A Review of Neural Radiance Field Approaches for Scene Reconstruction of Satellite Remote Sensing Imagery
-
摘要: 随着高分辨率卫星遥感图像成为认知地理空间不可或缺的重要手段,卫星遥感图像在城市建图、生态监测和导航等领域发挥着日益重要的作用,利用卫星遥感图像进行地球表面大规模3维重建成为了计算机视觉和摄影测量领域的研究热点。神经辐射场(NeRF)利用可微渲染学习场景的隐式表示,在复杂场景新视图合成任务中实现了逼真的视觉效果,并在3维场景重建和渲染领域获得了极大的关注。近期的研究主要集中在利用神经辐射场技术,从卫星遥感图像中提取场景表示及其重建。面向卫星遥感图像的神经辐射场方法主要集中在光线空间优化、场景表示优化以及模型高效训练3方面。该文全面归纳了神经辐射场技术在卫星遥感应用中的最新进展。首先介绍神经辐射场技术的基本概念及相关数据集。然后提出一个面向卫星遥感图像的神经辐射场方法分类框架,用于系统性地回顾和整理该技术在卫星遥感领域的研究进展。接着详述了神经辐射场技术在实际卫星遥感场景应用中的相关成果。最后,基于当前研究所面临的问题和挑战进行分析和讨论,同时对未来的发展趋势和研究方向进行了展望。Abstract: High-resolution satellite remote sensing images have been recognized as an indispensable means for understanding geographical spaces, and their role in areas such as urban mapping, ecological monitoring, and navigation, has become increasingly important. The use of satellite remote sensing images for large-scale 3D reconstruction of the Earth’s surface is currently a subject of active research in the fields of computer vision and photogrammetry. Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), which utilizes differentiable rendering to learn implicit representations of scenes, has achieved the most realistic visual effects in novel view synthesis tasks of complex scenes and has attracted significant attention in the field of 3D scene reconstruction and rendering. Recent research has been primarily focused on using neural radiance field technology to extract scene representation and reconstruction from satellite remote sensing images. Ray space optimization, scene representation optimization, and efficient model training are mainly focused on by the neural radiance field methods for satellite remote sensing images. The latest progress in the application of neural radiance field technology in satellite remote sensing is comprehensively summarized in this paper. First, the basic concepts of neural radiance field technology and related datasets are introduced. Then a classification framework of neural radiance field methods for satellite remote sensing images is proposed to systematically review and organize the research progress of this technology in the field of satellite remote sensing. The relevant results of the application of neural radiance field technology in actual satellite remote sensing scenarios are detailed. Finally, analysis and discussion are conducted based on the problems and challenges faced by current research, and future development trends and research directions are prospected.
-
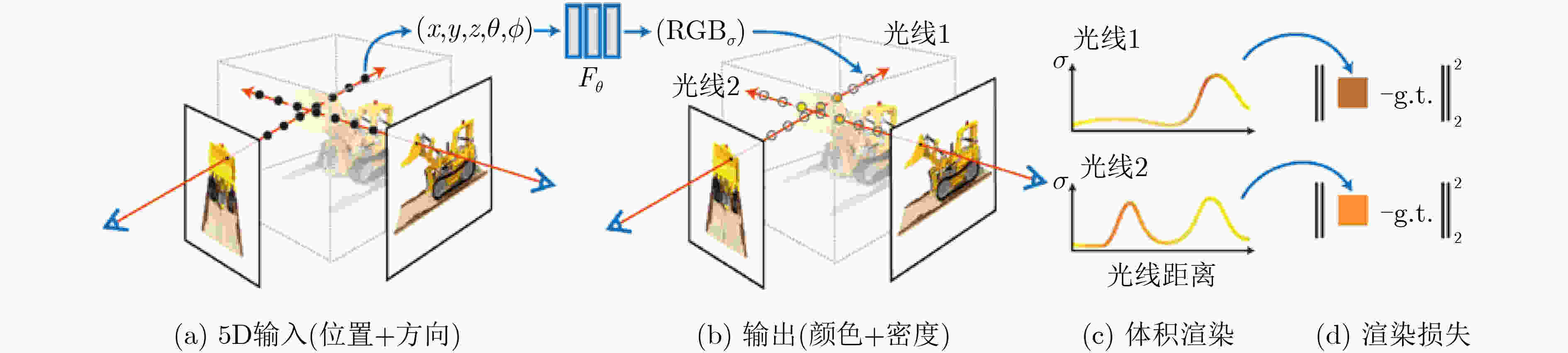
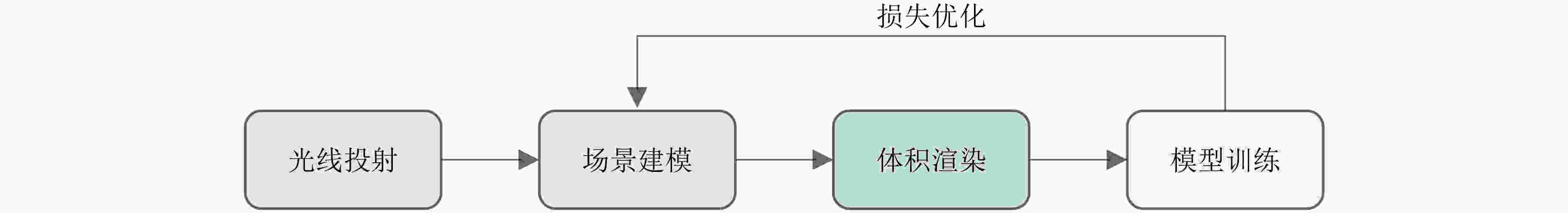
图 1 NeRF体积渲染和训练过程[1]
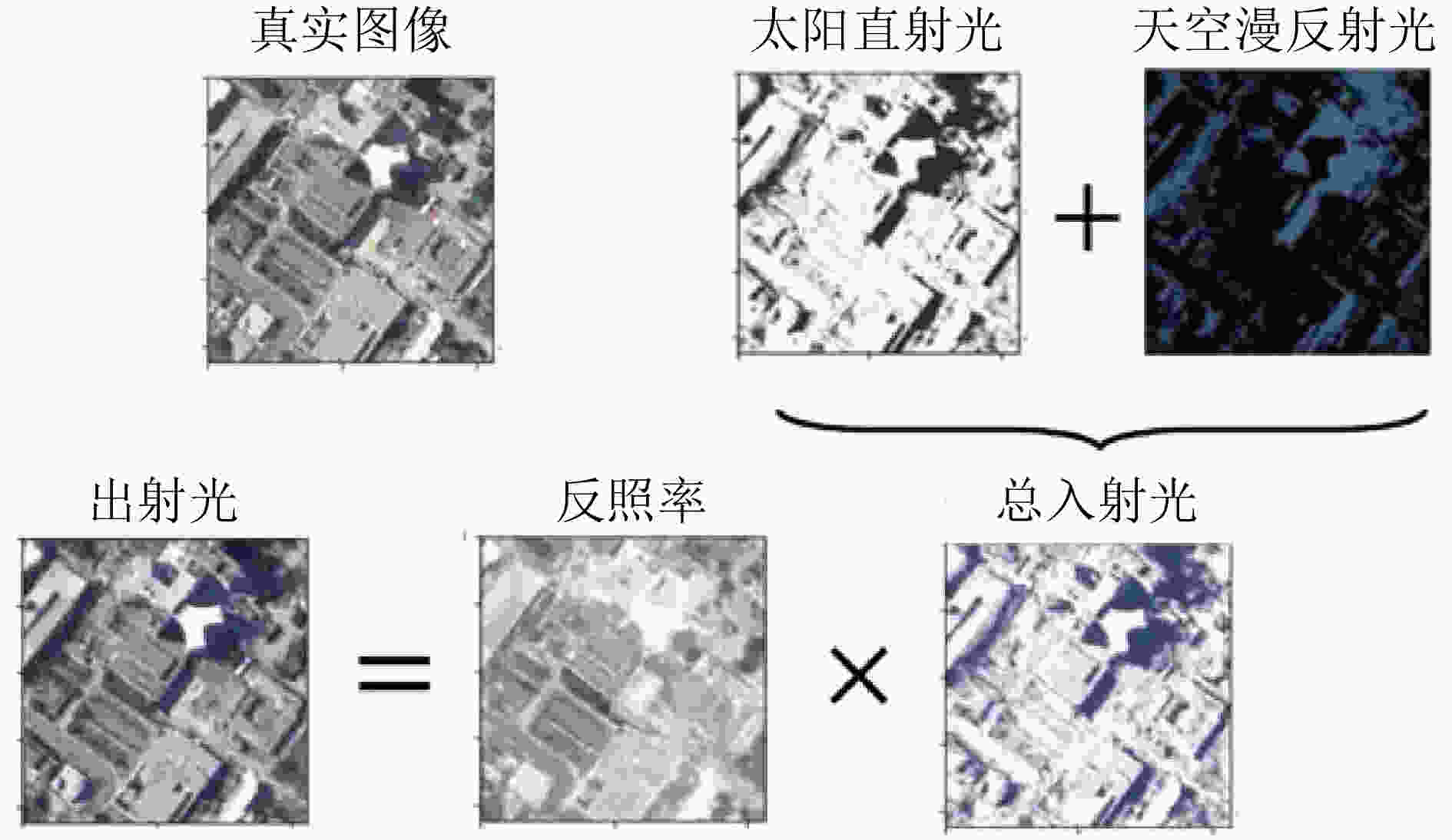
图 3 S-NeRF渲染模型[16]
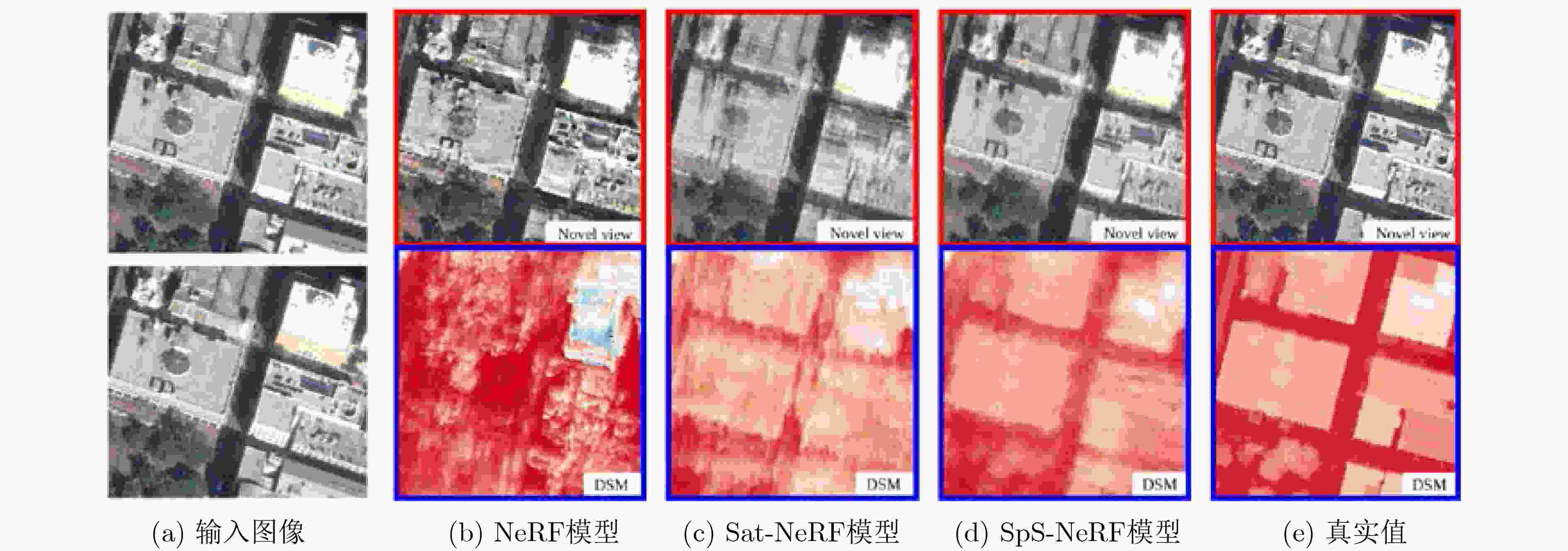
图 4 SpS-NeRF立体匹配重建结果[2]
图 5 Sat-Mesh网格模型重建结果[18]
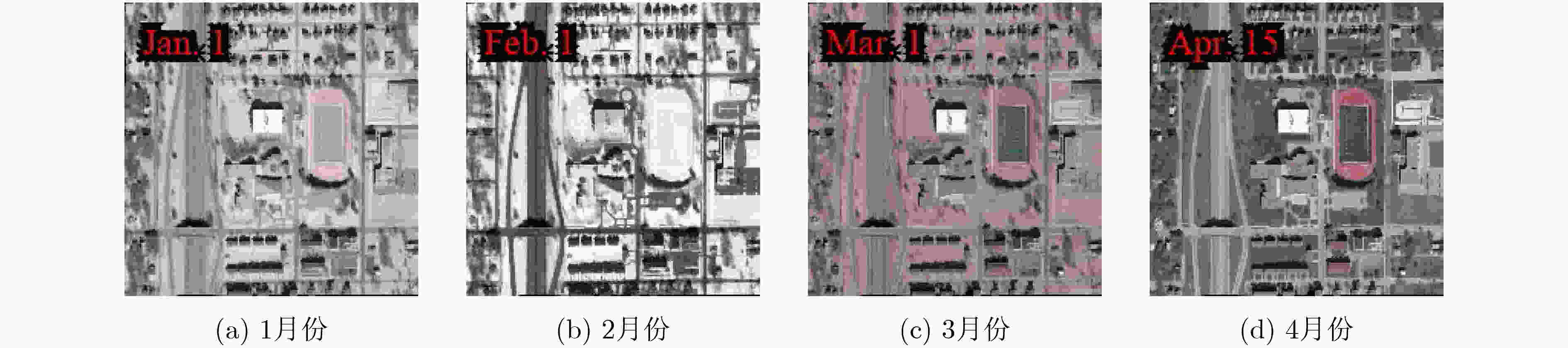
图 6 Season-NeRF季节特征风格转换[26]
表 1 神经辐射场常用数据集
数据集名称 类别 场景数量 分辨率/
像素每场景
图像数量Synthetic NeRF 物体 8 800×800 400 LLFF 前向场景 8 1008×756 20~62 Mip-NeRF 360 室内、室外场景 9 1237×822 100~330 Tanks and Temples 室外场景 4 1920×1080 283 表 2 DFC2019数据集详细信息
1 2 3 4 区域编号 004 068 214 260 输入图像 9 17 21 15 高度范围 [–24, 1] [–27, 30] [–29, 73] [–30, 13] 纬度 30.357 30.348 30.316 30.311 经度 –81.706 –81.663 –81.663 –81.663 表 3 光线空间优化方法总结
光线空间 优点 缺点 代表方法 球坐标表示 易于理解和计算 精度略低 S-NeRF(2021年) ECEF坐标表示 适合精确位置计算 计算变换复杂且不直观 Sat-NeRF(2022年) UTM坐标表示 易于理解和应用 需要额外的高度信息 EO-NeRF(2023年) RPC近似模型表示 精度较高,灵活性高 近似过程存在误差 Sat-Mesh(2023年) -
[1] MILDENHALL B, SRINIVASAN P P, TANCIK M, et al. NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2021, 65(1): 99–106. doi: 10.1145/3503250. [2] ZHANG Lulin and RUPNIK E. Sparsesat-NeRF: Dense depth supervised neural radiance fields for sparse satellite images[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.00277, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2309.00277. [3] BARRON J T, MILDENHALL B, TANCIK M, et al. Mip-NeRF: A multiscale representation for anti-aliasing neural radiance fields[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 5835–5844. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00580. [4] TANCIK M, SRINIVASAN P P, MILDENHALL B, et al. Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 632. [5] TANCIK M, CASSER V, YAN Xinchen, et al. Block-NeRF: Scalable large scene neural view synthesis[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8238–8248. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00807. [6] MAX N. Optical models for direct volume rendering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 1995, 1(2): 99–108. doi: 10.1109/2945.468400. [7] GAO K, GAO Yina, HE Hongjie, et al. NeRF: Neural radiance field in 3D vision, a comprehensive review[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2210.00379, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2210.00379. [8] LORENSEN W E and CLINE H E. Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm[M]. WOLFE R. Seminal Graphics: Pioneering Efforts that Shaped the Field. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 1998: 347–353. doi: 10.1145/280811.281026. [9] MILDENHALL B, SRINIVASAN P P, ORTIZ-CAYON R, et al. Local light field fusion: Practical view synthesis with prescriptive sampling guidelines[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(4): 29. doi: 10.1145/3306346.3322980. [10] BARRON J T, MILDENHALL B, VERBIN D, et al. Mip-NeRF 360: Unbounded anti-aliased neural radiance fields[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 5460–5469. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00539. [11] KNAPITSCH A, PARK J, ZHOU Qianyi, et al. Tanks and temples: Benchmarking large-scale scene reconstruction[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): 78. doi: 10.1145/3072959.3073599. [12] BOSCH M, FOSTER K, CHRISTIE G, et al. Semantic stereo for incidental satellite images[C]. 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1524–1532. doi: 10.1109/WACV.2019.00167. [13] LE SAUX B, YOKOYA N, HANSCH R, et al. 2019 data fusion contest [technical committees][J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2019, 7(1): 103–105. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2893783. [14] MARÍ R, FACCIOLO G, and EHRET T. Sat-NeRF: Learning multi-view satellite photogrammetry with transient objects and shadow modeling using RPC cameras[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1310–1320. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW56347.2022.00137. [15] SCHÖNBERGER J L and FRAHM J M. Structure-from-motion revisited[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4104–4113. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.445. [16] DERKSEN D and IZZO D. Shadow neural radiance fields for multi-view satellite photogrammetry[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, USA, 2021: 1152–1161. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW53098.2021.00126. [17] MARÍ R, FACCIOLO G, and EHRET T. Multi-date earth observation NeRF: The detail is in the shadows[C]. The 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 2035–2045. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW59228.2023.00197. [18] QU Yingjie and DENG Fei. Sat-mesh: Learning neural implicit surfaces for multi-view satellite reconstruction[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(17): 4297. doi: 10.3390/rs15174297. [19] MARTIN-BRUALLA R, RADWAN N, SAJJADI M S M, et al. Nerf in the wild: Neural radiance fields for unconstrained photo collections[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 7206–7215. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00713. [20] SUN Cheng, SUN Min, and CHEN H T. Improved direct voxel grid optimization for radiance fields reconstruction[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2206.05085, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2206.05085. [21] CHEN Anpei, XU Zexiang, GEIGER A, et al. TensoRF: Tensorial radiance fields[C]. The 17th European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 333–350. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-19824-3_20. [22] MÜLLER T, EVANS A, SCHIED C, et al. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2022, 41(4): 102. doi: 10.1145/3528223.3530127. [23] XIE Songlin, ZHANG Lei, JEON G, et al. Remote sensing neural radiance fields for multi-view satellite photogrammetry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(15): 3808. doi: 10.3390/rs15153808. [24] ZHANG Tongtong and LI Yuanxiang. Fast satellite tensorial radiance field for multi-date satellite imagery of large size[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.11767, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2309.11767. [25] ROESSLE B, BARRON J T, MILDENHALL B, et al. Dense depth priors for neural radiance fields from sparse input views[C]. Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 12882–12891. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01255. [26] GABLEMAN M and KAK A. Incorporating season and solar specificity into renderings made by a NeRF architecture using satellite images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(6): 4348–4365. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3355069. [27] REMATAS K, LIU A, SRINIVASAN P, et al. Urban radiance fields[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 12922–12932. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01259. [28] TURKI H, RAMANAN D, and SATYANARAYANAN M. Mega-NeRF: Scalable construction of large-scale NeRFs for virtual fly-throughs[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 12912–12921. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01258. [29] HO J, JAIN A, and ABBEEL P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 574. [30] RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 8748–8763. [31] YANG Jianing, CHEN Xuweiyi, QIAN Shengyi, et al. LLM-grounder: Open-vocabulary 3D visual grounding with large language model as an agent[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2309.12311, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2309.12311. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
