Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning of Vision Transformers for Remote Sensing Scene Understanding
-
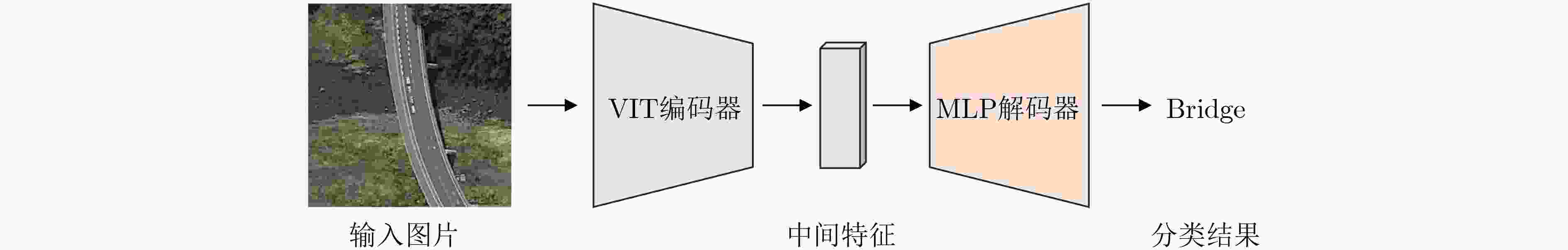
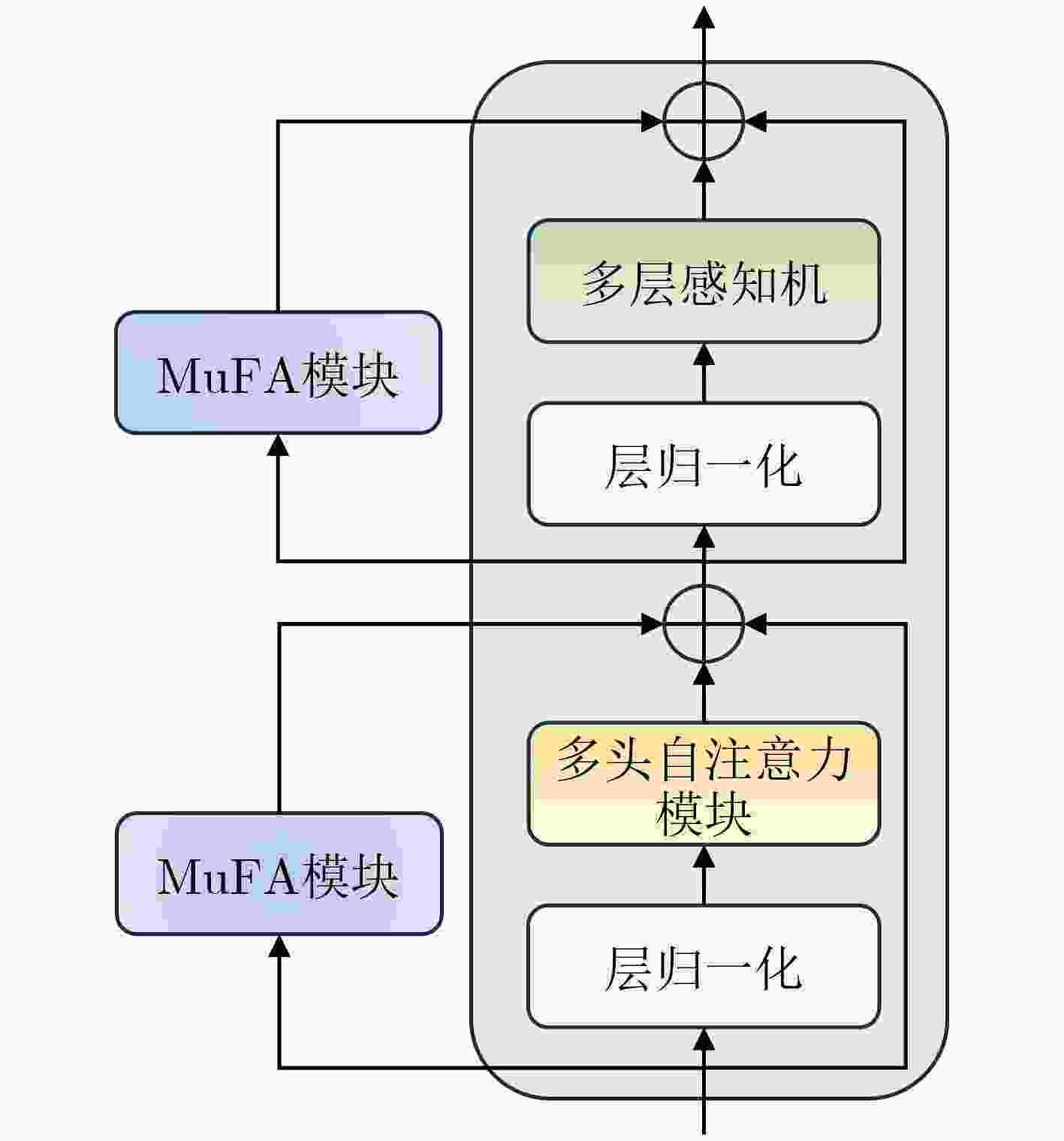
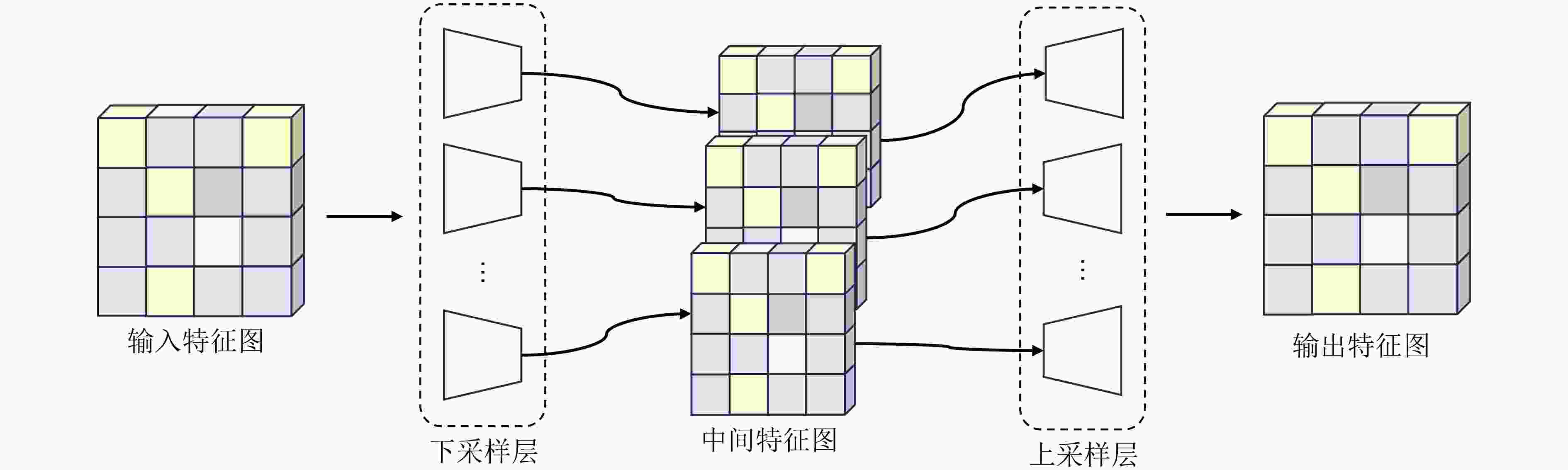
摘要: 随着深度学习和计算机视觉技术的飞速发展,遥感场景分类任务对预训练模型的微调通常需要大量的计算资源。为了减少内存需求和训练成本,该文提出一种名为“多尺度融合适配器微调(MuFA)”的方法,用于遥感模型的微调。MuFA引入了一个多尺度融合模块,将不同下采样倍率的瓶颈模块相融合,并与原始视觉Transformer模型并联。在训练过程中,原始视觉Transformer模型的参数被冻结,只有MuFA模块和分类头会进行微调。实验结果表明,MuFA在UCM和NWPU-RESISC45两个遥感场景分类数据集上取得了优异的性能,超越了其他参数高效微调方法。因此,MuFA不仅保持了模型性能,还降低了资源开销,具有广泛的遥感应用前景。Abstract: With the rapid development of deep learning and computer vision technologies, fine-tuning pre-trained models for remote sensing tasks often requires substantial computational resources. To reduce memory requirements and training costs, a method called “Multi-Fusion Adapter (MuFA)” for fine-tuning remote sensing models is proposed in this paper. MuFA introduces a fusion module that combines bottleneck modules with different down sample rates and connects them in parallel with the original vision Transformer model. During training, the parameters of the original vision Transformer model are frozen, and only the MuFA module and classification head are fine-tuned. Experimental results demonstrate that MuFA achieves superior performance on the UCM and NWPU-RESISC45 remote sensing scene classification datasets, surpassing other parameter efficient fine-tuning methods. Therefore, MuFA not only maintains model performance but also reduces resource overhead, making it highly promising for various remote sensing applications.
-
Key words:
- Remote sensing /
- Scene classification /
- Parameter efficient /
- Deep learning
-
表 1 以Vit-Base为基准模型的对比试验(%)
方法 微调参数 数据集 UCM RESISC45 Acc. 完全微调 100.00 99.05 91.66 完全冻结 0 90.95 76.55 微调Layer Norm 0.07 94.58 86.40 Adapter 2.08 97.66 89.12 LoRA 4.04 98.12 89.44 BitFit 0.24 94.76 87.22 AdaptFormer 2.08 98.12 90.98 Convpass 4.12 97.94 90.42 LoRand 1.84 97.80 90.17 VPT 0.78 95.47 88.15 IVPT 0.78 97.41 90.55 E2VPT 0.39 97.90 90.24 MuFA(本文方法) 3.64 98.57 91.29 表 2 以Swin-Tiny为基准模型的对比试验(%)
方法 微调参数 数据集 UCM RESISC45 Acc. 完全微调 100.00 99.76 94.70 完全冻结 0 96.67 84.21 微调Layer Norm 0.07 97.66 91.70 Adapter 2.08 98.80 92.26 LoRA 4.04 98.58 92.55 BitFit 0.24 98.12 91.76 AdaptFormer 2.08 99.05 93.88 Convpass 4.12 99.05 93.61 LoRand 1.84 98.53 92.75 VPT 0.78 98.17 92.10 IVPT 0.78 98.73 92.69 E2VPT 0.39 99.32 93.10 MuFA(本文方法) 3.64 99.52 94.10 表 3 以Swin-Tiny为基准模型的消融研究(%)
序号 消融研究 数据集 连接方式 融合结构 UCM RESISC45 串联 并联 单尺度 双尺度 多尺度 Acc. (1) √ √ 98.80 92.26 (2) √ √ 98.80 92.76 (3) √ √ 99.12 93.44 (4) √ √ 99.05 93.88 (5) √ √ 99.30 93.96 (6) √ √ 99.52 94.10 -
[1] 王佩瑾, 闫志远, 容雪娥, 等. 数据受限条件下的多模态处理技术综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(10): 2803–2834. doi: 10.11834/jig.220049.WANG Peijin, YAN Zhiyuan, RONG Xue’e, et al. Review of multimodal data processing techniques with limited data[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(10): 2803–2834. doi: 10.11834/jig.220049. [2] BI Hanbo, FENG Yingchao, YAN Zhiyuan, et al. Not just learning from others but relying on yourself: A new perspective on few-shot segmentation in remote sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5623621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3326292. [3] WANG Peijin, SUN Xian, DIAO Wenhui, et al. FMSSD: Feature-merged single-shot detection for multiscale objects in large-scale remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(5): 3377–3390. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2954328. [4] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [5] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [6] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Austria, 2021. [7] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986. [8] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848. [9] BEN ZAKEN E, GOLDBERG Y, and RAVFOGEL S. BitFit: Simple parameter-efficient fine-tuning for transformer-based masked language-models[C]. The 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), Dublin, Ireland, 2022: 1–9. doi: 10.18653/v1/2022.acl-short.1. [10] HOULSBY N, GIURGIU A, JASTRZEBSKI S, et al. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP[C]. 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2790–2799. [11] HU E J, SHEN Yelong, WALLIS P, et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models[C]. 10th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022. [12] YIN Dongshuo, YANG Yiran, WANG Zhechao, et al. 1% vs 100%: Parameter-efficient low rank adapter for dense predictions[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 20116–20126. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01926. [13] CHEN Shoufa, GE Chongjian, TONG Zhan, et al. AdaptFormer: Adapting vision transformers for scalable visual recognition[C]. The 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1212. [14] JIE Shibo and DENG Zhihong. Convolutional bypasses are better vision transformer adapters[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.07039, 2022. [15] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [16] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [17] LESTER B, AL-RFOU R, and CONSTANT N. The power of scale for parameter-efficient prompt tuning[C]. The 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 2021: 3045–3059. doi: 10.18653/v1/2021.emnlp-main.243. [18] JIA Menglin, TANG Luming, CHEN B C, et al. Visual prompt tuning[C]. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 709–727. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19827-4_41. [19] YOO S, KIM E, JUNG D, et al. Improving visual prompt tuning for self-supervised vision transformers[C]. 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, USA, 2023: 40075–40092. [20] TU Chenghao, MAI Zheda, and CHAO Weilun. Visual query tuning: Towards effective usage of intermediate representations for parameter and memory efficient transfer learning[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 7725–7735. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00746. [21] HAN Cheng, WANG Qifan, CUI Yiming, et al. E2VPT: An effective and efficient approach for visual prompt tuning[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 17445–17456. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01604. [22] HE Xuehai, LI Chunyuan, ZHANG Pengchuan, et al. Parameter-efficient model adaptation for vision transformers[C]. Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 817–825. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i1.25160. [23] ZHANG Yuanhan, ZHOU Kaiyang, and LIU Ziwei. Neural prompt search[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04673, 2022. [24] QI Wang, RUAN Yuping, ZUO Yuan, et al. Parameter-efficient tuning on layer normalization for pre-trained language models[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08682, 2022. [25] YANG Yi and NEWSAM S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification[C]. The 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, USA, 2010: 270–279. doi: 10.1145/1869790.1869829. [26] CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998. [27] SUN Xian, WANG Peijin, LU Wanxuan, et al. RingMo: A remote sensing foundation model with masked image modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5612822. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3194732. [28] GUO Xin, LAO Jiangwei, DANG Bo, et al. SkySense: A multi-modal remote sensing foundation model towards universal interpretation for earth observation imagery[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.10115, 2023. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
