Airborne Target Tracking Algorithm Using Multi-Platform Heterogeneous Information Fusion
-
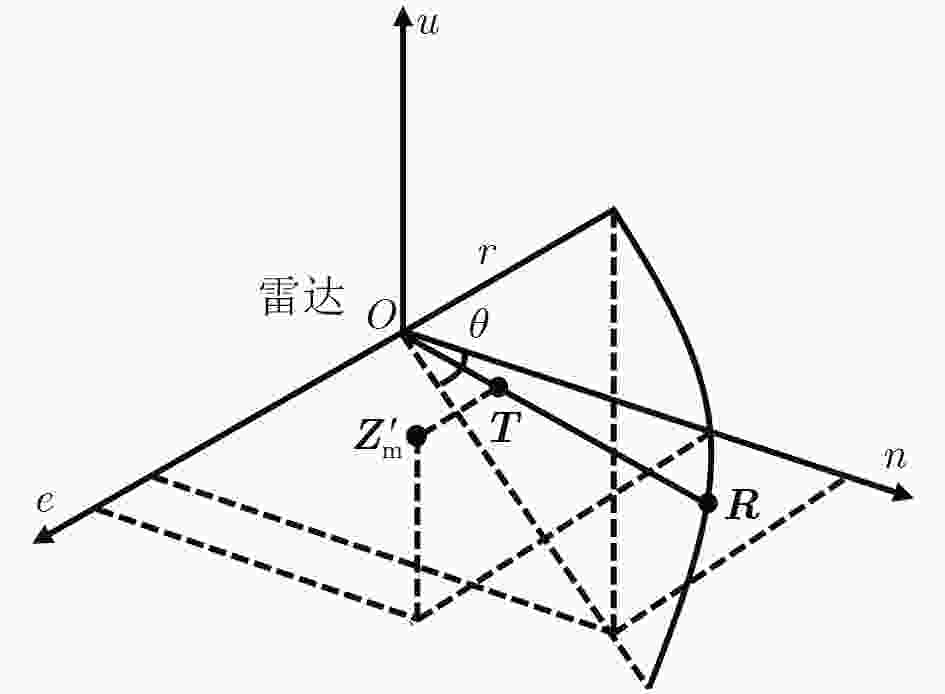
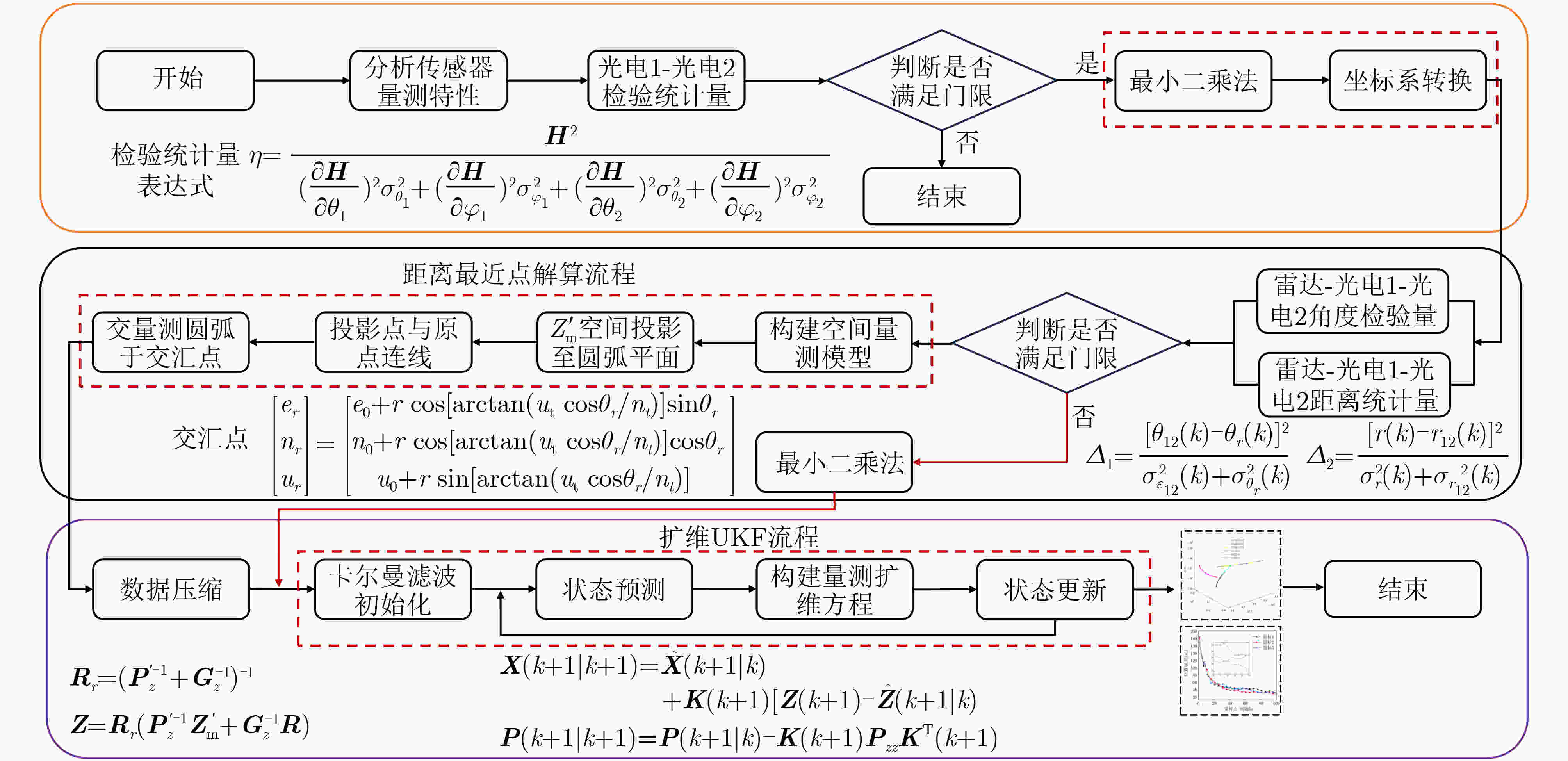
摘要: 该文以高空无人机(UAV)飞艇载双光电传感器,无人机载两坐标雷达对航空目标的精确定位跟踪为研究背景,针对参与融合的传感器均无法独立获得目标位置信息导致传统点迹关联、定位方法失效等问题,提出一种基于多平台异构信息融合的航空目标跟踪算法。首先,在坐标系转换的基础上提出基于角度-距离两级点迹关联算法,从而实现多传感器量测关联。其次,提出基于线面交汇融合定位算法,通过最小二乘法、交汇点投影、距离最近点解算及同源数据压缩确定目标的航迹起始位置。在此基础上,利用空基多平台侦察的异构信息,结合传统无迹卡尔曼滤波器(UKF)设计扩维UKF对航空目标进行跟踪。仿真结果表明,该算法实现了对航空高速目标的高精度跟踪。
-
关键词:
- 信息融合 /
- 目标跟踪 /
- 量测关联 /
- 扩维无迹卡尔曼滤波器 /
- 空基多平台
Abstract: An innovative aviation target tracking algorithm is presented in this paper, utilizing high-altitude unmanned airship dual photoelectric sensors in conjunction with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-borne two-coordinate radar. The algorithm addresses the challenge of integrating sensor data to accurately track targets when individual sensors lack complete target position information, thus overcoming limitations of traditional point-trace association methods. Initially, a two-level point-trace correlation algorithm based on angle and distance is introduced for multi-sensor measurement association following coordinate system transformation. Subsequently, a line-plane intersection fusion localization algorithm is proposed to determine the initial target track position through techniques such as least squares method, intersection projection, distance nearest point solution, and homologous data compression. Leveraging heterogeneous information from space-based multi-platform reconnaissance, an extended Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) is designed to track aviation targets by enhancing the traditional UKF. Simulation results demonstrate that this algorithm achieves superior precision in tracking high-speed aerial targets. -
表 1 仿真参数
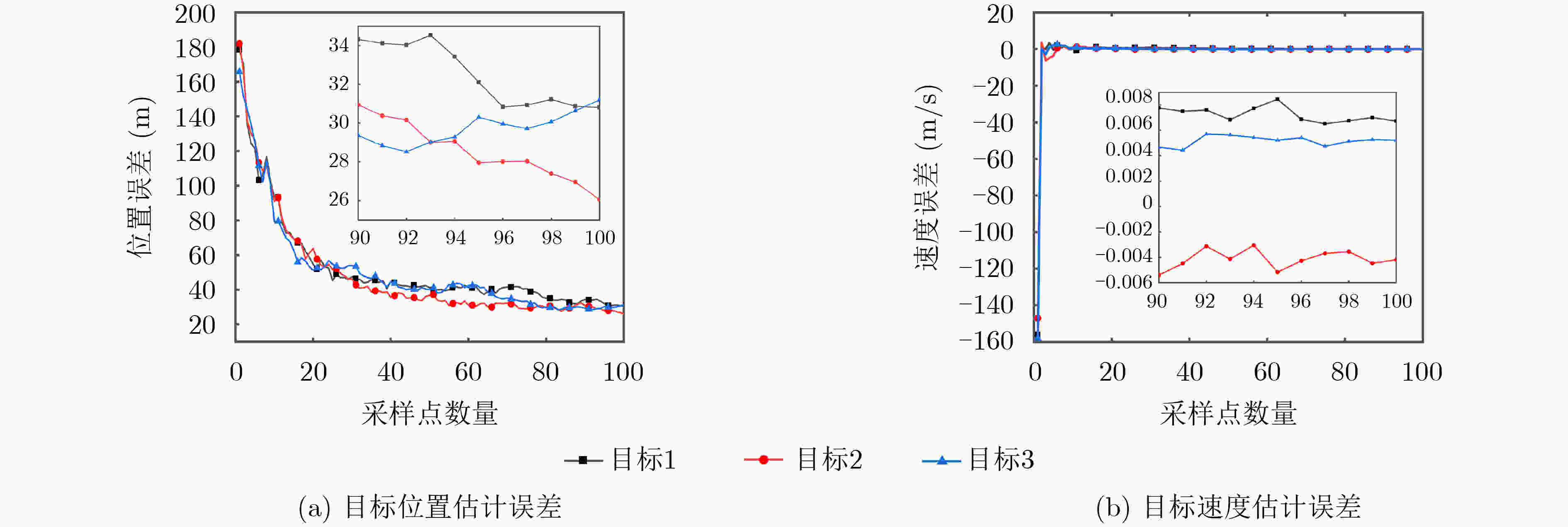
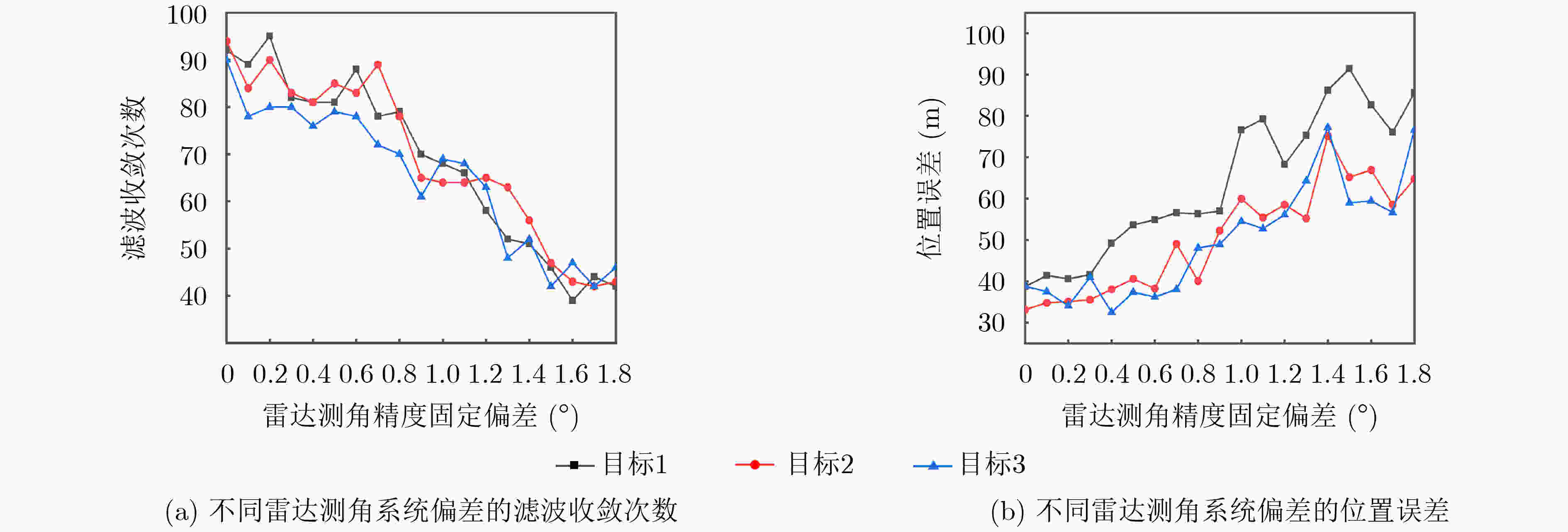
参数 名称 数值 参数 名称 数值 ${{\mathrm{S}}} {1_{{\mathrm{location}}}}$ 无人飞艇1坐标 (12.0°N, 130.0°E, 30 km) ${R_{{\mathrm{location}}}}$ 机载雷达地理坐标 (15.1°N, 138.0°E, 20 km) ${{\mathrm{S}}} {2_{{\mathrm{location}}}}$ 无人飞艇2坐标 (12.0°N, 140.0°E, 30 km) ${v_{\mathrm{R}}}$ 机载雷达速度(m/s) (200, 100, 5) ${{T}}_{{{\mathrm{location}}}}^1$ 目标1坐标 (12.3°N, 138.5°E, 6 km) ${v_{{\mathrm{T}}1}}$ 目标1速度(m/s) (300, 100, 10) ${{T}}_{{{\mathrm{location}}}}^2$ 目标2坐标 (12.4°N, 138.5°E, 6 km) ${v_{{\mathrm{T}}2}}$ 目标2速度(m/s) (–300, 100, 10) ${{T}}_{{{{\mathrm{location}}} }}^3$ 目标3坐标 (12.5°N, 138.5°E, 6 km) ${v_{{\mathrm{T}}3}}$ 目标3速度(m/s) (300, –100, 10) ${a_{\mathrm{T}}}$ 目标加速度(m/s2) (0.5, –0.2, 0.05) $\sigma $ 量测误差 100 m, 0.5°, 0.01°, 0.01°, 0.03°, 0.03° 表 2 位置仿真参数
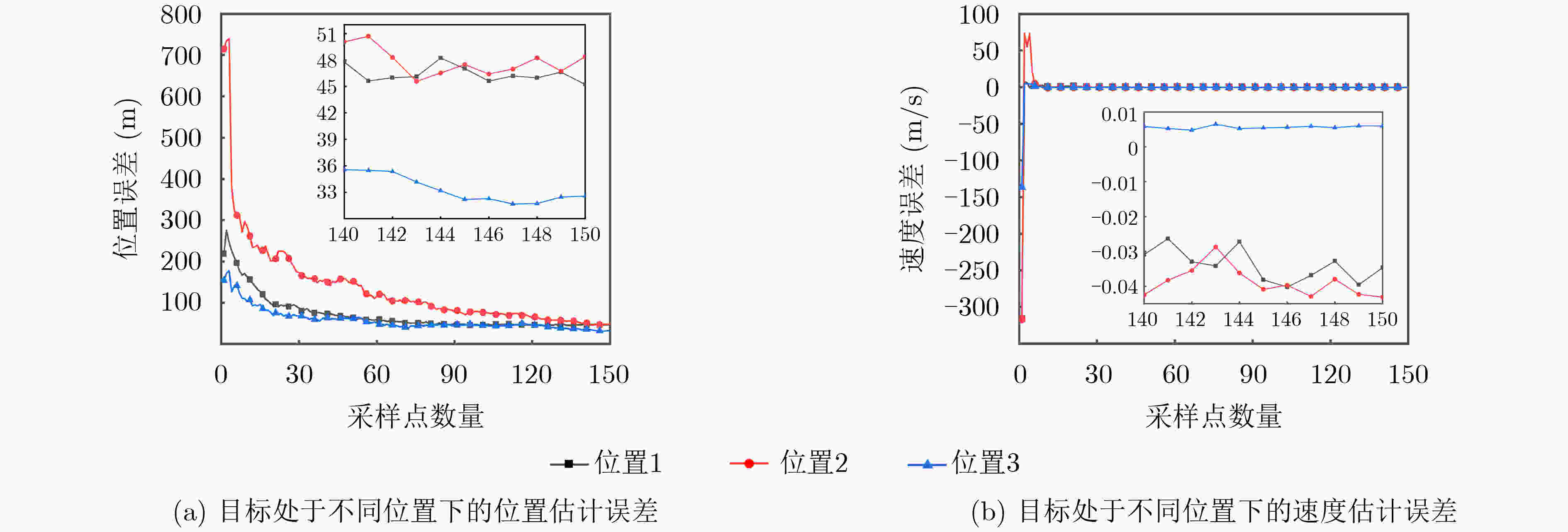
名称 数值 位置1 (16.2oN,127.1oE,6 km) 位置2 (14.6oN,136.5oE,6 km) 位置3 (12.3oN,138.5oE,6 km) 表 3 仿真具体结果
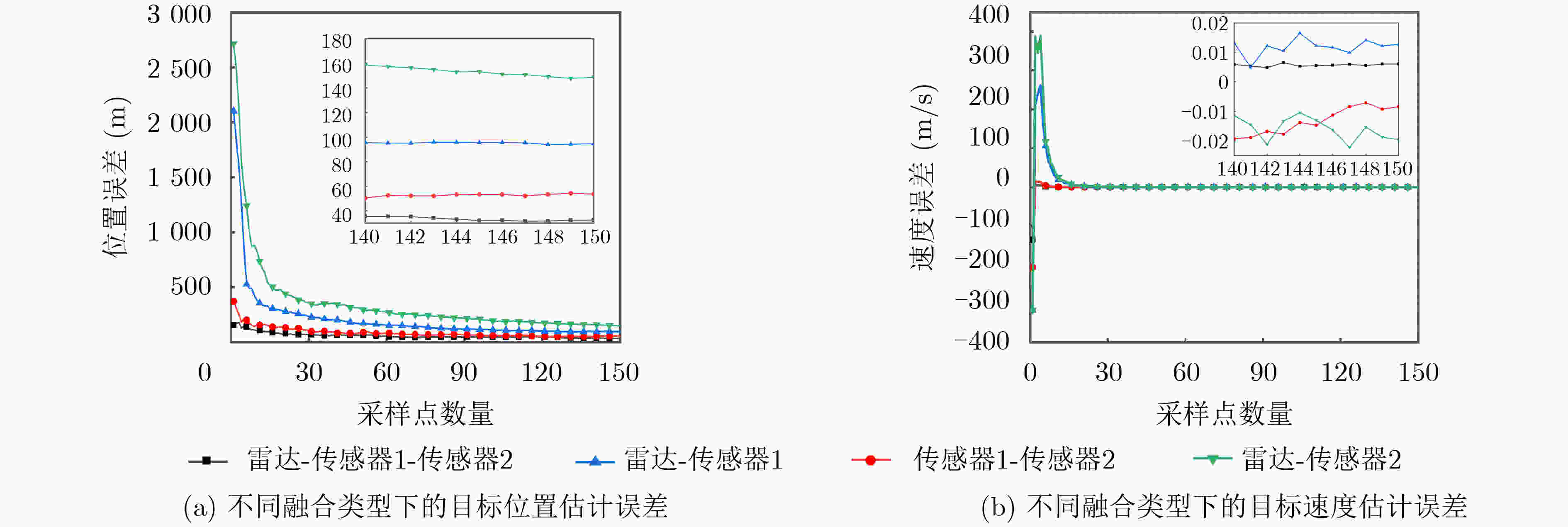
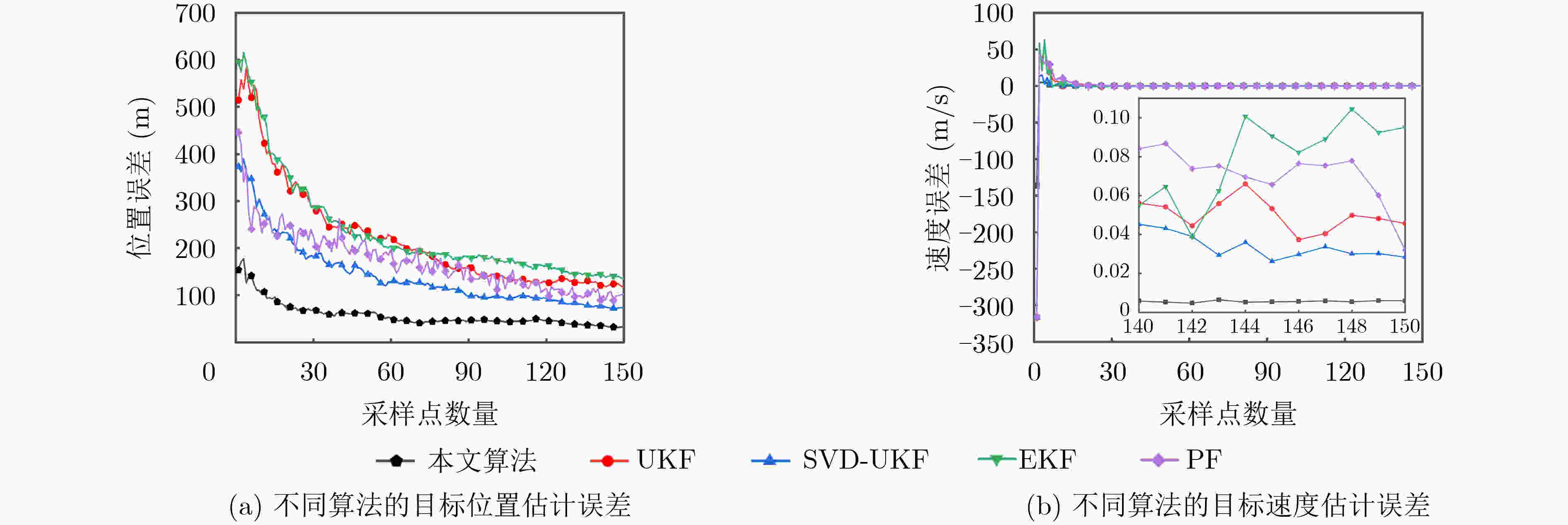
融合类型 位置估计误差(m) 速度估计误差(m/s) 雷达-传感器1-传感器2 32.6 0.006 传感器1-传感器2 53.7 0.008 雷达-传感器1 95.6 0.013 雷达-传感器2 150.7 0.020 -
[1] 周军, 董鹏, 卢晓东. 基于Sigma点卡尔曼滤波的天基红外低轨卫星目标跟踪[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2012, 41(8): 2206–2210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.08.045.ZHOU Jun, DONG Peng, and LU Xiaodong. Tracking algorithm for space-based infrared satellites in LEO based on Sigma-point Kalman filters[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2012, 41(8): 2206–2210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2012.08.045. [2] KONG Shangping, GAN Luoning, WANG Ruofan, et al. Target tracking algorithm of radar and infrared sensor based on multi-source information fusion[C]. 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Information Processing and Cloud Computing (AIIPCC), Kunming, China, 2022: 389–392. doi: 10.1109/AIIPCC57291.2022.00088. [3] 申屠晗, 李凯斌, 荣英佼, 等. 一种多传感器自适应量测迭代更新GM-PHD跟踪算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4168–4177. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211138.SHENTU Han, LI Kaibin, RONG Yingjiao, et al. A multi-sensor adaptive observation iteratively updating GM-PHD tracking algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4168–4177. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211138. [4] CHEN Shouqing, DOU Huijing, LIU Zonghao, et al. Multi-sensor track fusion algorithm research and simulation analysis[C]. 2022 Global Conference on Robotics, Artificial Intelligence and Information Technology (GCRAIT), Chicago, USA, 2022: 131–135. doi: 10.1109/GCRAIT55928.2022.00036. [5] 高嵩, 潘泉, 肖秦琨, 等. 多传感器自适应滤波融合算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2008, 30(8): 1901–1904. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00056.GAO Song, PAN Quan, XIAO Qinkun, et al. Multi-sensor adaptive filter data fusion algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(8): 1901–1904. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00056. [6] XU Yuan, DONG Jian, BAI Jinliang, et al. Spatial target tracking algorithm based on heterogeneous sensors data fusion[C]. 2023 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Qingdao, China, 2023: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT58241.2023.10277359. [7] MA Ke, ZHANG Hanguang, WANG Rentao, et al. Target tracking system for multi-sensor data fusion[C]. 2017 IEEE 2nd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chengdu, China, 2017: 1768–1772. doi: 10.1109/ITNEC.2017.8285099. [8] LUO Junhai, WANG Zhiyan, CHEN Yanping, et al. An improved unscented particle filter approach for multi-sensor fusion target tracking[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(23): 6842. doi: 10.3390/s20236842. [9] 胡振涛, 付春玲, 刘先省. 基于RB粒子滤波的多传感器目标跟踪融合算法[J]. 光电子·激光, 2012, 23(3): 566–571. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2012.03.030.HU Zhentao, FU Chunling, and LIU Xianxing. Multi-sensor target tracking fusion algorithm based on Rao-Blackwellised particle filter[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2012, 23(3): 566–571. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2012.03.030. [10] 胡振涛, 曹志伟, 李松, 等. 基于容积卡尔曼滤波的异质多传感器融合算法[J]. 光电子·激光, 2014, 25(4): 697–703. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2014.04.022.HU Zhentao, CAO Zhiwei, LI Song, et al. Heterogeneous multi-sensor fusion algorithm based on cubature Kalman filter[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 2014, 25(4): 697–703. doi: 10.16136/j.joel.2014.04.022. [11] 郑佳春, 于浩, 王夙歆, 等. 分布式自适应多传感器多目标跟踪算法[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2015, 23(4): 472–476. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2015.04.010.ZHENG Jiachun, YU Hao, WANG Suxin, et al. Distributed adaptive multi-sensor multi-target tracking algorithm[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(4): 472–476. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2015.04.010. [12] 高春艳, 卢建, 张明路, 等. 基于多传感器数据融合的多目标跟踪算法研究[J]. 制造业自动化, 2022, 44(7): 95–97, 101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2022.07.023.GAO Chunyan, LU Jian, ZHANG Minglu, et al. Research on multi-target tracking algorithm based on multi-sensor data fusion[J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2022, 44(7): 95–97, 101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2022.07.023. [13] 陈非, 敬忠良, 李锋. 空基多平台多传感器机动目标自适应跟踪[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2003, 37(4): 578–581. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2003.04.026.CHEN Fei, JING Zhongliang, and LI Feng. Adaptive tracking of maneuvering targets for multiple airborne mobile platforms and multiple sensors[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2003, 37(4): 578–581. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2003.04.026. [14] 戴瑜, 龙文佳. 基于多机载预警雷达的机动目标融合跟踪方法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2021, 46(4): 136–140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.04.025.DAI Yu and LONG Wenjia. Research on maneuvering targets fusion tracking method based on multi-airborne early warning radars fusion[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2021, 46(4): 136–140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.04.025. [15] 卢雨, 王海滨. 空基无源相干定位系统的机动目标跟踪算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(4): 875–882. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.04.03.LU Yu and WANG Haibin. Maneuvering target tracking algorithm for airborne passive coherent localization system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(4): 875–882. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.04.03. [16] 王增福, 邵毅, 祁登亮, 等. 一种基于一致性的分布式天基雷达组网空中目标高度估计与定位方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1249–1262. doi: 10.12000/JR23157.WANG Zengfu, SHAO Yi, QI Dengliang, et al. Consistency-based air target height estimation and location in distributed space-based radar network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1249–1262. doi: 10.12000/JR23157. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
