Micro-Doppler-assisted Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Formation Detection Method in Urban Environments
-
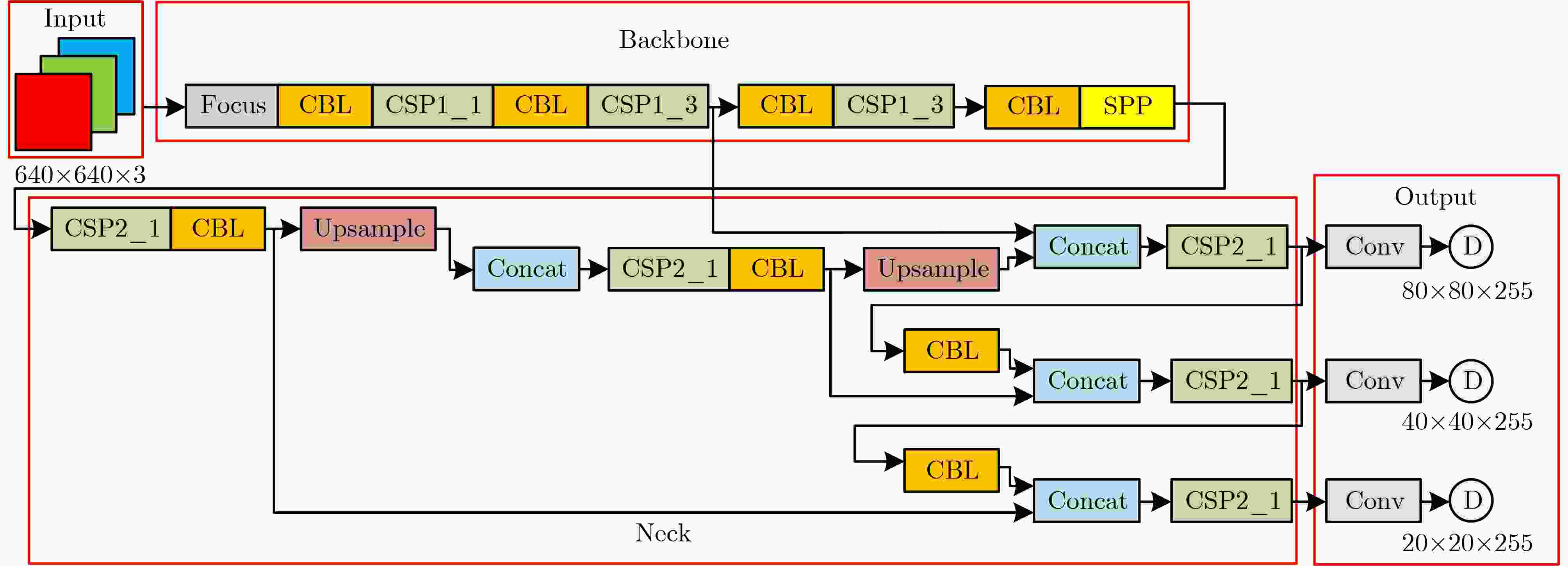
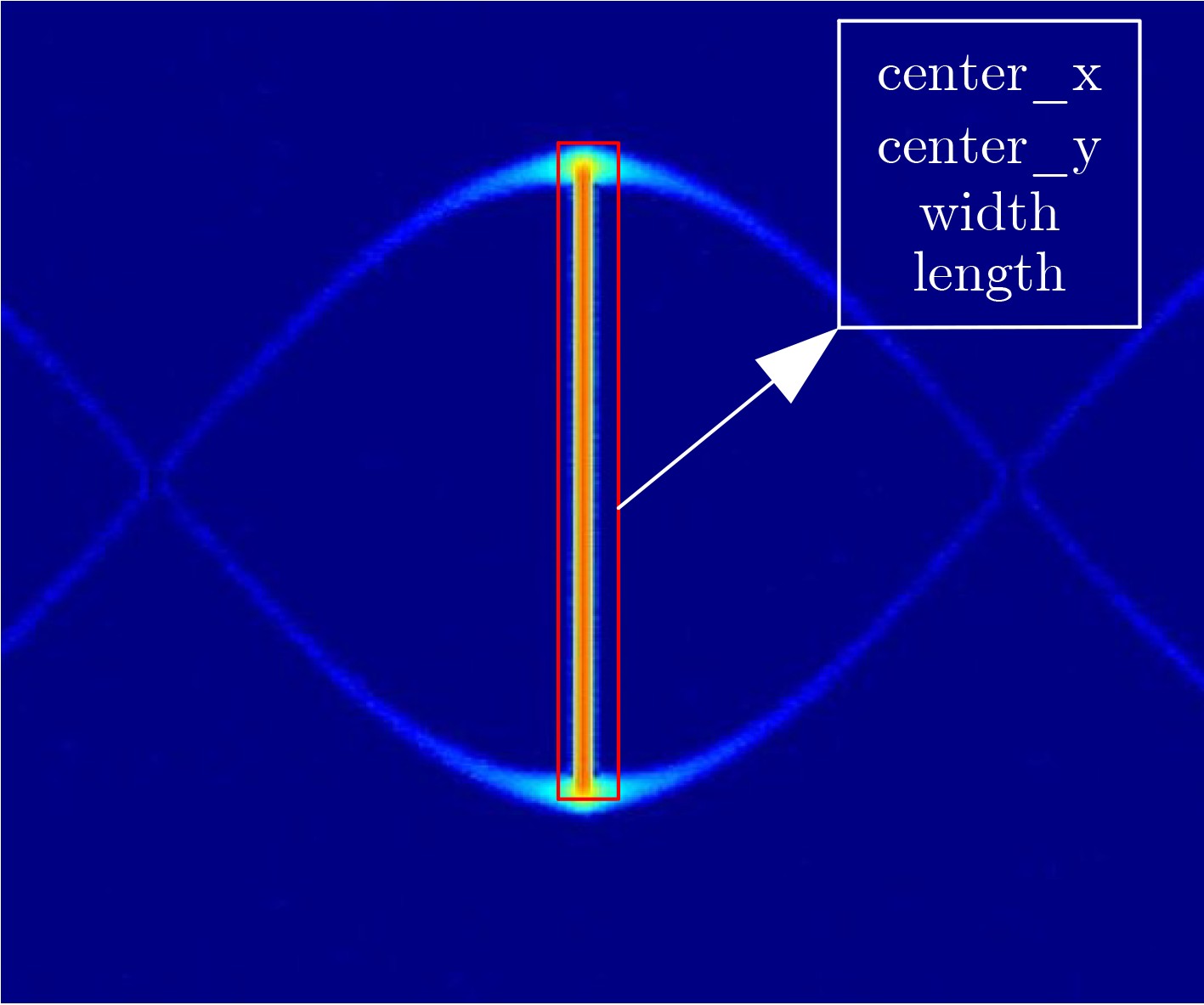
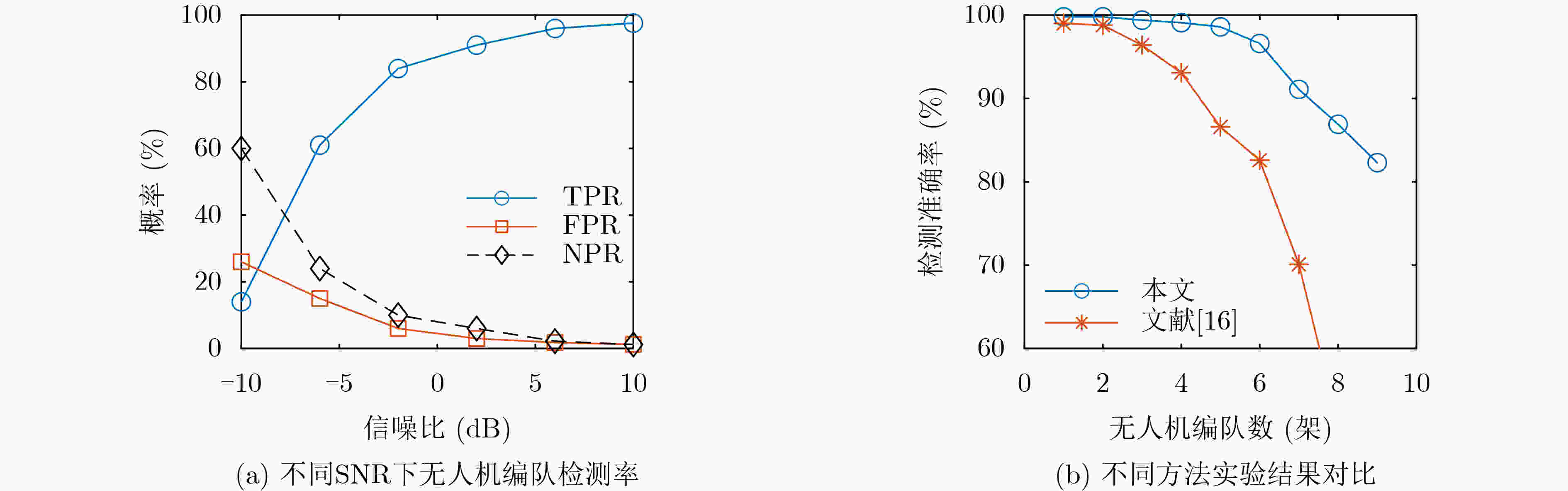
摘要: 针对城市复杂环境下电磁环境复杂、多径杂波和干扰信号密集等现象,传统的无人机(UAV)检测方法通过获取回波信号提取目标多普勒信息进行检测,易受到环境影响导致检测效果不理想。该文提出微多普勒辅助的城市环境无人机编队检测方法,充分利用无人机的微动特征,能够在复杂环境下提高检测精度。首先,参数化建模表征城市复杂环境下无人机旋翼的雷达回波微多普勒信号,利用YOLOv5s检测微多普勒闪烁脉冲,有效提取位置信息;然后,引入雷达信号分选方法的脉冲重复间隔(PRI)变换,分类获得无人机编队数量;最后,利用K-means算法验证无人机编队检测方法的准确性。结果表明,所提方法在信噪比2 dB时7架无人机的检测精度高于90%,能够用于城市复杂环境存在干扰脉冲、多径效应、局部脉冲丢失的无人机编队检测。Abstract: Considering the phenomena of complex electromagnetic environment, multipath clutter and dense interference signals in complex urban environments, the traditional Unmanned Aerial Vehicle(UAV) detection method extracts the target Doppler information for detection by obtaining echo signals, which is susceptible to environmental impacts and leads to unsatisfactory detection results. A micro-Doppler-assisted formation detection method for UAVs in urban environments is proposed in this paper, which makes full use of micro-motion characteristics to improve detection accuracy. Firstly, parametric modeling characterizes the radar echo micro-Doppler signals of UAV rotor blades in urban complex environments, and detects the micro-Doppler scintillation pulses by using YOLOv5s to effectively extract the positional information. Then, the Pulse Repetition Interval (PRI) transform of the radar signal sorting method is introduced to classify and obtain the number of UAV formations. Finally, K-means algorithm is utilized to verify the accuracy of the UAV formation detection method. The results show that the proposed method has a detection accuracy of more than 90% for seven UAVs at a signal-to-noise ratio of 2 dB, and can be used for UAV formation detection in urban complex environments where there are interfering pulses, multipath effects, and local pulse loss.
-
表 1 无人机编队参数
仿真参数 数值 旋翼叶片数目 2 旋翼长度(${\text{cm}}$) 1.73,1.91,1.82 无人机速度(${\text{m/s}}$) 1.9,2.5,2.3 旋翼转速(${\text{r/s}}$) 3.27,3.97,3.62 初相位($^\circ $) 0,18,36 弧度($^\circ $) 45,45,45 叶片散射系数(${\text{dBsm}}$) 1,1,1 表 2 YOLOV5s网络参数
网络参数 配置 Learning rate 0.01 Momentum 0.937 Weight decay 0.000 5 Batch size 16 Depth multiple 0.33 Width multiple 0.50 表 3 不同无人机编队数量下的检测准确率
无人机编队数量(架) 检测准确率(%) 1 99.8 2 99.4 3 99.1 4 98.5 5 98.0 6 95.6 7 91.1 8 85.5 9 81.2 -
[1] 任智, 张栋, 唐硕, 等. 无人机集群反制与对抗技术探讨[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2023, 9(6): 660–672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.06.0660.REN Zhi, ZHANG Dong, TANG Shuo, et al. Discussion on technologies of UAV swarm countermeasures and confrontation[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2023, 9(6): 660–672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.06.0660. [2] 于威, 侯学隆. 从纳卡冲突看无人机作战运用[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2022, 42(10): 8–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.10.003.YU Wei and HOU Xuelong. Application of unmanned aerial vehicles in nagorno-karabakh conflict[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2022, 42(10): 8–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.10.003. [3] 杨佳会, 朱超磊, 许佳. 俄乌冲突中的无人机运用[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2022(3): 116–123. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220081.YANG Jiahui, ZHU Chaolei, and XU Jia. Analysis of UAV deployment in Russia-Ukraine conflict[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2022(3): 116–123. doi: 10.16358/j.issn.1009-1300.20220081. [4] XU Chunbao, JIN Songpo, DING Zhoupeng, et al. Transmit beam control in low-altitude slow-moving small targets detection[C]. The 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 2022: 470–473. doi: 10.1109/ICSP54964.2022.9778645. [5] CHEN V C. Analysis of radar micro-Doppler with time-frequency transform[C]. The Tenth IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing (Cat. No. 00TH8496), Pocono Manor, USA, 2000: 463–466. doi: 10.1109/SSAP.2000.870167. [6] MA Beili, CHEN Baixiao, ZHANG Zhengrong, et al. Classification of UAV and ground targets by micro-Doppler signatures based on PD surveillance radar[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 1361–1365. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028361. [7] KANG K B, CHOI J H, CHO B L, et al. Analysis of micro-Doppler signatures of small UAVs based on Doppler spectrum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 3252–3267. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3074208. [8] JI Guangyu, SONG Chen, and HUO Hongtao. Detection and identification of low-slow-small rotor unmanned aerial vehicle using micro-Doppler information[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 99995–100008. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3096264. [9] BJÖRKLUND S and WADSTRÖMER N. Target detection and classification of small drones by deep learning on radar micro-Doppler[C]. 2019 International Radar Conference (RADAR), Toulon, France, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR41533.2019.171294. [10] GAO Chengshuai, ZHOU Tao, WANG Bingqi, et al. Research on Anti Drone swarm technology based on complex urban environment[C]. 2023 International Conference on Network, Multimedia and Information Technology (NMITCON), Bengaluru, India, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/NMITCON58196.2023.10275854. [11] LV Ning and BAI Yunpeng. A UAV target recognition method based on micro-Doppler feature fusion[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Science (EIECS), Changchun, China, 2023: 970–973. doi: 10.1109/EIECS59936.2023.10435590. [12] 张亚豪. 低空小型无人机雷达检测与识别[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.001396.ZHANG Yahao. Low altitude small drone radar detection and recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.001396. [13] DAHIROU Z and ZHENG Mao. Motion detection and object detection: Yolo (You Only Look Once)[C]. The 7th Annual International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers (ICNISC), Guiyang, China, 2021: 250–257. doi: 10.1109/ICNISC54316.2021.00053. [14] 张怡霄, 郭文普, 康凯, 等. 基于数据场联合PRI变换与聚类的雷达信号分选[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(7): 1509–1515. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.07.11.ZHANG Yixiao, GUO Wenpu, KANG Kai, et al. Radar signal sorting method based on data field combined PRI transform and clustering[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(7): 1509–1515. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.07.11. [15] 陈涛, 王天航, 郭立民. 基于PRI变换的雷达脉冲序列搜索方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.06.12.CHEN Tao, WANG Tianghang, and GUO Limin. Sequence searching methods of radar signal pulses based on PRI transform algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.06.12. [16] 杨波, 孙闽红, 仇兆炀, 等. 基于YOLOv5与PRI变换的无人机编队检测[J]. 现代雷达, 2023, 45(9): 53–60. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.09.009.YANG Bo, SUN Minhong, QIU Zhaoyang, et al. UAV-formations detection based on YOLOv5 and PRI transformation[J]. Modern Radar, 2023, 45(9): 53–60. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.09.009. -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
