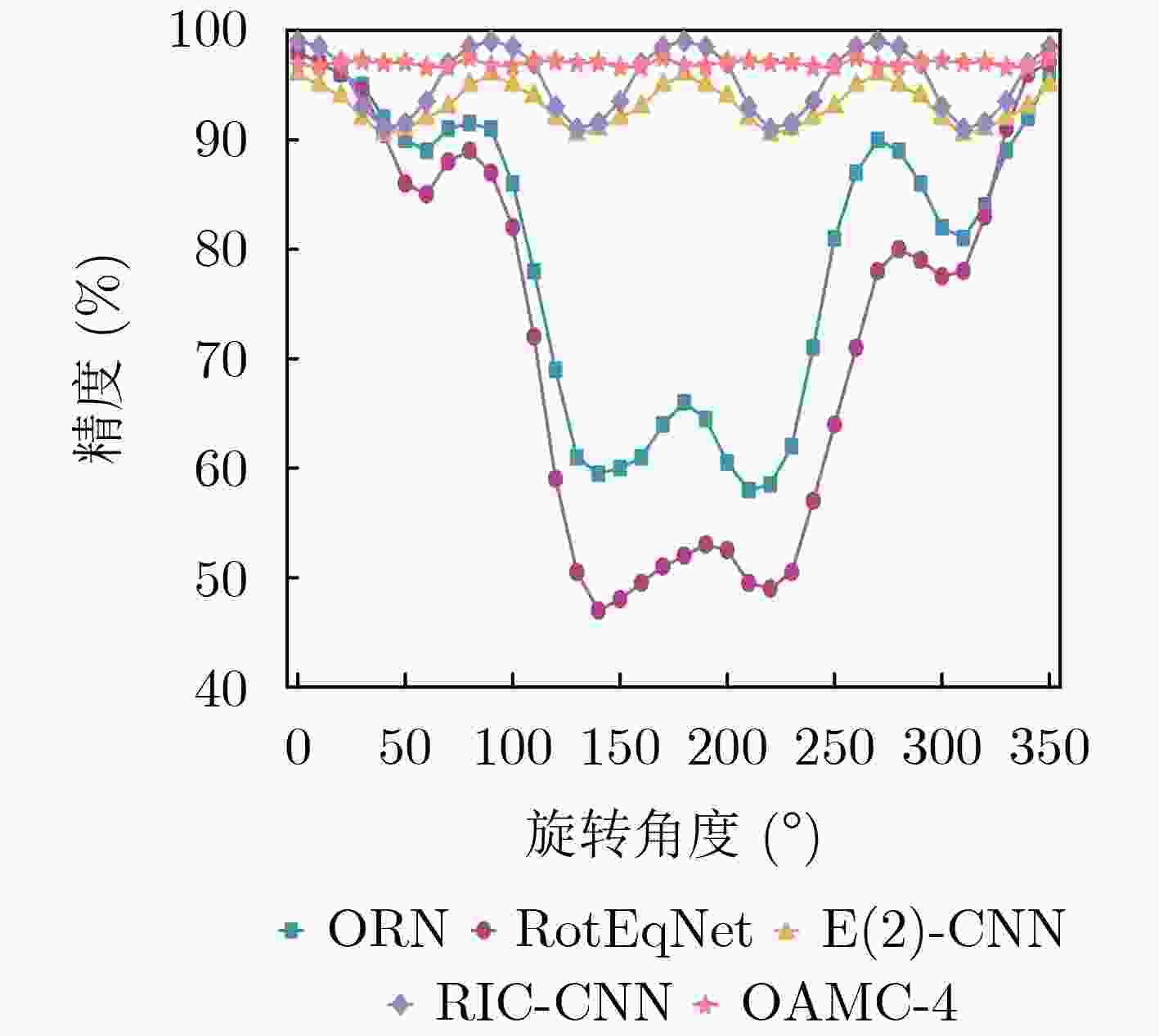


 下载:
下载:
