A Verifiable Privacy Protection Federated Learning Scheme Based on Homomorphic Encryption
-
摘要: 现有基于同态加密的联邦学习安全和隐私保护方案中,仍面临着服务器伪造聚合结果或与用户合谋导致隐私数据泄露风险。针对上述问题,该文提出抗合谋的隐私保护和可验证联邦学习方案。首先,通过结合秘密共享算法实现密钥的生成和协作解密,并采用同态加密等密码学原语进一步保护模型,防止用户与服务器的合谋攻击。然后基于双线性聚合签名算法使每个用户能够独立验证服务器提供的聚合结果。同时,为了鼓励更多拥有高质量数据的用户参与进来,该文提出一种激励机制,为用户提供相应的奖励。安全性分析表明,该文方案对系统中存在的合谋攻击具有鲁棒性。最后,理论分析和实验验证结果表明该方案具有可靠性、可行性和有效性。Abstract:
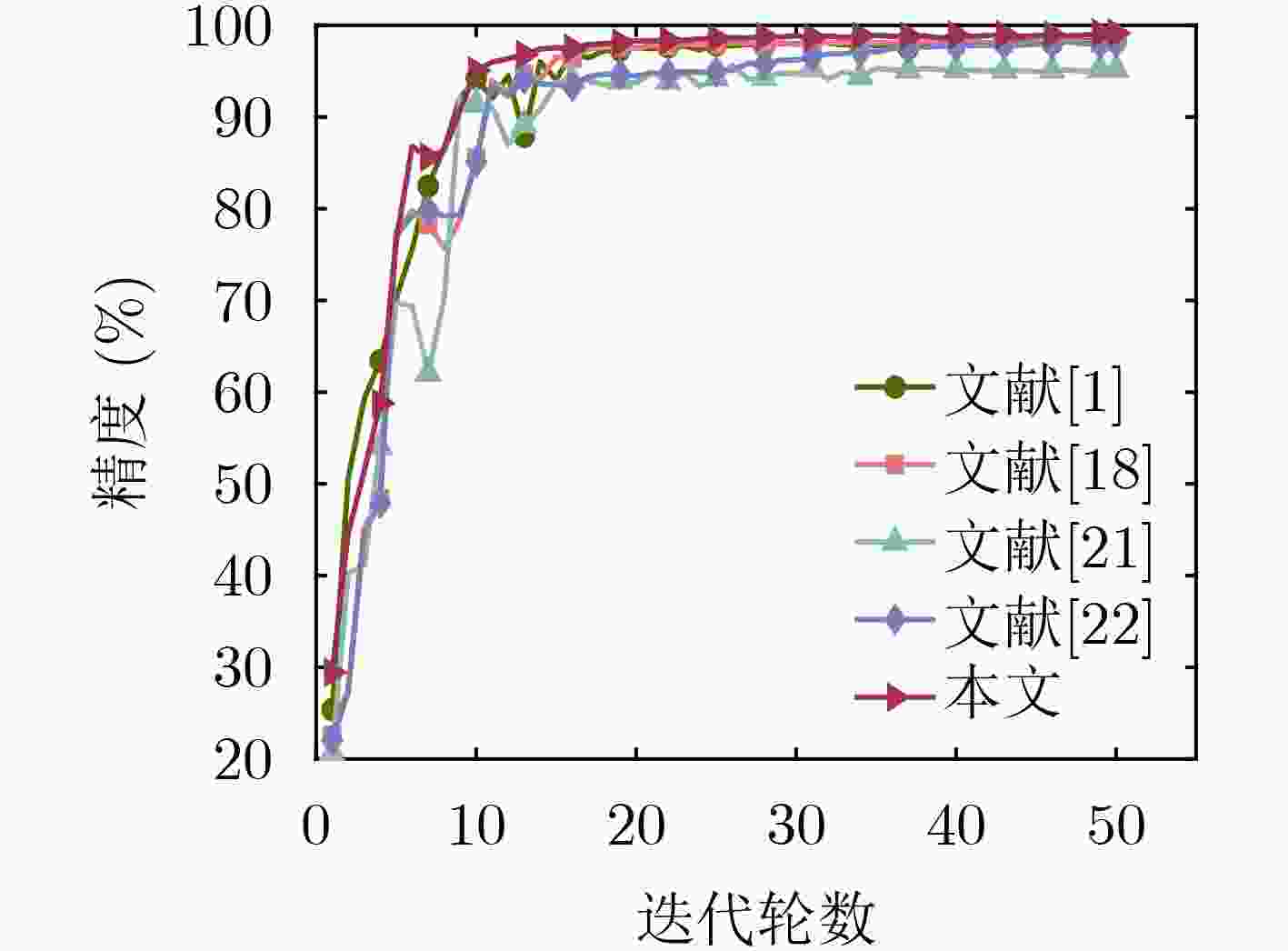
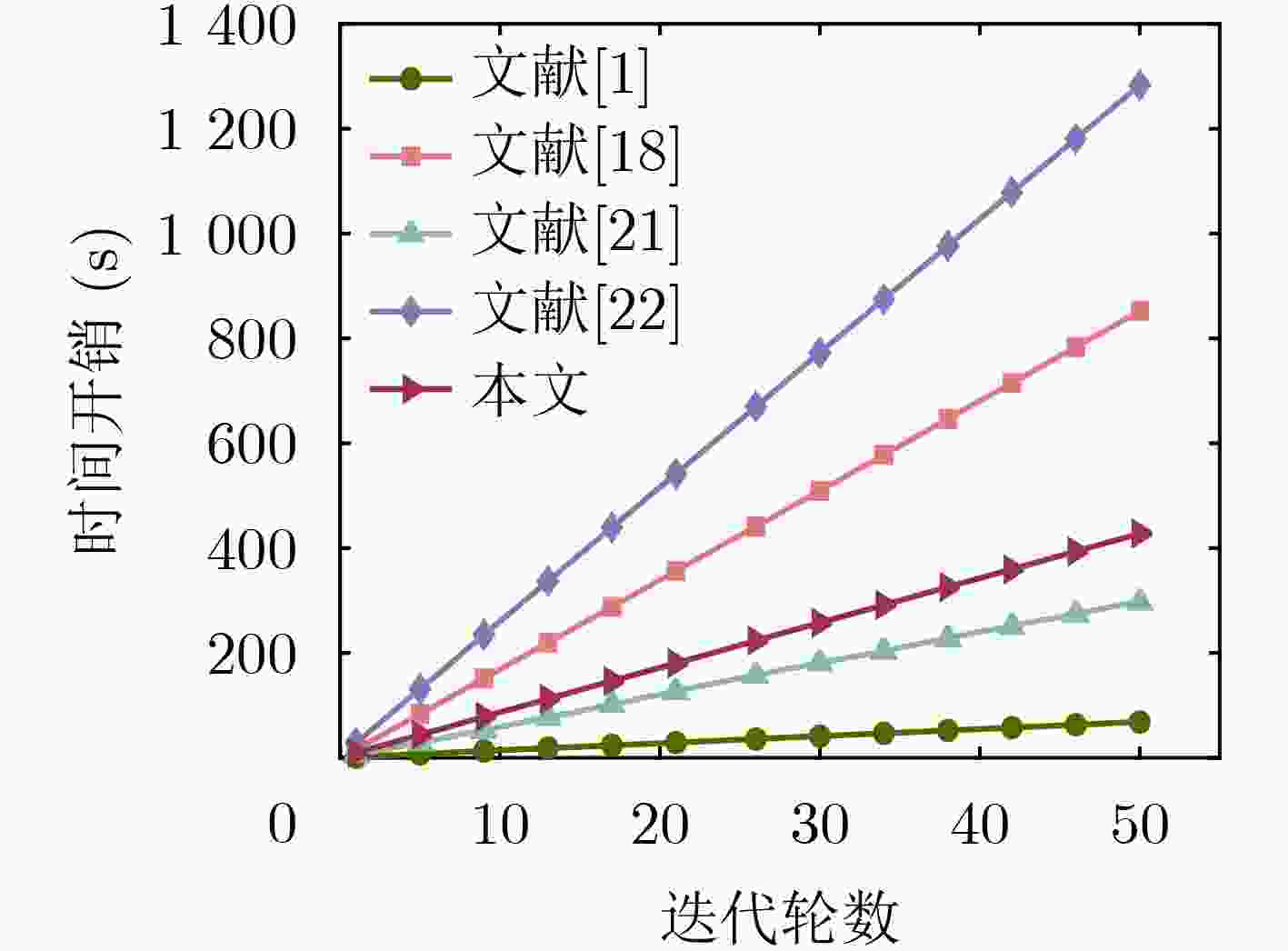
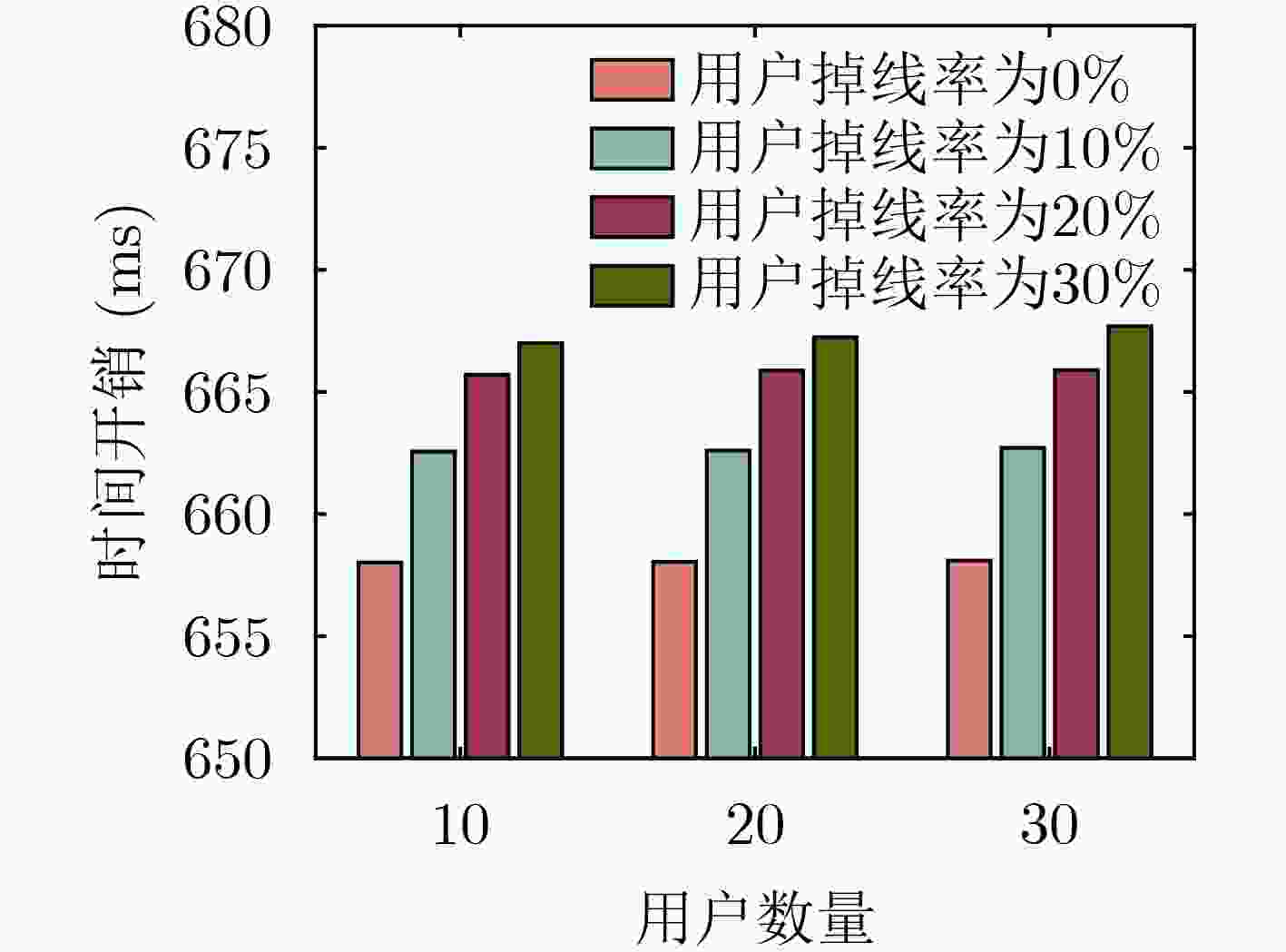
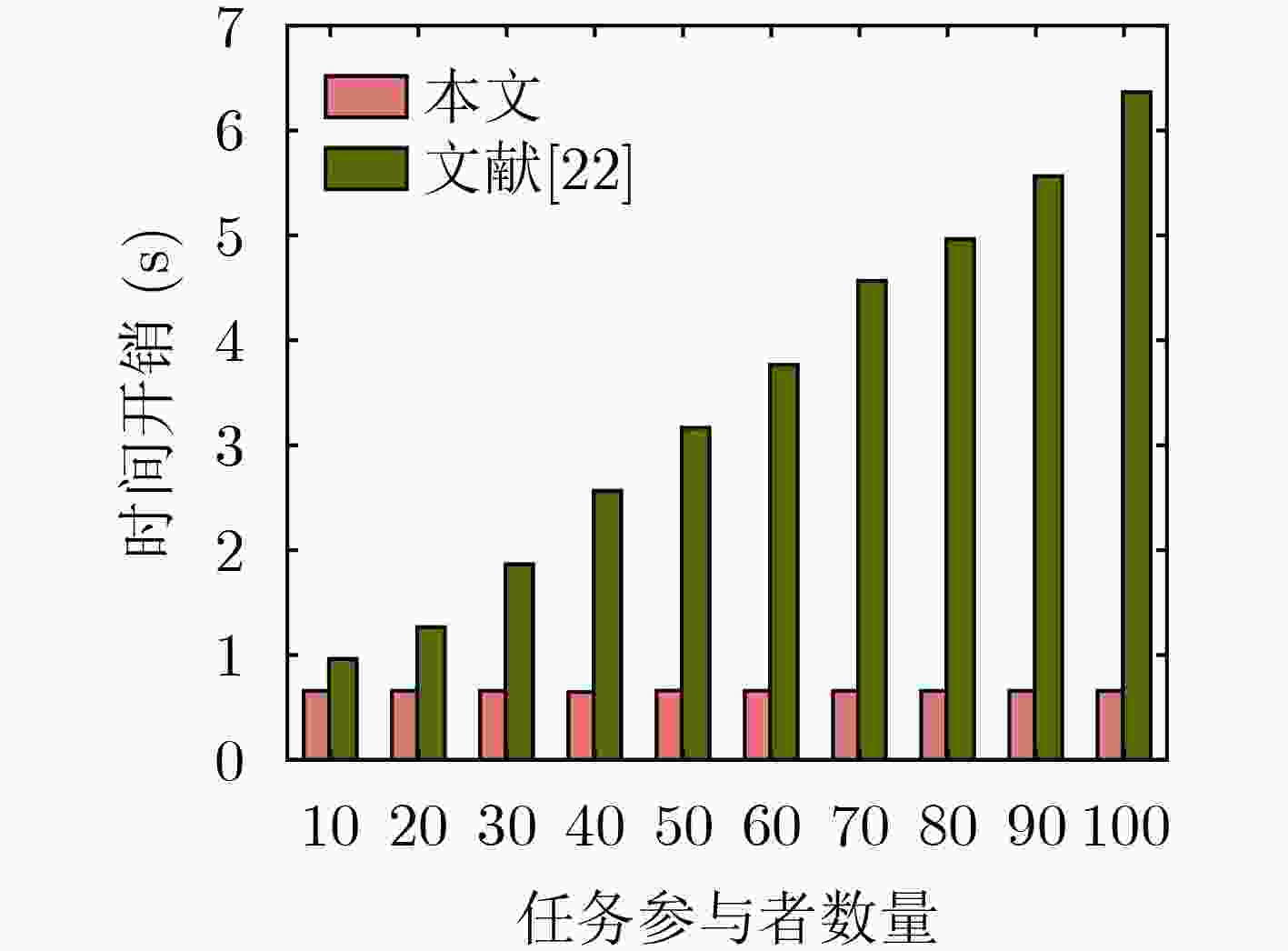
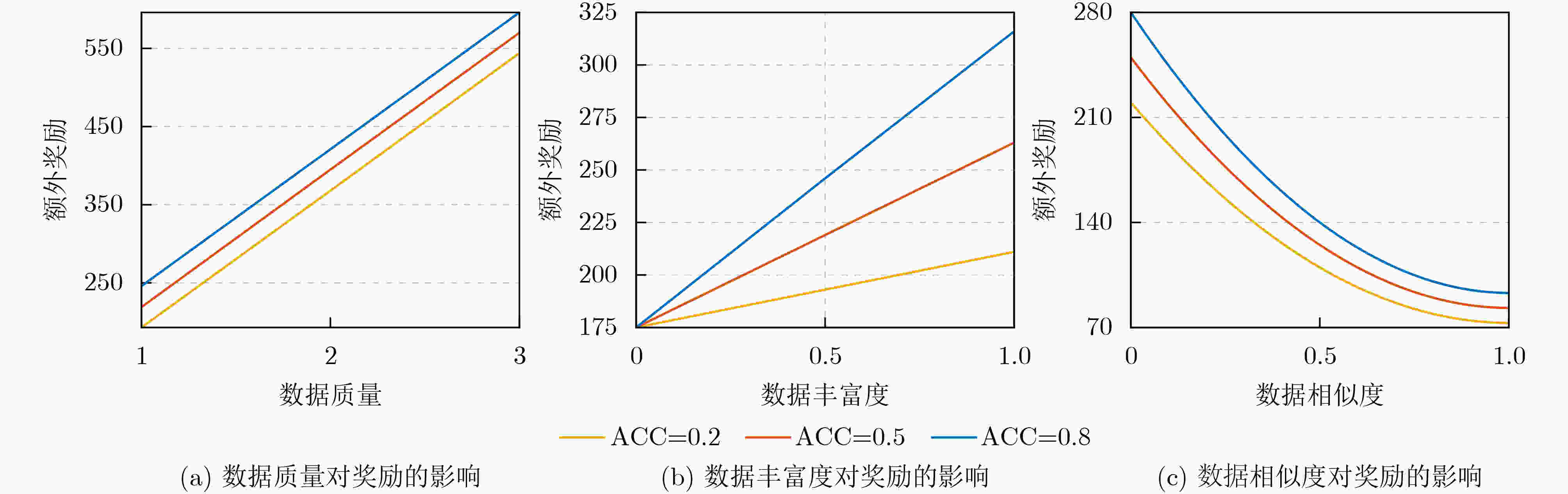
Objective The growing reliance on data in today’s digital age highlights the importance of effective data management across industries. Federated Learning (FL), an innovative approach, facilitates data collaboration and joint model development while maintaining privacy. However, existing homomorphic encryption-based security schemes for FL present several limitations. In some cases, FL servers may falsify aggregation results, leading to inaccurate models and subsequent issues, such as decision-making errors and erosion of trust in the system. Furthermore, servers may collude with users to steal private data, resulting in privacy breaches and potential misuse, including illegal marketing or cyberattacks. These issues undermine public confidence in data security and limit the broader adoption of FL, thus impeding innovation and efficiency gains. Many current schemes also depend heavily on trusted Third PArties (TPA) for key generation, introducing high communication overhead and diminishing model training efficiency, which discourages users from sharing data. This study proposes an optimized solution utilizing a distributed key generation protocol to prevent collusion and reduce third-party dependency. It integrates the Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT) to lower communication costs and introduces auxiliary nodes to ensure aggregation accuracy. Additionally, an incentive mechanism is designed to encourage users to share high-quality private data. Collectively, these measures address key challenges in existing systems, offering a safer, more efficient, and reliable framework for the widespread adoption of FL. Methods The proposed FL scheme is collusion-resistant, privacy-preserving, and verifiable, integrating a distributed key generation protocol to achieve interactive key generation. This method enables users to encrypt data using their private keys while requiring collaborative decryption from multiple participants, thereby eliminating the reliance on TPA. It effectively prevents server collusion involving fewer than n–1 users and incorporates a fault-tolerant mechanism to address potential user disconnections. Enhanced data security and reduced communication overhead are achieved by employing randomized model processing, combined with CRT based dimensionality reduction prior to encryption. Specifically, each user superimposes a random model of identical dimensions onto their local model, uploads the randomized model to the server for aggregation, and then decomposes the random model into a public matrix and a low-dimensional vector. After applying CRT to reduce the vector’s dimensionality, homomorphic encryption is performed, reducing the data that must be encrypted and uploaded. The scheme also introduces auxiliary nodes and utilizes a bilinear aggregate signature algorithm, enabling each user to independently verify the aggregation results provided by the server, ensuring correctness and verifiability. Additionally, an incentive mechanism based on data characteristics, such as quality and richness, encourages participation from users with high-quality data. By dynamically calculating and distributing rewards after task completion, the mechanism effectively promotes the active sharing of high-quality data by users. Results and Discussions The proposed scheme is comprehensively evaluated through extensive experiments. The results demonstrate improvements in both model accuracy and training efficiency. As shown in ( Fig. 4 ), the scheme achieves slightly higher accuracy on the MNIST dataset compared to FedAvg and three other approaches. This improvement is attributed to the incentive mechanism, which effectively encourages participation from users with high-quality data. Additionally, the preprocessing steps involving model randomization and CRT-based dimensionality reduction prior to encryption enhance communication efficiency, as evidenced by the time overhead comparison in (Fig. 5 ). The experimental evaluation of the designed verification scheme, shown in (Fig. 6 ), reveals that the verification time of user will not increase with the increase of the number of users. Even with 30 users, the verification time increases by only 1%, despite a 30% dropout rate, when compared to scenarios with no user dropouts. (Fig. 7 ) further confirms the verification time advantages of the proposed scheme over other verification approaches. Finally, the reward allocation mechanism demonstrates desirable fairness characteristics, as shown in (Fig. 8 ), where users contributing high-quality data consistently receive proportionally greater rewards throughout the training process.Conclusions The proposed privacy-preserving FL scheme, based on homomorphic encryption and verifiable mechanisms, effectively reduces the computational overhead associated with homomorphic encryption through optimized model parameter processing. This ensures data privacy while preventing excessive communication costs. Additionally, the framework incorporates a distributed key generation protocol to eliminate reliance on trusted third-party institutions and integrates the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol with Shamir’s secret sharing algorithm. This combination enables users to independently verify aggregation results provided by the server while supporting user dropouts and preventing collusion. To further encourage data contributions from users with high-quality data, an incentive mechanism is introduced, employing rational reward strategies to attract such users. Experimental results demonstrate excellent performance in model convergence speed and prediction accuracy, with verification time for aggregation results remaining stable regardless of the number of users. However, this study does not address potential malicious behaviors, such as individual users uploading erroneous or deceptive model updates that could compromise global model accuracy and fairness. Future work will focus on developing mechanisms to identify and mitigate attacks from malicious users while maintaining data privacy protection. -
Key words:
- Federated Learning (FL) /
- Homomorphic encryption /
- Privacy protection /
- Verifiability
-
表 2 初始化阶段生成时间
用户数量 时间(s) 10 0.008 30 0.230 50 1.060 100 8.000 -
[1] MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282. [2] RODRÍGUEZ-BARROSO N, JIMÉNEZ-LÓPEZ D, LUZÓN M V, et al. Survey on federated learning threats: Concepts, taxonomy on attacks and defences, experimental study and challenges[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 90: 148–173. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.09.011. [3] 孙钰, 严宇, 崔剑, 等. 联邦学习深度梯度反演攻防研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(2): 428–442. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230541.SUN Yu, YAN Yu, CUI Jian, et al. Review of deep gradient inversion attacks and defenses in federated learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(2): 428–442. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230541. [4] ZHANG Pengfei, CHENG Xiang, SU Sen, et al. Task allocation under geo-indistinguishability via group-based noise addition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2023, 9(3): 860–877. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2022.3215467. [5] FENG Jun, YANG L T, REN Bocheng, et al. Tensor recurrent neural network with differential privacy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2024, 73(3): 683–693. doi: 10.1109/TC.2023.3236868. [6] FENG Jun, YANG L T, ZHU Qing, et al. Privacy-preserving tensor decomposition over encrypted data in a federated cloud environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2020, 17(4): 857–868. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2018.2881452. [7] ALAZAB M, RM S P, PARIMALA M, et al. Federated learning for cybersecurity: Concepts, challenges, and future directions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(5): 3501–3509. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3119038. [8] 王冬, 秦倩倩, 郭开天, 等. 联邦学习中的模型逆向攻防研究综述[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(11): 94–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023209.WANG Dong, QIN Qianqian, GUO Kaitian, et al. Survey on model inversion attack and defense in federated learning[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(11): 94–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2023209. [9] WANG Xiaoding, HU Jia, LIN Hui, et al. Federated learning-empowered disease diagnosis mechanism in the internet of medical things: From the privacy-preservation perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(7): 7905–7913. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3210597. [10] WEI Kang, LI Jun, DING Ming, et al. User-level privacy-preserving federated learning: Analysis and performance optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(9): 3388–3401. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2021.3056991. [11] SUN Lichao, QIAN Jianwei, and CHEN Xun. LDP-FL: Practical private aggregation in federated learning with local differential privacy[C]. The Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 1571–1578. [12] HAN Liquan, FAN Di, LIU Jinyuan, et al. Federated learning differential privacy preservation method based on differentiated noise addition[C]. 2023 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics (ICCCBDA), Chengdu, China, 2023: 285–289. doi: 10.1109/ICCCBDA56900.2023.10154864. [13] GUO Shengnan, WANG Xibin, LONG Shigong, et al. A federated learning scheme meets dynamic differential privacy[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2023, 8(3): 1087–1100. doi: 10.1049/cit2.12187. [14] STEVENS T, SKALKA C, VINCENT C, et al. Efficient differentially private secure aggregation for federated learning via hardness of learning with errors[C]. 31st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 22), Boston, USA, 2022: 1379–1395. [15] BONAWITZ K, IVANOV V, KREUTER B, et al. Practical secure aggregation for privacy-preserving machine learning[C]. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 1175–1191. doi: 10.1145/3133956.3133982. [16] ZHENG Yifeng, LAI Shangqi, LIU Yi, et al. Aggregation service for federated learning: An efficient, secure, and more resilient realization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2023, 20(2): 988–1001. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2022.3146448. [17] WIBAWA F, CATAK F O, KUZLU M, et al. Homomorphic encryption and federated learning based privacy-preserving CNN training: Covid-19 detection use-case[C]. The 2022 European Interdisciplinary Cybersecurity Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2022: 85–90. doi: 10.1145/3528580.3532845. [18] WANG Bo, LI Hongtao, GUO Yina, et al. PPFLHE: A privacy-preserving federated learning scheme with homomorphic encryption for healthcare data[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 146: 110677. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110677. [19] ZHANG Xianglong, FU Anmin, WANG Huaqun, et al. A privacy-preserving and verifiable federated learning scheme[C]. ICC 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC40277.2020.9148628. [20] 余晟兴, 陈钟. 基于同态加密的高效安全联邦学习聚合框架[J]. 通信学报, 2023, 44(1): 14–28. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2023015.YU Shengxing and CHEN Zhong. Efficient secure federated learning aggregation framework based on homomorphic encryption[J]. Journal on Communications, 2023, 44(1): 14–28. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2023015. [21] MA Jing, NAAS S A, SIGG S, et al. Privacy-preserving federated learning based on multi-key homomorphic encryption[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2022, 37(9): 5880–5901. doi: 10.1002/int.22818. [22] MA Xu, ZHANG Fangguo, CHEN Xiaofeng, et al. Privacy preserving multi-party computation delegation for deep learning in cloud computing[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 459: 103–116. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.05.005. [23] XU Guowen, LI Hongwei, LIU Sen, et al. VerifyNet: Secure and verifiable federated learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 911–926. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2929409. [24] SHEN Xiaoying, LUO Xue, YUAN Feng, et al. Verifiable privacy-preserving federated learning under multiple encrypted keys[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(2): 3430–3445. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3296637. [25] SCHINDLER P, JUDMAYER A, STIFTER N, et al. EthDKG: Distributed key generation with Ethereum smart contracts[J]. Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2019. [26] YUN A, CHEON J H, and KIM Y. On homomorphic signatures for network coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2010, 59(9): 1295–1296. doi: 10.1109/TC.2010.73. [27] ELGAMAL T. A public key cryptosystem and a signature scheme based on discrete logarithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1985, 31(4): 469–472. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1985.1057074. [28] ZHANG Li, XU Jianbo, VIJAYAKUMAR P, et al. Homomorphic encryption-based privacy-preserving federated learning in IoT-enabled healthcare system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2023, 10(5): 2864–2880. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3185327. -





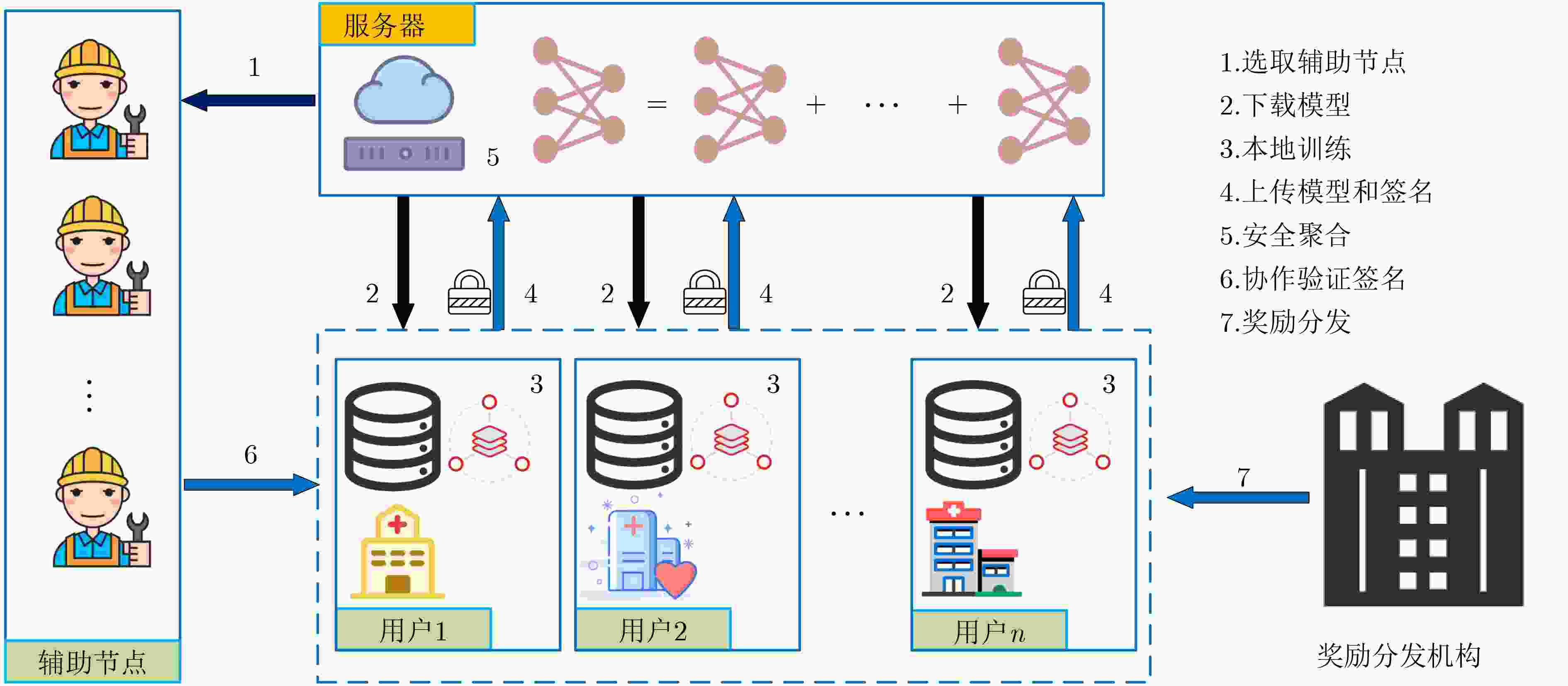
 下载:
下载:
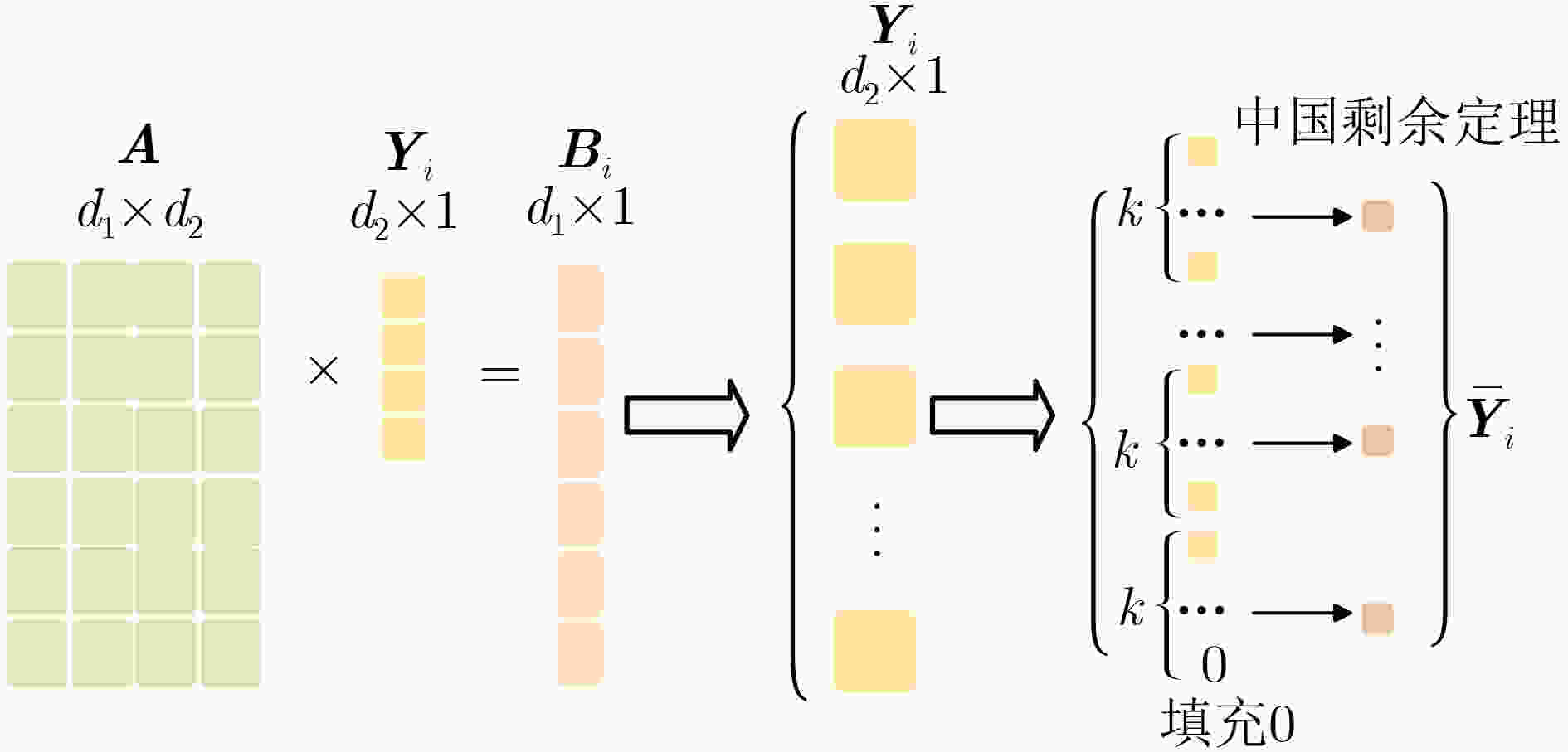
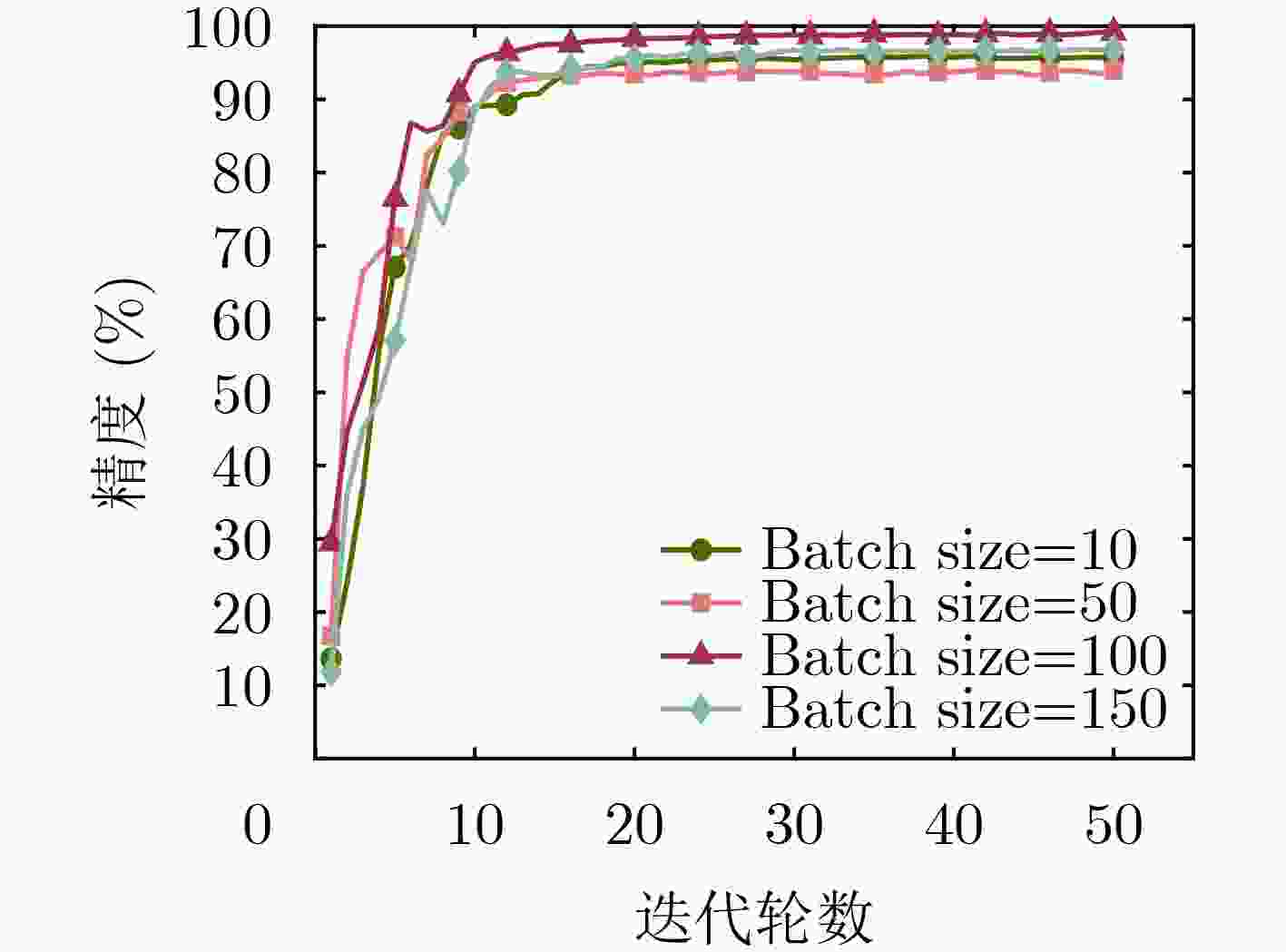


 下载:
下载:
