Task Offloading and Resource Allocation Method for End-to-End Delay Optimization in Digital Twin Edge Networks
-
摘要: 针对移动边缘计算(MEC)场景中任务卸载、计算和结果反馈全过程时延优化问题,该文提出了一种数字孪生(DT)辅助的联合MEC任务卸载、设备关联与资源分配的端到端时延优化方法。首先,在数字孪生边缘网络(DITEN)框架下,为包含传感器、边缘服务器以及执行器构成的边缘计算网络建立了物理模型与数字孪生模型,以及全过程边缘网络任务模型并推导了任务端到端时延,进而建立了时延、能耗等约束下的端到端时延优化问题。其次,为解决所提出的混合整数非凸优化问题,将原问题分解为4个子问题,并提出了一种基于内部凸近似方法和匈牙利算法的交替优化算法。在DT辅助下联合优化了设备关联、卸载比例、发射功率、传输带宽以及DT估计处理速率。最后,仿真结果表明,与其他基准方案相比,所提联合优化方案显著降低了端到端时延。Abstract:
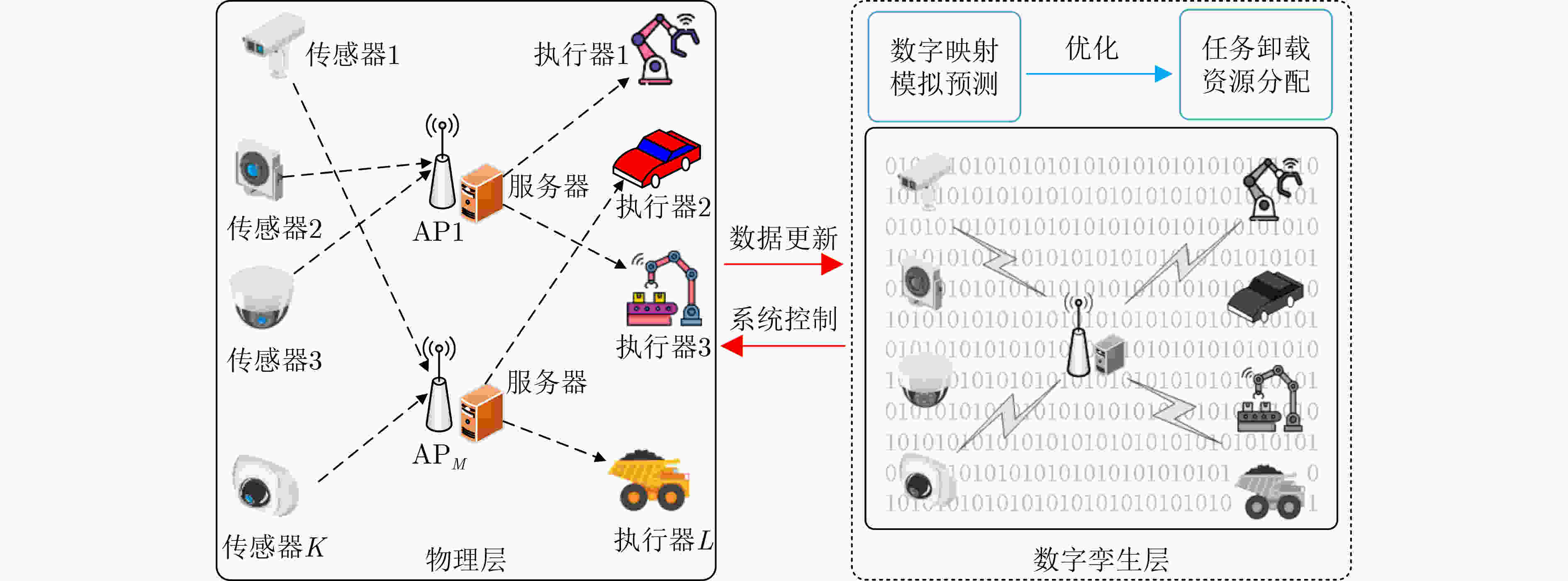
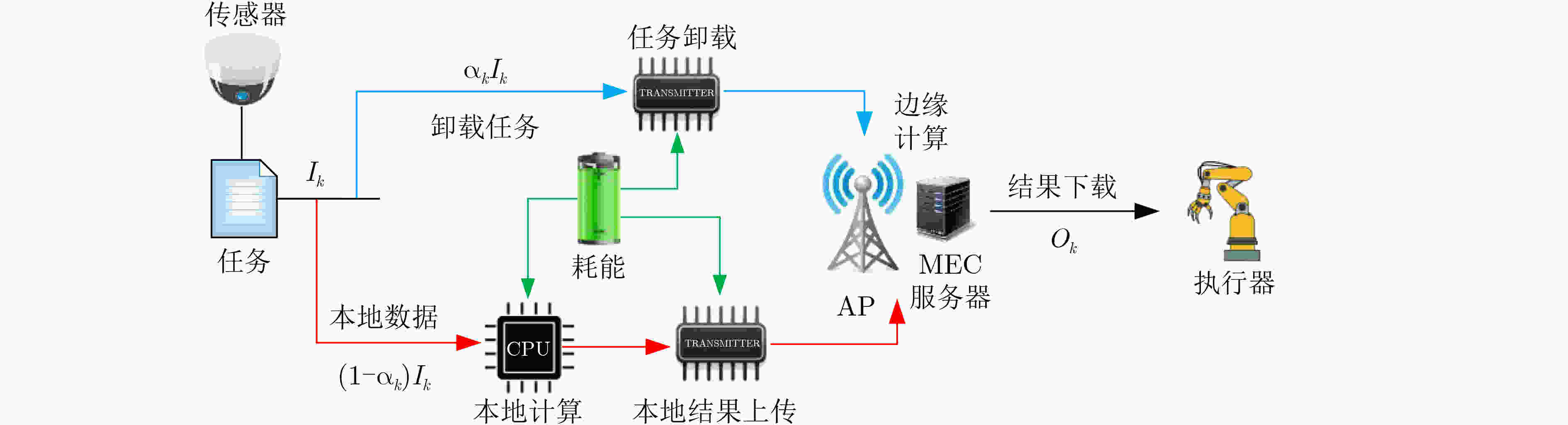
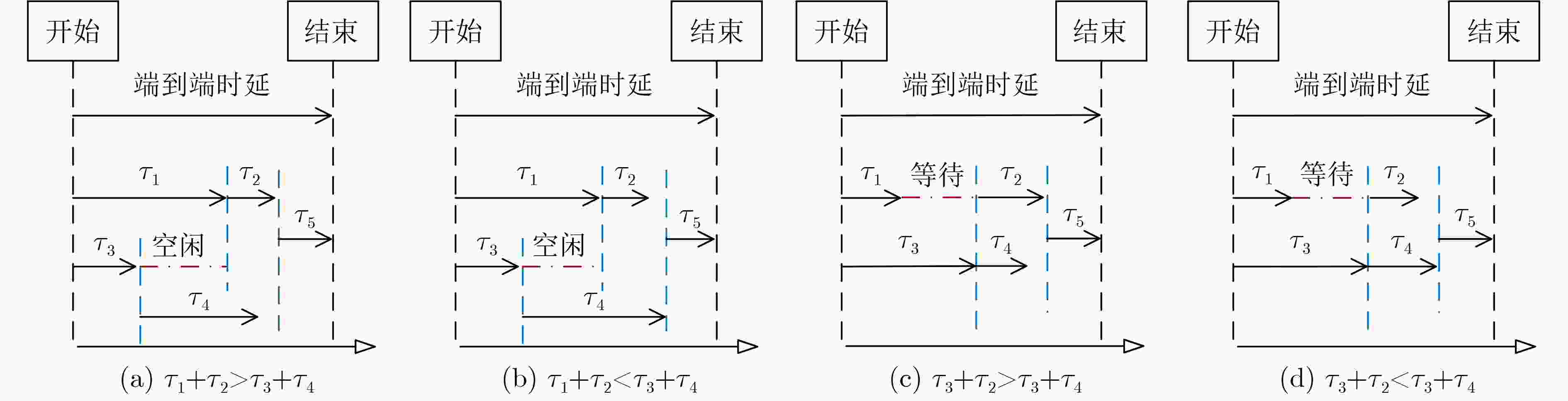
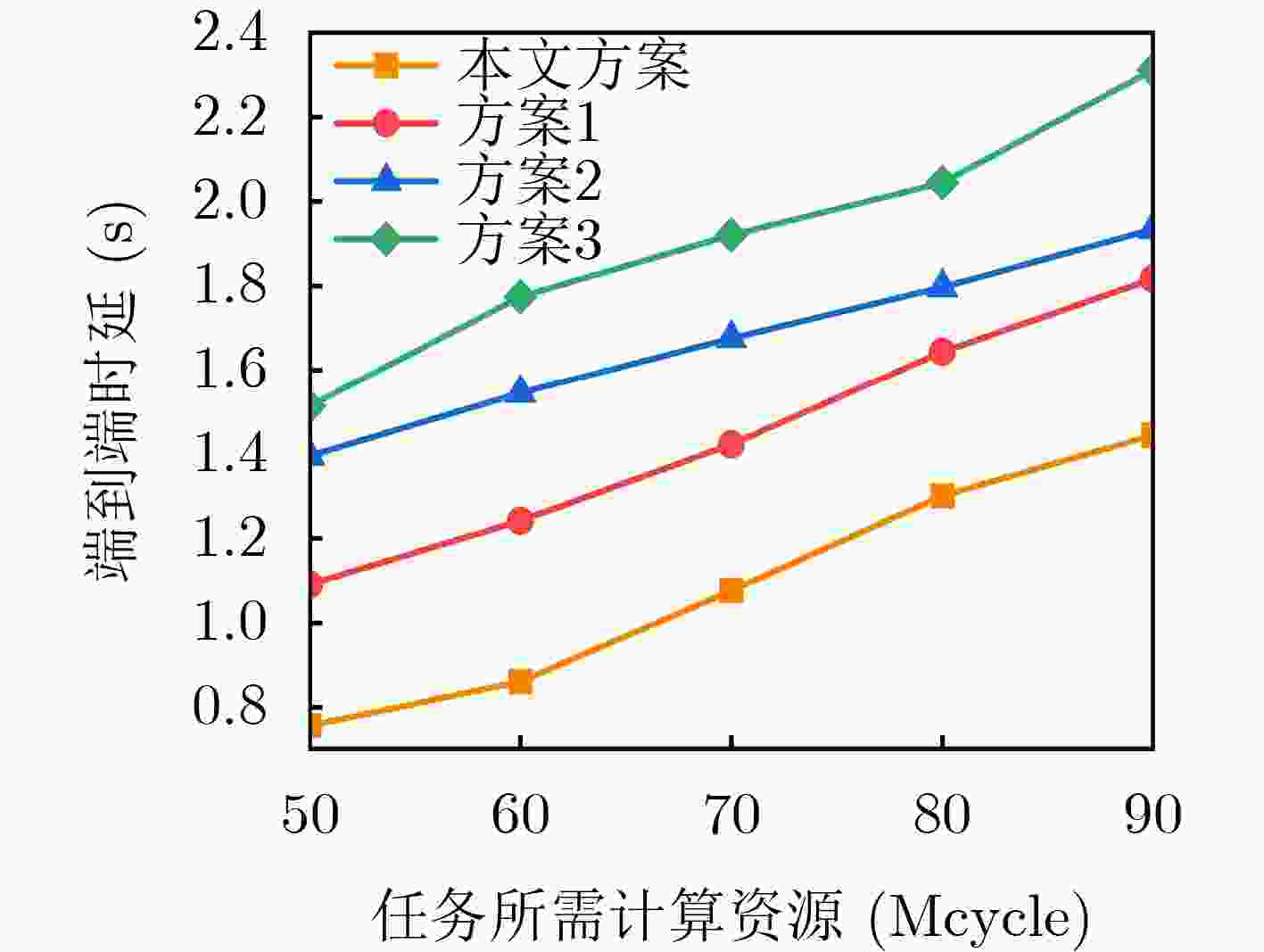
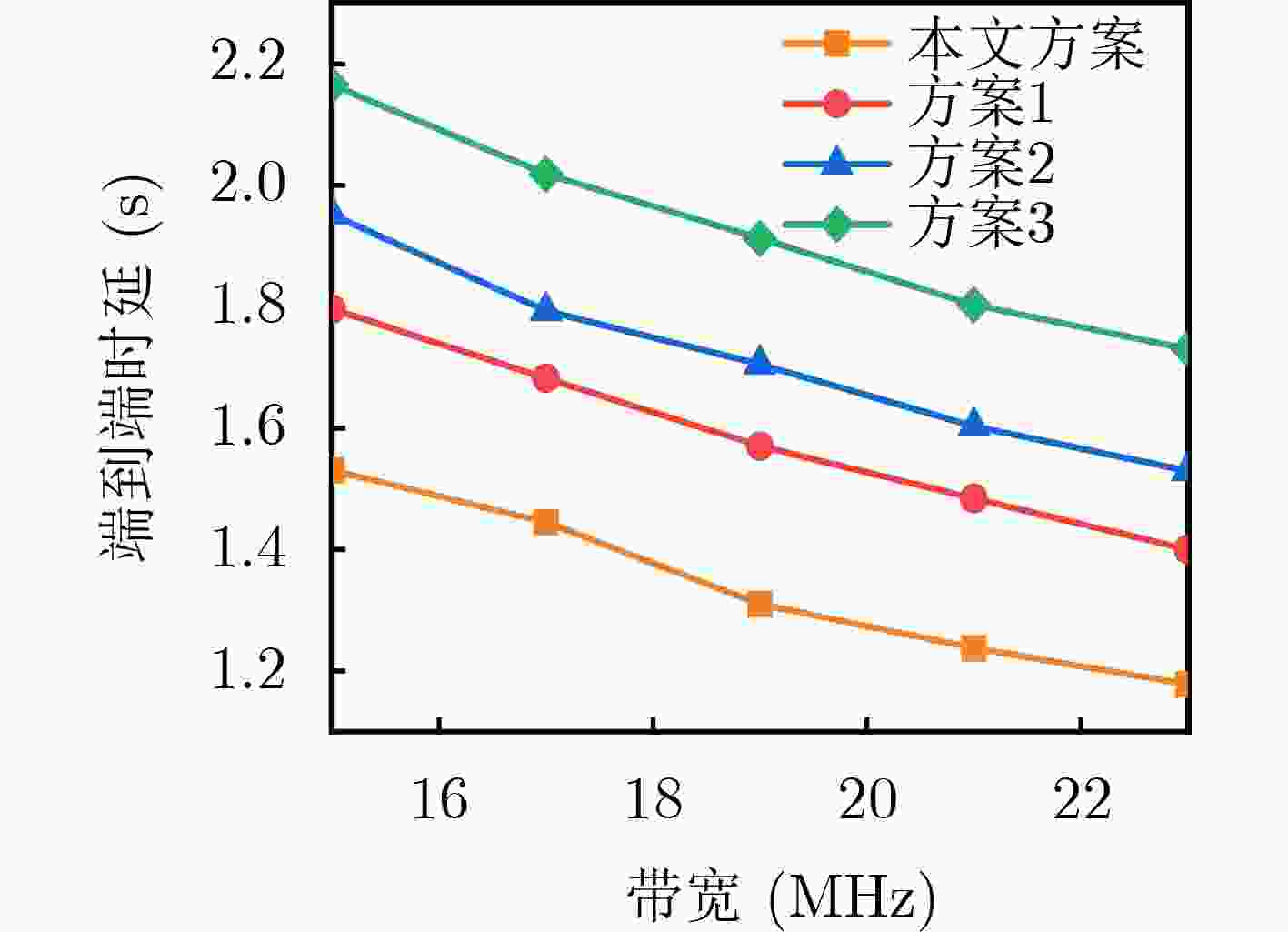
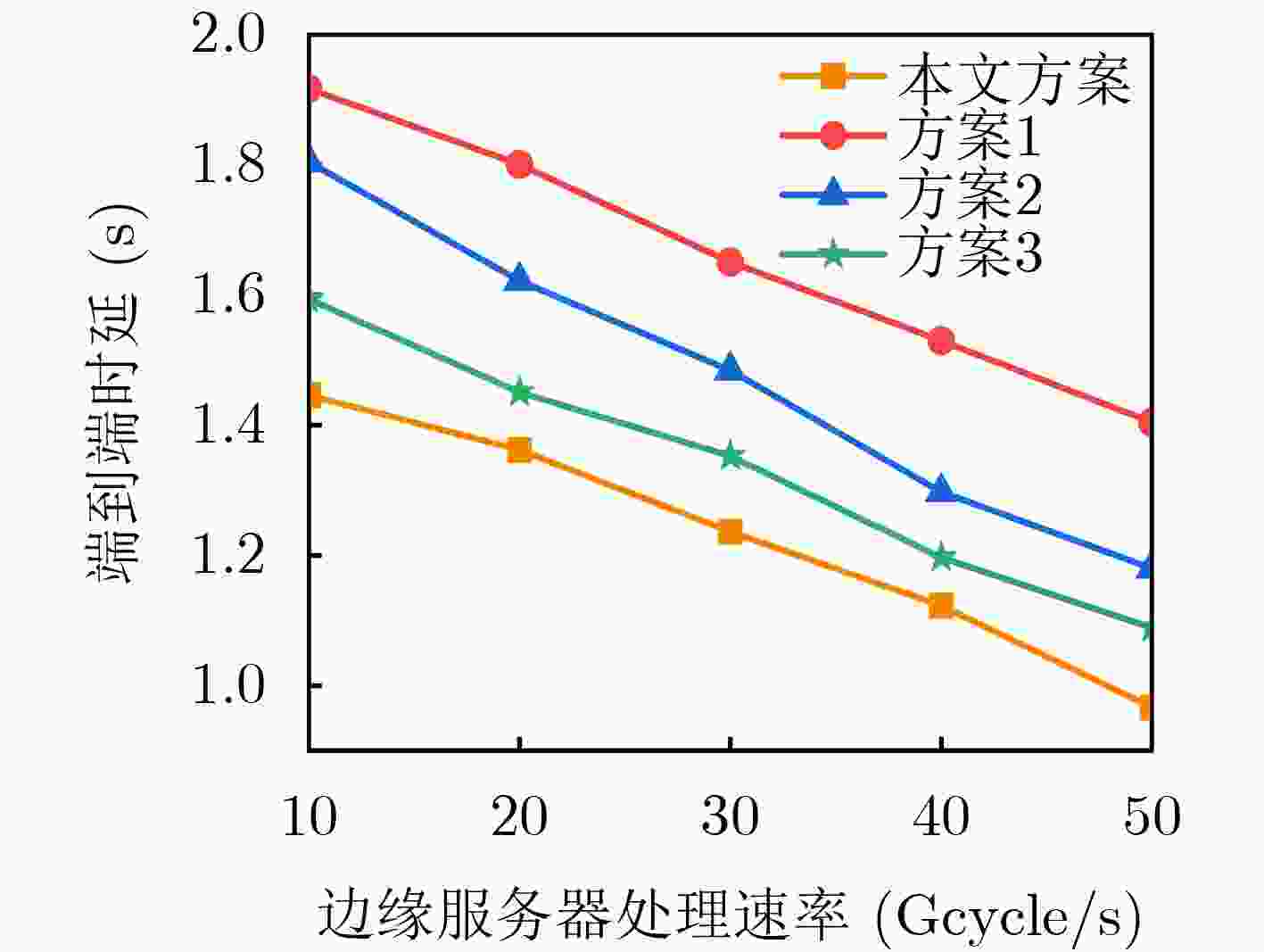
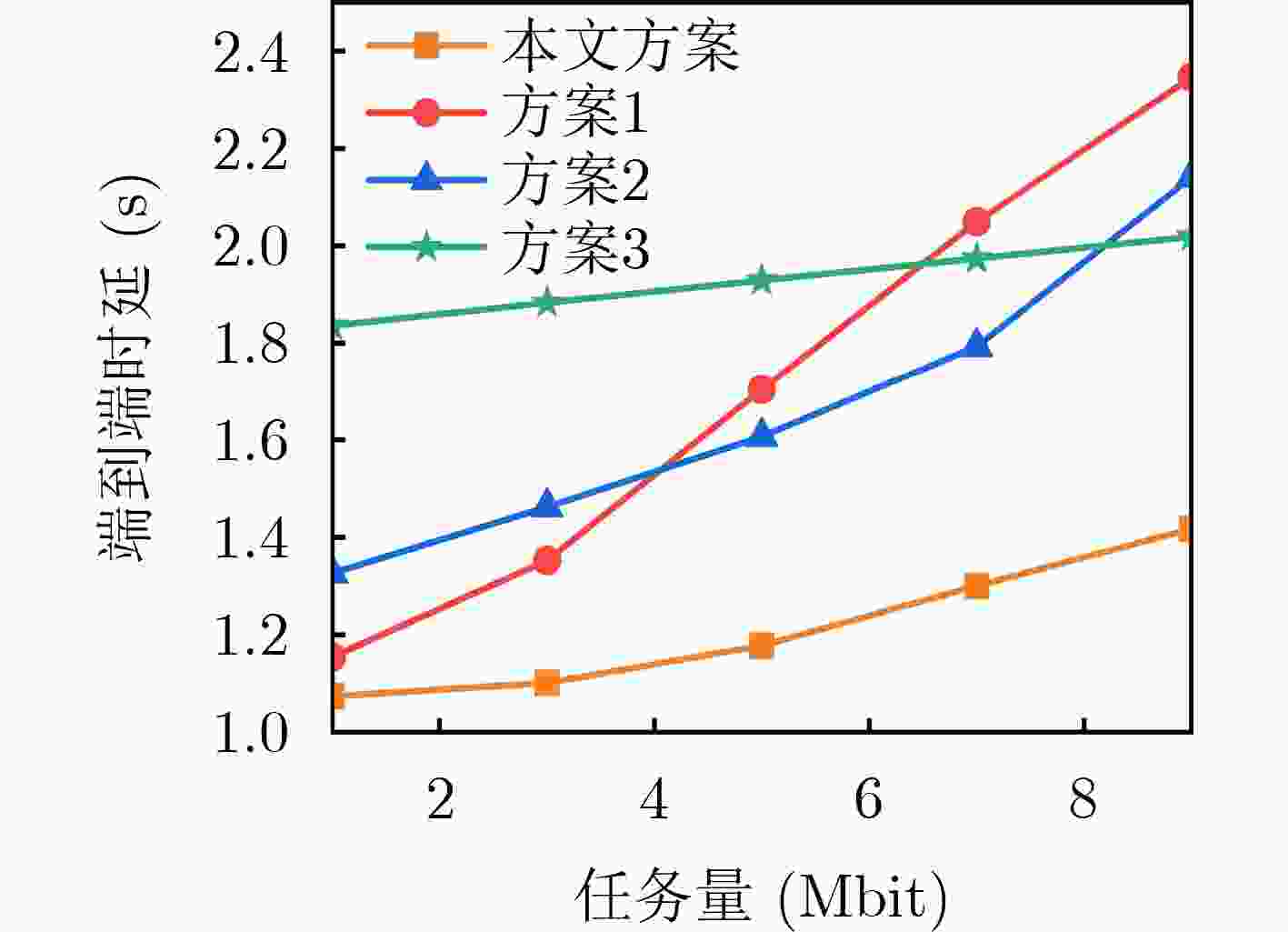
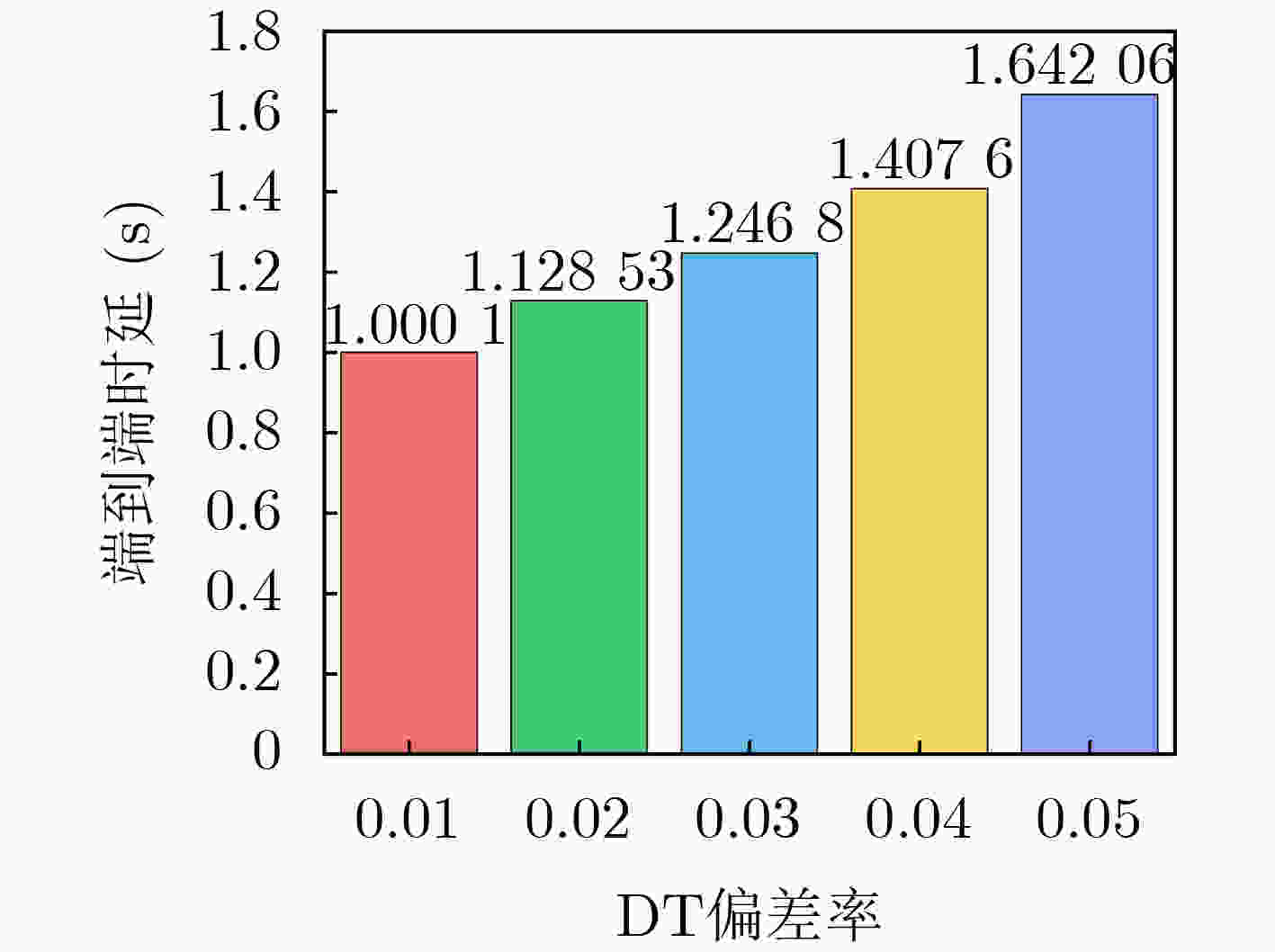
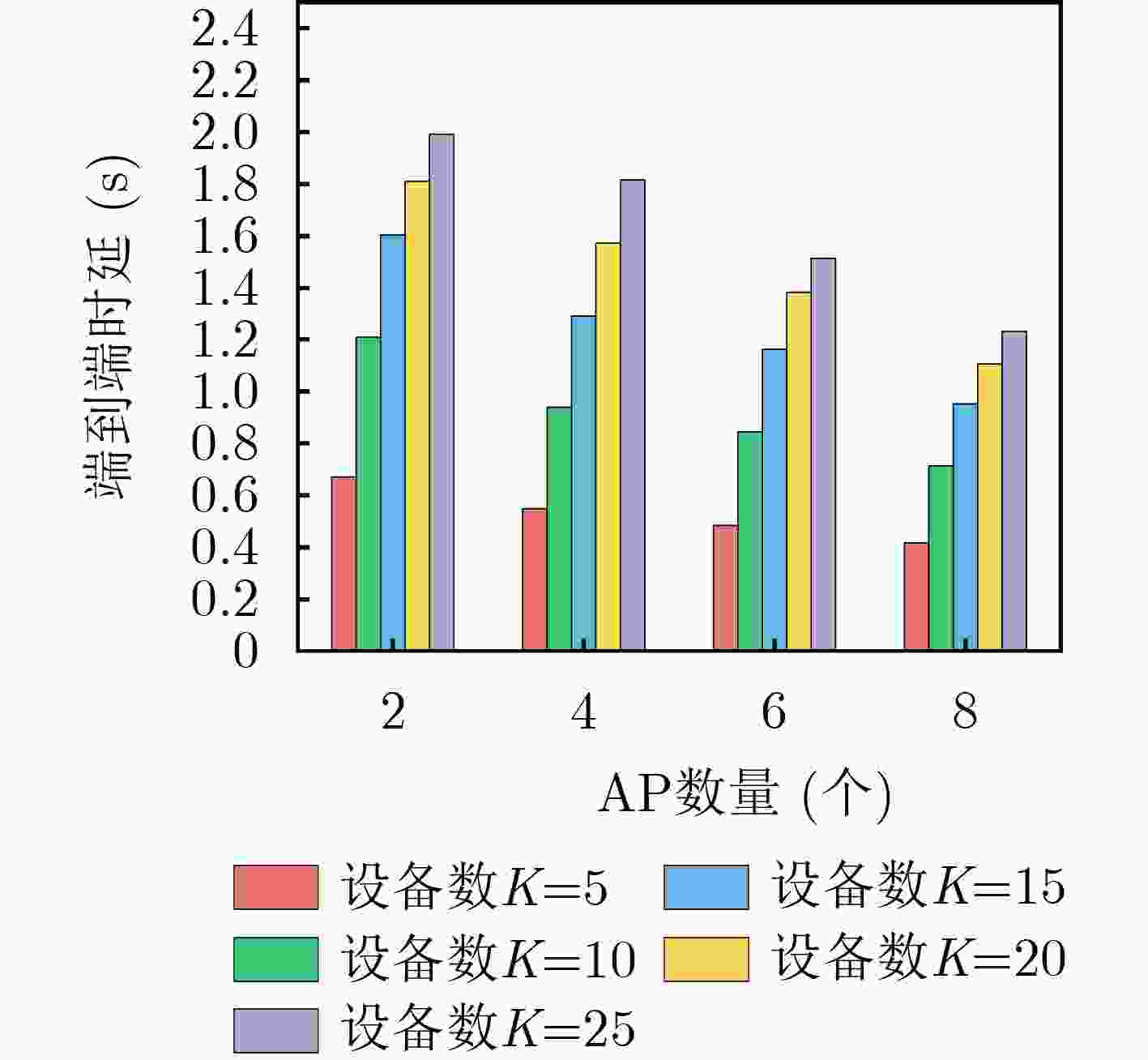
Objective The rapid development of wireless communication and the Internet of Things (IoT) has led to significant growth in compute-intensive and delay-sensitive applications, which impose stricter latency requirements. However, local devices often face challenges in meeting these demands due to limitations in storage, computing power, and battery life. Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) has emerged as a key technology to address these issues. Despite its potential, the dynamic and complex nature of edge networks presents significant challenges in task offloading and resource allocation. DIgital Twin Edge Networks (DITEN), which map digital twins to physical devices in real-time, offer a promising solution. By integrating MEC with Digital Twin (DT) technology, this approach not only alleviates resource limitations in devices but also optimizes resource allocation in the digital domain, minimizing physical resource waste. This paper tackles the End-to-End (E2E) optimization problem in the offloading, computation, and result feedback process within edge computing networks. A DT-assisted joint task offloading, device association, and resource allocation scheme is proposed for E2E delay optimization, providing theoretical support for improving resource utilization in edge networks. Methods The optimization problem in this paper involves a non-convex objective function with both binary and continuous constraints, making it a mixed integer non-convex problem. To address this, the original problem is decomposed into four subproblems: computation and communication resource optimization, device association optimization, offloading decision optimization, and transmission bandwidth optimization. Within the Alternating Optimization (AO) framework, the Internal Convex Approximation (ICA) method is applied to convert the non-convex problem into a convex one. Additionally, the many-to-one matching problem is transformed into a one-to-one matching problem, and the Hungarian Algorithm (HA) is employed to solve the device association subproblem. Finally, the ICA-HA-AO is proposed to address the E2E delay optimization problem effectively. Results and Discussions The ICA-HA-AO algorithm approximates non-convex constraints as convex ones through constraint transformation and iteratively solves the original problem, determining optimal strategies for task offloading, device association, and resource allocation. Simulation results show that the ICA-HA-AO algorithm achieves optimal performance across varying task resource requirements, bandwidth, edge processing rates, and task volumes. Compared to the worst-performing benchmark scheme, delays are reduced by approximately 0.8 s, 1.5 s, 0.5 s, and 1.2 s, respectively ( Fig. 5 –Fig. 8 ). As the DT deviation increases, the delay also increases more significantly, with a rise of about 0.13 s when the deviation increases from 0.01 to 0.02, emphasizing the importance of setting the DT deviation (Fig. 9 ). When the number of devices remains constant and the number of Access Points (APs) increases, the delay continues to decrease, highlighting the significance of AP deployment in practice. Additionally, when the number of APs remains fixed and the number of devices increases, the delay increases accordingly. However, the ICA-HA-AO algorithm effectively controls the rate of delay increase. For instance, when the number of devices is 10, 15, and 20, the delay increase is reduced from 0.39 s to 0.21 s (Fig. 10 ). These results demonstrate that the ICA-HA-AO algorithm can more efficiently utilize and schedule resources, achieving optimal resource allocation.Conclusions This paper investigates the joint optimization problem of task offloading, device association, and resource allocation in DITEN. Firstly, within the edge computing network, physical and DT models are established for a network comprising sensors, edge servers, and actuators. A comprehensive task model is developed, and the E2E delay for tasks is derived. The optimization problem for minimizing E2E delay is then formulated, subject to constraints such as power and energy consumption. Secondly, to solve the proposed mixed integer non-convex optimization problem, the original problem is decomposed into four subproblems. Based on the ICA and HA methods, an ICA-HA-AO algorithm is proposed to solve the problem iteratively. Finally, simulation results demonstrate that the proposed ICA-HA-AO algorithm significantly reduces E2E delay and outperforms benchmark schemes. Future work may explore integrating this method with techniques to improve spectrum utilization, thereby further enhancing spectrum efficiency and overall performance in DITEN systems. -
1 基于内部凸近似的计算与通信资源分配算法
输入:卸载因子$ \alpha $,关联变量$ \pi $,传输带宽$ \bar b,\underline b $,发射功率$ p $以及
计算频率$ {\mathbf{f}} $;初始化:迭代次数$ i = 0 $,容忍值$ \varepsilon $,最大迭代次数$ {I_{\max }} $ 输出:最优功率和计算频率$ ({p^*},{{\mathbf{f}}^*}) $ (1) while 1 do (2) 求解问题式(24)的可行解$ ({p^{(i + 1)}},{{\mathbf{f}}^{(i + 1)}}) $; (3) $ i = i + 1 $ (4) if 收敛or$ i \gt {I_{\max }} $ then (5) break; (6) end if (7) end while 2 基于匈牙利算法的传感器与AP关联优化算法
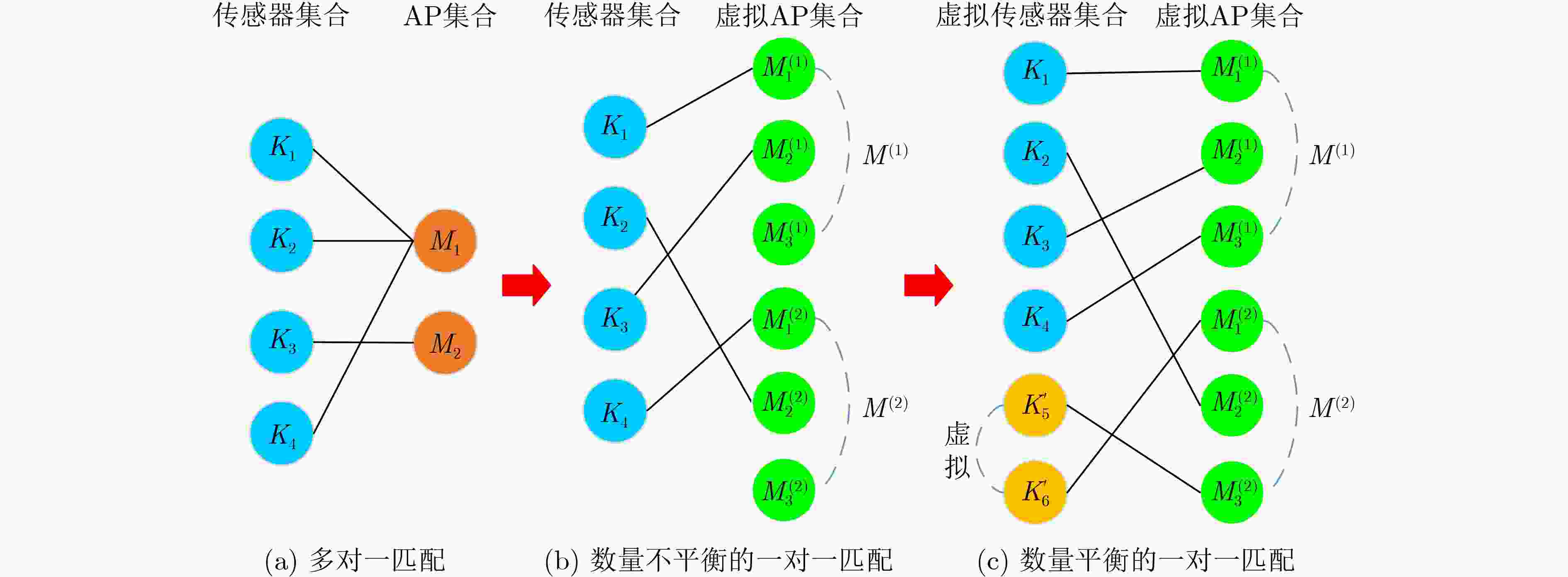
输入:卸载因子$ \alpha $,传输带宽$ \bar b,\underline b $,发射功率$ p $以及计算频率$ {\mathbf{f}} $; 输出:最优关联策略$ ({\pi ^*}) $ (1)给定传感器数量K,AP数量M,AP能够服务传感器的最大数
量N;(2)每个AP虚拟成N个,形成数量为NM的虚拟AP集合; (3)if $ K \lt NM $ then (4) 加边补零,增加$ NM - K $个虚拟传感器; (5)end if (6)执行匈牙利算法。 3 基于内部凸近似方法和匈牙利算法的ICA-HA-AO算法
输入:卸载因子$ {\alpha ^{(0)}} $,关联变量$ {\pi ^{(0)}} $,带宽$ {\bar b^{(0)}},\underline b^{(0)} $,发射功率$ {p^{(0)}} $,计算频率$ {{\mathbf{f}}^{(0)}} $,设置迭代次数$ i = 0 $,容忍值$ \varepsilon $和最大迭代次数$ {I_{\max }} $; 输出:最优资源分配$ ({\alpha ^*},{\pi ^*},{\bar b^*},{\underline {b} ^*},{p^*},{{\mathbf{f}}^*}) $ (1) while 1 do (2) 给定$ ({\alpha ^{(i)}},{\pi ^{(i)}},{\bar b^{(i)}},{\underline b} ^{(i)}) $,利用算法1求解子问题SP1,得到最优传感器计算频率以及AP的计算频率和发射功率$ ({p^{^{(i + 1)}}},{{\mathbf{f}}^{^{(i + 1)}}}) $; (3) 给定$ ({{\mathbf{f}}^{(i + 1)}},{p^{(i + 1)}},{\alpha ^{(i)}},{\bar b^{(i)}},\underline b^{(i)}) $,利用算法2求解子问题SP2,得到最优传感器与AP关联策略$ ({\pi ^{^{(i + 1)}}}) $; (4) 给定$ ({{\mathbf{f}}^{(i + 1)}},{p^{(i + 1)}},{\pi ^{(i + 1)}},{\bar b^{(i)}},{\underline b ^{(i)}}) $,利用内点法求解子问题SP3,得到最优卸载决策$ ({\alpha ^{^{(i + 1)}}}) $; (5) 给定$ ({{\mathbf{f}}^{(i + 1)}},{p^{(i + 1)}},{\pi ^{(i + 1)}},{\alpha ^{(i)}}) $,利用内点法求解子问题SP4,得到最优上下行带宽$ ({\bar b^{(i + 1)}},{\underline b^{(i + 1)}}) $; (6) $ i = i + 1 $ (7) if 收敛 or $ i \gt {I_{\max }} $ then (8) break; (9) end if (10) end while 表 1 仿真参数
参数名 参数值 参数名 参数值 传感器发射功率$ {\bar p_k} $ 10 dBm[8] 传感器最大计算频率$ F_{\max }^{\rm{se} } $ 3 GHz[7] AP最大发射功率$ {P_{\max }} $ 40 dBm[18] AP最大计算频率$ F_{\max }^{\rm{AP} } $ 10 GHz[7] 输入任务量$ {I_k} $ 100 Mbit[18] 路径损耗$ {\beta _0} $ –30 dB[14] 任务所需计算资源$ {C_k} $ 960×106 cycle[7] 参考距离$ {d_0} $ 10 m[9] 传输总带宽$ B $ 20 MHz[18] 噪声功率$ {N_0} $ –174 dBm/Hz[18] 最大时延与能耗$ {T_{\max }},{E_{\max }} $ 2 s, 1.5 J 有效交换电容系数$ \xi $ 10–28[9] -
[1] DJIGAL H, XU Jia, LIU Linfeng, et al. Machine and deep learning for resource allocation in multi-access edge computing: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(4): 2449–2494. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2022.3199544. [2] MACH P and BECVAR Z. Mobile edge computing: A survey on architecture and computation offloading[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1628–1656. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2682318. [3] WANG Zhiying, SUN Gang, SU Hanyue, et al. Low-latency scheduling approach for dependent tasks in MEC-enabled 5G vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(4): 6278–6289. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3309940. [4] DENG Xiaoheng, YIN Jian, GUAN Peiyuan, et al. Intelligent delay-aware partial computing task offloading for multiuser industrial internet of things through edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(4): 2954–2966. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3123406. [5] MEI Jing, TONG Zhao, LI Kenli, et al. Energy-efficient heuristic computation offloading with delay constraints in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2023, 16(6): 4404–4417. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2023.3324604. [6] ZHANG Haibo, LIU Xiangyu, XU, Yongjun, et al. Partial offloading and resource allocation for MEC-assisted vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(1): 1276–1288. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3306939. [7] VAN HUYNH D, NGUYEN V D, KHOSRAVIRAD S R, et al. URLLC edge networks with joint optimal user association, task offloading and resource allocation: A digital twin approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(11): 7669–7682. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3205692. [8] VAN HUYNH D, NGUYEN V D, CHATZINOTAS S, et al. Joint communication and computation offloading for ultra-reliable and low-latency with multi-tier computing[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(2): 521–537. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3227088. [9] LI Song, SUN Weibin, SUN Yanjing, et al. Energy-efficient task offloading using dynamic voltage scaling in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(1): 588–598. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3046014. [10] ZHANG Yongchao, HU Jia, and MIN Geyong. Digital twin-driven intelligent task offloading for collaborative mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(10): 3034–3045. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3310058. [11] 唐伦, 单贞贞, 文明艳, 等. 工业物联网中数字孪生辅助任务卸载算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(4): 1296–1305. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230317.TANG Lun, SHAN Zhenzhen, WEN Mingyan, et al. Digital twin-assisted task offloading algorithms for the industrial internet of things[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(4): 1296–1305. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230317. [12] TANG Fengxiao, CHEN Xuehan, RODRIGUES T K, et al. Survey on digital twin edge networks (DITEN) toward 6G[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 1360–1381. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3197811. [13] 张彦, 卢云龙. 数字孪生边缘网络[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2023, 29(3): 21–25. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202303005.ZHANG Yan and LU Yunlong. Digital twin edge networks[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2023, 29(3): 21–25. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202303005. [14] 苏健, 钱震, 李斌. 数字孪生使能的智能超表面边缘计算网络任务卸载[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2416–2424. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220180.SU Jian, QIAN Zhen, and LI Bin. Digital twin empowered task offloading for RIS-assisted edge computing networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2416–2424. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220180. [15] DAI Yueyue, ZHANG Ke, MAHARJAN S, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for stochastic computation offloading in digital twin networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(7): 4968–4977. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3016320. [16] LU Yunlong, MAHARJAN S, and ZHANG Yan. Adaptive edge association for wireless digital twin networks in 6G[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(22): 16219–16230. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3098508. [17] SUN Wen, ZHANG Haibin, WANG Rong, et al. Reducing offloading latency for digital twin edge networks in 6G[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 12240–12251. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3018817. [18] SUN Yaping, XU Jie, and CUI Shuguang. Joint user association and resource allocation optimization for MEC-enabled IoT networks[C]. Proceedings of the ICC 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Korea, 2022: 4884–4889. doi: 10.1109/ICC45855.2022.9839276. [19] DONG Rui, SHE Changyang, HARDJAWANA W, et al. Deep learning for hybrid 5G services in mobile edge computing systems: Learn from a digital twin[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(10): 4692–4707. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2927312. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
