Frequency Separation Generative Adversarial Super-resolution Reconstruction Network Based on Dense Residual and Quality Assessment
-
摘要: 生成对抗网络因其为盲超分辨率重构提供了新的思路而备受关注。针对现有方法未充分考虑图像退化过程中的低频保留特性而对高低频成分采用相同的处理方式,缺乏对频率细节有效利用,难以获得较好重构效果的问题,该文提出一种基于密集残差和质量评估引导的频率分离生成对抗超分辨率重构网络。该网络采用频率分离思想,对图像的高频和低频信息分开处理,从而提高高频信息捕捉能力,简化低频特征处理。该文对生成器中的基础块进行设计,将空间特征变换层融入密集宽激活残差中,增强深层特征表征能力的同时对局部信息差异化处理。此外,利用视觉几何组网络(VGG)设计了专门针对超分辨率重构图像的无参考质量评估网络,为重构网络提供全新的质量评估损失,进一步提高重构图像的视觉效果。实验结果表明,同当前先进的同类方法比,该方法在多个数据集上具有更佳的重构效果。由此表明,采用频率分离思想的生成对抗网络进行超分辨率重构,可以有效利用图像频率成分,提高重构效果。Abstract: With generative adversarial networks have attracted much attention because they provide new ideas for blind super-resolution reconstruction. Considering the problem that the existing methods do not fully consider the low-frequency retention characteristics during image degradation, but use the same processing method for high and low-frequency components, which lacks the effective use of frequency details and is difficult to obtain better reconstruction result, a frequency separation generative adversarial super-resolution reconstruction network based on dense residual and quality assessment is proposed. The idea of frequency separation is adopted by the network to process the high-frequency and low-frequency information of the image separately, so as to improve the ability of capturing high-frequency information and simplify the processing of low-frequency features. The base block in the generator is designed to integrate the spatial feature transformation layer into the dense wide activation residuals, which enhances the ability of deep feature representation while differentiating the local information. In addition, no-reference quality assessment network is designed specifically for super-resolution reconstructed images using Visual Geometry Group (VGG), which provides a new quality assessment loss for the reconstruction network and further improves the visual effect of reconstructed images. The experimental results show that the method has better reconstruction effect on multiple datasets than the current state-of-the-art similar methods. It is thus shown that super-resolution reconstruction using generative adversarial networks with the idea of frequency separation can effectively utilize the image frequency components and improve the reconstruction effect.
-
表 1 不同方法各数据集的PSNR (dB)和SSIM均值比较(×4)
算法 Set5 Set14 BSDS100 Manga109 PSNR↑ SSIM↑ PSNR↑ SSIM↑ PSNR↑ SSIM↑ PSNR↑ SSIM↑ SRGAN[11] 28.574 0.818 25.674 0.692 25.156 0.654 26.488 0.828 ESRGAN[12] 30.438 0.852 26.278 0.699 25.323 0.651 28.245 0.859 SFTGAN[14] 27.578 0.809 26.968 0.729 25.501 0.653 28.182 0.858 DSGAN[17] 30.392 0.854 26.644 0.714 25.447 0.655 27.965 0.853 SRCGAN[13] 28.068 0.789 26.071 0.696 25.659 0.657 25.295 0.796 FxSR[15] 30.637 0.849 26.708 0.719 26.144 0.684 27.647 0.844 SROOE[16] 30.862 0.866 27.231 0.731 26.195 0.687 27.852 0.849 WGSR[19] 30.373 0.851 27.023 0.727 26.372 0.684 28.287 0.861 本文 30.904 0.872 27.715 0.749 26.838 0.701 28.312 0.867 表 2 自制数据集不同方法NIQE和FVSD平均值比较(×4)
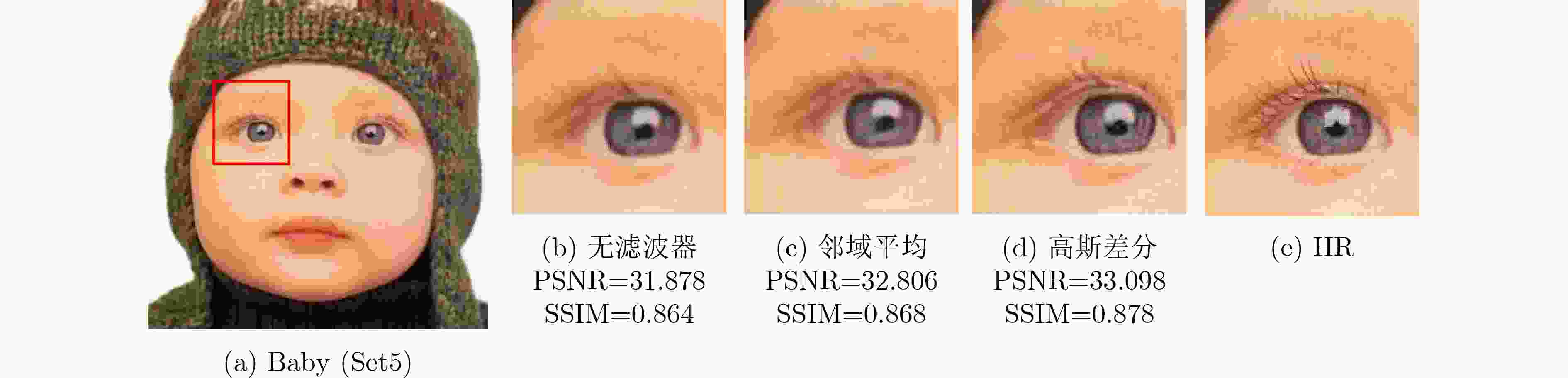
表 3 不同滤波器重构效果的影响
滤波器 PSNR(dB)↑ SSIM↑ 无 28.831 0.835 邻域平均 28.941 0.833 高斯差分 29.015 0.837 表 4 含有不同模块对应的PSNR (dB)和SSIM均值
分支结构 SFT层 质量评估网络 PSNR (dB)↑ SSIM↑ $\surd $ $ \times $ $ \times $ 28.772 0.828 $ \times $ $\surd $ $ \times $ 28.402 0.821 $ \times $ $ \times $ $\surd $ 28.642 0.823 $\surd $ $\surd $ $\surd $ 29.015 0.837 表 5 不同损失函数的影响
损失
组合颜色损失 多层感知损失 对抗损失 FVSD损失 PSNR (dB)↑ SSIM↑ Lcol Lcol-1 Ladv Ladv-1 组合1 $ \times $ $\surd $ $\surd $ $ \times $ $\surd $ $ \times $ 28.352 0.818 组合2 $ \times $ $\surd $ $\surd $ $ \times $ $\surd $ $\surd $ 28.831 0.835 组合3 $\surd $ $ \times $ $\surd $ $\surd $ $ \times $ $ \times $ 28.437 0.821 本文 $\surd $ $ \times $ $\surd $ $\surd $ $ \times $ $\surd $ 29.015 0.837 -
[1] 蔡文郁, 张美燕, 吴岩, 等. 基于循环生成对抗网络的超分辨率重建算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 178–186. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201046.CAI Wenyu, ZHANG Meiyan, WU Yan, et al. Research on cyclic generation countermeasure network based super-resolution image reconstruction algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 178–186. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201046. [2] ZHOU Chaowei and XIONG Aimin. Fast image super-resolution using particle swarm optimization-based convolutional neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 1923. doi: 10.3390/s23041923. [3] WU Zhijian, LIU Wenhui, LI Jun, et al. SFHN: Spatial-frequency domain hybrid network for image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(11): 6459–6473. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3271131. [4] 程德强, 袁航, 钱建生, 等. 基于深层特征差异性网络的图像超分辨率算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 1033–1042. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230179.CHENG Deqiang, YUAN Hang, QIAN Jiansheng, et al. Image super-resolution algorithms based on deep feature differentiation network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 1033–1042. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230179. [5] SAHARIA C, HO J, CHAN W, et al. Image super-resolution via iterative refinement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(4): 4713–4726. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3204461. [6] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_13. [7] KIM J, LEE J K, and LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.182. [8] TONG Tong, LI Gen, LIU Xiejie, et al. Image super-resolution using dense skip connections[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4809–4817. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.514. [9] LAN Rushi, SUN Long, LIU Zhenbing, et al. MADNet: A fast and lightweight network for single-image super resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(3): 1443–1453. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2970104. [10] WEI Pengxu, XIE Ziwei, LU Hannan, et al. Component divide-and-conquer for real-world image super-resolution[C]. The 16th Europe Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 101–117. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58598-3_7. [11] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZÁR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.19. [12] WANG Xintao, YU Ke, WU Shixiang, et al. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2019: 63–79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11021-5_5. [13] UMER R M, FORESTI G L, and MICHELONI C. Deep generative adversarial residual convolutional networks for real-world super-resolution[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1769–1777. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW50498.2020.00227. [14] WANG Xintao, YU Ke, DONG Chao, et al. Recovering realistic texture in image super-resolution by deep spatial feature transform[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 606–615. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00070. [15] PARK S H, MOON Y S, and CHO N I. Flexible style image super-resolution using conditional objective[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 9774–9792. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3144406. [16] PARK S H, MOON Y S, and CHO N I. Perception-oriented single image super-resolution using optimal objective estimation[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 1725–1735. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00172. [17] FRITSCHE M, GU Shuhang, and TIMOFTE R. Frequency separation for real-world super-resolution[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3599–3608. doi: 10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00445. [18] PRAJAPATI K, CHUDASAMA V, PATEL H, et al. Direct unsupervised super-resolution using generative adversarial network (DUS-GAN) for real-world data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 8251–8264. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3113783. [19] KORKMAZ C, TEKALP A M, and DOGAN Z. Training generative image super-resolution models by wavelet-domain losses enables better control of artifacts[C]. 2014 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 5926–5936. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00566. [20] MA Chao, YANG C Y, YANG Xiaokang, et al. Learning a no-reference quality metric for single-image super-resolution[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2017, 158: 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2016.12.009. [21] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [22] YANG Jianchao, WRIGHT J, HUANG T S, et al. Image super-resolution via sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(11): 2861–2873. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2050625. [23] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. Deep plug-and-play super-resolution for arbitrary blur kernels[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00177. [24] TIMOFTE R, AGUSTSSON E, VAN GOOL L, et al. NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 114–125. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.149. [25] BEVILACQUA M, ROUMY A, GUILLEMOT C, et al. Low-complexity single image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding[C]. The British Machine Vision Conference, 2012. doi: 10.5244/C.26.135. [26] ZEYDE R, ELAD M, and PROTTER M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations[C]. The 7th International Conference on Curves and Surfaces, Avignon, France, 2012: 711–730. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-27413-8_47. [27] ARBELÁEZ P, MAIRE M, FOWLKES C, et al. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(5): 898–916. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2010.161. [28] MATSUI Y, ITO K, ARAMAKI Y, et al. Sketch-based manga retrieval using manga109 dataset[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(20): 21811–21838. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-4020-z. -






 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载:
