Partially Overlapping Channels Dynamic Allocation Method for UAV Ad-hoc Networks in Emergency Scenario
-
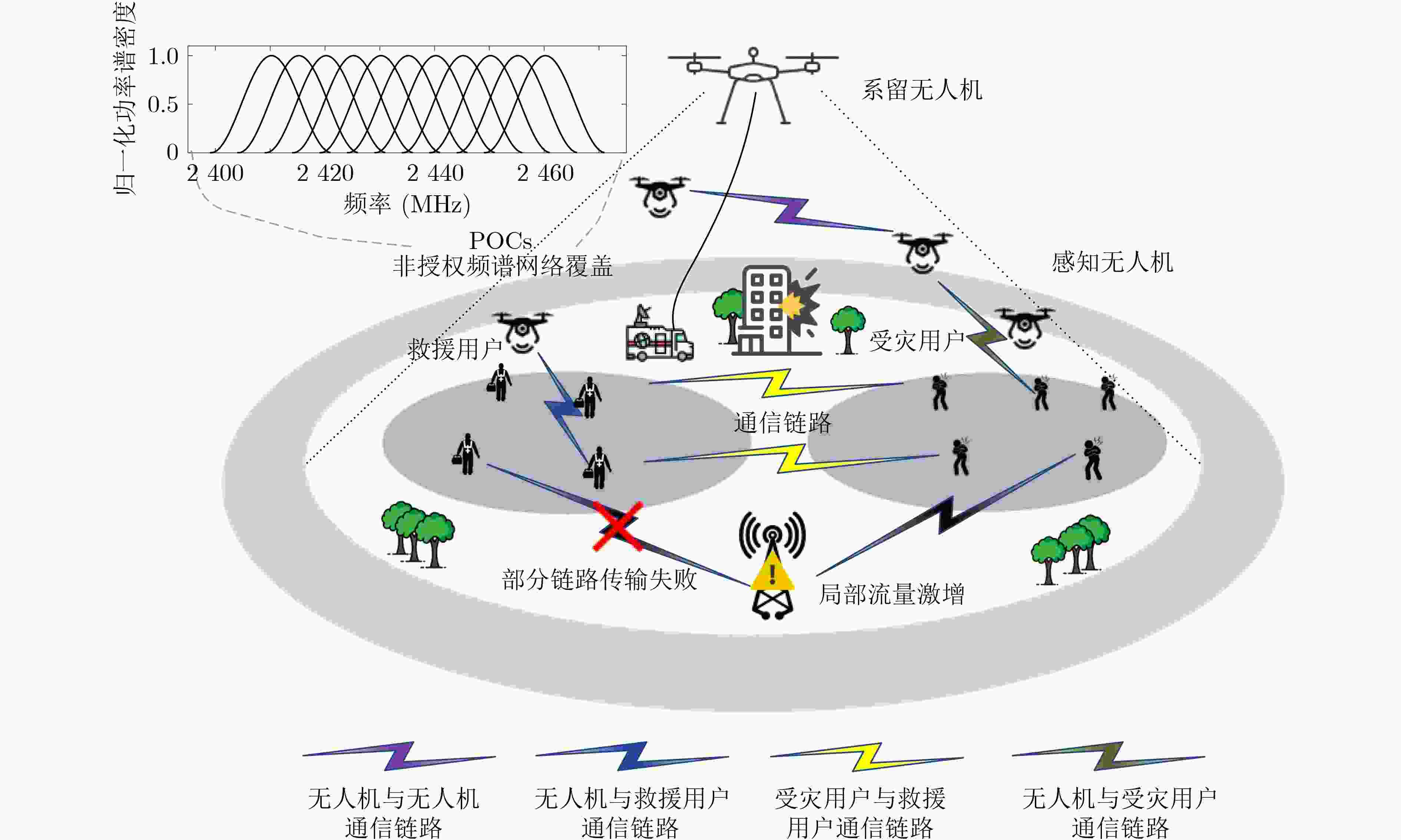
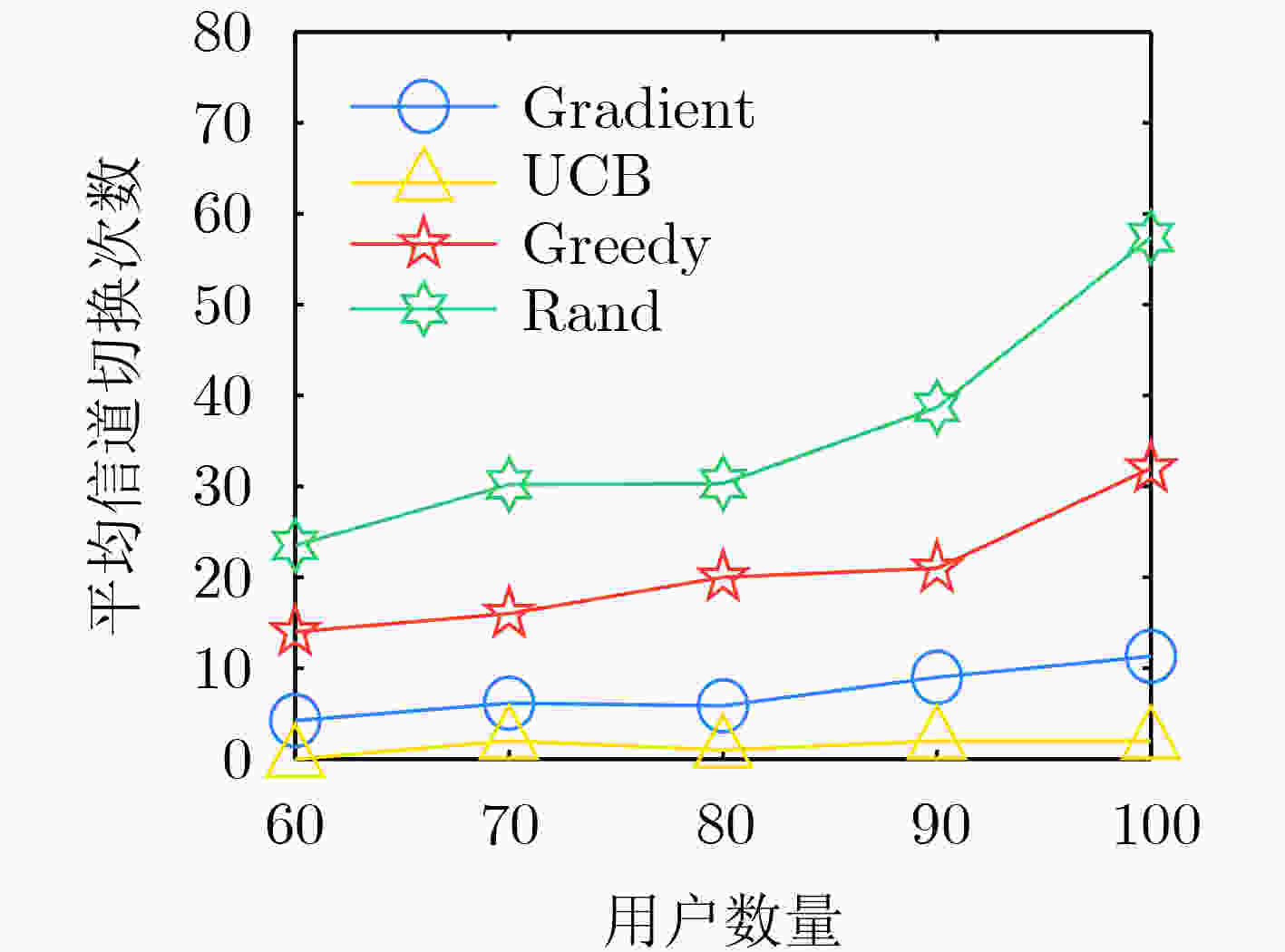
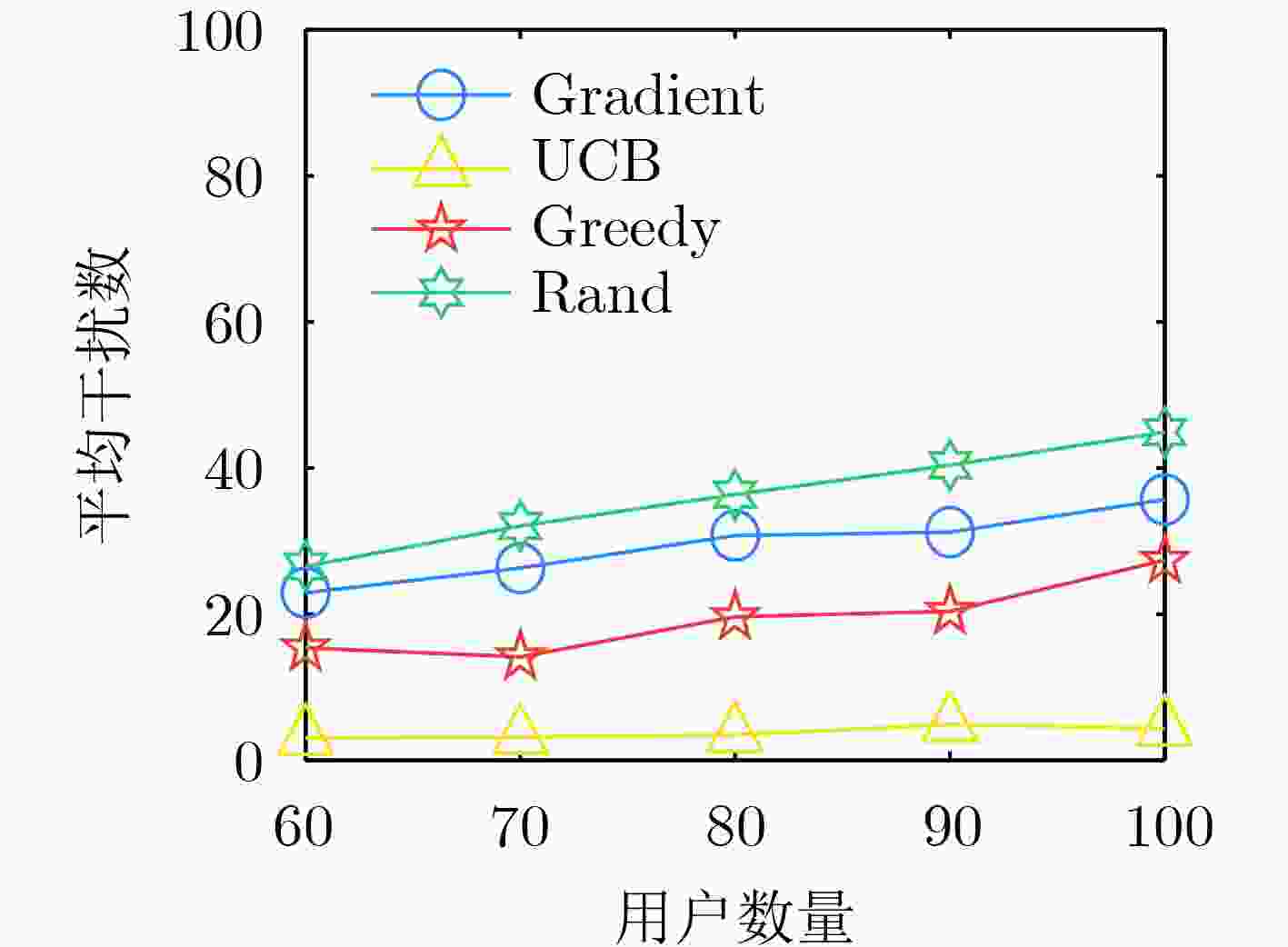
摘要: 飞行自组网(FANETs)因具有高机动、自组织等特点,被广泛应用于应急救援场景。在应急场景中,大量用户寻呼请求造成局部流量激增与有限频谱资源之间产生难以协调的矛盾,FANET中面临严重的信道干扰问题,亟需将频谱利用率高的部分重叠信道(POCs)扩展到应急场景中。然而,POCs的邻信道特性,导致干扰复杂难以刻画。因此,该文研究了FANET部分重叠信道分配方法,通过几何预测重构时变干扰图和无干扰最小信道间隔矩阵刻画POCs干扰模型,在此基础上提出一种基于上界置信区间的POCs动态分配算法(UCB-DAL),通过分布式决策求解近似最优信道分配方案。仿真结果表明,该算法实现了网络干扰和信道切换次数之间性能折中,具有较好的收敛性能。Abstract: The Flying Ad-hoc NETworks (FANETs) are widely used in emergency rescue scenarios due to their high mobility and self-organization advantages. In emergency scenarios, a large number of user paging requests lead to a challenging coordination between the surge in local traffic and the limited spectrum resources, significant channel interference issues in FANETs are resulted from. There is an urgent need to extend the high spectrum utilization advantage of Partially Overlapping Channels (POCs) to emergency scenarios. However, the adjacent channel characteristics of POCs leads to complex interference that is difficult to characterize. Therefore, partial overlapping channel allocation methods in FANETs are studied in this paper. By utilizing geometric prediction to reconstruct time-varying interference graphs and characterizing the POCs interference model with the interference-free minimum channel spacing matrix, a Dynamic Channel Allocation algorithm for POCs based on Upper Confidence Bounds (UCB-DCA) is proposed. This algorithm aims to solve for an approximately optimal channel allocation scheme through distributed decision-making. Simulation results demonstrate that the algorithm achieves a trade-off between network interference and channel switching times, and has good convergence performance.
-
表 1 干扰范围
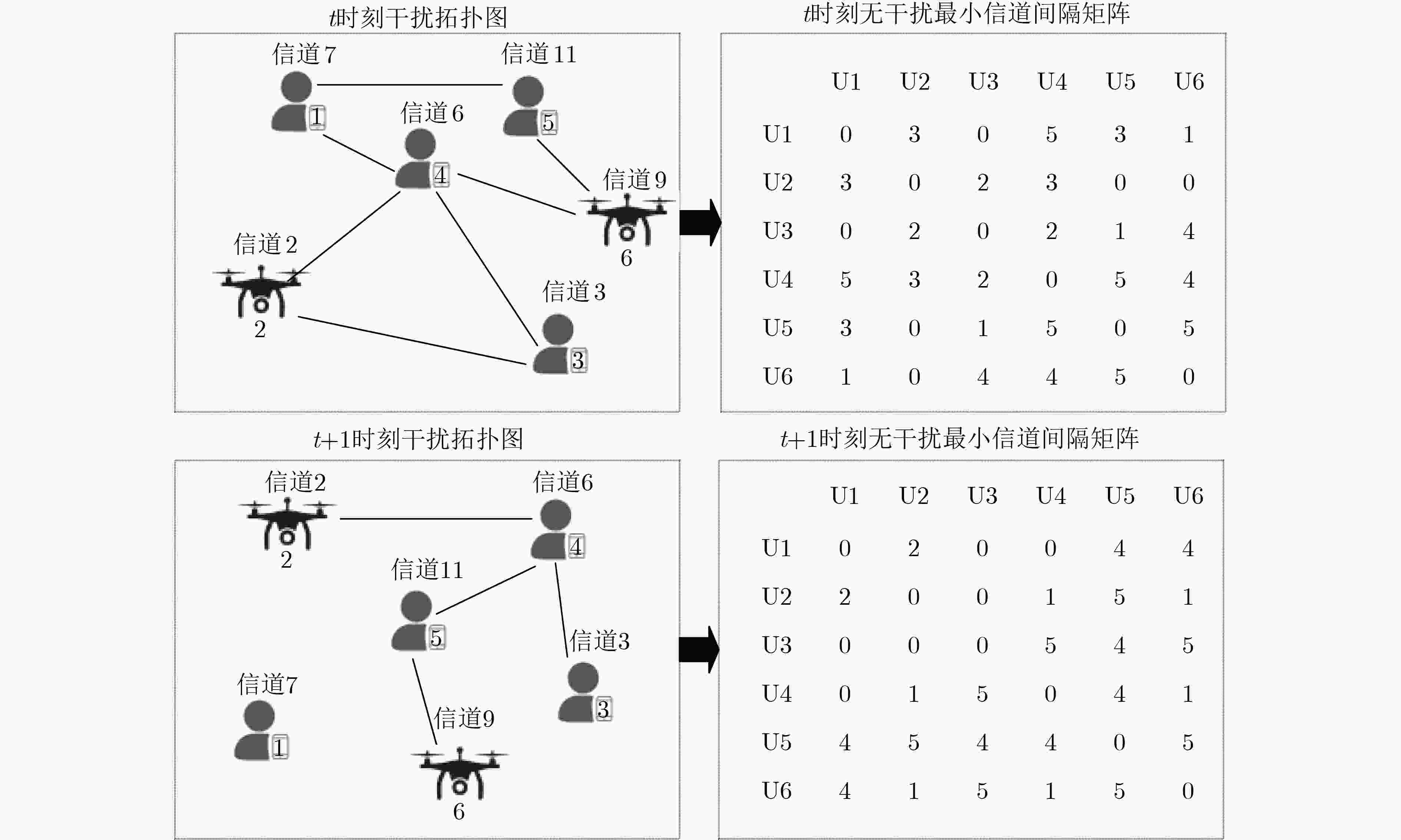
δ(t) 0 1 2 3 4 5 IR(δ(t)) 132.6 90.8 75.9 46.9 32.1 0 1 构建干扰图和无干扰最小信道间隔矩阵算法
输入:节点进行交互,获取位置信息及建立通信链路的节点信息。 输出:预测干扰图GIN(t)和无干扰最小信道间隔矩阵K_C(t)。 (1) 初始化:干扰图GIN(t)、矩阵K_C(t)。St(ui), Sr(uj)为节点
集合的子集。(2) for $ \forall $ui$\in $St(ui)do (3) for $ \forall $uj$\in $Sr(uj)do (4) if ui与uj建立通信对 then (5) 进行下一次迭代; (6) end if (7) if ui与uj之间距离不大于预测干扰距离 (8) ui与uj之间存在干扰边; (9) end if (10) 根据式(12)求出ui与uj预测的信道间隔δ; (11) end for (12) end for 2 UCB的部分重叠信道动态分配学习算法(UCB-DAL)
输入:预测干扰图GIN(t)及无干扰最小信道间隔矩阵K_C(t),
信道分配矩阵C_U(t–k–1)。输出:信道分配方案C_U(t)。 (1) 初始化:所有玩家获取奖励R_M和累积奖励C_M。
Sv(un)为节点集合,Sn(un)为un邻居节点集合。(2) for epi =1:max_epi do (3) for $ \forall {u_n} \in {\text{Sv}}({u_n}) $do (4) 根据式(17)选取效益最大的动作; (5) for$ \forall {u_j} \in {\text{Sn}}({u_n}) $ do (6) if 玩家$ {u_n} $与邻居节点$ {u_j} $的信道间隔大于等于无干扰
最小信道间隔then(7) 对玩家un当前选择动作给予奖励并更新R_M和累积
奖励C_M;(8) else (9) 对当前动作根据式(18)给予惩罚并更新R_M和累积
奖励C_M;(10) end if (11) 更新玩家un所选信道及信道矩阵C_U(t); (12) end for (13) end for (14) if 所有玩家都找到收益最大动作 then (15) 结束循环; (16) end if (17) end for -
[1] MU Junsheng, ZHANG Ronghui, CUI Yuanhao, et al. UAV meets integrated sensing and communication: Challenges and future directions[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(5): 62–67. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.008.2200510. [2] DAI Jun, HU Qunpeng, LIU Xu, et al. Cluster head selection method of multiple UAVs under COVID-19 situation[J]. Computer Communications, 2022, 196: 141–147. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2022.09.026. [3] CALAMONERI T, CORÒ F, and MANCINI S. A realistic model to support rescue operations after an earthquake via UAVs[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 6109–6125. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3141216. [4] 国务院关于印发“十四五”国家应急体系规划的通知 国发〔2021〕36号[J]. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 2022(6): 30–48.Circular of the state council on printing and issuing the plan for building the national emergency response system during the 14th Five-Year Plan period[J]. Gazette of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China, 2022(6): 30–48. [5] ZHAO Wei, NISHIYAMA H, FADLULLAH Z, et al. DAPA: Capacity optimization in wireless networks through a combined design of density of access points and partially overlapped channel allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(5): 3715–3722. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2437714. [6] 叶方, 孙雪, 李一兵. 基于改进离散蝙蝠算法的无线Mesh网络部分重叠信道分配[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4265–4273. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211029.YE Fang, SUN Xue, and LI Yibing. Partial overlapped channel assignment for wireless mesh networks based on improved discrete bat algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4265–4273. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211029. [7] CHEN Jiaxin, XU Yuhua, WU Qihui, et al. Interference-aware online distributed channel selection for multicluster FANET: A potential game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3792–3804. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2902177. [8] DAI Minghui, LUAN T H, SU Zhou, et al. Joint channel allocation and data delivery for UAV-assisted cooperative transportation communications in post-disaster networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(9): 16676–16689. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3178789. [9] TANG Fengxiao, FADLULLAH Z M, KATO N, et al. AC-POCA: Anticoordination game based partially overlapping channels assignment in combined UAV and D2D-based networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1672–1683. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2753280. [10] FAN Chaoqiong, LI Bin, HOU Jia, et al. Robust fuzzy learning for partially overlapping channels allocation in UAV communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(4): 1388–1401. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.3023789. [11] FENG Zhenhua and YANG Yaling. How much improvement can we get from partially overlapped channels?[C]. 2008 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Las Vegas, USA, 2008: 2957–2962. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2008.517. [12] FENG Zhenhua and YANG Yaling. Characterizing the impact of partially overlapped channel on the performance of wireless networks[C]. IEEE GLOBECOM 2008 – 2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, USA, 2008: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2008.ECP.958. [13] GHOSAL S and GHOSH S C. Channel assignment in mobile networks based on geometric prediction and random coloring[C]. 2015 IEEE 40th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Clearwater Beach, USA, 2015: 237–240. doi: 10.1109/LCN.2015.7366315. [14] 李兴旺, 田志发, 张建华, 等. IRS辅助NOMA网络下隐蔽通信性能研究[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(6): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174.LI Xingwang, TIAN Zhifa, ZHANG Jianhua, et al. Performance analysis of covert communication in IRS-assisted NOMA networks[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2024, 54(6): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0174. [15] 李兴旺, 王新莹, 田心记, 等. 基于非理想条件可重构智能超表面辅助无线携能通信-非正交多址接入系统通感性能研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(6): 2434–2442. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231395.LI Xingwang, WANG Xinying, TIAN Xinji, et al. Communication and sensing performance analysis of RIS-assisted SWIPT-NOMA system under non-ideal conditions[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(6): 2434–2442. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231395. [16] WANG Bowen, SUN Yanjing, SUN Zhi, et al. UAV-assisted emergency communications in social IoT: A dynamic hypergraph coloring approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7663–7677. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2988445. [17] BROYLES D and ABDUL J. Design and analysis of a 3-D Gauss-Markov model for highly dynamic airborne networks[C].The 46th Annual International Telemetering Conference and Technical Exhibition, San Diego, USA, 2010. [18] 薛建彬, 王海牛, 关向瑞, 等. 车载边缘计算网络中基于MAB的动态任务卸载方案研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2023, 50(11A): 230200186–9. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230200186.XUE Jianbin, WANG Hainiu, GUAN Xiangrui, et al. Study on dynamic task offloading scheme based on MAB in vehicular edge computing network[J]. Computer Science, 2023, 50(11A): 230200186–9. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.230200186. [19] KALATHIL D, NAYYAR N, and JAIN R. Decentralized learning for multiplayer multiarmed bandits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(4): 2331–2345. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2302471. [20] ROSENSKI J, SHAMIR O, and SZLAK L. Multi-player bandits: A musical chairs approach[C]. The 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 155–163. -





 下载:
下载:
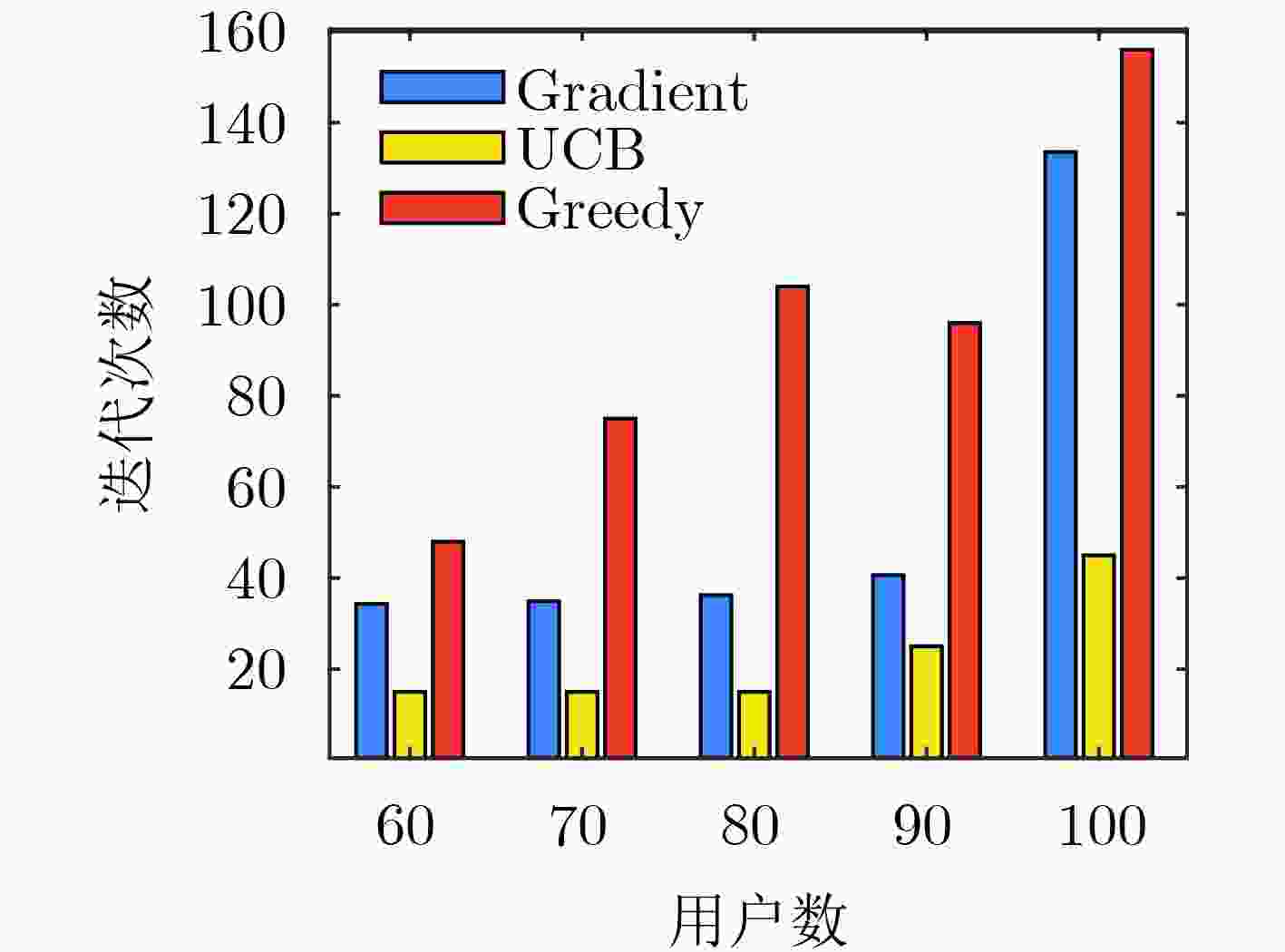
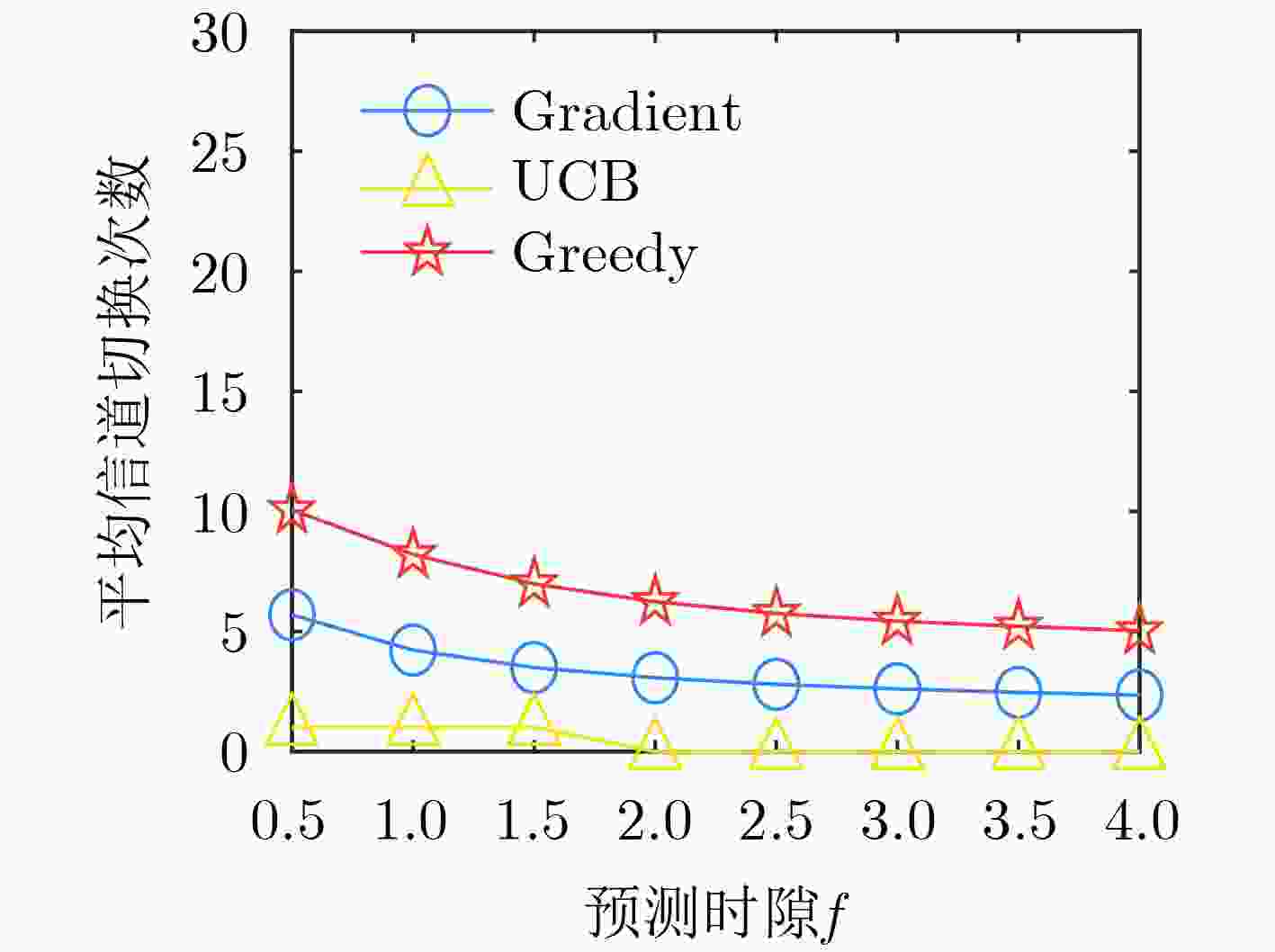
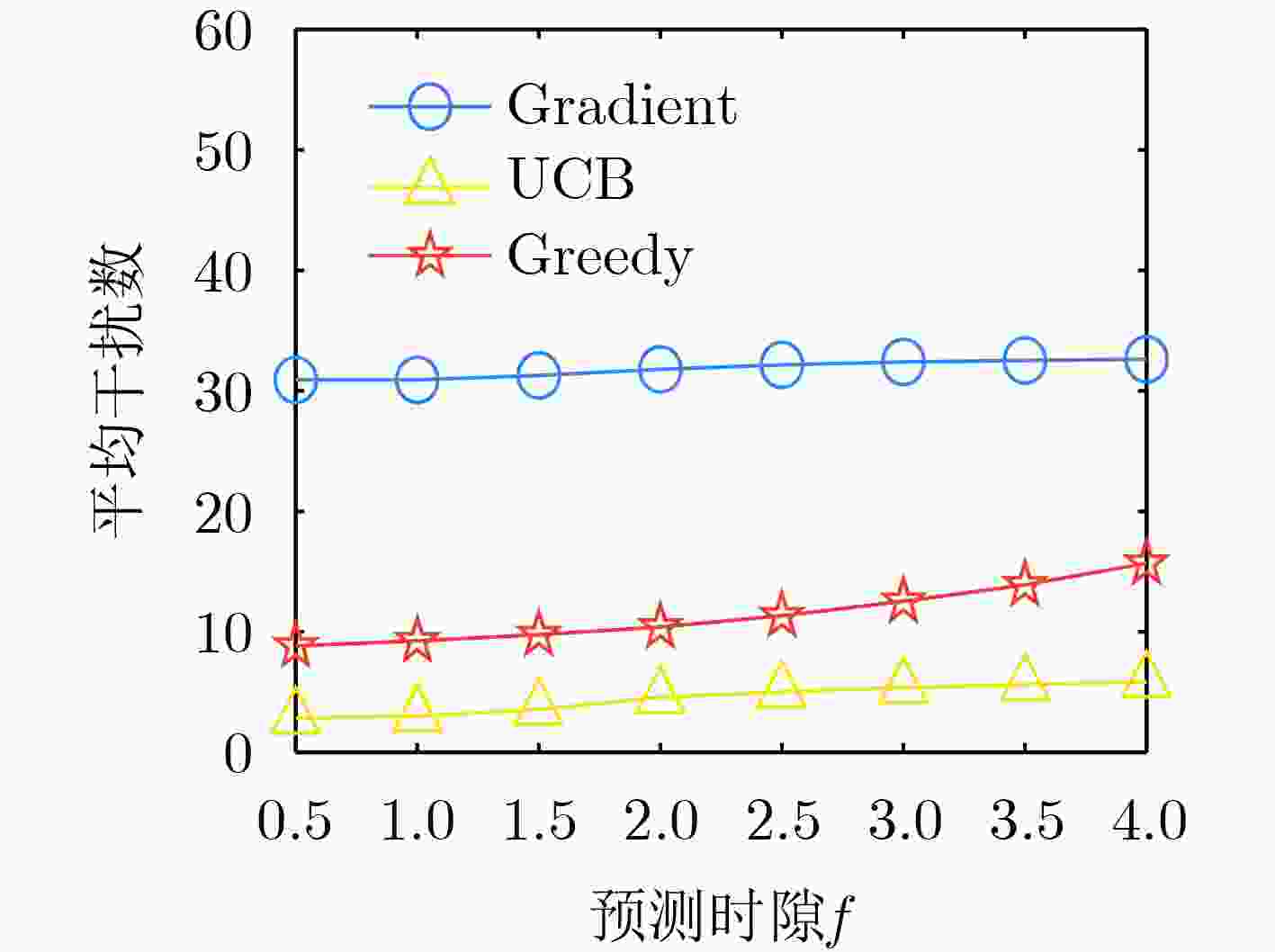
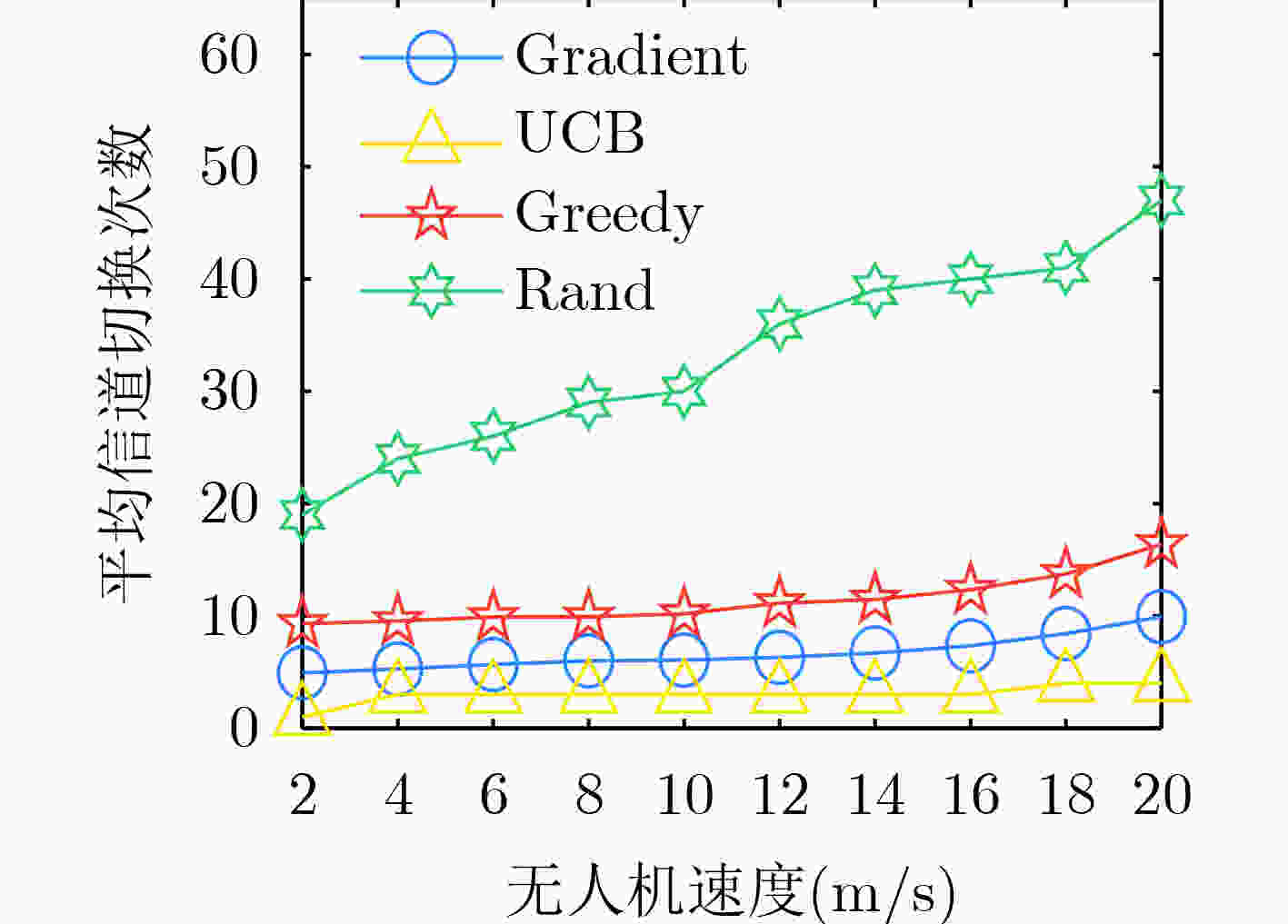


 下载:
下载:
