A Lightweight and Provably Secure Authentication Protocol for Internet of Vehicles Using Physical Unclonable Function
-
摘要: 车联网(IoVs)广泛用于获取车辆和道路状况等信息,但是这些信息都是在公共信道中进行传输,所以最重要和关键的要求之一就是在严格延迟要求下的数据安全。其中,认证是解决数据安全最常用的方法,但是由于车联网的资源受限和对延迟敏感等特点,车辆认证需要在一定的消耗和延迟内完成。然而,现有方案容易遭受物理、伪造和共谋等攻击,同时也产生了昂贵的通信和计算成本。该文提出一种基于物理不可克隆函数(PUF)的车路云协同轻量级安全认证方案。所提议方案采用轻量级的物理不可克隆函数作为车联网实体的信任保证,抵御攻击者对实体的物理和共谋等攻击;采用车路云协同的架构,在经过可信机构(TA)认证的路边单元(RSU)上完成认证运算,大大减轻了TA的计算压力,并将挑战响应对(CRPs)的更新应用到假名的构造更新中,保护身份和轨迹隐私的同时也能在身份追踪阶段披露恶意车辆身份。在实际场景的模拟实验中,通过与其它方案进行比较,表明该方案更加安全和高效。Abstract: The Internet of Vehicles (IoVs) is widely used to obtain information about vehicles and road conditions, which is transmitted in public channels. Hence, the most important requirement is the data security. Because of characters of IoVs, we need to make it keep in a strict delay. Authentication is a common method to solve it. Due to limited resources and delay sensitivity of IoVs, vehicles must complete authentication within appropriate resources cost and delay. However, existing schemes are prone to physical, forgery and collusion attacks, and moreover, they are computationally heavy. Therefore, a lightweight security identity authentication scheme for vehicle-road collaboration is proposed in this paper, which utilizes lightweight Physical Unclonable Function (PUF) as the trust root of entities to resist physical and collusion attacks; Besides, most of computations are offloaded to Road Side Units (RSUs) certified by Trusted Authority (TA) through the vehicle-road-cloud collaboration architecture; In addition, vehicular pseudonym construction and update include Challenge-Response Pairs (CRPs), which are utilized to protect identity and trajectory privacy and expose malicious vehicular identities in identity tracking phase. Furthermore, there are formal and informal security analyses to prove our scheme is secure. Finally, the simulation experiment shows our scheme is more secure and efficient than other schemes in real scenarios.
-
表 1 参数含义对照表
符号 描述 TA 可信中心 Vi 第i个车辆 ID 实体身份 X, x 实体的公钥和私钥 CRP PUF的挑战响应对 T 时间戳 SK 会话密钥 表 2 实体的计算开销(ms)
表 3 实体的通信开销(bit)
-
[1] XIE Qi and HUANG Juanjuan. Improvement of a conditional privacy-preserving and desynchronization-resistant authentication protocol for IoV[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(6): 2451. doi: 10.3390/app14062451. [2] JAVAID U, AMAN M N, and SIKDAR B. A scalable protocol for driving trust management in internet of vehicles with blockchain[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(12): 11815–11829. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3002711. [3] ELHALAWANY B M, EL-BANNA A A A, and WU Kaishun. Physical-layer security and privacy for vehicle-to-everything[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(10): 84–90. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900141. [4] KUMAR V, AHMAD M, MISHRA D, et al. RSEAP: RFID based secure and efficient authentication protocol for vehicular cloud computing[J]. Vehicular Communications, 2020, 22: 100213. doi: 10.1016/j.vehcom.2019.100213. [5] XIONG Jinbo, MA Rong, CHEN Lei, et al. A personalized privacy protection framework for mobile crowdsensing in IIoT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(6): 4231–4241. doi: 10.1109/tii.2019.2948068. [6] AMAN M N, JAVAID U, and SIKDAR B. A privacy-preserving and scalable authentication protocol for the internet of vehicles[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(2): 1123–1139. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2020.3010893. [7] XIE Qi, DING Zixuan, and ZHENG Panpan. Provably secure and anonymous V2I and V2V authentication protocol for VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(7): 7318–7327. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3253710. [8] UMAR M, ISLAM S K H, MAHMOOD K, et al. Provable secure identity-based anonymous and privacy-preserving inter-vehicular authentication protocol for VANETS using PUF[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(11): 12158–12167. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3118892. [9] WU Anmulin, GUO Yajun, and GUO Yimin. A decentralized lightweight blockchain-based authentication mechanism for Internet of Vehicles[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2023, 16(3): 1340–1353. doi: 10.1007/s12083-022-01442-0. [10] LI Jie, LIN Yuanyuan, LI Yibing, et al. BPA: A novel blockchain-based privacy-preserving authentication scheme for the internet of vehicles[J]. Electronics, 2024, 13(10): 1901. doi: 10.3390/electronics13101901. [11] XI Ning, LI Weihui, JING Lv, et al. ZAMA: A ZKP-based anonymous mutual authentication scheme for the IoV[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(22): 22903–22913. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3186921. [12] LIU Jingwei, PENG Chuntian, SUN Rong, et al. CPAHP: Conditional privacy-preserving authentication scheme with hierarchical pseudonym for 5G-enabled IoV[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(7): 8929–8940. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3246466. [13] WEI Fushan, ZEADALLY S, VIJAYAKUMAR P, et al. An intelligent terminal based privacy-preserving multi-modal implicit authentication protocol for internet of connected vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(7): 3939–3951. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2998775. [14] LIANG Yangfan, LUO Entao, and LIU Yining. Physically secure and conditional-privacy authenticated key agreement for VANETs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(6): 7914–7925. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3241882. [15] WANG Denghui, YI Yuping, YAN Shan, et al. A node trust evaluation method of vehicle-road-cloud collaborative system based on federated learning[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2023, 138: 103013. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2022.103013. [16] WAZID M, BAGGA P, DAS A K, et al. AKM-IoV: Authenticated key management protocol in fog computing-based Internet of vehicles deployment[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(5): 8804–8817. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2923611. [17] GOPE P, DAS A K, KUMAR N, et al. Lightweight and physically secure anonymous mutual authentication protocol for real-time data access in industrial wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(9): 4957–4968. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2895030. [18] BELLARE M and ROGAWAY P. Random oracles are practical: A paradigm for designing efficient protocols[C]. Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Fairfax, USA, 1993: 62–73. doi: 10.1145/168588.168596. [19] NURKIFLI E H and HWANG T. Provably secure authentication for the internet of vehicles[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 2023, 35(8): 101721. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.101721. [20] YADAV K A and VIJAYAKUMAR P. LPPSA: An efficient Lightweight Privacy-Preserving Signature-based Authentication protocol for a vehicular ad hoc network[J]. Annals of Telecommunications, 2022, 77(7/8): 473–489. doi: 10.1007/s12243-021-00897-1. -






 下载:
下载:





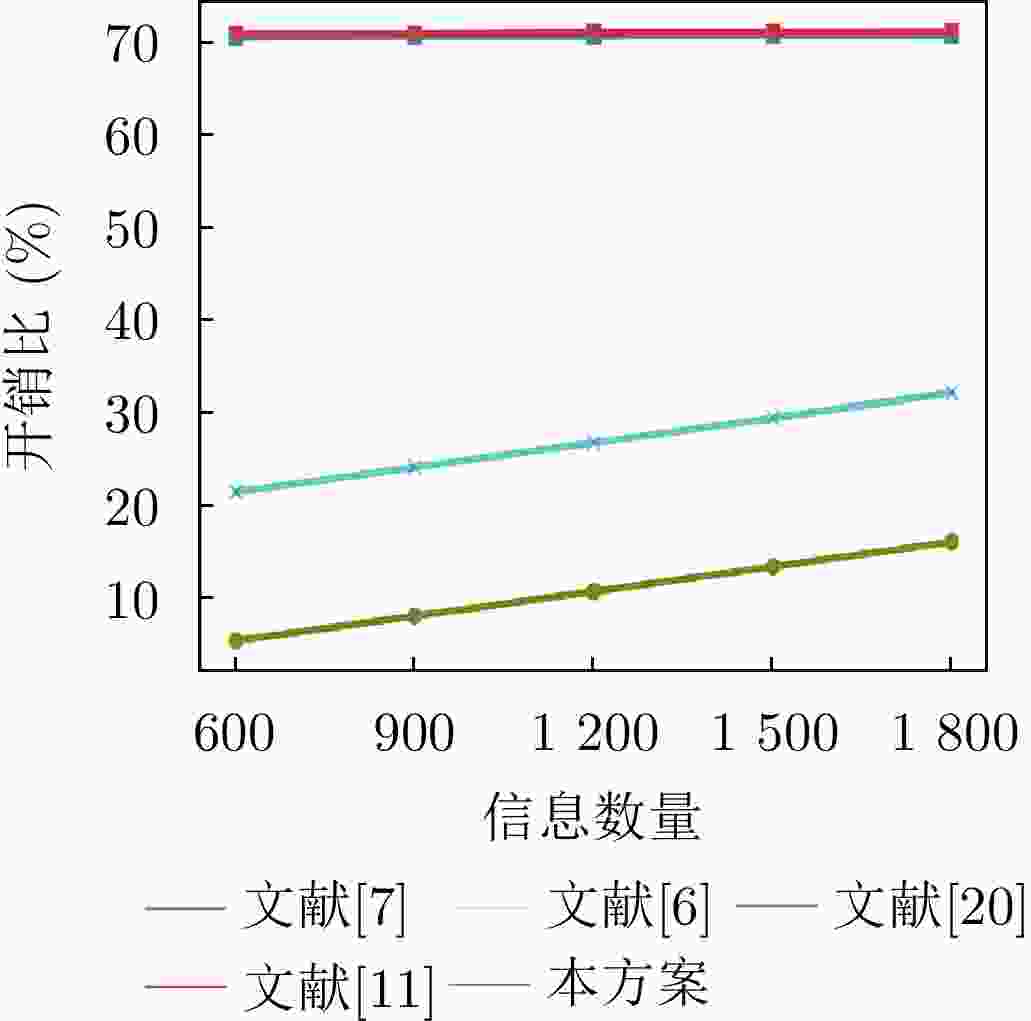

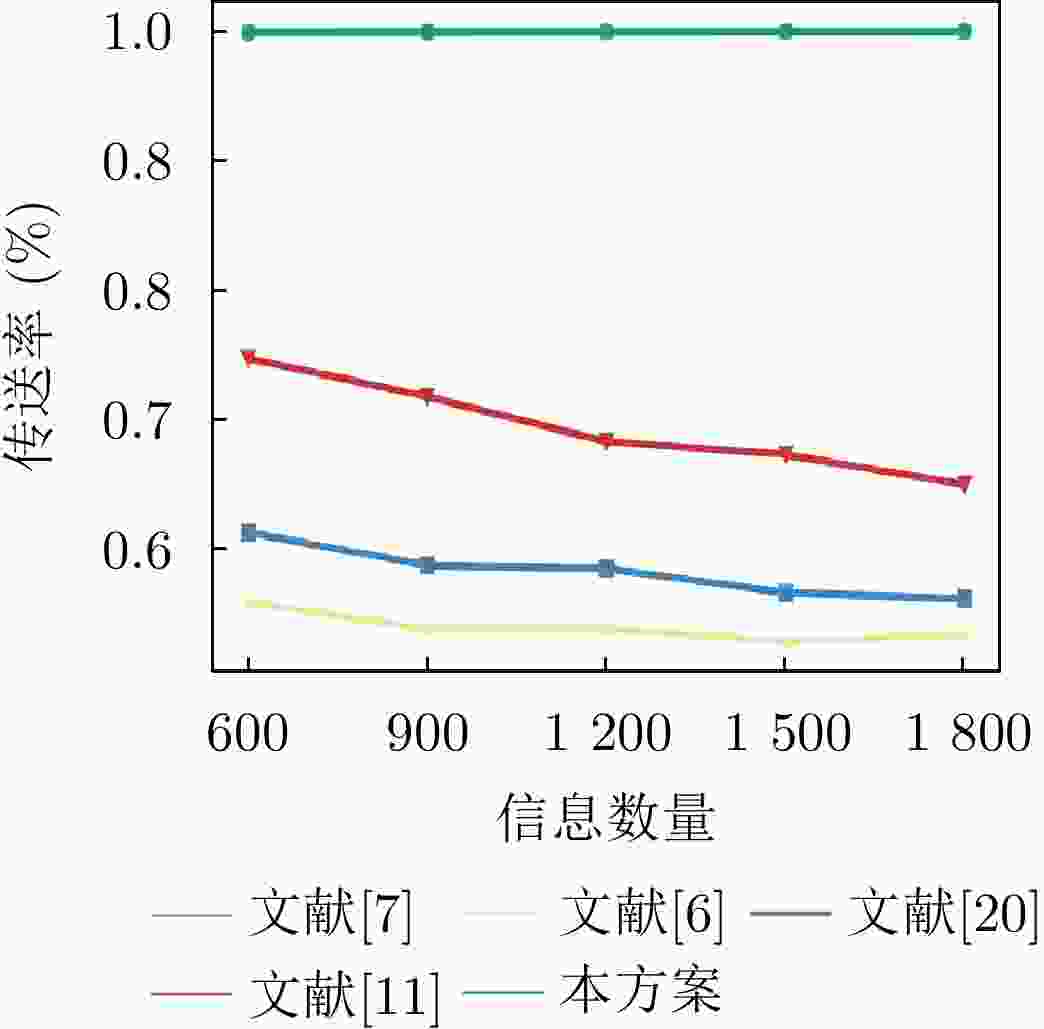


 下载:
下载:
