Interference Coordination Algorithm of Co-frequency and Co-time Full Duplex Device-to-Device underlaying Cellular Network
-
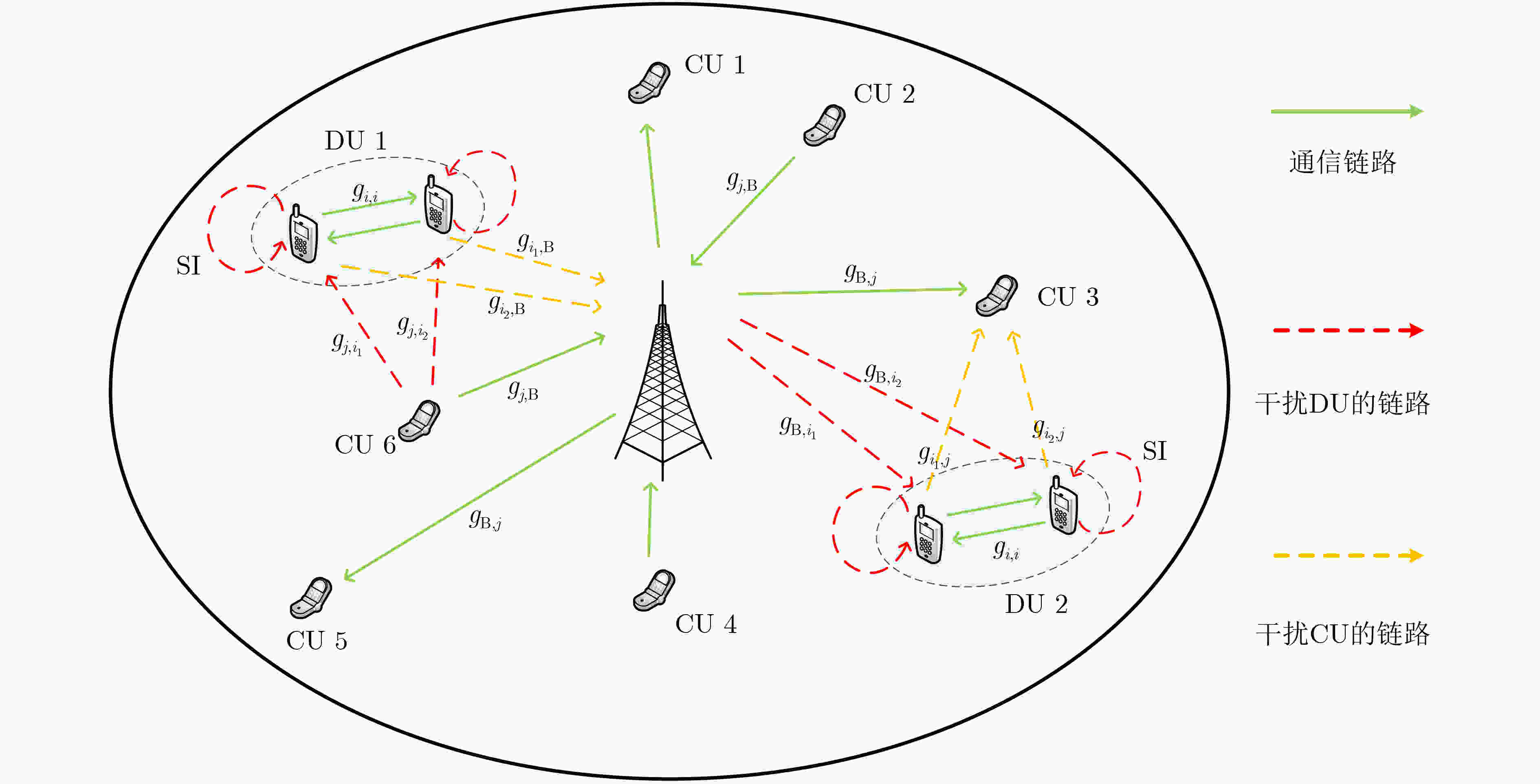
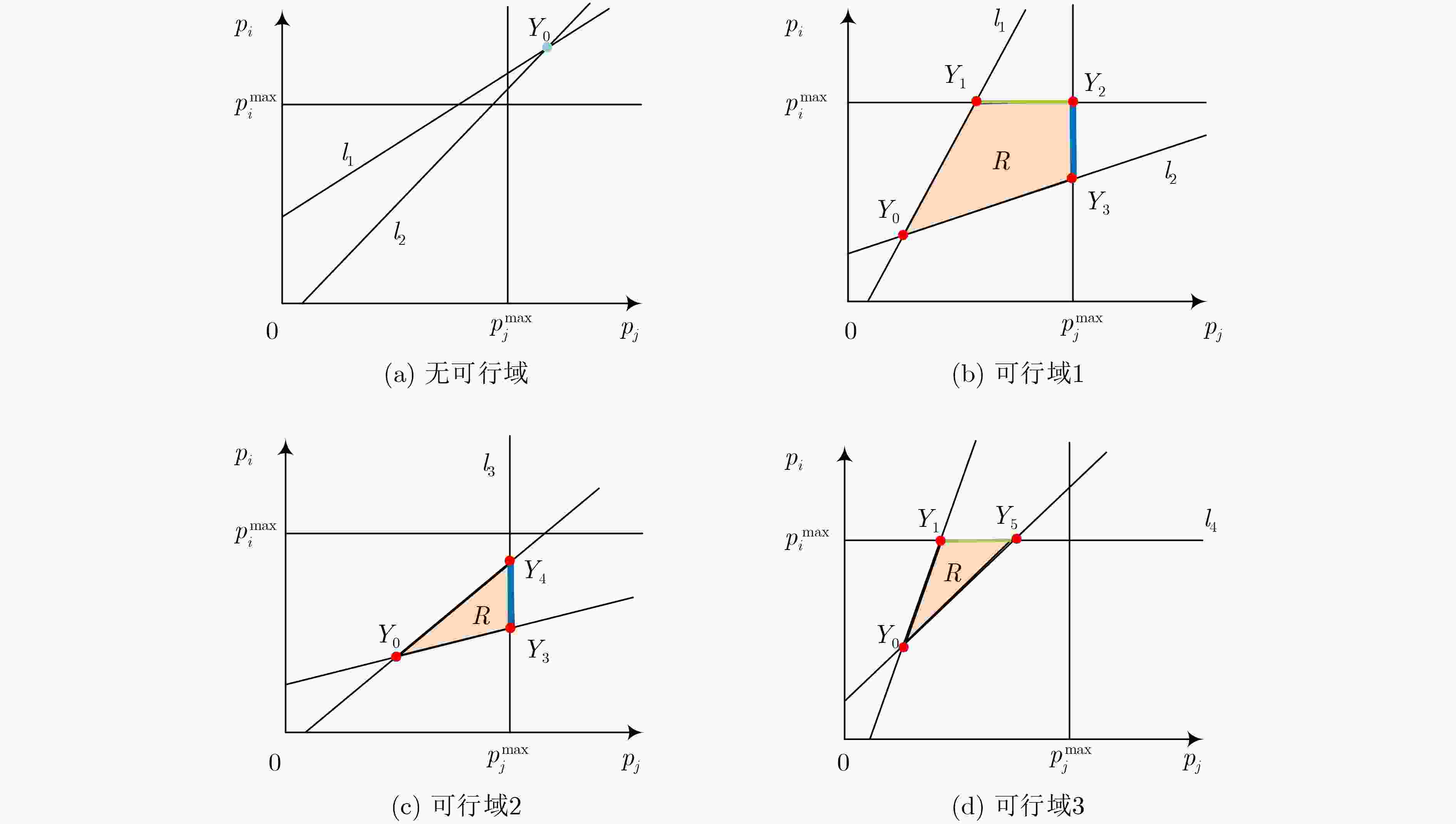
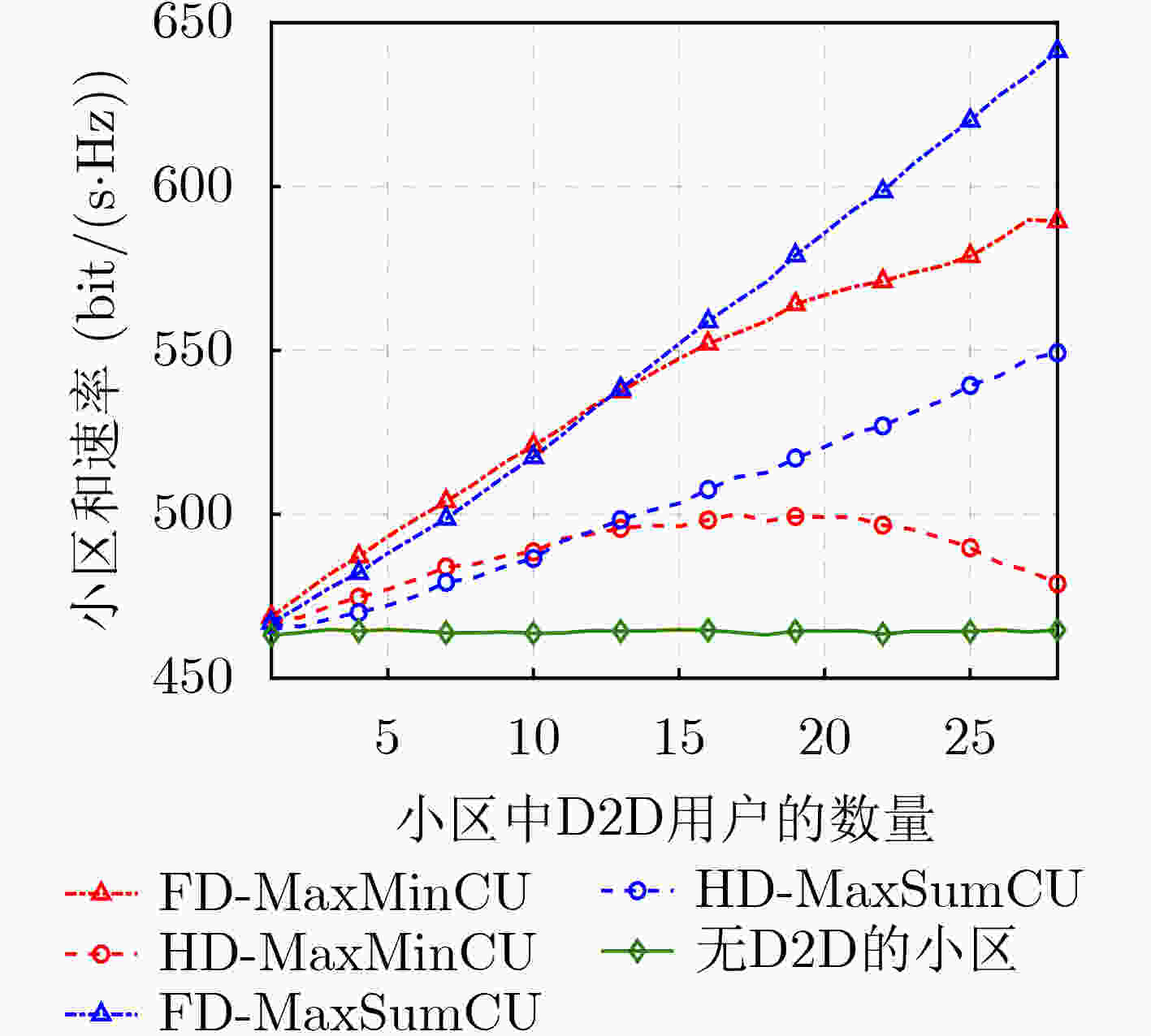
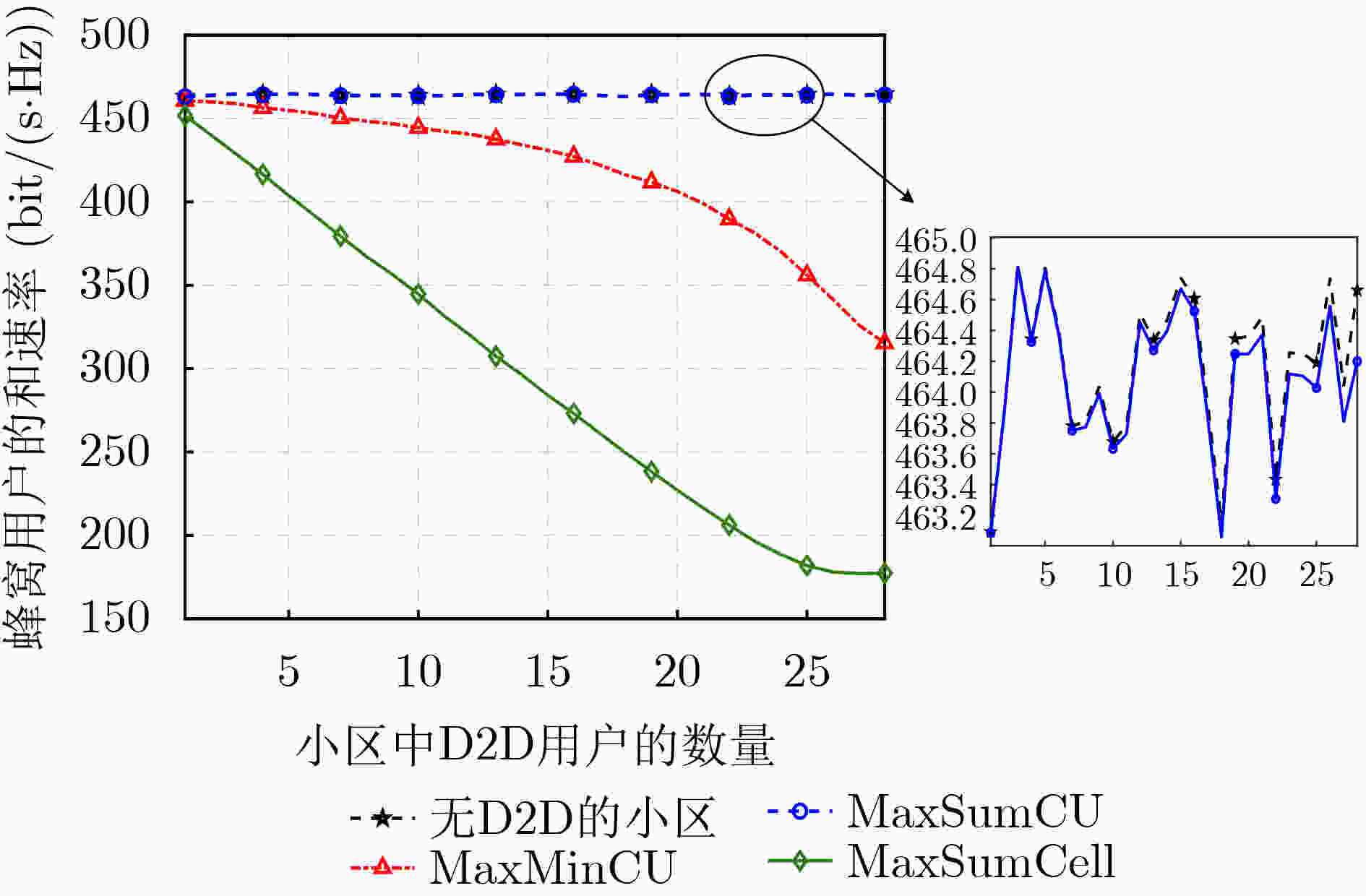
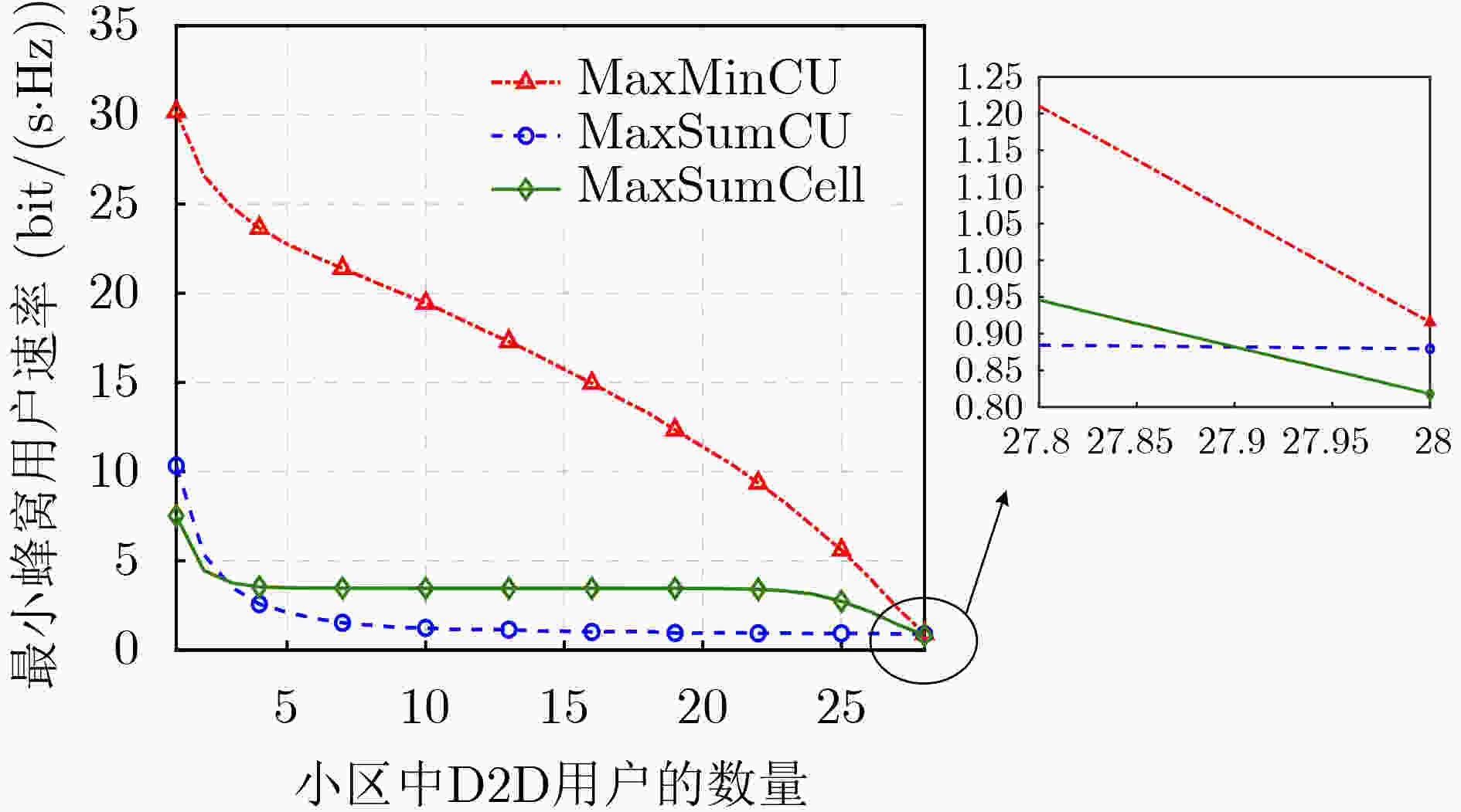
摘要: 蜂窝网络下的同时同频全双工(CCFD)设备到设备(D2D)组网可以进一步提升网络频谱效率,然而由此引入的残余自干扰(RSI)及蜂窝用户(CU)与D2D用户(DU)之间共享频谱的干扰会严重影响到蜂窝用户的体验。因此,该文为蜂窝网络下同时同频全双工组网设计了两种干扰协调算法,即CU和速率最大化算法(MaxSumCU)与CU最小速率最大化算法(MaxMinCU),在小区频谱效率得到提升的同时尽可能地保证CU的体验。对于MaxSumCU算法,该文以CU和速率为优化目标建立混合整数非线性规划问题(MINLP),其在数学上为非确定性多项式(NP-hard)问题。算法将其分解为功率控制与频谱资源分配两个子问题,并用图形规划找到最优功率解后,使用二向图最大权值匹配算法决定频谱共享的CU与DU。为了保证每一个蜂窝用户体验的公平性,该文设计了MaxMinCU算法用以最大化所有CU速率中的最小值,该算法基于二分查找与二向图最小权值匹配算法来完成用户的资源分配。数值结果表明,与小区和速率最大化(MaxSumCell)设计相比,该文所提的两种算法在提升小区和速率的同时均有效地提升了蜂窝用户的体验。
-
关键词:
- 蜂窝网络下设备到设备组网 /
- 同时同频全双工 /
- 二向图最大(小)权值匹配 /
- 公平性算法
Abstract: The Residual Self-Interference (RSI) caused by Co-frequency and Co-time Full Duplex Device-to-Device (CCFD-D2D) and the interference introduced by spectrum sharing between D2D User (DU) and Cellular User (CU) lead to a degradation in the quality of experience for CUs. Therefore, the CCFD-D2D underlaying cellular system is considered and two algorithms are proposed, that is Maximizing Sum-rate of CU (MaxSumCU) and Maximizing Minimum-rate of CU (MaxMinCU) algorithm, to enhance the experience for CUs while spectral efficiency of the system is improved. For the MaxSumCU algorithm, an optimization problem is investigated to maximize the sum rate of CUs in the system, and formulate it as a Mixed Integer NonLinear Programming problem (MINLP) which is NP-hard in mathematics. MaxSumCU is designed to decompose it into two sub-problems as power control and spectral resource allocation. The power control is solved by geometric programming, and the resource allocation is achieved by employing Kuhn-Munkres algorithm to determine the spectrum sharing pairs of CUs and DUs. To provide a more uniform rate performance across all CUs, the MaxMinCU algorithm is designed to maximize the minimum rate among the CUs. The novel spectrum resource allocation algorithm based on bisection searching and Kuhn-Munkres minimum-weight algorithm is proposed to solve this optimization problem. Numerical results show that, compared with Maximizing Sum-rate of Cell (MaxSumCell) design, our proposed algorithm effectively optimize the CU’s experience while improve the spectral efficiency of system in CCFD-D2D underlaying cellular networks. -
1 公平性算法
(1) 计算已配对CU的速率矩阵$ {{\{R}_{i,j}^{\mathrm{C}}\}}_{Q\times P} $。 (2) 对$ {{\{R}_{i,j}^{\mathrm{C}}\}}_{Q\times P} $中元素降序排列成向量$ \mathit{v} $,并初始化索引
$ m=1,n=QP $。(3) while $ (n-m) > 1 $ do (4) $ l=(n-m)/2 $; (5) 初始化一个矩阵$ {\left\{{F}_{i,j}\right\}}_{Q\times P} $,并为其中元素赋值,
$ {R}_{i,j}^{{\mathrm{C}}} < \mathit{v}\left(l\right) $时对应位置赋1,否则为0(6) 对$ {\left\{{F}_{i,j}\right\}}_{Q\times P} $使用KM最小权值算法,返回分配指示矩阵
$ {\mathit{E}}_{Q\times P} $与对应的权值$ w $。(7) if $ w=0 $ then (8) $ n=l $; (9) else (10) $ m=l $; (11) $ {\left\{{\rho }_{i,j}\right\}}_{Q\times P}=\mathit{E} $; (12) end if (13)end while (14)在$ {{\{R}_{i,j}^{\mathrm{C}}\cdot {\rho }_{i,j}\}}_{Q\times P} $中搜索除0元素外最小的元素,即为最大
CU最小速率$ {R}_{i,j}^{{\mathrm{C}},\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $。(15)返回$ {\left\{{\rho }_{i,j}\right\}}_{Q\times P} $与$ \mathrm{max}{R}_{i,j}^{\mathrm{C},\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $。 -
[1] ZHANG Hongliang, SONG Lingyang, and HAN Zhu. Radio resource allocation for device-to-device underlay communication using hypergraph theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(7): 4852–4861. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2547862. [2] NI Minming and PAN Jianping. Throughput analysis for downlink resource reusing D2D communications in cellular networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 2017: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2017.8254846. [3] LEE N, LIN Xingqin, ANDREWS J G, et al. Power control for D2D underlaid cellular networks: Modeling, algorithms, and analysis[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33(1): 1–13. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.2369612. [4] KAI Caihong, WU Yan, PENG Min, et al. Joint uplink and downlink resource allocation for NOMA-enabled D2D communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(6): 1247–1251. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3063169. [5] KAI Caihong, LI Hui, XU Lei, et al. Joint subcarrier Assignment with power allocation for sum rate maximization of D2D communications in wireless cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4748–4759. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2903815. [6] 徐磊. 5G蜂窝网络中D2D通信的资源分配算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 合肥工业大学, 2019.XU Lei. Research on resource allocation algorithms for D2D communications in 5G cellular networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Hefei University of Technology, 2019. [7] SHI Chengzhe, PAN Wensheng, and SHAO Shihai. RF wideband self-interference cancellation for full duplex phased array communication systems[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Korea, 2022: 1094–1099. doi: 10.1109/ICC45855.2022.9838572. [8] SHI Chengzhe, PAN Wensheng, SHEN Ying, et al. Robust transmit beamforming for self-interference cancellation in STAR phased array systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 2622–2626. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2022.3229641. [9] YANG Tinghan, ZHANG Rongqing, CHENG Xiang, et al. Graph coloring based resource sharing (GCRS) scheme for D2D communications underlaying full-duplex cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(8): 7506–7517. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2657791. [10] HEMACHANDRA K T, RAJATHEVA N, and LATVA-AHO M. Sum-rate analysis for full-duplex underlay device-to-device networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 2014: 514–519. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2014.6952081. [11] NGUYEN T H and NGUYEN T T. On performance of STAR-RIS-enabled multiple two-way full-duplex D2D communication systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 89063–89071. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3200834. [12] YANG Yihuai, YANG Bin, SHEN Shikai, et al. Covert rate study for full-duplex D2D communications underlaid cellular networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(17): 15223–15237. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3265275. [13] VU H V, TRAN N H, and LE-NGOC T. Full-duplex device-to-device cellular networks: Power control and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3952–3966. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2898999. [14] FENG Daquan, LU Lu, YI Yuanwu, et al. Device-to-device communications underlaying cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(8): 3541–3551. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.071013.120787. [15] LIANG Le, LI G Y, and XU Wei. Resource allocation for D2D-enabled vehicular communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(7): 3186–3197. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2699194. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
