Optical Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces-Assisted Distributed OMC for UAV Clusters
-
摘要: 随着无人机(UAV)系统的规模持续扩大以及对更高通信速率的需求增长,UAV光移动通信(UAV-OMC)已经成为一个有前景的技术方向。然而,传统的UAV-OMC难以支持多UAV之间的通信。该文基于光学智能反射表面(OIRS)技术,提出一个适用于UAV群的分布式OMC系统。通过在特定的UAV上设置OIRS,利用OIRS将光信号从单个UAV节点扩散到多个UAV节点。这一系统在保留UAV-OMC系统的高能效和高速度的同时,能够支持分布式UAV群的通信。对所提出的系统进行了数学建模,考虑了一系列现实因素,如OIRS的光束控制、UAV之间的相对运动和UAV的抖动等,这些因素都符合实际系统的特点。此外,该文还推导出了系统的误比特率(BER)和渐进中断概率的闭式表达式。基于理论分析和模拟结果,讨论了各个参数和系统设计的影响。Abstract:
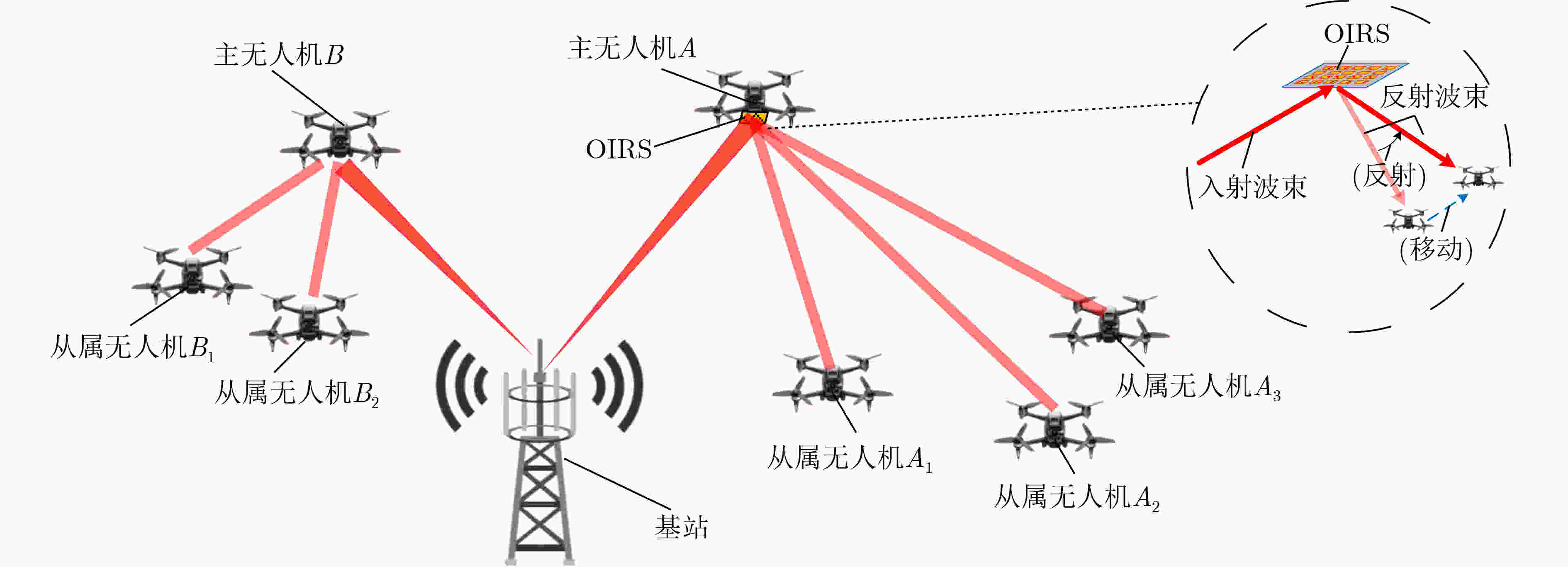
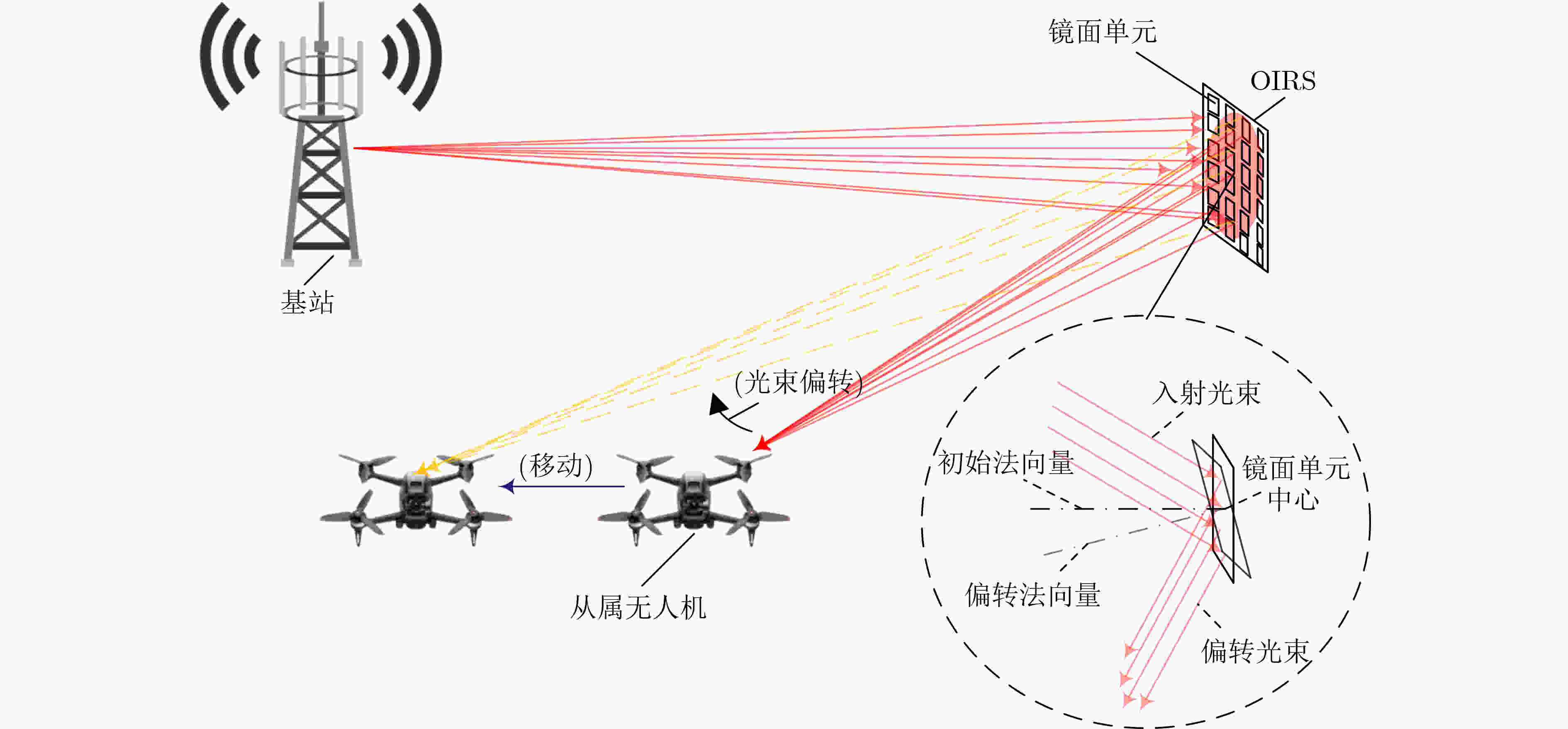
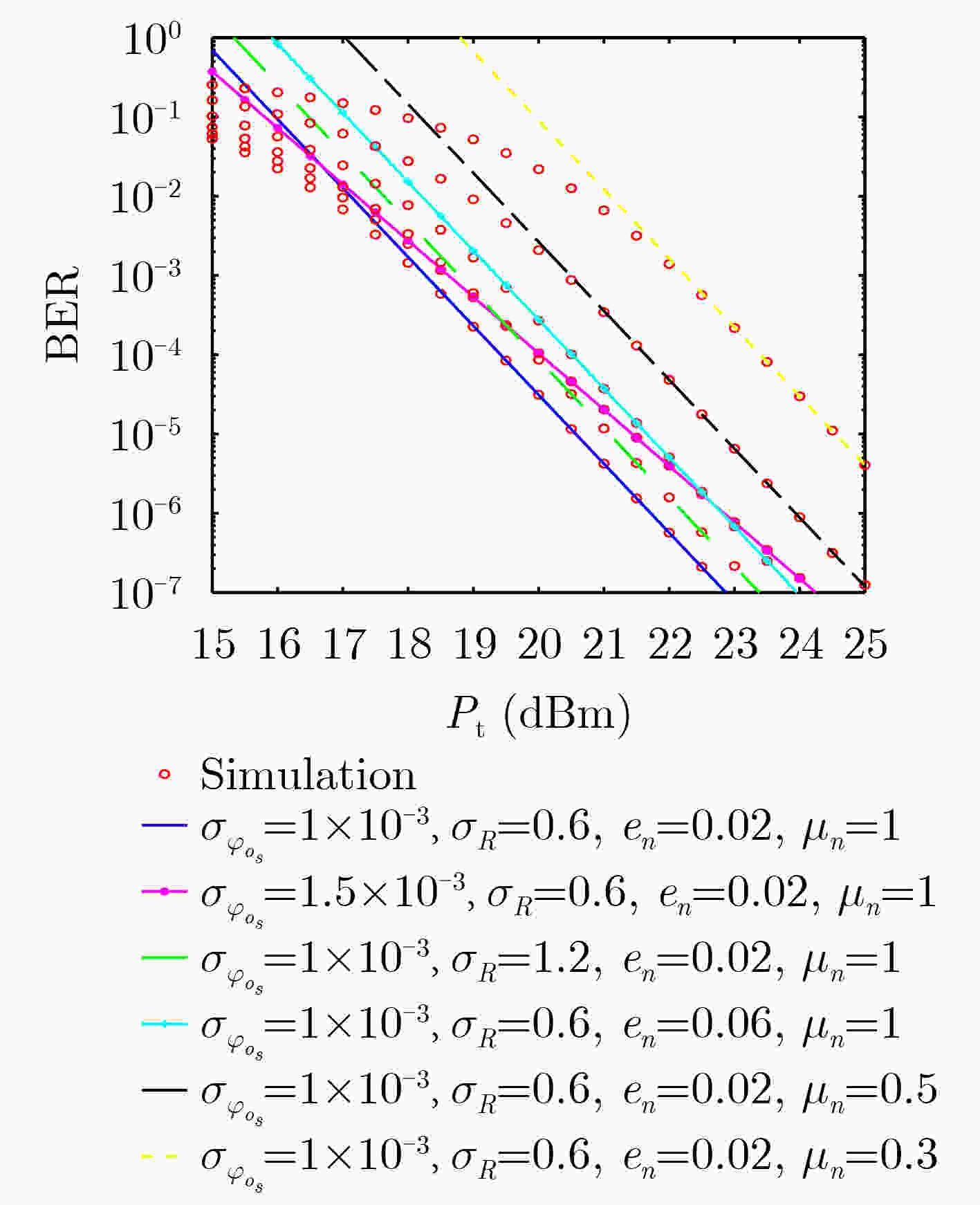
Objective The development of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) technology has led to new applications, such as UAV-based high-altitude base stations and UAV three-dimensional mapping. These applications demand higher communication rates and wider bandwidths. Optical Mobile Communications (OMC), a wireless communication method with high energy efficiency, wide bandwidth, and high speed, has become a crucial direction for UAV communication. However, traditional UAV-OMC systems primarily focus on point-to-point transmission. As the number of UAVs increases, these systems struggle to meet the real-time, high-speed communication requirements of multi-UAV networks. Therefore, a technology is needed that can preserve the energy efficiency and speed of the UAV-OMC system while supporting multi-UAV communication. This study proposes a solution where Optical Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (OIRS) are deployed on specific UAVs to spread the optical signal from a single UAV node to multiple UAV nodes, thus maintaining the high energy efficiency and speed of the UAV-OMC system, while enabling stable and energy-efficient communication for distributed UAV clusters. Methods OIRS is a new type of programmable passive optical device capable of deflecting, splitting, and reconstructing light beams. Due to its small size and light weight, OIRS is suitable for installation on drones. Based on this technology, this study proposes a distributed OMC system for UAV clusters. OIRS is installed on select UAVs and is used to diffuse optical signals from a single UAV to multiple UAVs. Since each OIRS has limited beam splitting capabilities and coverage, the UAV cluster is divided into several regions, with each OIRS handling communication and power allocation for UAVs in its designated region. The OIRS not only forwards the optical signal but also performs beam alignment and focusing to ensure that each UAV receives a focused and aligned beam. A mathematical model of the OIRS-assisted distributed OMC system for UAV clusters is developed, considering factors such as OIRS beam control, UAV relative motion, UAV jitter, and strong turbulence at high altitudes. The model’s validity is assessed by analyzing the communication performance of the backend UAV nodes in the cluster. Additionally, closed-form expressions for the average Bit Error Rate (BER) and asymptotic outage probability are derived, and key parameters influencing system performance are discussed. Results and Discussions (1) Using the derived OIRS unit control algorithm, the OIRS can be controlled to align beams with the slave UAVs. The diffuse beam initially reaching the master UAV is refocused onto the slave UAVs. For multi-UAV beam splitting, regional control of the OIRS selects specific mirror units to direct beams to particular slave UAVs, thus enabling beam splitting. This method effectively exploits the adjustable nature of OIRS and dynamically adjusts the direction of each mirror unit to serve multiple targets, thereby extending the communication coverage ( Fig. 2 ). This regional control strategy allows the system to adapt to environmental changes and the dynamic configuration of the UAV group, optimizing communication efficiency and network quality. The technology maximizes power allocation and utilization while ensuring sufficient signal strength for each slave UAV. (2) The performance degradation caused by the inherent parameters of OIRS, such as jitter and turbulence coefficient, in the OMC channel is substantial. However, OIRS beam alignment has an even more significant effect on system performance. Without beam alignment, the system performance is notably worse, with a more substantial impact on communication performance than severe weather conditions (Fig.3 ). (3) Simulation results show that system performance deteriorates significantly with each additional slave UAV. Thus, it is essential to determine the optimal number of slave UAVs that each OIRS should handle. Under the simulation conditions, it is most effective for each master UAV to manage three slave UAVs. Beyond this, maintaining stable communication becomes increasingly difficult.Conclusions This paper proposes an OIRS-assisted distributed OMC system for UAV clusters, utilizing the beam reflection and deflection capabilities of OIRS to extend the OMC link from a single UAV to multiple UAVs. OIRS’s refocusing capability ensures that UAVs at the rear can still receive a concentrated beam. Performance analysis and simulations show that slave UAVs maintain strong communication performance using OIRS for signal transmission. The beam alignment function of OIRS enhances system performance. However, due to power constraints, the addition of slave UAVs results in significant performance degradation. Future work will focus on optimizing the OIRS-assisted UAV OMC network architecture. -
表 1 系统参数
参数 值 光波长 ($\lambda $) 1550 nm接收机的噪声方差($ \sigma _n^2 $) ${10^{ - 6}}$ 发射端发散角度($ \phi $) 6 mrad 发射端抖动标准差($ {\sigma _{{\varphi _{{t_s}}}}} $) $2 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ 从发射端到OIRS的链路距离($ {l_{s,o}} $) 100 m 大气衰减系数(${\iota _n}$) 0.9 OIRS到从属UAV n的链路距离($ {l_{o,{r_n}}} $) 50 m 接收机直径 (2a) 20 cm -
[1] 张在琛, 江浩. 智能超表面使能无人机高能效通信信道建模与传输机理分析[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(10): 2623–2634. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221352.ZHANG Zaichen and JIANG Hao. Channel modeling and characteristics analysis for high energy-efficient RIS-assisted UAV communications[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(10): 2623–2634. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221352. [2] 朱秋明, 倪浩然, 华博宇, 等. 无人机毫米波信道测量与建模研究综述[J]. 移动通信, 2022, 46(12): 2–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20221114-0001.ZHU Qiuming, NI Haoran, HUA Boyu, et al. A survey of UAV millimeter-wave channel measurement and modeling[J]. Mobile Communications, 2022, 46(12): 2–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.20221114-0001. [3] DABIRI M T, SADOUGH S M S, and ANSARI I S. Tractable optical channel modeling between UAVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(12): 11543–11550. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2940226. [4] ZHANG Zaichen, DANG Jian, WU Liang, et al. Optical mobile communications: Principles, implementation, and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 471–482. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2880817. [5] NAJAFI M, SCHMAUSS B, and SCHOBER R. Intelligent reflecting surfaces for free space optical communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(9): 6134–6151. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3084637. [6] JAMALI V, AJAM H, NAJAFI M, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted free-space optical communications[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(10): 57–63. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2100406. [7] WANG Haibo, ZHANG Zaichen, ZHU Bingcheng, et al. Approaches to array-type optical IRSs: Schemes and comparative analysis[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(12): 3576–3591. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3152812. [8] MING Rui, ZHOU Zhiyan, LUO Xiwen, et al. Optical tracking system for multi-UAV clustering[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(17): 19382–19394. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3091280. [9] DABIRI M T, REZAEE M, MOHAMMADI L, et al. Modulating retroreflector based free space optical link for UAV-to-ground communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(10): 8631–8645. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3167945. [10] NATH S, SENGAR S, SHRIVASTAVA S K, et al. Impact of atmospheric turbulence, pointing error, and traffic pattern on the performance of cognitive hybrid FSO/RF system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(4): 1194–1207. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2952116. [11] SANDALIDIS H G, TSIFTSIS T A, KARAGIANNIDIS G K, et al. BER performance of FSO links over strong atmospheric turbulence channels with pointing errors[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2008, 12(1): 44–46. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2008.071408. [12] IJAZ M, GHASSEMLOOY Z, PEREZ J, et al. Enhancing the atmospheric visibility and fog attenuation using a controlled FSO channel[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2013, 25(13): 1262–1265. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2013.2264046. [13] WANG Zhengdao and GIANNAKIS G B. A simple and general parameterization quantifying performance in fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2003, 51(8): 1389–1398. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2003.815053. [14] SUN Shiyuan, WANG Tengjiao, YANG Fang, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided visible light communications: Potentials and challenges[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2022, 17(1): 47–56. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2021.3127869. [15] AJAM H, NAJAFI M, JAMALI V, et al. Modeling and design of IRS-assisted multilink FSO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(5): 3333–3349. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3163767. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
